The Normal Aging Process
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
General Model of Aging
Structural changes:
↑ Atrophy
↑ Dystrophy
↑ Edema
==>
↓ Elasticity
↑ Demyelinatization
↑ Neoplasm
↑ Mutation
General Model of Aging
Functional consequences:
↓ Accuracy
↓ Speed
↓ Range
↓ Endurance
↓ Coordination
↓ Stability
↓ Strength
Factors Influencing Aging
genetics
environmental factors and exposure
injuries
personalities and attitude
lifestyle
exercise!!!
advancesin medicine
Nervous System Changes:
Central Nervous System
Cerebral Atrophy
e.g., front lobe deterioration (e.g., decreased filter)
Reduced cerebral blood flow
Plaque deposits and neurofibrillary tangles
Nervous System Changes:
Peripheral Nervous System
Changes in peripheral receptors
Slower nerve conduction and velocities
Musculoskeletal Changes
Sarcopenia age related loss of muscle mass
Muscles: decrease in strength and mass
More pronounced in LE (flexors) than in UE
Changes in flexibility and reaction time
“use it or lose it” (i.e., being in bed rest, you lose SO much muscle mass)
Bone: loss of skeletal mass
Osteoporosis
bone weakens to a fracture threshold, even under mild stress
double in women than in men
Joints: More prone to injury
Decrease in cartilage, synovial fluid
Osteoarthritis
Postural changes
forward head
rounded shoulders
flattened back
Ligaments are less elastic
Integumentary System
Changes in the skin, glands, hair, and nails
Skin: thinning and atrophy, “age spots”, wrinkling
results in more susceptibility to abrasions, blisters, pressure ulcers, etc.
so, you must avoid having older adults sit in the same spot for hours and not move!!!
also, use kinesiotape with caution (especially on the face; more hypersensitivity)!!!
Glands: decrease in number of sebaceous and sweat glands
Hair: graying, thinning, and loss
Nails: thickening
more susceptibility to skin infections if the nails are digging into the hand
Cardiovascular Changes
Structural changes to the heart
Changes in electrical conduction system
Decrease in maximal heart rate
Changes in ability of heart to meet demands
Leads to decreased ability to oxygenate which leads to fatigue and decreased endurance
—> exercises should look different older adults
Changes in blood vessels
Increased resistance makes heart work harder
Increased systolic BP
