Ch 15: Important Signals in IR Spectroscopy
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
1500
IR absorption of aromatic ring 1450-1600; 1650-2000 (1500)
Medium
1650
Ethylene - weak/short signal
If connect to 2 hydrogens and 2 carbons - dipole - signal
if conjugated - 1600
if connect to 4 of the same groups - no dipole - signal at 1650
1680-1600
C=N Imine
1680
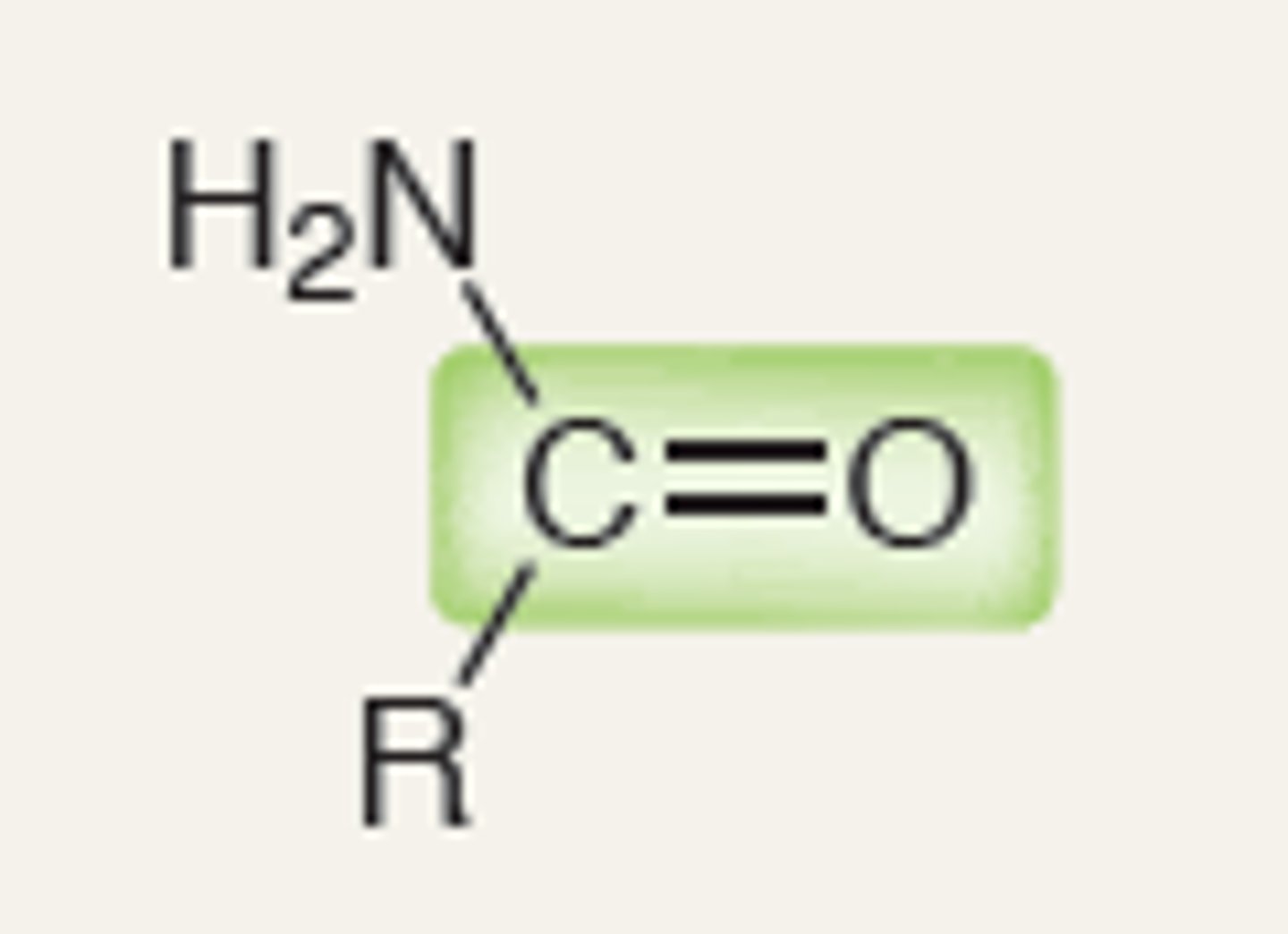
Amide
1680
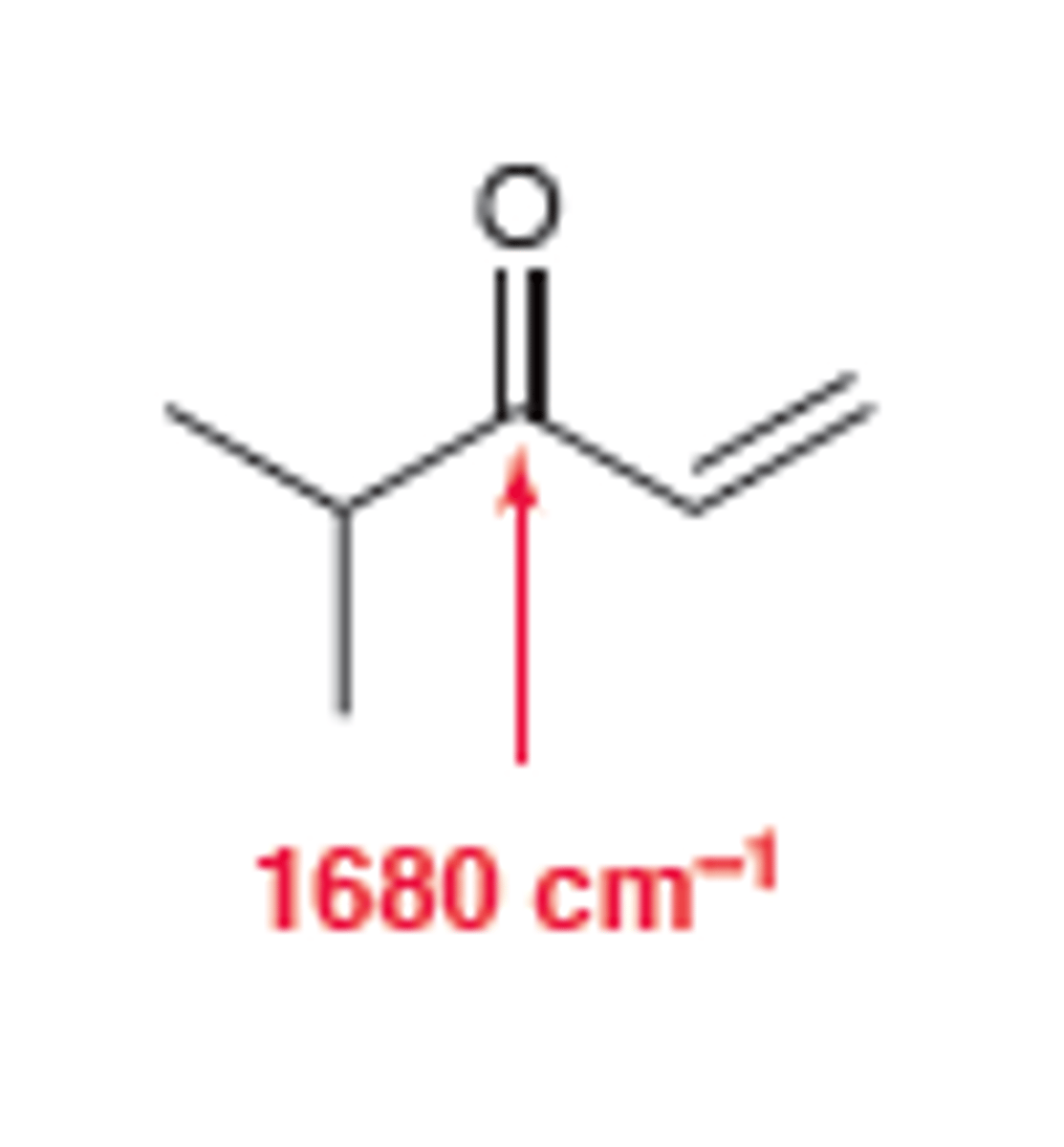
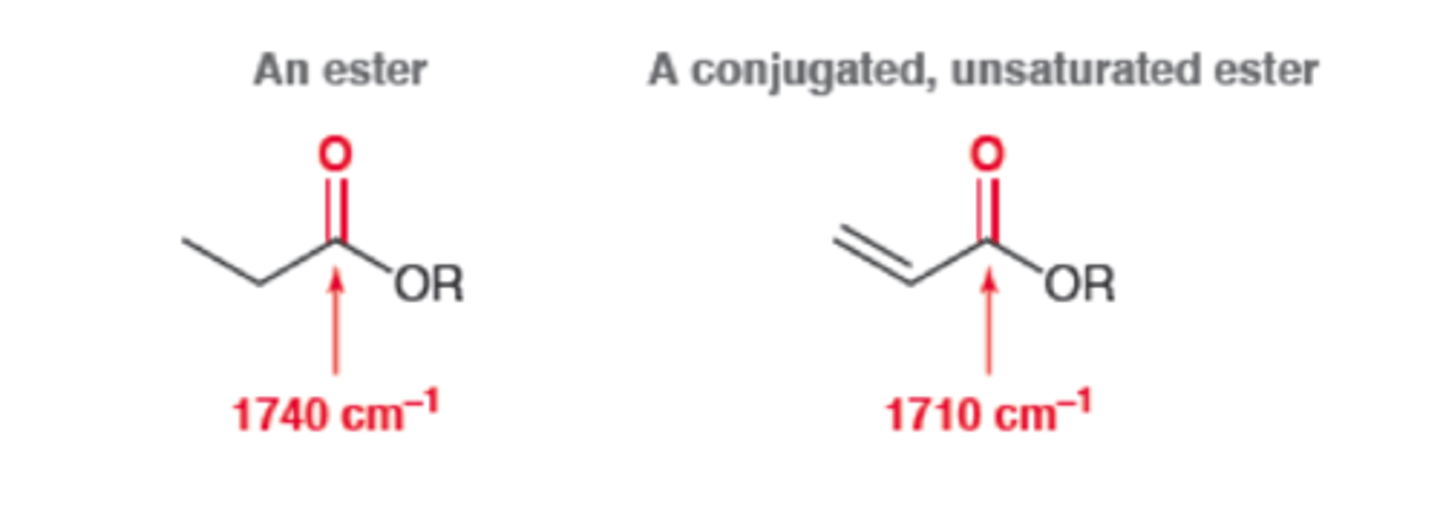
Conjugated Ketone
1710
Conjugated Ester
