Kin Exam
1/136
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 1: Principles and Terminology Chapter 2: The Skeletal System Chapter 3: The Muscular System Chapter 4: Joints Mechanics and Injuries Chapter 5 - Energy Systems & Muscle Fiber Types Chapter 6 - Nervous System Chapter 7 - Cardiovascular & Respiratory Systems UNIT2: Chapter 10 - Nutrition and Performance Chapter 11 - Performance Enhancing Substances Chapter 13 - Training Principles and Methods
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
origin of sternocleidomastoid (neck)
sternum and clavicle
insertion of sternocleidomastoid
mastoid process
function of sternocleidomastoid
Flexes head and rotates head
origin of splenius
C4,5,6,7\upper thoracic cavity
insertion of splenius
nuchal line\c1,2,3
function of splenius
rotates head and neck
origin of diaphragm
sternum: costal cartilage,lumbar vertebrae
insertion of diaphragm
central tendon
function of diaphragm
Increase thoracic volume, decrease pressure in cavity to draw air in
origin of intercostal muscles
inferior ribs
insertion of ribs
superior ribs
origin of rectus abdominis
pubic crest and symphysis pubis
insertion of rectus abdominis
xiphoid process, inferior ribs (costal cartilages 5-7)
function of rectus abdominis
flexes trunk, aids in expiration, pushing actions
origin external oblique and transversus abdominis
lower 8 ribs
insertion of external oblique and transversus abdominis
illac crest, linea alba,pubis
function of external oblique and transversus abdominis
flex, rotate vertebral column, compress abdomen
origin of pectoralis major
clavicle, sternum, ribs 1-6
insertion of pectoralis major
intertubercular groove of humerus
function of pectoralis major
Internal rotation, adduction and flexion of arm
origin of latissimus dorsi
lower thoracic vertebrae, lumbar, crest of ilium, sacrum
insertion of latissimus dorsi
intertubercular groove of humerus
function of latissimus dorsi
extends, adducts, and medially rotates arm
origin of supraspinatus
posterior scapula, supraspinous fossa
insertion of supraspinatus
greater tubercle of humerus
function of supraspinatus
stabllizer shoulder, adducts shoulder, laterally rotates shoulder
What does ATP stand for?
Adenosine triphosphate
What does it do?
Stores chemical energy used to fuel cellular processes.
What does it consist of?
Three phosphate attached to one adenosine by sugar molecule
Enzyme that breaks apart the bonds
ATPase
What is the anaerobic system used for?
Used for quick and powerful movements but does not last long.
When does the aerobic system begin?
After anaerobic systems is used up.
Where does the aerobic system occur and what is its function?
Occurs in Mitochondria and helps break down fats and proteins once carbohydrates have been used.
What are the three metabolic pathways
ATP-PC Pathway (anaerobic alactic)
Glycolysis (anaerobic lactic)
Cellular Respiration (aerobic)
How long does ATP-PC last?
10-15 seconds
What does PC stands for?
Stands for Phosphocreatine
What is Phosphocreatine?
A high energy molecule similar to ATP, PC will lose phosphate and release a large amount of energy.
Chemical Formula
PC+ADP= ADP+ Creatine
What events would use this pathway?
Sprints, jumping, hitting a ball, series in football
This system generally kicks in once the ATP-PC system is used up
Glycolysis
How long does glycolysis last?
1-3 minutes
(Fill in) During this process, glucose is partially broken down to provide _ ATP per glucose
2
Where does it occur and does it require oxygen?
Occurs in the cytoplasm and does not require oxygen.
What event pathway use this pathway?
Boxing, hockey shift, short distance running.
Main byproduct of Glycolysis
Pyruvic Acid
What is pyruvic acid converted into?
Lactic acid without the presence of oxygen
This system comes into play after 90 seconds of activity and also known as cellular respiration
Aerobic System
Energy sources:
Fats and proteins
Fill in: Oxygen is present in these reactions and they occur in _______.
Mitochondria
Cellular Respiration 3 pathways:
Glycolysis, Kreb’s cycle, Electron Transport Chain
Takes the high energy electrons and produces large amounts of ATP with water and carbon dioxide as its by products.
Electron Transport Chain
A series of 8 reactions yields 2 ATP, plus compounds (FADH2, NADH) which have high energy electrons, they are sent to the next pathway.
Kreb’s cycle
Pyruvate from the previous pathway is converted into Acetyl-Coa since oxygen is present, which is sent to the Kreb’s cycle (citric acid cycle)
Glycolysis
A protein called ____ stores and delivers oxygen in working muscles.
