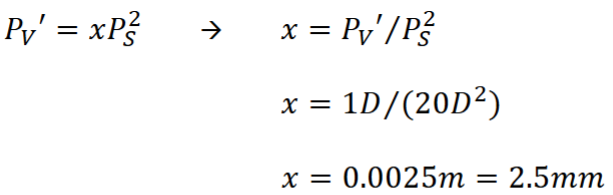3 Power Specif
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Nominal Power / Approximate power - how do we find it?
Thin lens power (ignore lens thickness)
Algebraic sum of lens surfaces (P1+P2)
Power found using Lens Clock
How do you get Nominal power using Jackson crosses?
Make cross for front and back surfaces, sum them
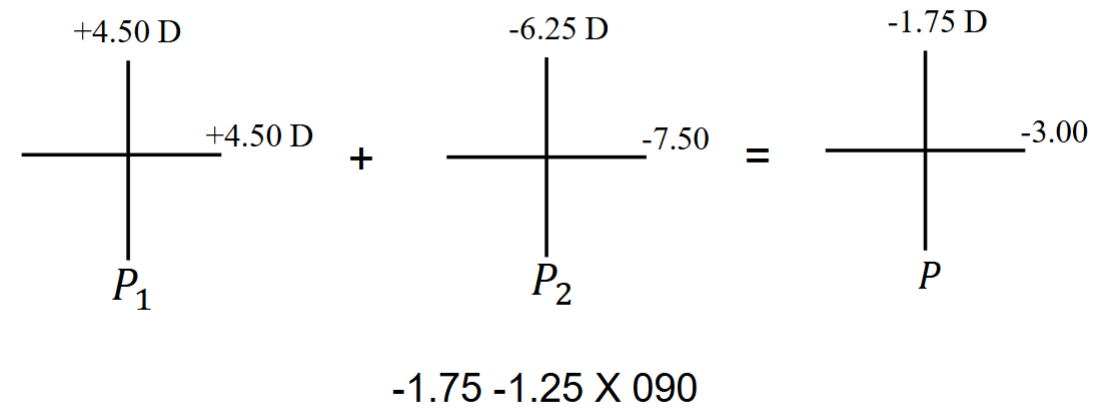
Equivalent power (true power) - definition, when is it used?
Models optical system into a single, infinitely thin lens
Used to specify low vision devices (otherwise, not really used in opt)
Front vertex power (neutralizing power) definition, when is it used?
Refracting power for rays emerging at front surface of lens (vergence of light if it were to enter the back and go to the front)
Or, vergence of light needed to enter front of lens to be parallel leaving the back
Found with hand neutralization
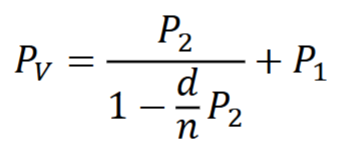
Back vertex power - definition, when is it used?
Refracting power for rays emerging at back surface of lens
we use this a LOT for power specification in ophthalmic prescriptions (spec and CL)
Normally, a lensometer measures BVP
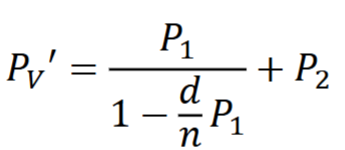
Why do we use back vertex power so much?
because it gives the secondary focal point of a prescribed lens, which should coincide with the far point of the eye for a Rx
Effective power
Describes apparent change in power the patient receives (the refractive behavior of the lens) with changing the vertex distance of a lens
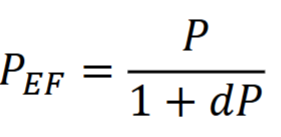
If lens is moved toward the eye, d is (positive or negative?)
positive
If lens is moved away from the eye, d is (positive or negative)?
negative
Compensated power
The power of a lens needed to replace a given lens when changing the vertex distance
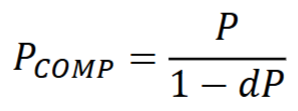
When moving a plus lens closer to a screen, the lens power must ___ to maintain a clear image on the screen
increased
When fitting contact lenses, myopes have CL power less than spectacle lens power - and hyperopes have CL power greater than spectacle power - when powers ___?
≥ ±4.00D
image deviates towards the
apex
Where would the image move if a minus lens was moved up on a patient’s face?
up (towards apex)
Where would the image move if a plus lens was moved up on a patient’s face?
down (towards apex)
Hand neutralization (shaking out a lens)
Neutralize motion seen through lens by
Holding lens of known power against unknown lens while moving it side to side (or up and down)
Observe motion of objects within lens aperture compared to those outside the lens
Hand neutralization determines which power?
front vertex power
If “with” motion is observed in hand neutralization, there is net __ power
minus
If “against” motion is observed in hand neutralization, there is net __ power
plus
in hand neutralization, should we use spherical or cylindrical lens to neutralize principal meridians?
spherical, to neutralize each meridian separately
How should the final known lens in hand neutralization be changed to find the unknown, neutralized lens?
equal power but opposite sign
Lensometry uses what kind of power
BVP, when back of lens is placed against lens stop
exception: FPV when measuring Add power of multifocal lenses
power of Standard Lens in lensometer
+20 to +25D
Where is the lens stop located in a lensometer and why?
