Lab 1
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
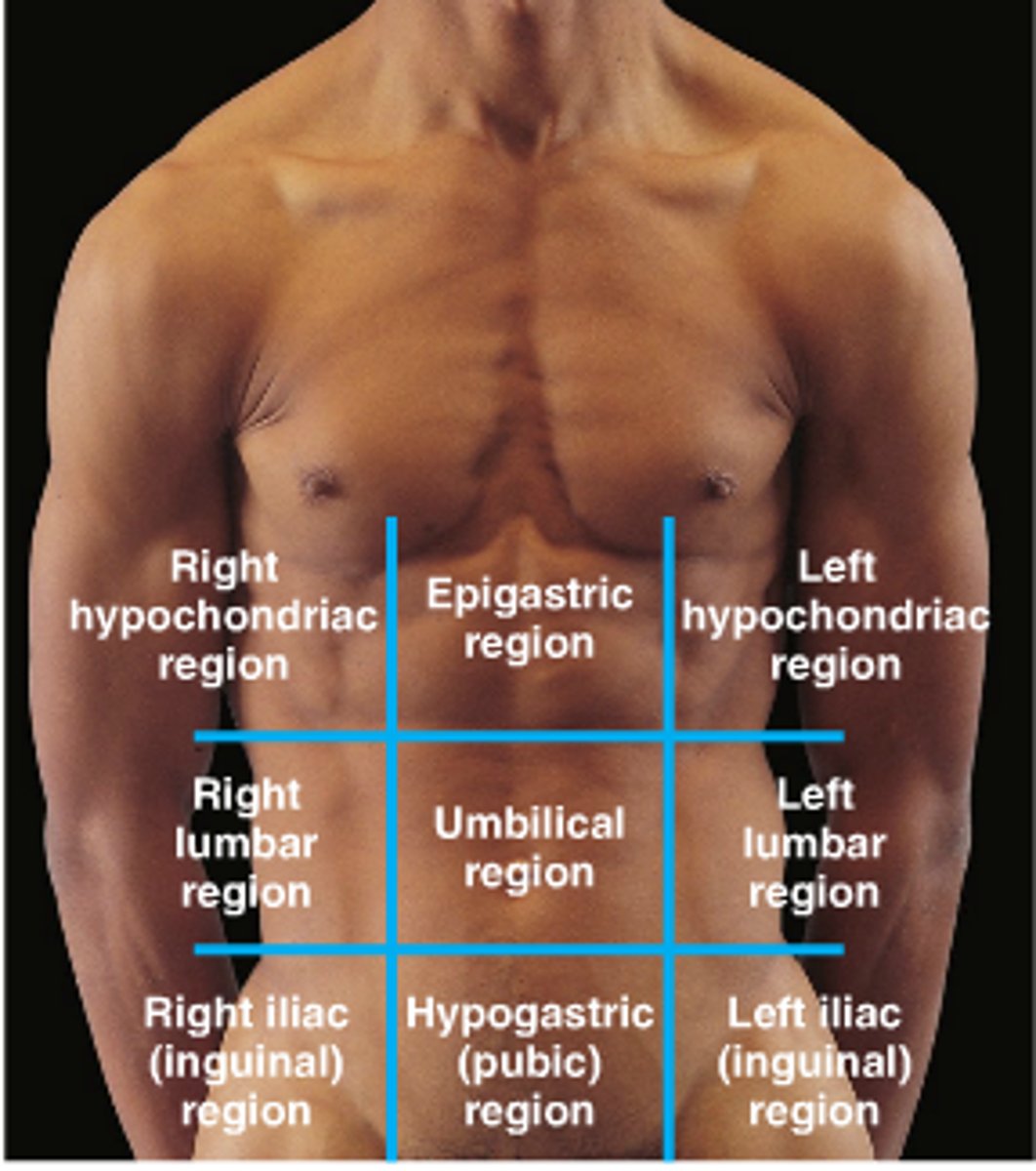
Abdominal Region (Left Upper to Right Lower)
Acromial
Most lateral/superior shoulder region
Abdominal
anterior region superior to umbilical
Antebrachial
Forearm (the portion of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist)
Axillary
armpit
Brachial
Proximal arm
Buccal
Cheek
Carpal
Wrist
Cephalic
head region
Cervical
neck region
Coxal
hip
Cranial
superior most region of the head
Crural
Leg inferior of the patella
Cubital
elbow
Deltoid
shoulder
Mental
Chin
Nasal
Nose
Oral
Mouth
Orbital
Eyes
Parotid
near the ear
Name the Facial Regions
Mental
Nasal
Oral
Orbital
Parotid
Femoral
Thigh
Digital
Toes/Fingers
Dorsum Surface
Anterior surface of the foot
Plantar Surface
Posterior surface of the foot
Calcaneal
Heel
Name the regions of the foot
Digital
Dorsum
Plantar
Calcaneal
Frontal
Forehead
Gluteal
butt
Palmar
palm of the hand
Dorsal (hand)
back of hand
Inguinal
groin
Lumbar
Lower Back
Mammary
Breast
Occipital
Back of head
Olecranal
back of elbow
Otic/Auricular
Ear
Patellar
Knee
Pectoral
chest
Pelvic
Pelvis
Perineal
region between the anus and the external reproductive organs
Pollex
big thumb
Popliteal
Posterior Knee
Pubic
genital region
Sacral
Posterior region between the hip bones
Scapular
Back shoulders
Sternal
breastbone
Tarsal
Ankle
Thoracic
upper trunk
Umbilical
Lower trunk
Vertebral
Back
What are the layers of thick skin?
