Ch 24 Urinary System Learning Objectives & PPTs
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Describe the functions of the urinary system
- water, electrolyte, and acid-base balance
- removal of nitrogenous wastes
- blood is filtered into filtrate, then concentrated into urine
Kidneys
pair of organs that form and concentrate urine
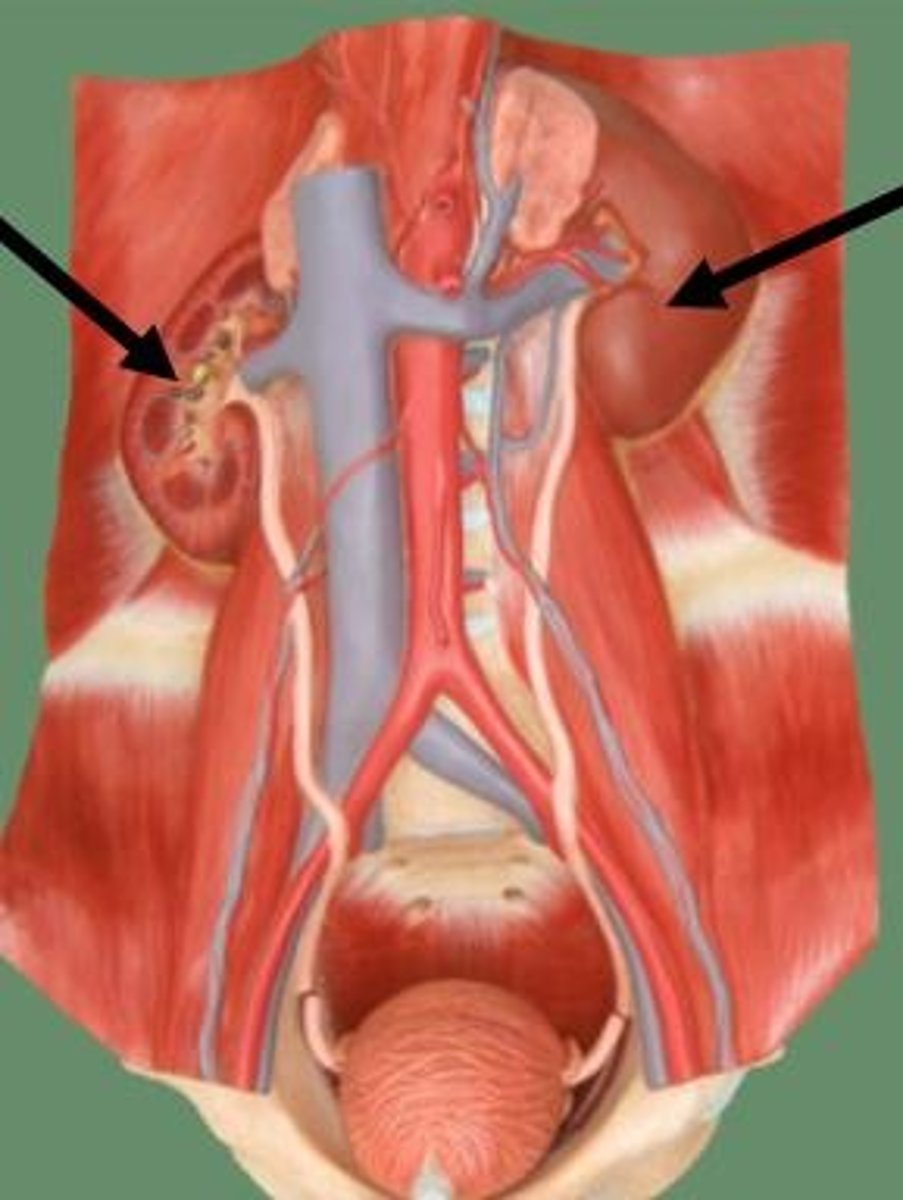
Ureters
transport urine from kidneys to urinary bladder
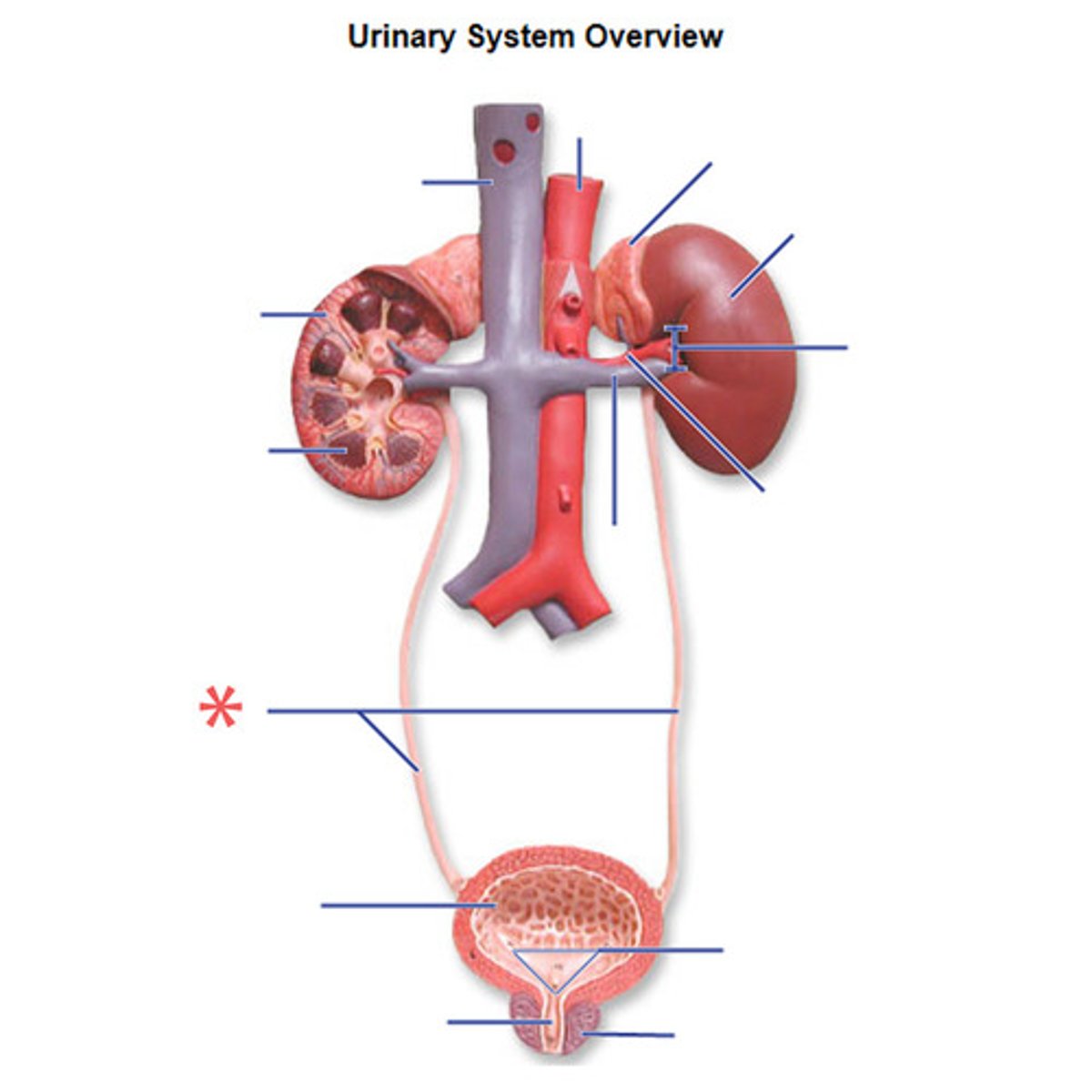
Urinary bladder
temporary storage reservoir for urine
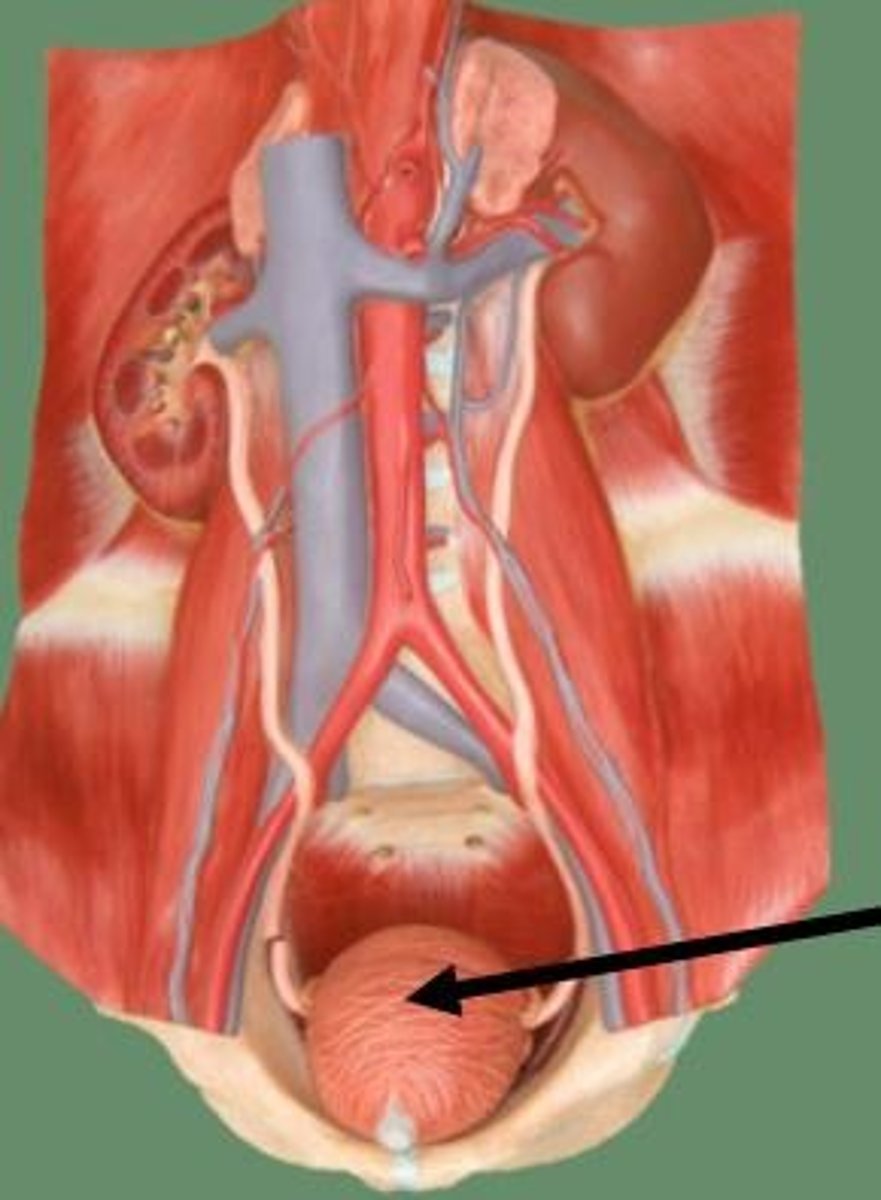
Urethra
transports urine from urinary bladder out of the body
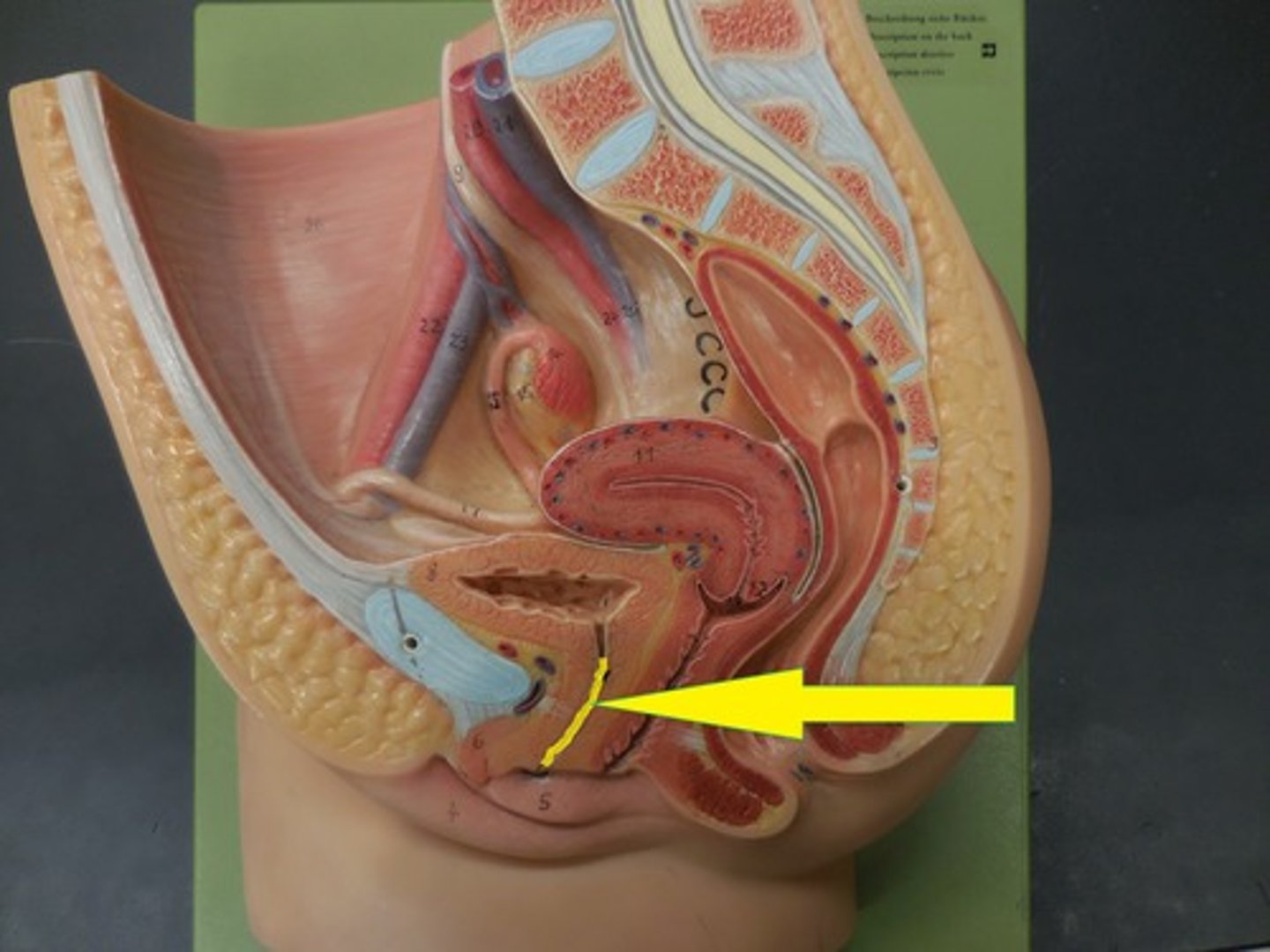
3 Regions of urethra in males
Prostatic; Immediate; Spongy
Prostatic urethra
passes through the prostate gland
