unit 4 - Autonomic Nervous System
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Adrenergic Agonist
Autonomic nervous system
Alpha
(Eye) Dilate pupil
Alpha 1
Blood vessels
Vasoconstriction
> BP
Beta 1
Heart
> heart rate
Beta 2
(Lungs) bronchodilation
Beta 1
Heart
> heart rate
Beta 2
Gastrointestinal
Relax (reduce gastric secretions and motility)
Beta 2
Bladder
Relax (< urination)
Beta 2
Uterus
Relax (decrease contractions)
Beta 2
Liver
Glucose release
> blood glucose
Alpha 1
Constriction
Alpha 2
Dilation ?
Beta 1
Increase heart
(Indirectly) > BP
Beta 2
Increase lungs ?
Bronchodilation
Beta 3
Increase bladder relaxation
-zosin
Alpha 1 blocker
-stigmine
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (AChEI)
-Chol
Muscarinic Cholinergic agonist
-enic-
Nicotinic
-olol
Beta 1 blocker
Antiarrythmics & Blood clotting drugs - cardiovascular system
Class I Sodium channel blocker
-mide
Class II antiarrhythmics are essentially all Beta-1 antagonists (beta blockers)
-olol
Class III Potassium channel blocker
-darone (long word like potassium)
Class IV Calcium channel blocker
Verapamil
(NSAIDs) Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
NSAIDs reduce:
Inflammation
Pain
Fever

Antiplatelet
-grel (grinch-green slime- sticky-Antiplatelet)
Use - reduce heart attack
MOA - inhibit platelets which prevent blood from sticking to each other

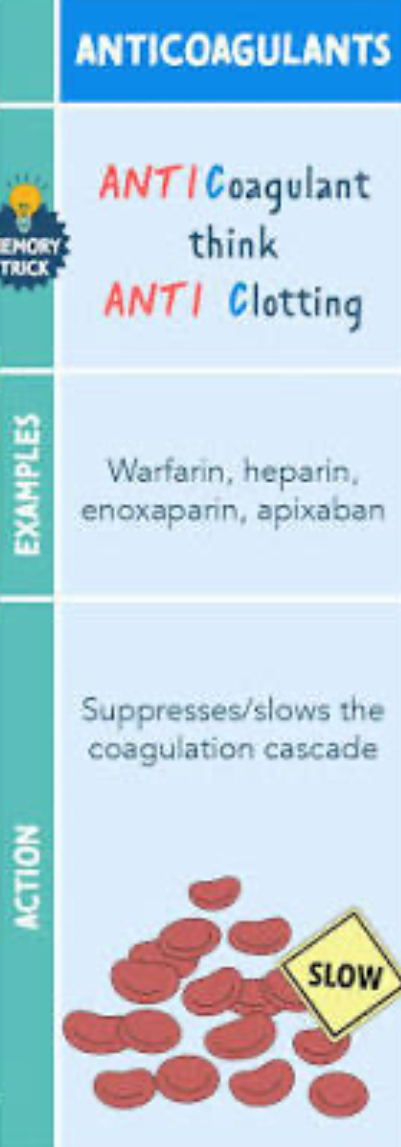
Anticoagulant
-arin , -xaban
Thrombolytic
-plase (plaTe)

Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
(–zolamide drugs) promote bicarbonate excretion, causing mild diuresis and metabolic acidosis.
ARBs Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker
(–sartan drugs) lower blood pressure by blocking angiotensin II receptors, causing vasodilation and reduced aldosterone release.
ACE = make less Ang II
ARB = Ang II can’t work
ACE inhibitors
(–pril drugs) lower blood pressure by blocking Ang I to Ang II conversion, causing vasodilation and reduced aldosterone.
“PRIL drugs prevent pressure, but cause cough, angioedema, and high potassium.”