Histology: Cartilage and Bone
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
what are the 3 types of cartilage?
hyaline cartilage
elastic cartilage
fibrocartilage
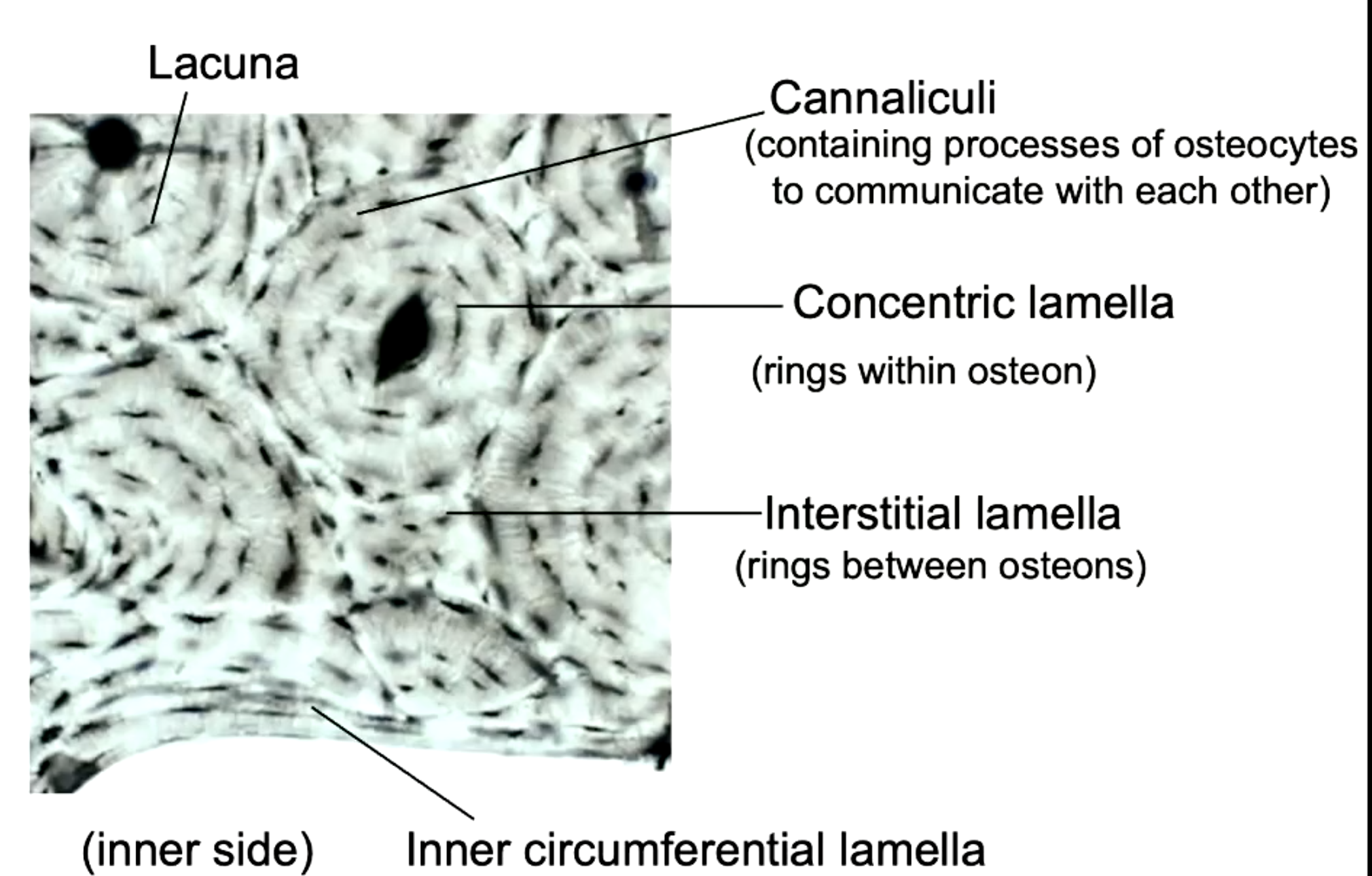