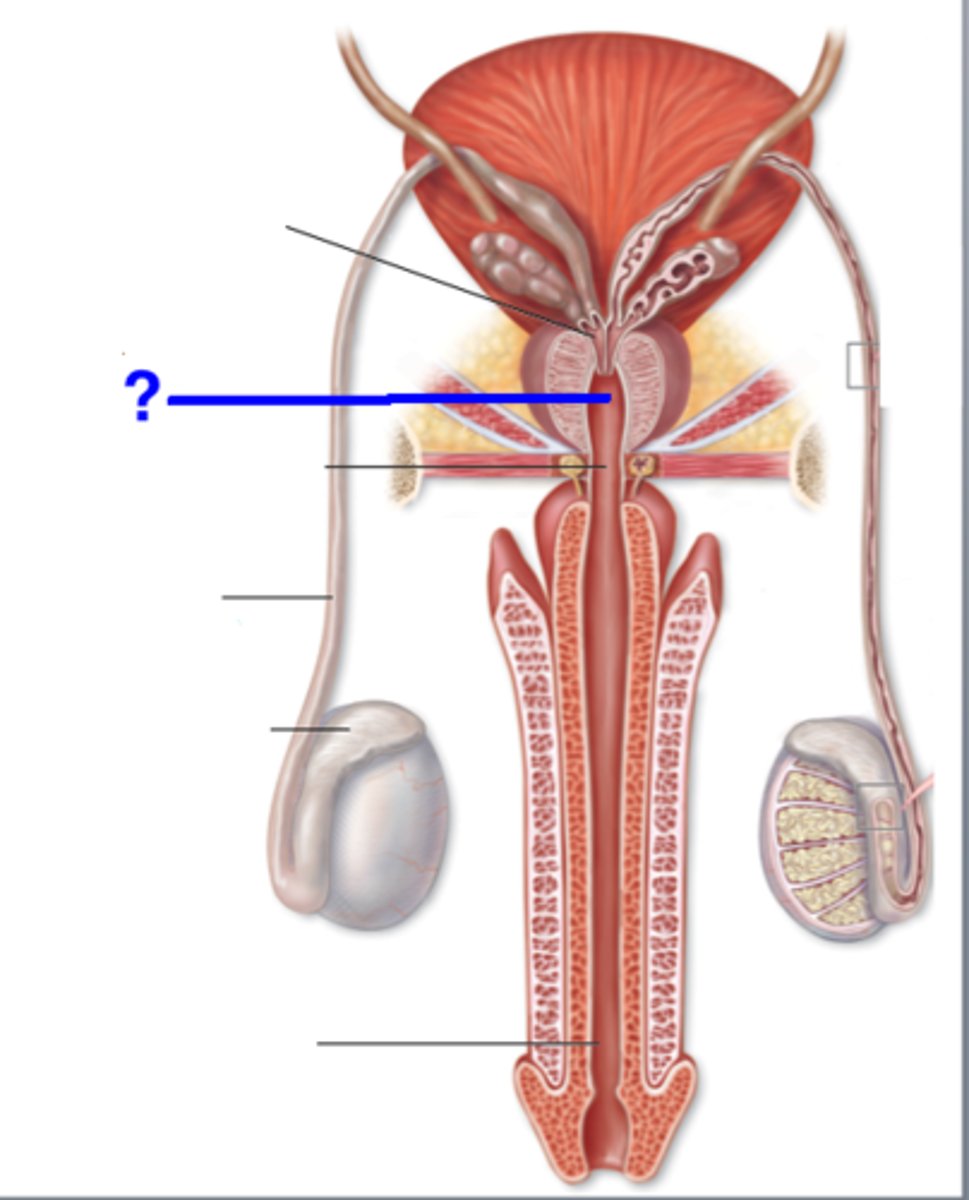
Immediate urethra
runs through urogenital diaphragm to beginning of pelvis (7)
Spongey urethra
runs through penis; opens at external urethral orifice
Location of kidney
below liver and posterior to stomach; on posterior wall of abdominal cavity and protected by floating ribs; right kidney lower than left kidney
Kidney functions
regulate total water volume; regulate total ion and solute concentration; maintaining acid-base balance; producing hormones (erythropoietin and renin); activating vitamin D; carrying out gluconeogenesis
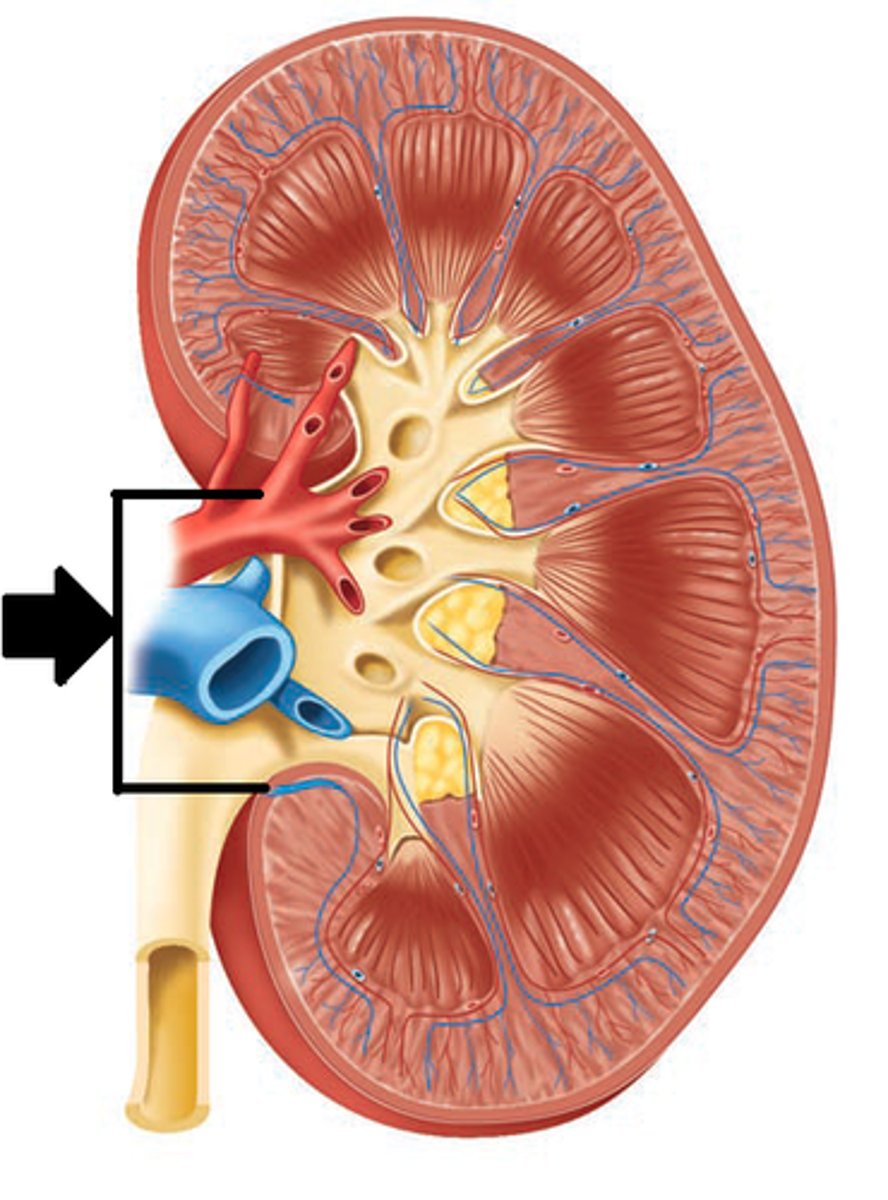
Kidney hilum
medial indentation, entry point for renal artery, nerves, exit renal vein, ureter
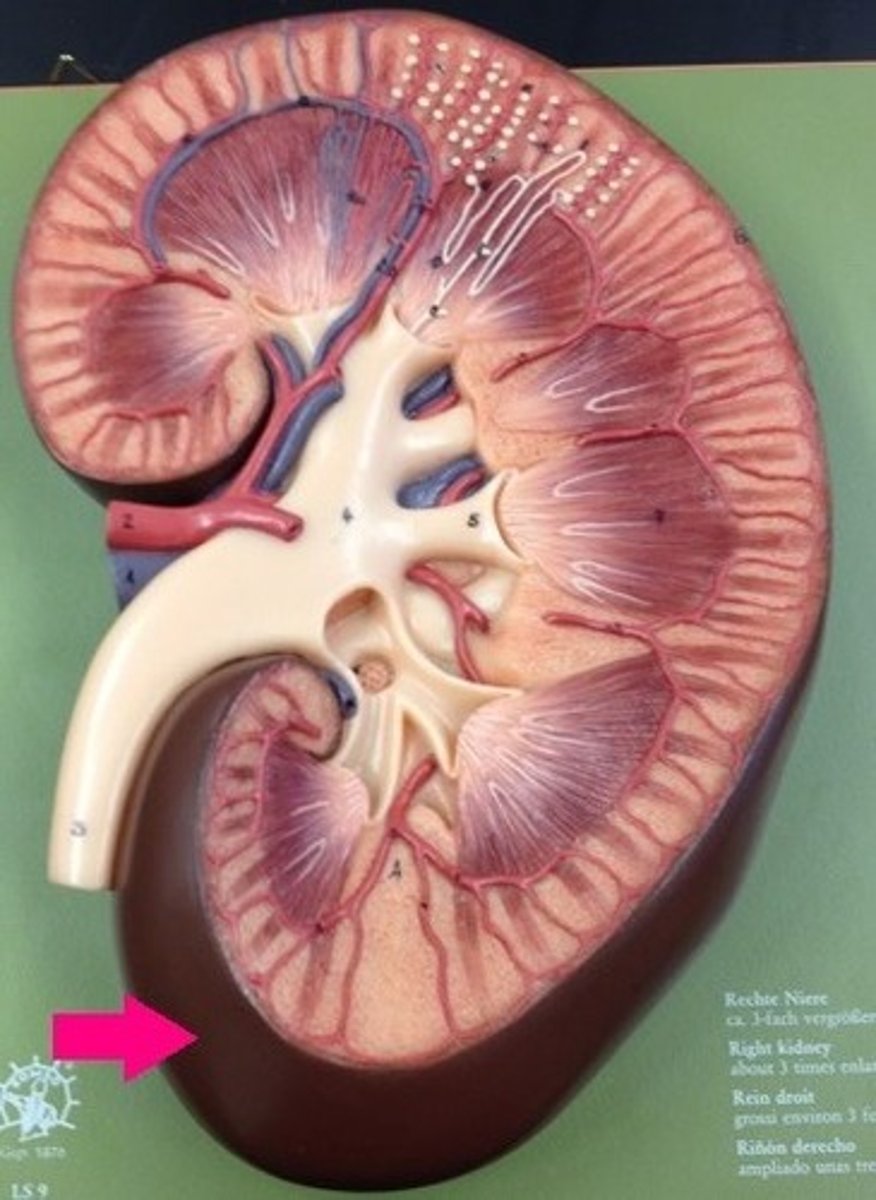
Layers of the kidney
1. renal fascia
2. perirenal fat capsule
