NS 4410 HTN Lecture A
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
Clinical Signs/symptoms of HTN it is a “Silent Killer” why?
Most common clinical signs/symptoms are that there are no symptoms
After a long asymptomatic period, persistent hypertension develops into complicated hypertension with end-organ damage to ____ and small arteries of what four areas?
aorta
heart
kidneys
retina
CNS
Patients may present with symptoms/signs of?
end stage organ damage (CVD, stroke, kidney disease, retinopathy)
Note: The best evidence indicates that high blood pressure does not cause?
headaches, dizziness or nosebleeds
Hypertensive Crisis: High Blood Pressure (_____) + Symptoms of what 7 things? is a medical emergency, call 911
(> 180/120);
chest pain,
shortness of breath,
back pain,
numbness,
weakness,
change in vision,
difficulty speaking
What is Blood Pressure
pressure exerted by the blood on the arterial walls
Systolic BP/ Diastolic BP
Arterial BP varies with contractions of the heart: What is Systolic BP?
peak pressure exerted by blood on arterial walls during systole (contraction phase of the cardiac cycle)
Arterial BP varies with contractions of the heart: What is Diastolic BP?
minimum pressure exerted by blood on arterial walls during diastole (relaxation phase of cardiac cycle)
What tools do we use to measure BP? What are the units of BP?
manual sphygmomanometer (blood pressure cuff) and stethoscope or automated oscillometric BP device
mmHg
Best Practices for Accurate In-Office Blood Pressure Measurement

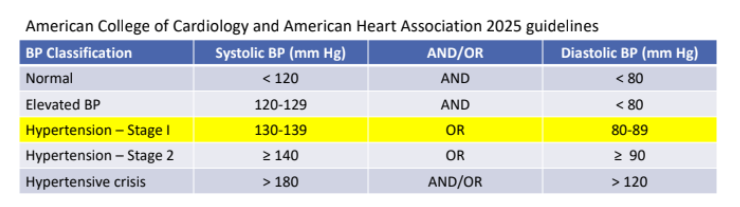
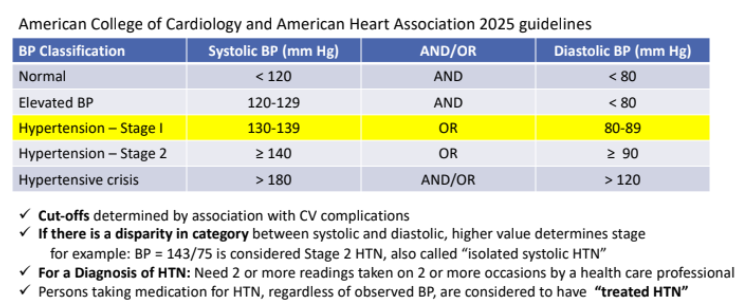
Classification of Blood Pressure: Cut-offs determined by association with?
CV complications
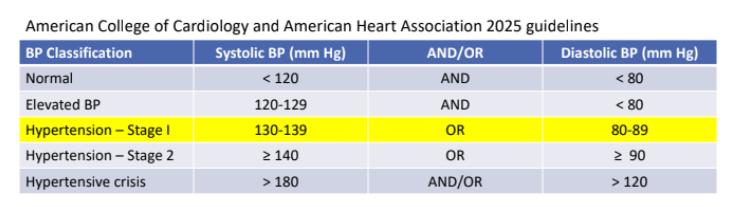
If there is a disparity in category between systolic and diastolic, what determines the stage?
the higher value
for example: BP = 143/75 is considered Stage 2 HTN, also called “isolated systolic HTN”
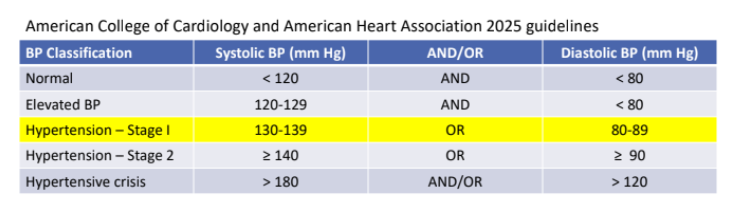
For a Diagnosis of HTN, how many readings do we need?
