Fiscal policy
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Who manages fiscal policy?
UK government
What does the government have to do in a recession (expansionary/ loose)
the government will want to use fiscal policy to increase aggregate demand. They will therefore choose to decrease taxes in order to encourage consumption. They will also spend more money. By decreasing tax and increasing spending they will need to borrow more money, which will worsen the budget deficit.
What is contractionary/ tight fiscal policy?
Contractionary fiscal policy is when the government raises taxes and cuts government spending, in order to decrease the budget deficit.
What is the definition of fiscal policy?
When the government uses tax and government spending to influence the economy.
Does expansionary fiscal policy involve an increase or a decrease in income tax? What is the impact of this on high income earners?
Expansionary fiscal policy involves expanding the economy by decreasing taxand increasing government spending.
A lower income tax rate means that high earning workers pay less tax to the government. This means that they can keep more of their disposable income. So, they will spend more, increasing consumption, which will rise aggregate demand.
Explain the multiplier effect on the economy following a reduction in the income tax rate.
A lower income tax rate means that workers have a higher disposable income and therefore consume more. The increase in consumption increases aggregate demand. As consumers spend more, firms will make more sales and therefore more profit. This means that they can invest more. Because investment is a positive component of aggregate demand, AD will increase further.
As consumers spend more and firms make more profit, corporation tax and VAT revenues will increase. This means that the government can spend more and so AD will increase further. As firms expand, they will increase their derived demand for labour, so incomes will increase. This will further increase spending and income tax revenue, causing consumption and government spending to increase further. So, the overall impact on aggregate demand will be much larger.
What is the immediate impact of a reduction in the income tax rate?
revenue from income tax will fall.
what is one advantage and one disadvantage of lowering the income tax rate for high earners?
One advantage is that a lower income tax rate will increase disposable incomes for the rich. This will increase consumption and aggregate demand, and lead to the multiplier
effect.
One disadvantage is that this will reduce the government’s revenue from income tax, which will decrease government spending and decrease aggregate demand.
What policy is likely to include an increase in income tax?
Fiscal policy uses government spending and taxation. Contractionary fiscal policy involves contracting AD by increasing tax and decreasing government spending.
What is the impact of a higher income tax rate?
A higher income tax rate means that high earning workers pay more tax to the government. This means that they have less disposable income, so they will spend less. This will decrease consumption, which will decrease aggregate demand.
However, the governments tax revenue will increase and inflation will fall
Explain the downward multiplier effect following an increase in the income tax rate.
A higher income tax rate means workers have a lower disposable income and therefore consume less. The decrease in consumption decreases aggregate demand. As consumers spend less, firms will make fewer sales and therefore less profit. This means that they can invest less and so AD will decrease further as investment is a positive component of AD.
As consumers spend less and firms make less profit, corporation tax and VAT revenues will decrease. This means the government can spend less and so AD will decrease further. As firms contract, they will decrease their derived demand for labour and so incomes will decrease. This will further decrease spending and income tax revenue and so consumption and government spending will further decrease. So, the overall impact on aggregate demand will be much larger.
Explain one advantage and one disadvantage of raising the income tax rate for high earners
Raising the income tax rate for high earners decreases their disposable income. This will decrease consumption and aggregate demand, which will help to bring the price level down and control inflation. Also, a higher income tax rate will increase income tax revenue and help the government to balance its budget.
However, a reduction in aggregate demand will reduce real GDP. Also, an increase in income tax may increase tax evasion and avoidance which could even mean that income tax revenue decreases.
What are benefits?
Benefits are payments made by the government to unemployed or low income workers.
Is it expansionary fiscal, or contractionary if the government increases spending on benefits?
expansionary
Do benefit payments count as government spending in AD?
no, the government is not buying anything, just transferring money. Benefit result in additional consumption.
Explain one disadvantage and one advantage of increasing benefits.
Increasing benefits means more money is transferred to unemployed workers. This will increase their consumption, which will increase AD. Also, increasing benefits will help to reduce income inequality.
However, if benefits are too high, there is a significant disincentive for unemployed people to find a job, because they may earn more by claiming benefits. This is known as the benefits trap.
