Cardiopulmonary Radiology and Biomarkers
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Correct technique for taking radiographs includes (3):
1.) correct positioning
2.) correct exposure
3.) correct phase of respiration
What is correct positioning?
in lateral or dorsoventral position with legs angled away from the spine
What is the correct phase of respiration?
inspiration
Why is it problematic to take radiographs during expiration?
lung expiratory films will always look abnormal, which could lead towards misinterpretation
How does age affect the heart in cats?
their aortic root can become enlarged, or the heart can become horizonatally positioned in the chest (rather than an oblique angle like normal)
How is the heart size quantified using radiography?
using the vertebral heart scale (VHS)
vertebral heart scale (VHS)
relates the length and width of the heart to the length of the vertebral bodies
There is a _________ relationship betwen caridac and vertebral dimensions
linear
How is the vertebral heart scale (VHS) determined? (5)
1.) measure the long axis of the heart
2.) measure the short axis of the heart (width)
3.) interpose both measurements onto the vertebrae, starting at T4
4.) count each of the vertebrae that span over both measurements
5.) add the number of vertebrae for the long and short axis together
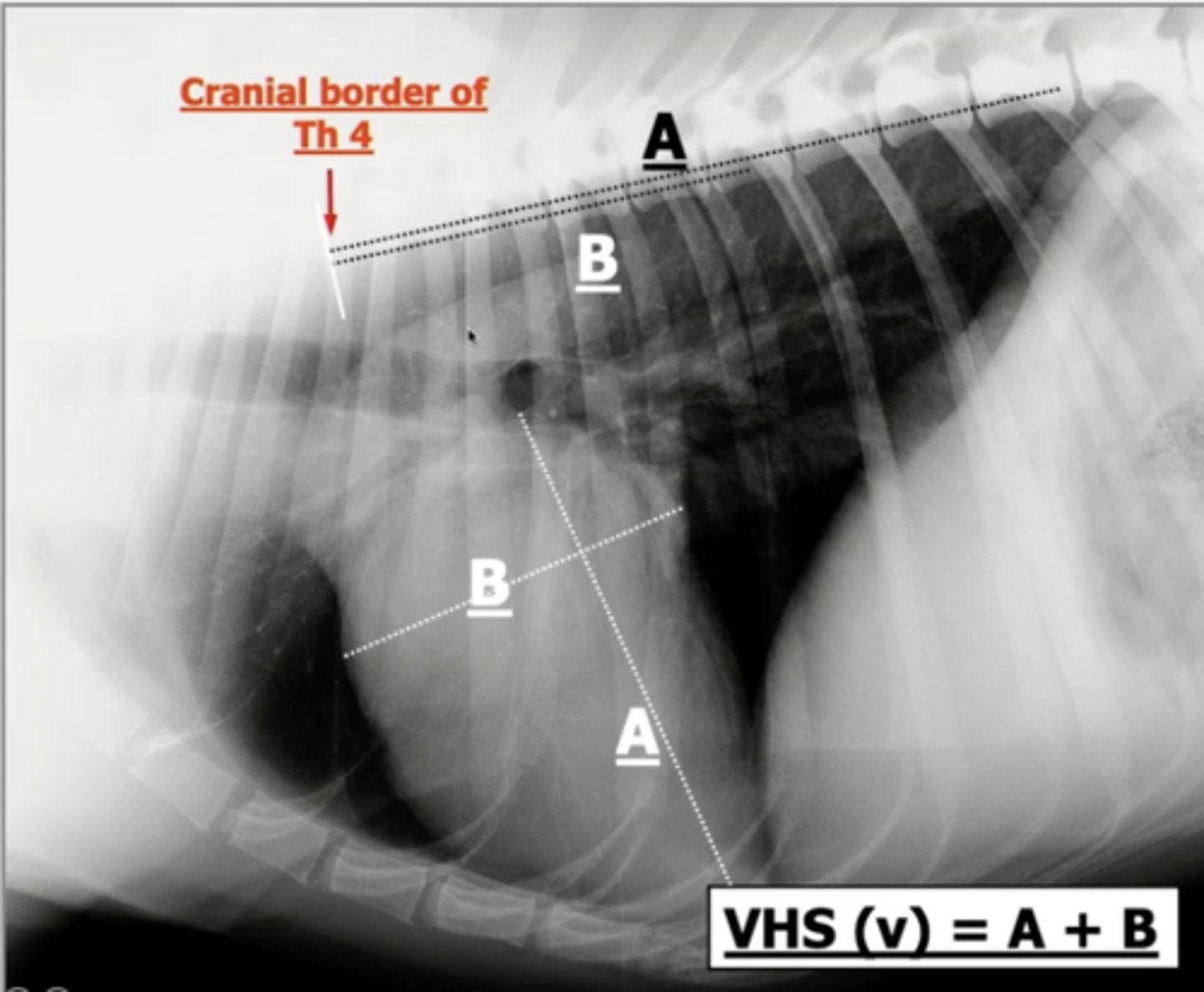
What position are animals in to measure the vertebral heart scale (VHS)?