3. fibrous capsule
renal fascia
outer layer of dense fibrous connective tissue that anchors the kidney to abdominal wall
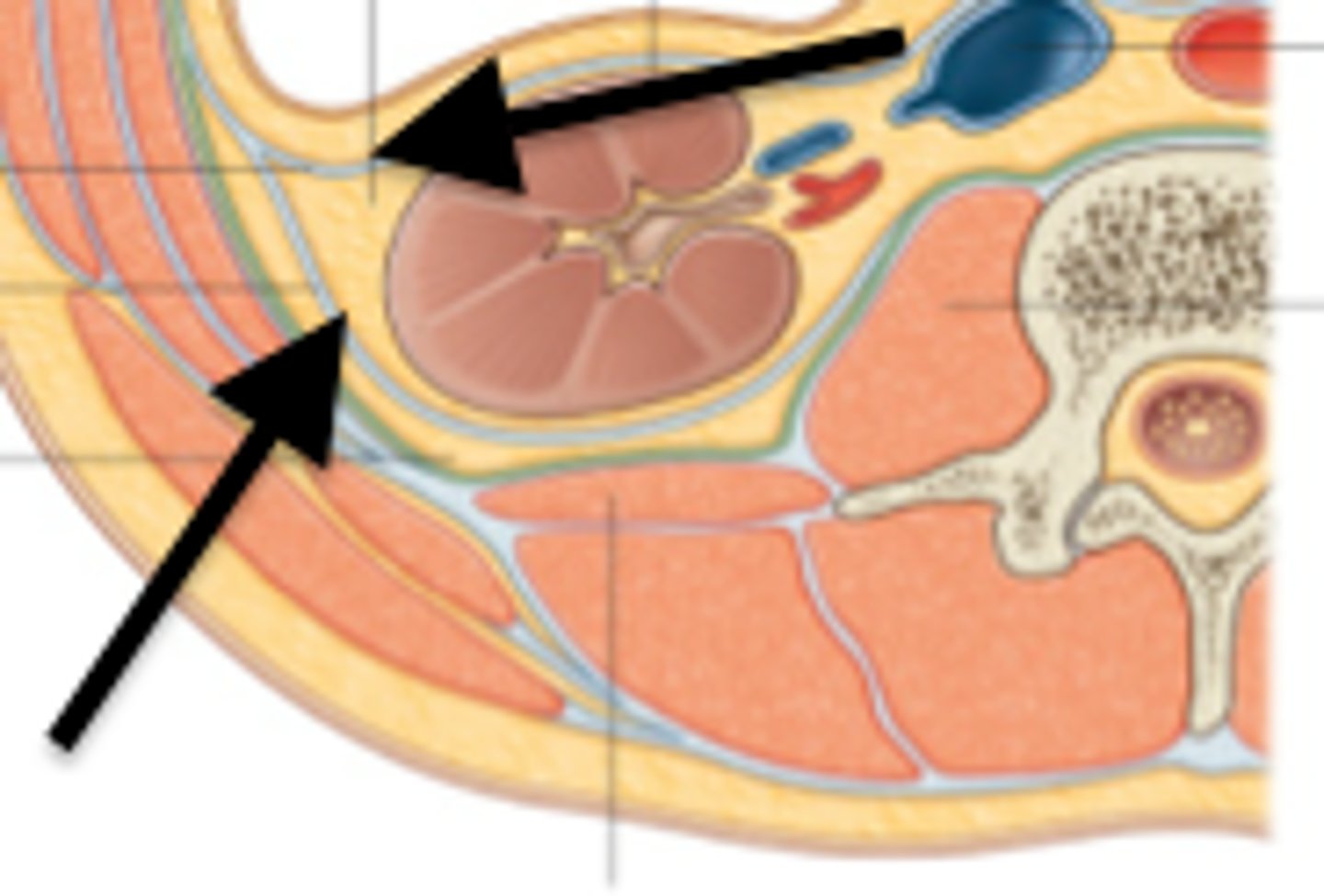
perirenal fat capsule
fatty cushion inside renal fascia
fibrous capsule
capsule surrounding each individual kidney
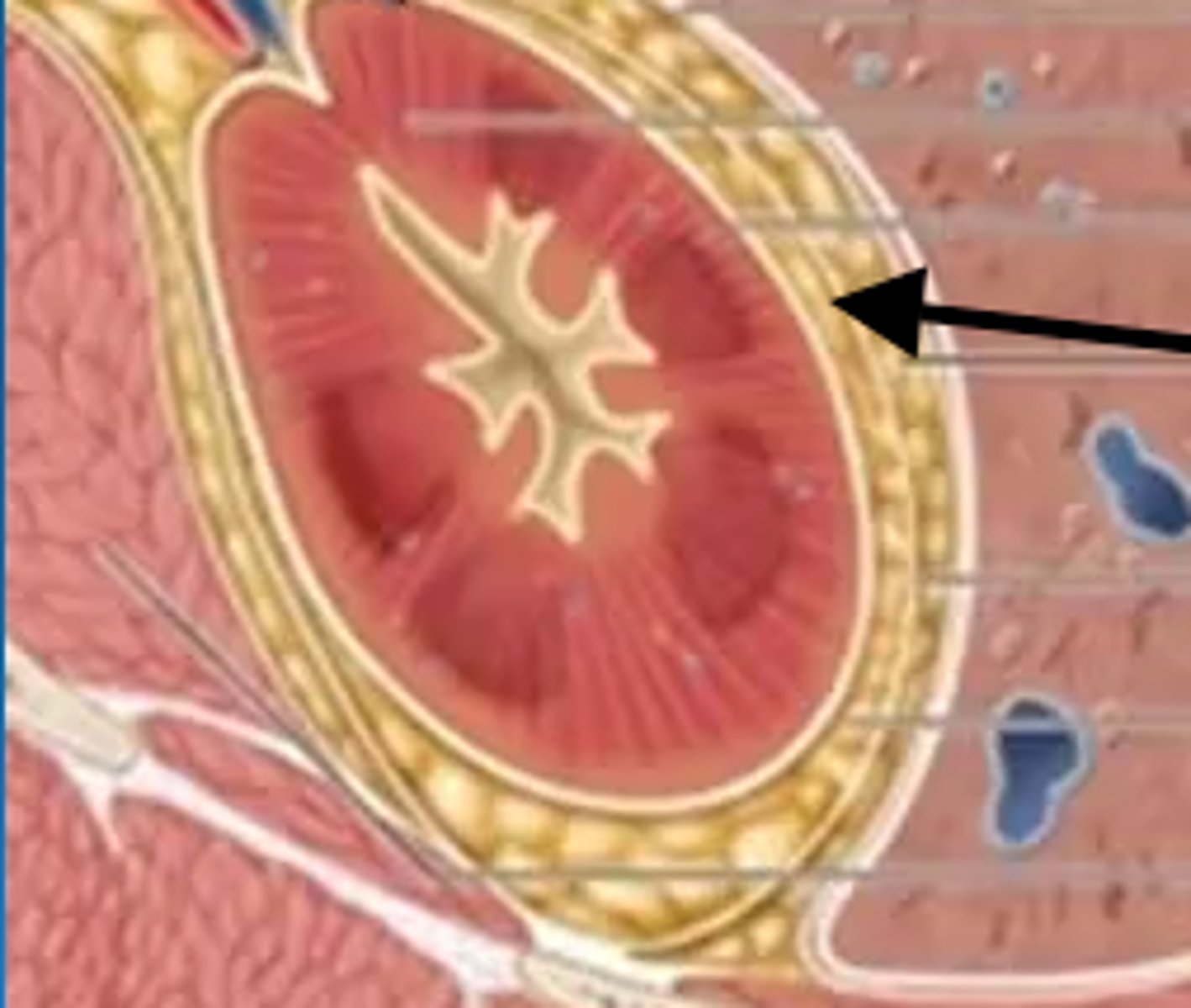
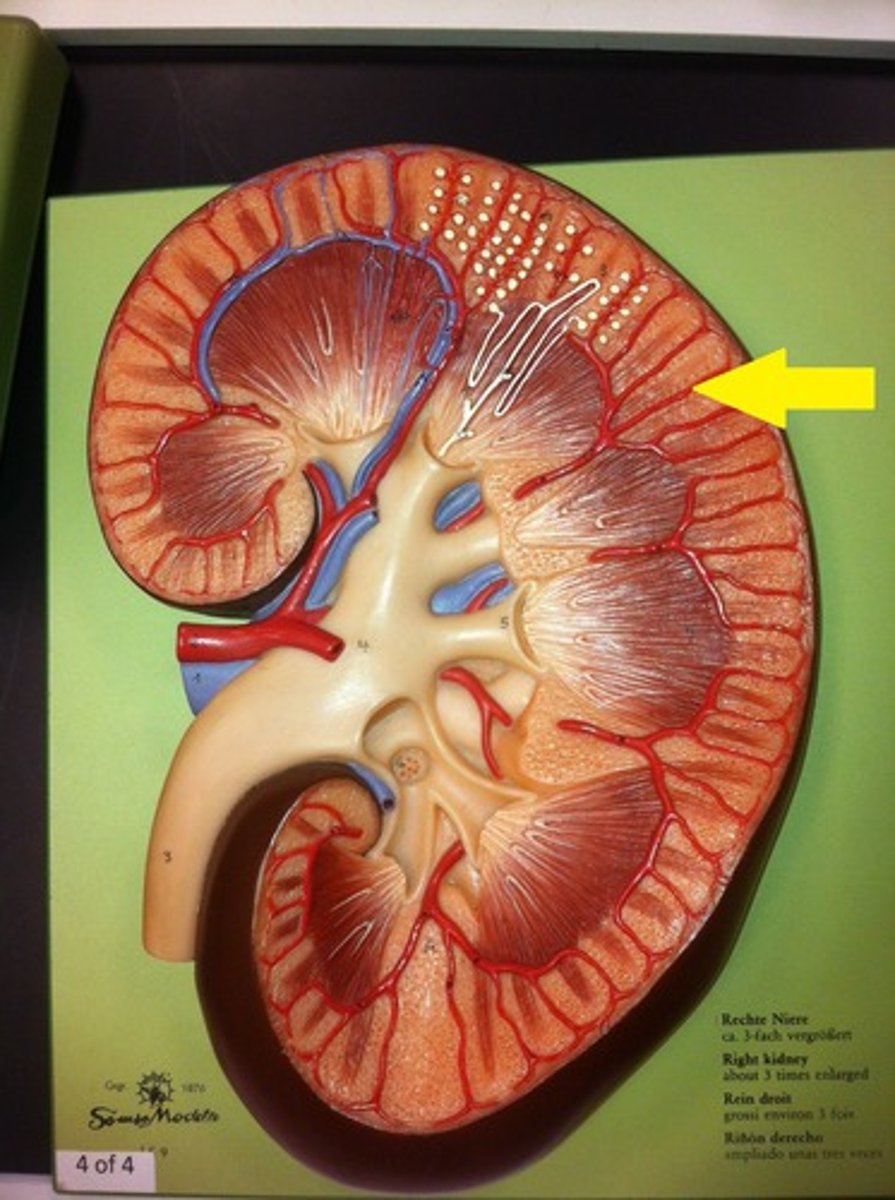
3 main regions of kidney
1. renal cortex
2. renal medulla
3. renal pelvis
renal cortex
granular-appearing superficial region
renal medulla
inner portion of the kidney
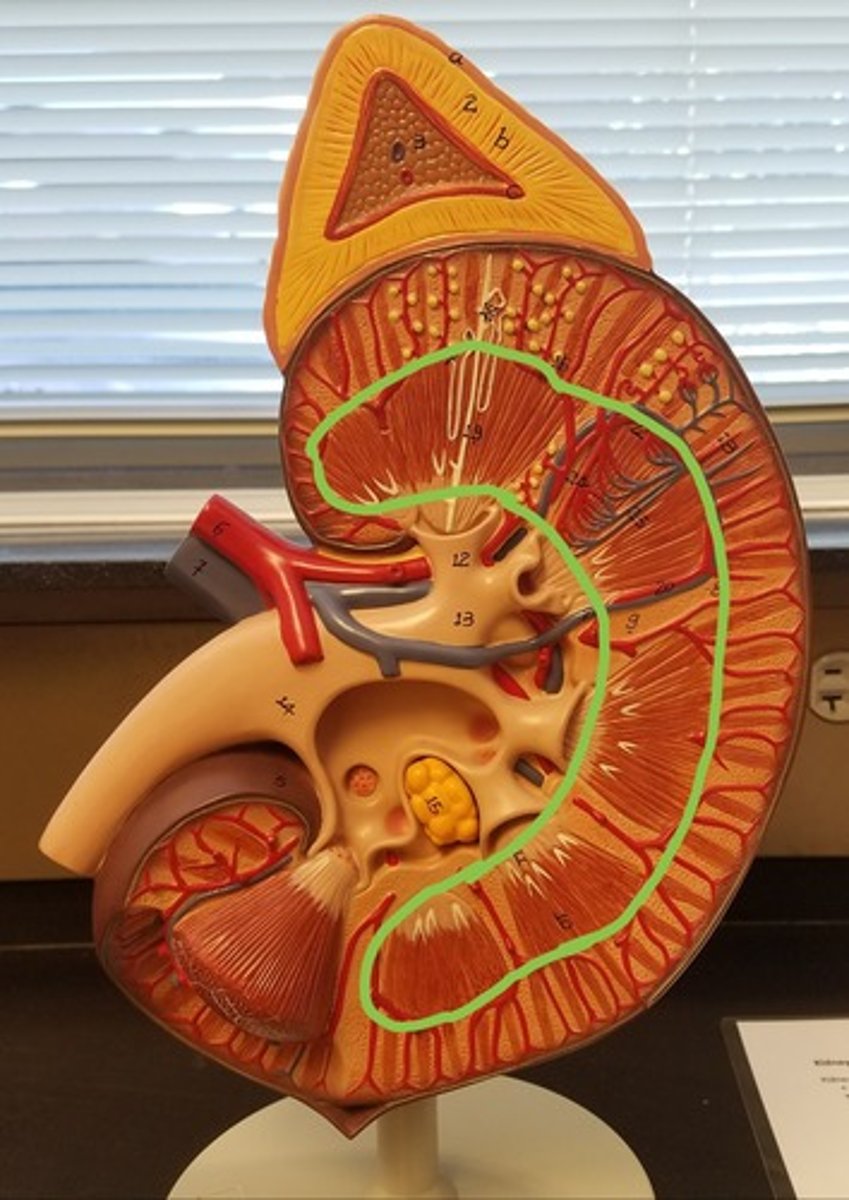
parts of renal medulla
renal pyramids and renal columns
renal pyramids
triangular-shaped areas of tissue in the medulla of the kidney; contain corticomedullary junction and papillae
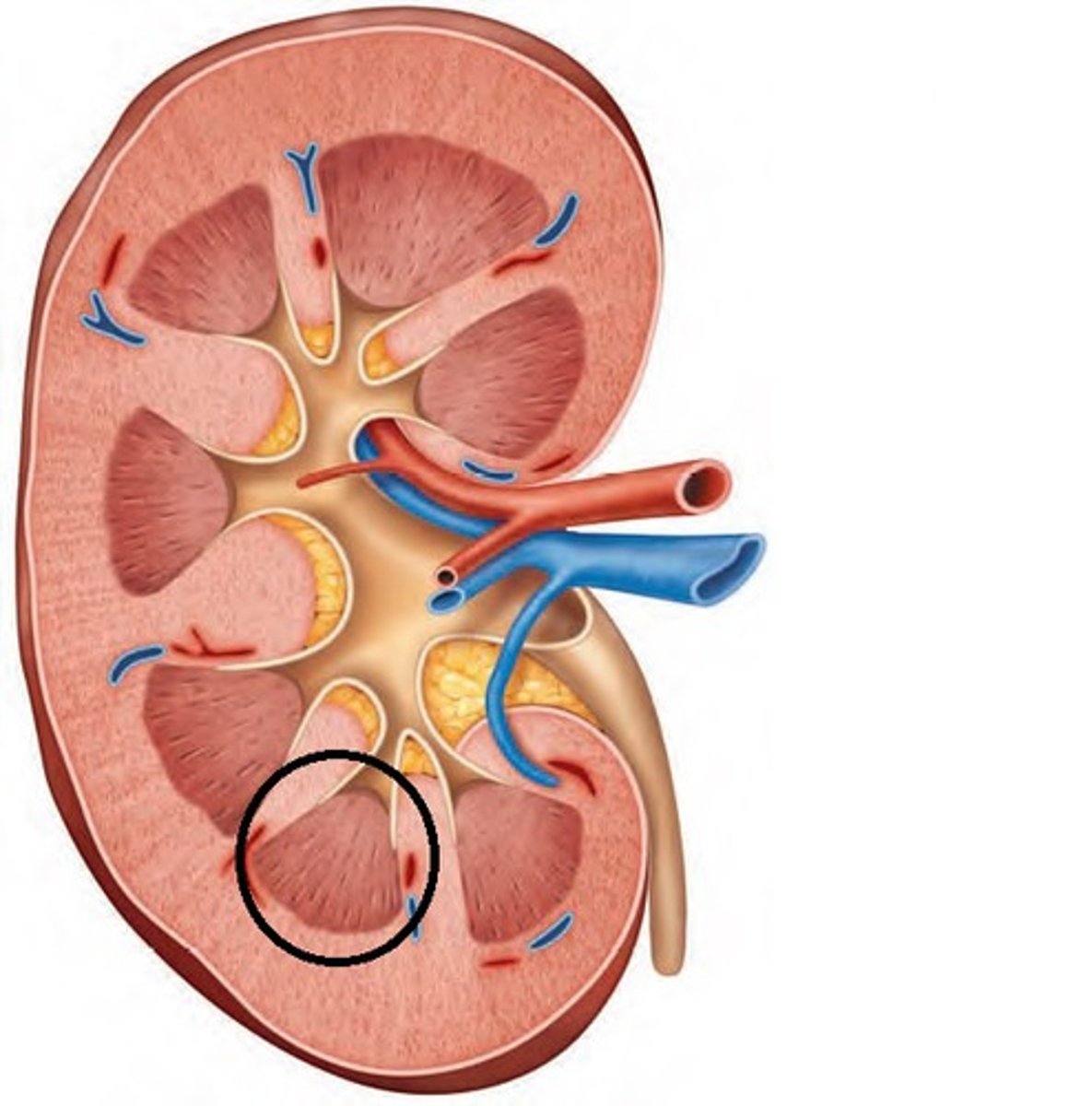