Explain one disadvantage and one advantage of the government reducing spending on benefits.
One advantage in reducing benefits is that the budget deficit will improve as the government is paying out less. Lower benefits may get the unemployed out of the benefits trap by increasing the incentive to work - this will reduce unemployment.
However, poor households will have less to spend, so consumption will fall, which will decrease AD. Also, income inequality will worsen as the poor get poorer.
Continue
What is corporation tax?
Corporation tax is a tax on profits made by a firms.
What is likely to happen if the government pursues a contractionary fiscal policy to corporation tax?
Corporation tax rates will increase
Explain one advantage and one disadvantage to increasing corporation tax.
Increasing corporation tax should increase tax revenue for the government, helping to improve the budget. Or, the increased tax revenue could be used to increase government spending, which will lead to economic growth.
However, increasing corporation tax means that firms make less profit and are likely to reduce their investment in capital, which causes depreciation in productivity. This makes them less productive and reduces LRAS limiting long run growth.
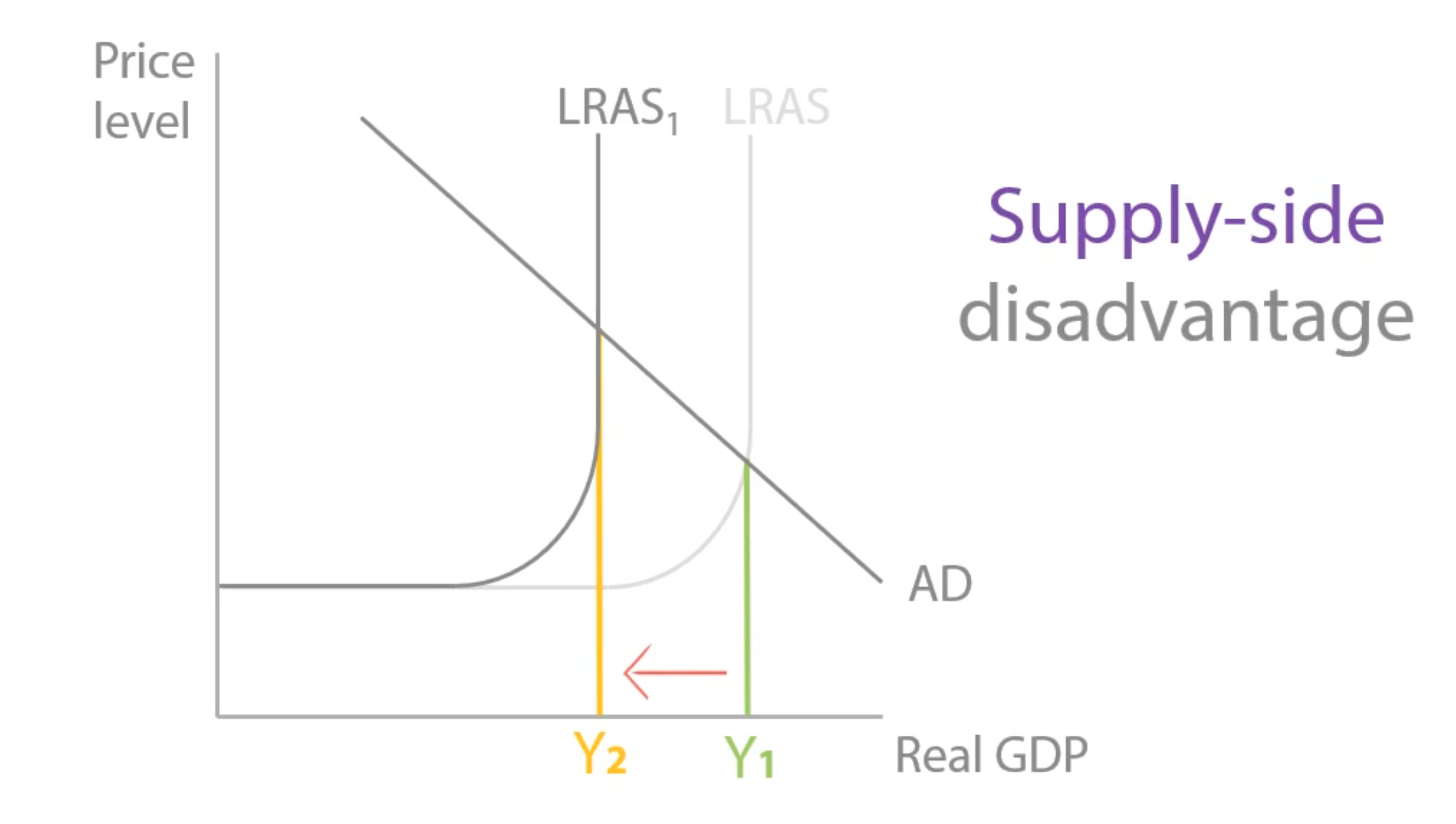
Explain one advantage and one disadvantage of decreasing corporation tax.