1720
Carbonyl
1720
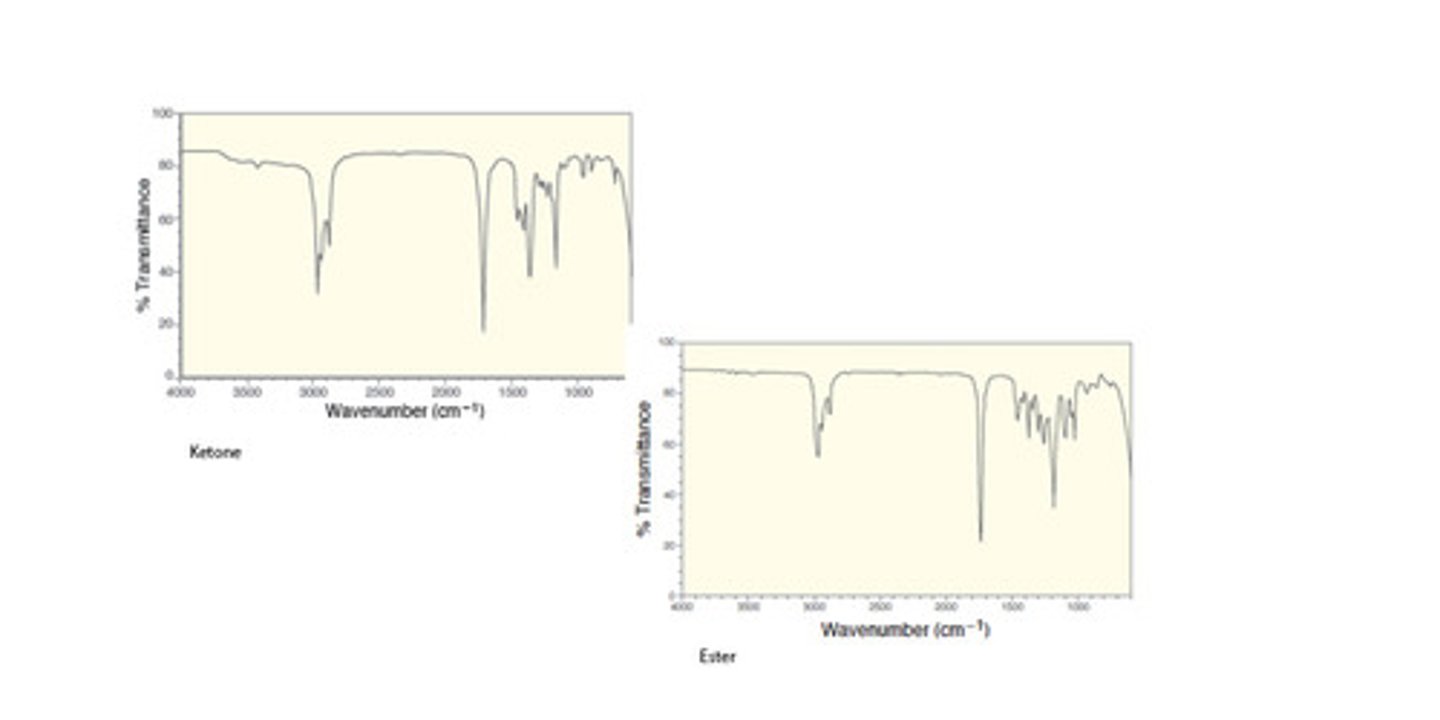
Ketone
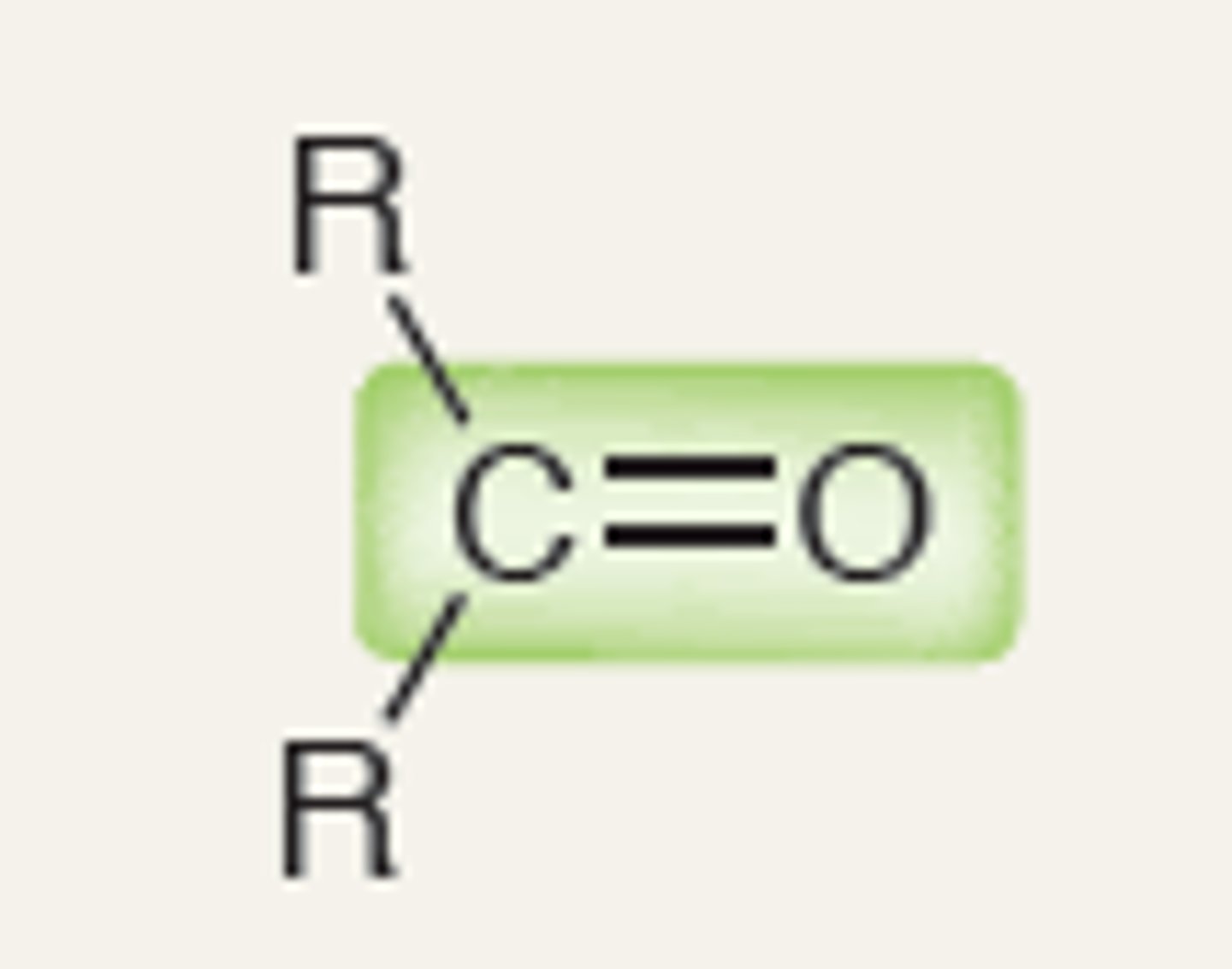
1740
Ester
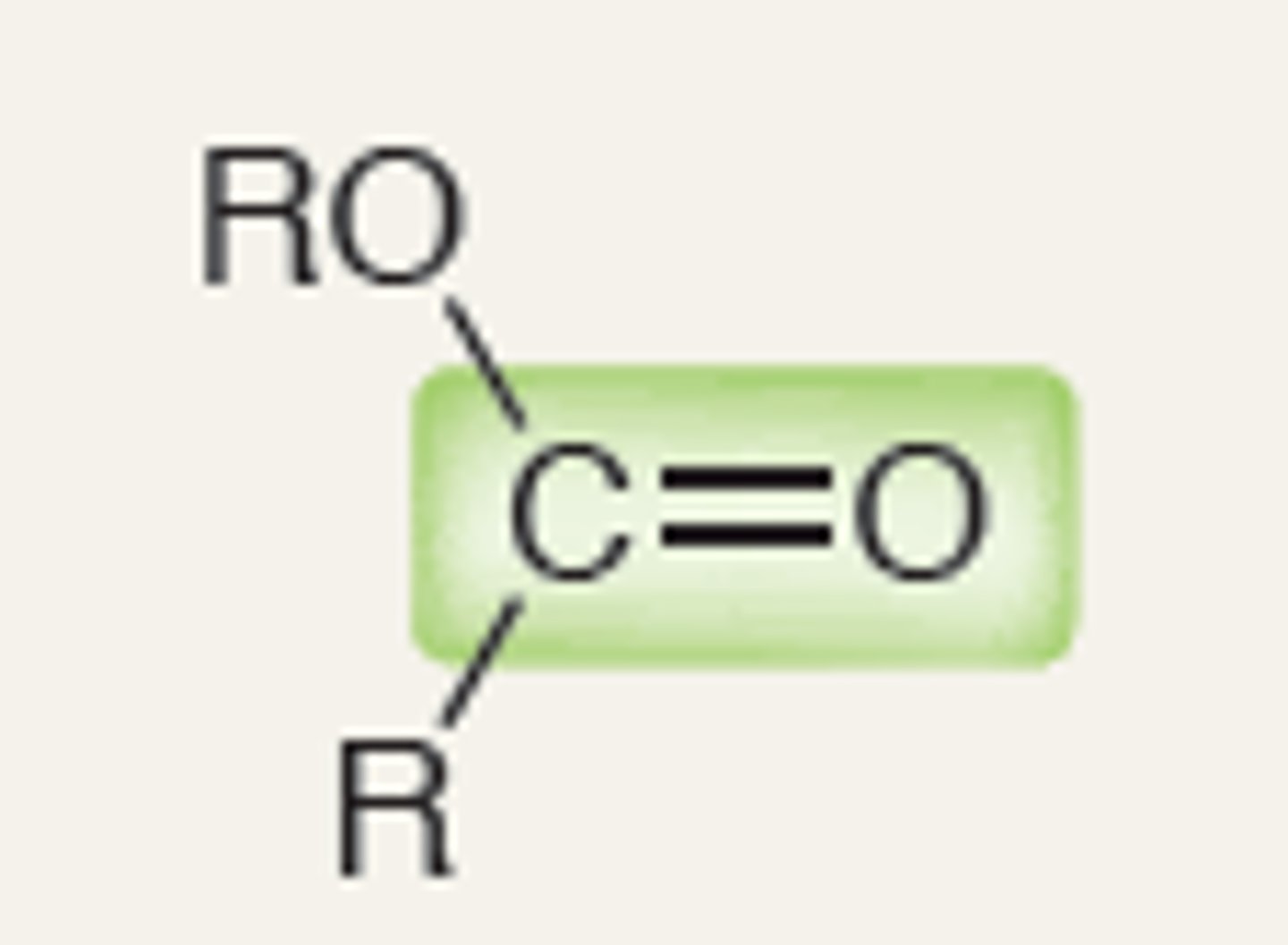
1760
Carboxylic Acid
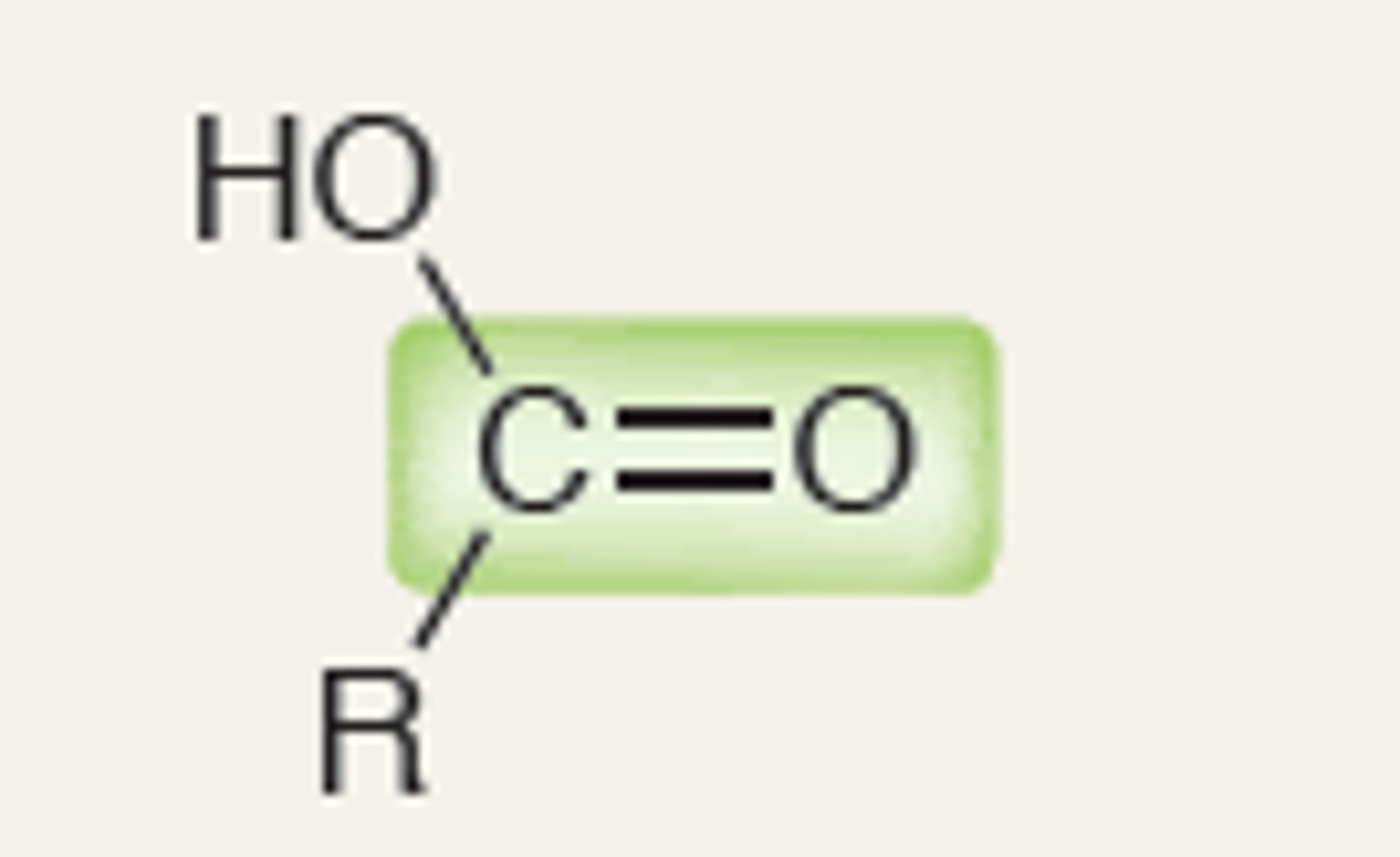
1760, 1820
Acid Anhydride
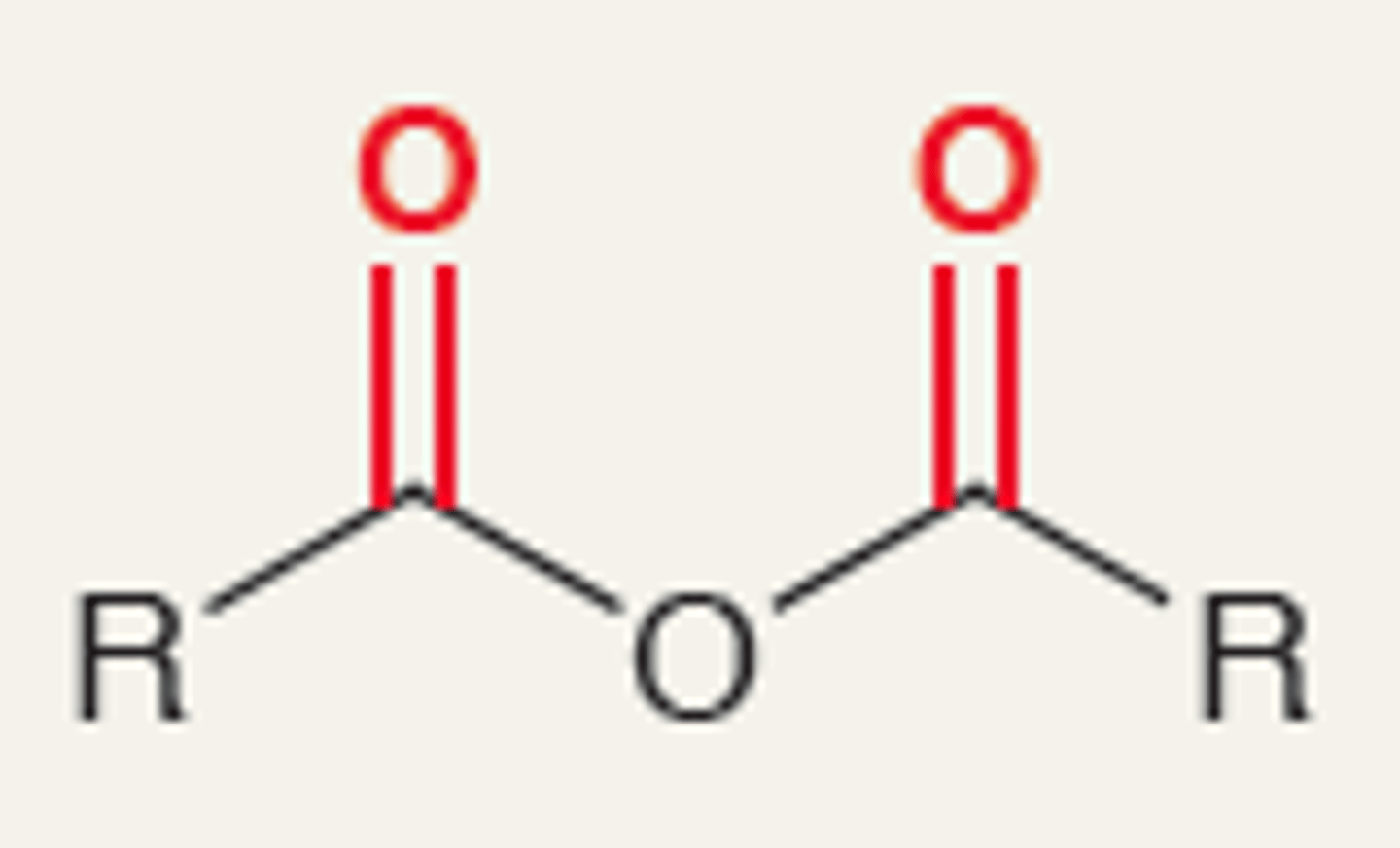
1800
Acid Chloride
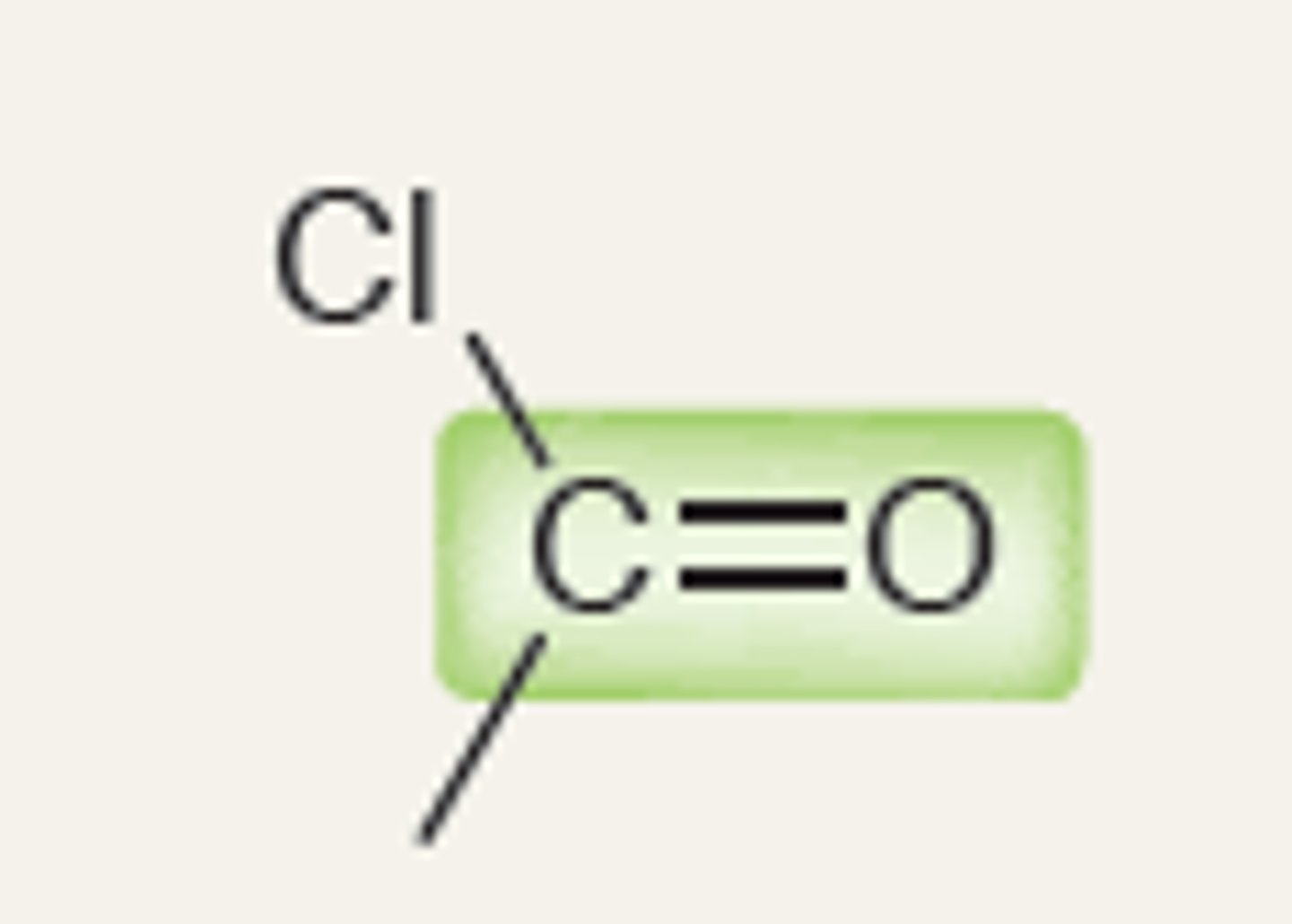
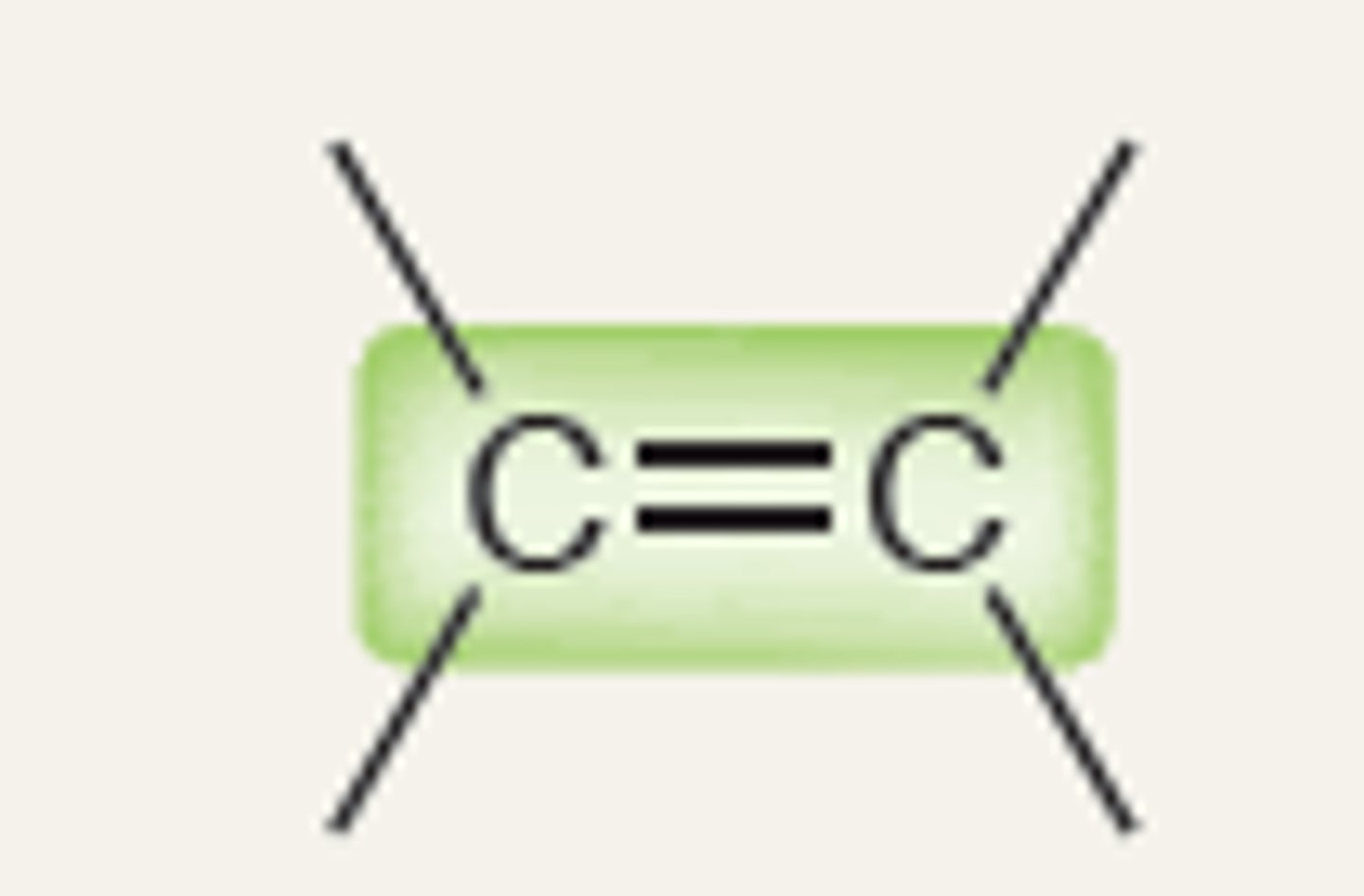
2100-2200
Alkyne
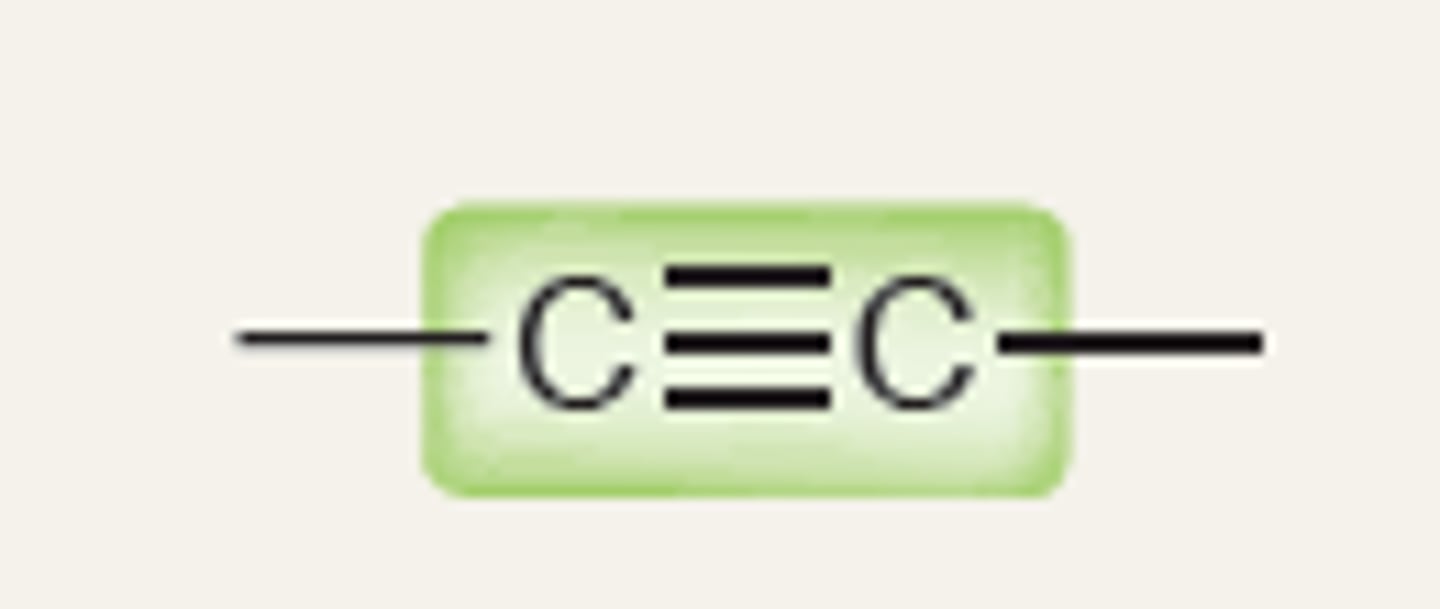
2200-3600
Oxygen of an Ester
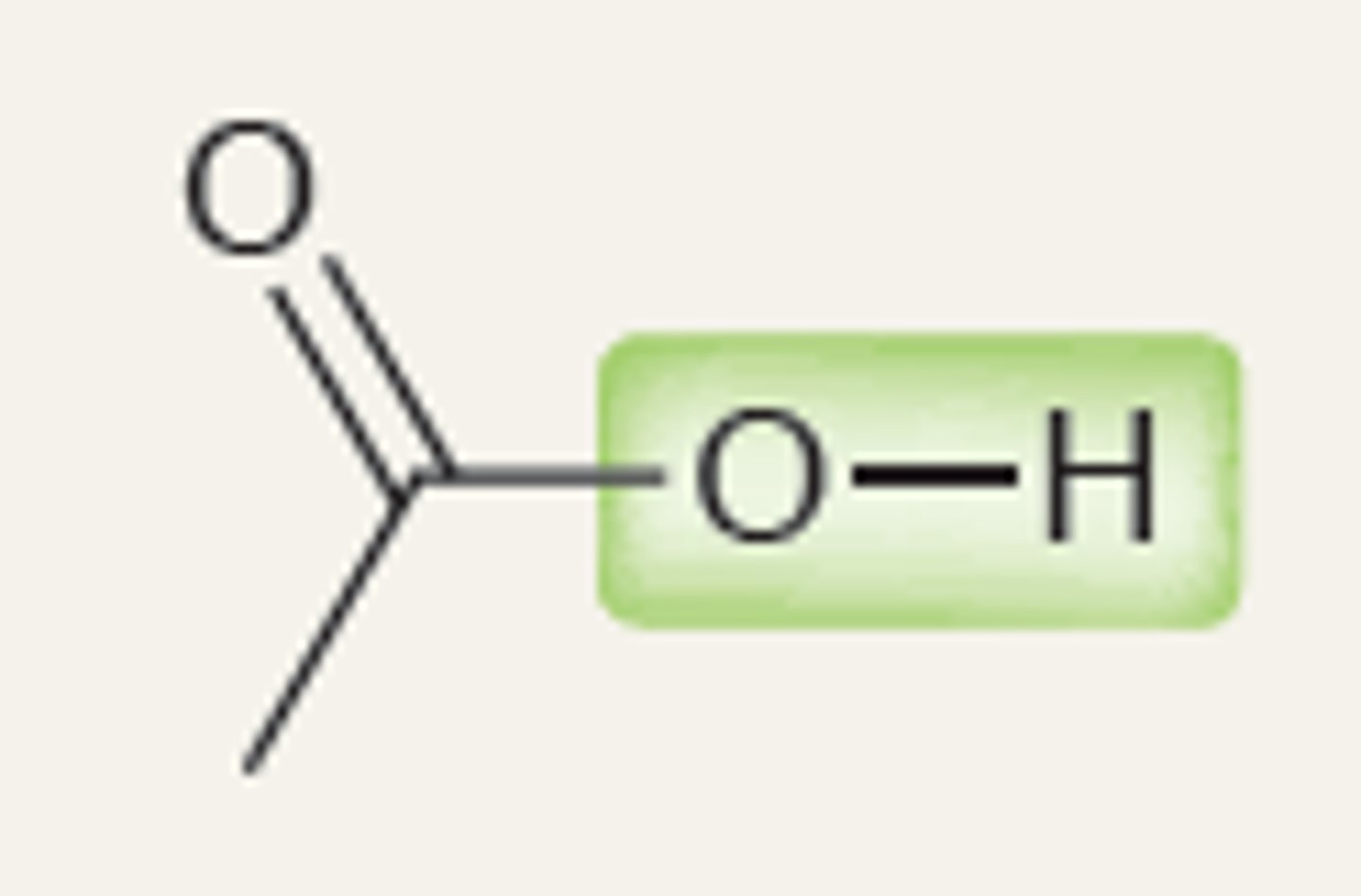
2230
Nitrile

2750
Aldehyde
