2020 SACE Stage 2 Chemistry -Topic 3
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
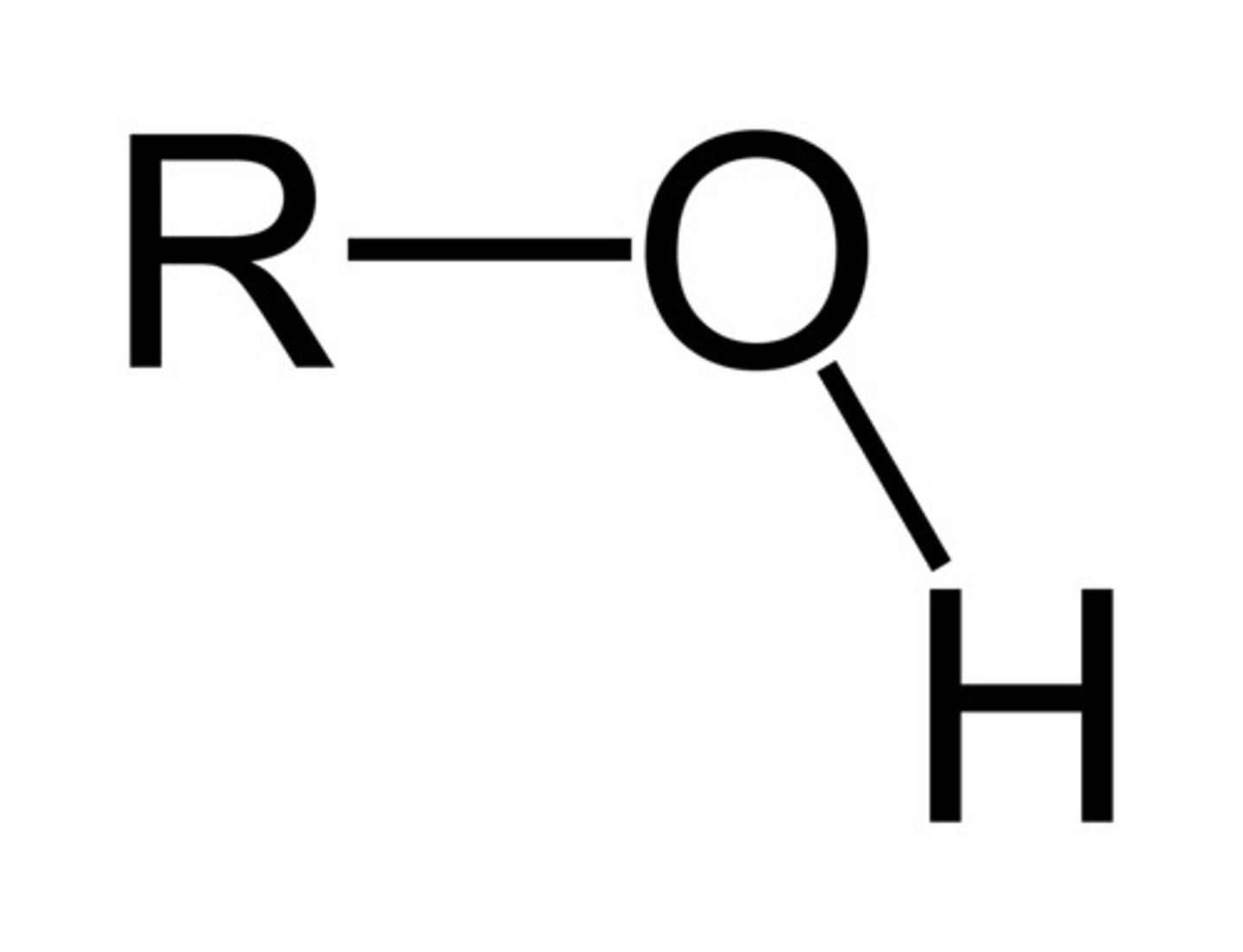
Alcohol
R-OH (-an # -ol)
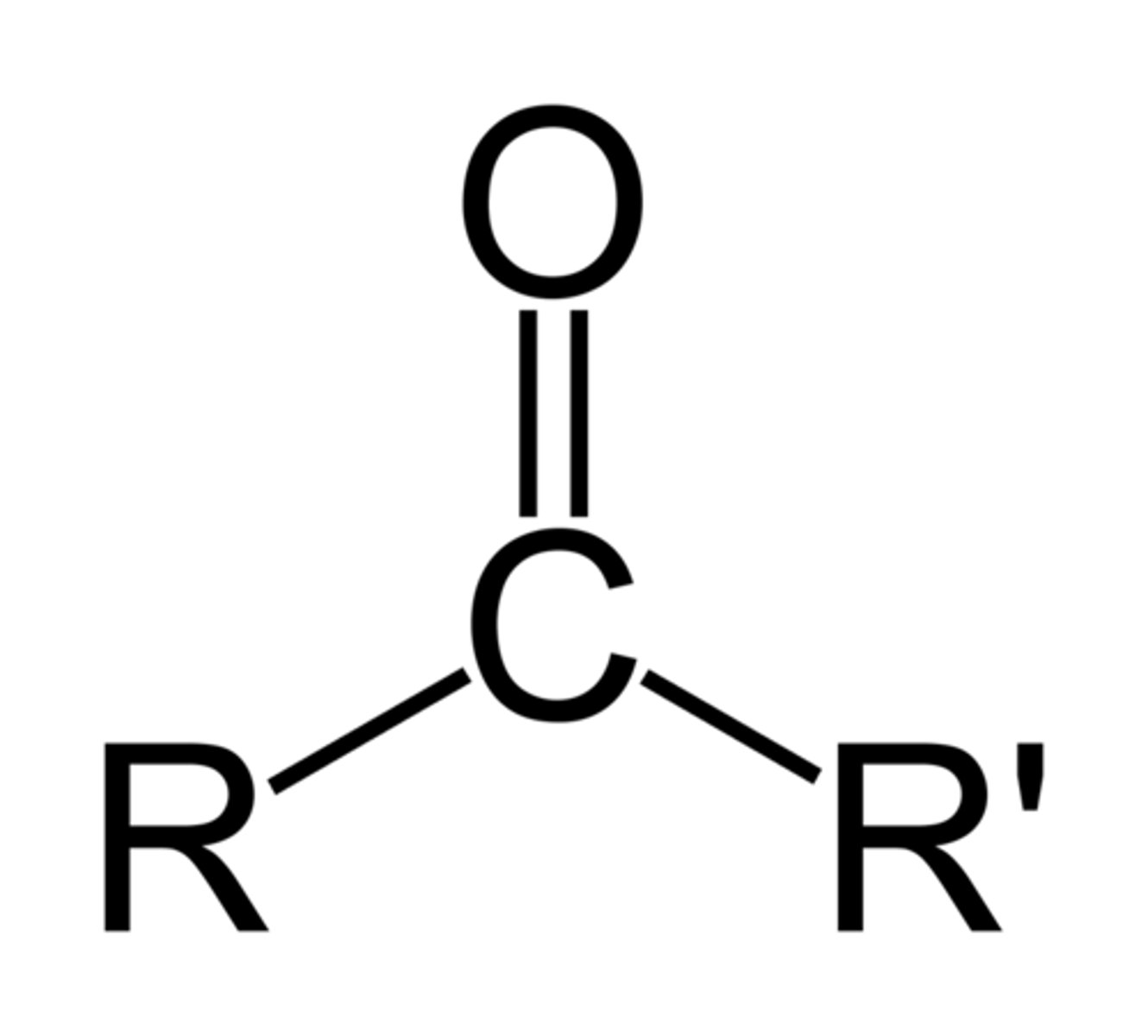
Ketone
RCOR (-one)
Alkenes
CnH2n (-ene)
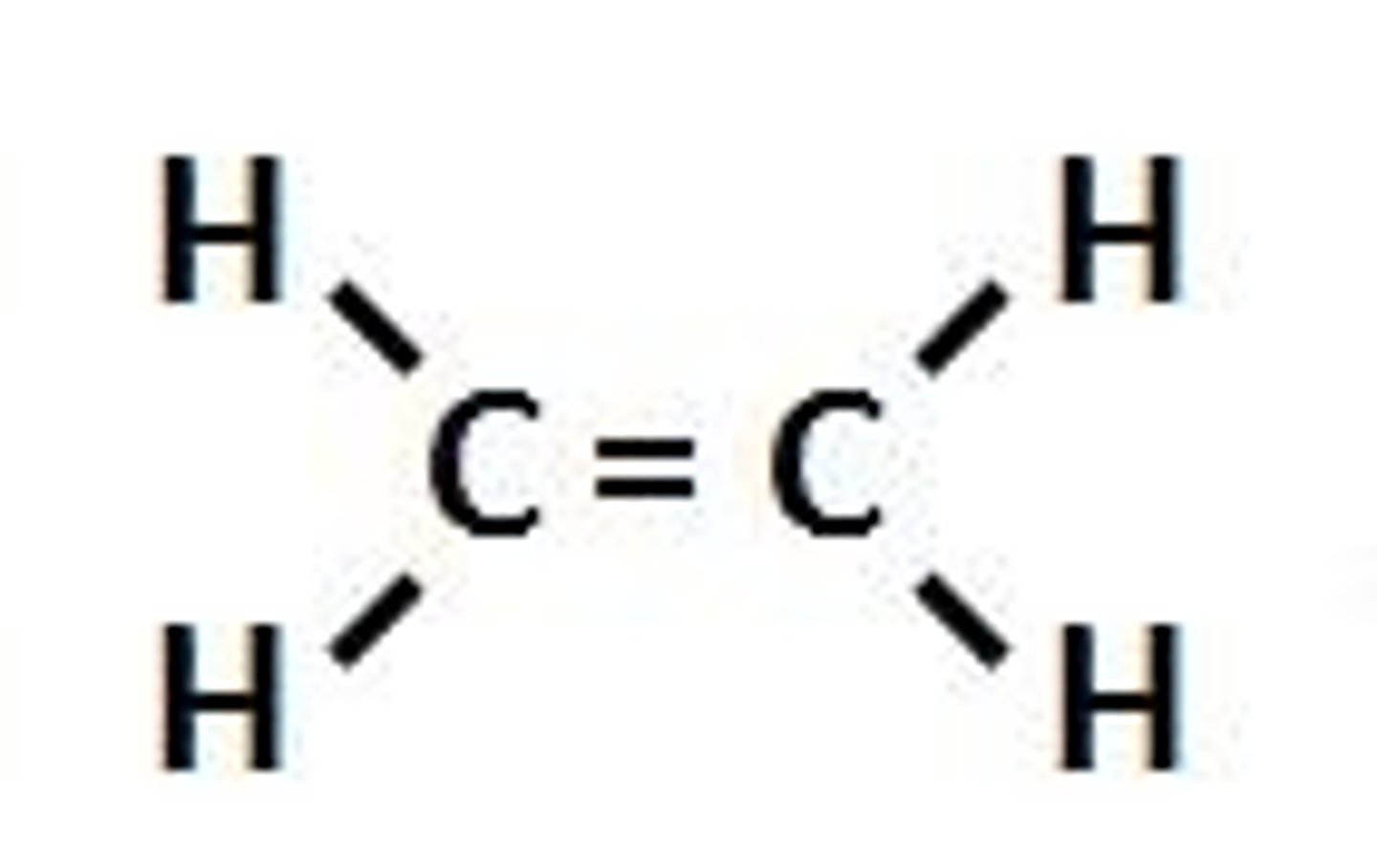
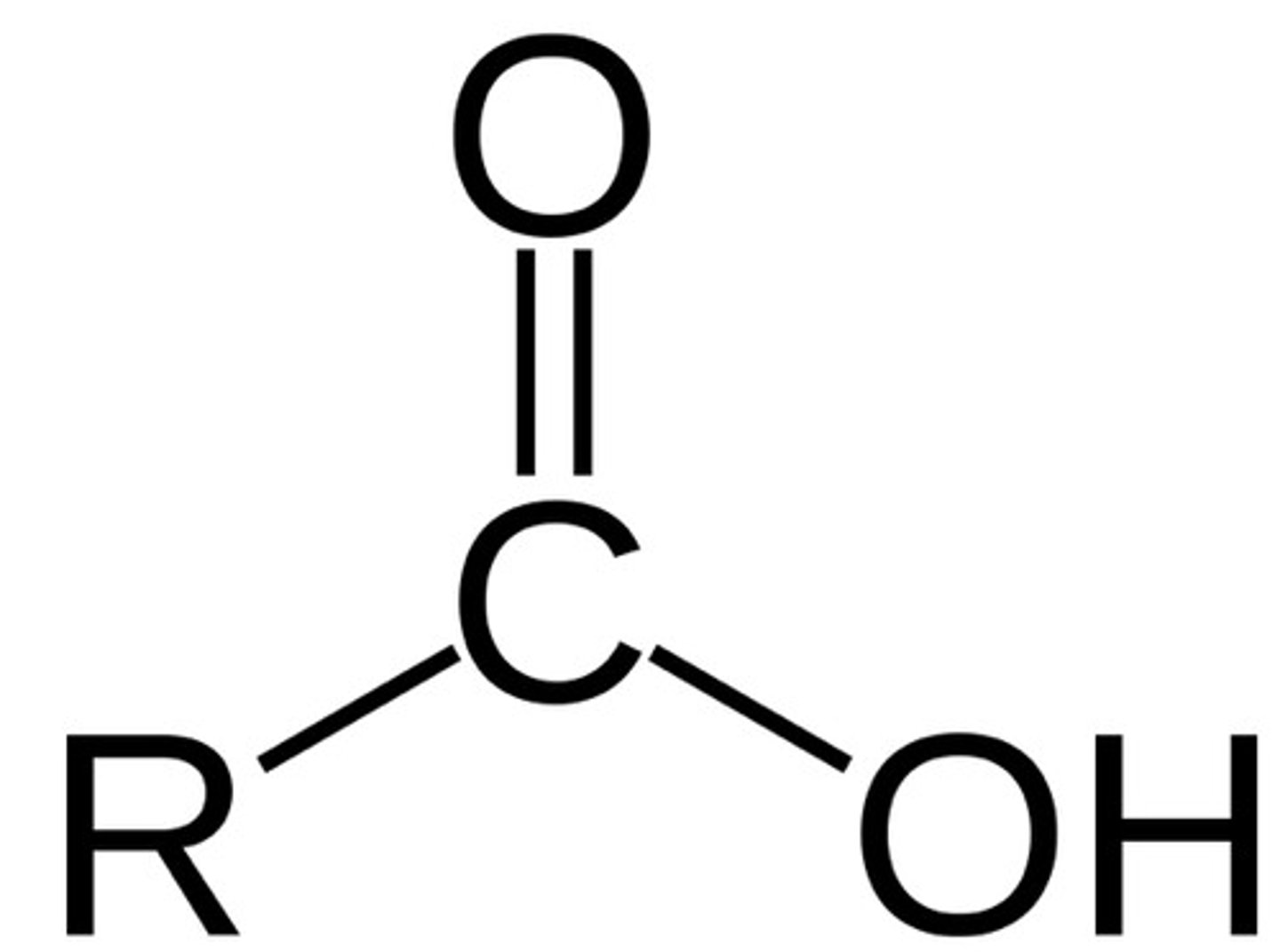
Carboxilic Acid
R-COOH
Amides
RCONH2
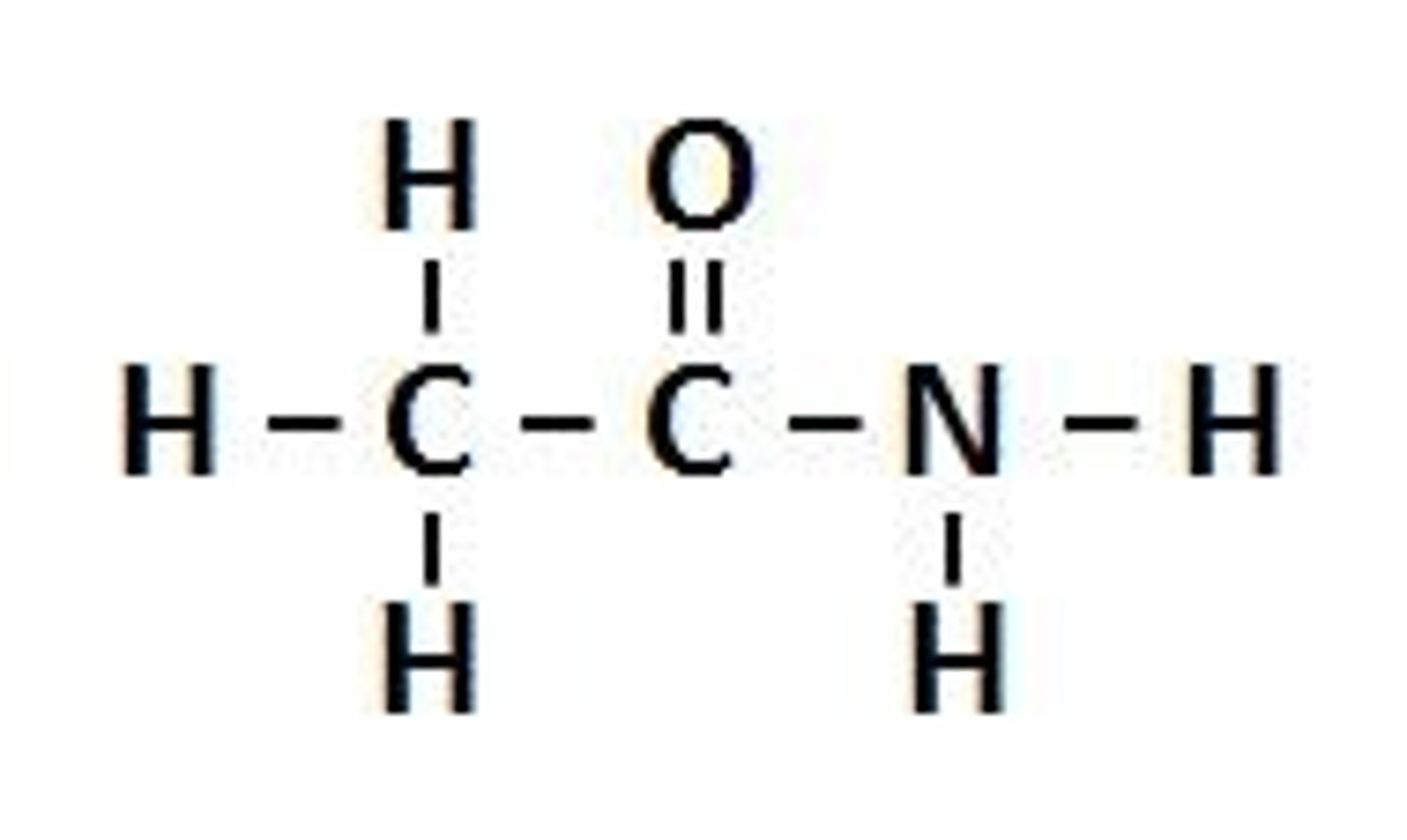
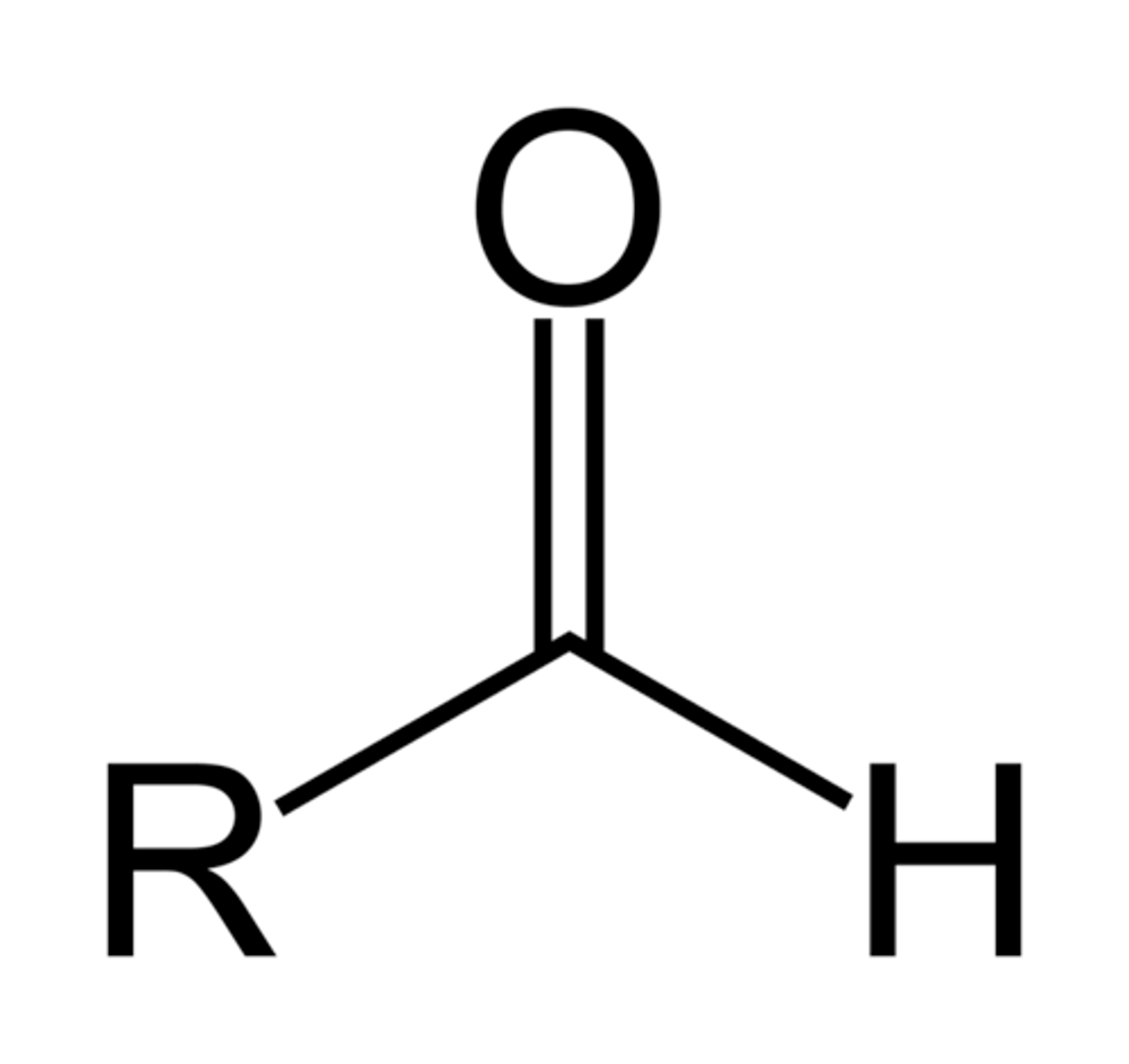
Aldehydes
RCHO
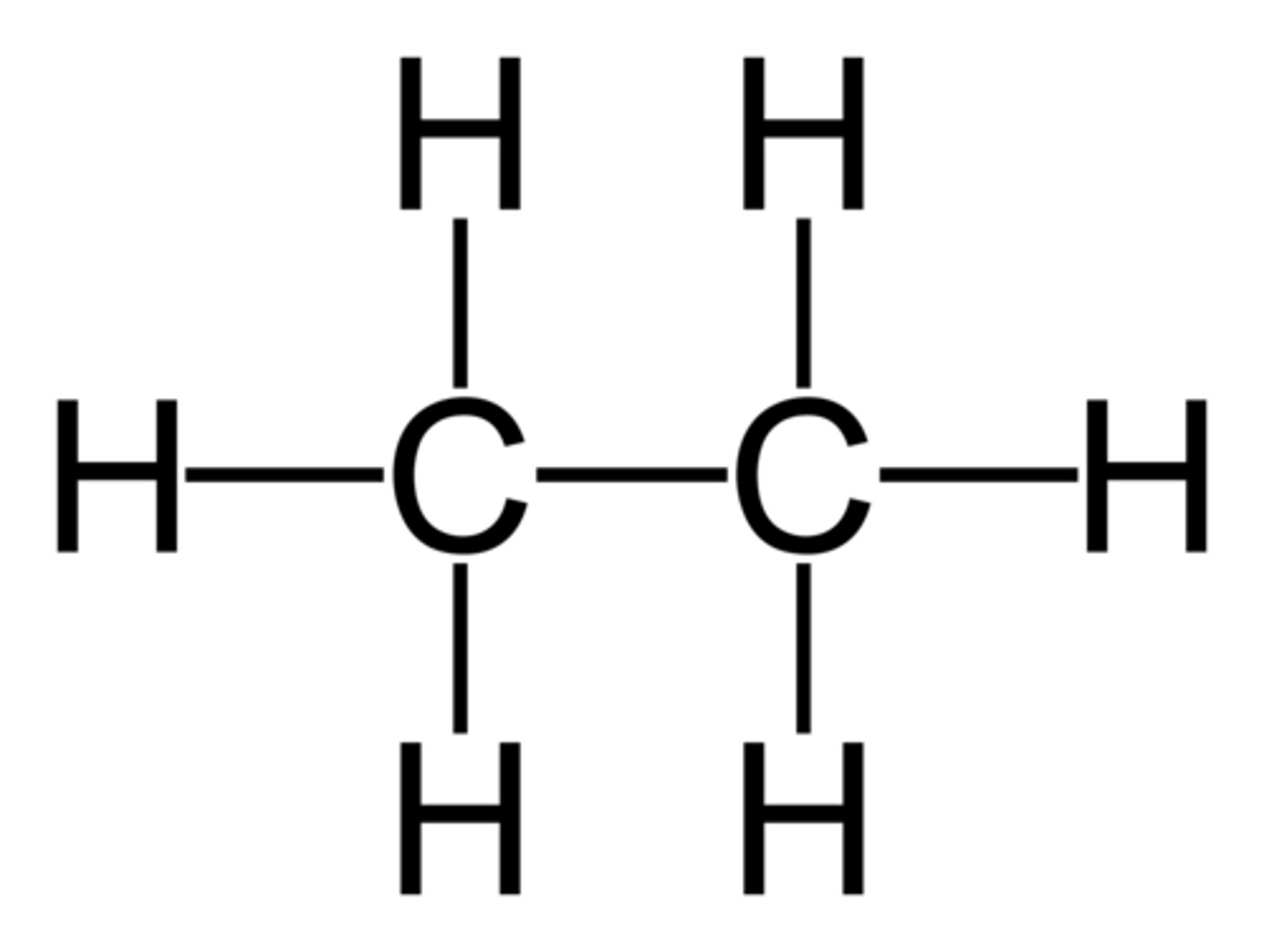
Alkanes
CnH2n+2 (-ane)
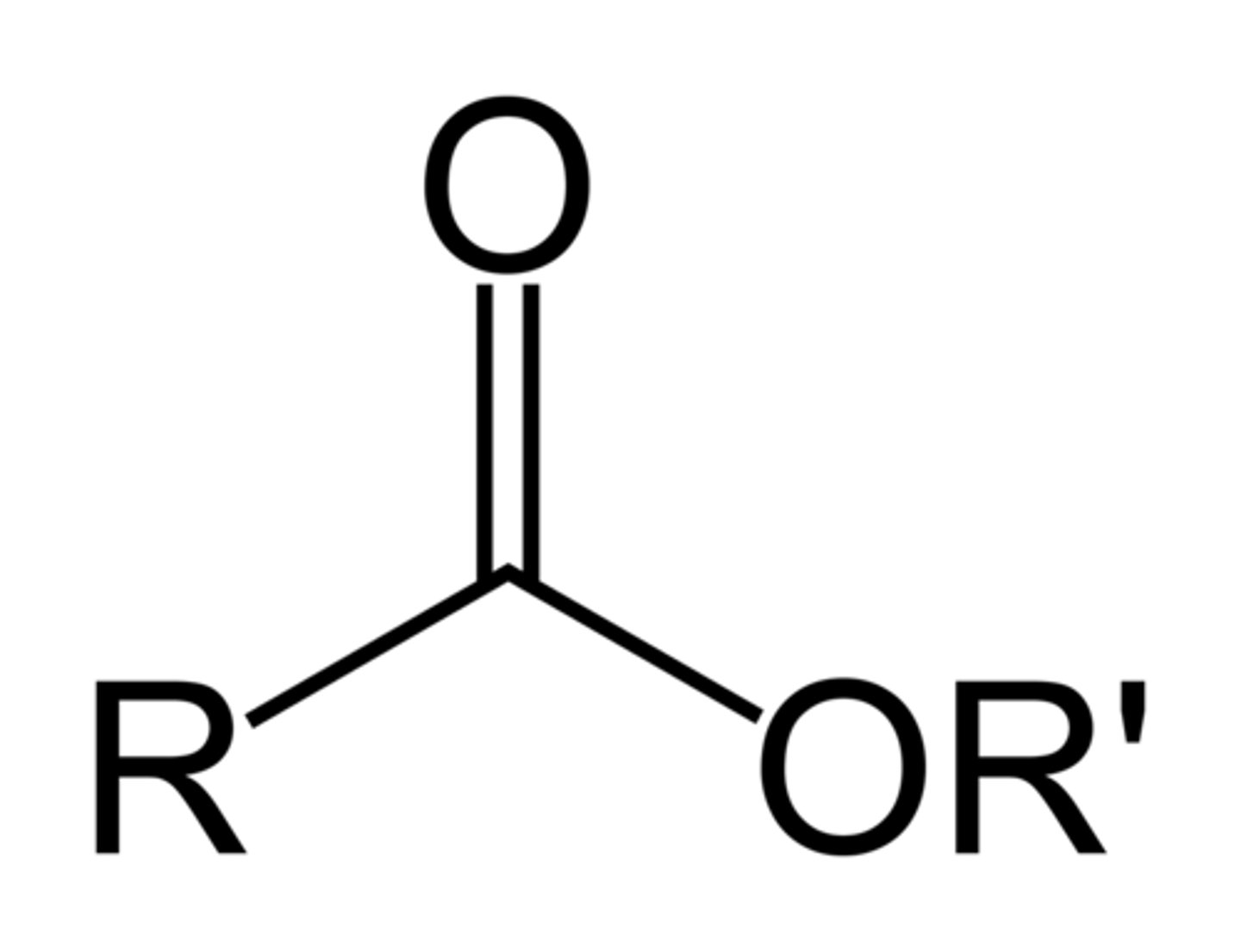
Esters
RCOOR
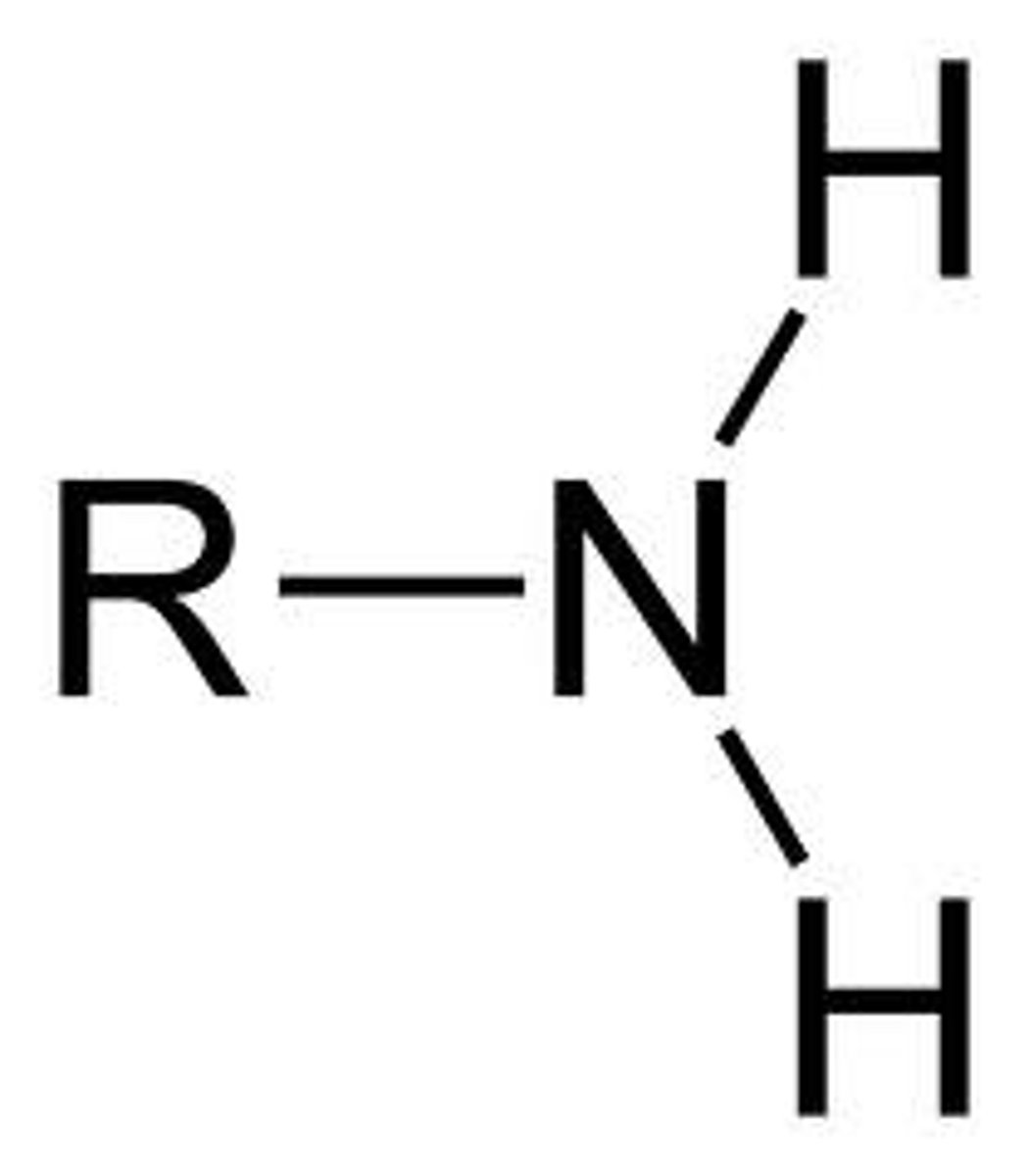
Amines
R-NH2
Alkynes
CnH2n-2 (-yne)
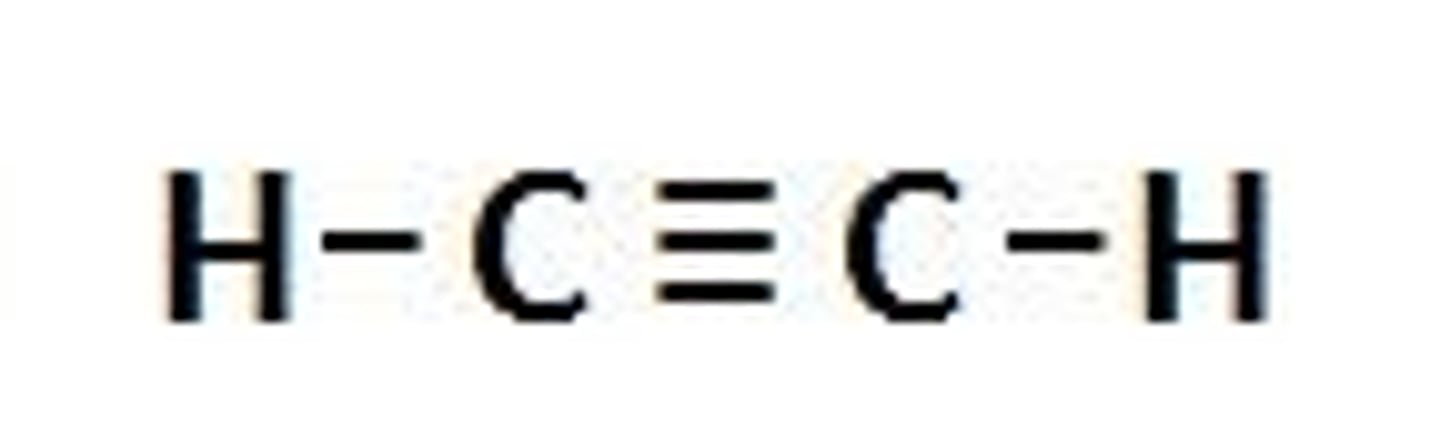
Saturated
the most # H to the number of carbons
Unsaturated
they will have triple or double bonds so there is less H then the # of C can have.
Tollen's reaction
how to tell if you have a aldehyde