renal columns
extensions of cortex in between pyramids to divide them
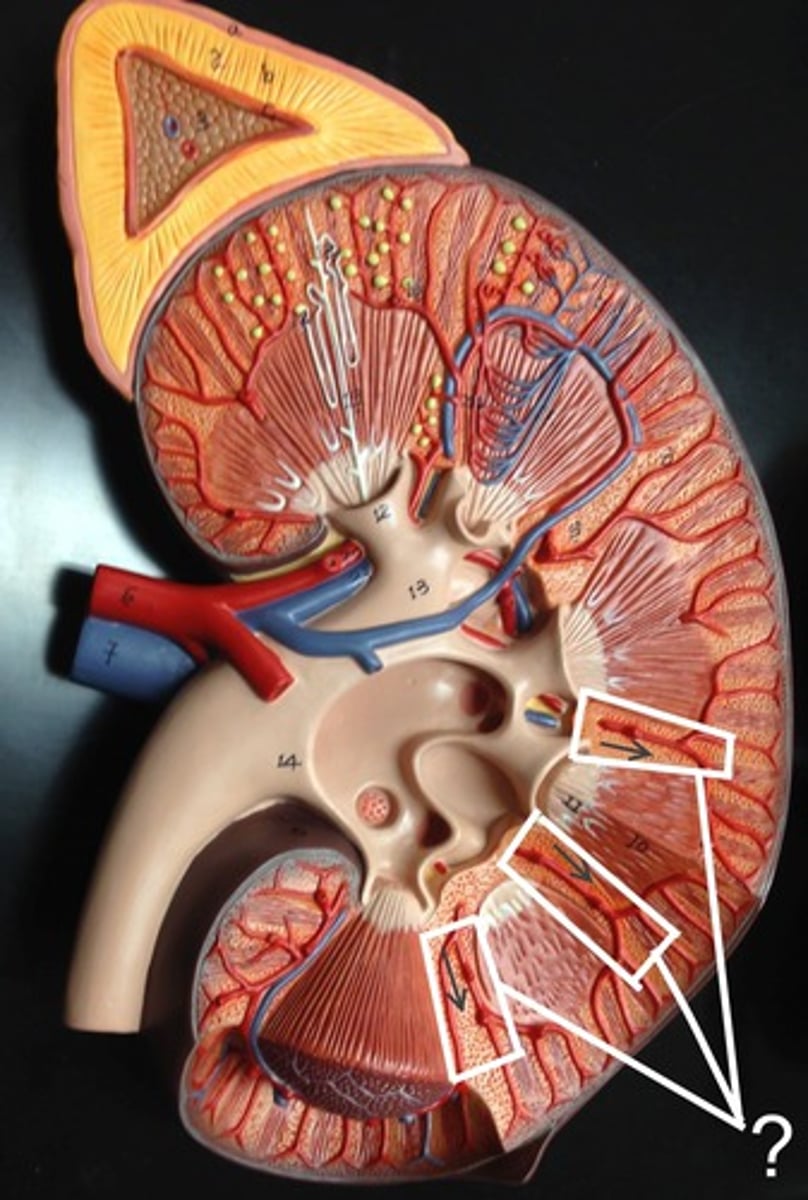
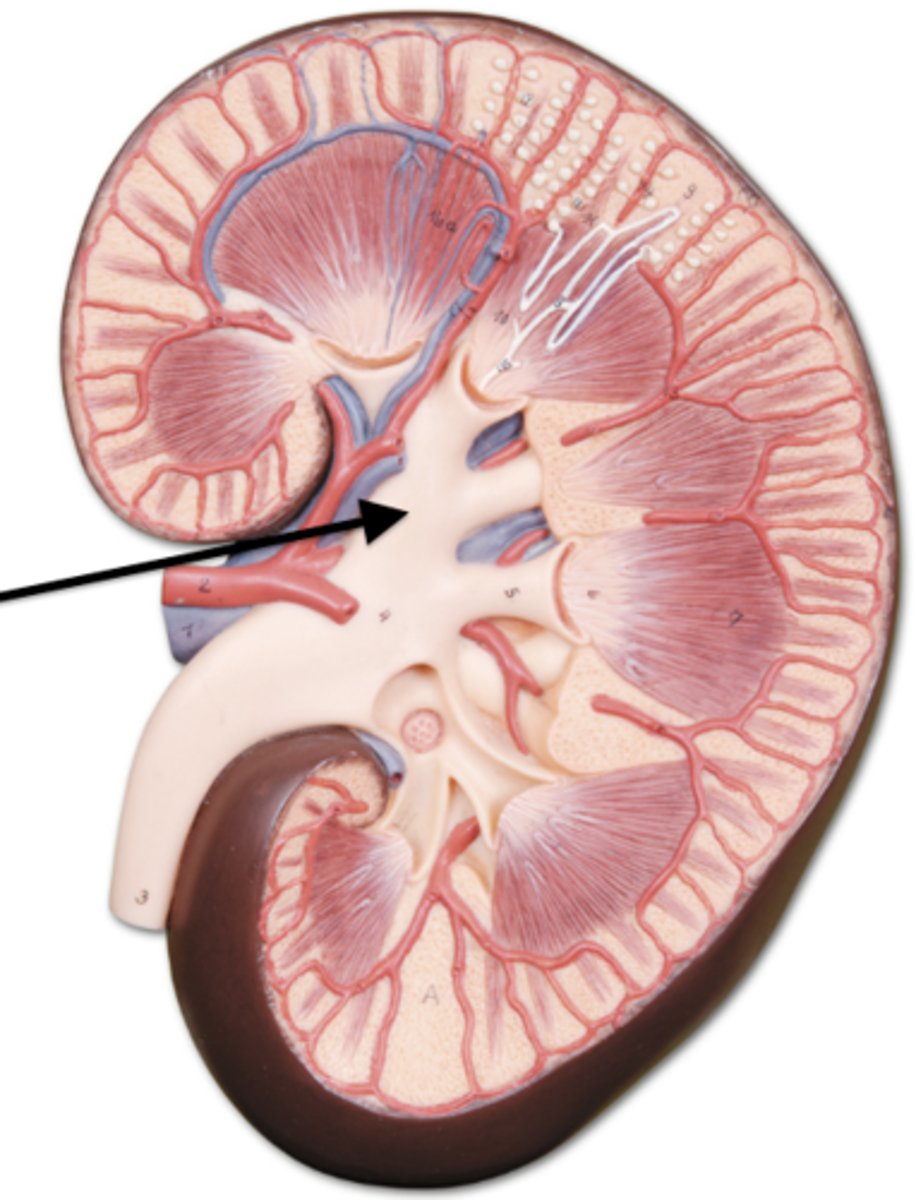
Renal sinus
a set of tubes/opening that drain urine from the medulla
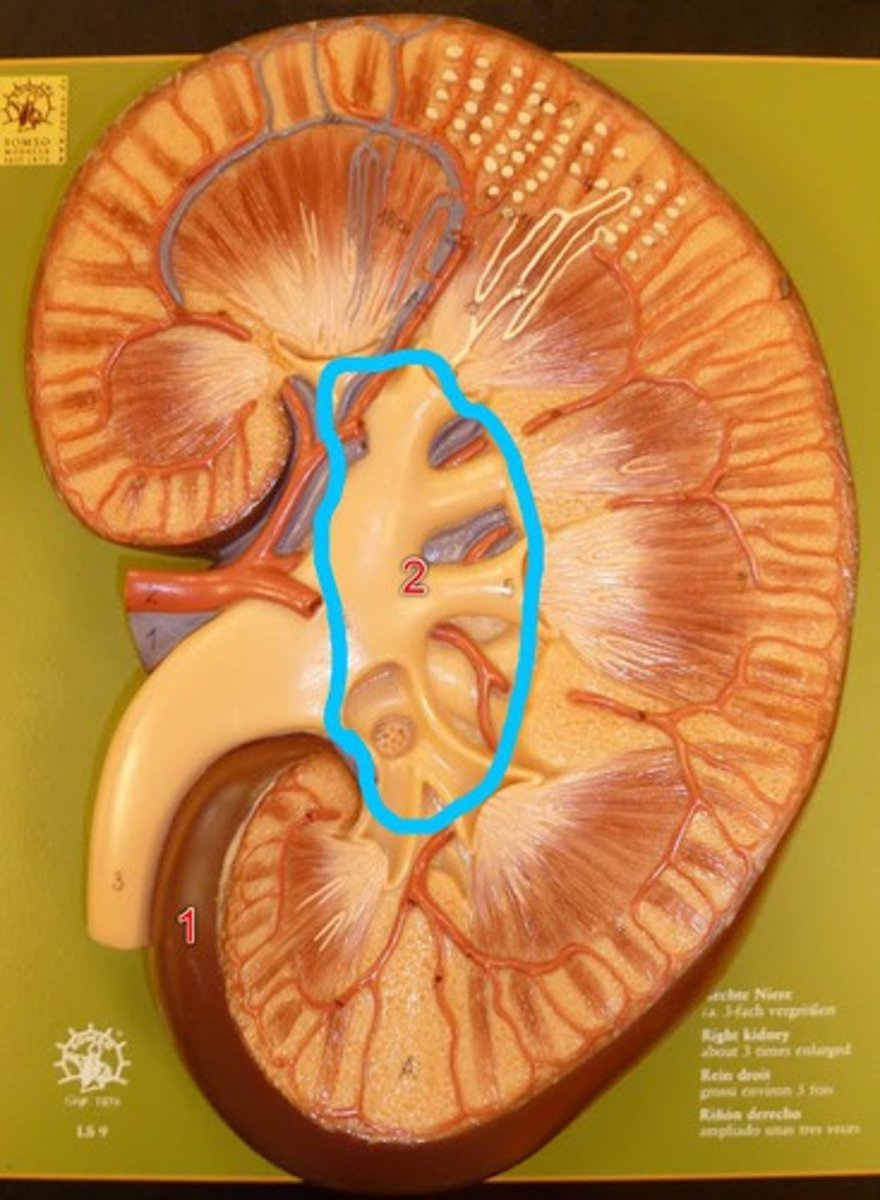
parts of renal sinus
1. minor calyx 2. major calyx 3. renal pelvis
renal pelvis
funnel-shaped reservoir that collects the urine from major calyx and passes it to the ureter
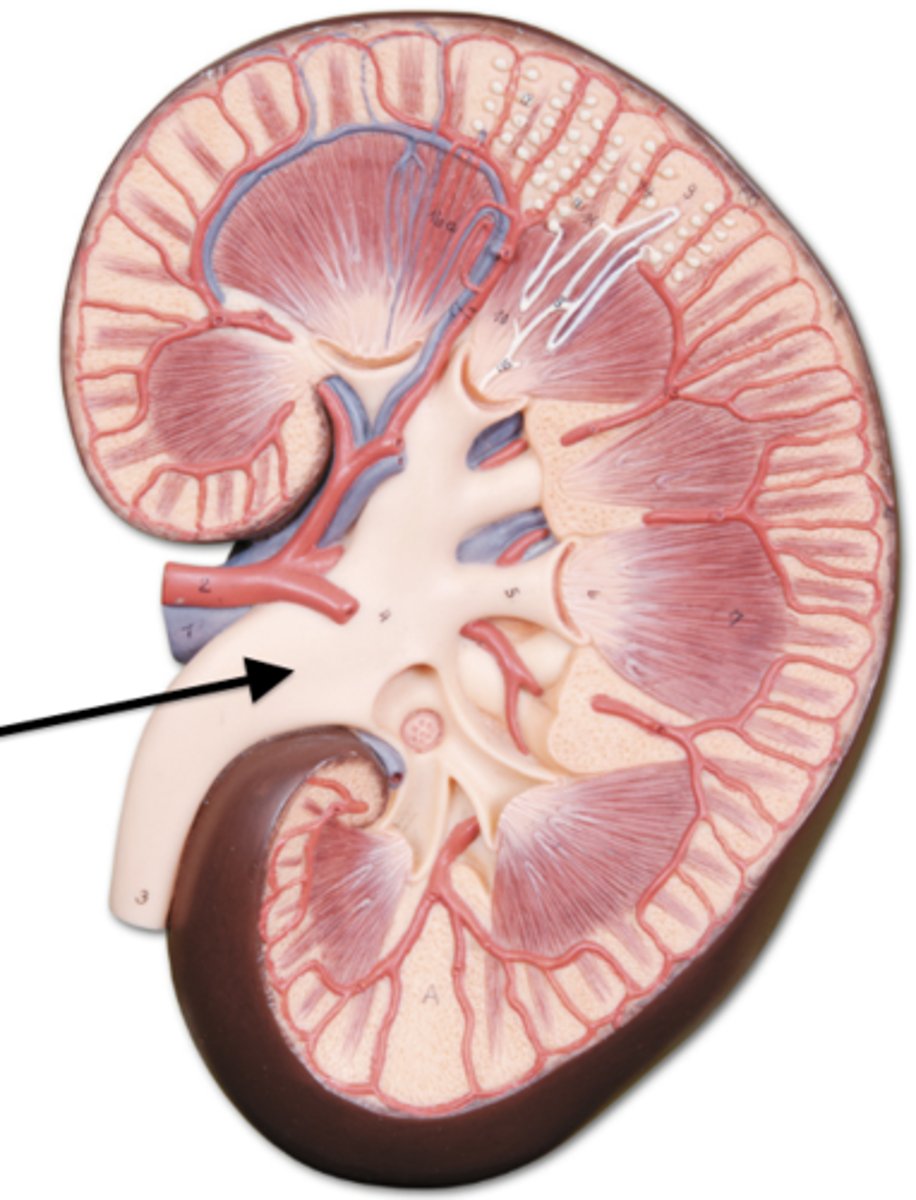
minor calyx
drains a renal pyramid
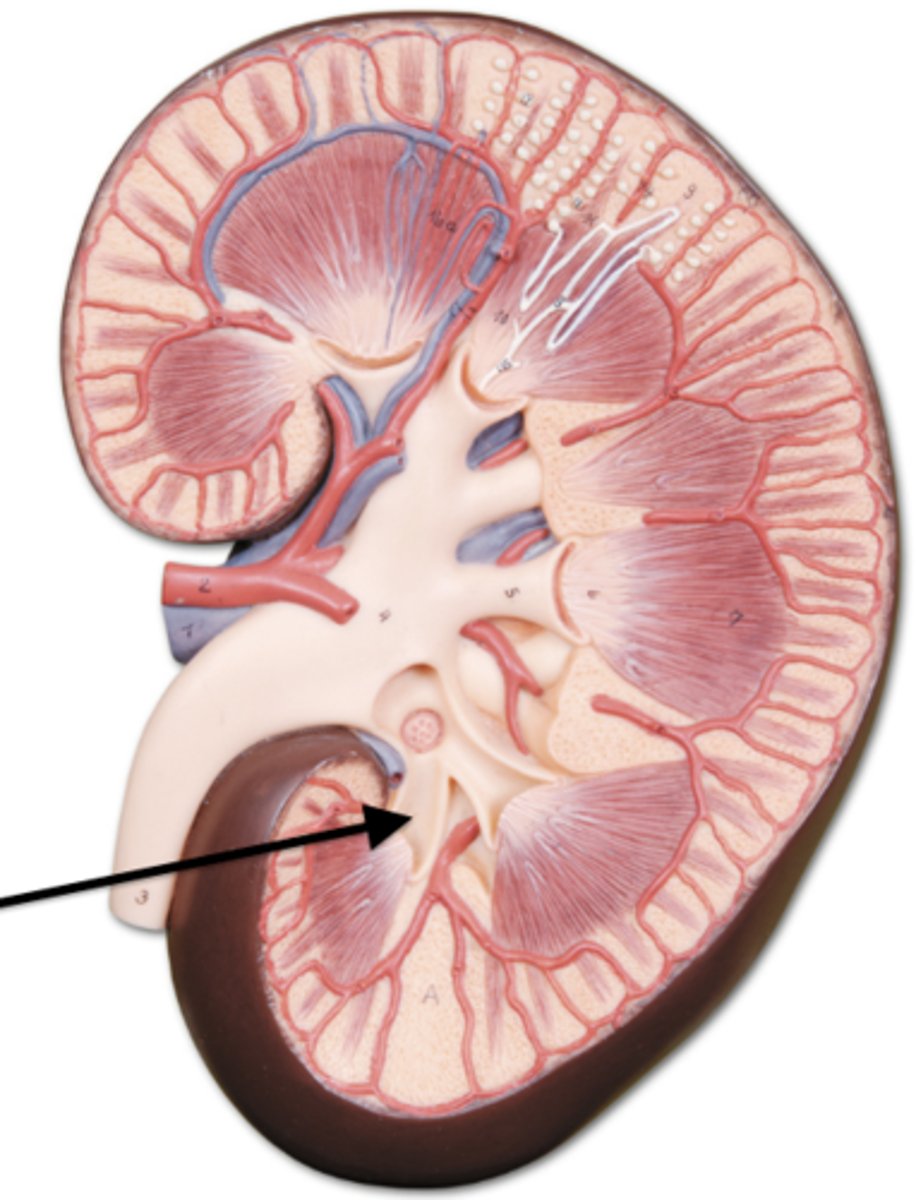
major calyx
drains urine from minor calyces
kidney stones
a hard mass formed in the kidneys, typically consisting of insoluble calcium compounds; caused by dehydration, diet or genetic factors
hydronephrosis