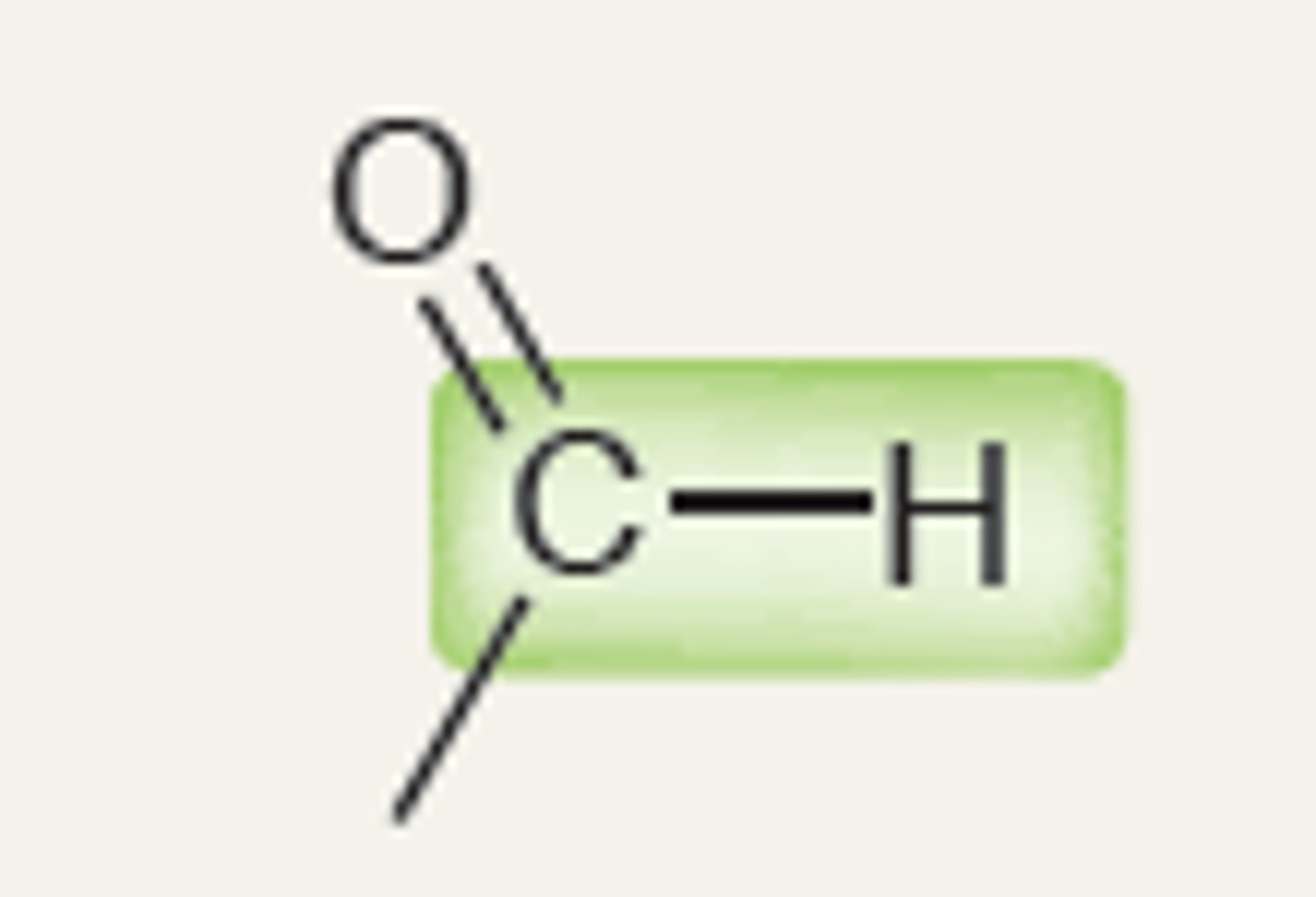
2900
Alkane
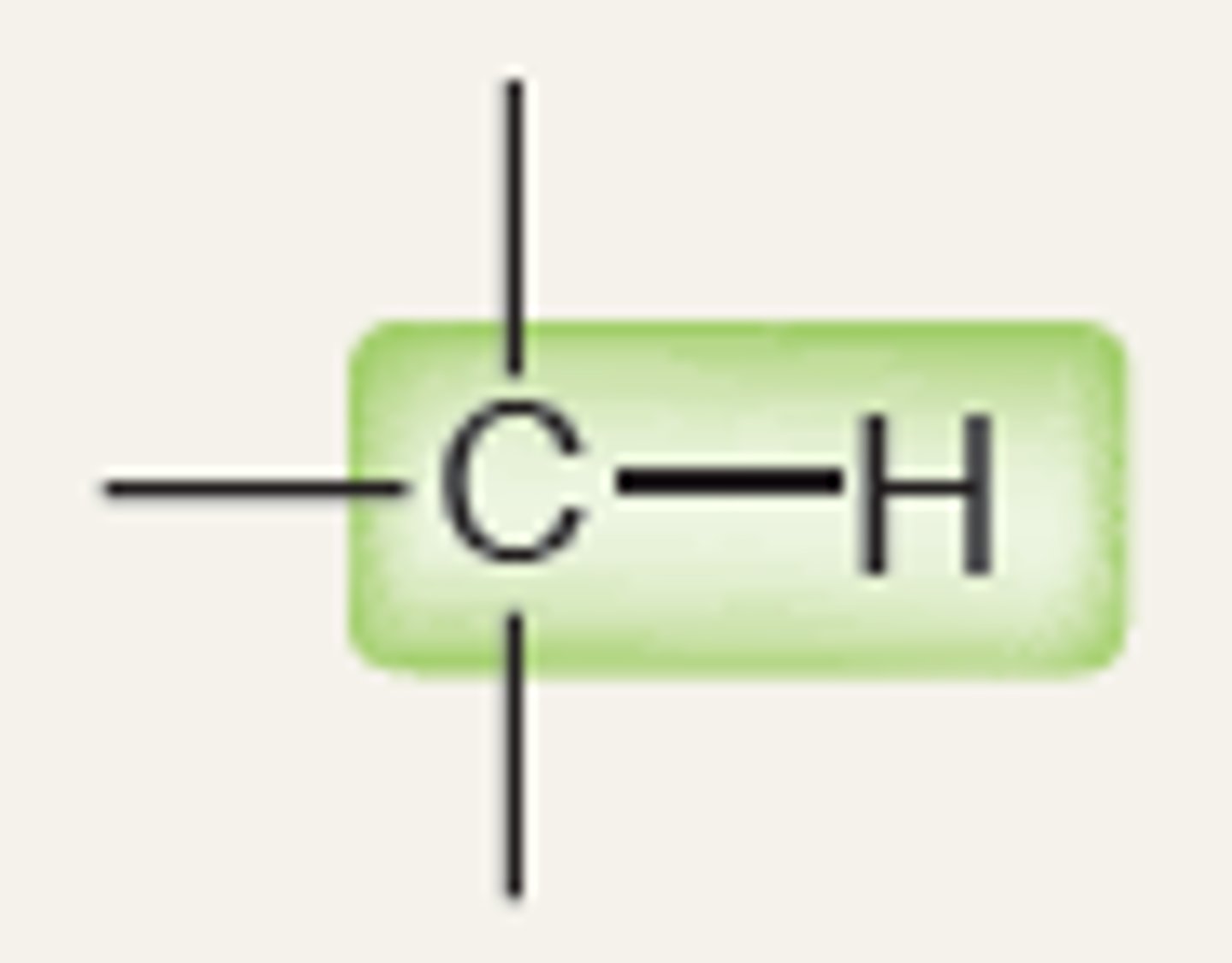
3100
Alkene (sp2)(vinylic C-H bond)
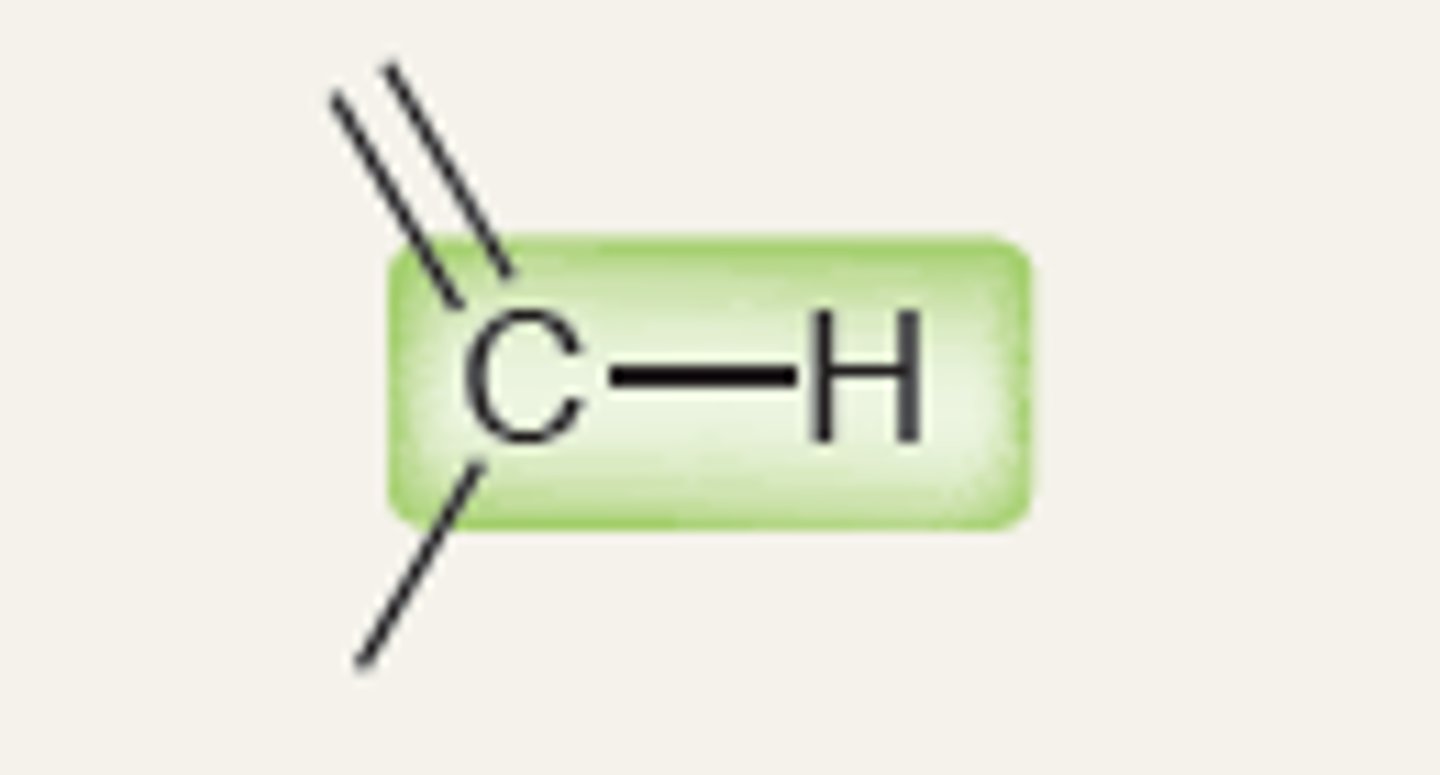
3200
Secondary Amine
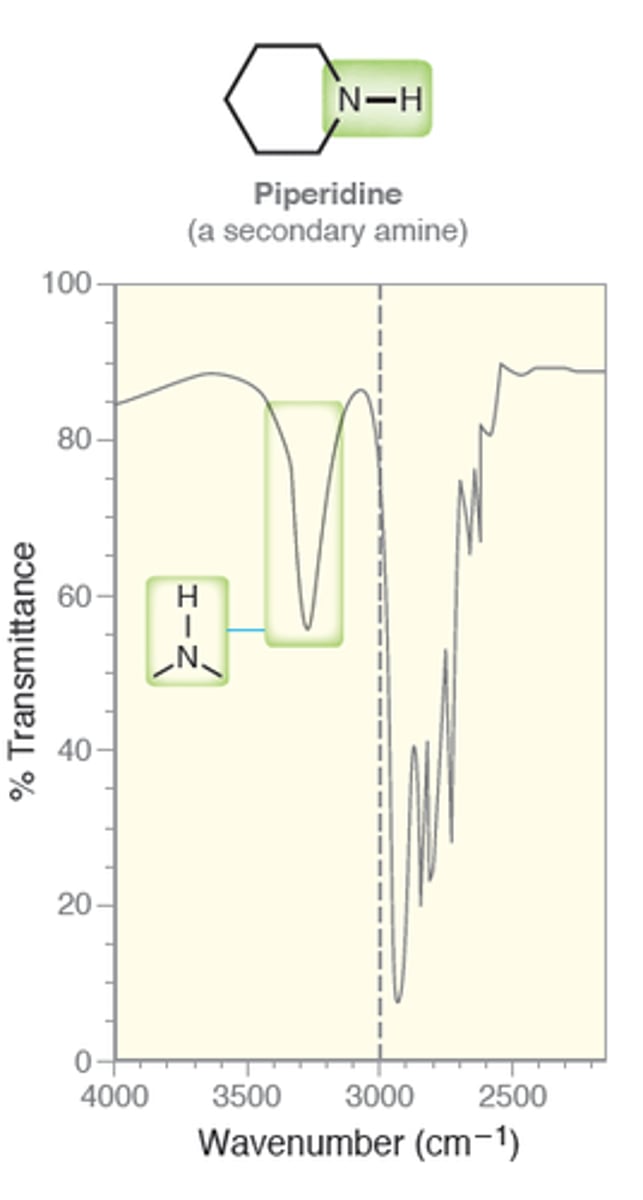
3300
Alkyne (sp)
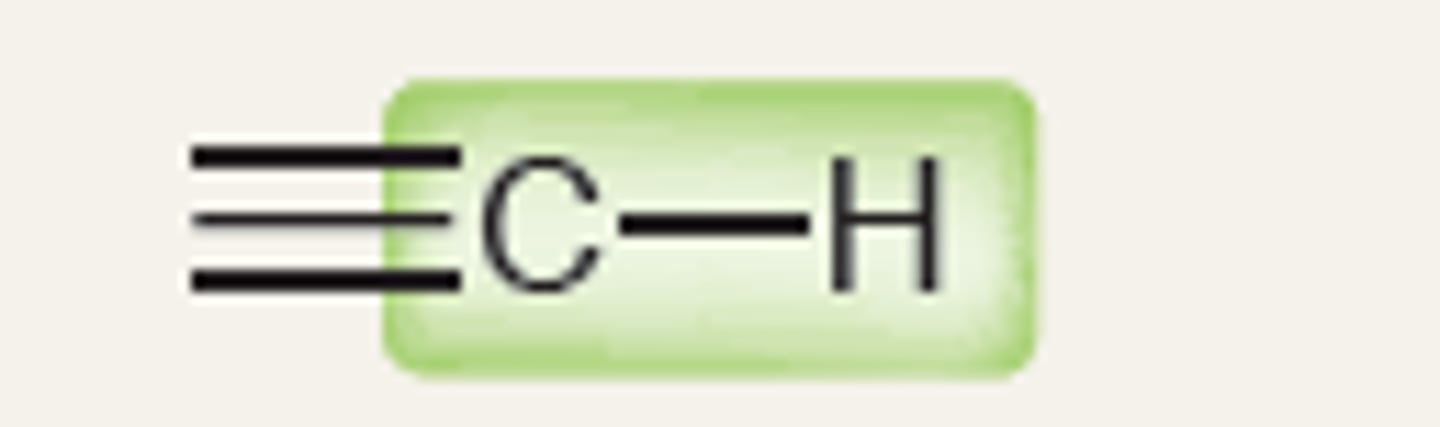
3350, 3450
Primary Amine
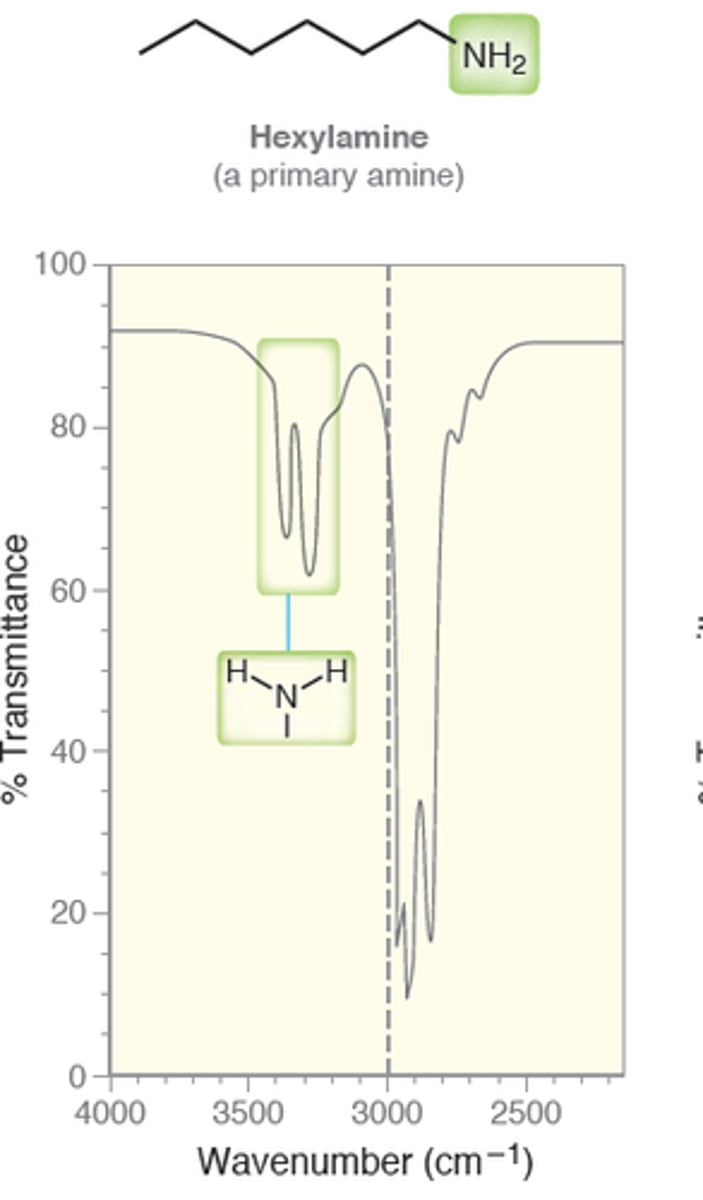
3200-3600
Alcohol
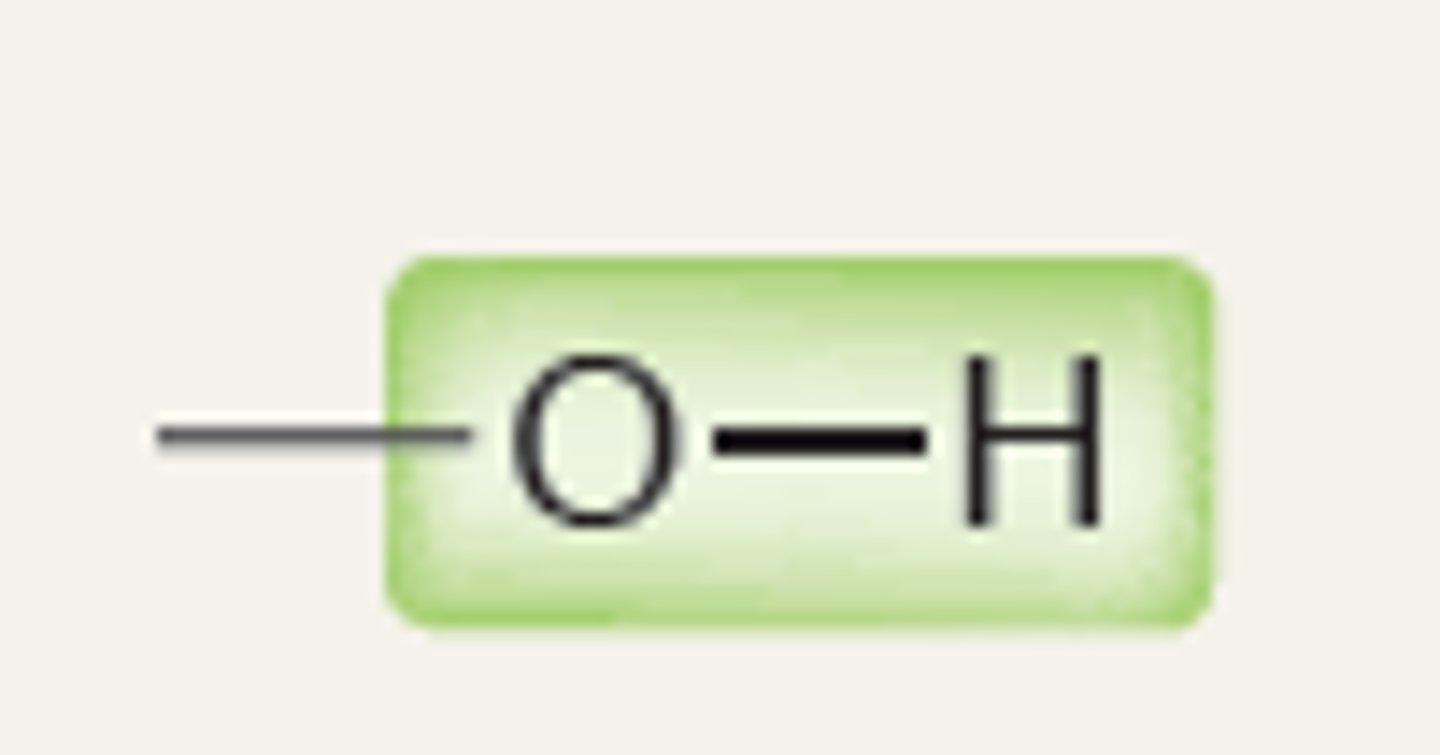
3000
Ether
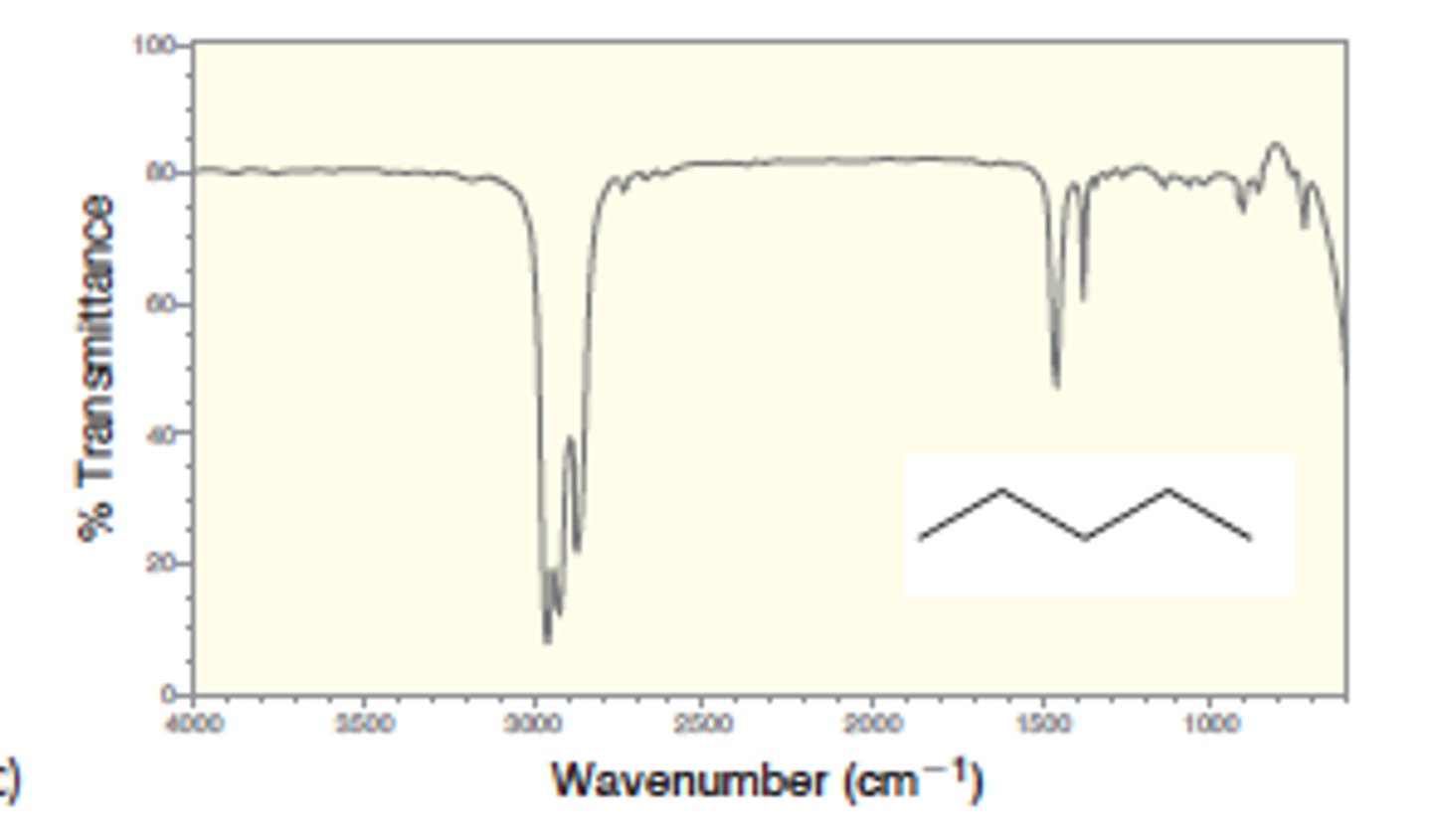
IR absorption of Alkane (bond to H- sp3)
2900
Medium
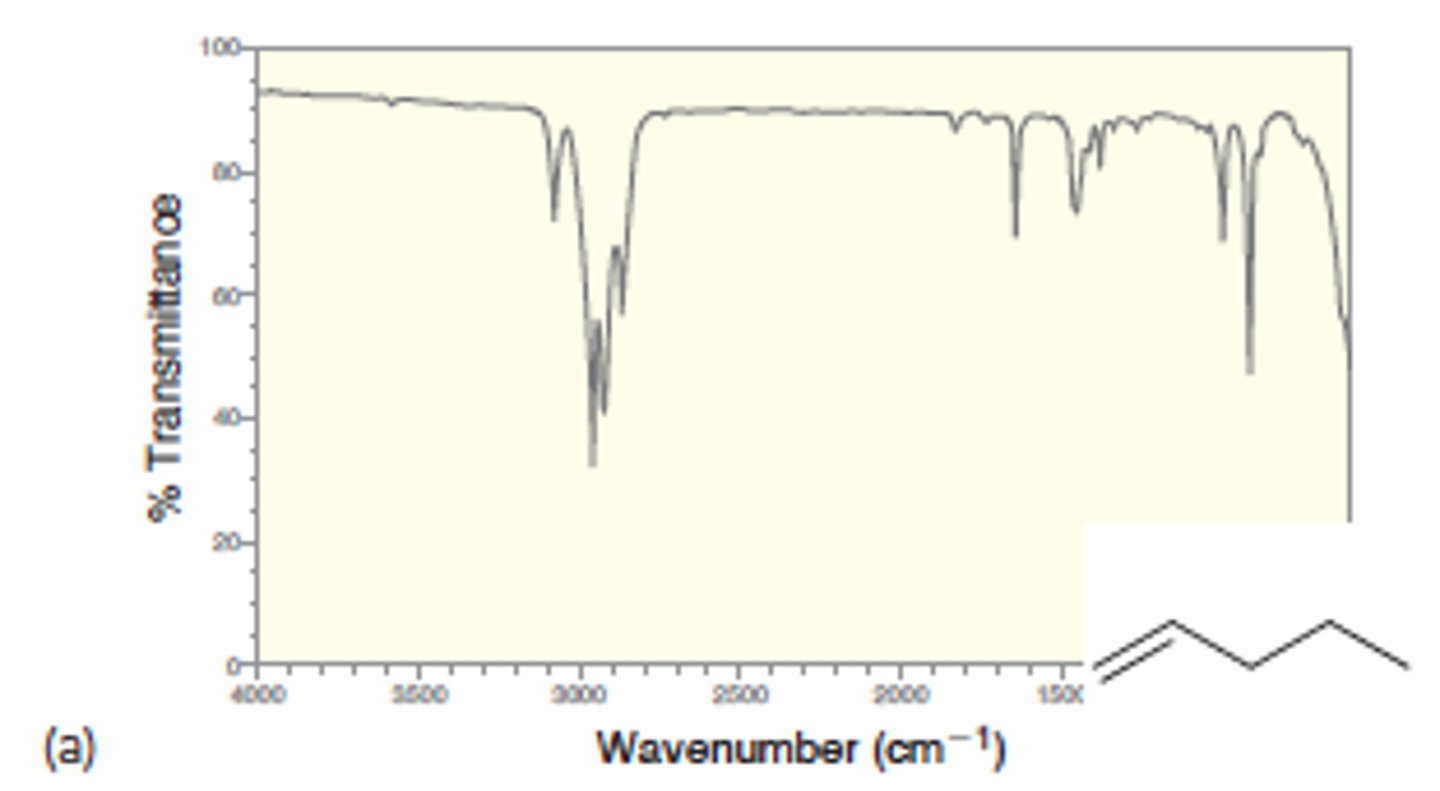