lateral recumbency
Normal vertebral heart scale (VHS) measurement in dogs
< 11.5
Normal vertebral heart scale (VHS) measurement in cats
< 8.1
Two factors that can affect the cardiac silhouette when measuring the vertebral heart scale (VHS):
1.) obesity
2.) breed
How is the left atrial size quantified using radiography?
vertebral left atrial heart scale (VLAS)
vertebral left atrial heart scale (VLAS)
relates the length of the left atrium to the length of the vertebrae
How is the vertebral left atrial heart scale (VLAS) determined?
1.) measure the length of the left atrium
2.) interpose measurement onto the vertebrae, starting at T4
3.) count each of the vertebrae that span over the measurement
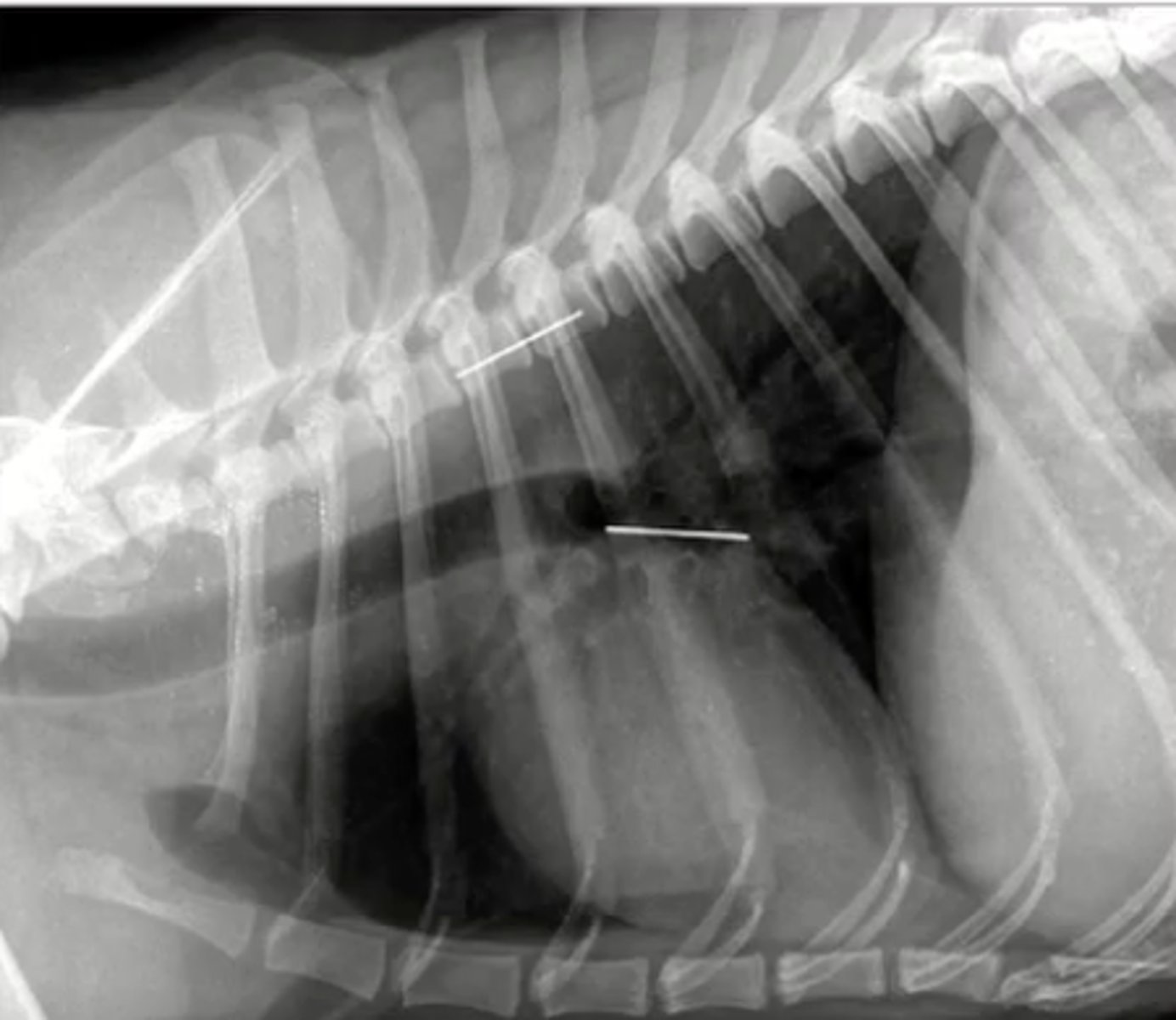
The left atrium is measured from the _________.... to ______....
ventral border of mainstem bronchus to dorsal border of vena cava
Normal vertebral left atrial heart scale (VLAS) measurement in dogs
< 2.3
Normal vertebral left atrial heart scale (VLAS) measurement in cats
< 1.5
The heart appears as an ________ __________ on radiography. Why?
opaque silhouette; the blood, myocardium, vessels, and fat are all similar radiographic densities
If the heart appears as an opaque silhouette and you can only visualize its borders, how are chamber abnormalities noted?
bulges on the border are noted and then projected on the "clock face" to determine what structure is diseased
Six cardiac structures visualized on a D/V image:
1.) main pulmonary artery
2.) left auricle
3.) left ventricle
4.) right ventricle
5.) right atrium
6.) aorta
The main pulmonary artery corresponds to what clock face time?
1
The left auricle corresponds to what clock face time?
2-3
The left ventricle corresponds to what clock face time?
3-6
The right ventricle corresponds to what clock face time?
6-9
The right atrium corresponds to what clock face time?
9-11
The aorta corresponds to what clock face time?
11-1
Four cardaic structures visualized on a lateral image:
1.) left atrium
2.) left ventricle
3.) right venrtricle
4.) right auricle
The left atrium corresponds to what clock face time? (lateral)
12-3
The left ventricle corresponds to what clock face time? (lateral)
3-6
The right ventricle corresponds to what clock face time? (lateral)
6-9
The right auricle corresponds to what clock face time? (lateral)
9-12
What artery and vein can be seen in the lateral view?
pulmonary artery and vein
Location of the pulmonary artery and vein on lateral view
located cranially and dorsally on the heart
The pulmonary artery and vein are separated by what on the image?