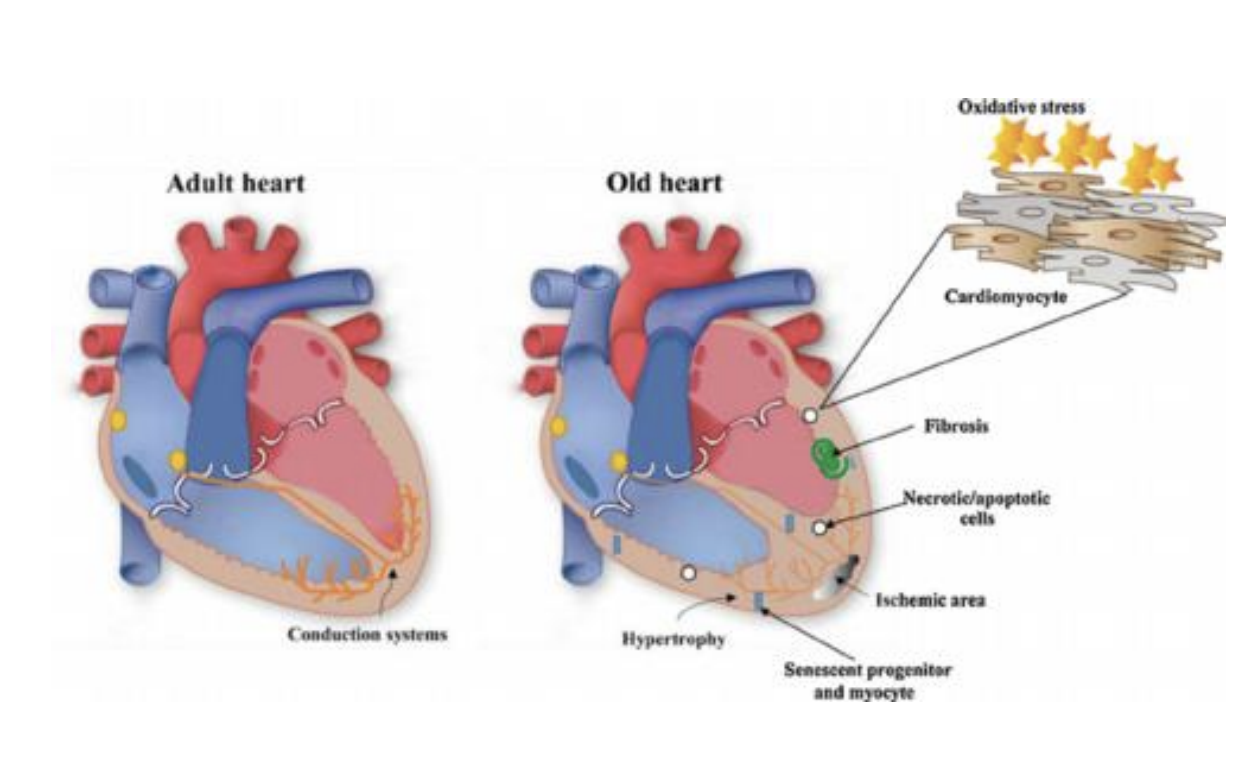
Vascular System
Vessels thicken and become less elastic
“Stiff Arteries”
Increased resistance: heart works harder
Atherosclerotic changes
Narrowing
Reduced blood flow: Ischemia
Arterial Occlusion
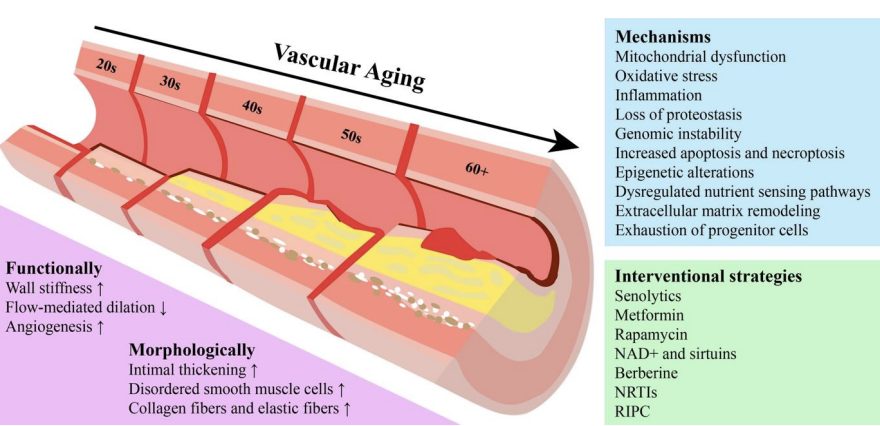
Respiratory System
Decline in pulmonary functioning
e.g., more susceptibility to pulmonary embolism
Changes in lungs and chest wall lead to problems with ventilation and gas exchange
Less efficient breathing
Decreased capacity to cough
Increased susceptibility to infections and complications
Digestive System Changes
Structural changes- orally
e.g., dry mouth, reduced swallowing and speech, working with dentures
Changes in ability to break down substances
e.g., gastritis, altered drug metabolism
Genitourinary System Changes
Less efficient functioning of kidneys and other urinary structures
e.g., problems with incontinence, decreased bladder, hypertrophy of prostate, loss of nephrons
Endocrine System Changes
Changes in thyroid function
e.g., decreased ability to regulate body temperatures
Sexual Function (+ men vs women)
Changes in hormone levels
Men:
Testosterone level decrease very little
Decreased size and firmness
Decreased sperm production and ejaculatory force
Prostate enlargement
Erectile dysfunction and problems with vascular blood flow
Women
Women
Vaginal dryness
Changes in shape and muscle tone
Thinning of vaginal wall
Reduce size of clitoris
***all impacts sexual ADLs!!!
Cognitive Functions
Attention
May be more distractible
Complex attention tasks are more difficult
Language
Word-finding problems common
Executive function-changes
Decreased processing speed- some increased difficulty with complex multi-step tasks
Memory
Semantic, procedural, and long-term memory are intact
Changes in short-term and episodic memory (decreases over time)
reminiscence groups are so important!!!
Prospective- decreases but can often compensate
Does Personality Change with Age?
personality ~generally~ stays the same, but behaviors may look different over time
Neuroticism
Extroversion
Agreeableness
Conscientiousness
Openness
Importance of promoting self efficacy for successful aging
Sensory Changes
Occurs in all modalities
May affect ADLs, ability to interact with your environment, or even just safety in general!
