Introduction to Accounting and Business (Video) - Key Terms
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Service
A type of business that provides intangible services rather than physical goods.
Retail
A business that sells goods directly to end customers for personal use.
Manufacturing
A business that produces goods from raw materials and components for sale.
Operating activities
Activities related to the day-to-day operations of a business.
Investing activities
Activities that involve acquiring or disposing of long-term assets and investments.
Financing activities
Activities that raise capital and repay lenders or owners.
Role of Accountants
Provide information to users, assess information needs, design information to fit users’ needs, record economic data, and prepare accounting reports.
Goal of Accounting
Record, report, and interpret economic data for decision makers.
Owner
The person who has an ownership interest in a business.
Investors/Stockholders
People or entities that own shares and are interested in the profitability and value of the investment.
Bankers
Lenders who provide financing and assess creditworthiness of the business.
Governmental agencies
Regulatory bodies that use financial information for oversight and compliance.
Managers
Internal decision makers who use accounting information to plan, organize, and control operations.
Employees
Individuals who work for the business and may be affected by its financial performance.
Customers
People who purchase goods or services and rely on the business’s stability and reliability.
Competitors
Other firms in the same market that are analyzed for performance comparisons.
Financial accounting
Field focused on recording, summarizing, and reporting financial information for external users.
Auditing
Independent examination of financial statements and related disclosures.
Management accounting
Information used internally to aid planning, controlling, and decision making.
Cost accounting
Analysis of production costs to help control and price goods or services.
Tax accounting
Planning and compliance with tax laws and regulations.
Accounting systems
Methods and processes for collecting, processing, and reporting accounting information.
International accounting
Accounting across borders, including IFRS and cross-border standards.
FASB
Financial Accounting Standards Board; sets U.S. GAAP standards.
GAAP
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles; the framework for financial reporting in the U.S.
SEC
Securities and Exchange Commission; U.S. regulator of securities markets and disclosures.
IFRS
International Financial Reporting Standards; global accounting standards.
Proprietorship (sole proprietorship)
A business owned by one person; simple structure and often unlimited liability.
Partnership
A business owned by two or more people who share profits, losses, and responsibilities.
Corporations
A separate legal entity owned by shareholders with limited liability and potential to raise capital by stock.
Monetary unit assumption
Financial reports are expressed in a single monetary unit or currency.
Time period assumption
Financial statements are prepared for a specific, regular time period (e.g., a year).
Business entity assumption
Economic activity is reported for the business as a separate entity from its owners.
Going concern
Assumes the business will continue operating in the foreseeable future.
Measurement principle
Determines the amount that will be recorded and reported.
Historical cost
Report cost at the purchase price or cost
Report cost at the purchase price or cost
Revenue is recorded when earned (when goods or services are delivered) not necessarily when cash is received
Expense recognition
Requires expenses to be recorded in the same period as the related revenue.
Accounting Equation
Assets = Liabilities + Owners Equity or (Stockholders’ Equity)
Accounting Equation
Assets – Liabilities = Owner’s Equity (Stockholders’ Equity)
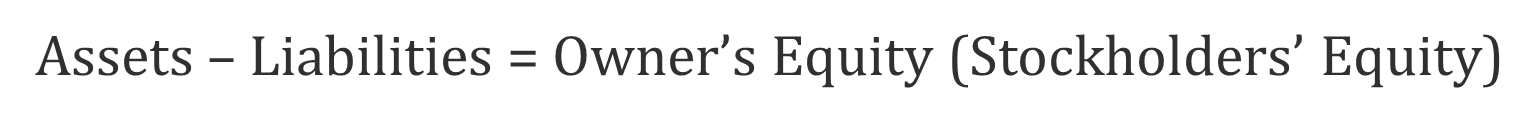
Assets
•Resources owned and used by a business
Liabilities
Debt that a business owes to creditors, representing financial obligations.
Owner’s Equity
What is left or the residual value when the assets are use to pay off all the business debts
Asset accounts
All accounts have a debit and credit side. The debit is on the left and the credit is on the right. Assets increase on the debit side and decrease on the credit side.

Liabilities
•All accounts have a debit and credit side. The debit is on the left and the credit is on the right. All liabilities increase on the credit side and decrease on the debit side.
Owner’s Equity
All accounts have a debit and credit side. The debit is on the left and the credit is on the right. Owner’s equity increases on the credit side and decreases on the debit side.
Owner Equity Accounts that increase Owner’s Equity and credit side
Capital Stock
Retained earnings
Revenue
Owner Equity Accounts that decrease Owner’s Equity and increase on the debit side
Expenses
Dividends
Four Financial Statements
Income statement, Statement of Stockholders’ Equity, Balance sheet, Statement of Cash Flow
Income Statement
Expenses and Revenues
Statement of Stockholders’ Equity
Capital Stock and Retained Earnings (Net Income – Dividends)
Balance Sheet
Assets, Liabilities, Stockholders’ Equity
Statement of Cash Flow
Use and receipt of cash
What are Ethics
Moral principles
Integrity
Conscience
Beliefs
Values
Honesty
Fairness
Role of Ethics in Accounting
Objective to provide:
Relevant information
Timely information
Decision makers
Trustworthy information
Managers
Operations
What causes the downfall in
Ethics?
Failure of Individual character and Culture of greed and ethical indifference