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Lucidum
Stratum Granulosum
Stratum Spinosum
Stratum Basale
What are the layers of thin skin?
stratum corneum
stratum granulosum
stratum spinosum
stratum basale
Which layer of skin does thin skin not have?
Stratum Lucidum
Which layer of skin are melanocytes and stem cells found?
Stratum Basale
What does glabrous skin mean?
Skin devoid of hair
What makes fingerprints?
epidermal ridges
What do free nerve endings detect?
Pain and Temperature
What doe Merkel's Discs detect?
Light pressure and touch
What do mesissner's corpuscles detect?
Light Vibration and touch
Papillary layer
outer layer of the dermis, directly beneath the epidermis
Reticular layer
Deeper layer of the dermis that supplies the skin with oxygen and nutrients
What do ruffini corpuscles detect?
Stretching
What are the epidermal receptors?
Free Nerve Ending
Merkel's Discs
What are the dermal receptors?
Meissner's Corpuscles
Ruffini Corpuscles
Dermal Papilla
A small, cone-shaped area at the base of the hair follicle that fits into the hair bulb
Sebaceous Gland
oil-secreting gland in the dermis that is associated with hair follicles
Arrector Pili Muscle
An involuntary muscle fiber attached to the underside & base of the hair follicle
Apocrine Sweat Glands
Found in armpits, around nipples, and groin; Secrete products into hair follicles; Produce sticky, cloudy secretions; Break down and cause odors;
Merocrine Sweat Glands
secrete a watery fluid directly onto the surface of the skin.
What type of tissue is found in the papillary layer of the dermis?
Areolar connective tissue
What type of tissue is found in the reticular layer of the dermis?
Dense irregular connective tissue
What causes goosebumps?
arrector pili muscle
What is another name for merocrine?
eccrine
Name the three sections of skin, superficial to deep.
Epidermis
Dermis
Hypodermis
What is the hypodermis receptor?
Pacinian Corpuscle
What does the pacinian corpuscle detect?
Deep pressure
What is deep to the hypodermis?
Loose connective tissue
Periosteum
A dense fibrous membrane covering the surface of bones (except at their extremities) and serving as an attachment for tendons and muscles.
Circumferential Lamellae
layers between periosteum and inner bone
Sharpey's Fibers
fibers connecting periosteum to the compact bone
Interstitial Lamellae
fill spaces between osteons
Perforating Canal (Volkmann's Canal)
horizontal canals between two osteons
Osteon
functional unit of compact bone
Name the five parts of an osteon
Concentric Lamellae
Central Canal
Osteocytes
Lacunae
Canaliculi
Concentric Lamellae
layers of bony matrix around a central canal
Central (Haversian) Canal
opening in the center of an osteon, carries blood vessels and nerves
Osteocytes
mature bone cells
Lacunae
small cavities in bone that contain osteocytes
Canaliculi
Hairlike canals that connect lacunae to each other and the central canal
What are the three parts of spongy bone?
Endosteum
Trabeculae
Bone Marrow
Endosteum
membranous lining of the hollow cavity of the bone
Trabeculae
extension of lamellae separated by bone marrow cavities
Bone Marrow
A soft tissue inside the bone that produces blood cells
Osteoporosis
A condition in which the body's bones become weak and break easily.
Nucleus
large central structure
carries genetic information
Chromatin
hair-like structures within the nucleus
bundles of chromosomes
Nuclear Pores
Holes in the nuclear envelope
allows for passage of materials
Nucleolus
globule within the nucleus
makes ribosomal subunits
Cytoplasm
Liquid within the cell
structural support and protection