backup of urine from ureteral obstruction or other causes; can lead to death of kidney tissue
path of blood flow from aorta, to kidney, to nephron, and back to IVC
1. aorta
2. renal artery
3. segmental artery
4. interlobar artery
5. arcuate artery
6. interlobular artery
7. afferent arteriole
8. glomerulus
9. efferent arteriole
10. peritubular capillaries of convoluted tubules and vasa recta of nephron loop
11. interlobular vein
12. arcuate vein
13. interlobar vein
14. renal vein
nephron
structural and functional unit of the kidneys that form urine
2 parts of nephron
1. renal corpuscle
2. renal tubule
renal corpuscle
consists of a tuft of capillaries called glomerulus and glomerular capsule; fed by afferent arteriole
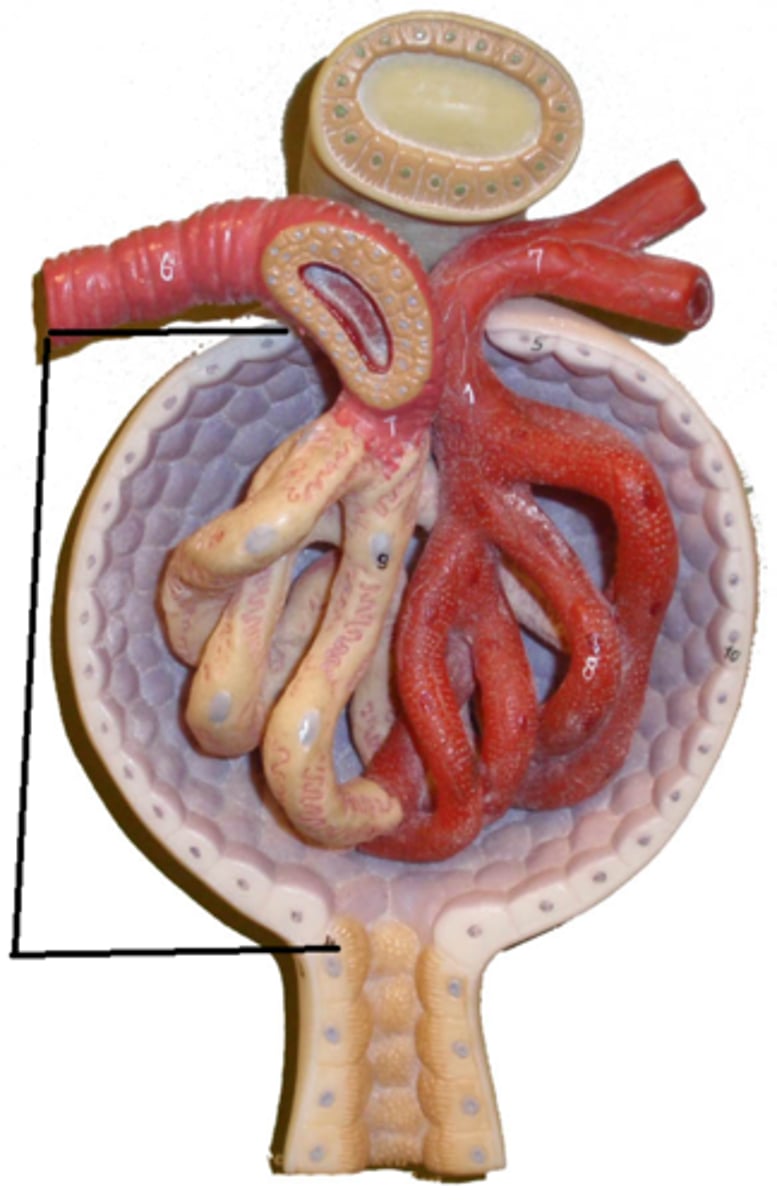
glomerulus
