lecture 7: gender gap, wash
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
define the concept of a gender gap and give examples of the gender gap and its consequences throughout the world
sudan has the greatest gender gap,
compare the gender gap score to 1.0 which means equality between males and females
would take 5 generations to fix gender gap
Common areas: education, employment, income, politics, healthcare, and personal freedoms.
evaluate the role of womens education and empowerment in reducing poverty, undernutrition, and conflict
educating women reduces poverty, and reductions in child malnutrition
improved food availability and status of women
peace is more stable and longer lasting when women are involved
more likely to reach an agreement if there was strong influence by women
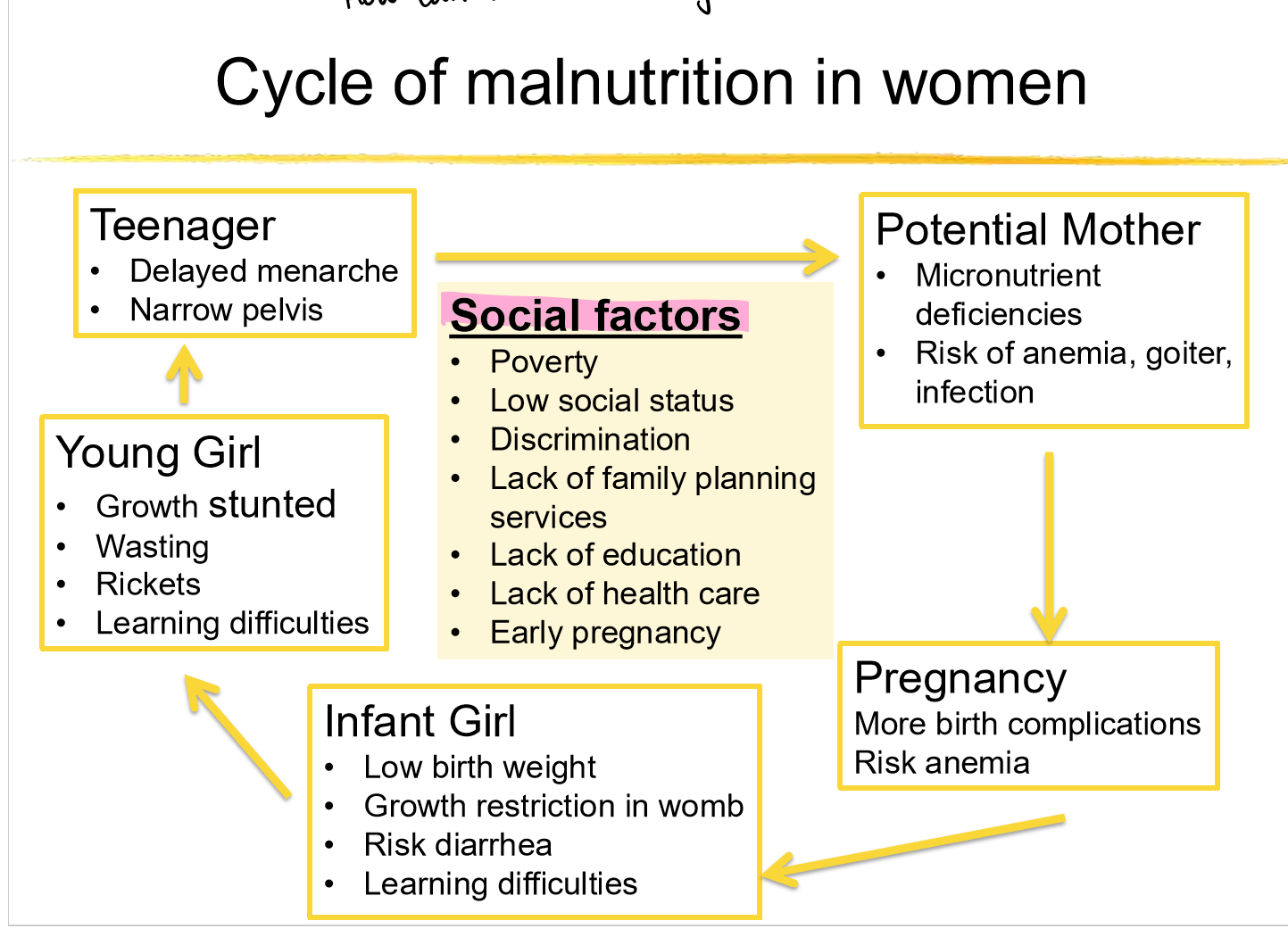
how can we stop the intergenerational cycle of malnutrition in women
target social factors
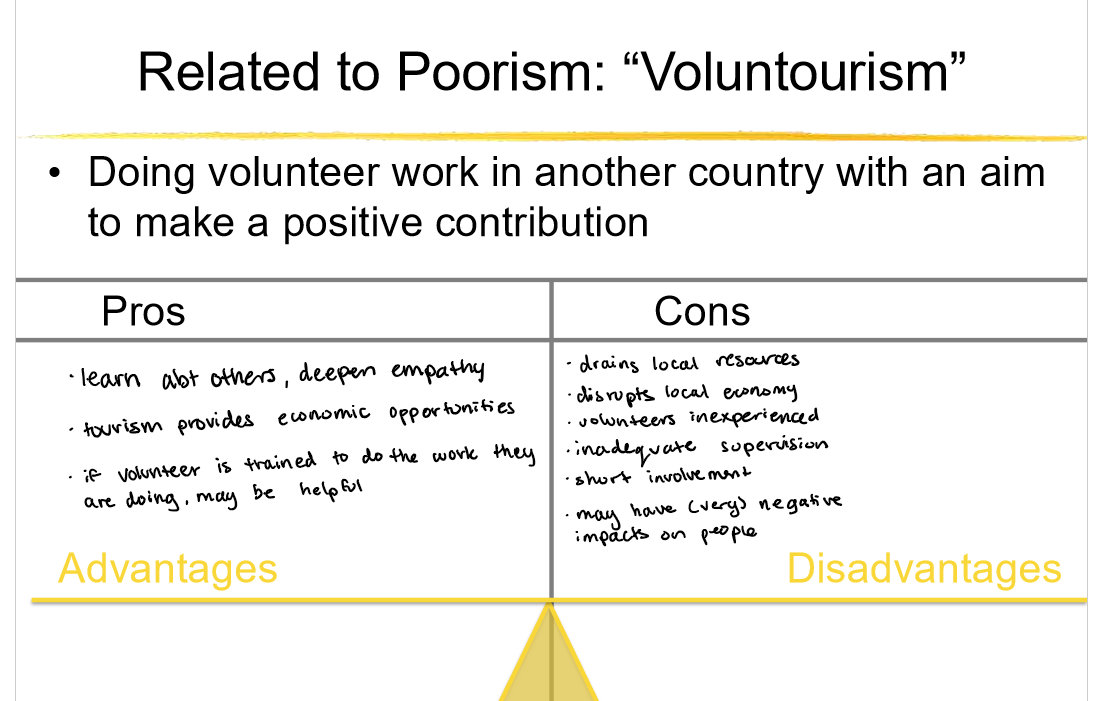
pros and cons of strategies: poorism, voluntourism, building latrines and wells
Poorism
Raises awareness among visitors about global poverty.
Can create empathy and motivate future advocacy or donations.
Generates some income for local communities through tourism.
Can exploit vulnerable communities for the tourist experience.
Often lacks long-term benefit or sustainability for locals.
Reinforces stereotypes and a savior mentality.
Visitors may leave with simplified or distorted views of poverty.
Building Latrines
Pros:
Improves sanitation and reduces the spread of disease.
Encourages dignity, safety, and privacy—especially for women.
