excretion
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
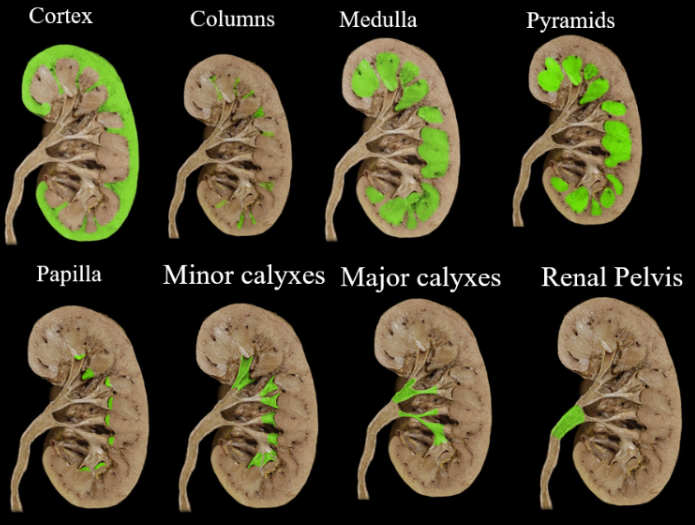
the kidneys
Main function: water balance
Renal artery = main artery
Vasa recta: network of BVs surrounding the loop of Henle
Using the flat kidney diagram on the practical
contains macula densa
macula densa
Macula densa: sense sodium chloride (salt) and pressure
Draws water to it when salt concentration is high
Decreases resistance to blood flow in afferent arterioles
Forces more blood to flow through the arterioles → raises BP
Increases renin release → will increase water reabsorption
Juxtaglomerular cells: cells that line the macula densa
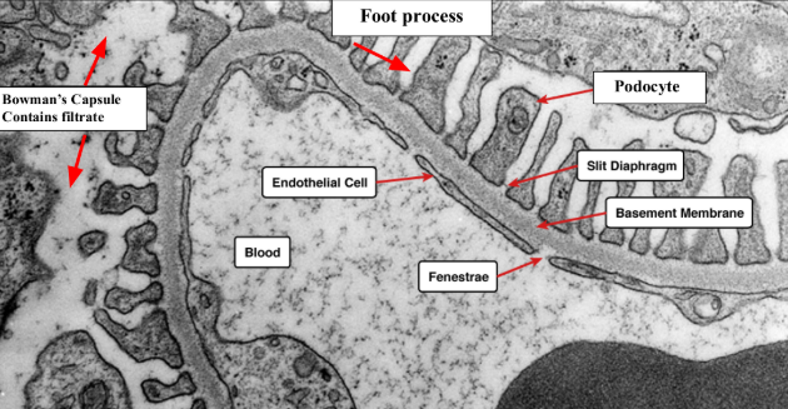
filtration barrier of kidneys
Filtration barrier: negatively charged that repels proteins → want proteins to be reabsorbed (you could die)
podocytes
Inside filtration barrier
Podocytes: cell bodies form foot processes that wrap around the glomerular capillaries
Form the barrier
Things that are filtered out of the filtrate (stuff you want) go back into the bloodstream
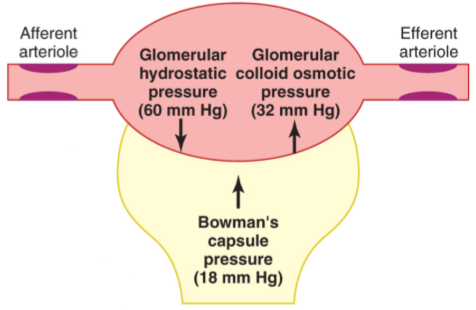
pressure
Pressure is positive if water flows from the capillaries to the Bowman's capsule
Pressure is pushing against the wall of the capillary
Glomerular colloid osmotic pressure: pressure of large proteins
Albumins → set up colloid osmotic pressure to prevent protein loss from blood
Can’t get out but they have pressure acting on them
Pressure from Bowman’s capsule is pushing on the capsule
Net filtration pressure (10 mmHg) = glomerular hydrostatic pressure (60 mmHg) - [ Bowman’s capsule pressure (18 mmHg) + glomerular osmotic pressure (32 mmHg) ]
If it's negative then you’re in kidney failure
Easier to add up Bowman’s capsule and osmotic pressure before subtracting because they act in the same direction
renal tubules
Filtration + secretion - reabsorption = excretion
tubule epithelium
simple cuboidal
ureter epithelium
transitional epithelium
holds volume
bladder epithelium
smooth muscle and skeletal muscle