bronchus
Order of the pulmonary artery and vein and bronchus on lateral image
dorsal --> artery
middle --> bronchus
ventral --> vein
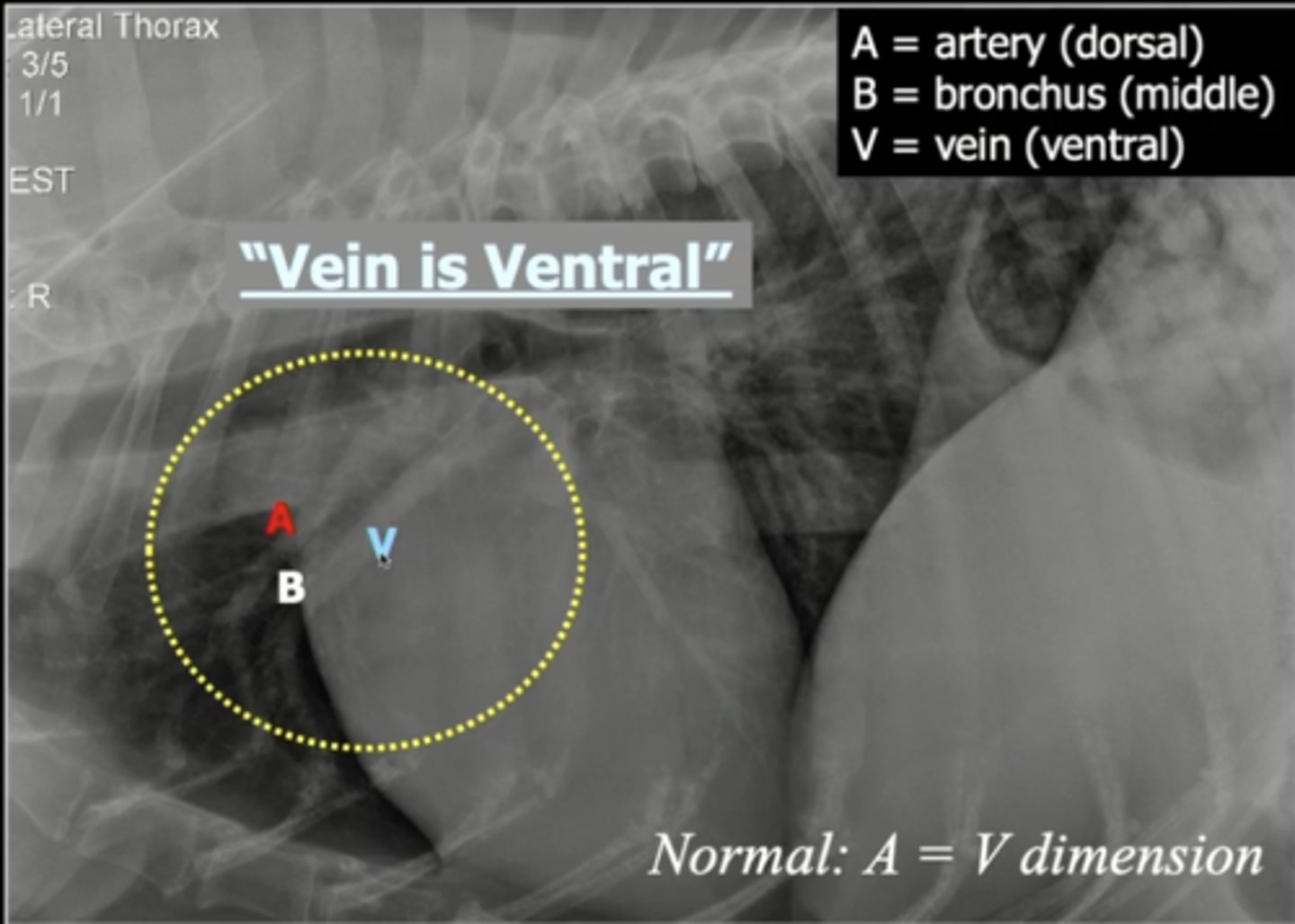
The pulmonary vein and artery can also be seen on what view?