composed of fenestrated capillaries that allow a large amount of solute-rich fluid to pass from blood to glomerular capsule
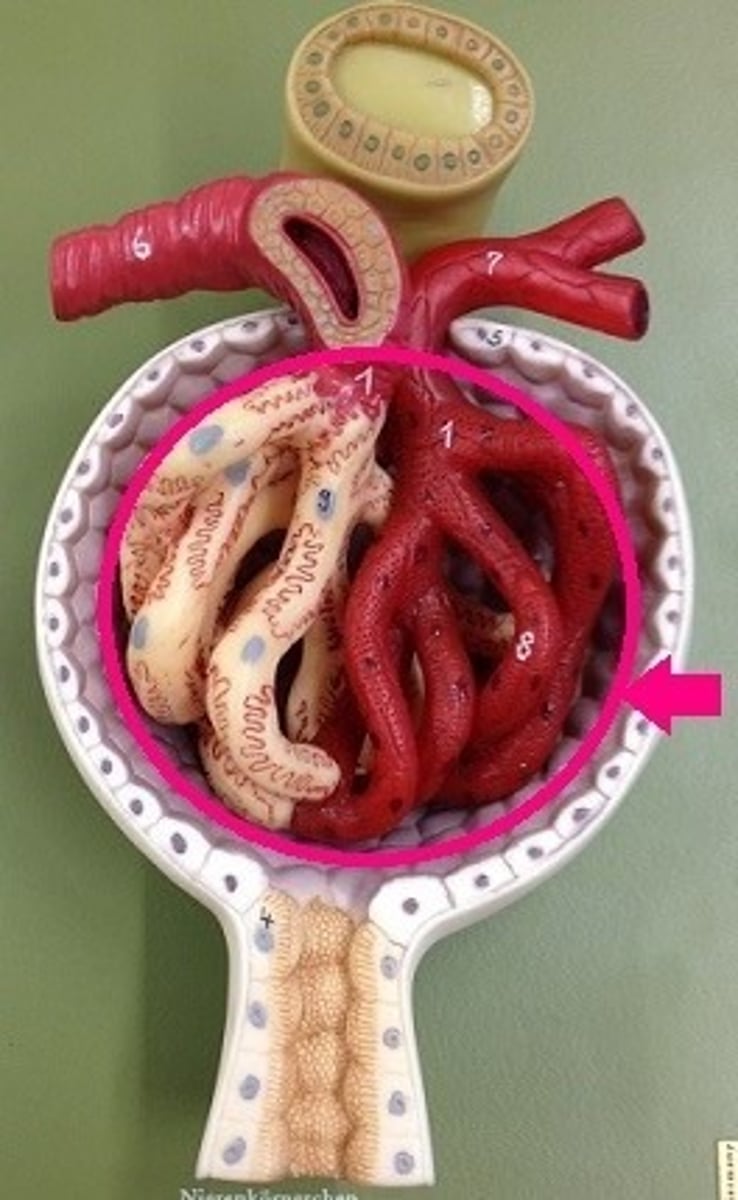
glomerular capsule
cup-shaped hollow structure that surrounds glomerulus
layers of glomerular capsule
1. parietal- simple squamous epithelium (structural)
2. visceral- podocytes (filtration membrane)
renal tubule
microscopic tube in the kidney where urine is formed after filtration; made up of a single layer of epithelial cells
3 regions of renal tubule
proximal convoluted tubule, nephron loop, distal convoluted tubule
proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
reabsorption/secretion
nephron loop
simple squamous cells; water reabsorption and urine concentration
distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
secretion
collection duct