Need 2 or more readings taken on 2 or more occasions by a health care professional
Persons taking medication for HTN, regardless of observed BP, are considered to have?
“treated HTN”
Hazard ratios for Cardiac Outcomes
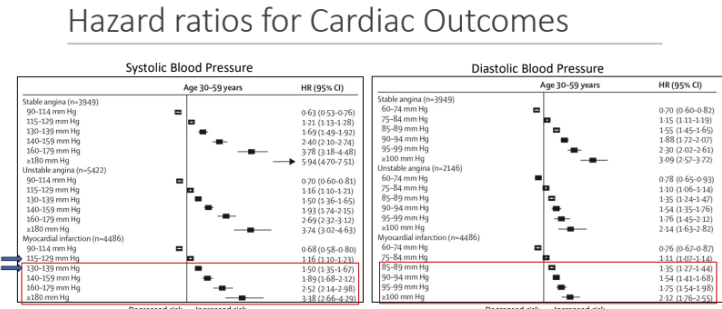
What is the most prevalent and modifiable risk factor for the development of Cardiovascular Diseases.
high blood pressure
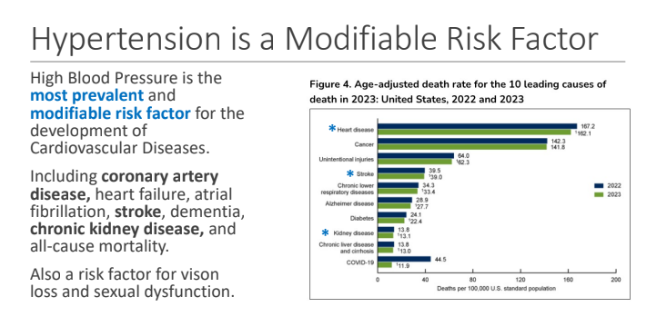
High blood pressure is also a risk factor for what two things?
Vision loss
Sexual dysfunction
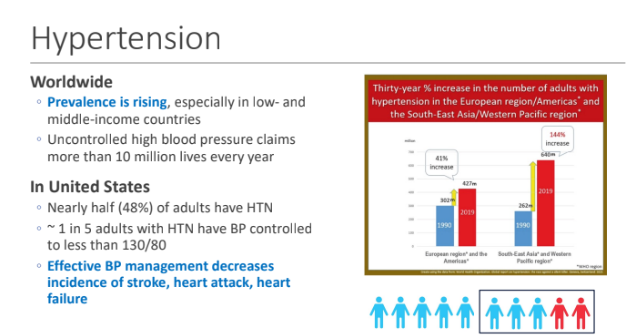
Hypertension Worldwide: Prevalence is rising, especially in?; Uncontrolled high blood pressure claims more than_____ lives every year
low- and middle-income countries; 10 million
In United States Nearly half (48%) of adults have HTN ~ 1 in 5 adults with HTN have BP controlled to less than 130/80: Effective BP management decreases incidence of what 3 things?
Stroke
Heart attack
Heart failure
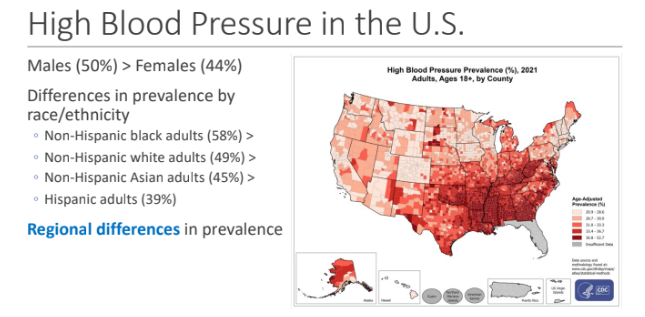
High Blood Pressure in the U.S.; Slightly higher in males → Males (50%) > Females (44%); Differences in prevalence by race/ethnicity what are the 4 examples?