osteocytes extend cytoplasmic processes into canaliculi and communicate with each other through
GAP junctions
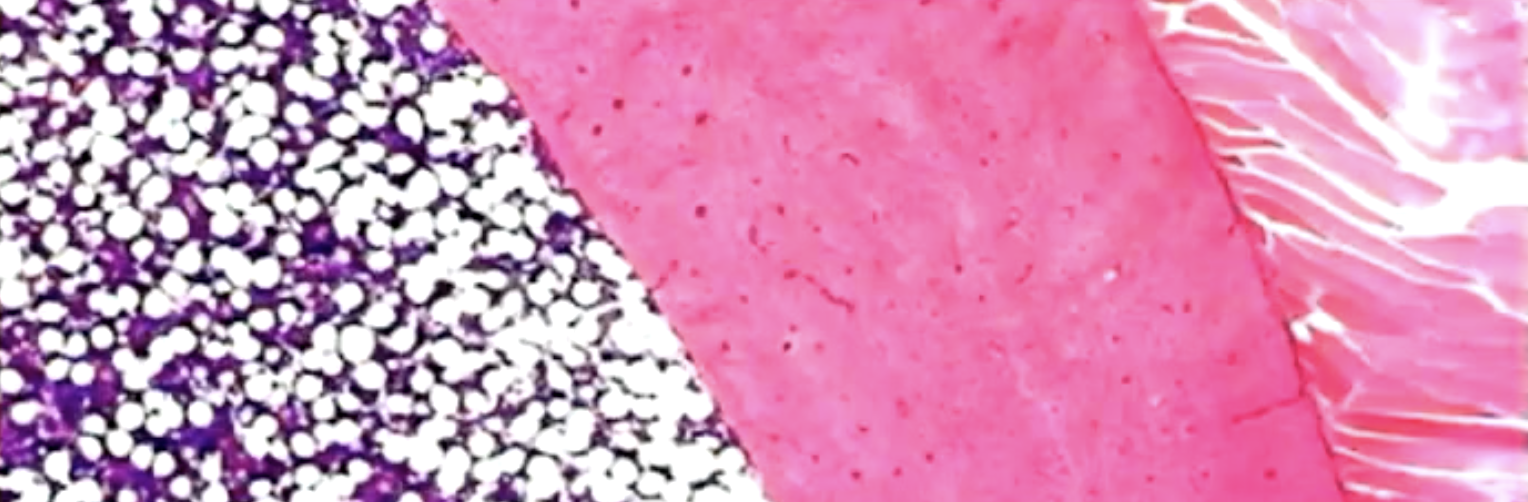
what does this show
decalcified compact bone
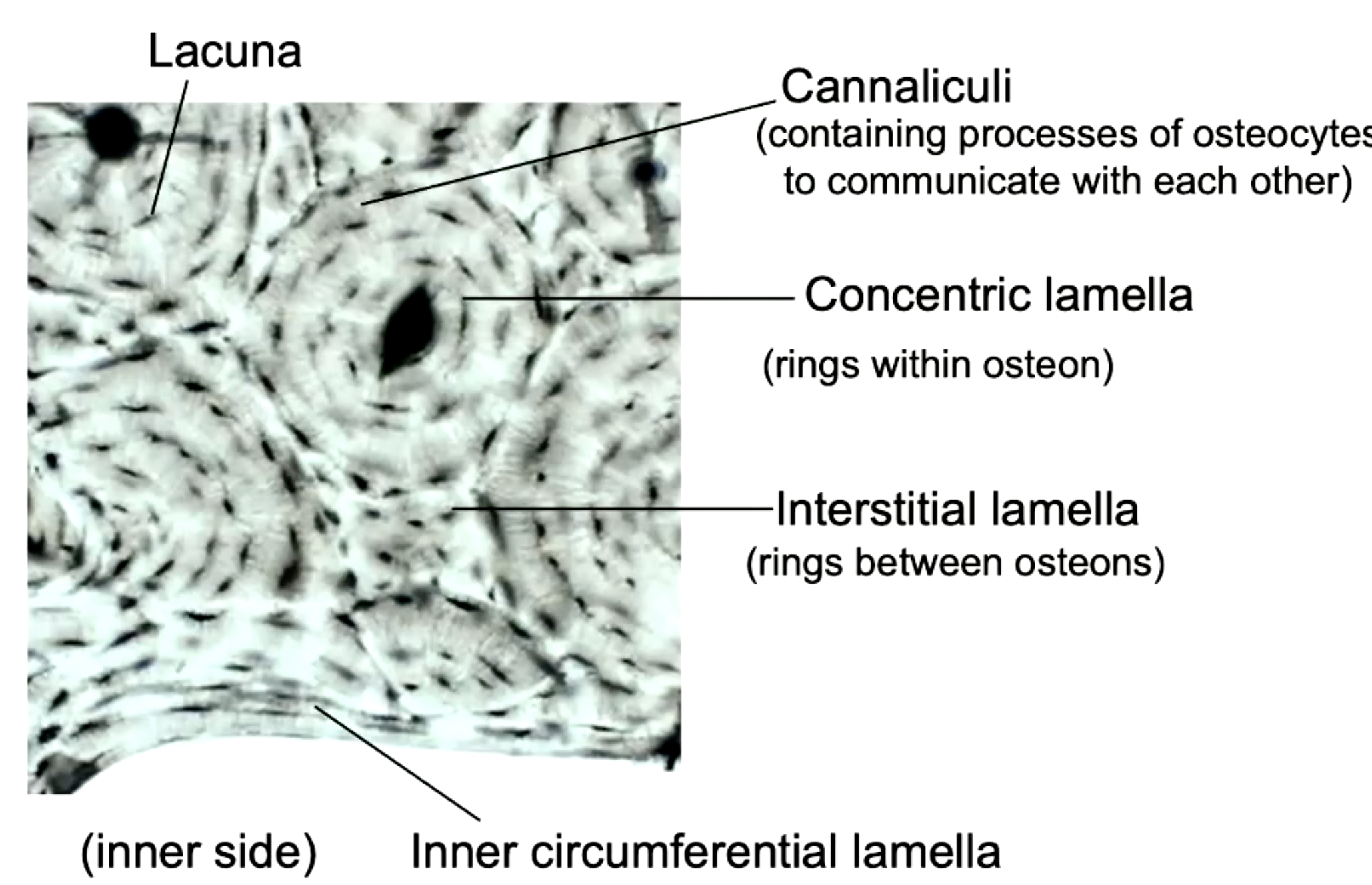