Vision
e.g., can’t drive
Hearing
e.g., can’t drive, can’t hear safety alarms
Taste
e.g., sweet taste diminishes as you get older (may discourage people from eating, resulting in dehydration and malnutrition)
Smell
e.g., can’t smell smoke, can’t smell if a food has gone bad
Somatosensory
e.g., decreased ability to experience pleasure and pain (e.g., tactile stimulation)
Somatosensory Changes
Decline in sensitivity to tactile stimuli
Temperature sensitivity
e.g., decreased ability to detect temperature could lead to burns when bathing
Alterations in kinesthetic sensitivity
Alterations in peripheral nervous system
Functional Implications
Safety-increased risk of injury
Diminished fine motor skills
Visual Changes
Reduced visual acuity
Decreased ability to accommodate/focus
Decreased ability to adjust to changes in illumination
Decreased resistance to glare
Changes in color sensitivity
Presbyopia
decreased tissue elasticity and tone in the eye
age-related farsightedness (i.e., can see far but have trouble focusing on near objects)
e.g., needing reading classes
Hearing Loss
Presbycusis
Age-related hearing loss
***Difficulty hearing high frequencies
especially when in a crowded environment
Diminished ability for pitch/tone threshold
Most age-related hearing loss is sensorineural
Interferes with ability to interact with environment (social and physical)
Diminished speech reception, discrimination, and understanding
may even result in suspicion and paranoid behavior
may see depression and anger
functional implications
e.g., can you hear a car coming? can you hear an alarm? should you be giving visual instructions, instead of just verbal ones?
Vestibular System
Loss of receptor organs and structures
Saccules, utricles, semi-circular canals
Increased postural sway, wide-based gait (beyond shoulder width)
Unsteadiness in standing/walking
Alterations in righting and equilibrium reactions
Presbyastatis
Age-related disequilibrium
Taste
Overall decrease in taste perception
sweet, salty, sour, bitter
Decreased sensitivity to sweet substances
Related to decreased number of papillae and taste buds on tongue
Atrophy of neurons in taste centers
Mild dysgeusia
chronic bad taste in your mouth (e.g., usually due to medication or diseases)
results in people not wanting to eat, even just for things like water
Decreased saliva flow
Due to medication, dental problems, and conditions
Olfactory System
Decline in threshold sensitivity for odors
Due to combination of changes
Changes in CNS ability to detect smell
Nerve damage
Changes in nasal passages and membranes
can impact episodic memory
can impact a person’s appetite
can bring safety concerns
e.g., can you smell smoke? can you smell bad food?
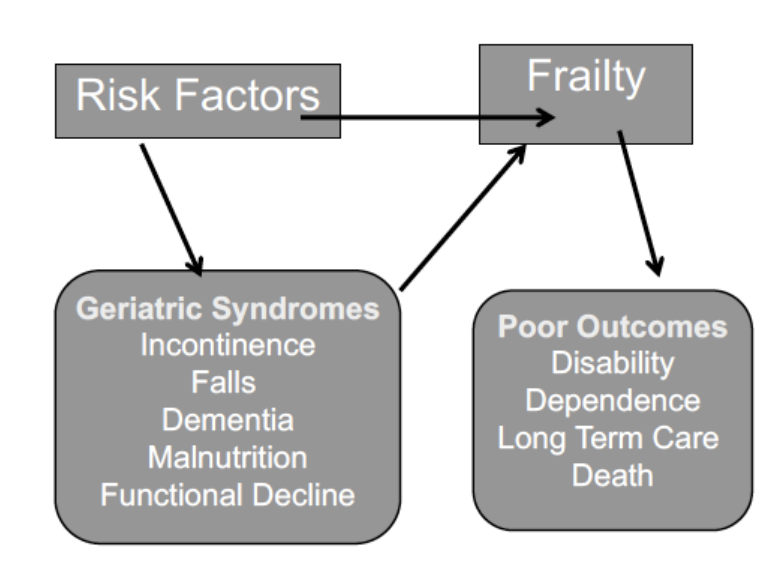
Older Adults and Disease
Average older adult has 3-4 different diseases
Diseases tend to occur in clusters
Interaction may result in “Geriatric Syndromes”
More common in advanced older age
Geriatric Syndrome
Used to capture conditions in older adults that do not fit into discrete disease categories
Impact quality of life
Disability is great
Multiple underlying factors including multiple organ systems contribute to syndrome
Normative Aging vs. Pathology
Normal physiological changes occur during the aging process
Pathology is not an expected part of aging although there is a higher prevalence
Prevention and health promotion are key in decreasing the risk of onset and for promoting successful aging