Retinal Interneurons - Ocular Physiology Spring 2025
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
bipolar and horizontal cells
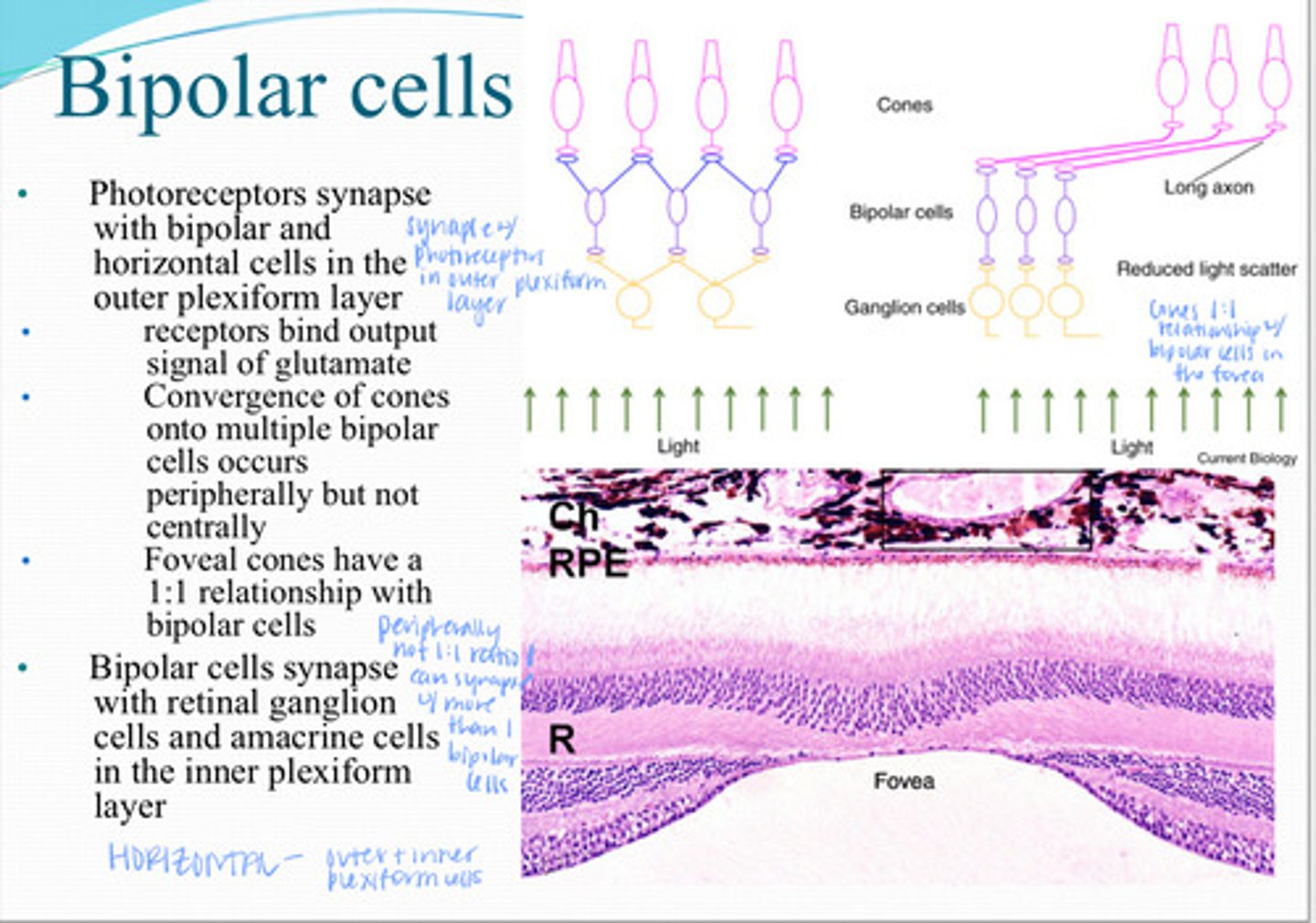
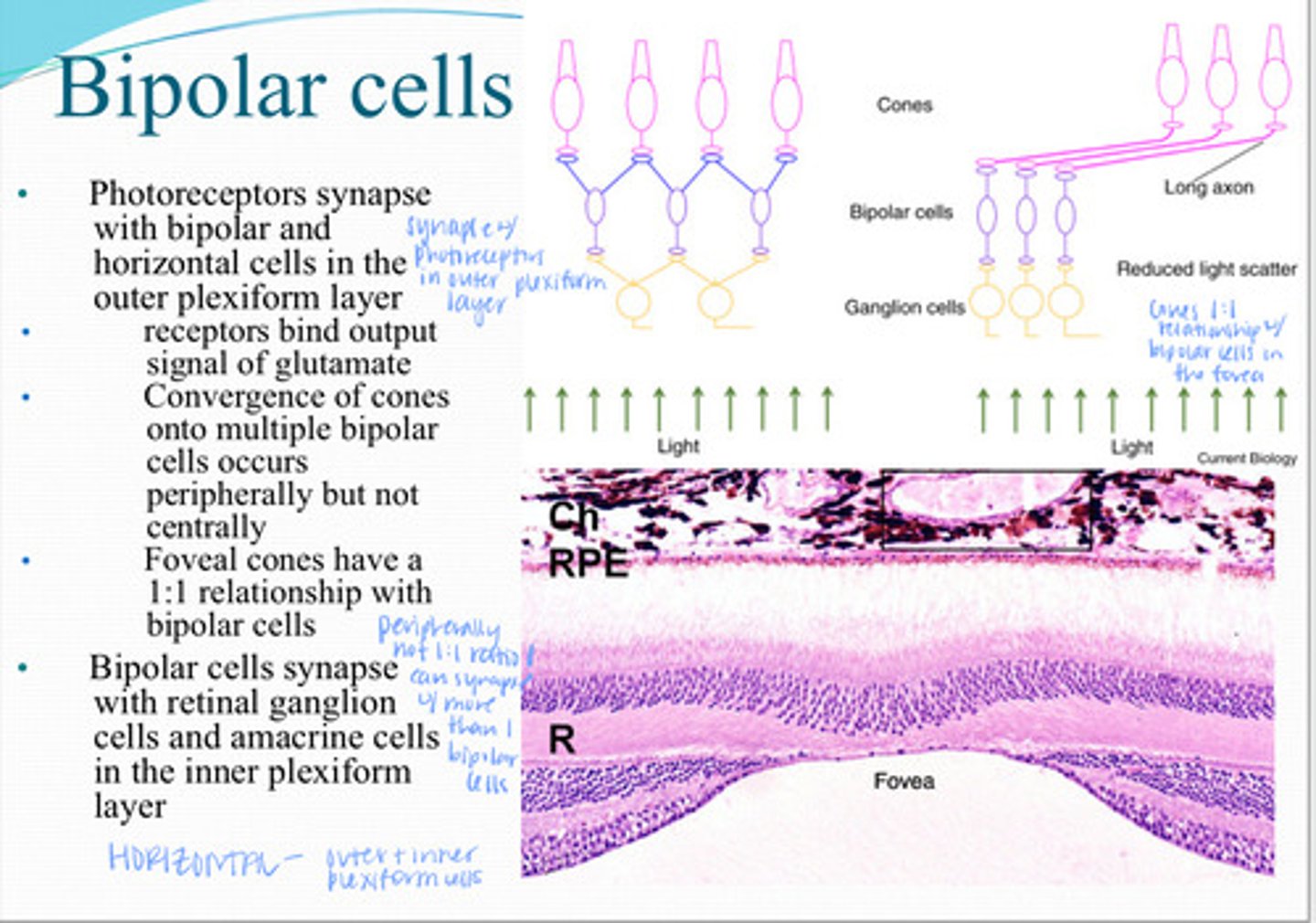
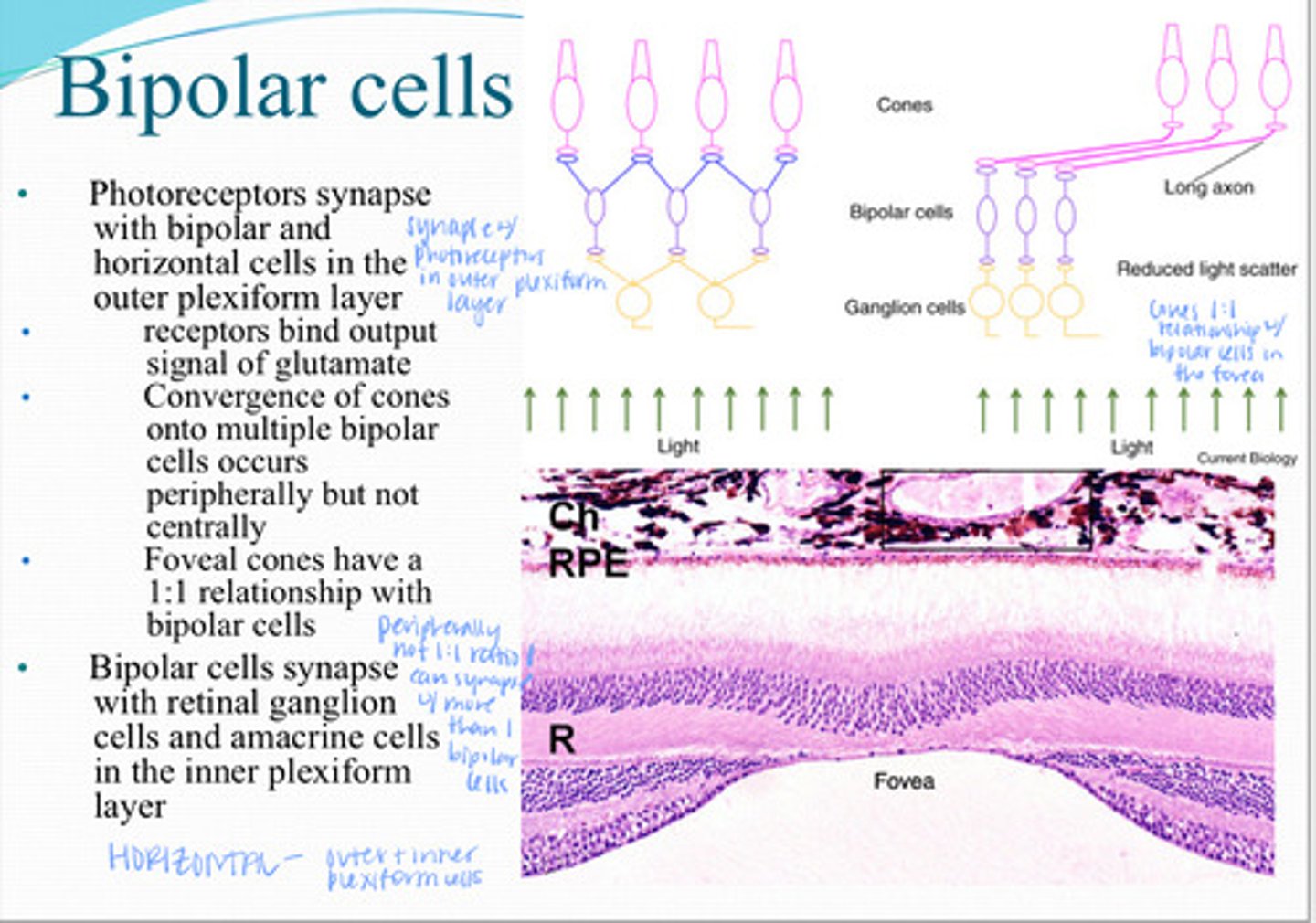
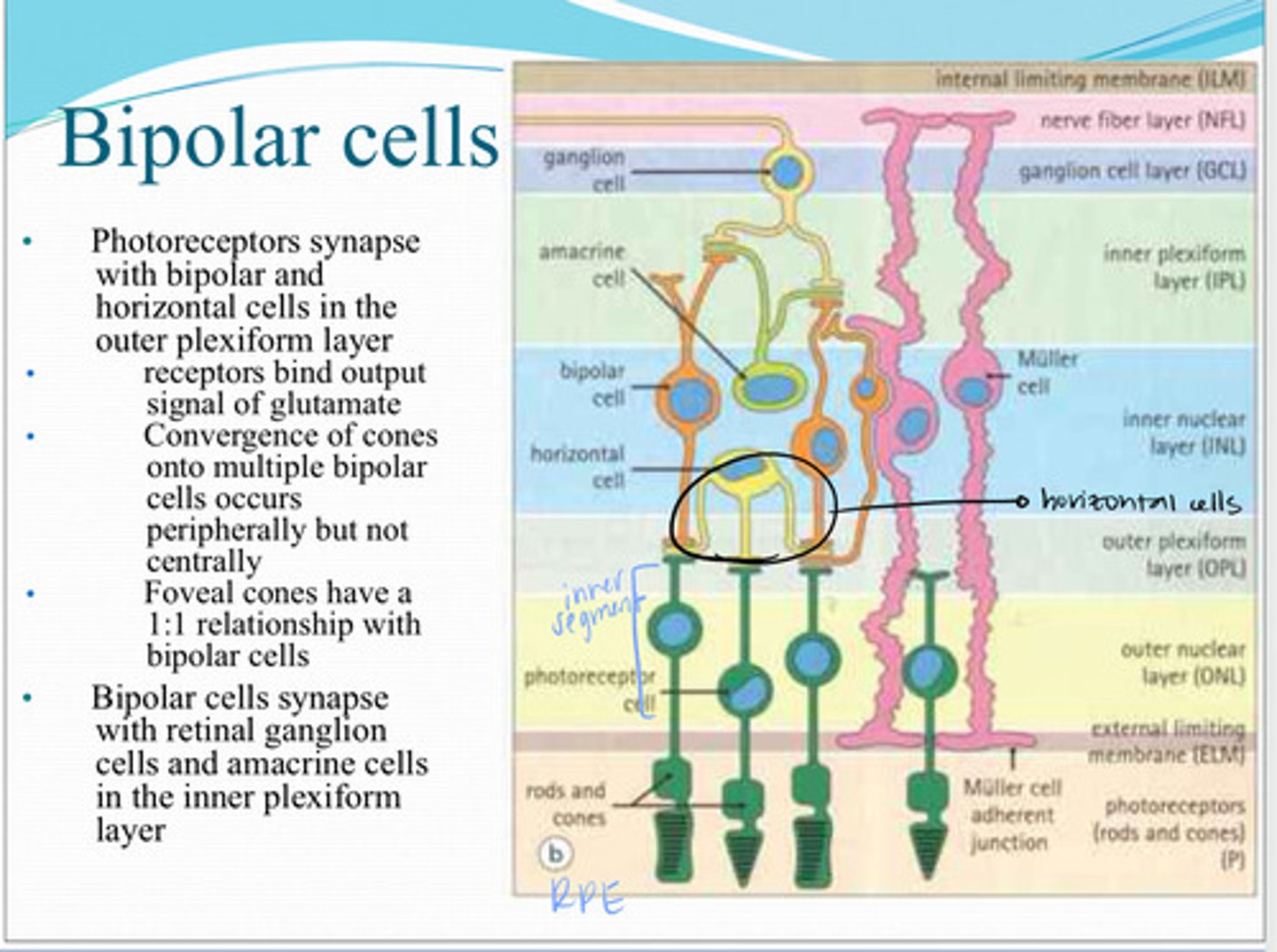
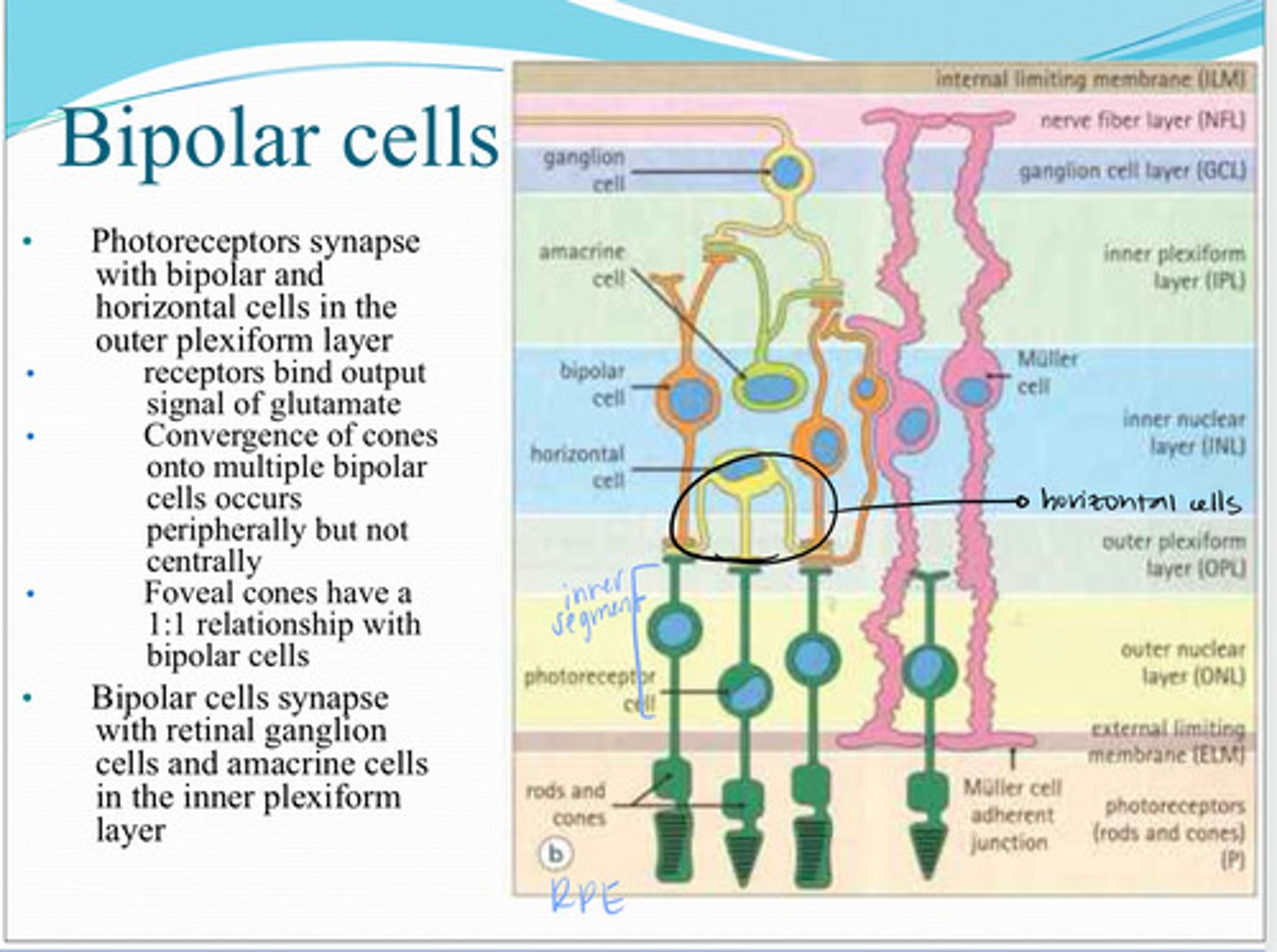
Photoreceptors synapse with _____ and _____ cells in the outer plexiform layer
glutamate
Receptors on bipolar cells bind output signal of ________
peripherally but not centrally
Convergence of multiple cones onto multiple bipolar cells occurs ____ but not ______
1:1
Foveal cons have a ______ relationship with bipolar cells
retinal ganglion cells and amacrine cells
Bipolar cells synapse with what 2 things in the inner plexiform layer?