rings within osteon
concentric lamella
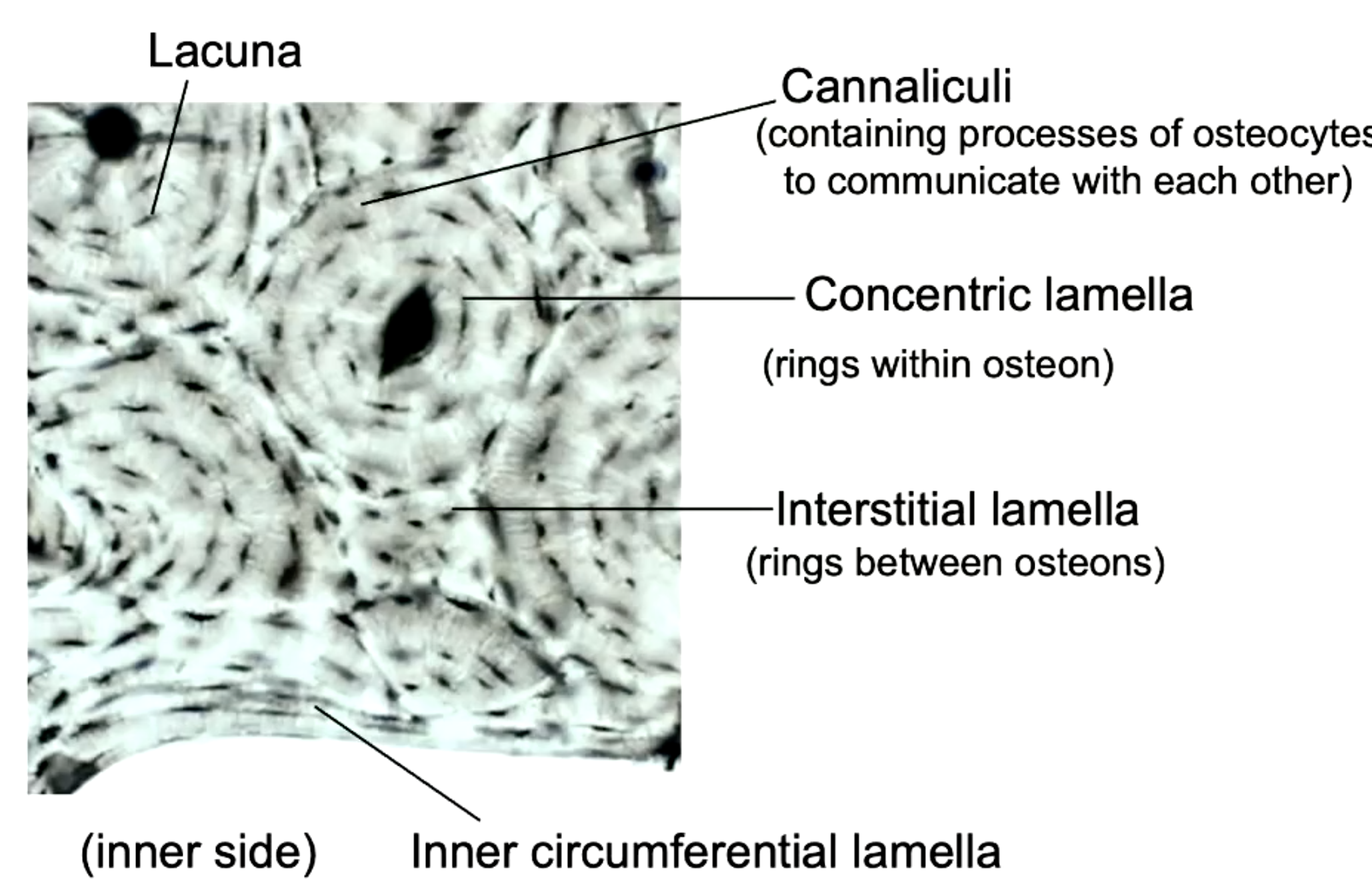
containing processes of osteocytes to communicate with each other
cannaliculi
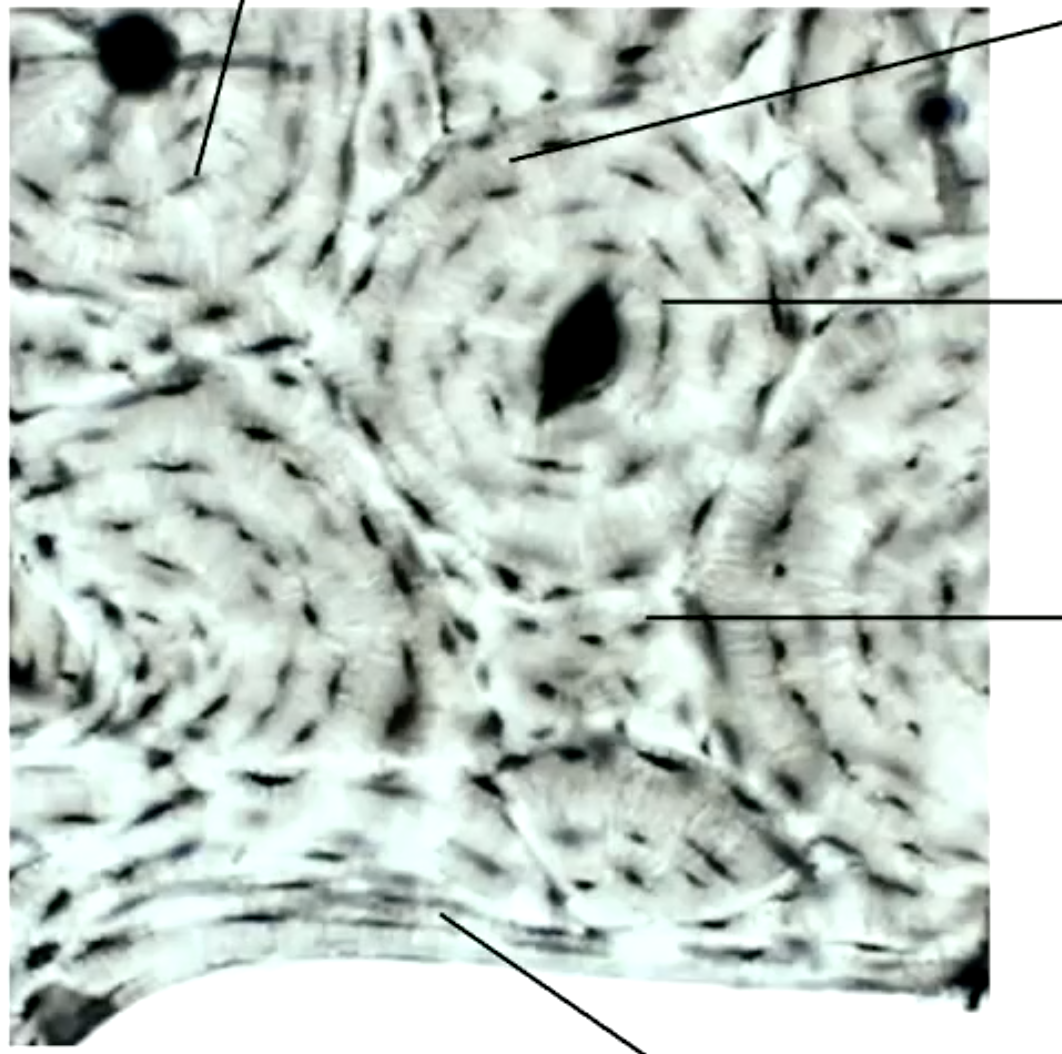
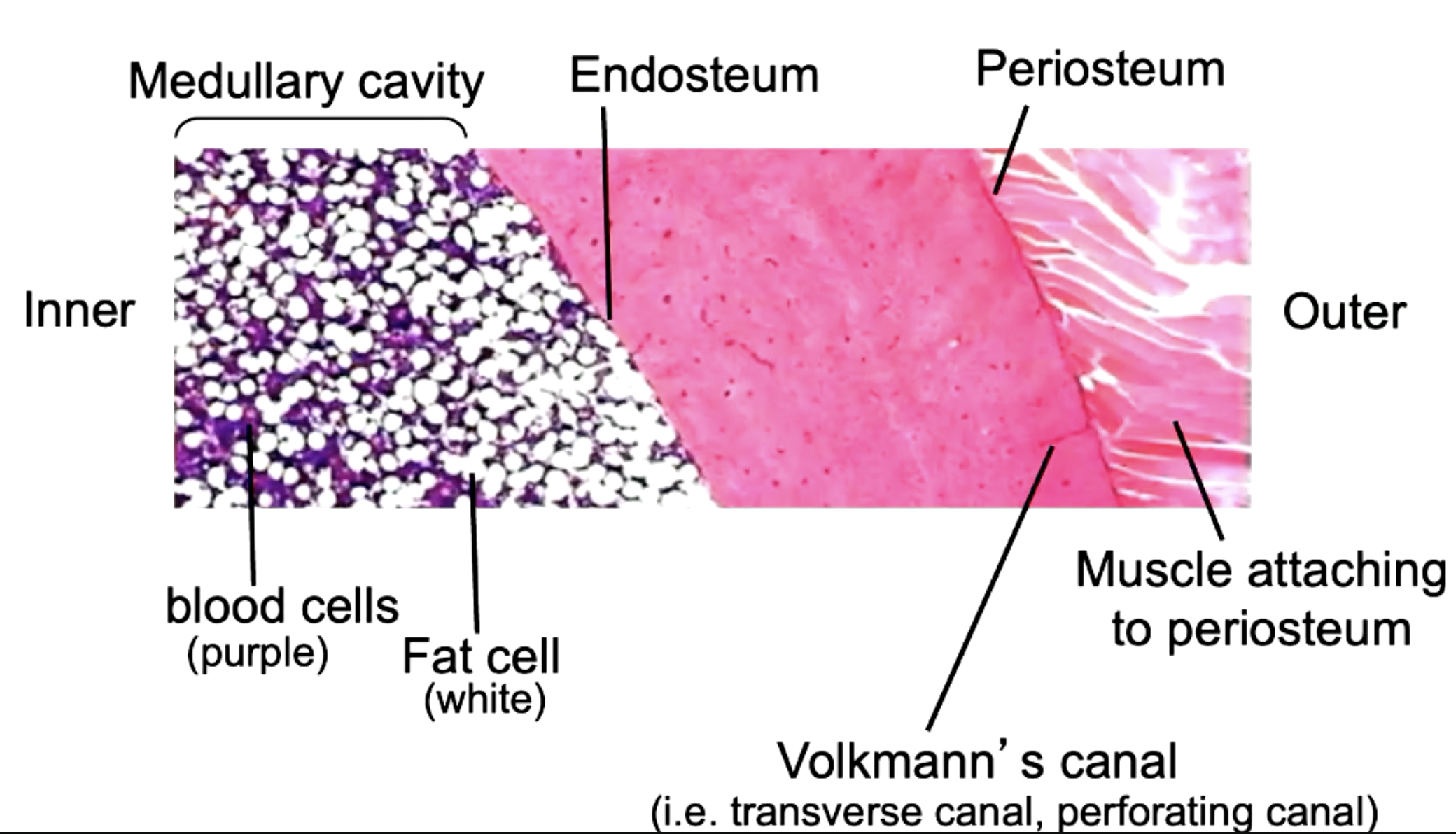
