Lab #3 Review - Osmosis
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lab #3 Review Terms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Osmosis
Passive process (no ATP spent), water molecules move from one crowded area to an area where are more spread apart
Concentration Gradient
When two areas have different concentrations of dissolved substances
Tonicity
Ability of a solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water
Osmolarity
Total solute concentration, tonicity is based on this
Hypertonic
Solution has a relatively higher solute concentration
Hypotonic
Solution has a lower solute concentration
Isotonic
Solutions of equal solute concentration
Water movement
Water moves out of hypotonic solution to a hypertonic solution
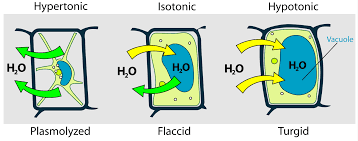
Plasmolysis
Process involving a plant cell losing water content and therefore contracting and shrinking its cytoplasm and plasma membrane away from the inside of its cell wall
Turgid
a cell that is swollen and firm due to being filled with water
Osmosis effect on Plant Cells
Central Vacuoles
Found in plant cells, stores water and dissolved sugars
Salt Concentration
Influences plant cell osmosis
Diameter of Central vacuole OR diameter of plasma membrane
Internal structure to measure to indicate changes that occur within the cell under varying salt concentrations
Elodea
Cells tightly packed together like bricks in a wall, rectangular shaped cells, not free swimming (non-motile), green color
Euglena
Single, isolated, fully motile cells move through aquatic environment with flagellum. Protists, greenish-blue. No cell wall, flexible pellicle under plasma membrane.
If a cell has a smaller SA & Volume, it is able to supply the greatest proportion of its volume with nutrients. Larger cell would be a risk of starving.
Surface Area/Volume & Feeding Efficiency
Increase in size, decrease % fed
as cells get larger, their Volume increase at a faster rate than do their surface area, thus feed and remove waste less efficiently
As cell increases in size, how does the portion of the cell that receives nutrients change?
Sa/V ratios need to be large enough to sustain high transport/exchange of efficiencies
As cells grow larger, they can either… 1. divide into 2 smaller cells. 2. grow thin cellular extensions that maximize surface area
Why is cell size limited?