Non-Hispanic black adults (58%) >
Non-Hispanic white adults (49%) >
Non-Hispanic Asian adults (45%) >
Hispanic adults (39%)
High Blood Pressure in the U.S.; _____ differences in prevalence
regional
HTN is Preventable and Treatable: For all adults, lifestyle changes, are strongly recommended to prevent or treat elevated blood pressure and hypertension, including what 7 changes?
Maintaining or achieving a healthy weight
Following a heart-healthy eating pattern (such as DASH [Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension])
Reducing sodium intake
Increasing dietary potassium intake
Adopting a moderate physical activity program
Managing stress
Reducing or eliminating alcohol intake
Primary HTN is?
essential hypertension; no known cause → unlikely to havea single cause (multiple factors in involved in sustaining HTN)
Primary HTN accounts for what percentages of HTN cases?
90-95%
What is secondary HTN?
HTN due to (secondary to) another disease condition
kidney disease,
sleep apnea,
hyperaldosteronism,
medication
single gene mutations
Secondary HTN accounts for what percentages of HTN cases?
5-10%
Secondary HTN typically has a ____ onset; no _____; and there is a clear cause
earlier; family history
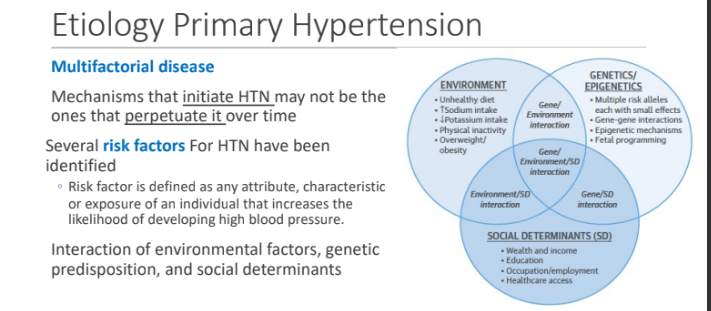
Etiology Primary Hypertension: It is multifactorial disease. Mechanisms that _____HTN may not be the ones that _______ it over time
initiate; perpetuate
Several risk factors For primary HTN have been identified. These risk factors are defined as?
any attribute, characteristic or exposure of an individual that increases the likelihood of developing high blood pressure.
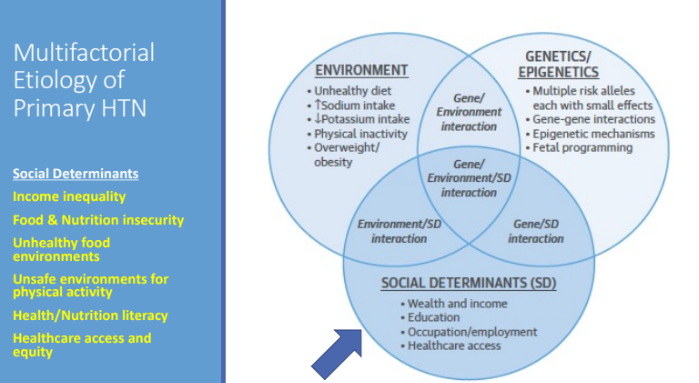
Primary HTN is an interaction of?
Environmental factors
Genetic predisposition
Social determinants
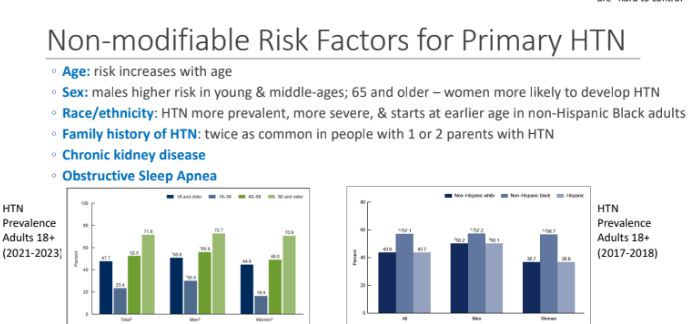
What are the 6 Non-modifiable Risk Factors for Primary HTN
Age→ risk increases with age
Sex→ males higher risk in young & middle-ages; 65 and older – women more likely to develop HTN
Race/ethnicity → HTN more prevalent, more severe, & starts at earlier age in non-Hispanic Black adults
Family history of HTN → twice as common in people with 1 or 2 parents with HTN
Chronic kidney disease
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
What are the 6 Modifiable Risk Factors for Primary HTN?