Aldehydes oxidised under acidic solutions
will give you a carboxylic acid
Alderhyde oxidised under basic conditions
will give you a salt of carboxylic acid (carboxylate)
oxidising agent
Cr2O7/H+ orange to green
monosaccharide to a polysaccharide formula examples
nC6H12O6 -->C6nH10n+2O5n+1 + (n-1)H2O
(the numbers will be changed if a different carbohydrate is used)
(10 H is 2 less as the each carbohydrate lose 2 H but the end to only lose 1 that's why it is + 2)
monosaccharides (Carbohydrates)
example is glucose.
condensation reaction will give you a: disaccharide and water or polysaccharide and water
Monosaccharide + Monosaccharide formula example
Cx"Hz"Oy" + Cx'Hz'Oy' --> CxHzOy + H2O
and then balance
meth
1 carbon
eth
2 carbons
prop
3 carbons
but
4 carbons
pent
5 carbons
hex
6 carbons
7 carbons
hept
oct
8 carbons
9 carbons
non
dec
10 carbons
11 carbons
undec
12 carbons
dodec
Homologous series and is properties
A series of organic compounds with the same functional group adjacent members differs by CH2
Mp and Bp increase
increasing M = increasing dispersion forces = larger and stronger temporary dipoles
solubility properties
ability to bond with water is stronger then it ability to bond to its self
hydrophilic components compared to hydrophobic component
decreases with increased chain size (more carbons) opposite in organic solvents
hydrogen bonding increase solubility increases
like dissolves like.
-OH -NH2 Solubility
can hydrogen bond with water and themselves
-O- C=O
cant hydrogen bond with themselves but can with water
-COOH -CONH2
can hydrogen bond with water and themselves
polar
having a pair of equal and opposite charges that don't balance/cancel out each other
Non-polar
equal sharing of electrons charges that balance/cancel out each other
RCH2OH -[O]-> RCHO -[O]-> RCOOH