ventral/dorsal
Order of the pulmonary artery and vein and bronchus on ventral/dorsal image
lateral --> artery
middle --> bronchus
medial --> vein
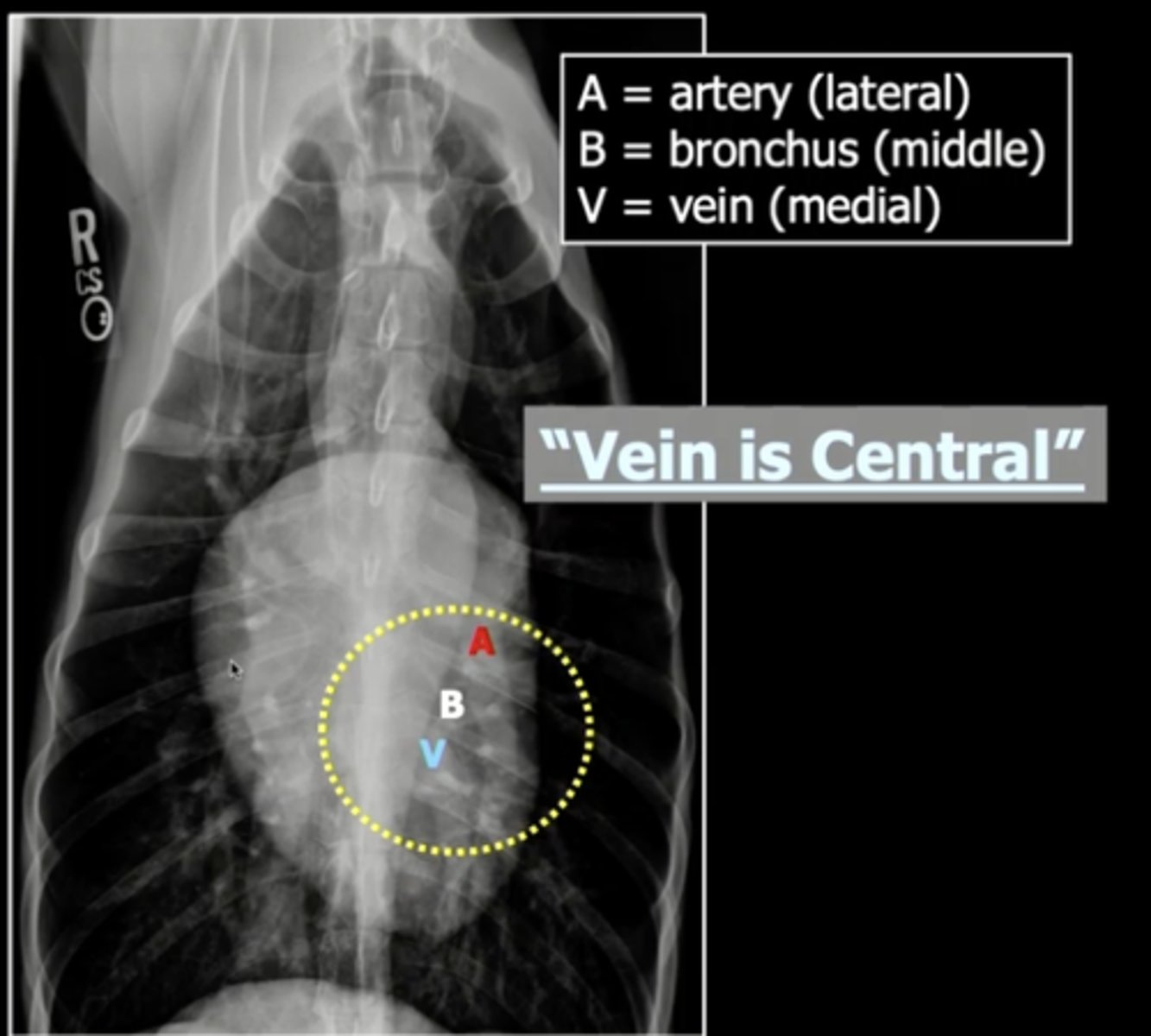
The pulmonary artery and vein should be the _________ size
same
Two types of circulating biomarkers:
1.) leakage markers
2.) functional markers
leakage markers
markers that leak into the blood stream due to damage of cardiomyocytes
Most common leakage marker
Cardiac troponin I (cTnI)
Cardiac troponin I
Inhibitory troponin; released into the bloodstream if myocytes degrade
Detection of Cardiac troponin I is NOT _________ specific
disease
*only indicates that cardiomyocytes are being degraded, not the reason why
Detection of Cardiac troponin I has very high cardiac ______. Why?