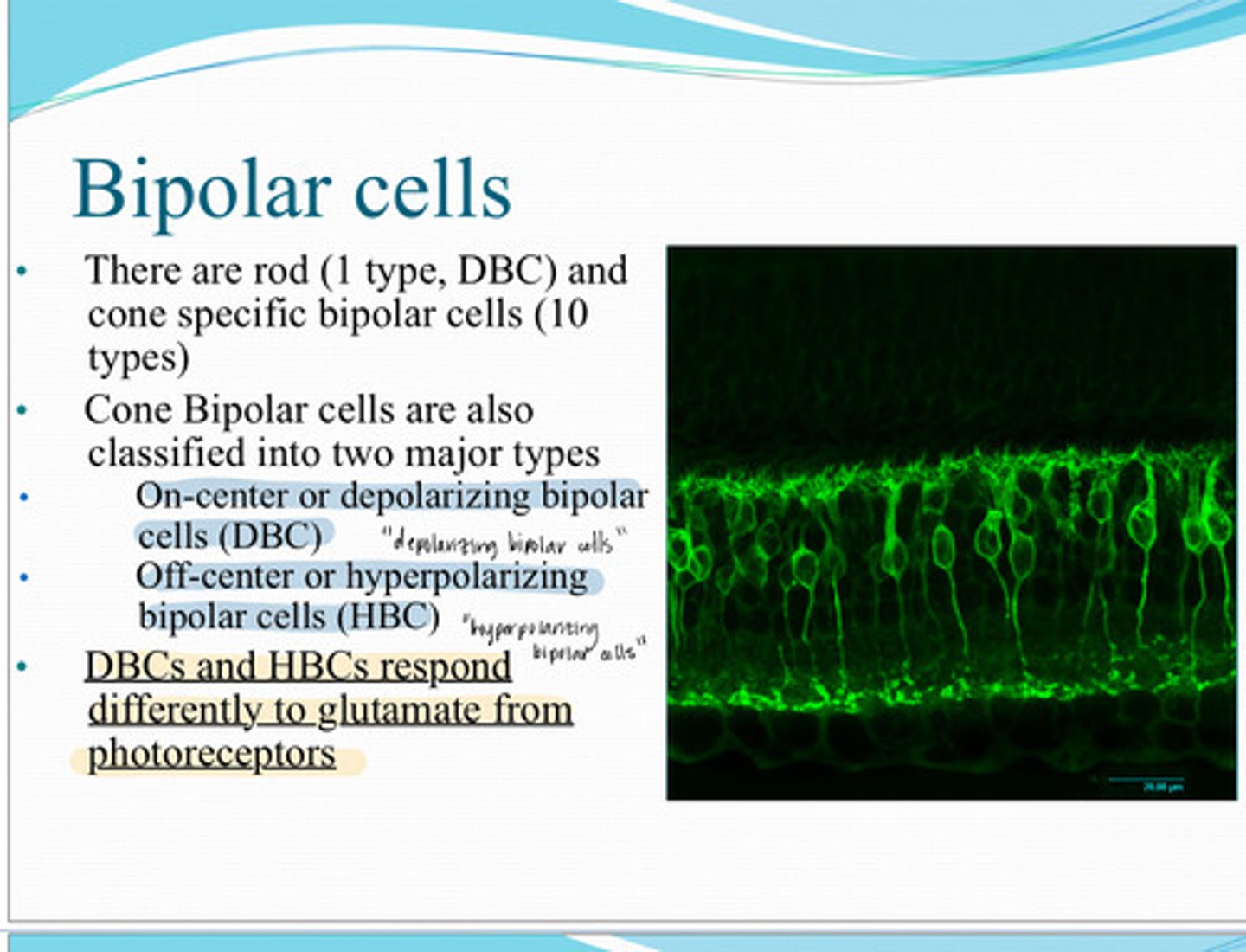
1 type, DBC
How many types of rods are there?
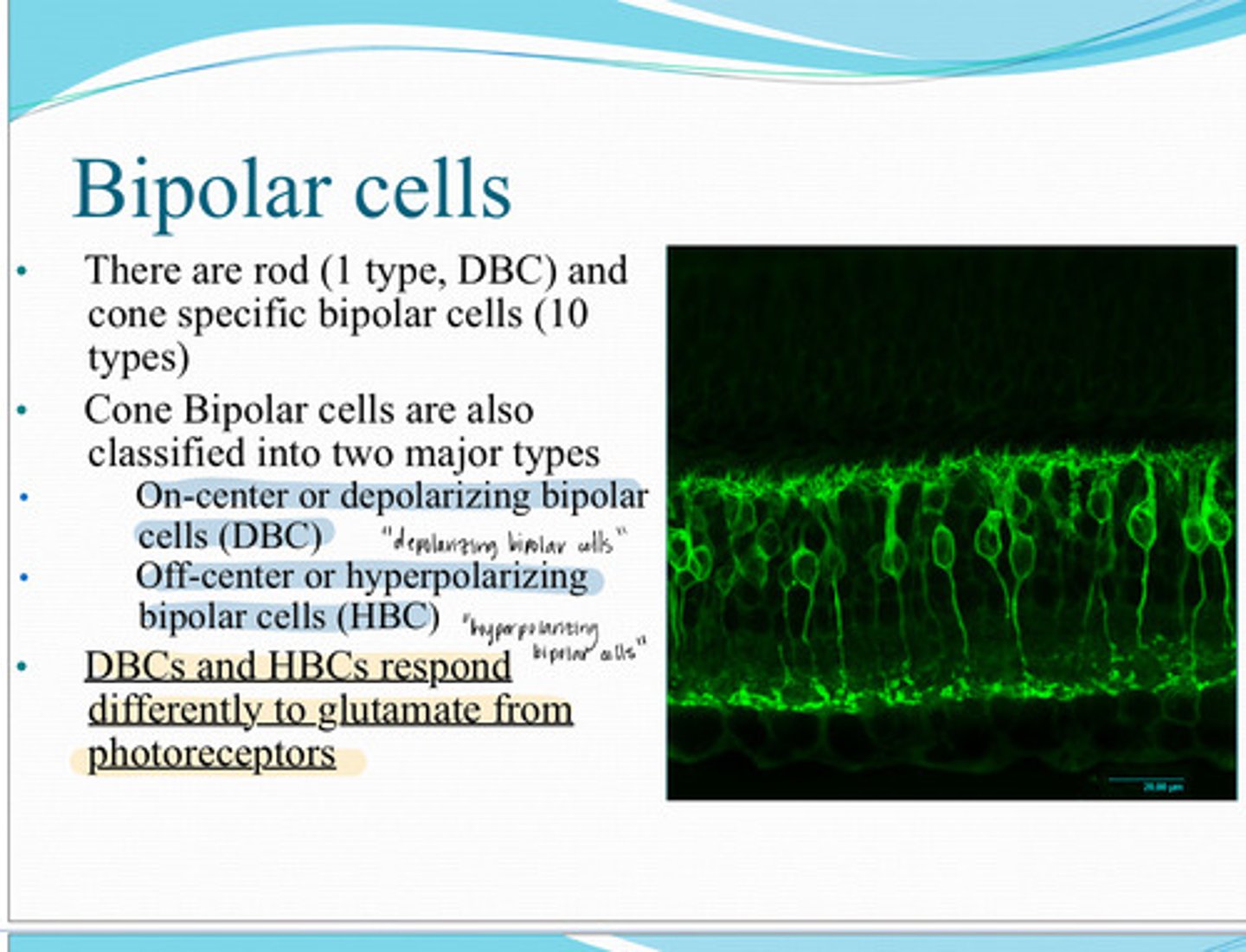
10 types
How many types of cones are there?
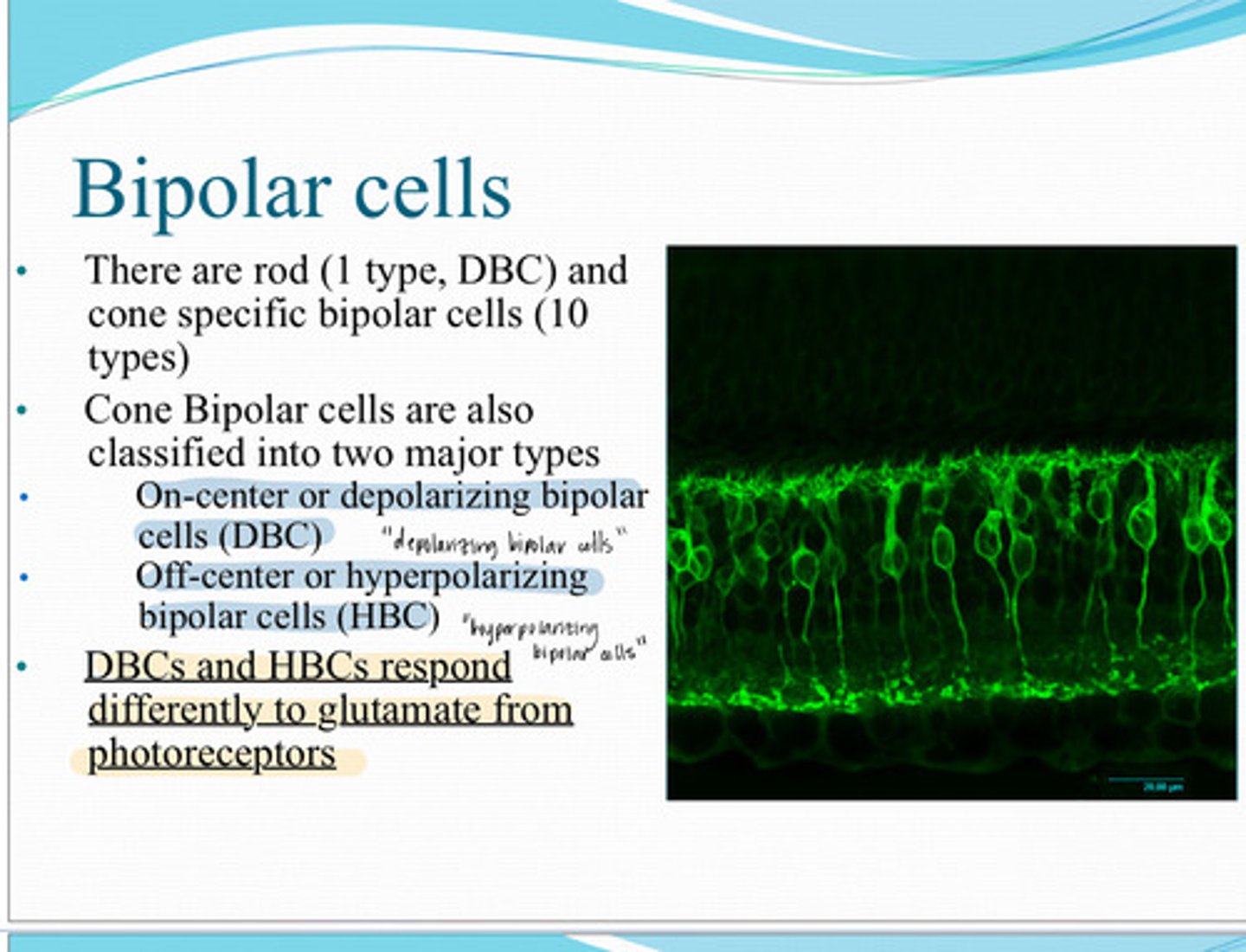
1) On center or depolarizing bipolar cells (DBC)
2) Off center or hyperpolarizing bipolar cells
What are the 2 major types of cone bipolar cells?
differently
DBCs and HBCs respond (the same/differently) to glutamate from the photoreceptors
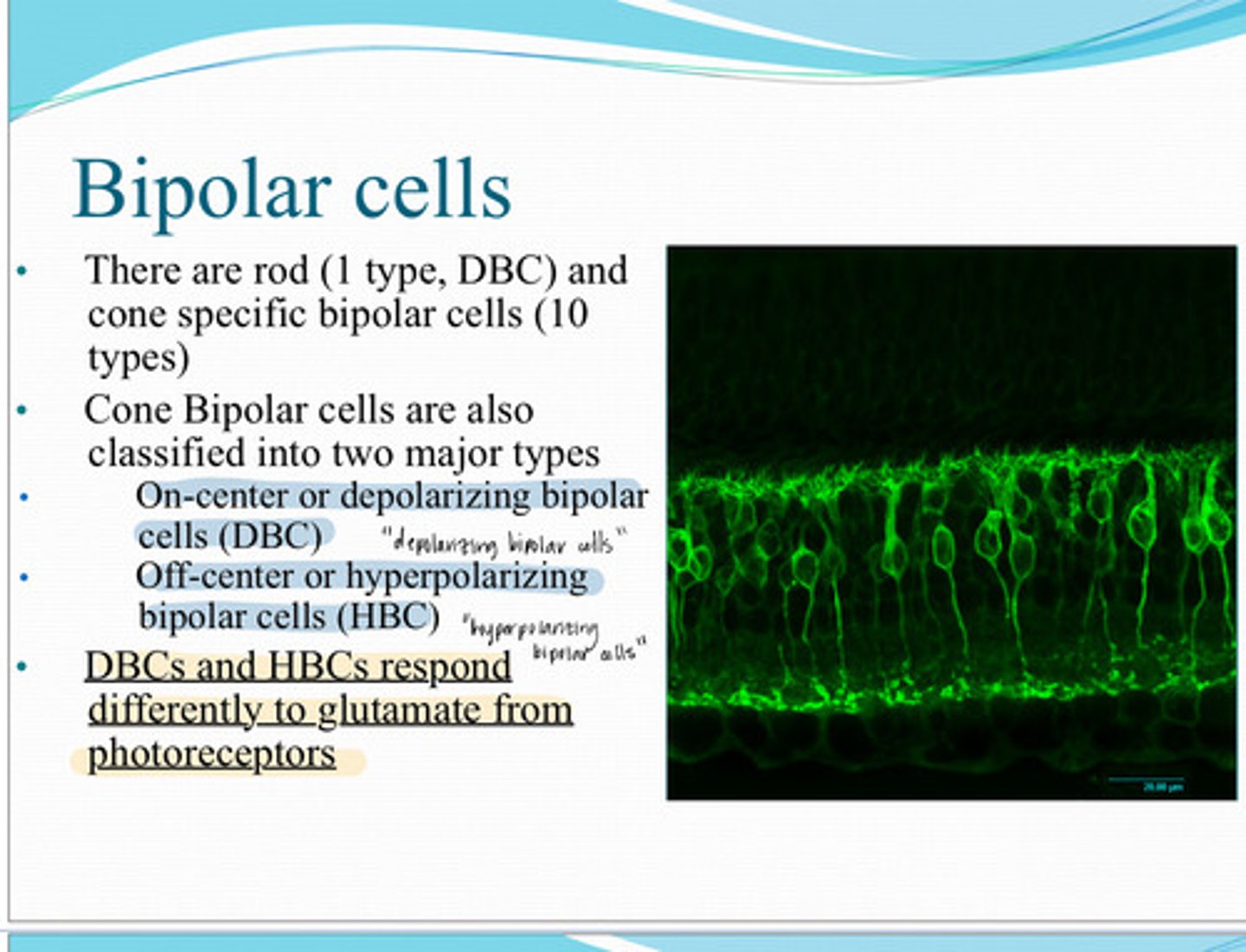
hyperpolarize
Hyperpolarizing bipolar cells ______ with light
cation channel closure
Reduced glutamate release from the photoreceptor causes what on the hyperpolarizing bipolar cell?
cation channel opening
Increased glutamate release from the photoreceptor causes what on the hyperpolarizing bipolar cell?
depolarize
Depolarizing bipolar cells _____ with light
cation channel opening of DBCs
Reduced glutamate release from the photoreceptor causes what on the depolarizing bipolar cell?
cation channel closure of DBCs
Increased glutamate release from the photoreceptor causes what on the depolarizing bipolar cell?