Myoglobin (muscles with higher amount of myoglobin can perform for a longer time)
Red or dark in colour and small in diameter
Slow-Twitch Muscles FIbres
Pale appearance and large in diameter
Fast-Twitch Muscle Fibres
Nervous System
Major components of Nervous System
Central Nervous System, Peripheral Nervous System
Made up of the brain and spinal cord, involuntary system
Central Nervous System
The rest o f the body, this includes both voluntary and involuntary movements
Peripheral Nervous System
Control center for this system, controls activities necessary for human survival
Brain.
Fill in: The _______ _________ provides a passway for nerves to travel to organs and tissues
Vertebral column
6 main components of brain:
Cerebrum, Cerebellum, Brain stem, Diencephalon, Limbic System, Reticular Activating System
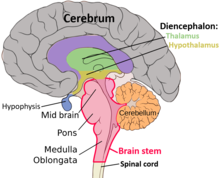
Cerebrum is the largest component and…
is responsible for intelligence, controls motor and sensory activities
controls muscles movement and balance
Cerebellum
Links with the cerebrum
Brain Stem
Helps with muscle tone and eye movement
Brain Stem
Includes the thalamus (screens incoming signals, pain response) and the hypothalamus (controls body temperature, appetite, emotions)
Diencephalon
within the cerebrum regulates behaviours needed for survival
Limbic System
through the cerebral cortex, directs information,maintains consciousness
Reticular Activating System
Consists of the parts of the nervous system that lie outside the central nervous system
Peripheral Nervous System
It includes 12 cranial nerves and ______ pairs of spinal nerves
31
_____________ or ___________ carry signals away from the central nervous systems to the body.
Efferent or motor nerves
___________ or ____________ carry signals from sensory receptors to the central nervous system.
Afferent or sensory nerves
The peripheral nervous system consists of both _________ and _________ components
autonomic (involuntary) and somatic ( voluntary) components
In which system are involuntary muscle contractions regulated?
Involuntary muscle contractions are regulated by the autonomic system
Two branches which work together to prepare the body for emergencies or return to regular functioning.
Sympathetic system and Parasympathetic system
prepares the body for emergencies by releasing adrenaline, increasing the heart rate and dilating blood vessels.
Sympathetic system
returns everything back to normal once the threat is over
Parasympathetic system
Allows us to cope with our every changing environment and react accordingly.
Somatic Nervous System
What nerves does it contain?
afferent and efferent nerves
_______ nerves send information to the central nervous system
Afferent nerves
_______ nerves send instructions to the skeletal muscles.
Efferent nerves
Both autonomic and somatic systems often together?
Yes. ( Start of sprint race)
Some reflexes are controlled by the _______ _________ involving smooth and cardiac muscles such as digestion, elimination, blood pressure and sweating.
Autonomic System
Other reflex are ______ and involves skeletal muscles and don’t require the brain to coordinate the response
Somatic
The ______ ___ is a name given to the pathways an initial stimulus travels in order to coordinate a response
Reflex arc
Brain is involved in this type of reflex
False. Brain is not involved.
5 Main parts of refex arc
Receptor, Sensory (afferent) Nerve, Intermediate Nerve Fibre, Motor (Efferent) Nerve, Effector Organ
receives the initial stimulus
Receptor
carries the impulse to the spinal column
Sensory (Afferent) Nerve
Interprets the signal and issues a response
Intermediate Nerve Fibre
carries the response from the spinal cord to the muscle/organ
Motor (Efferent) Nerve
generally a skeletal muscle will carry out the response
Effector Organ
involves golgi tendon organs which are sensory receptors that end where tendons join muscle to bone. These receptors sense a change in tension and cause the muscle to relax preventing injury
Tension Reflex
occurs when am arm or leg automatically compensates for the reflex action of another arm or leg. This involves multiple synapses and muscle and groups, therefore is classified as a polysynaptic reflex.
Crosses-Extensor Reflex
Cardiovascular System
Cardiovascular system is compromised of 3 parts:
blood vessels,blood and the heart
Main functions of cardiovascular system:
Delivery of oxygen and nutrients
removal of carbon dioxide and other waste products
Maintenance of constant body temperature
Prevention of infection
Arteries
carry oxygenated blood (with the exception of the pulmonary artery), have thick walls to withstand high pressure flow, blood is bright red in colour, carry blood AWAY from the heart.