specficitiy; Cardiac troponin I is mostly found in the heart, so if it is detected we know there is an issue with the heart and not another organ
Three locations Cardiac troponin I is released from:
1.) cell membrane
2.) cytosolically dissolved
3.) structuraly bound
Which location is Cardiac troponin I found 90-95% of the time?
structurally bound
Which are better for screening tests: leakage markers or functional markers?
functional markers
functional markers
determine how well the heart is functioning in terms of pressure, stretch, and overall performance
Two most common functional markers
1.) atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
2.) brain natriuretic peptide (BNP)
atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
hormone secreted from atrial cells in response to atrial stretching and an increased heart rate
Where is atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) stored?
granules in atrial muscle
atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) is diagnostically _______ to brain natriuretic peptide (BNP)
inferior
brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) is ________ in the atria
atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) is ________ in the atria
produced
stored
Two reasons brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) is produced:
1.) in response to increased stretch (increased volume)
2.) in response to abnormal hypertrophy (thicker walls)
How is brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) produced in the atria?
it is produced as its precursor, proBNP
proBNP is cleaved into what?
BNP (active hormone) and NT-proBNP (metabolically inactive)
Which part of BNP is actually used as a biomarker?
NT-proBNP
brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) is detected during acute or subacute cardiac diseases?
subacute (chronic)
*takes a couple of days for it to be able to be detected
brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) detection is __________ specific
species
*unlike leakage biomarkers in which human detection methods can be used
brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) is used as a screening tool almost exclusively in what species?
cats (rarely in dogs)
Two clinical indicators for brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) detection:
1.) respiratory distress (open mouth breathing)
2.) soft heart murmurs (to decide if clinically relevant or not)
What is a clinicial using brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) detection for regarding respiratory distress?