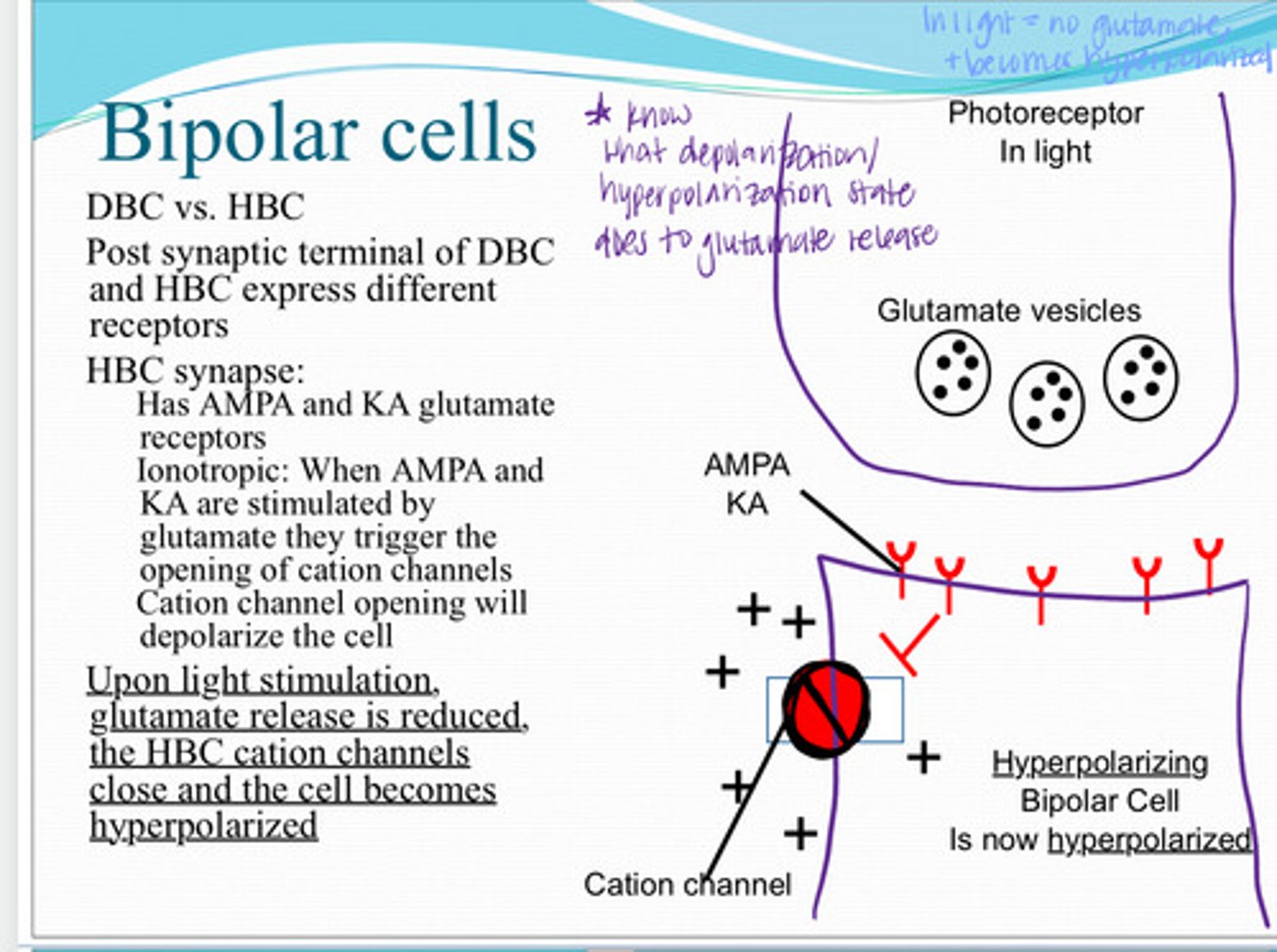
AMPA & KA glutamate receptors
Post synaptic terminal of the depolarizing bipolar cell and hyperpolarizing bipolar cell express different receptors. What receptors do hyperpolarizing bipolar cells expres?
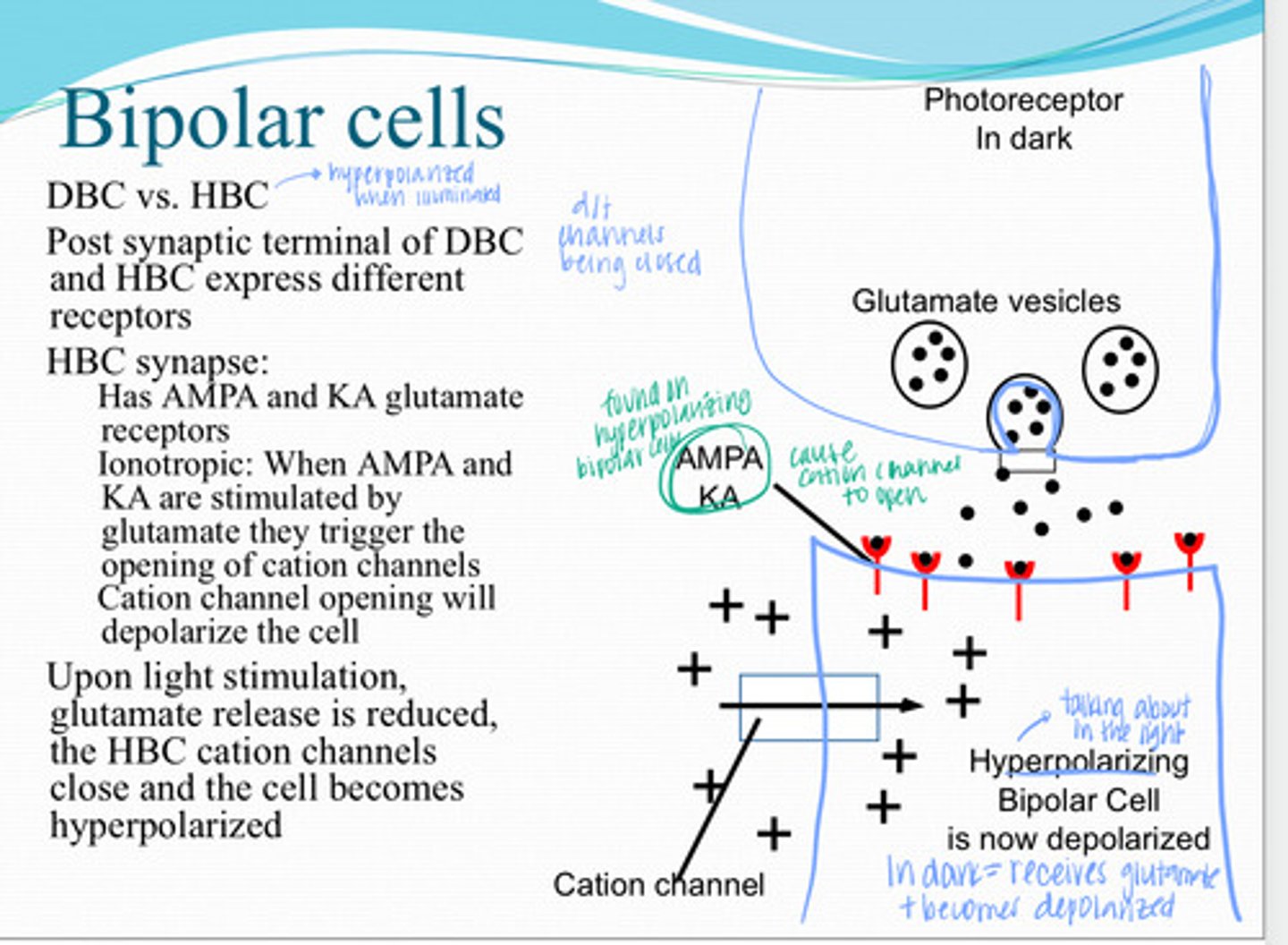
ionotrophic
AMPA & KA glutamate receptors are (metabotropic/ionotrophic)
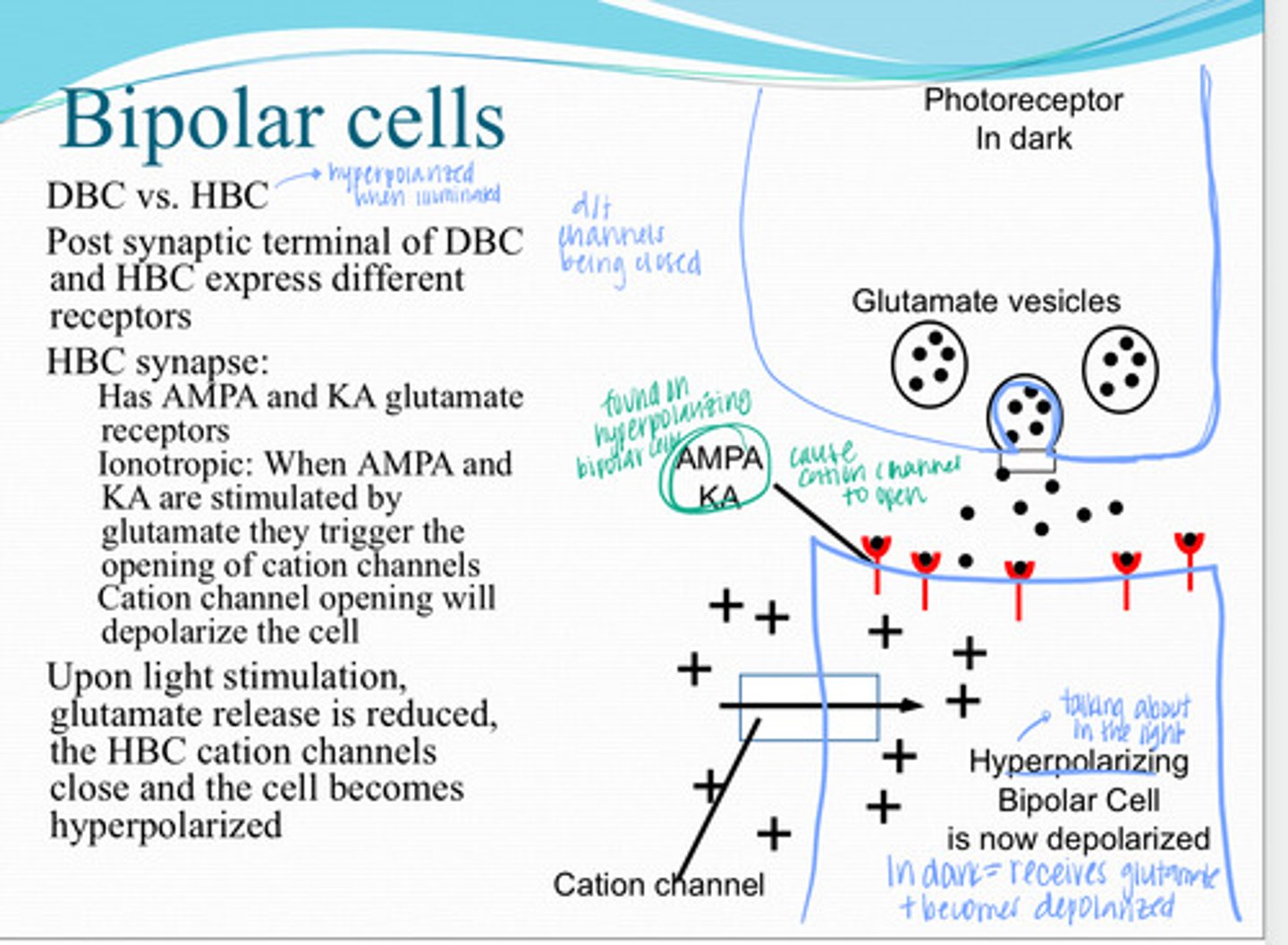
When AMPA and KA are stimulated by glutamate they trigger the opening of cation channels. Cation ion channel will depolarize the cell
What is the mechanism of ionotropic AMPA & KA receptor?
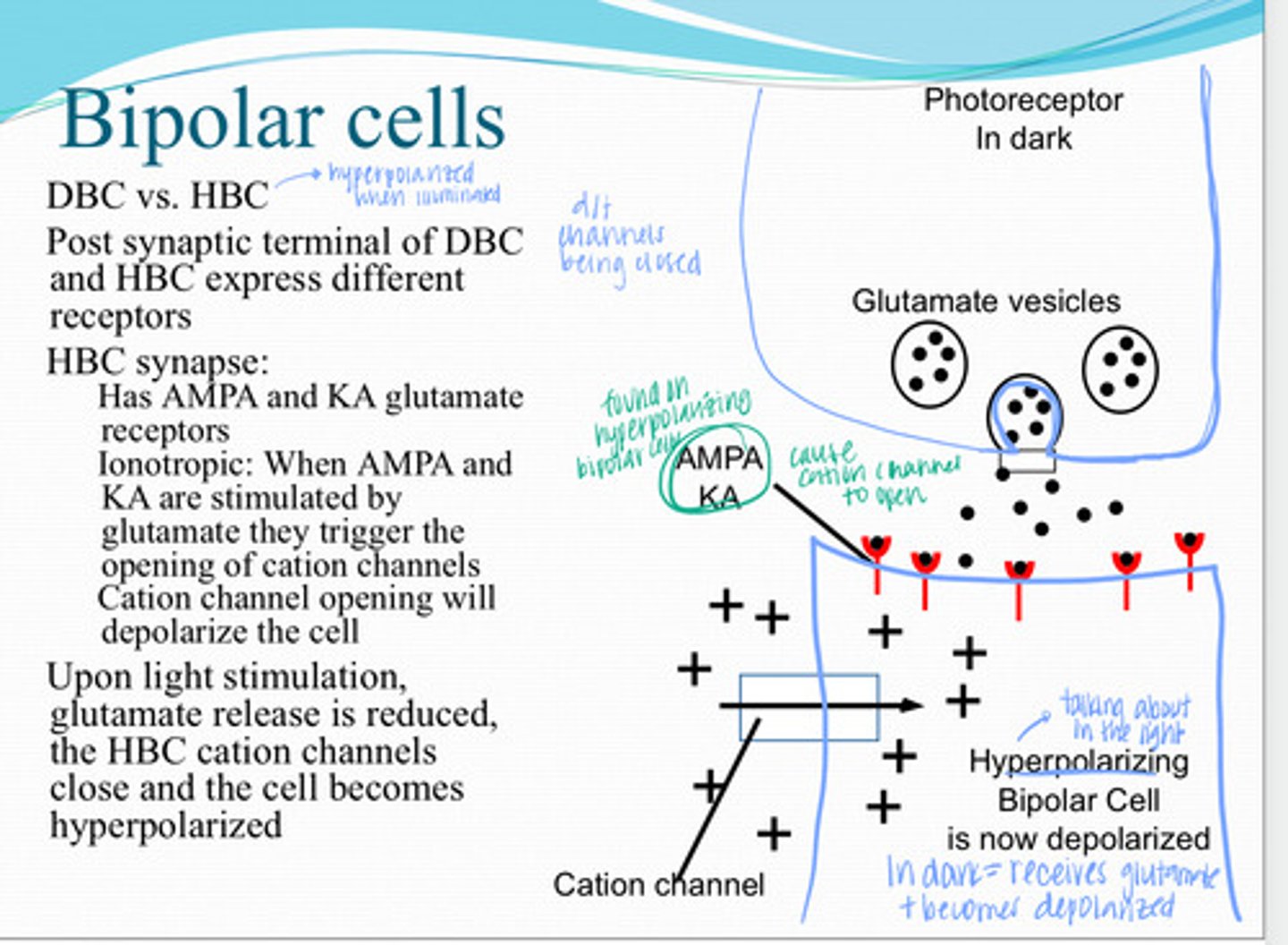
Glutamate release is reduced, HBC cation channels close and the cell becomes hyperpolarized
Upon light stimulation, what happens to the hyperpolarizing bipolar cell?
mGluR6 glutamate receptors
Post synaptic terminal of the depolarizing bipolar cell and hyperpolarizing bipolar cell express different receptors. What receptors do depolarizing bipolar cells express?