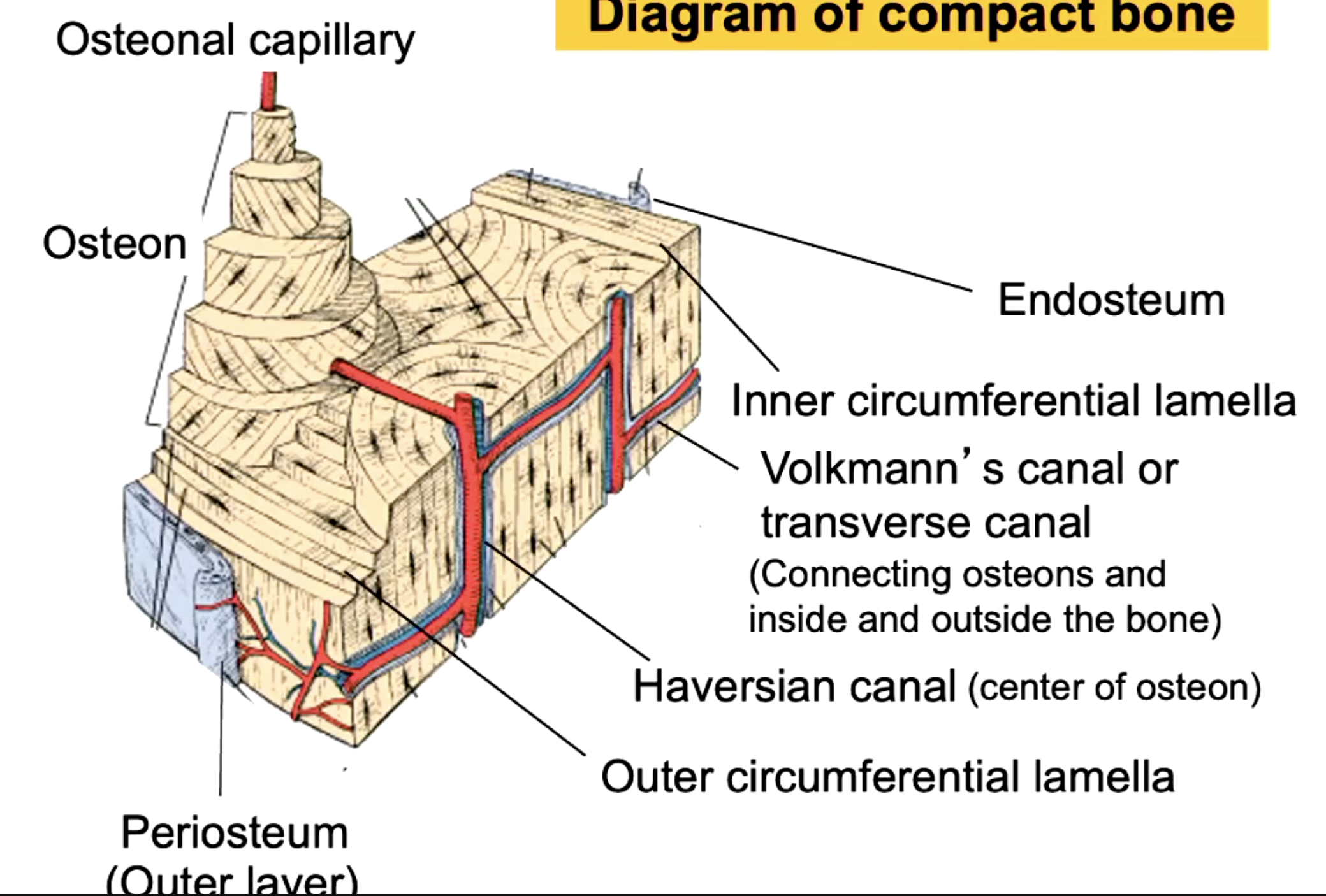
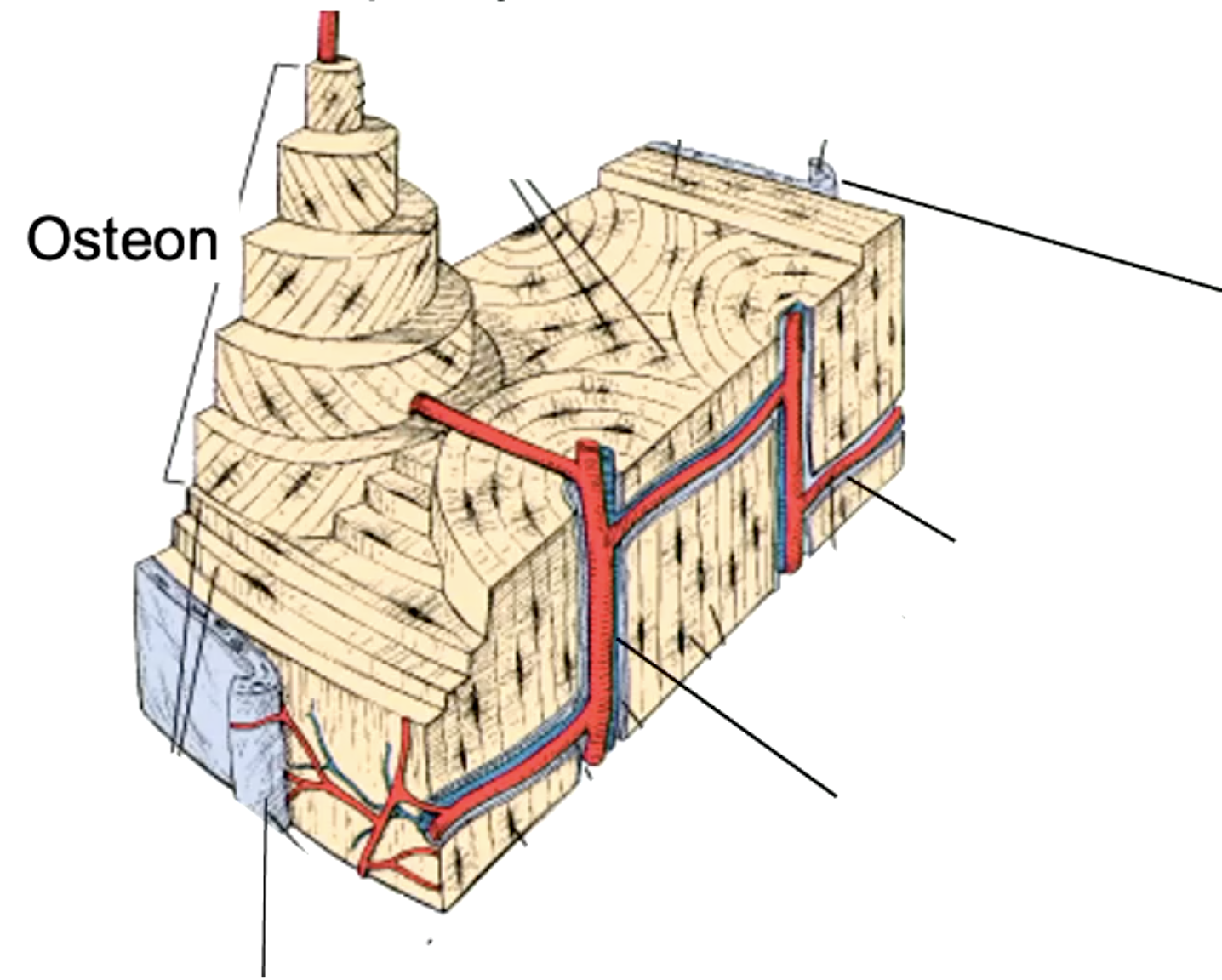
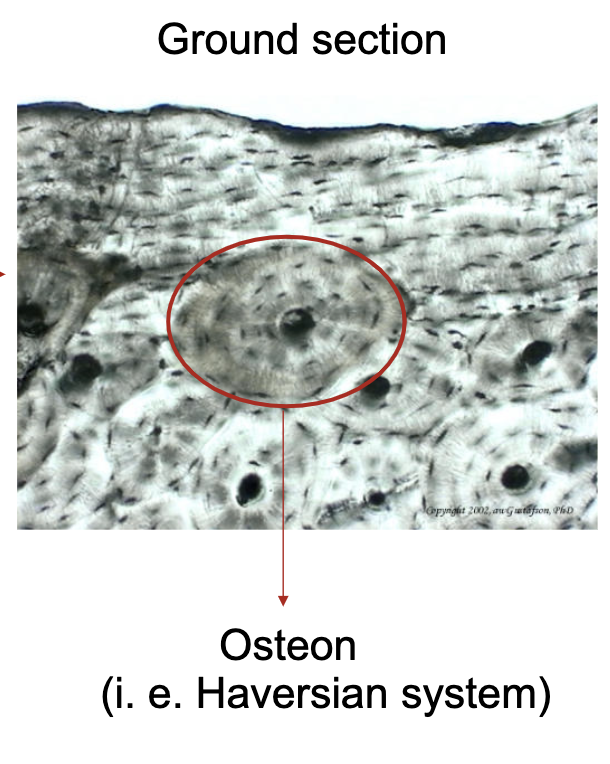
label the parts of the ground section of compact bone
how does compact bone get nutrients?