Overweight and Obesity:
High sodium diet: > 3000mg/day of sodium
Excessive alcohol consumption > 2 alcoholic drinks/day
Physical inactivity: less active individuals 30-50% more likely to develop HTN
Type II DM: 50% to 80% of patients with Type 2 diabetes have HTN
Smoking (including second hand smoke) chronic effects on BP unclear
Risk of HTN is ___ times higher among adults with obesity < 60 years of age; More than 85% of HTN cases occur in individuals with a BMI?
5; > 25 kg/m2

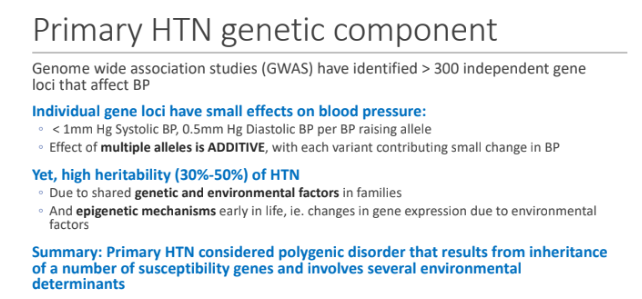
Primary HTN genetic component: Genome wide association studies (GWAS) have identified > 300 independent gene loci that affect BP; What have small effects on blood pressure?
Individual gene loci
< 1mm Hg Systolic BP, 0.5mm Hg Diastolic BP per BP raising allele
Effect of multiple alleles is ADDITIVE, with each variant?
contributing small change in BP
There is a high heritability (30%-50%) of HTN due to shared ____ and ____ in families
genetic; environmental factors
High heritability (30%-50%) of HTN because of epigenetic mechanism in early life, for example?
changes in gene expression due to environmental factors
Primary HTN genetic component: Primary HTN considered _____ that results from inheritance of a number of _____ genes and involves several ______ determinants
polygenic disorder; susceptibility; environmental
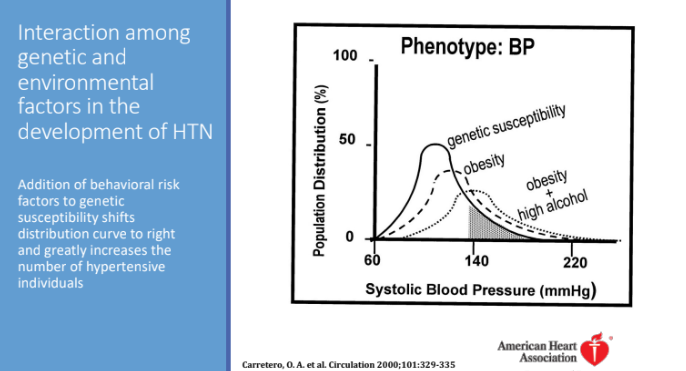
Interaction among genetic and environmental factors in the development of HTN: Addition of behavioral risk factors to genetic susceptibility shifts distribution curve to?
the right and greatly increases the number of hypertensive individuals
Multifactorial Etiology of Primary HTN: What are 6 examples of social determinants that affects etiology of primary HTN?