Can reduce open defecation when paired with education.
Inexpensive compared to other infrastructure.
Cons:
If not maintained, latrines can become unusable or hazardous.
May be built without proper community input or usage training.
Doesn’t guarantee behavior change without hygiene education.
Poor design can contaminate groundwater if improperly placed.
Building Wells
Pros:
Provides access to clean water, improving health outcomes.
Reduces time spent (especially by women/children) fetching water.
Supports agriculture and local economic activity.
Helps prevent waterborne diseases.
Cons:
Wells can run dry or become contaminated if not maintained.
May create dependency if local capacity to repair is not built.
Some areas have groundwater with unsafe levels of fluoride/arsenic.
Projects may fail if communities aren’t involved in planning.
provide examples of nutrition related challenges associated with living in an urban slum
inadequate acess to sanitation & infrastructure = disease and sickness = impacts nutrition
no access to food, or high food prices = undernutrition, wasting stunting etc
Overcrowded conditions with poor sanitation increase exposure to disease, affecting nutrient absorption
ex unsafe toilets = creates disease
low unstable income
limited access to dietary diversity= lack of micronutrients
consider the role of social norms and personal beliefs in strategies to reduce open defecation and give examples of initiatives that have aimed to change social norms
social pressure, no toilet no bride in haryana india
encourage sanitation facilities in the families that women are being married into