One advantage of decreasing corporation tax is that it should lower costs for firms. This will shift SRAS to the right and increase real GDP in the short run. Also, firms can keep more of their profit, so they are likely to increase investment, which will increase AD. Increasing investment will increase the productivity of capital and shift LRAS to the right, leading to economic growth.
However, decreasing corporation tax means that the government will receive less tax revenue. Also, the extra profit from reducing corporation tax might just be kept by the owners instead of being used for investment.
Would expansionary fiscal policy involve an increase or decrease in spending on healthcare and education?
Expansionary fiscal policy involves reducing taxation and increasing government spending, which includes spending on healthcare and education
Explain one advantage and one disadvantage to the government spending more on healthcare and education.
An increase on government spending is an increase in G, which increases aggregate demand and, therefore, real GDP. Specifically, spending on healthcare and education will make the workforce healthier and more productive, so the LRAS will shift right.
However, this spending will worsen the government’s budget deficit. Furthermore, spending on schools and education could go towards unproductive bureaucracy or useless degrees.
Explain one advantage and one disadvantage to the government spending less on healthcare and education.
A reduction in spending on education means a higher labour supply which can lower wages and therefore lower real costs for firms. This will shift SRAS to the right and increase real GDP.
However, a reduction in spending on healthcare and education means that the workforce is less productive, so LRAS will shift left, reducing real GDP.
What is VAT?
VAT stands for Value Added Tax and is charged as a percentage of the price of the good sold.
Explain one advantage and one disadvantage to the government increasing VAT.
An increase in VAT will increase tax revenue for the government, which will improve the budget deficit.
However, an increase in VAT will increase costs for firms, which will shift SRAS inwards. This can reduce economic growth and leads to cost push inflation.
Explain one advantage and one disadvantage to the government decreasing VAT
A decrease in VAT will decrease costs for firms, which will increase SRAS. This will increase real GDP and economic growth, and also bring the price level down.
However, a decrease in VAT will also decrease tax revenue and worsen the budget deficit.
Write the definition of: Infrastructure
Items needed for businesses to operate such as roads and telecommunications networks.
What are some examples of infrastructure spending?
roads, railways, sewer systems, telecommunication networks and electricity grids.