Income inequality
Food and nutrition insecurity
Unhealthy food environments
Unsafe environments for physical activity
Health/nutrition literacy
Healthcare access and equity
Risk of Primary HTN
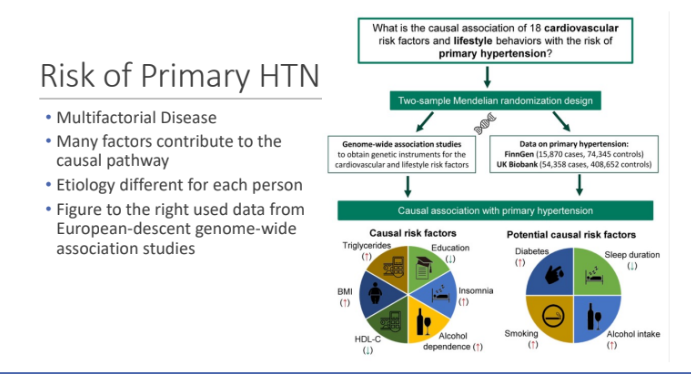
Hypertension Causes, from Lifestyle to Genetics: What are 5 dietary intake factors?
Higher sodium intake
Lower potassium intake
Lower calcium/ magnesium intake
Lower diet quality (lower intake of fruits/ vegetables, plant proteins, fiber)
Alcohol intake
What are the 6 Non-Dietary Factors?
Genetics variants
Overweight/obesity
Lower physical activity/fitness
Sleep disturbances(related to duration, quality, regularity and/or disordered breathing)
Psychosocial stressors
Air pollution
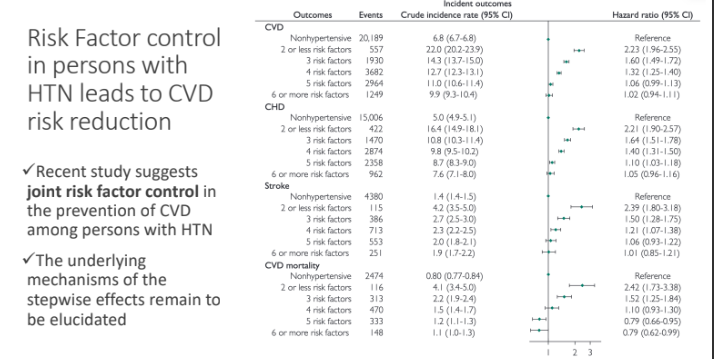
Risk Factor control in persons with HTN leads to CVD risk reduction
What is blood pressure?
pressure of the blood in the arterial system
Blood pressure reflects intermittent?
contraction and relaxation of the left ventricle of the heart.
Maintenance of BP is necessary for organ?
perfusion
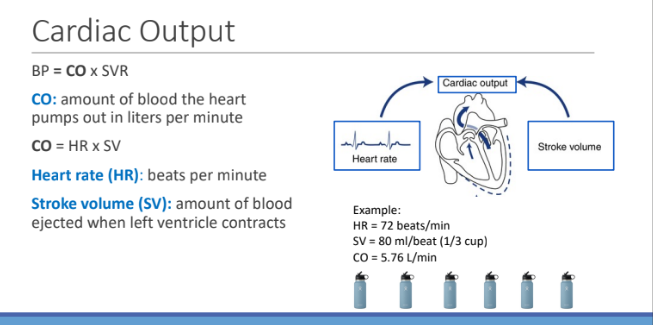
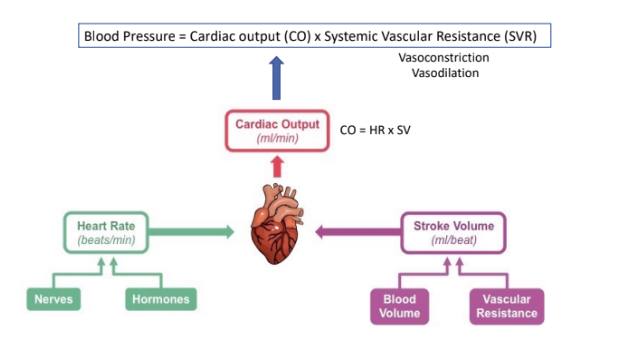
What is the equation for BP?