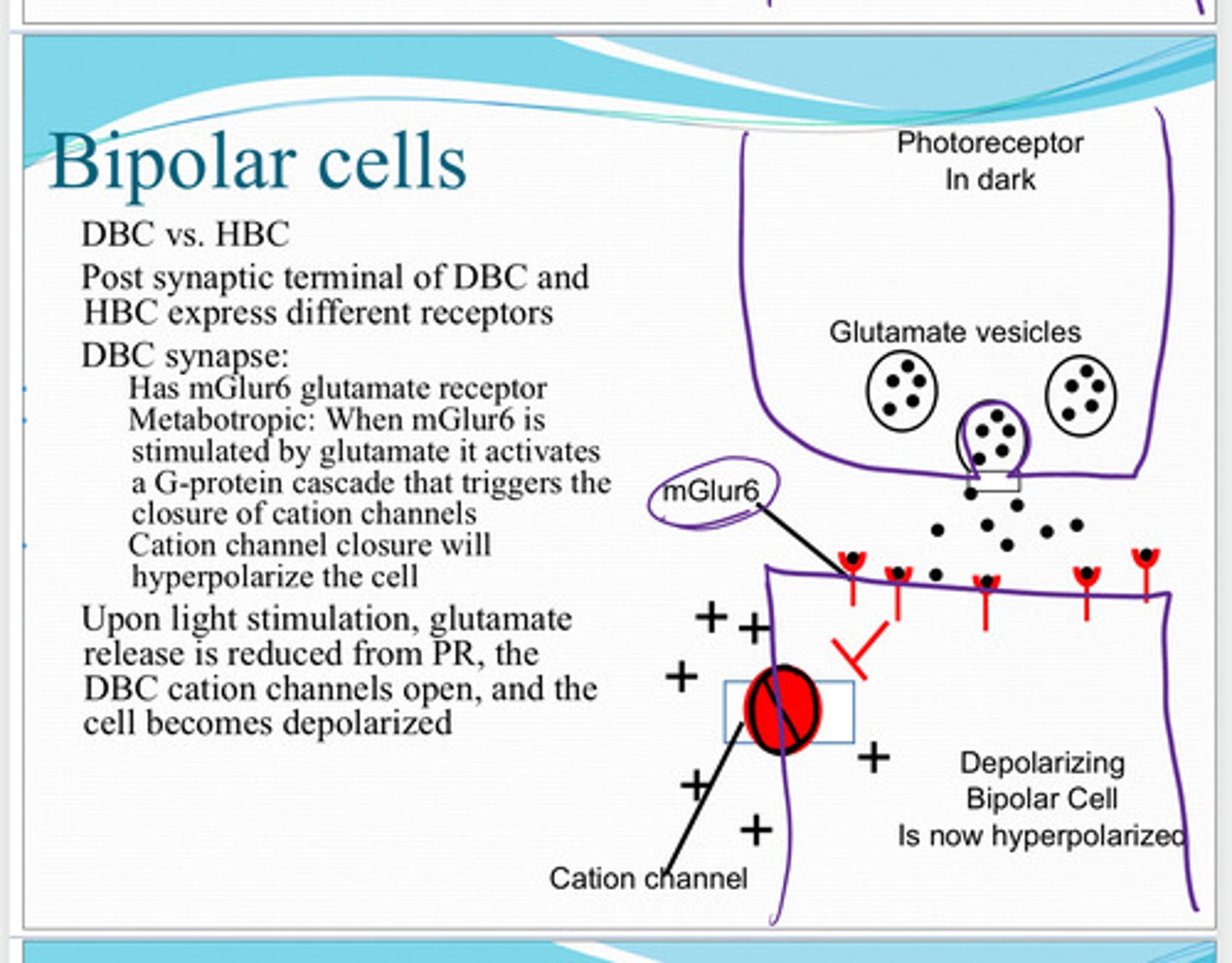
metabotropic
mGluR6 glutamate receptors are (metabotropic/ionotrophic)
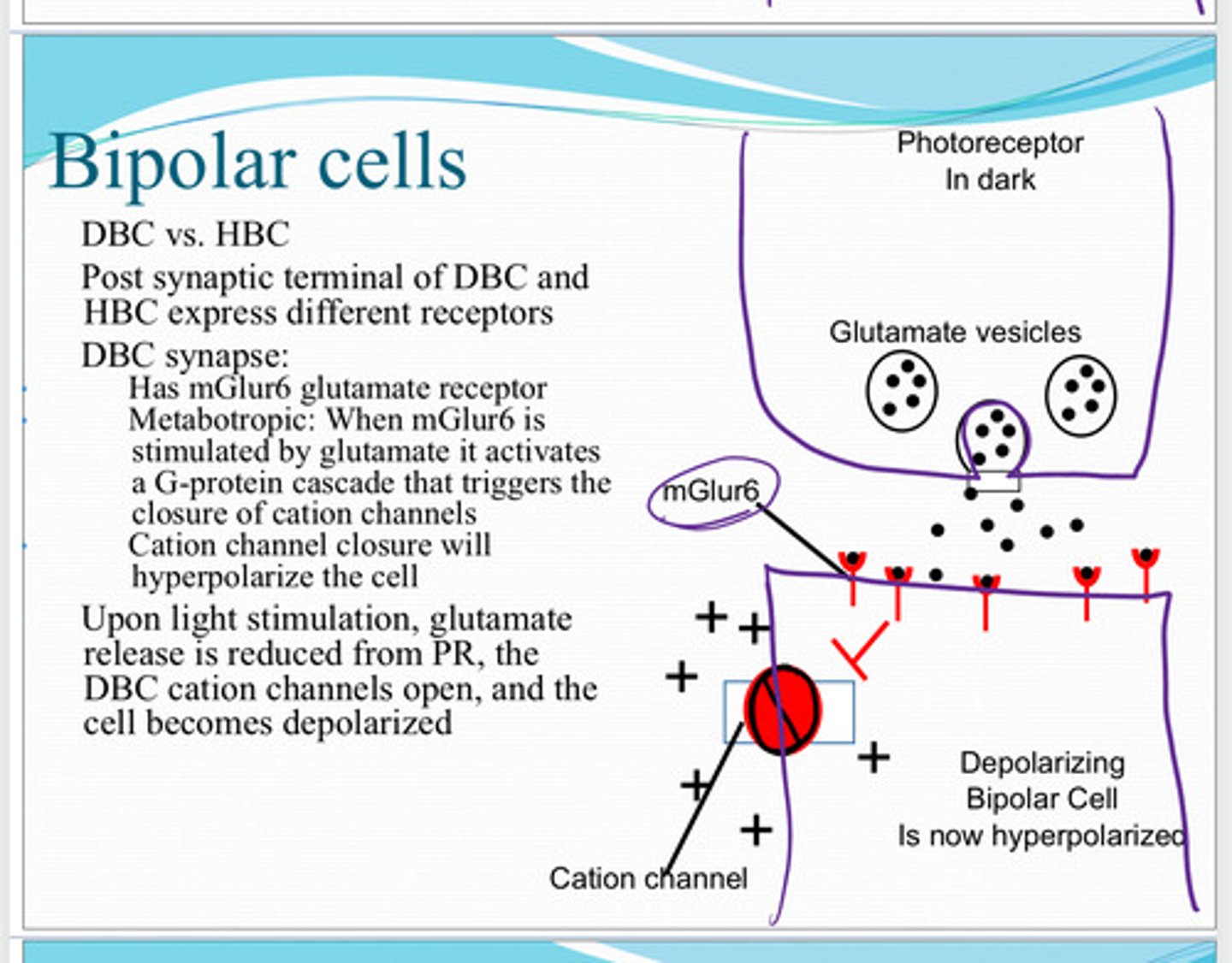
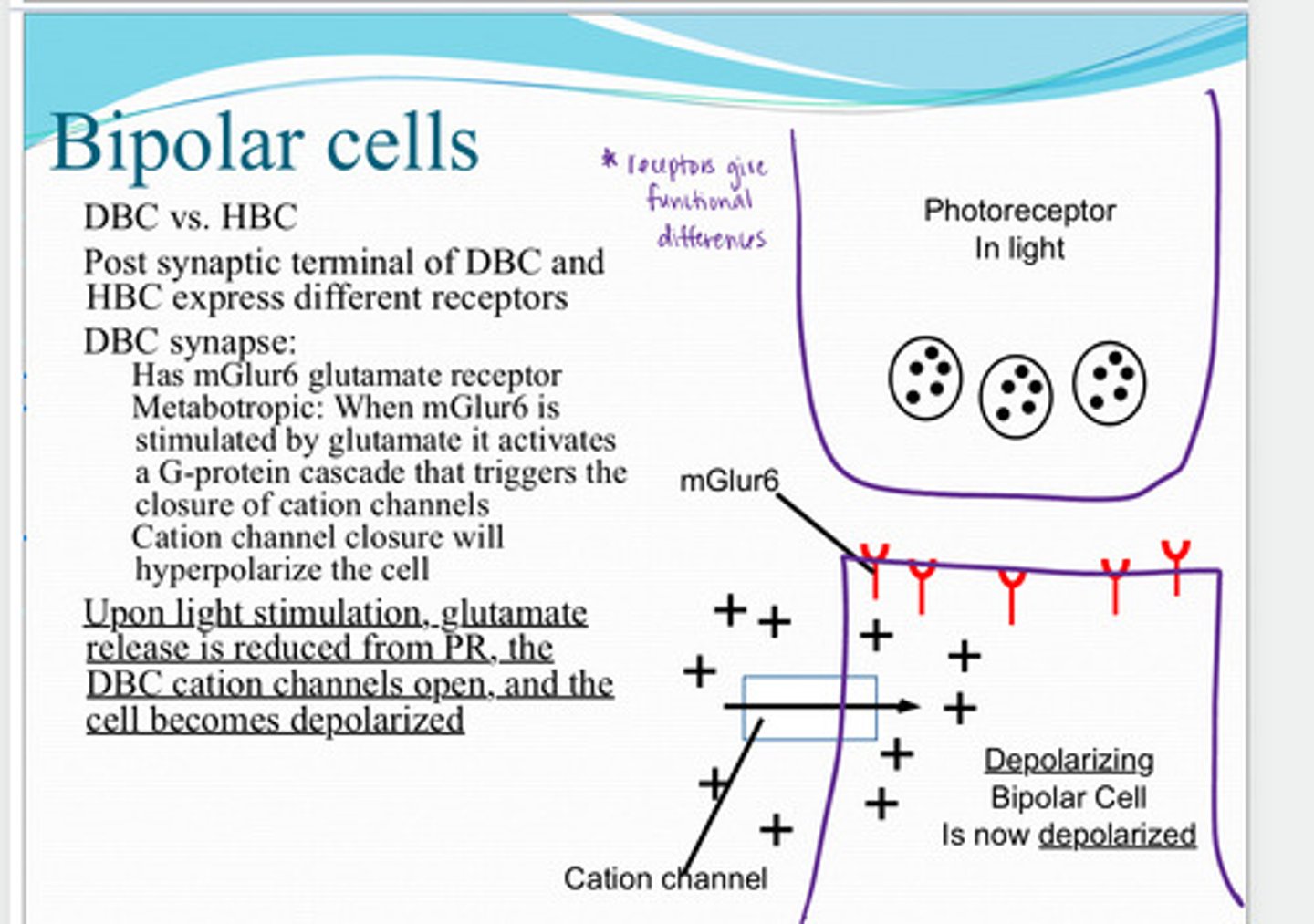
When mGluR6 is stimulated by glutamate it activates a G protein cascade that triggers the closure of cation channels. Cation channel closure will hyperpolarize the cell
What is the mechanism of metabotrophic mGluR6 receptor?
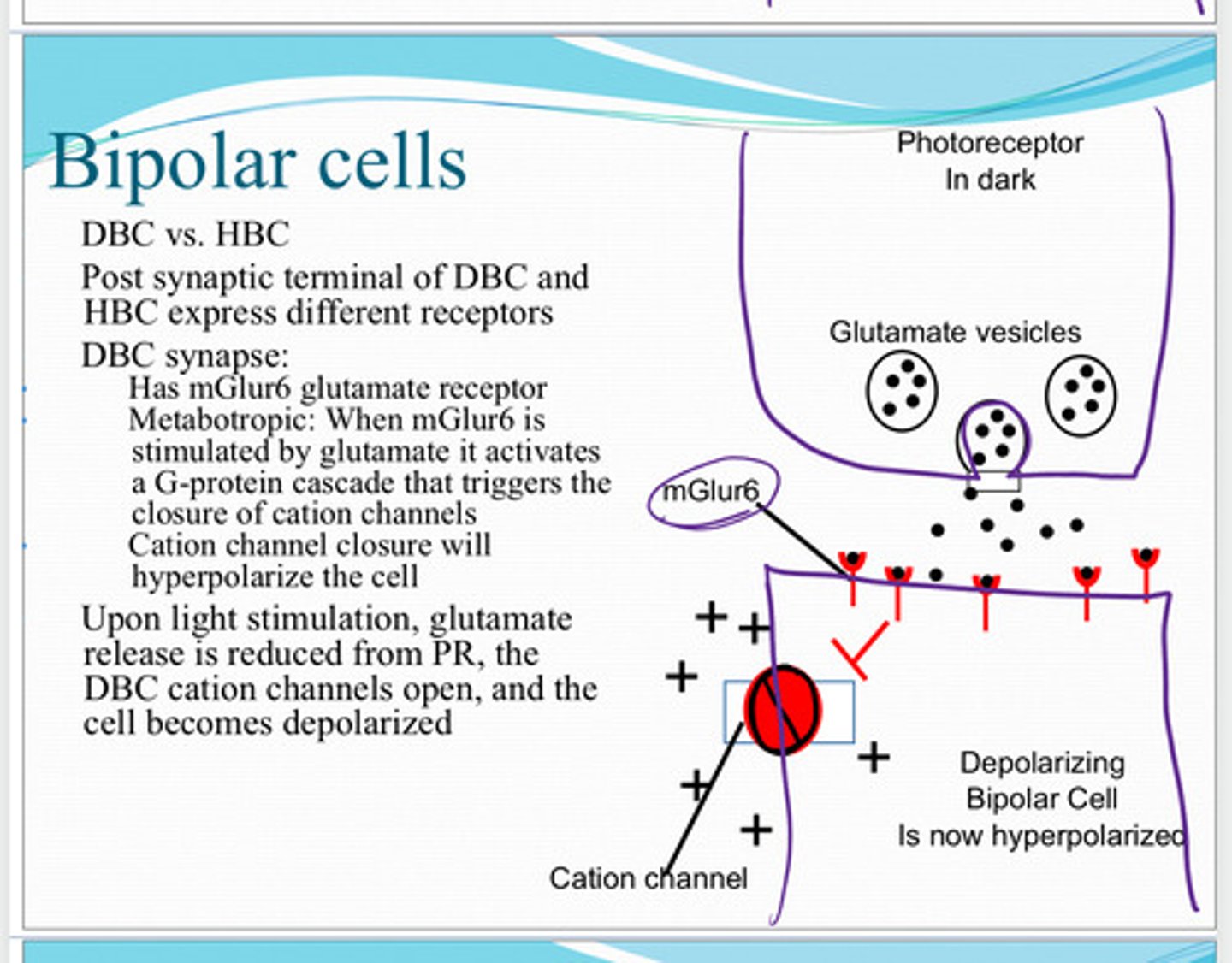
glutamate release is reduced from the photoreceptor. the depolarizing bipolar cell cation channels will open, and the cell will become depolarized
Upon light stimulation, what happens to the depolarizing bipolar cell?
False -- they respond to light differently
True or False:
HBCs and DBCs respond to light in the same way
glutamate
When bipolar cells (HBCs and DBCs) are depolarized, they release what to retinal ganglion cells?
they reduce glutamate release to ganglion cells
When bipolar cells (HBCs and DBCs) are hyperpolarized, what happens to the glutamate release from these cells?