to determine if it is related to heart disease (positive test) or respiratory disease (negative test)
Why would brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) be used as a screening test?
to determine if echocardiography, which is very expensive, is justified to use
Switch terms and definitions
Switch terms and definitions
4. LA and RV
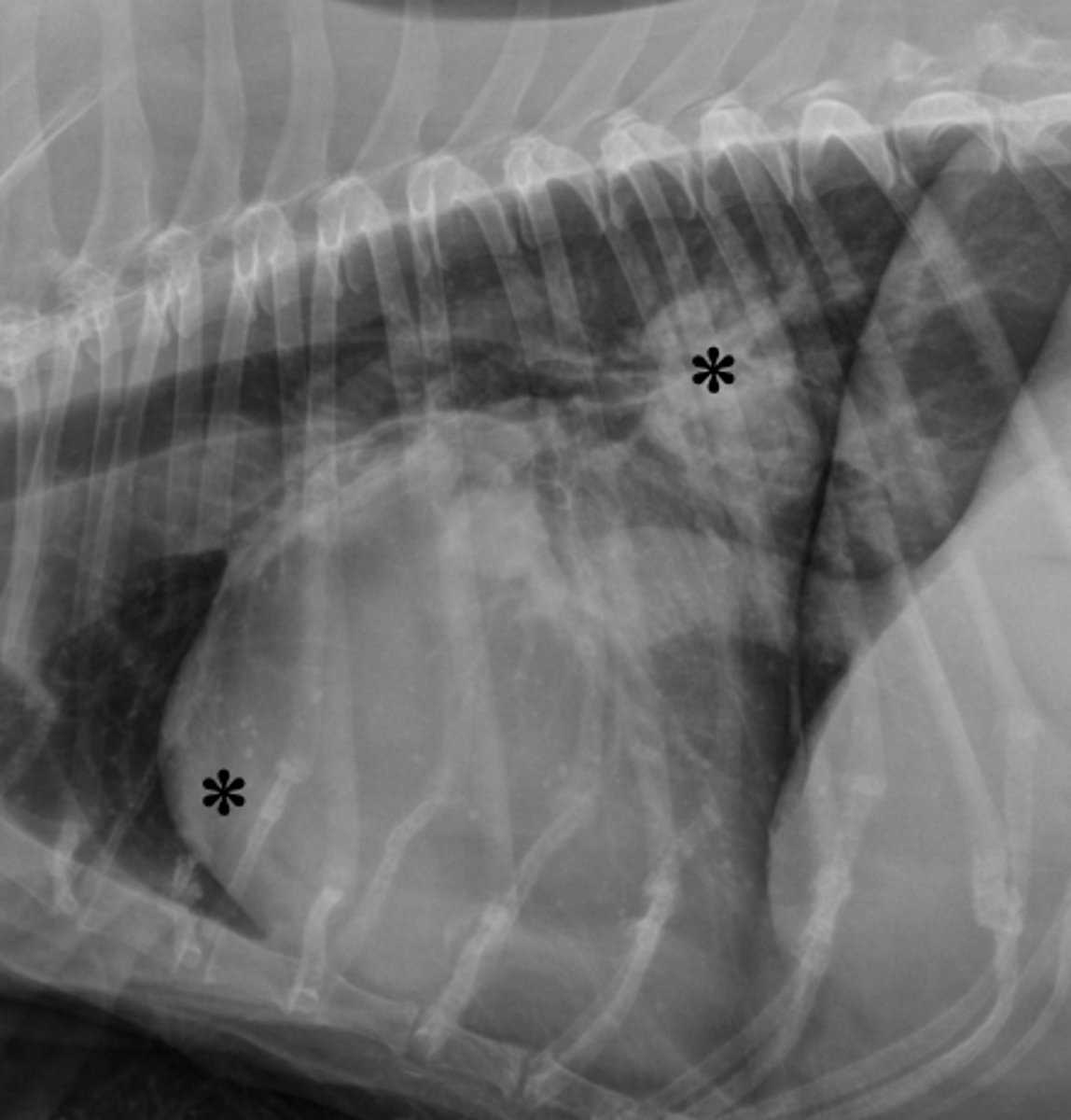
In the radiographic image of a dog seen below. What cardiac chambers as indicated by an asterisks (*) are enlarged?
1. LA and LV
2. LA and pulmonary artery
3. RA and RV
4. LA and RV
5. LV and RV
4. Values of cardiac length and width are transposed to the spine and added, starting with the 4 th vertebral body.
What statement regarding calculation of vertebral heart score (VHS) is CORRECT?
1. VHS is a radiographic metric to diagnose congestive heart failure.
2. Adding cardiac length and width should be no more than 10.5 cm in a dog with normal heart size.
3. VHS should always be measured from a ventral-dorsal radiographic image.
4. Values of cardiac length and width are transposed to the spine and added, starting with the 4 th vertebral body.
5. Normal VHS in a cat is <11.5 and in a dog <8.1
3. Enlargement of the pulmonary trunk (main pulmonary artery) is identified by a bulge at 1 o'clock.
What statement regarding application of the 'clock-face analogy' to identify cardiac structures during interpretation of thoracic radiographs is CORRECT?
1. Aortic root enlargement is identified by a bulge at 2-3 o'clock.
2. LV enlargement is identified by chamber enlargement at 6-9 o'clock.
3. Enlargement of the pulmonary trunk (main pulmonary artery) is identified by a bulge at 1 o'clock.
4. RV enlargement is identified by chamber enlargement at 9-12 o'clock.
5. RA enlargement is identified by chamber enlargement at 3-6 o'clock.
1. The major clinical indication of NT-proBNP as a diagnostic tool is in cats with respiratory distress: Is it heart disease or lung disease?
Which statements regarding cardiac biomarkers is CORRECT:
1. The major clinical indication of NT-proBNP as a diagnostic tool is in cats with respiratory distress: Is it heart disease or lung disease?
2. cTnI is a biomarker of LV stretch (preload).
3. The molecular structure of NT-proBNP is well-preserved among species. Therefore, the human assay can also be used for samples from dogs, cats, and horses.
4. cTnI can be analyzed with a simple snap test in veterinary practice.
5. The NT-proBNP test can reliably be used (very high sensitivity and specificity) as a screening test for heart disease in dogs and cats.