Primary alcohol -[O]->aldehyde -[O]-> carboxylic acid
oxidisation of a primary alcohol or aldehyde gives a carboxylic acid
single -COOH group
-anoic acid
two -COOH group
-ane-#,#-dioic acid
carboxylic acid with bases
acid + base --> salt (cation + anion/carboxylate) + water
carboxylic acid with bases reaction with hydroxides
R-COOH + OH- --> R-COO- + H2O
carboxylic acid with bases reaction with hydroxides (spectator ions)
R-COOH + NaOH --> R-COO-Na+ + H2O
carboxylic acid with bases reaction with carbonates
2R-COOH + CO3 --> 2R-COO-+ + H2O + CO2
carboxylic acid with bases reaction with carbonates (spectator ions)
2R-COOH + Na2CO3 --> 2R-COO-Na+ + H2O + CO2
carboxylic acid with bases reaction with hydrogen carbonates (spectator ions)
R-COOH + NaHCO3 --> R-COO-Na+ + H2O + CO2
carboxylic acid with bases reaction with hydrogen carbonates
R-COOH + HCO3 --> R-COO- + H2O + CO2
converting carboxylic acid into its conjugate base by adding a base
more soluble in water as it changes the carboxylic functional group into a salt
ionic -COOH- group and Na+ for and ion-dipole bond with water stronger then hydrogen bonding between -COOH and water
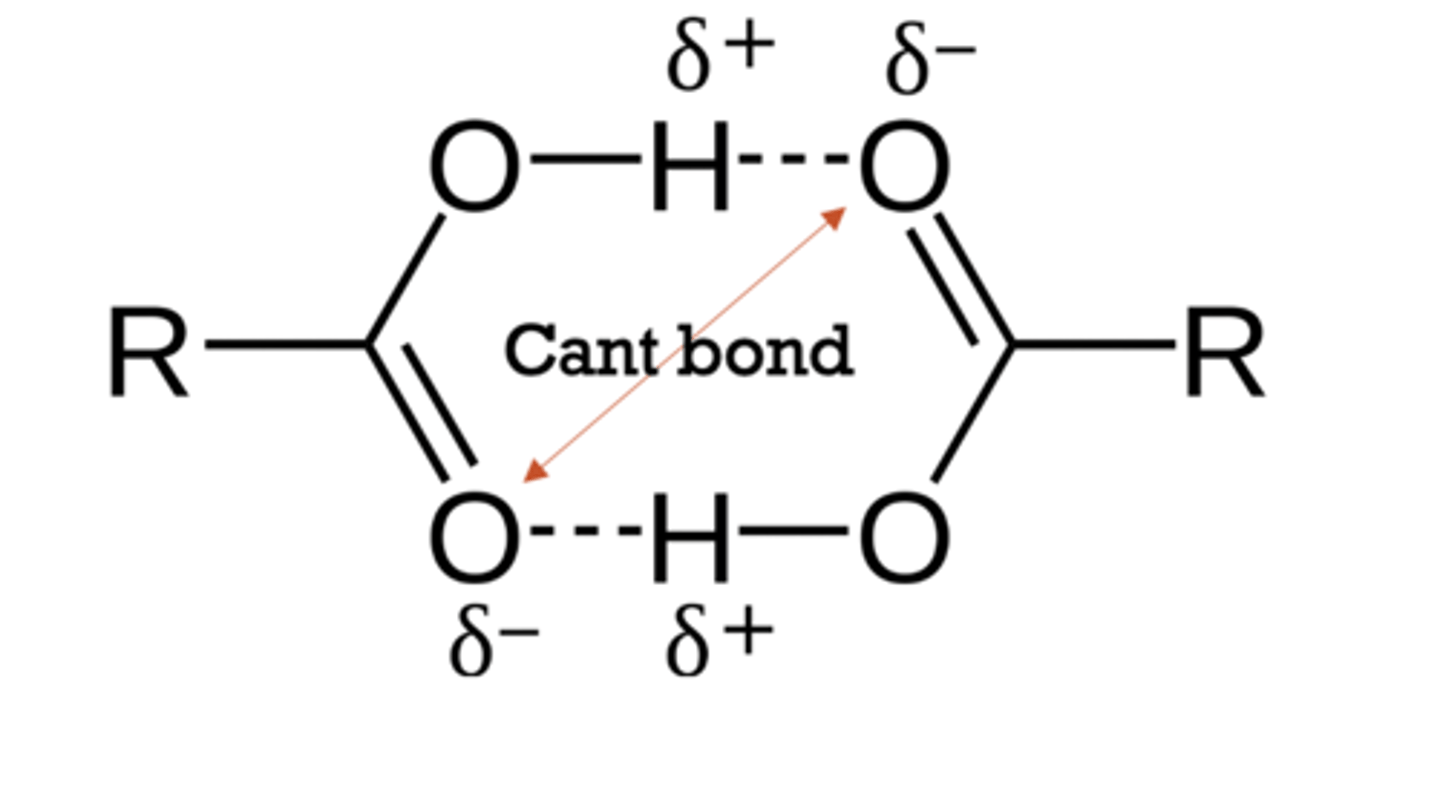
carboxylic acids can form 2 hydrogen bonds per molecule
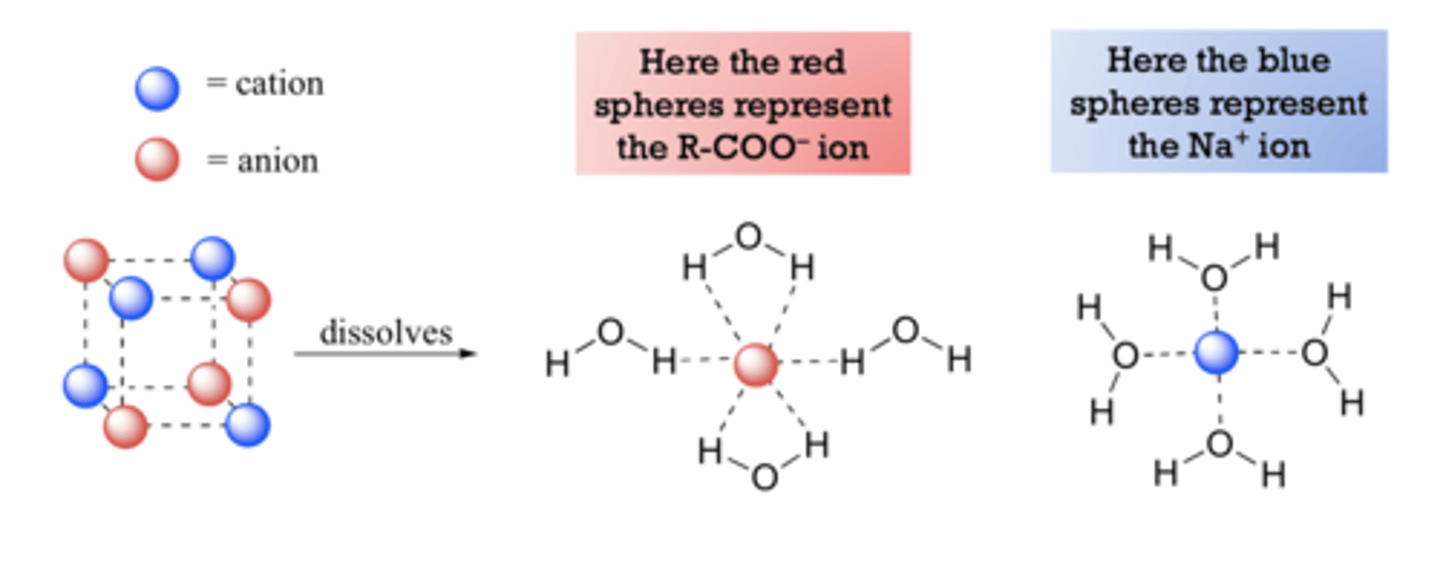
the ionic -COO- groups prevent hydrogen bonding between
-COOH groups
prefer to hydrogen bond to them rather than water lowering its solubility.
single -NH2 group
-an-#-amine
two -NH2 group
-ane-#,#-diamine
1° 2° 3° structures amines
# C attached to N
Are amines bases?
yes they can accept H+ to become ammonium ions
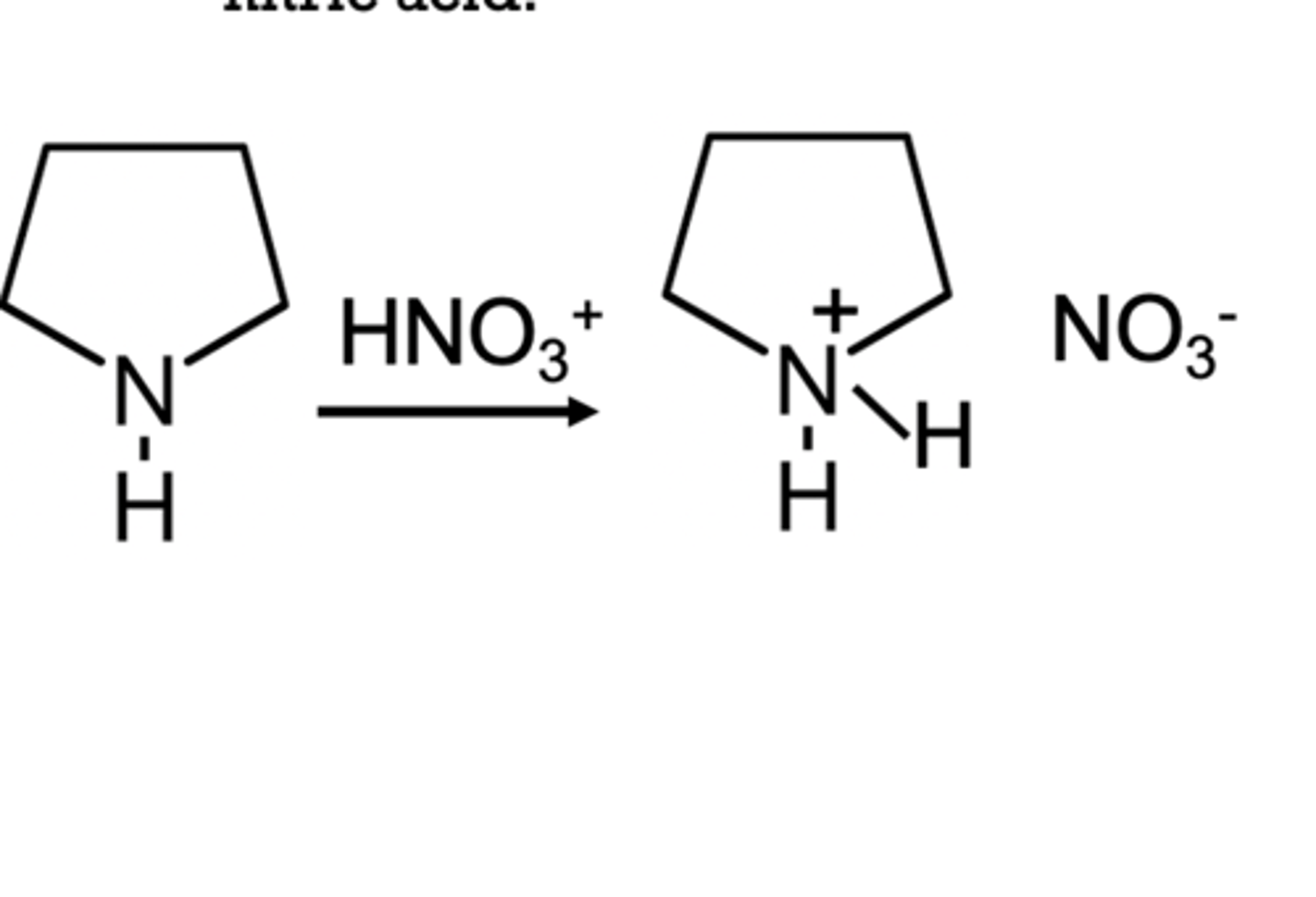
Alkyl ammonium salts
solid @ room temp
highly soluble as they can form ion dipole bonds with water
(drugs with amine functional group often cget converted into their corresponding ammonium forms to improve shel life and/or solubility)