true
True or False;
Retinal ganglion cells have a basal firing rate (constantly fire action potentials)
increases
Glutamate release from the bipolar cells (increases/decreases) the ganglion cell firing rate
decreases
Reduction of glutamate release from the bipolar cells (increases/decreases) the ganglion cell firing rate
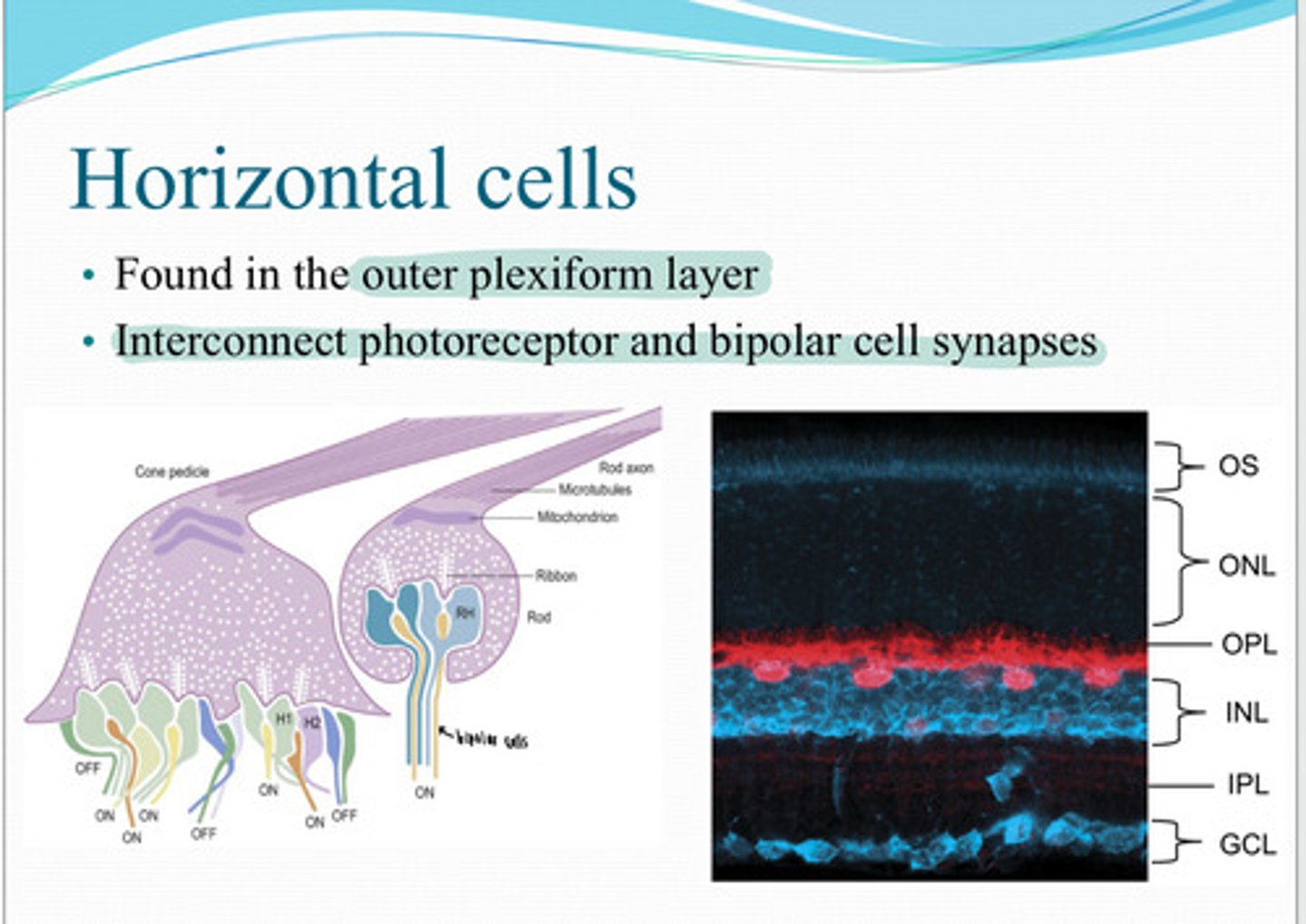
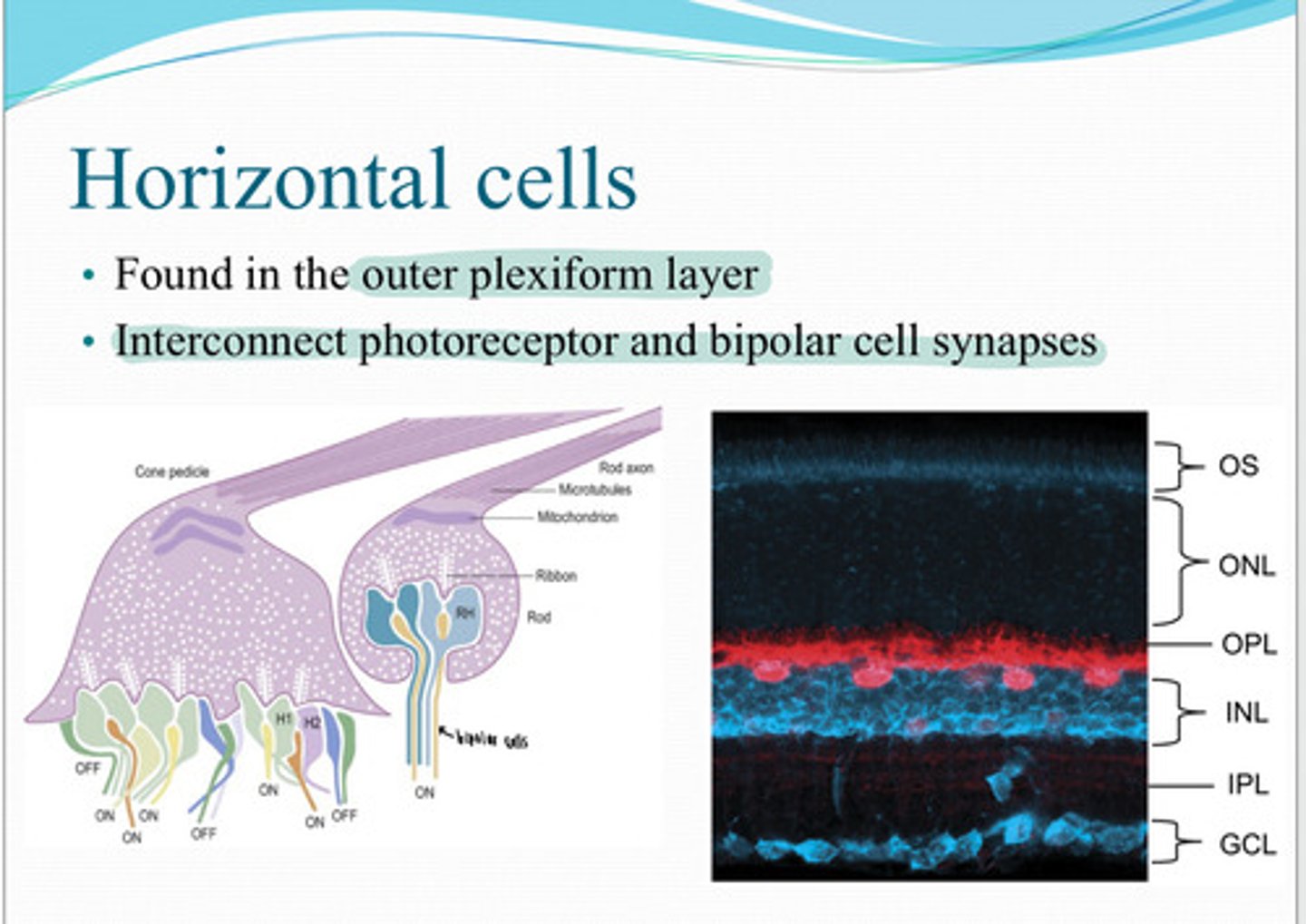
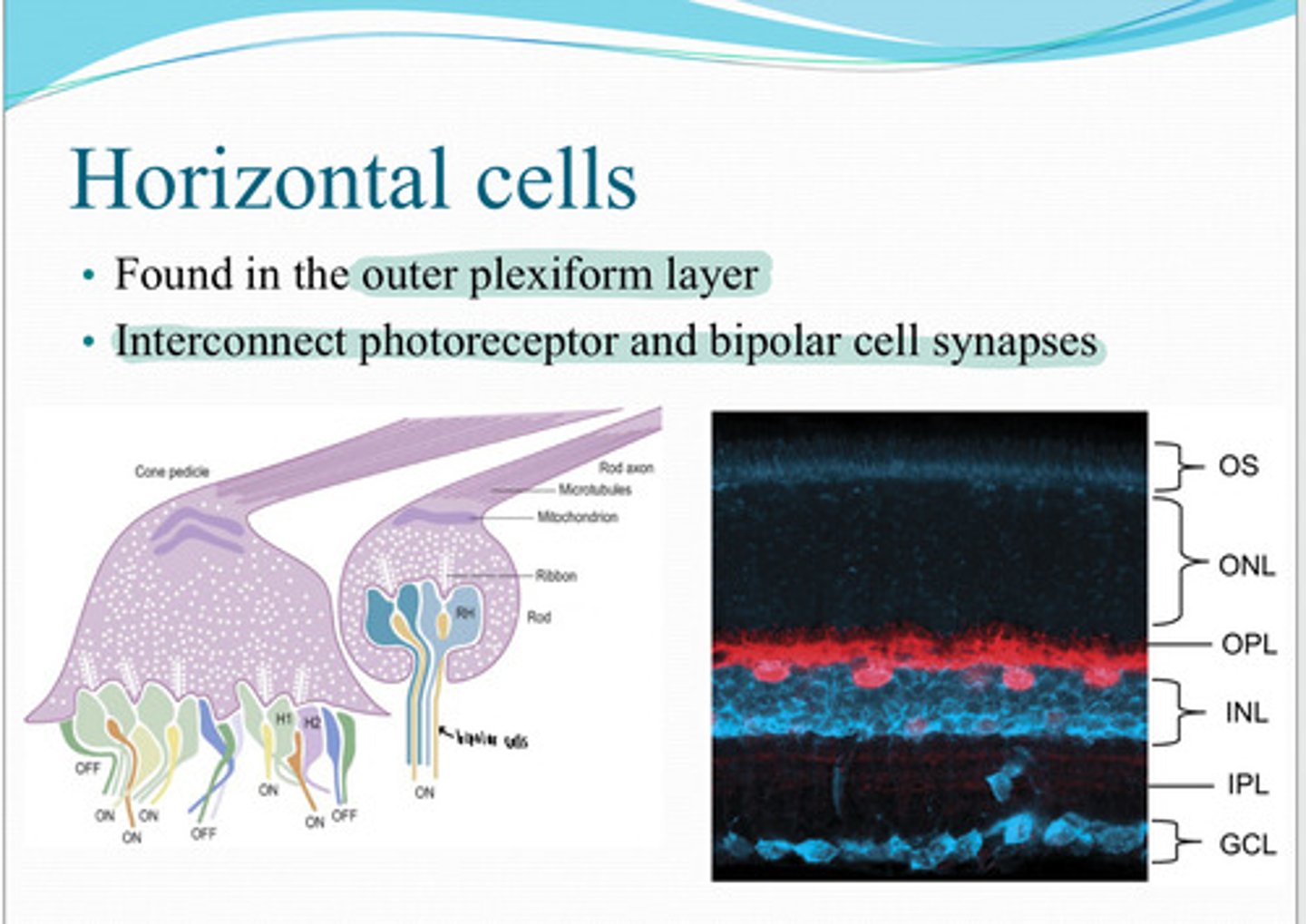
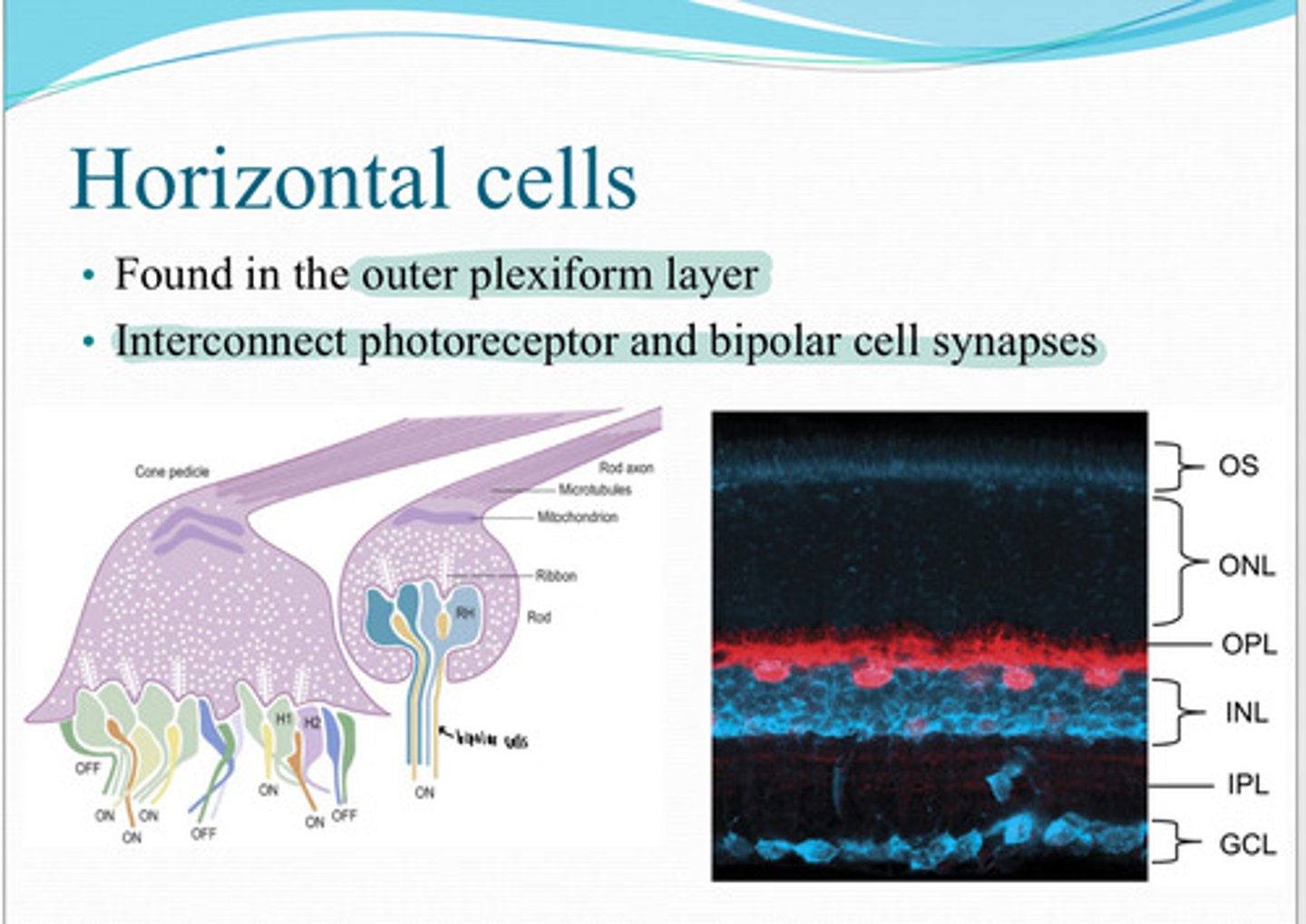
horizontal cells
These cells are found in the outer plexiform layer and interconnect photoreceptor and bipolar cell synapse?
lateral inhibition
What are horizontal cells responsible for?
limit
Horizontal cells (increase/limit) glutamate release from the photoreceptors
-enhances image contrast
-facilitates color discrimination
-assists with light adaption
What do horizontal cells help with in vision?
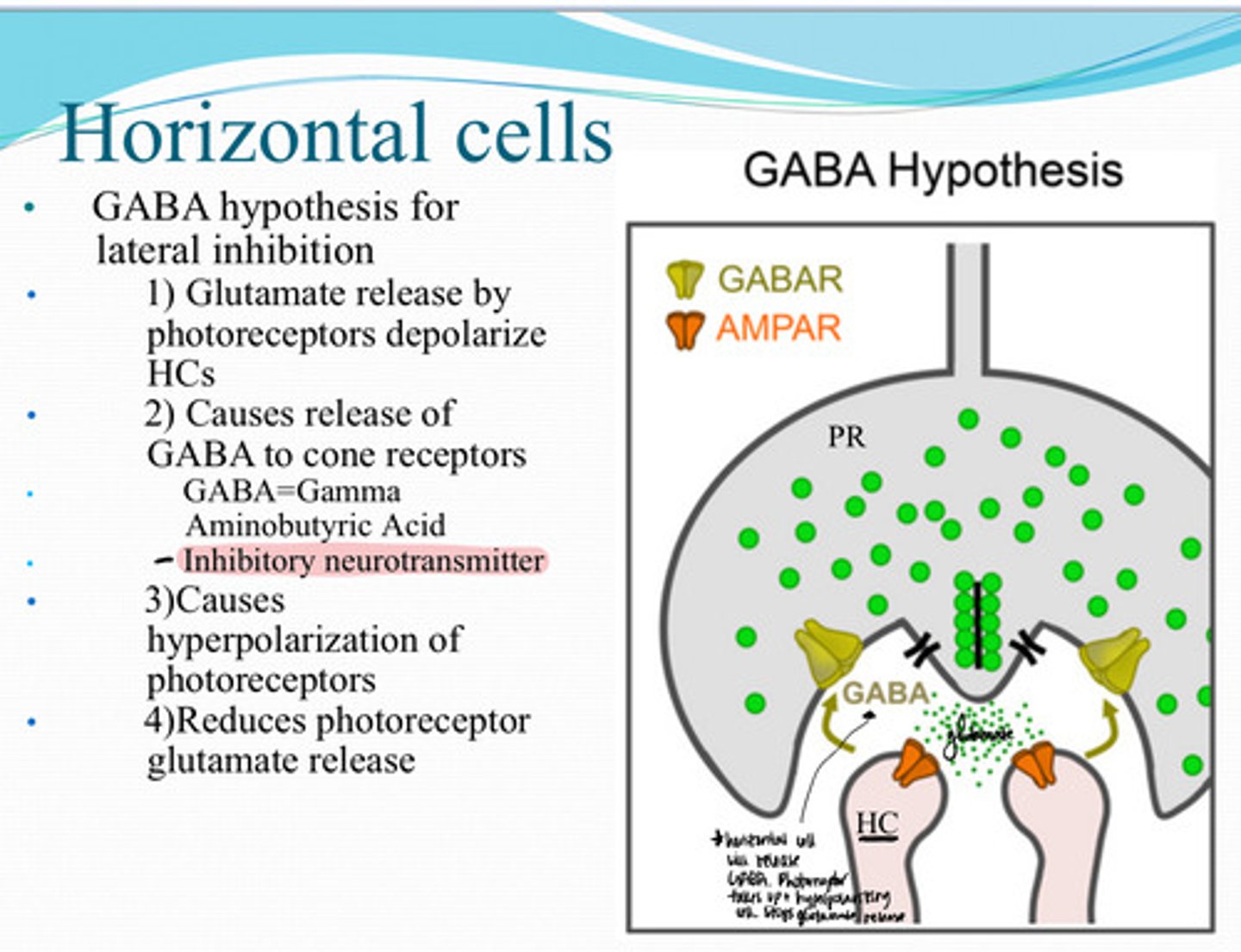
1) Glutamate release by the photoreceptors depolarize horizontal cells
2) Release of GABA to cone receptors (inhibitory neurotransmitter)
3) Causes hyperpolarization of photoreceptors
4) Reduces photoreceptor glutamate release
What is the Mechanism of GABA use for Lateral Inhibition of Bipolar cells?
