ADH2 Seizures+Encephalitis
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Whats epilespy?
when person has 2+ unprovoked seizures (chronic, recurring)
seizures form identifiable causes does NOT = epilepsy!!
ex: low sodium
alcoholic
drugs)
What things increases seizure risks? (10)
head trauma
fever (especially children)
brain swelling
infx
stroke
brain tumor
hypoxic
alcohol withdrawal
stopping seizure meds abruptly
electrolyte imbalances
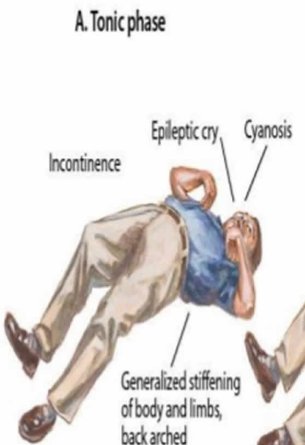
What is a tonic seizure?
s/s: (5)
only STIFFENING part happens
s/s:
increased muscle tone
loss of LOC
stop breathing
pee themselves
salivate
Whats a clonic seizure?
only JERKING phase
repeated rhythmic twitching for several minutes
Whats a tonic-clonic seizure aka grand mal? (3)
starts w/ tonic episode where muscle stiffens, person collapses and loses LOC
then clonic episode where pt jerks for 1-2 minutes
may bite tongue and lose bladder control
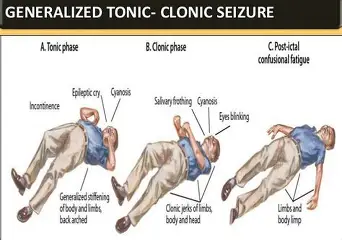
Whats the post ictal phase?
after seizing the pt is very tired, confused and wants to sleep
Whats a myoclonic seizure?
Sudden quick jerks/ twitches of muscles (like being startled)
Whats an atonic (drop) seizure?
sudden LOSS of muscle tone → person drops to ground
very high falls/banging head risk
Whats a complex partial seizure? (4)
hint:
what actions do they perform?
duration
whats their LOC?
person not fully aware (can blackout)
may do repeated actions (automatisms)
lasts minutes
no memory of it
What are automatisms? (3)
lip smacking
picking at clothes
staring
Whats a simple partial seizure?
whats their LOC?
what do they sense? (6)
person stays conscious
has strange sensations
deja vu
weird smell/taste (rubber burning)
one-sided mvmts
heart racing
flushing
tingling/ pain
What would nurse do DURING seizure? (4)
turn on side
loosen clothes
suction PRN
pad head
What to NOT DO during seizure? (4)
DONT restrain pt
DONT open jaw or put anything in it
DONT give food/water
DONT use padded tongue blade

Nurse care during POST-Ictal phase: (5)
keep side-lying
check for injuries+breathing
assess neuro status
reorient and calm them
ask abt aura and triggers
List the meds/therapeutic procedures for seizures: (4)
antiepileptic (phenytoin)
Vagal Nerve Stimulator
Conventional Surgery
Partial Corpus Callosotomy
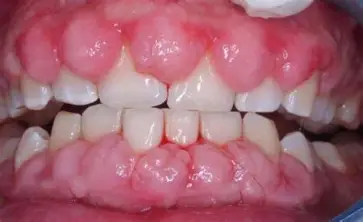
Teachings for phenytoin: (5)
take @ same time daily
causes gum overgrowth → good oral care
no oral contraceptives (reduced effectiveness)
no WARFARIN!!!!!