Secondary focal plane of standard lens, keeps target size constant
What is located at secondary focal plane of lensometer?
lens stop, reticle
What kind of telescope is used in lensometer?
Keplerian
Advantages of Badal arrangement
Image size is constant regardless of target position
Equal increments of change in target position result in equal increments of change in vergence in plane of f’
At neutrality of a lensometer, parallel light will leave the
spectacle lens
What limits the range of measurement of a lensometer?
Standard lens (-20.00D has range of ± 20.00 D)
For minus lens measurement, target should move (closer or away) from standard lens?
away
Moving target towards standard lens in lensometer is (positive/negative) distance
positive

How is add power measured in multifocal lenses?
Using Front Vertex Power
Measure distance power
Measure power through the addition (near power)
Add = the additional plus to get to near power
relisten to why…parallel light, something something
Where should distance vision be measured on a PAL?
Distance Reference Point
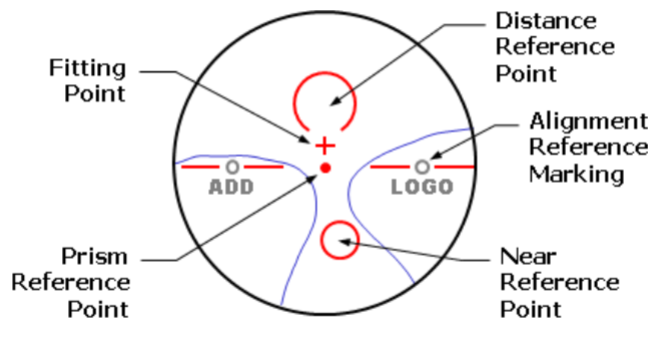
Where should reading addition be measured on a PAL?
Near Reference point
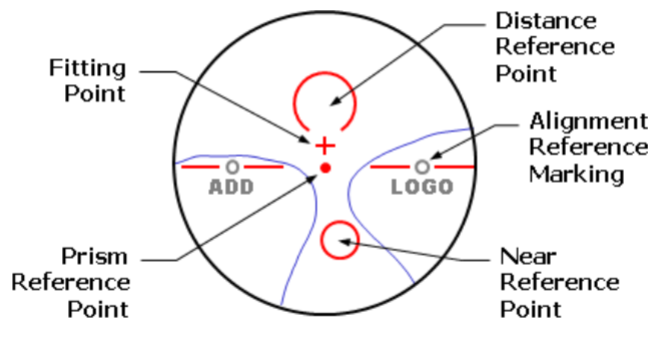
Where should center of pupil be on PAL?
Fitting Point/Cross
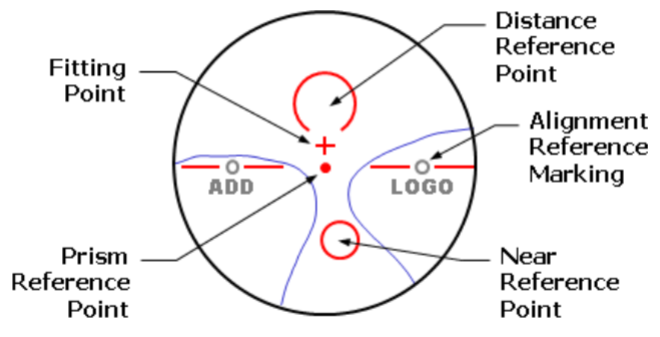
Where should prism be measured?
Prism Reference Point
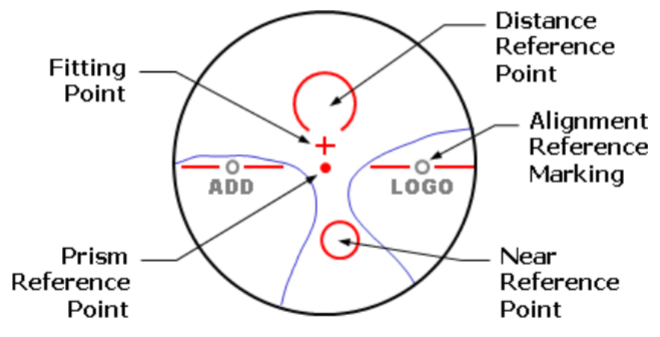
How much target movement is there (per diopter for tested lens) for a lensometer with a +20.00D standard lens?