What is the benefit of building HS2
increase in geographical mobility of labour
more workers from Manchester would be ab;e to commute to work in London
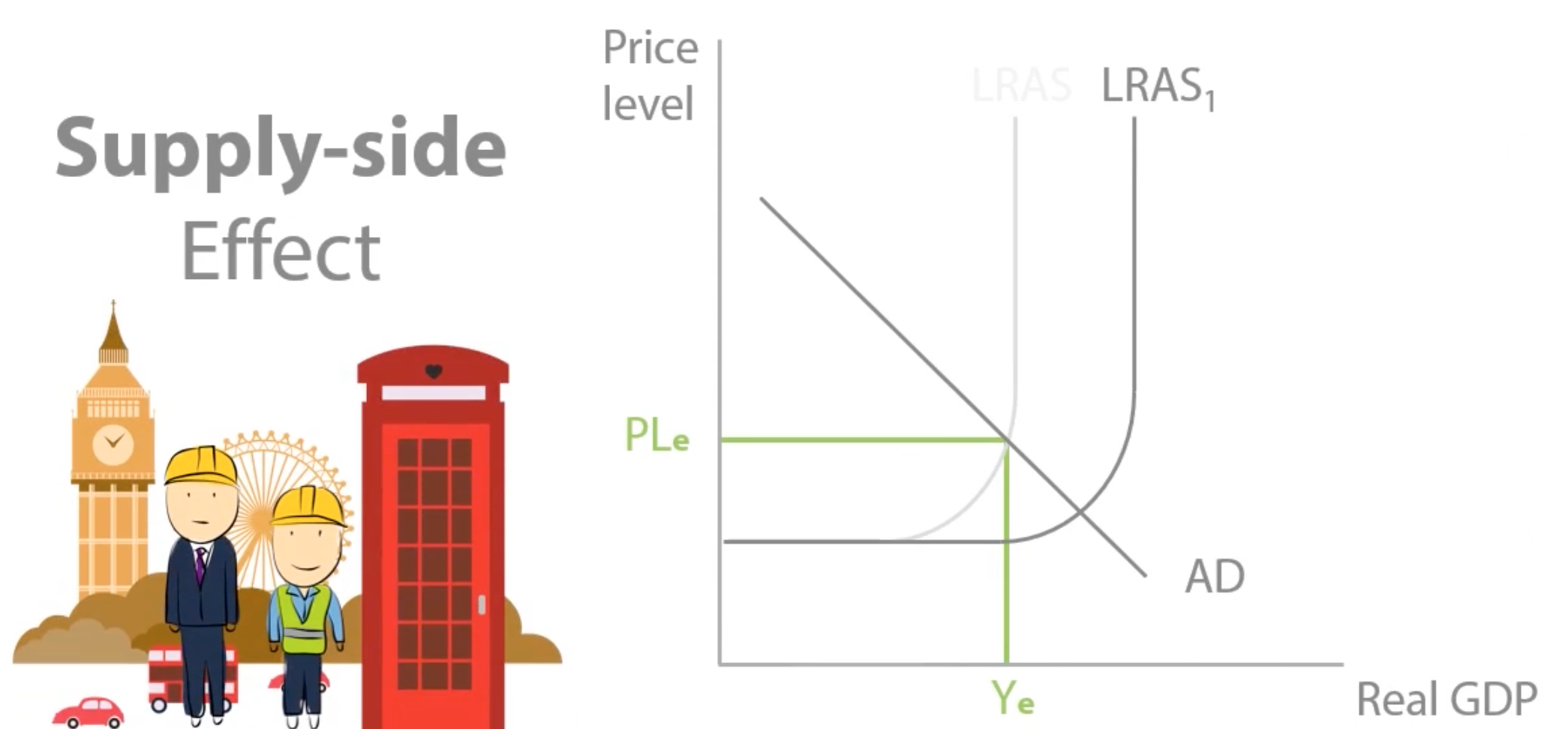
What is the government likely to demand in order to build new infrastructure?
FOP
what shows a likely impact for a private firm of the government borrowing to spend on land, labour and capital?
Government borrowing has pushed up the interest rate and the price of land, labour and capital. This means prices for firms are higher and so their costs will increase. An increase in costs will reduce supply and shift the firm’s supply curve to the left.
Write the definition of: Crowding Out
When government spending increases, the government demands more borrowed money, land, labour and capital. The price and interest rate increases which increases costs for firms and reduces supply.
What describes an expansionary fiscal policy?
An increase in government spending and a decrease in tax rates
Which of the following is the government likely to demand in order to build new infrastructure? What was the effect off this?
had to borrow £50bn to spend on Land, labour and capital
resulted in an increase in demand for these FOP, increasing the prices and also leading to an increase in the interest rate
What can be referred to as the price of money?
interest rates
Which of the following shows a likely impact for a private firm of the government borrowing to spend on land, labour and capital?
Government borrowing has pushed up the interest rate and the price of land, labour and capital. This means prices for firms are higher and so their costs will increase. An increase in costs will reduce supply and shift the firm’s supply curve to the left.
What is a likely impact for the economy of the government borrowing to spend on land, labour and capital?
Left shift of short run aggregate supply