need blood level monitoring
What to avoid w/ VNS (vagal nerve stimulator) (4)
microwaves
shortwave radios
MRI (implanted in left chest wall like a pacemaker)
ultrasound
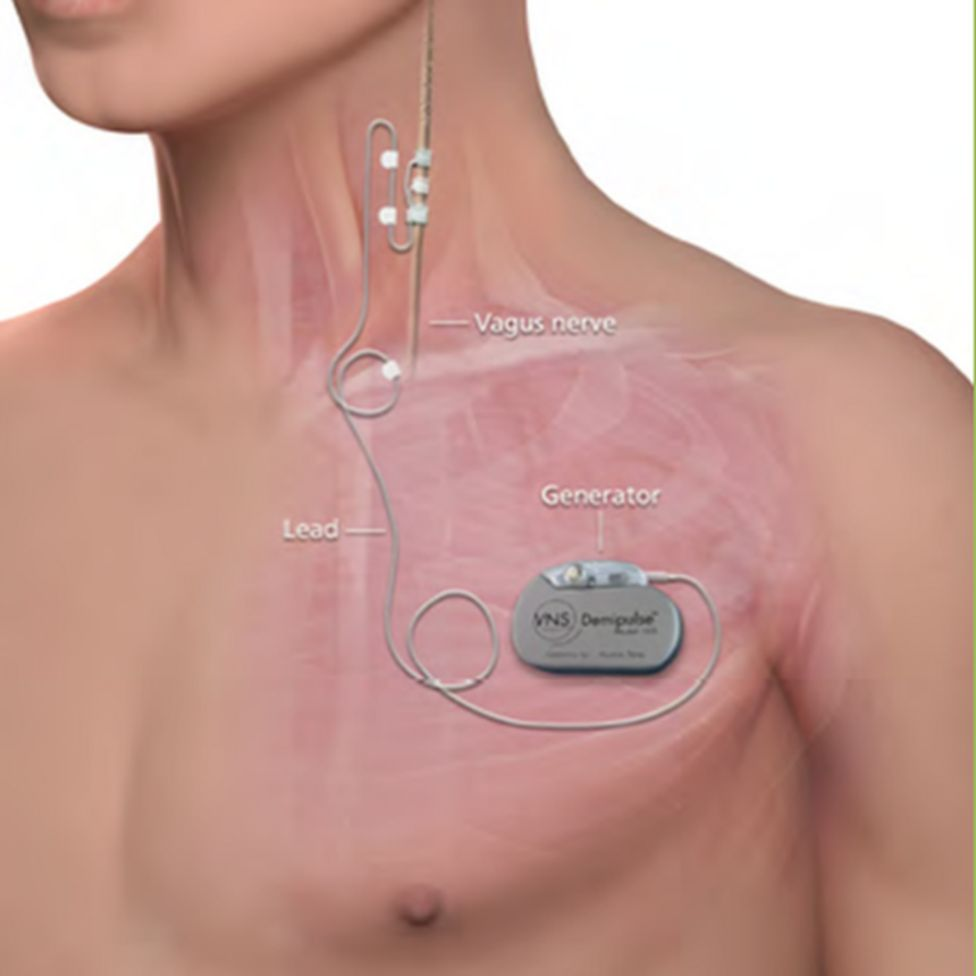
What can the pt do @ seizure onset if they have VNS?
swipe a magnet over device to stop/reduce seizure activity

What surgeries help treat seizures? (2)
conventional: remove seizure-causing brain area
discontinue AEDs first
partial corpus callosotomy: for those that arent candidates for conventional surgery
resects corpus callosum so prevents seizures from spreading b/w hemispheres
Major complication from a seizure?
what are 2 scenarios?
Status Epilepticus
one seizure lasts 5+ minutes OR
multiple seizures back to back for 30 mins
What causes Status Epilepticus? (5)
stopping seizure meds abruptly
alc/drug withdrawal
head injury
infx
metabolic problems
Emergency Actions for Status Epilepticus? (6)
maintain airway
give O2
IV access
diazepam or lorazepam IV (benzos)
then phenytoin or fosphenytoin
check ABGs
What is Encephalitis?
Inflammation of the brain, usually caused by a virus
Common causes of Encephalitis? (3)
Herpes simplex virus (HSV)
Mosquito-borne viruses (West Nile, St. Louis)
Fungal infx
Symptoms of encephalitis: (6)
Photophobia (light sensitivity)
Phonophobia (sound sensitivity)
Nuchal rigidity (stiff neck)
fever
HA
neurological problems
Meds for encephalitis? (2)
antivirals (HSV)
antifungals
Nursing interventions for encephalitis? (6)
HOB 30-45 degrees
dark, quiet room (phonophobia, photophobia)
seizure precautions
encourage fluids
reposition q2hrs
stool softeners (no straining)