osteonal capillary (blood vessels)
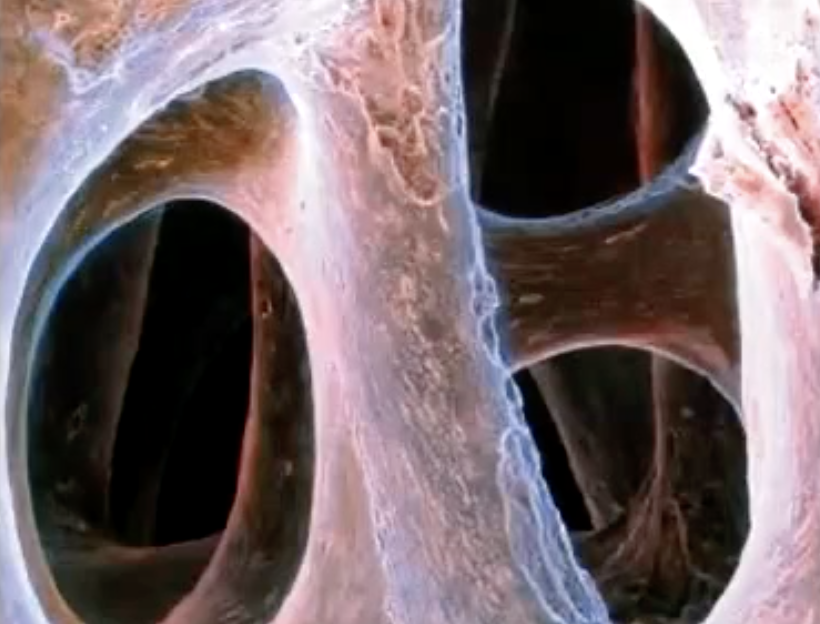
what is this
spongy bone
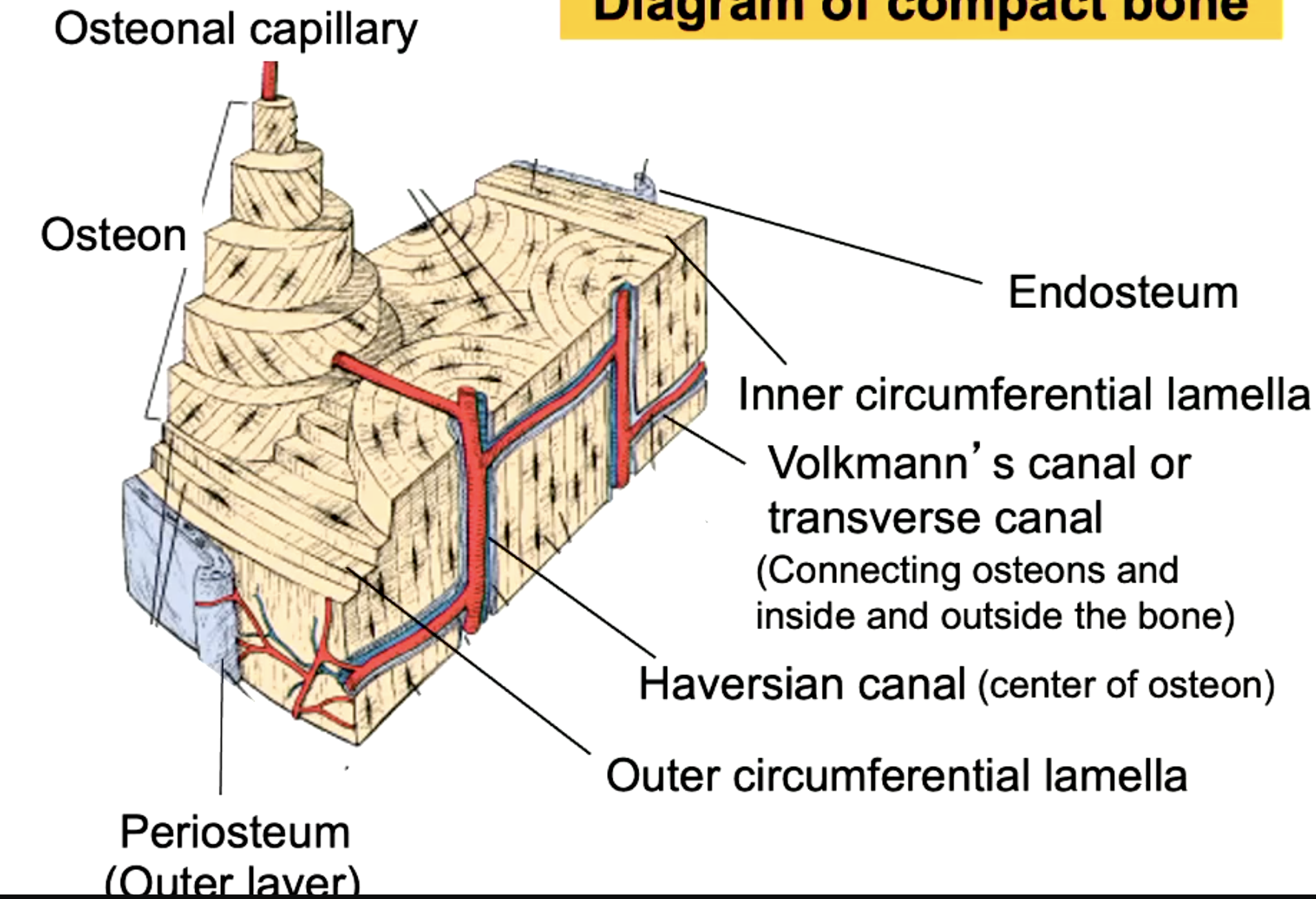
label the parts of the compact bone
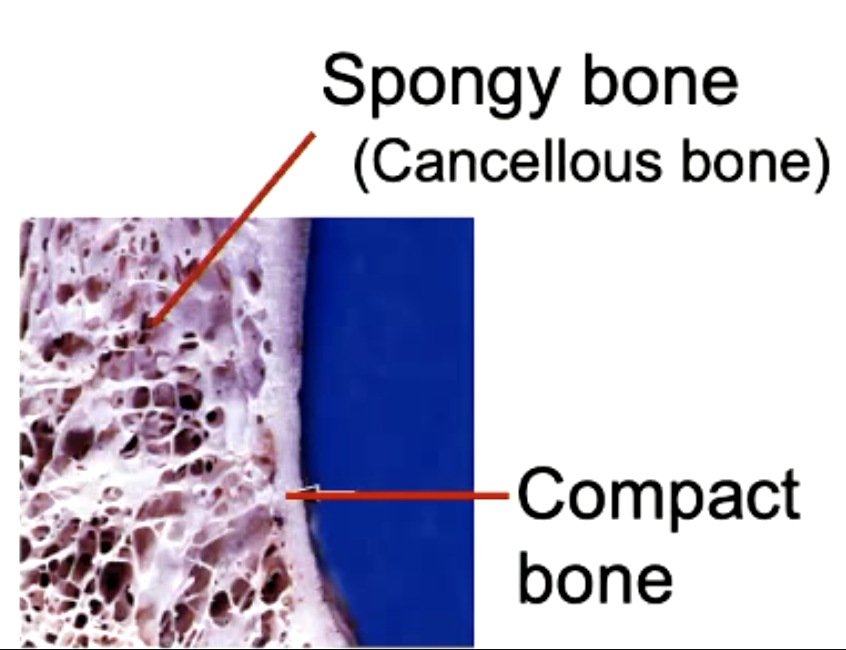
spongy bone has a ____________ matrix but it does NOT have
lamellated
Haversian or interstitial lamellae
how do nutrients get into spongy bone?
diffusion
bone organ refers to
bone tissue, hemopoietic tissue, fat tissue, blood vessels, nerves, articualr cartilage
identify the different types of bone
types of growth for bone?
appositional
types of growth in cartilage
appositional and interstitial
bloody supply for cartilage
avascular
blood supply for bone
vascular
Paget disease is caused by
overactive osteoclast
osteopetrosis is caused by a defect in
osteoclast function (little bone resorption)
osteoporosis is caused by a decrease in
osteoblast activity
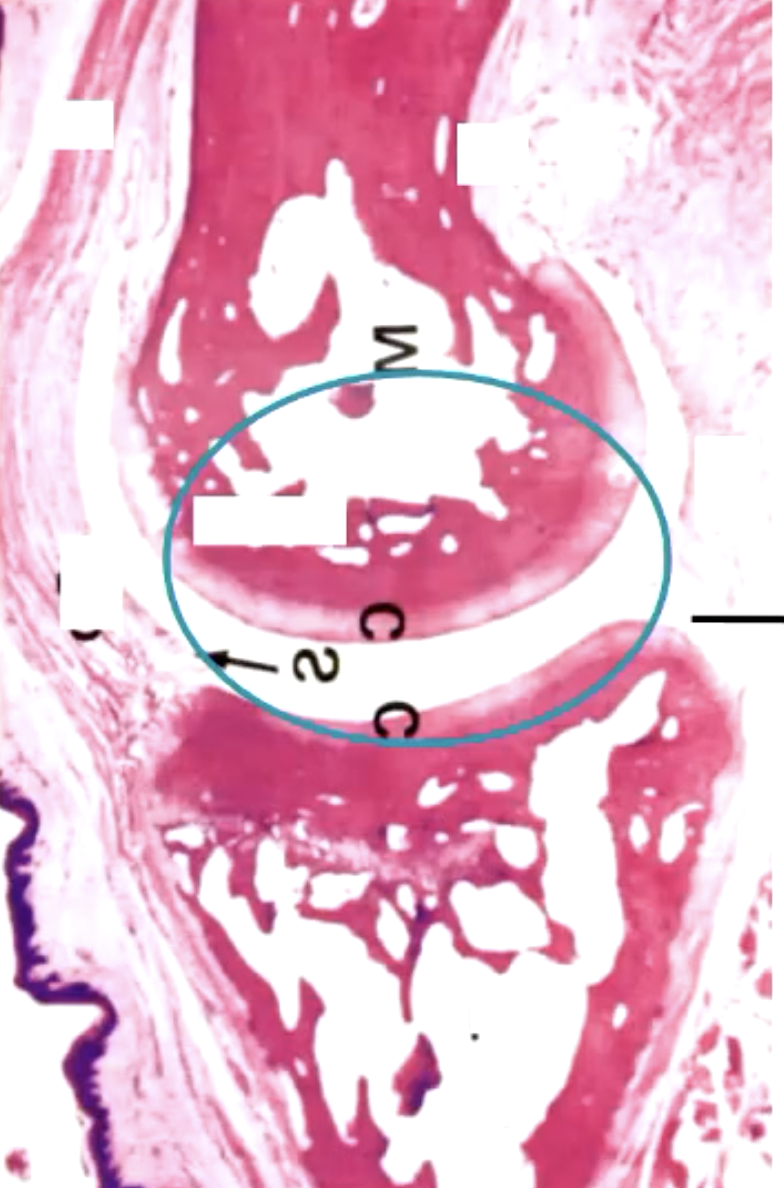
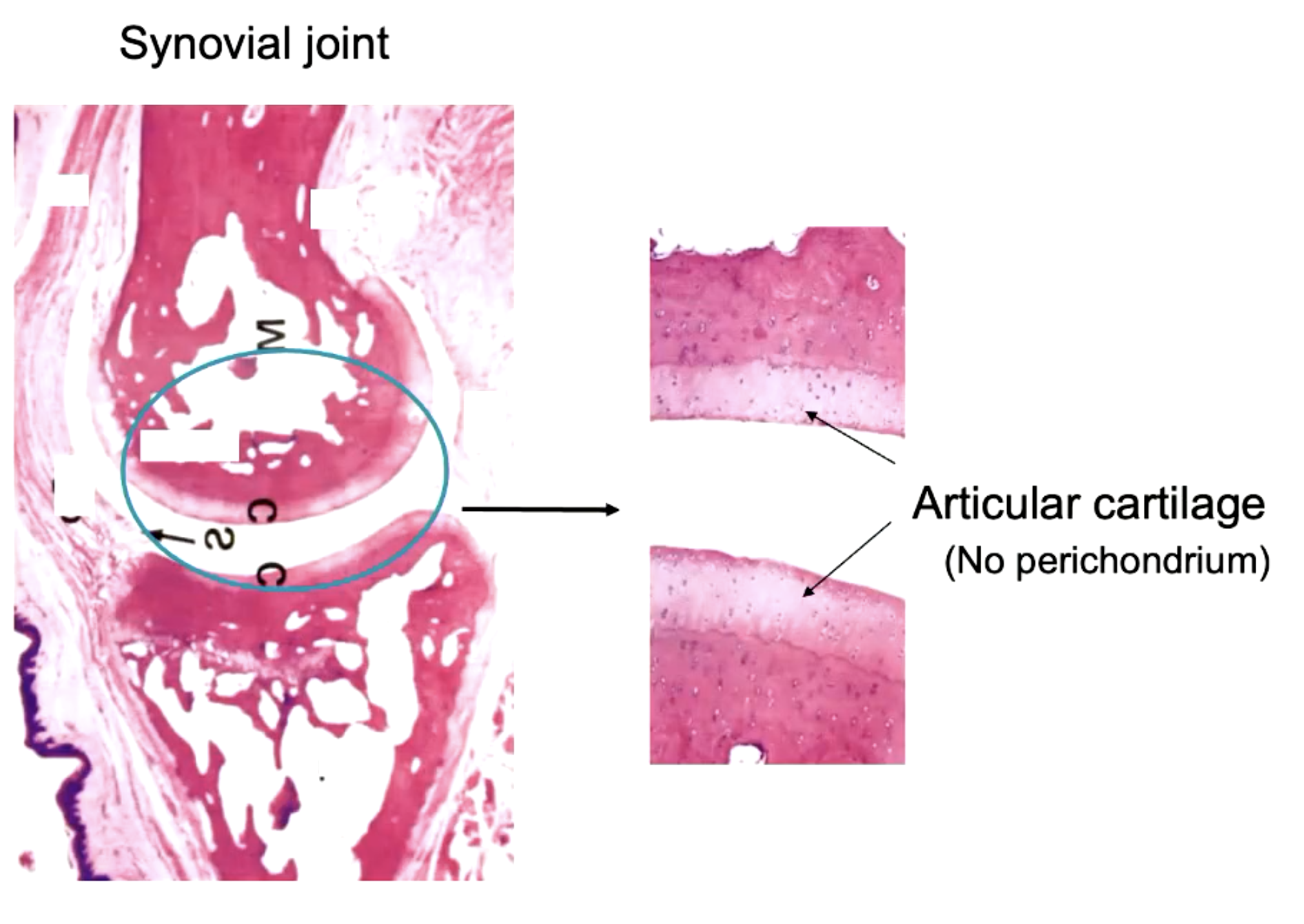
what is this?
synovial joint (specialized adult CT)