IR absorption of Alkene: =C-H (bond to H - sp2)
3100
Medium
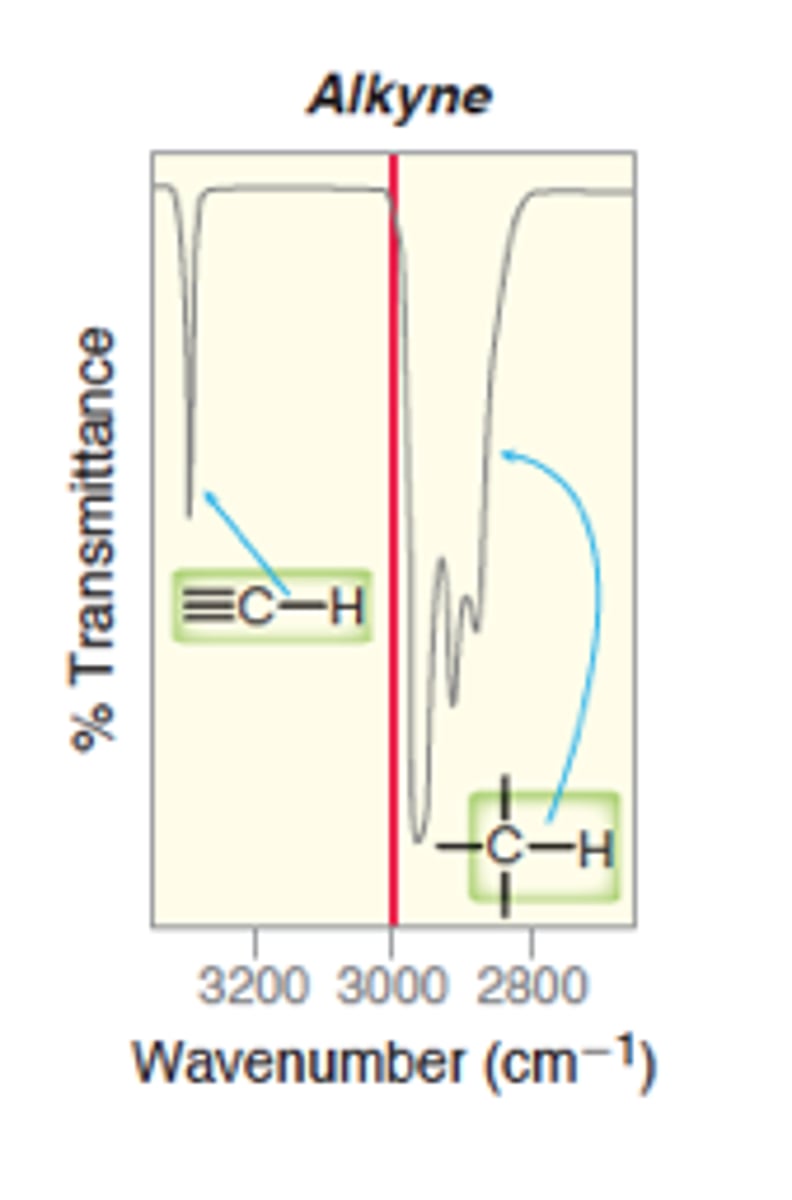
IR absorption of Alkyne: =C-H (bond to H - sp)
3300
Strong
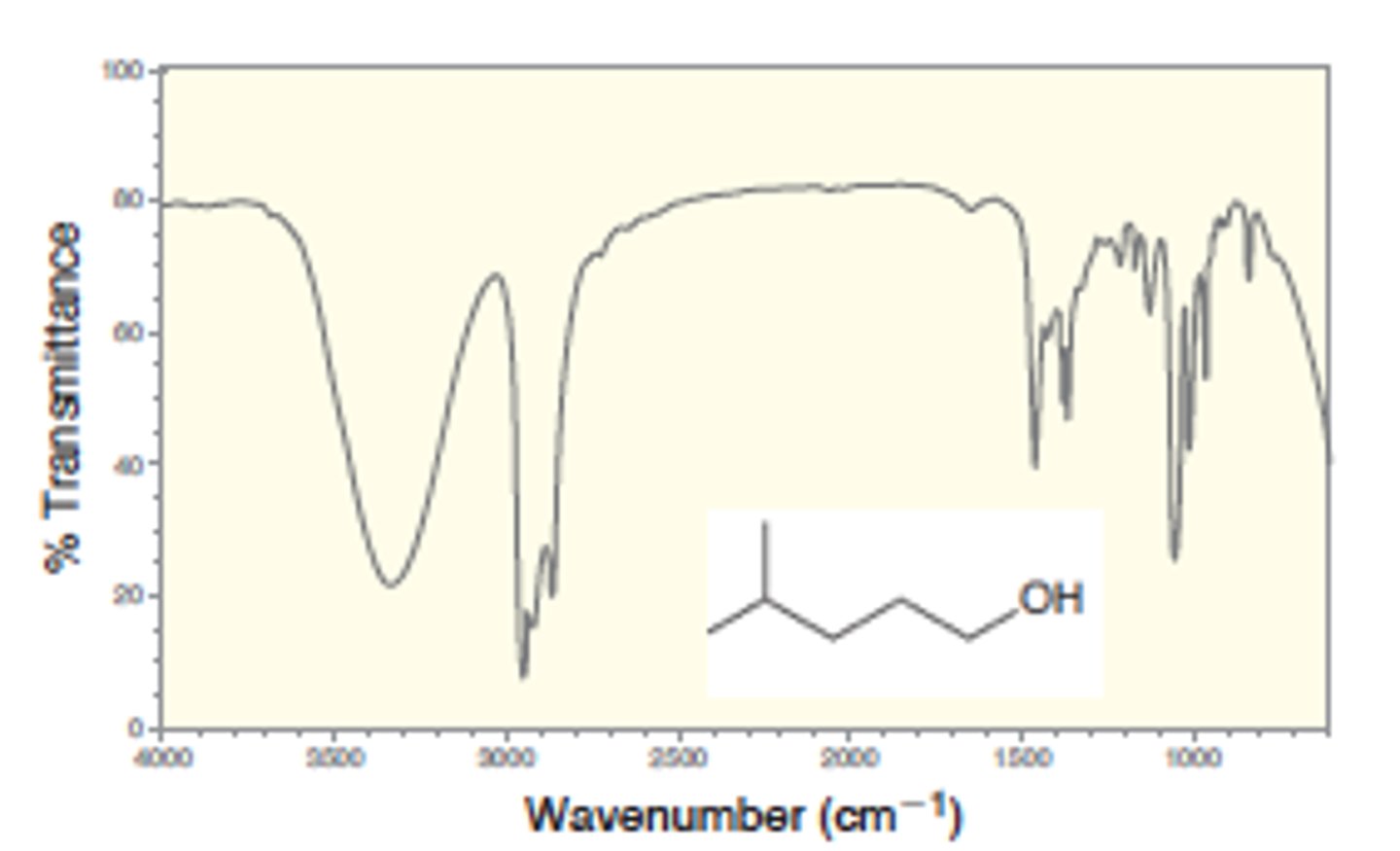
IR absorption of Alcohol
3500
1.) O-H bonds participating in H bonding - broad signal - 3200- 3600
2.) no O-H bonds participating in H bonding - narrow signal - 3600
Strong, broad
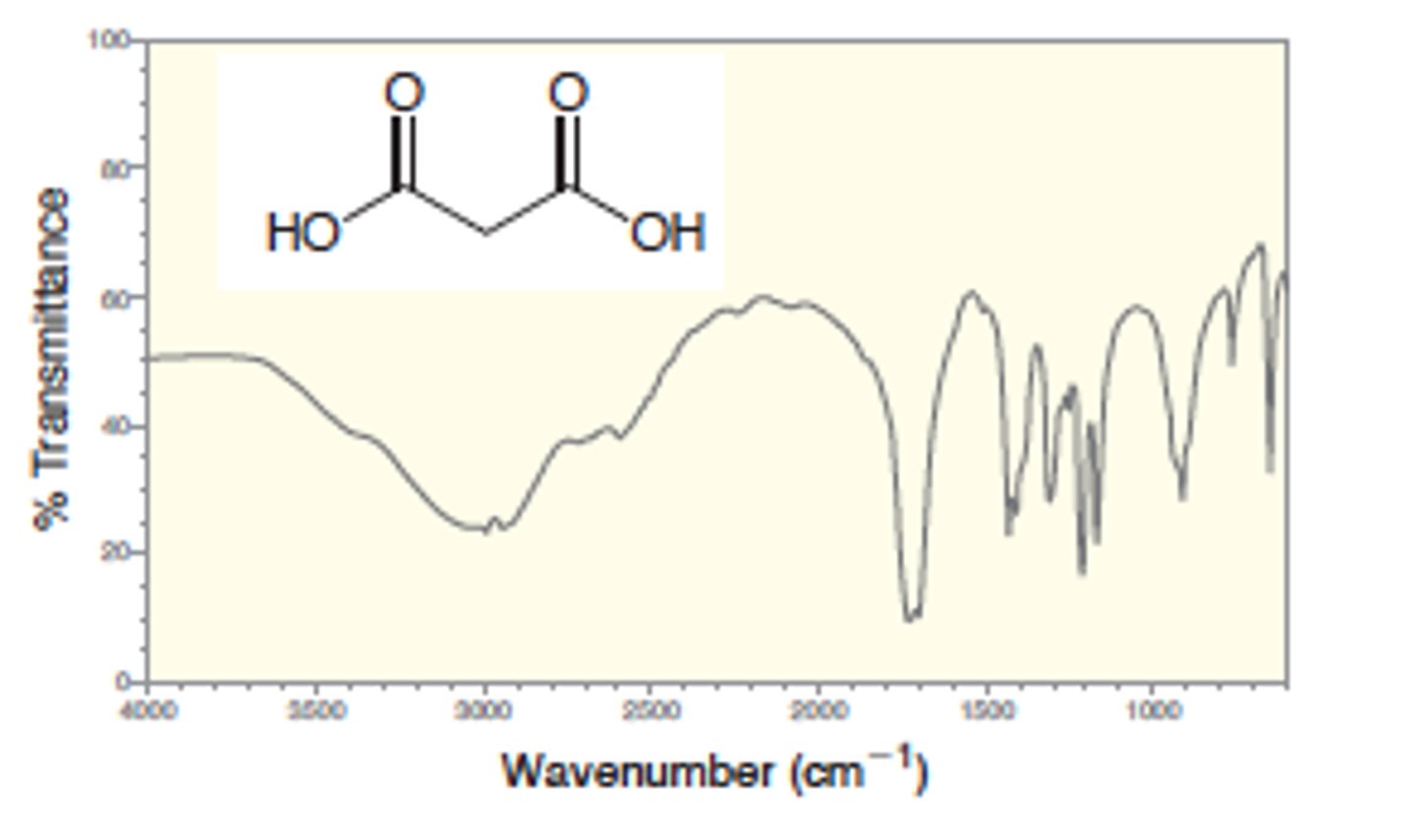
IR absorption of Carboxylic Acid
1.) O-H with strong H bonding: 2500 - 3600
2.) also accompanied by broad C=O signal: 1700