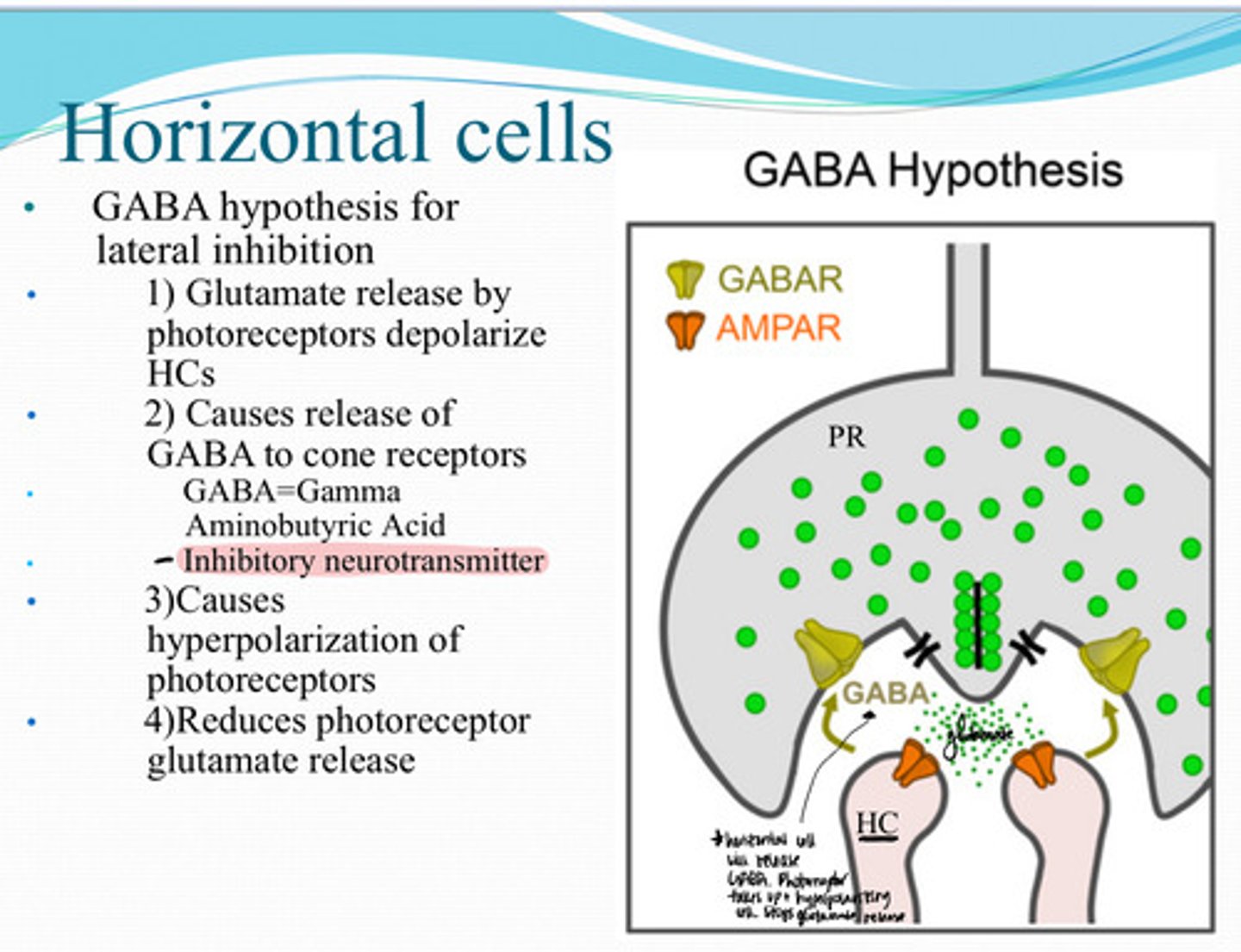
Glutamate release by the photoreceptors depolarize horizontal cells
Mechanism of GABA use for Lateral Inhibition of Bipolar Cells
What is the first step in this mechansim?
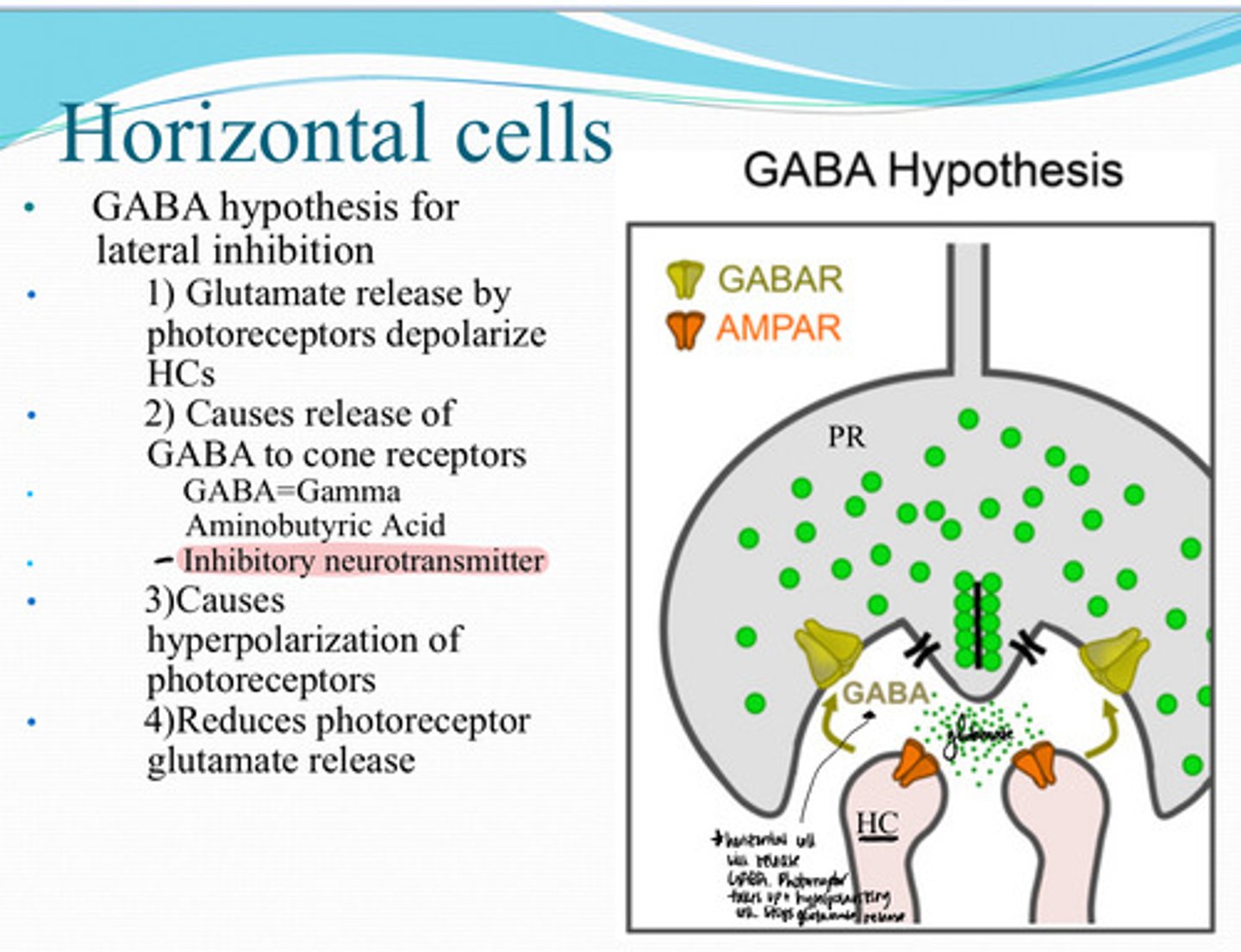
Release of GABA to cone receptors (inhibitory neurotransmitter)
Mechanism of GABA use for Lateral Inhibition of Bipolar Cells
After Glutamate release by the photoreceptors depolarize horizontal cells, what happens next?
Causes hyperpolarization of photoreceptors
Mechanism of GABA use for Lateral Inhibition of Bipolar Cells
After Release of GABA to cone receptors (inhibitory neurotransmitter), what happens next?
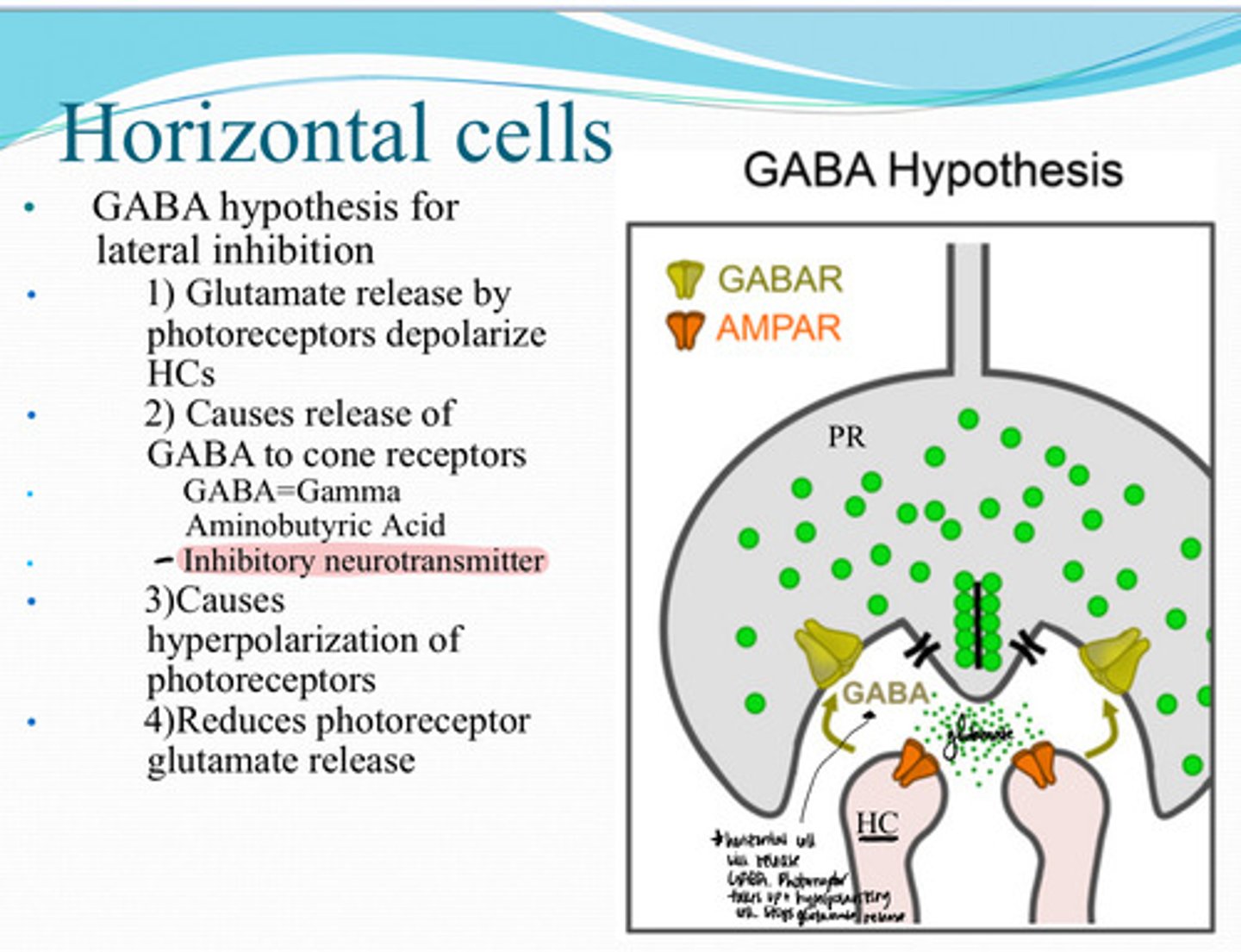
Reduces photoreceptor glutamate release
Mechanism of GABA use for Lateral Inhibition of Bipolar Cells
What is the last step in this mechanism?
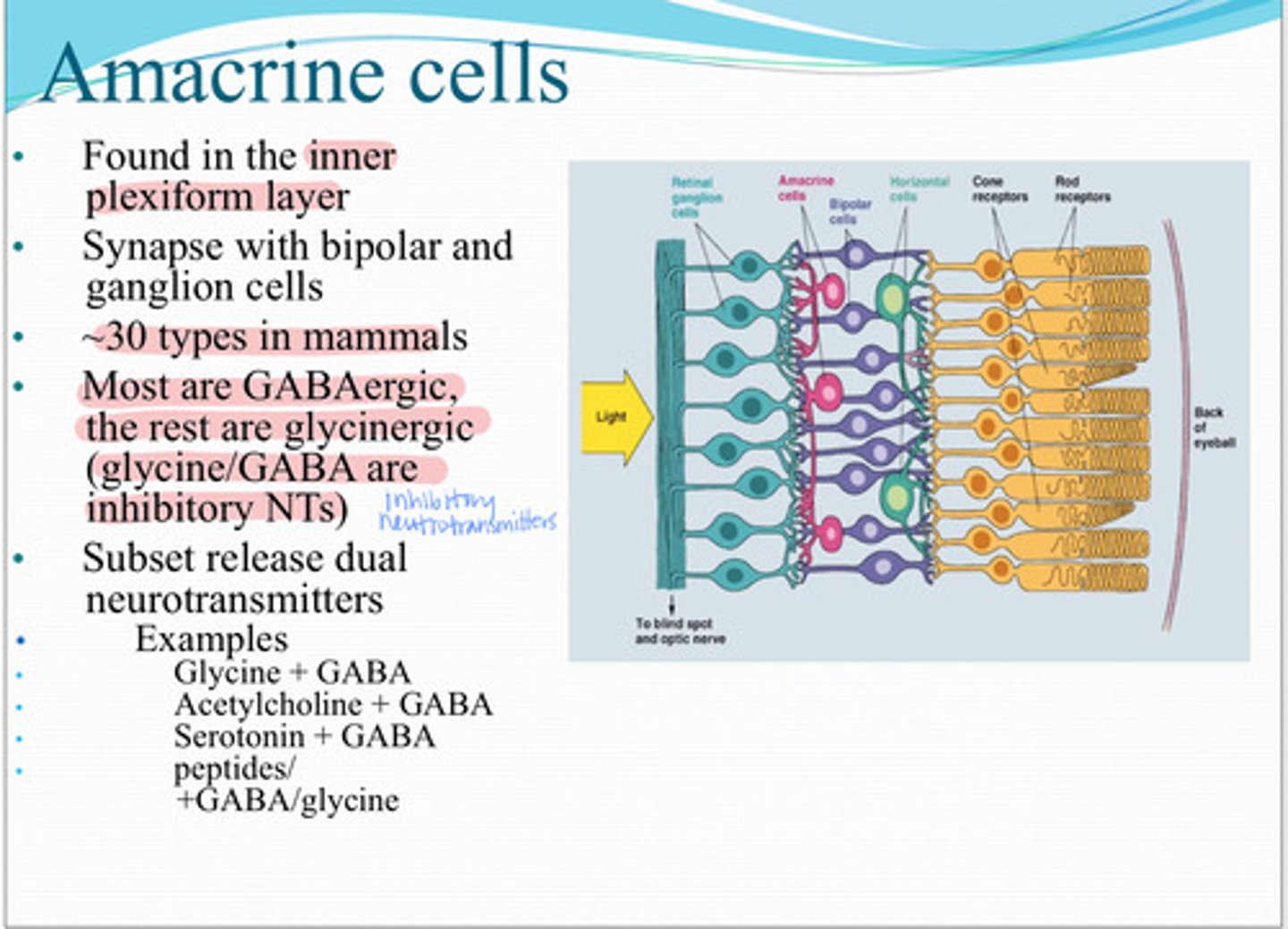
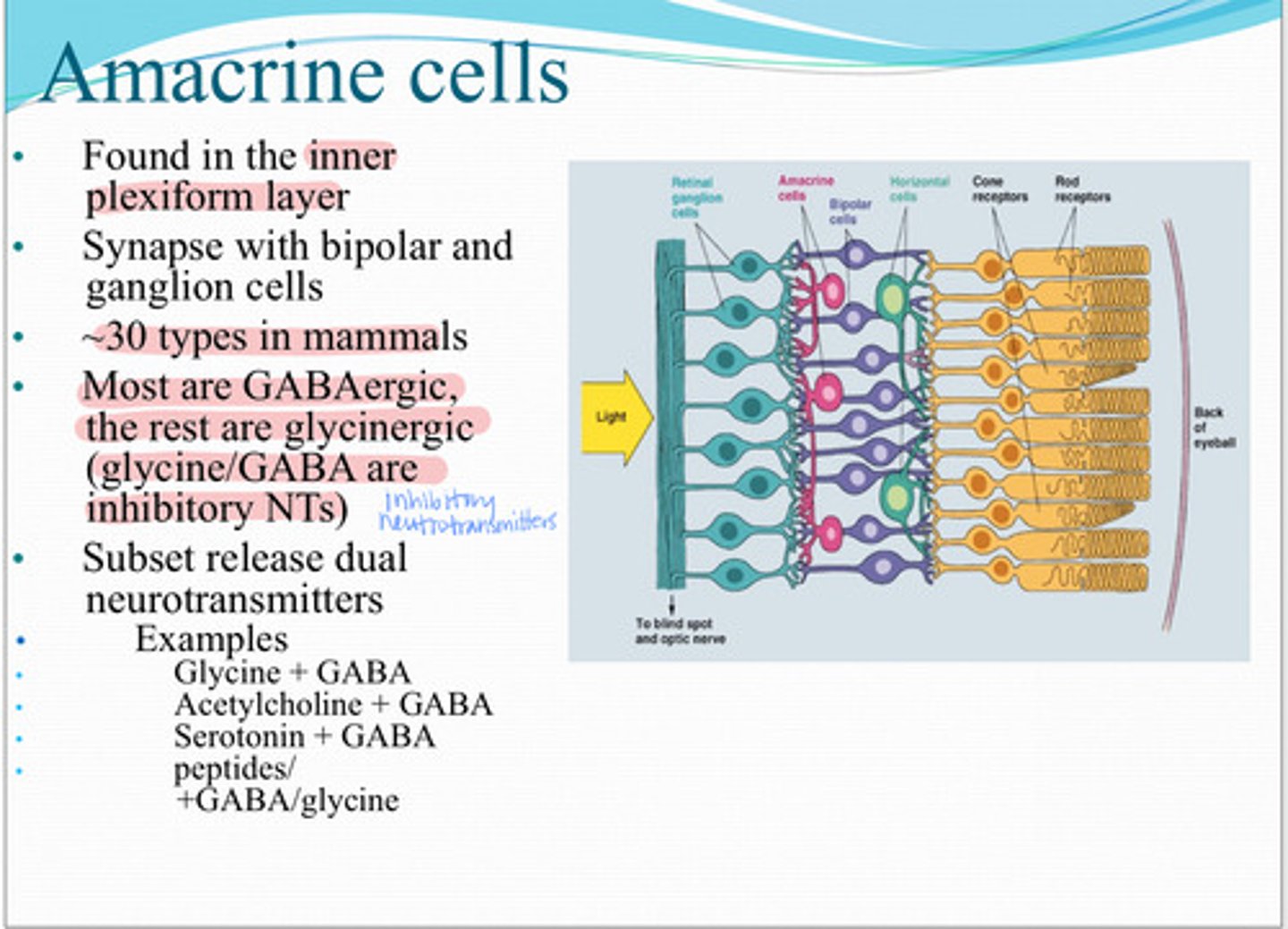
amacrine cells
These cells are found in the inner plexiform later and synapse with bipolar and retinal ganglion cells
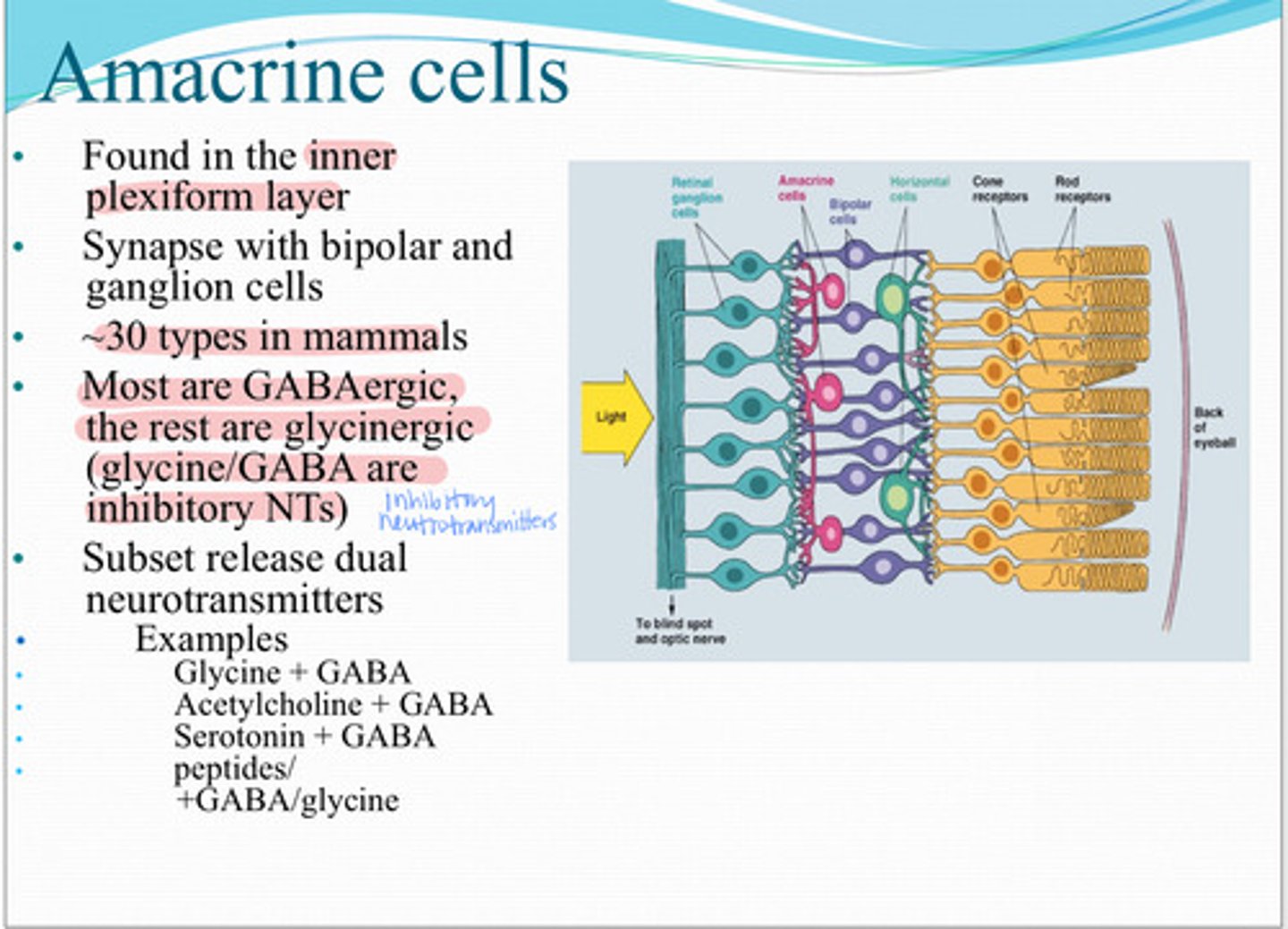
30 types
Approx how many types of amacrine cells are found in mammals
most - GABAergic
the rest - glycinergic
**both are inhibitory
Most amacrine cells are _____? The rest are ______?