carboxylic acid + alcohol + heat (reflux) (condensation/esterification reaction) -- H2SO4 ⇌
ester + water
Under reflux
continual boiling without loss of volatile compounds
To name an ester,
split the alcohol and carboxylic acid (C=O) and name
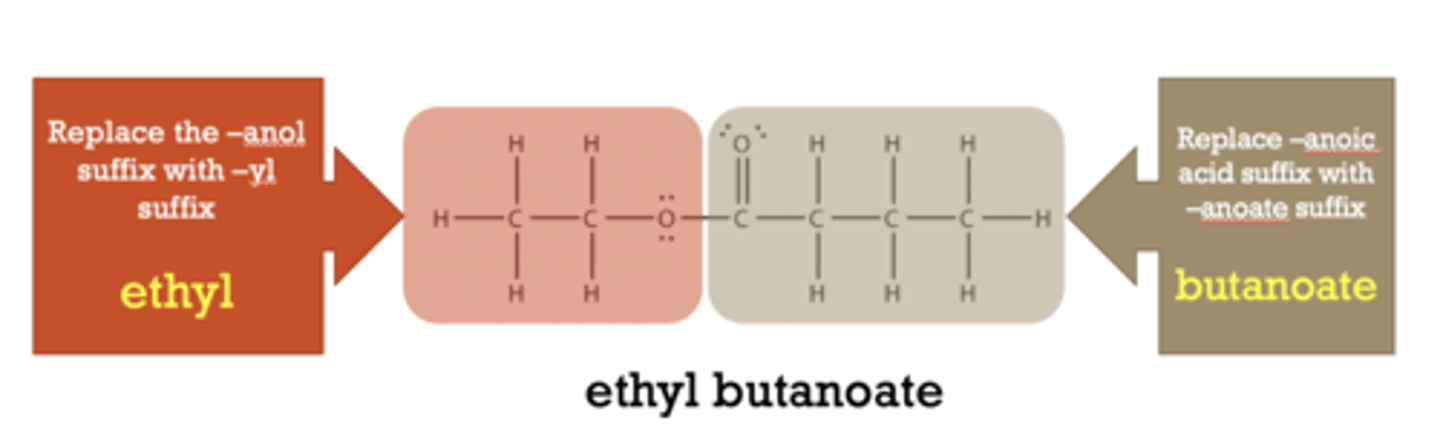
Flip the functional groups to face
esters
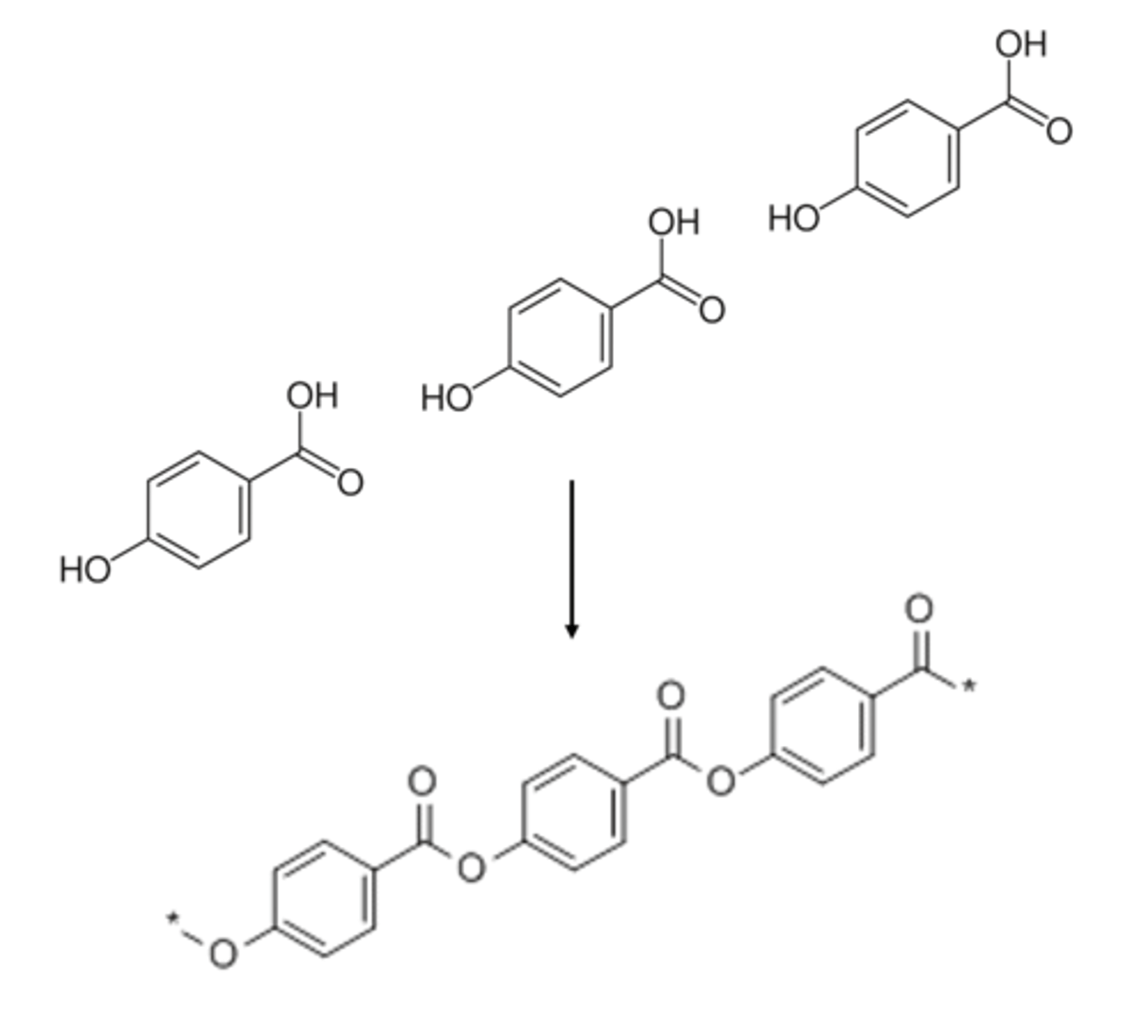
diols and dicarboxylic acids for ester bonds creating
polyesters (condensation polymers)
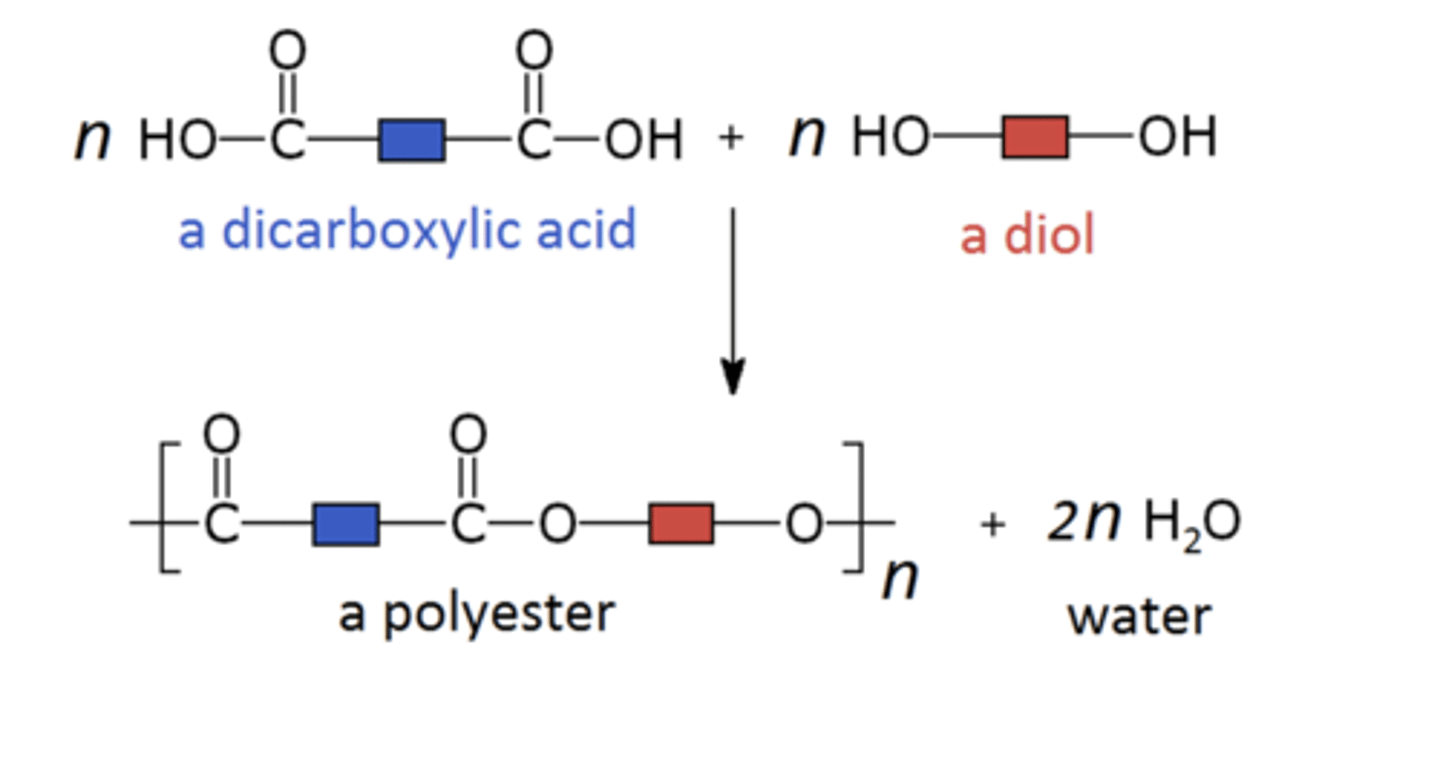
a monomer with and alcohol functional group and a carboxylic acid functional group will form a
polyester
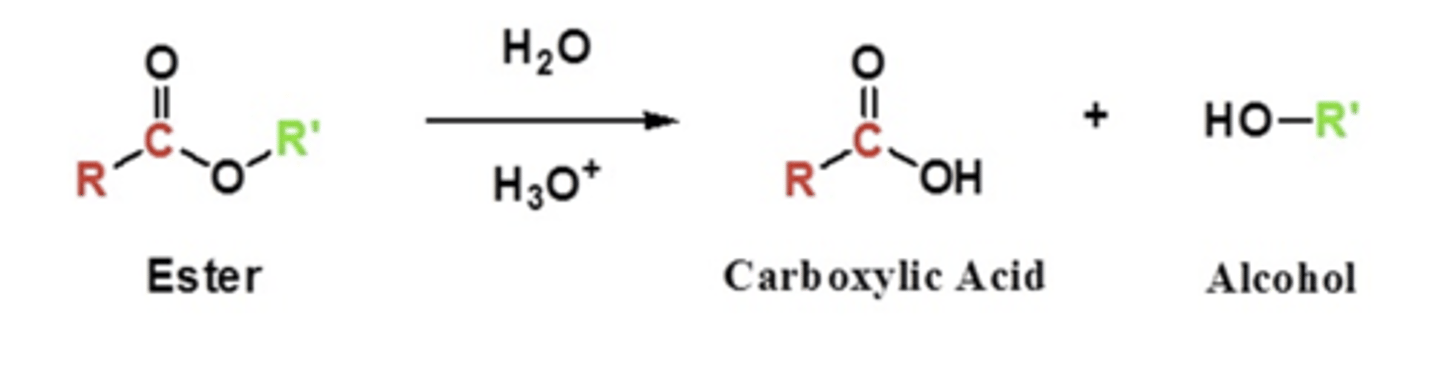
ester bonds hydrolysed under acid catalyst
opposite to ester formation you get the acid and alcohol
ester bonds hydrolysed under basic catalyst
forms the conjugative base (carboxylate -COO-) and alcohol.