Strong
Ketone
1720
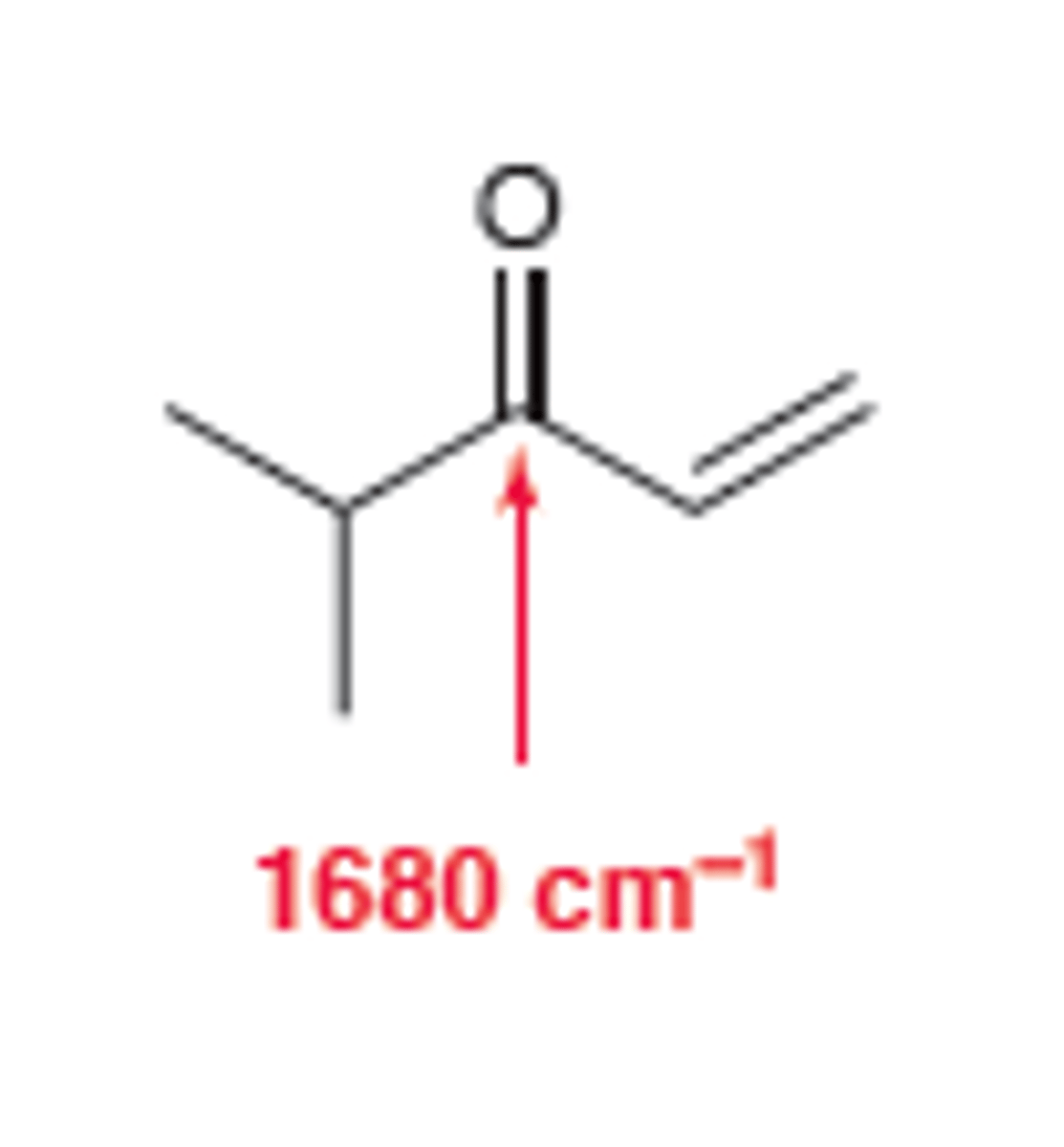
Conjugated Ketone
broad and strong C=O signal appears at 1680
IR absorption of Ester
1740
Strong
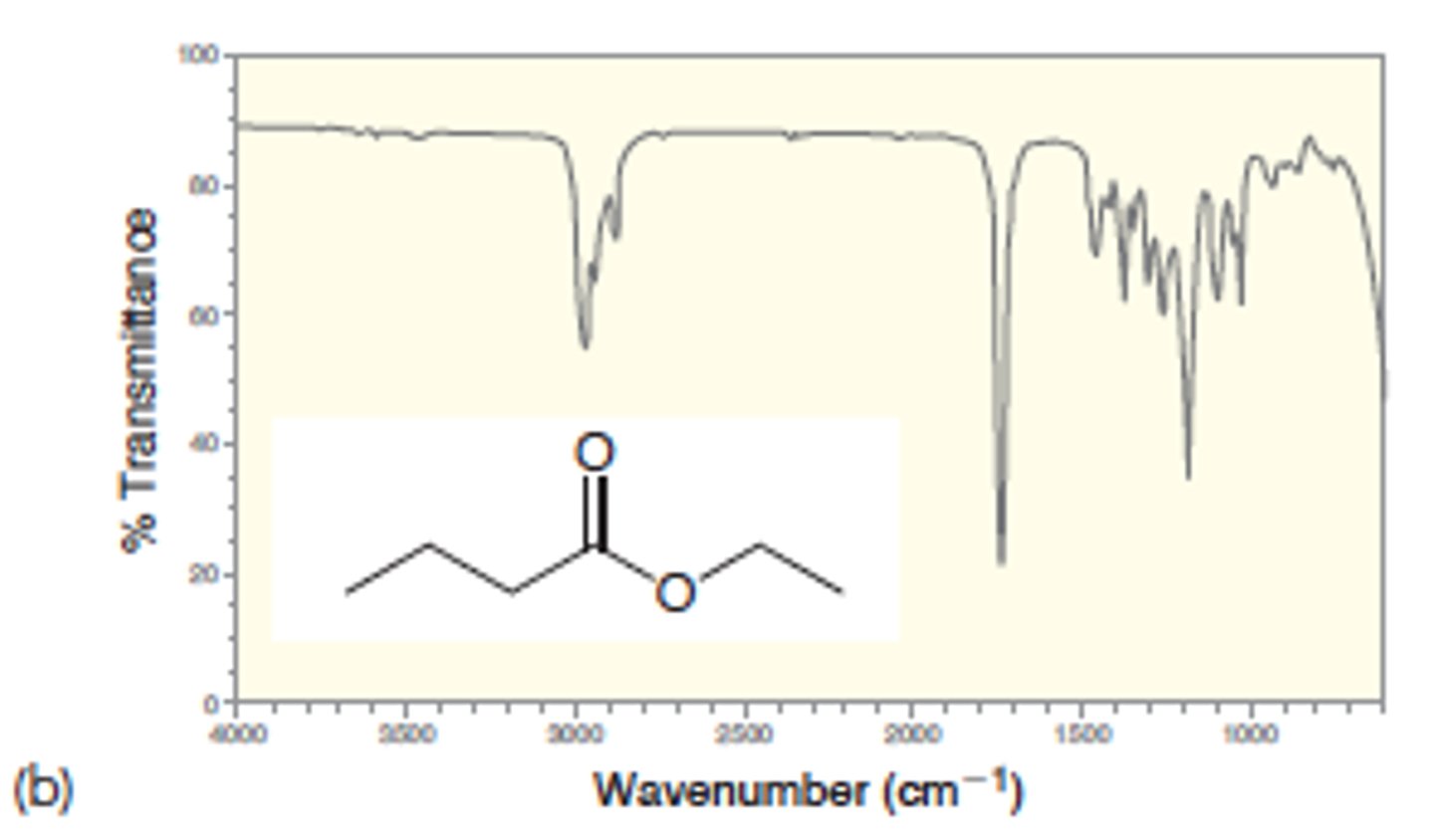
Ketone vs Ester
IR absorption of Aldehyde
1700 - 2700 (2750)
Strong
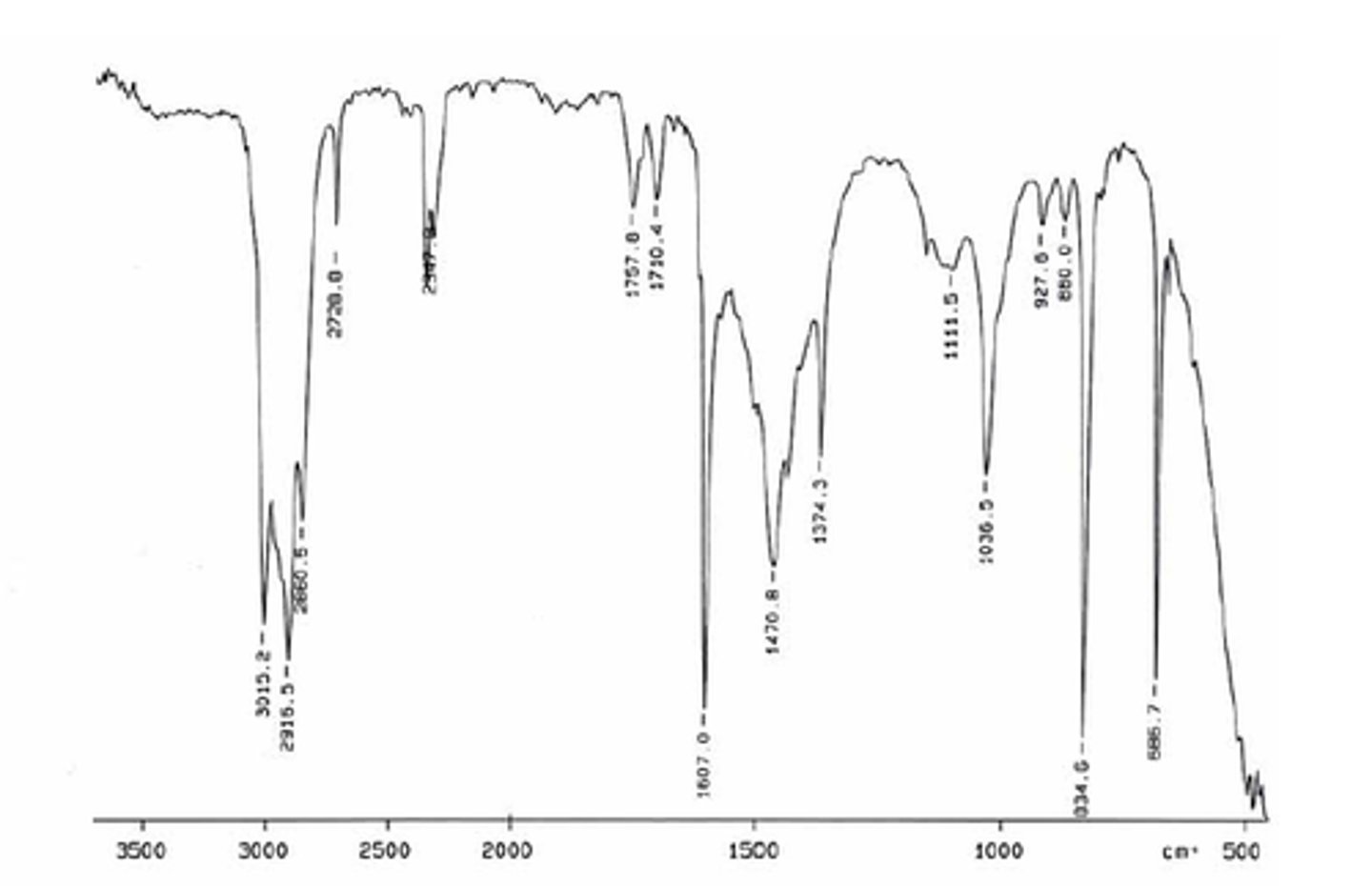
IR absorption of Conjugated Ester
1710
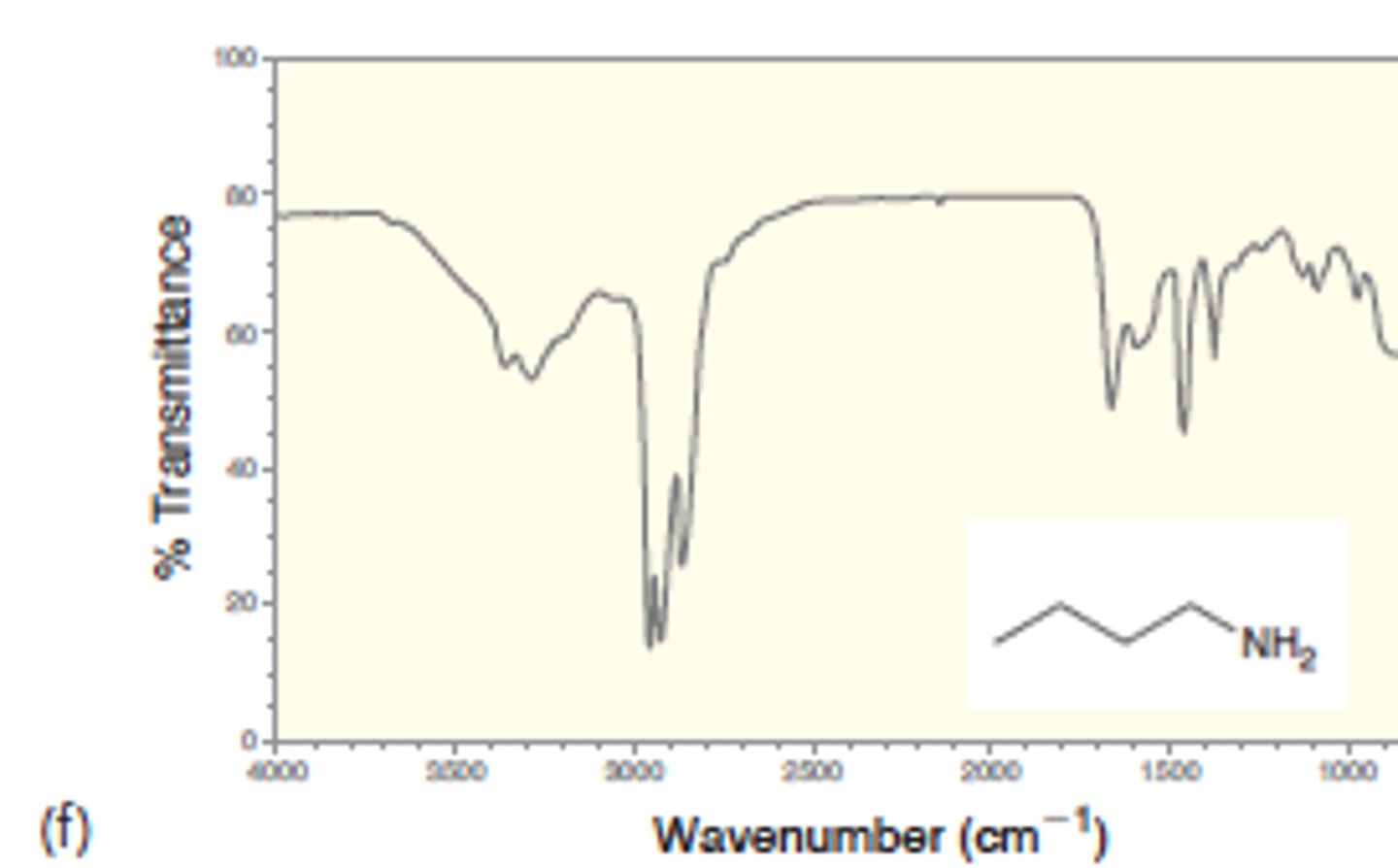
IR absorption of Primary Amines: N - H2
two signals at 3350 and 3450
Medium
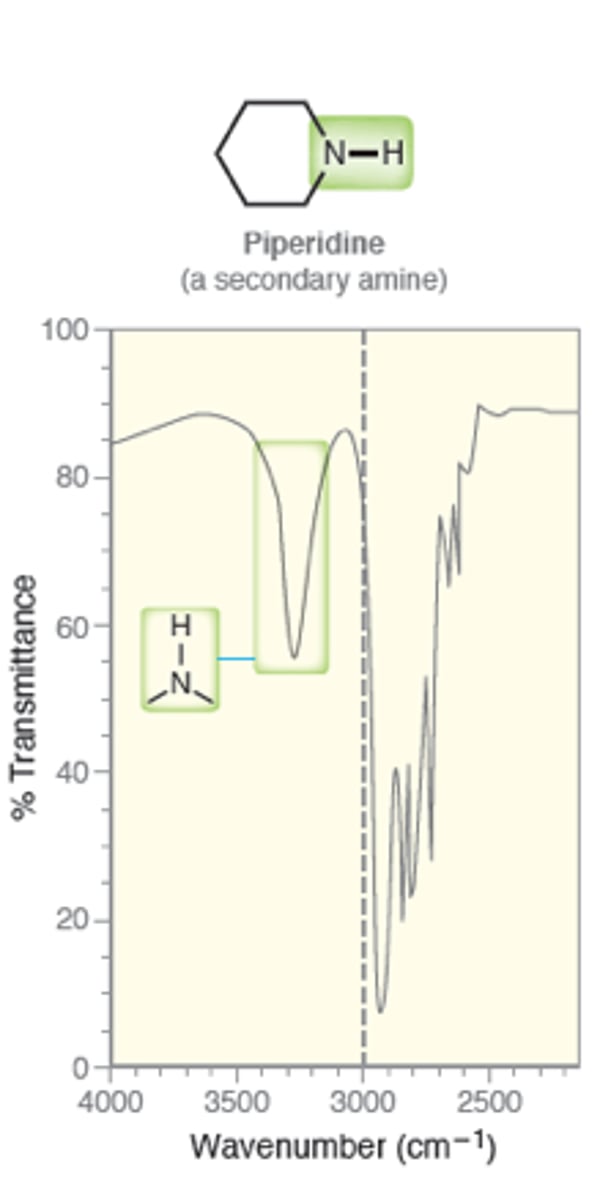
IR absorption of Secondary Amines: N - H