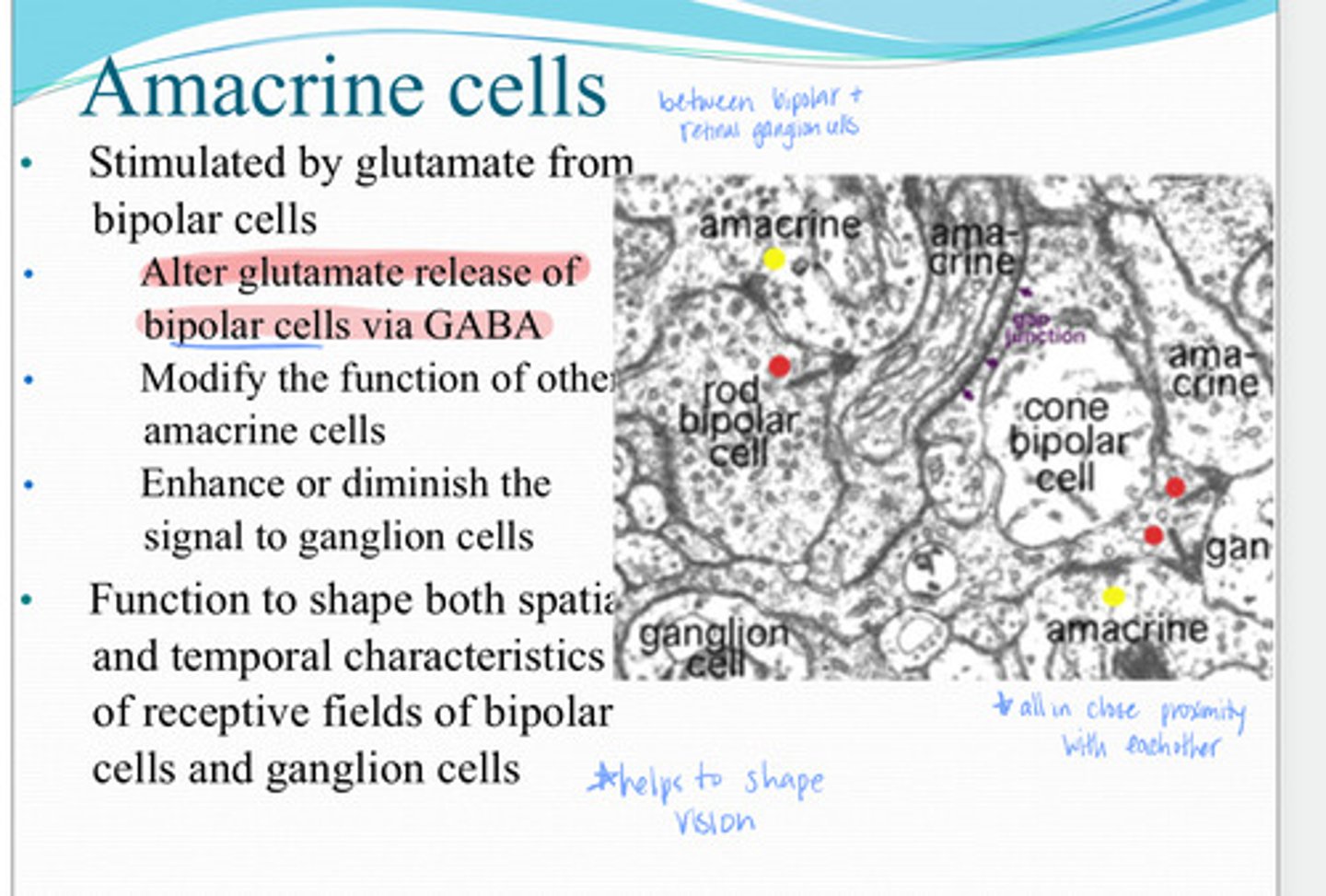
glutamate
Amacrine cells are stimulated by _____ from the bipolar cells
-alter glutamate release of bipolar cells via GABA
-modify the function of other amacrine cells
enhance or diminish the signal to ganglion cells
What is the function of amacrine cells?
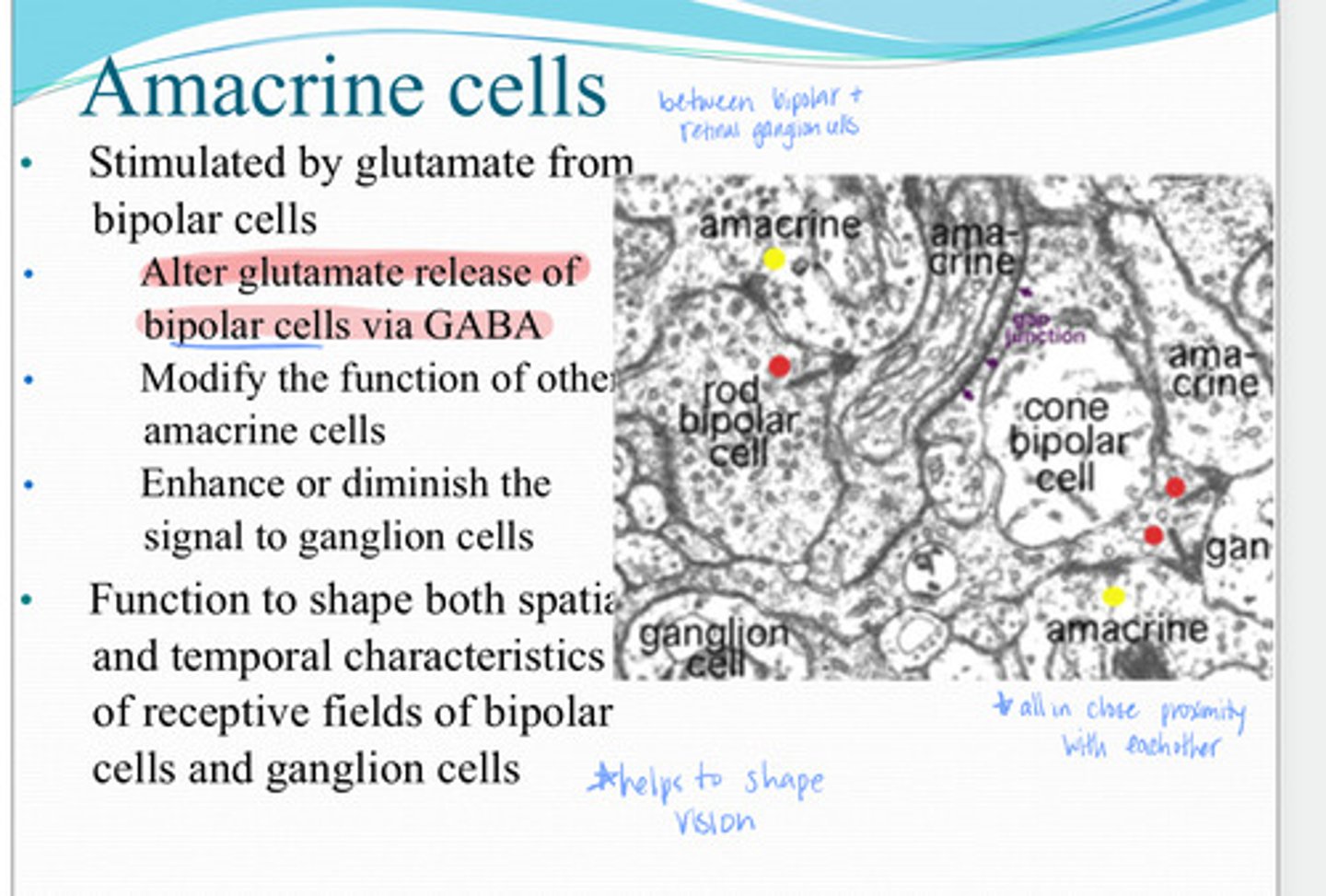
spatial and temporal
Amacrine cells function in shaping both the ____ and _____characteristics of receptive fields of bipolar cells and retinal ganglion cells
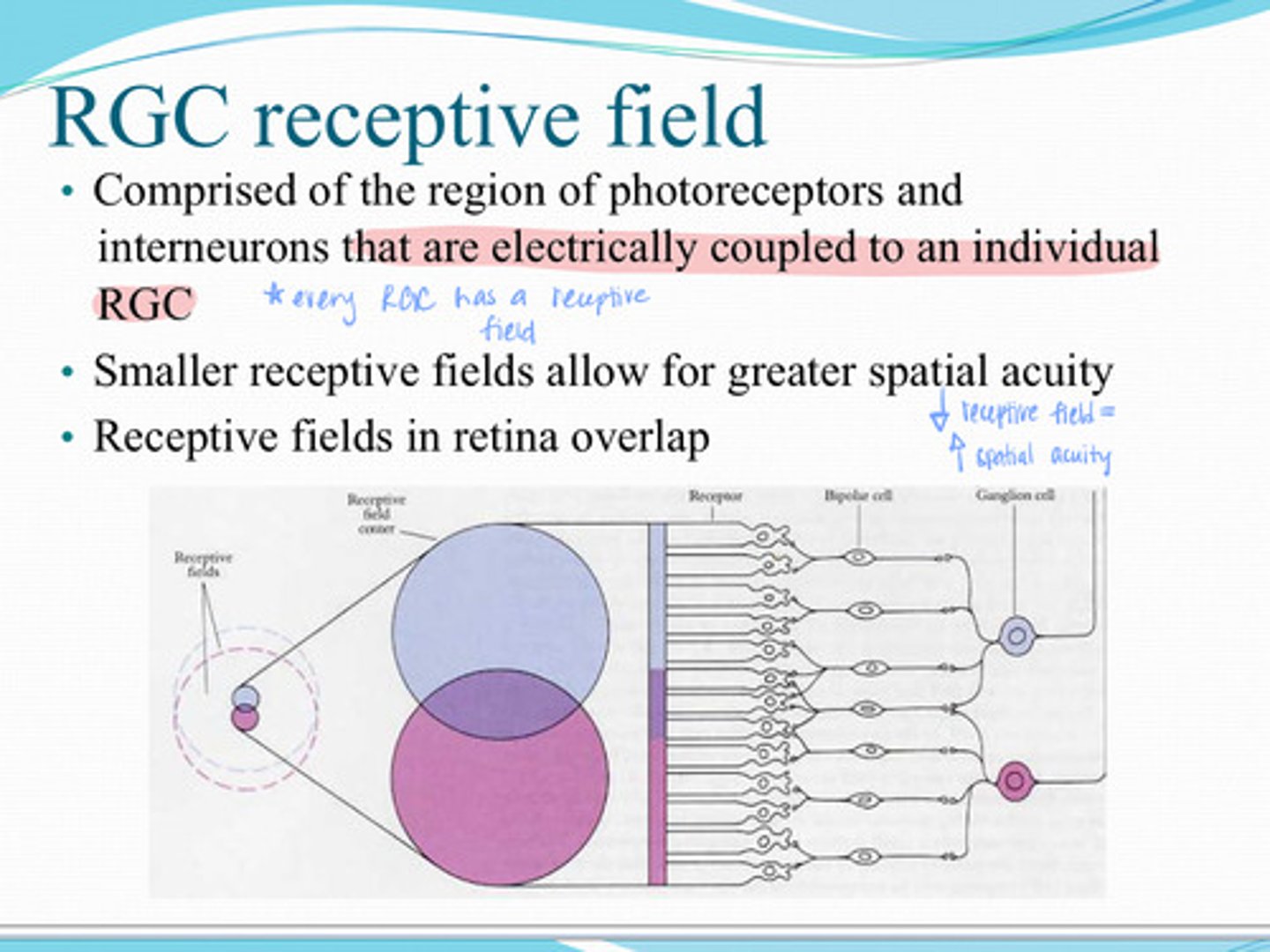
comprised of the region of photoreceptors and interneurons that are electrically coupled to an individual RGC
What is the RGC receptive field?