collects urine from DCT of several nephrons and drains into renal pelvis
cortical nephrons
85% of nephrons; almost entirely in cortex and loops does not descend into medulla
juxtamedullary nephrons
long nephron loops invade medulla; important in production of more concentrated urine
micturition
act of passing urine
stretch receptors
found in bladder and detect when its full; trigger micturition reflex
actions of micturition
1. contraction of detrusor muscle (smooth)
2. relaxation of bladder neck and urethral sphincters (skeletal and smooth)
what controls detrusor muscle
parasympathetic nervous system
what controls internal sphincter
sympathetic nervous system
what controls external sphincter
Somatic nervous system (voluntary)
what initiates urine storage
sympathetic fiber via T11-L2 spinal nerves and somatic fibers via the pudendal nerve
somatic fibers via pudendal nerve
promotes internal and external urethral sphincters
sympathetic fibers via T11-L2 spinal nerves
inhibit detrusor contraction and activate internal sphincter contraction
urinary incontinence
caused by weakened pelvic floor muscles; normal in infants
urinary retention
inability to empty the bladder; common after general anesthesia or opioids; need catheter
how do opiods and anethesia block urination
1. decreasing sensation of bladder fullness (stretch receptors)
2. inhibition of parasympathetic fibers (detrusor contraction)
benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
noncancerous enlargement of the prostate; located below bladder; caused by age; treat with ablation, alpha-blockers, Cialis/viagra