one signal at 3200
weak
IR absorption of Amide
1680
Stong
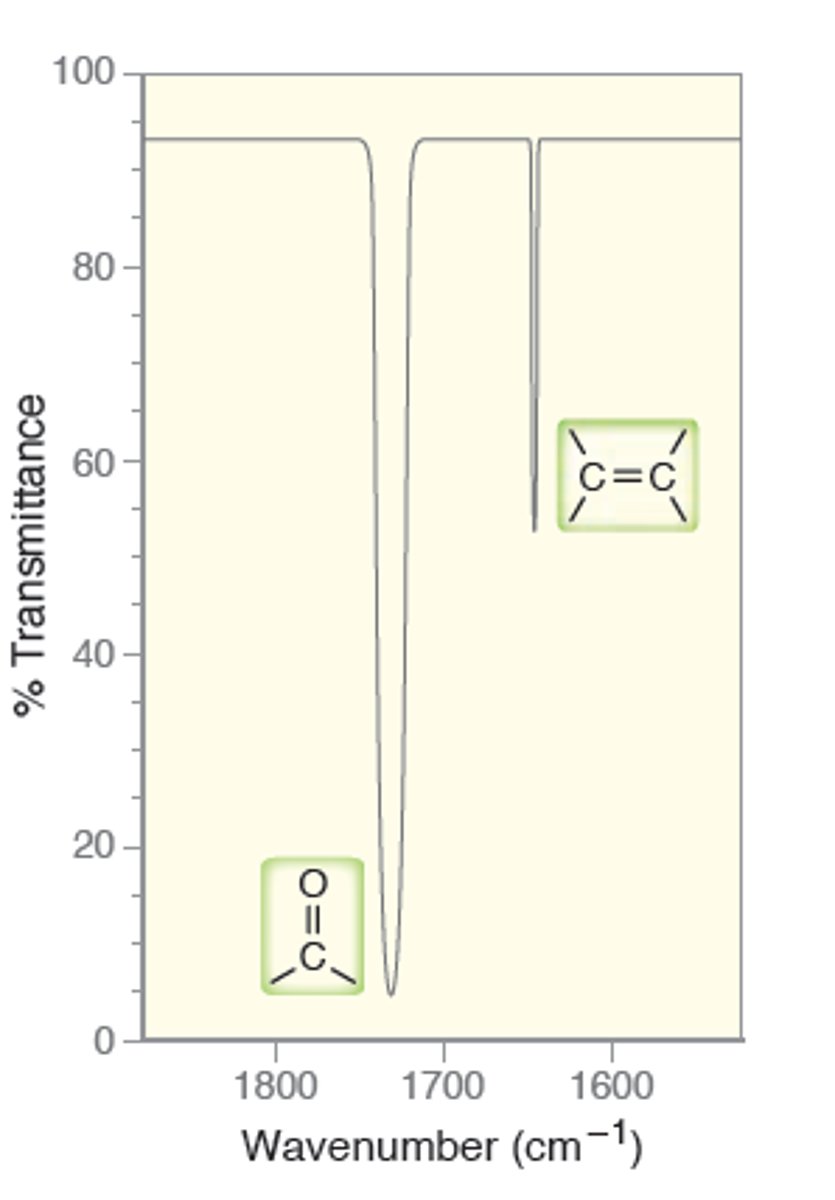
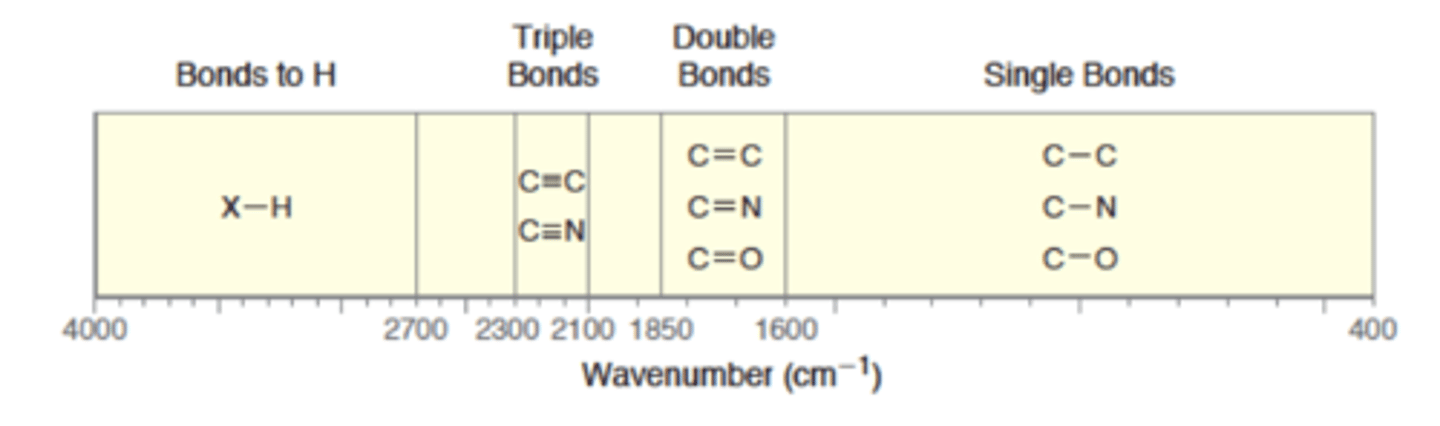
Diagnostic Region
1500-4000
Fingerprint Region
400-1500
IR absorptions of C - N, C - O, and C - C are located in the _______ region.
fingerprint (1600-400)
IR Single Bond Region Alkane
400-1600
IR Double Bond Region Alkene
1600 - 1850
IR Triple Bond Region Alkyne
2100-2300
Medium
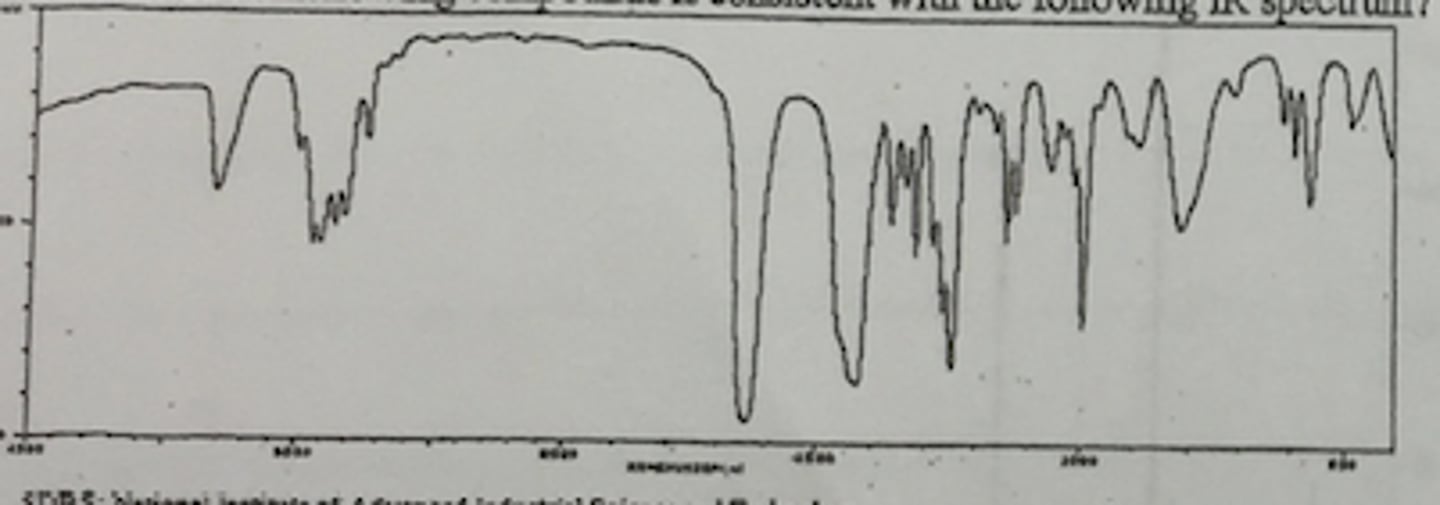
Analyzing IR spectrums:
1.) draw line at 1500
2.) focus on any signals to left of this line (diagnostic) and identify Alkanes (3000); Alkenes (1600+); Alkynes (2200)
-use tables below
- each signal appearing in diagnostic region will have 3 characteristics: wavenumber, intensity, and shape
3.) when looking for X—H bonds - draw line at 3000 and look for signals that appear to left
Calculating HDI
1.) rewrite the molecular formula as if the compound had no elements other than C and H
- Add one H for each halogen
- Ignore all oxygen atoms
- Subtract one H for each nitrogen
2.) determine how many Hs missing
C6H12 - 6 carbon atoms require (2 X 6) + 2 = 14 - missing 2H atoms - one degree of unsaturation for 2 H missing
C4H6 - 4 carbon atoms require (2 X 4) + 2 = 10 - missing 4H - 2 degrees for 4 H missing
HDI of 4 or more indicates:
aromatic ring
HDI = 0
no rings or double bonds
HDI = 1
must have either 1 double bond or 1 ring but NOT both
HDI = 2
then there are a few possibilities: two rings, two double
bonds, one ring and one double bond, or one triple bond
sp bond has shortest bond length
strongest bond
sp3 has longest bond length
weakest bond