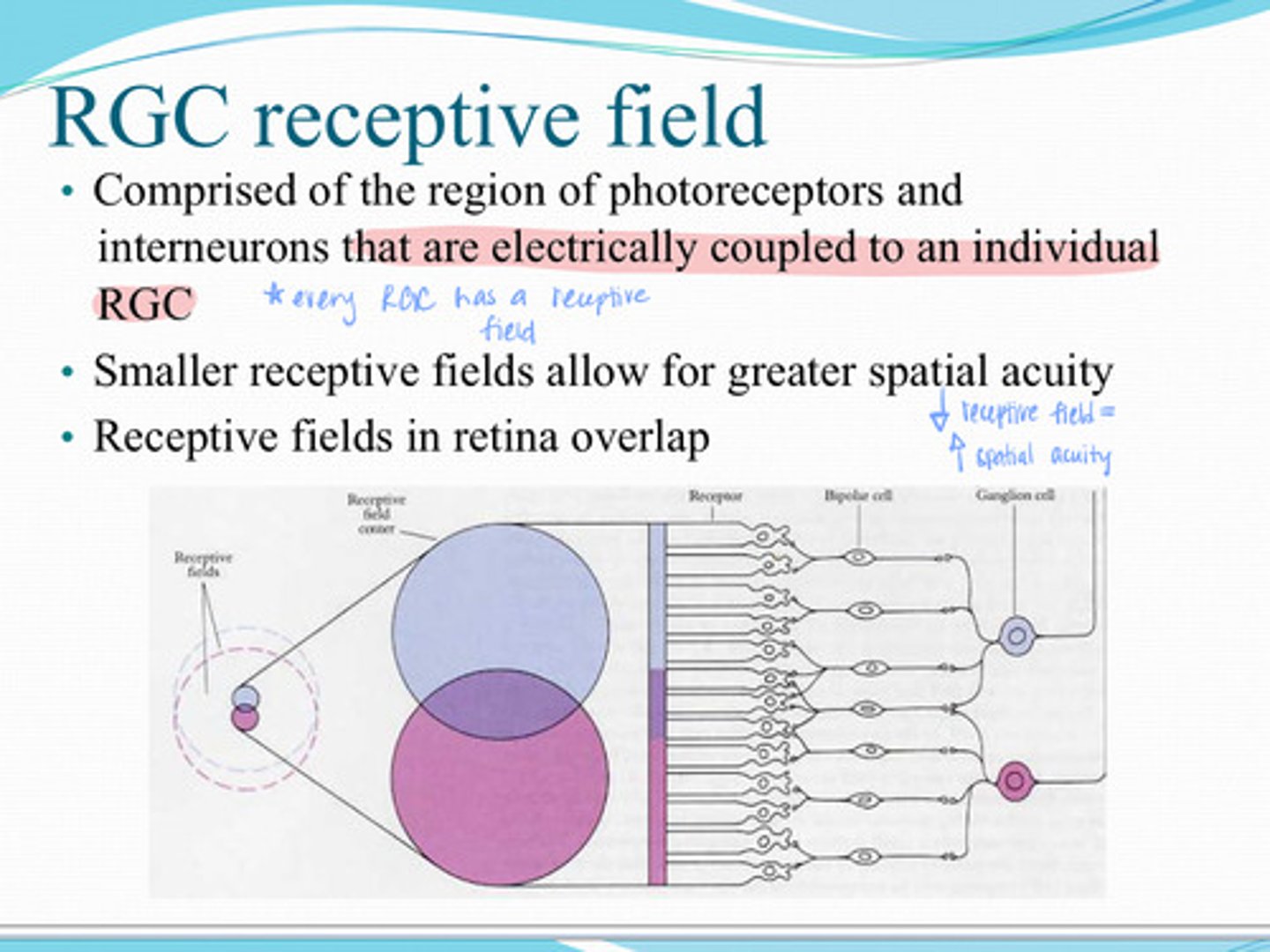
greater
Smaller receptive field = (less/greater) spatial acuity
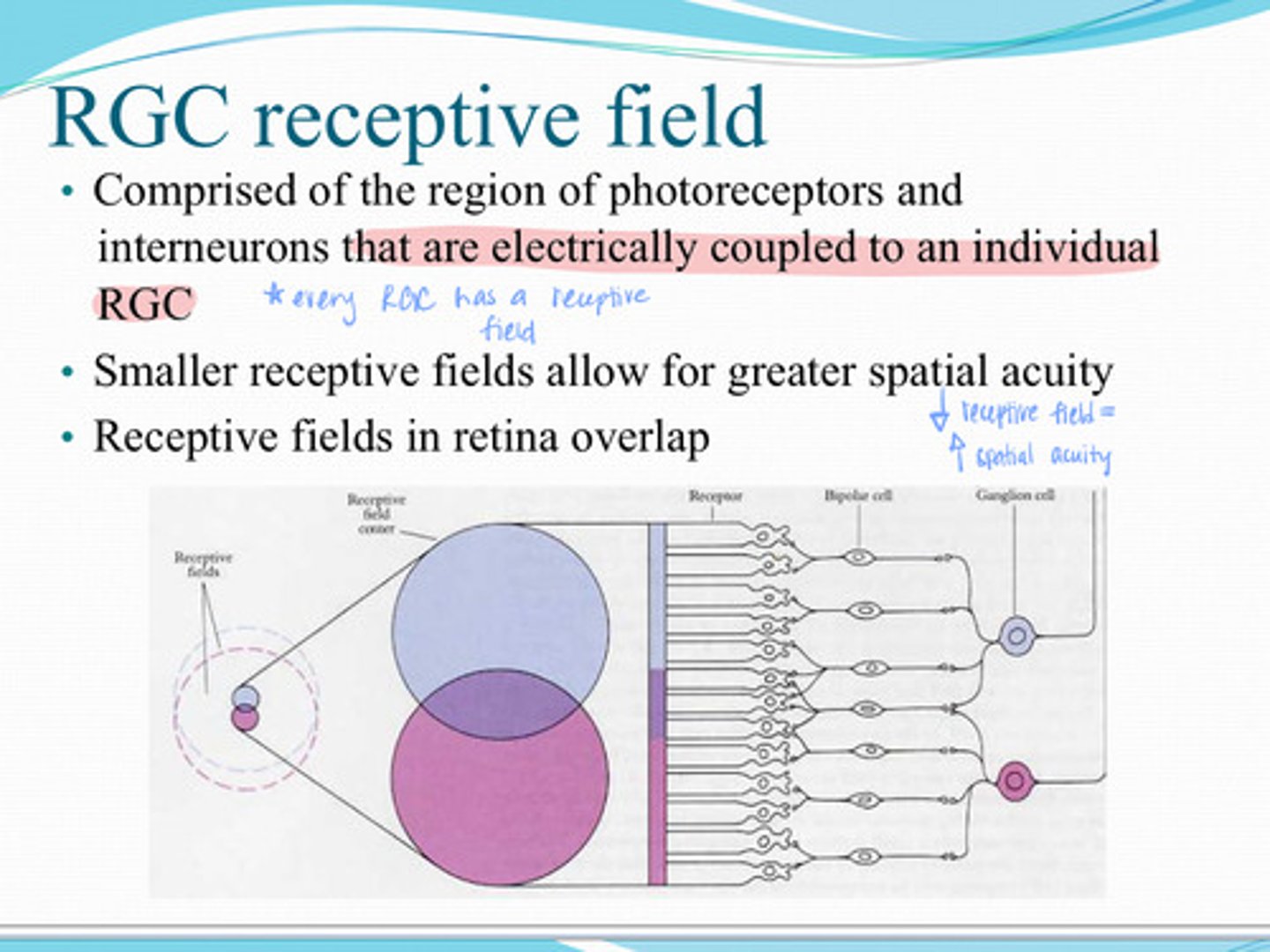
yes
Do receptive fields in the retina overlap?
depending on whether the stimulus is on or off center
By HBCs and DBCs being distinct, receptive filed can send distinct signals depending on what?
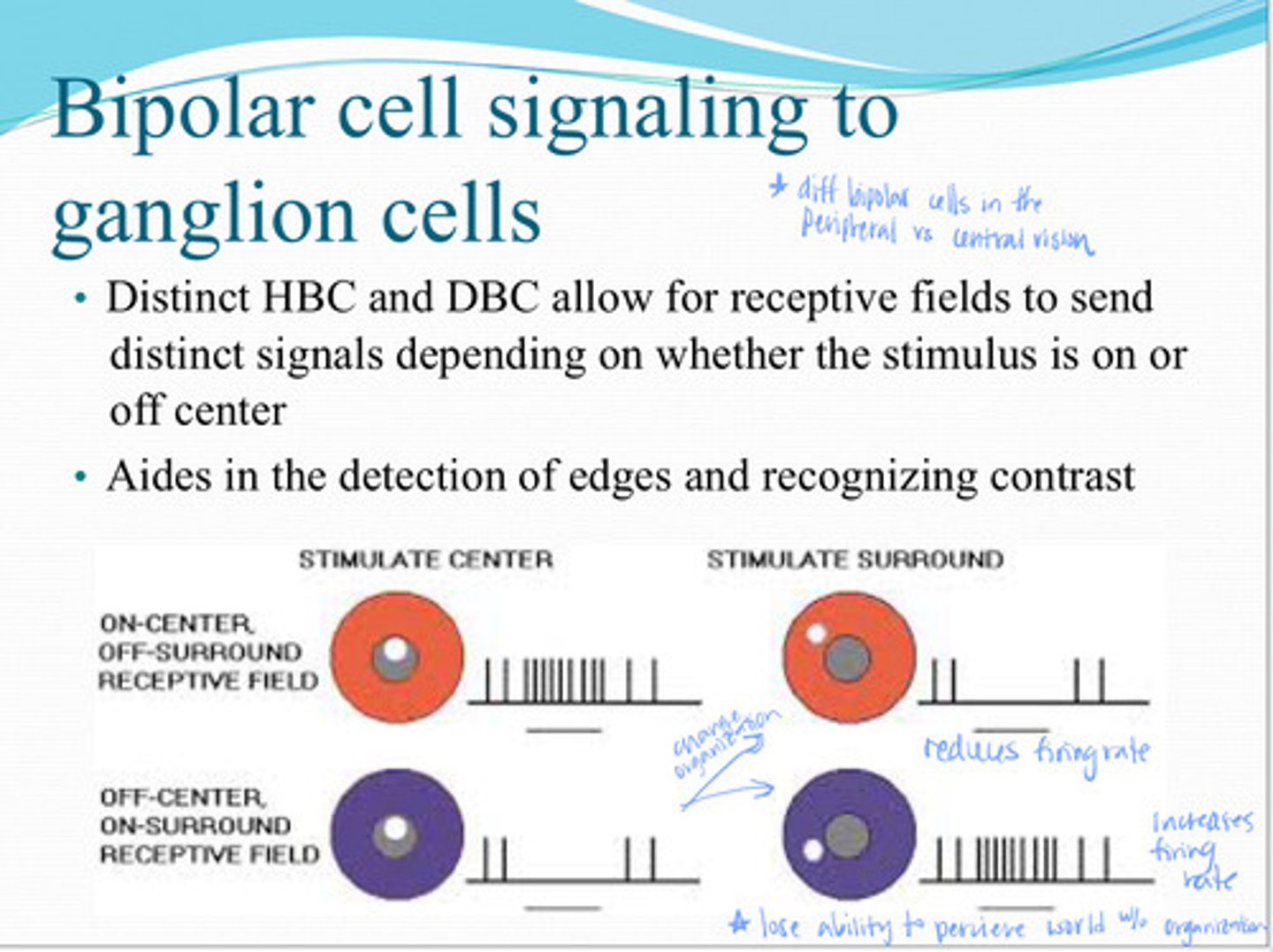
the detection of edges and recognizing contrast
What do receptive fields aid in?
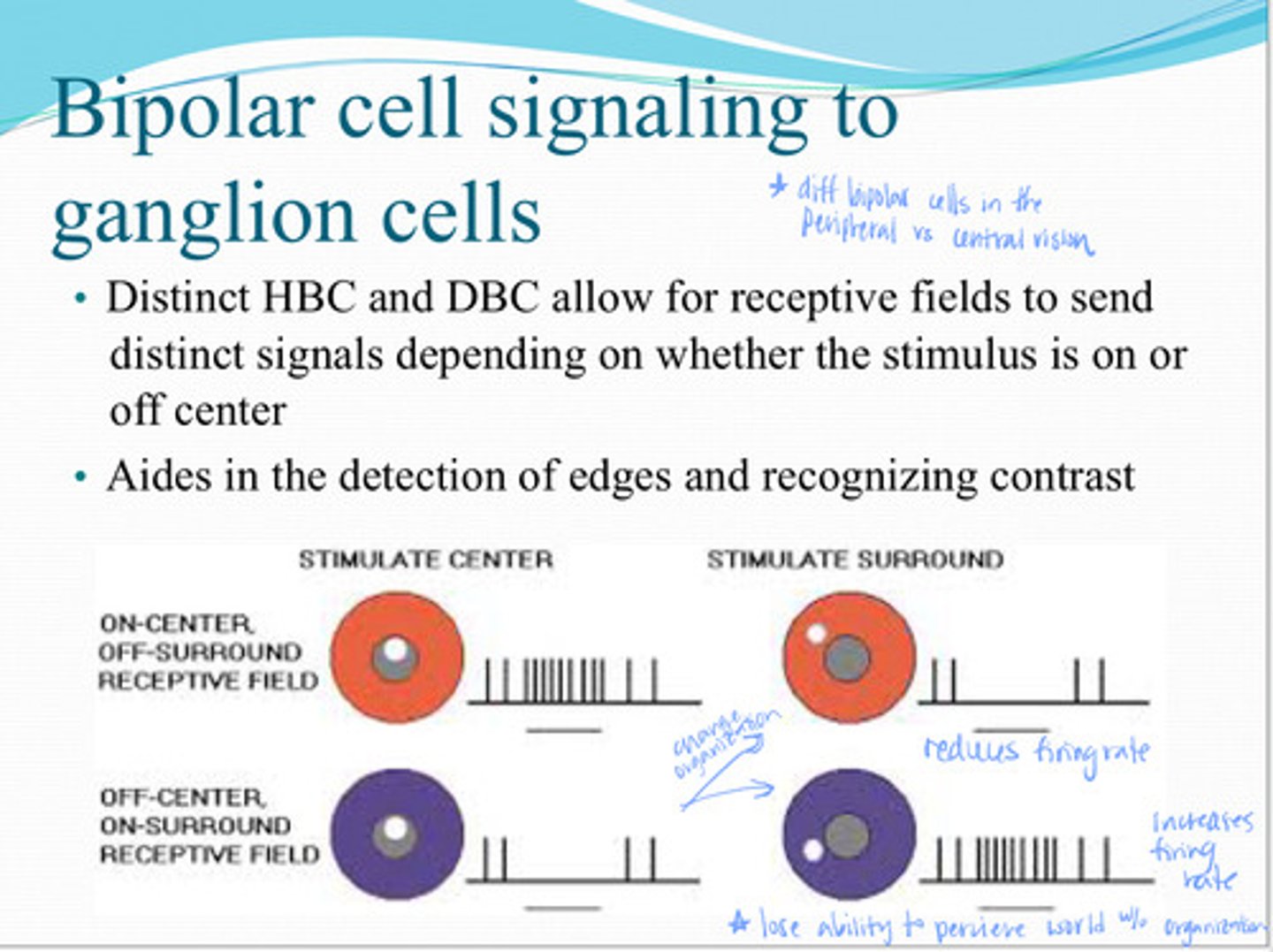
Center Surround Antagonist Receptive Field (CSARF)
Functions to encode spatial information due to distinct types of bipolar cells (HBCs and DBCs) and amacrine/horizontal cell inhibition
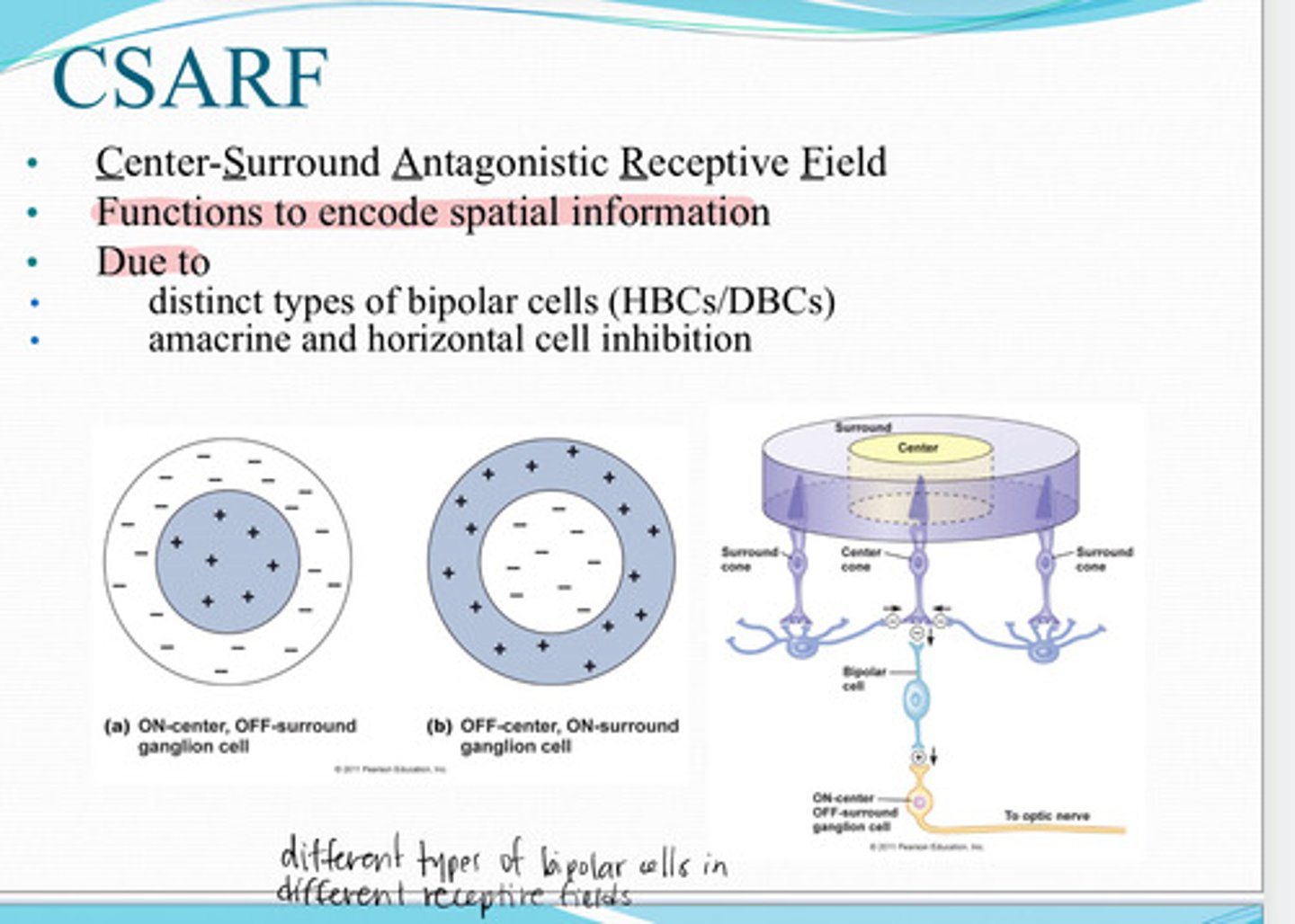
-RGC firing rate
-the type of RGC
-Location of photoreceptors that trigger RGC
-location of the RGC axon synapse within the LGN
What is the information that is encoded within an RGC a combination of?