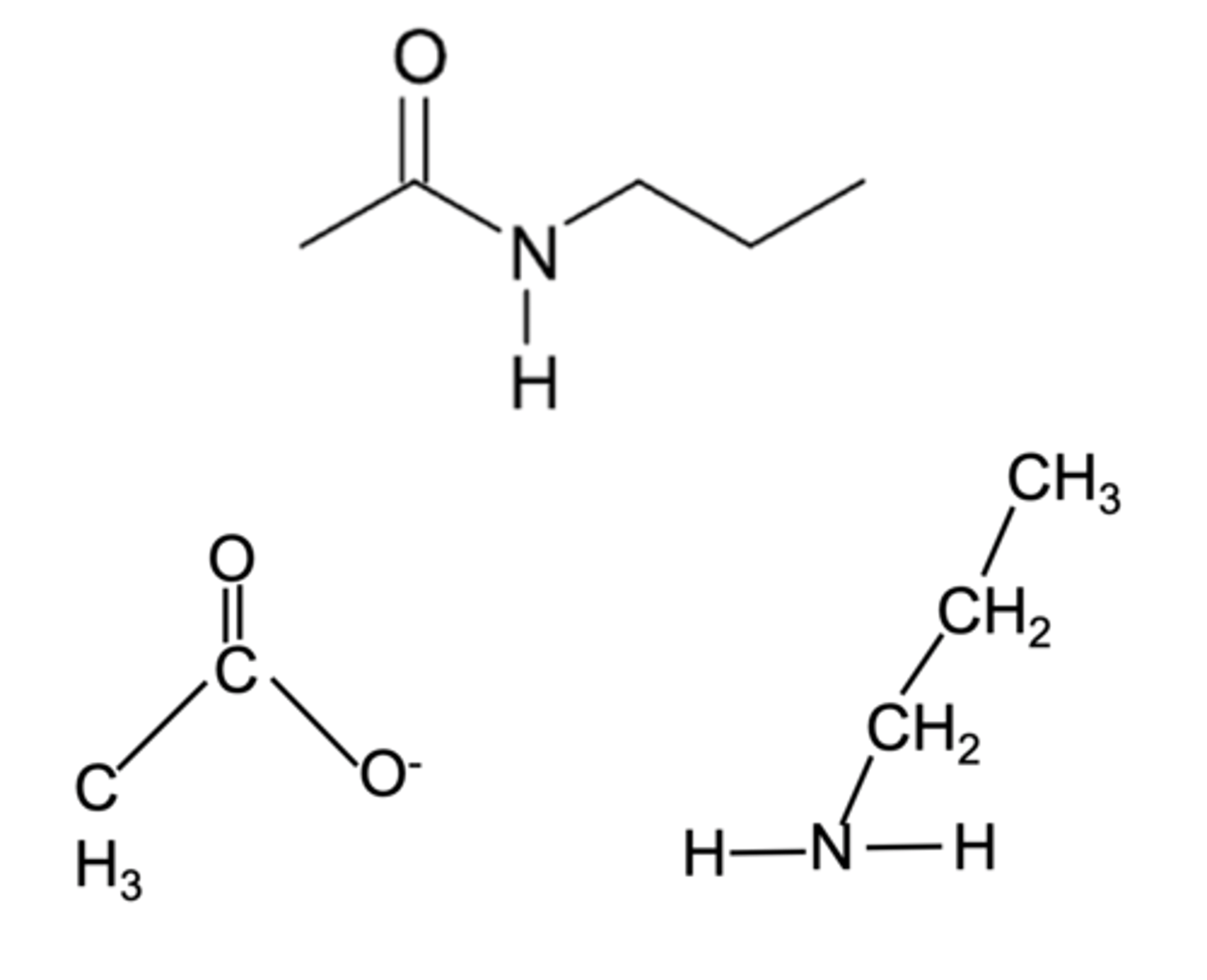
carboxylic acids + amines =
amides
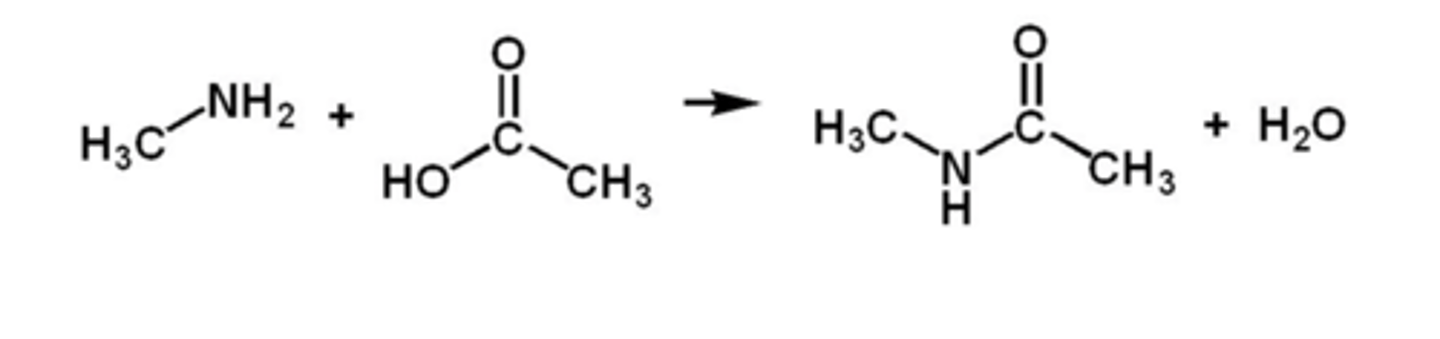
to deduce the amine and acid
find the C-N bond, split it, add add OH to the amine side and OH to the acid side.
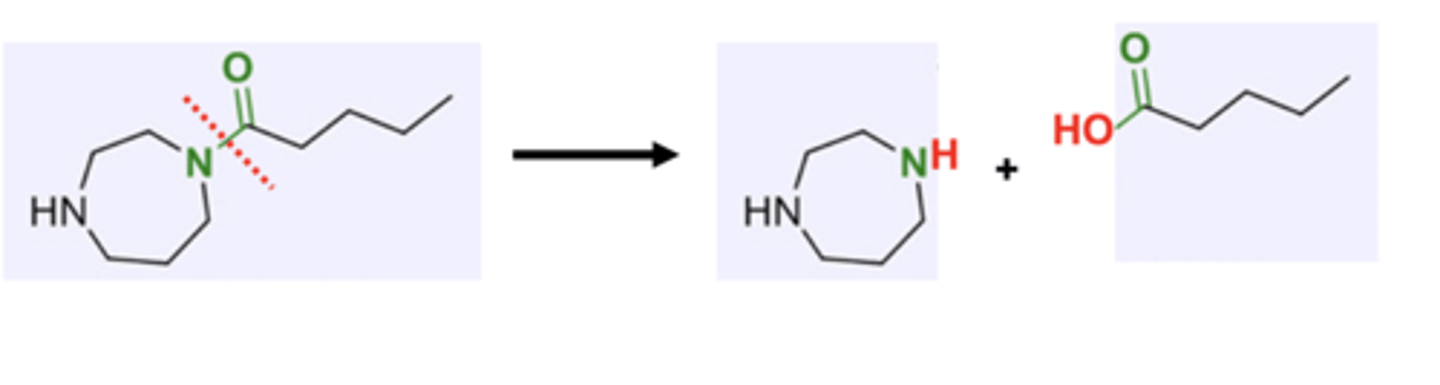
polyamides
diamine + dicarboxylic acid
or a monomer with a one amine and one carboxylic acid
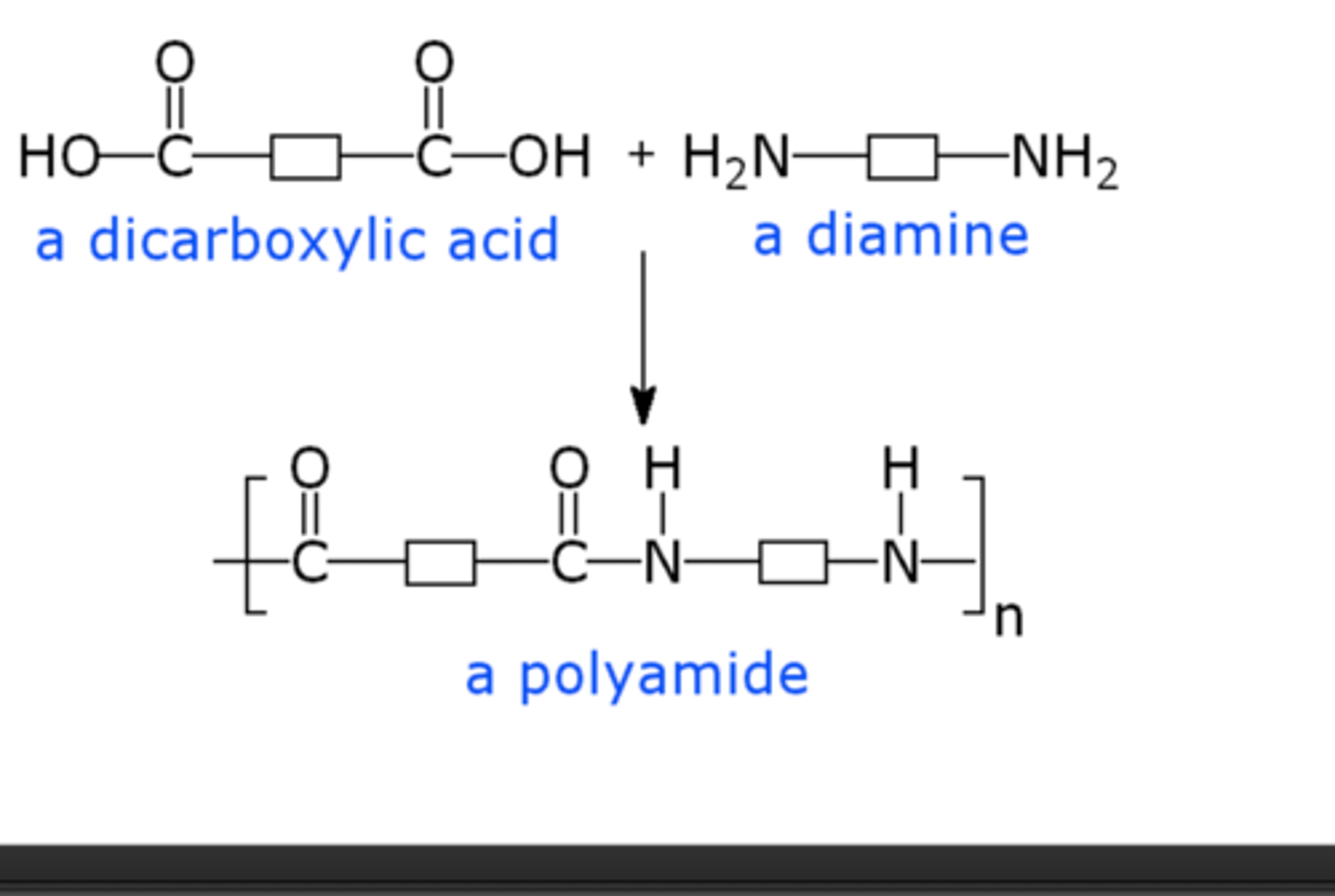
polyamides are stronger then polyesters due to
its ability to hydrogen bond to adjacent chains