what kind of cartilage is found in the synovial joint?
articular cartilage (no perichondrium)
herniated disc is caused by defect in the
fibrocartilage
osteoarthritis is caused by defect in
hyaline carilage (degradation of articular cartilage)
osteoarthritis is caused by
overuse and mechanical stress
hyaline cartilage is found in
fetal, articular respiratory, costal rib
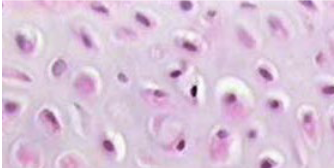
hyaline cartilage function
resist compression cushioning
hyaline cartilage matrix
collagen II
aggrecan (lots of bound water)
which types of collagen have perichondrium?
hyaline (except articular)
elastic
what is perichondrium?
fibrous covering on top of cartilage tissues
what is appositional growth?
from perichondrium, form at surface
increases in girth
what is interstitial growth
cell division within matrix
increases length and girth
isogenous groups
descendants from a single cell
fibrocartilage is a combination of
dense connective tissues and hyaline cartilage
portion of the nucleus pulposus protrudes into the intervertebral foramen, pressing on one of the spinal nerves in the process
herniated disc
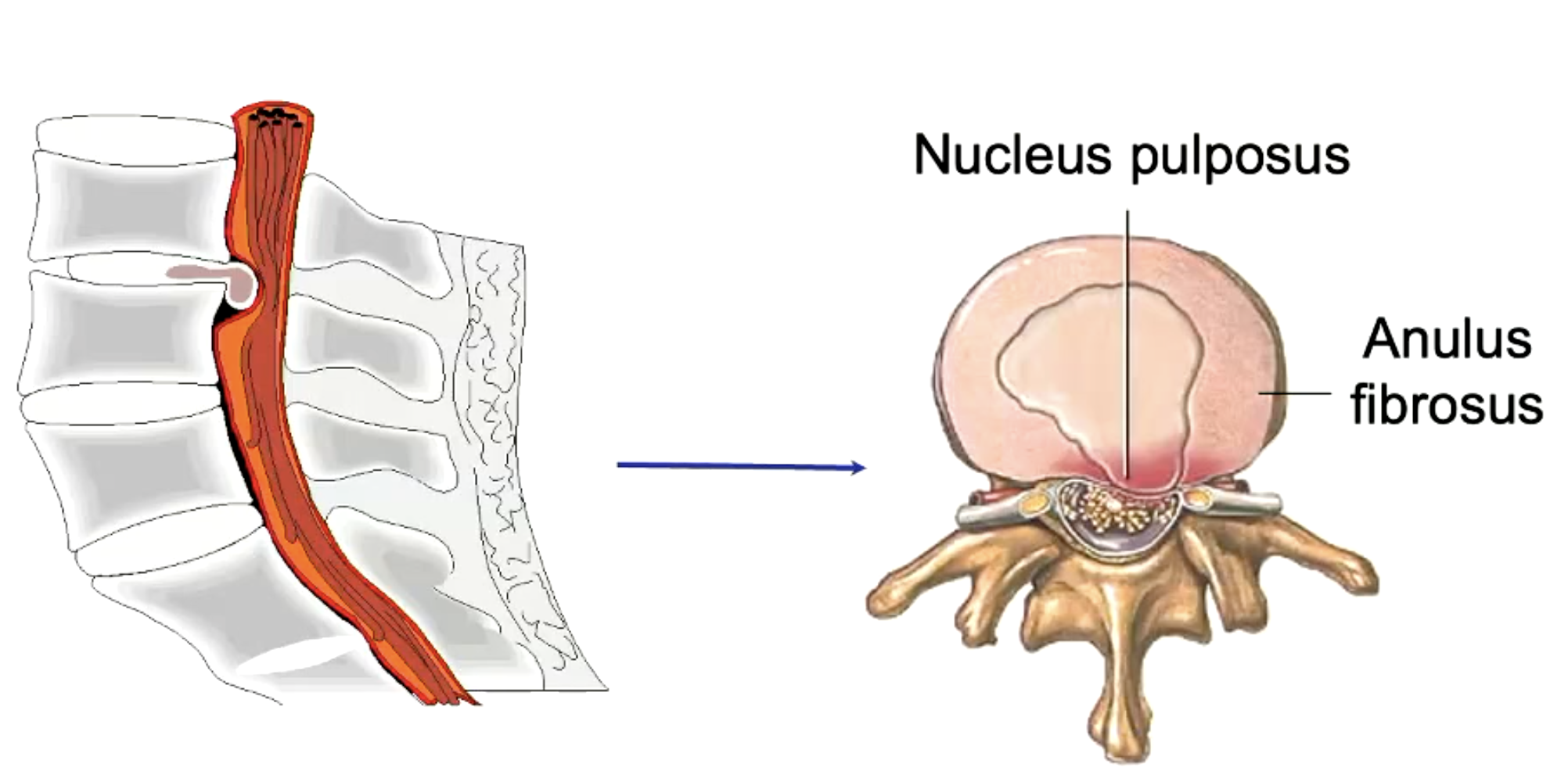
what is the outer component vs inner component of the intervertebral disc called
outer: anulus fibrosus
inner: nucleus pulposus
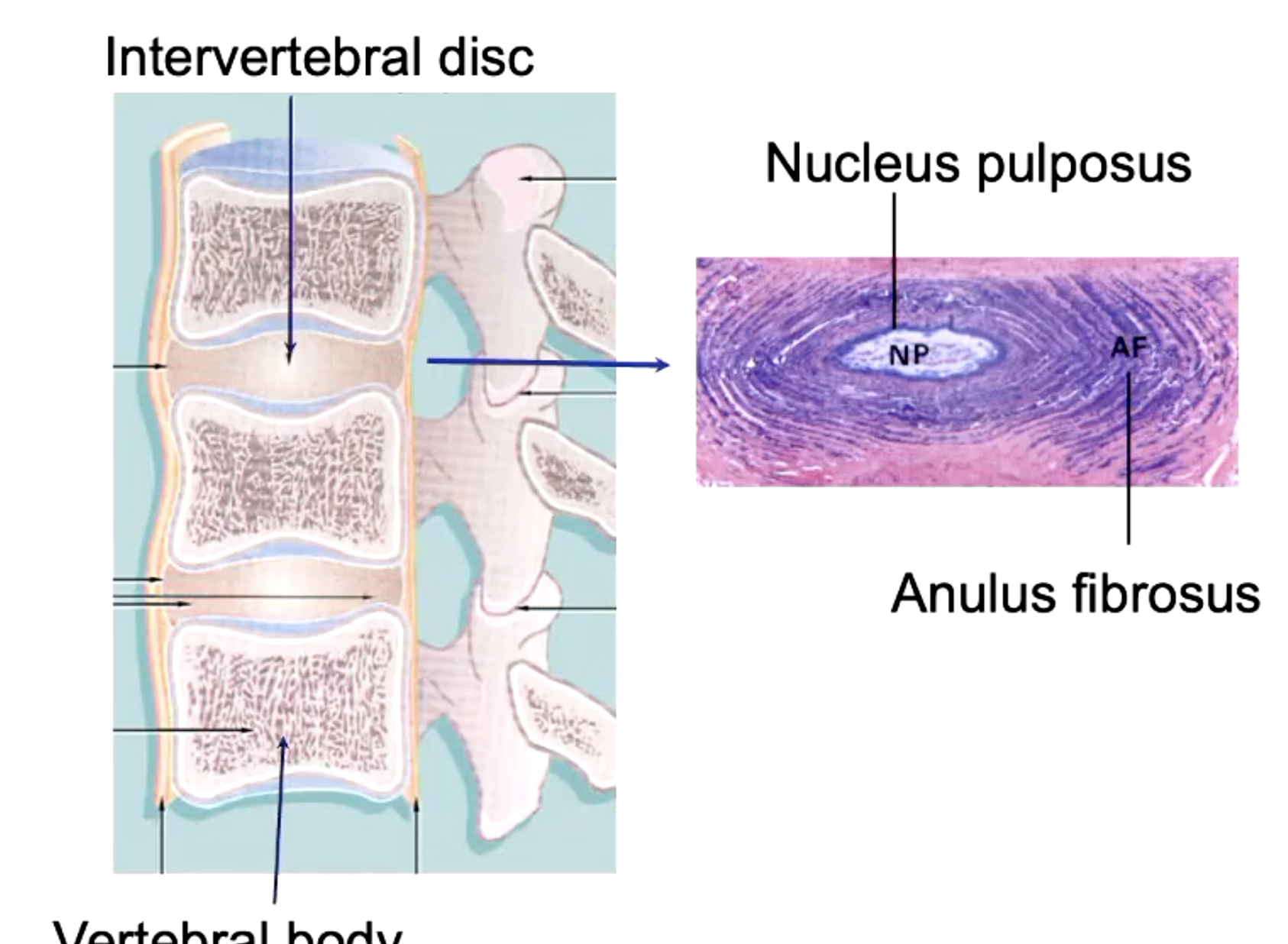
arthritis is caused by
degradation of articular cartilage
elastic cartilage location
ear, larynx (epiglottis)
elastic cartilage function
flexible support
elastic cartilage matrix
collagen II
aggrecan
elastic fibers
fibrocartilage location
IVC, mensicus, TMJ
fibrocartilage function
resist compression
resist shearing forces
fibrocartilage matrix
collagen II
collagen I
versican, aggrecan
what are organic and inorganic components of bone extracellular matrix?
organic: collagen I + proteoglycan
inorganic: hydroxyapatite
function of bone
support
calcium & phosphate storage
mature compact bone is composed of
osteons (Haversian system)
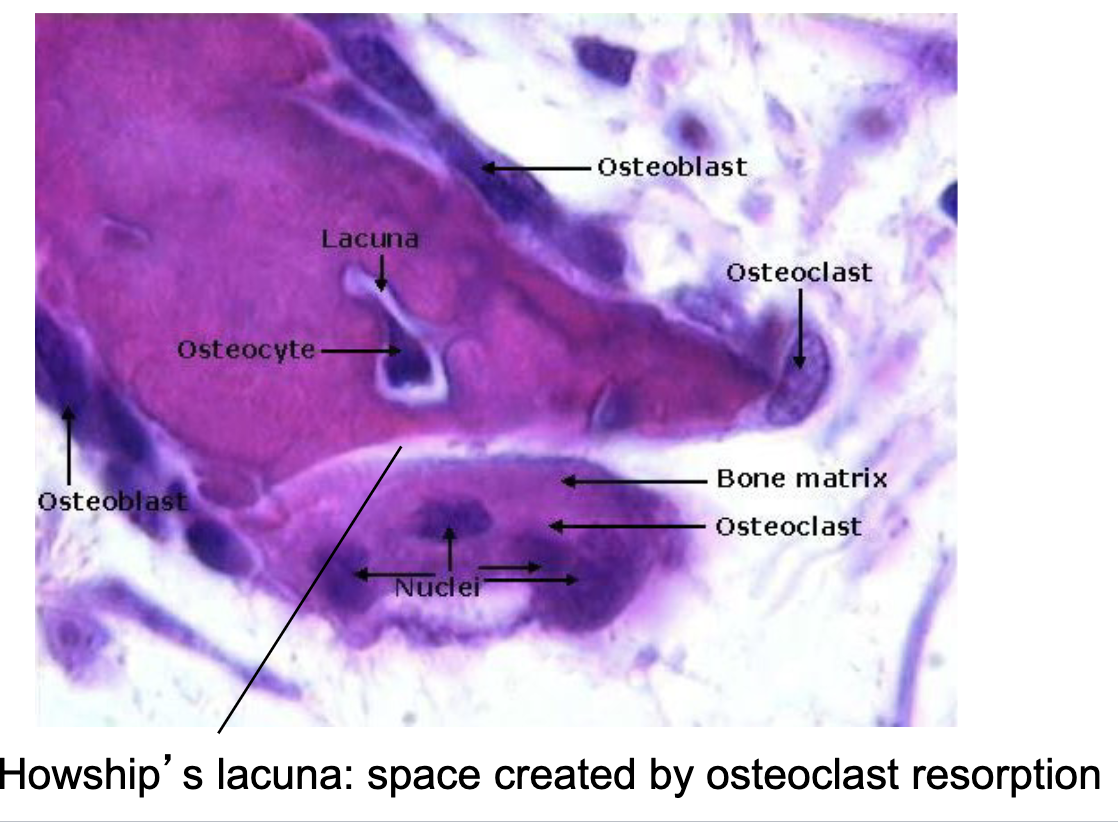
what are the bone making cells?