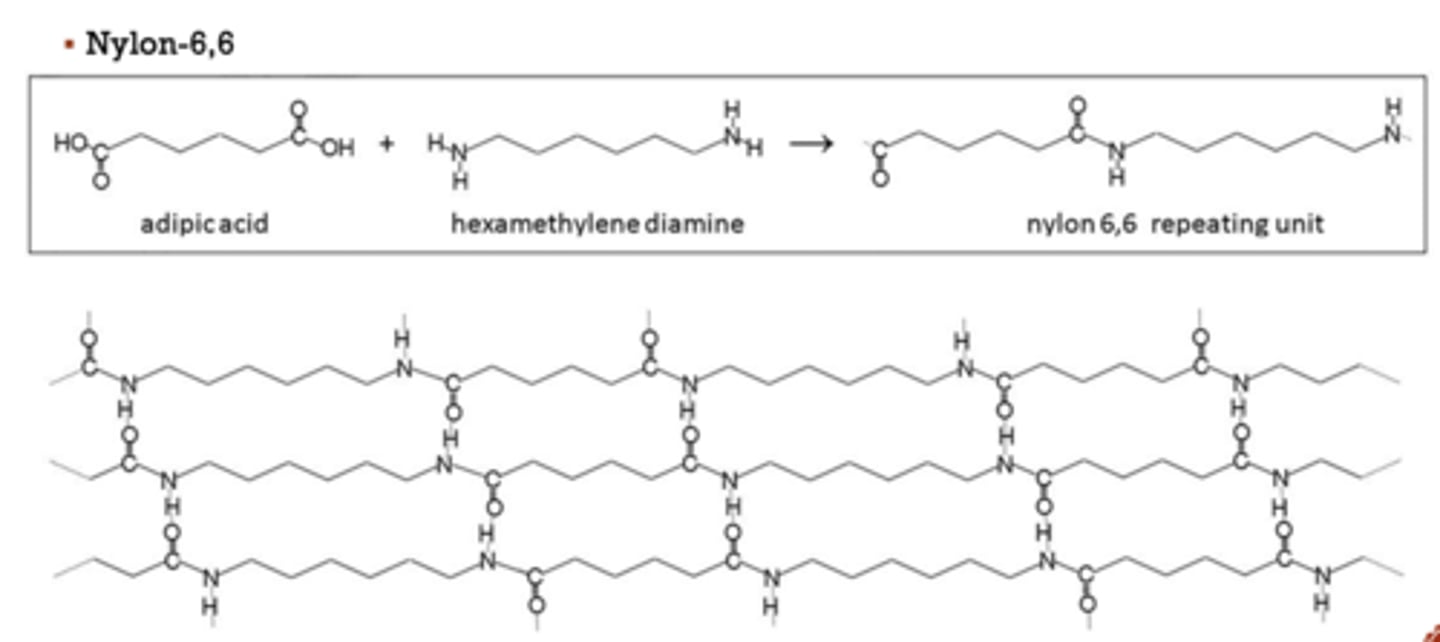
drawing a polyamide
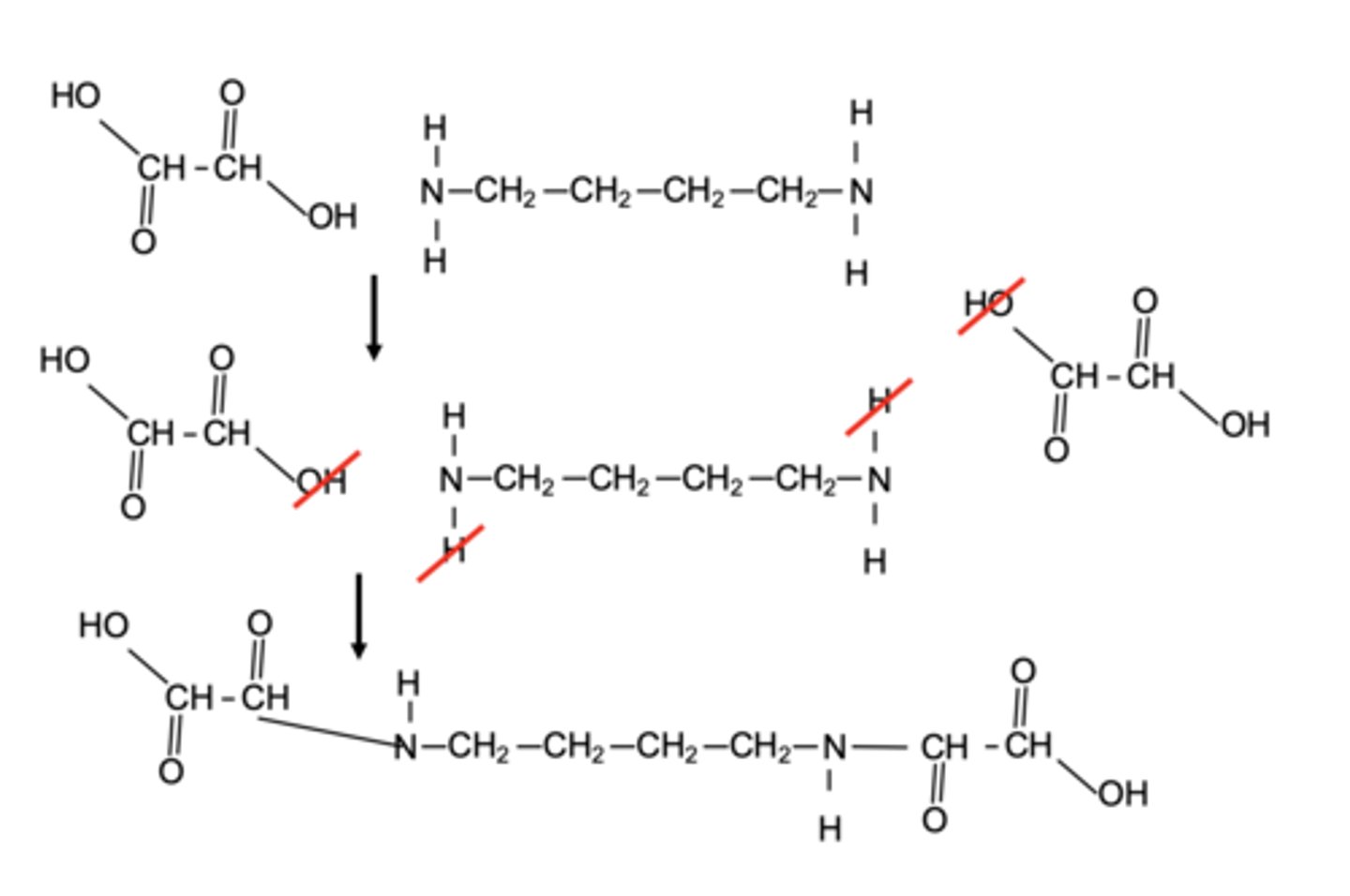
Polyamide can undergo hydrolyse under acidic conditions it will form alcohol and amine
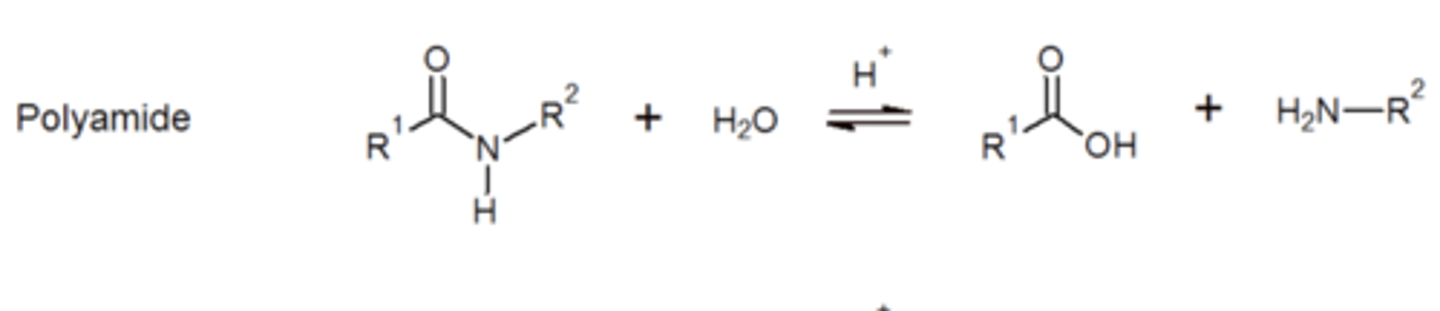
Polyamide can hydrolyse under basic conditions it will form alcohol and amine
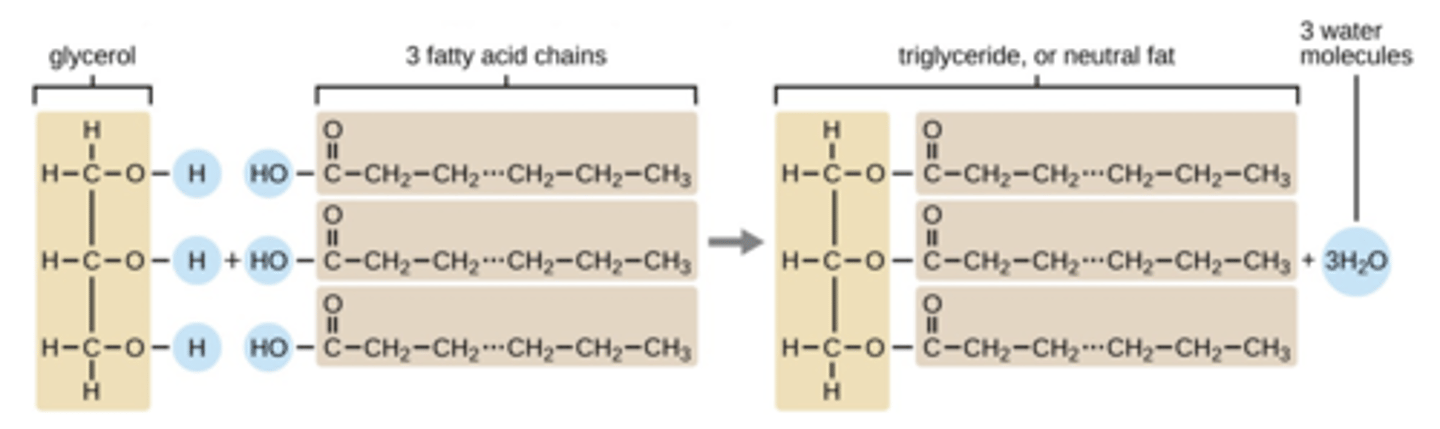
Triglycerides (triesters) are formed between
propane-1,2,3-triol (glycerol) and "fatty acids"
I got up to Triglycerides pg 3
I got up to Triglycerides pg 3