osteoprogenitor cells
osteoblast
osteocyte
what are the bone resorption cells?
osteoclast
space created by osteoclast resorption is called
Howship’s lacuna
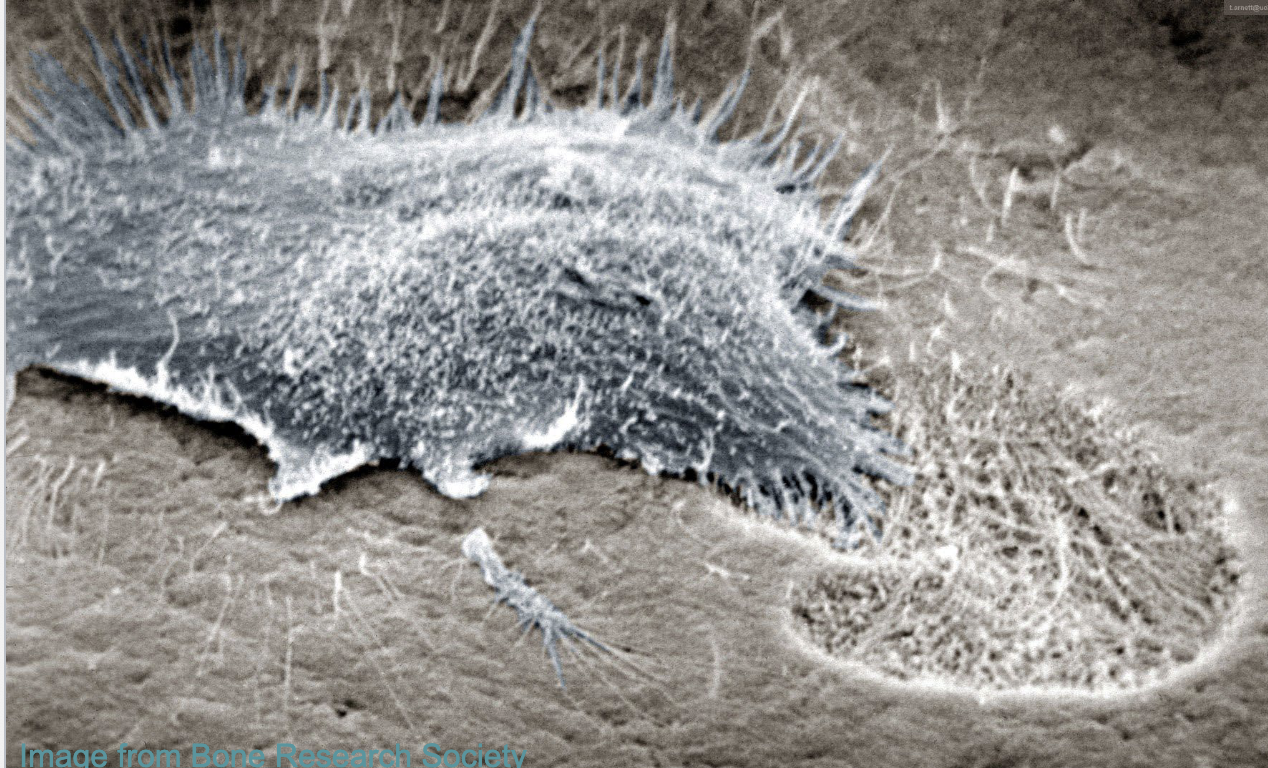
what is this?
scanning EM of osteoclast
describe the steps of resorption in localized areas.
decalcify through acidification
degradation of bone matrix
clean up: recycle (endocytosis)
identify the bone disease:
low bone mass, structure deterioration of bone tissue
bone fragility and more susceptible to fracture
osteoporosis
identify the bone disease:
increased bone mass, due to defect osteoclast function
bone fragility (susceptible to fracture)
unerrupted teeth
osteopetrosis
identify the bone disease:
increased bone remodeling, overactive osteoclast
softer bone (susceptible to fracture)
paget disease
osteoporosis can be caused by high dose treatment of
corticosteroid
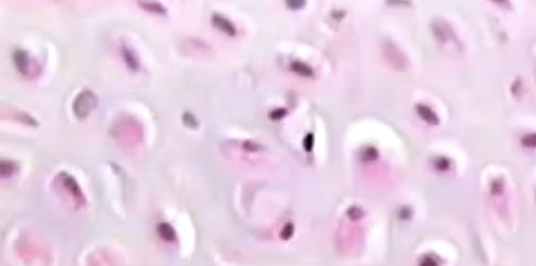
what is this?
hyaline cartilage

what is this?
elastic cartilage
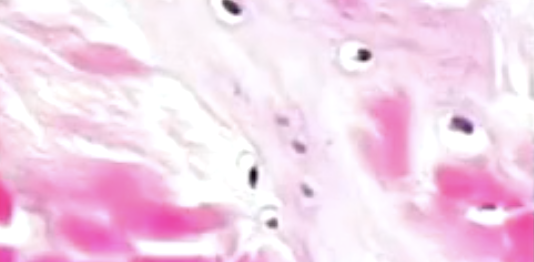
what is this?
fibrocartilage
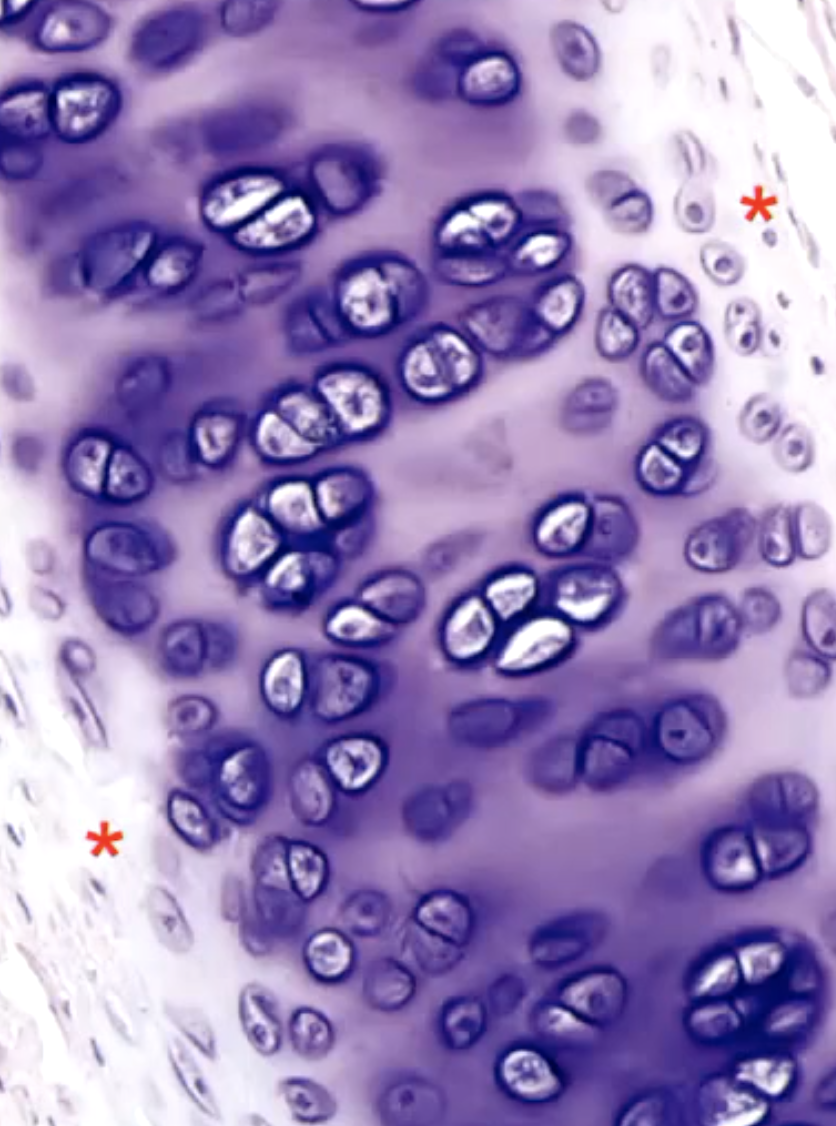
hyaline