Cardiac output (CO) x Systemic Vascular Resistance (SVR)
What is Cardiac output?
the amount of blood the heart pumps out in liters in one minute
What is the equation for CO?
Heart rate (beats per min) x Stroke volume (amount of blood ejected when left ventricle contracts)
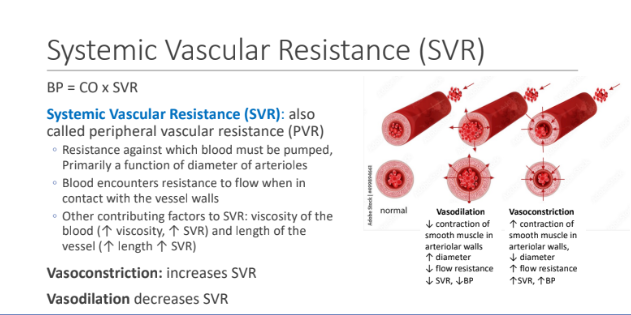
What is Systemic Vascular Resistance (SVR)?
Resistance against which blood must be pumped, Primarily a function of diameter of arterioles
Blood encounters resistance to flow when in contact with the vessel walls. What 2 things contribute to SVR?
viscosity of the blood (↑ viscosity, ↑ SVR)
Length of vessel (↑ length ↑ SVR)
Vasoconstriction increases or decreases SVR? Vasodilation increases or decreases SVR?
Vasoconstriction: increases SVR
Vasodilation decreases SVR
What happens to SVR in obesity, where there is an increase in tissue and vasculature?
What happens to SVR in atherosclerosis?
How do these changes impact BP?
increases; increases
What do you predict happens to HR, SV, CO, and SVR in each of the following conditions, to maintain blood pressure?
(A) Exercise (B) Sudden blood loss (hemorrhaging)
Exercise
HR increases
SV increases
CO increases
SVR decreases
Sudden Blood loss
HR increases
SV decreases
CO decreases
SVR increases
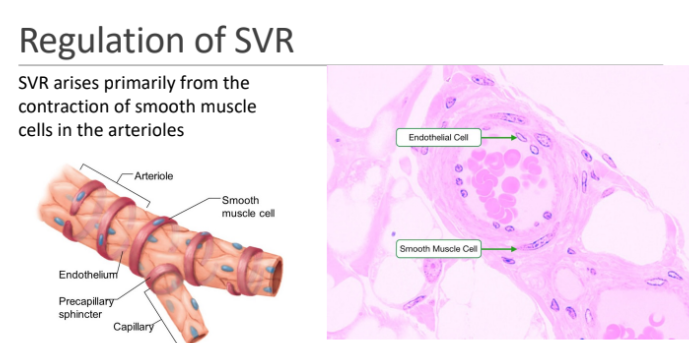
SVR arises primarily from the contraction of?
smooth muscle cells in the arterioles
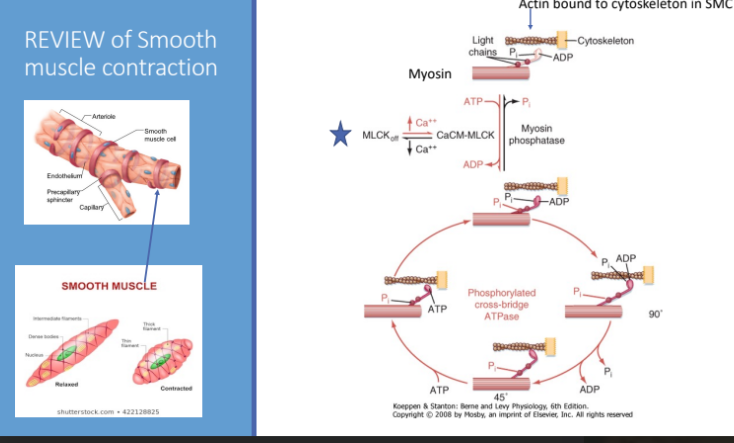
REVIEW of Smooth muscle contraction
actin bound to cytoskeleton in SMC
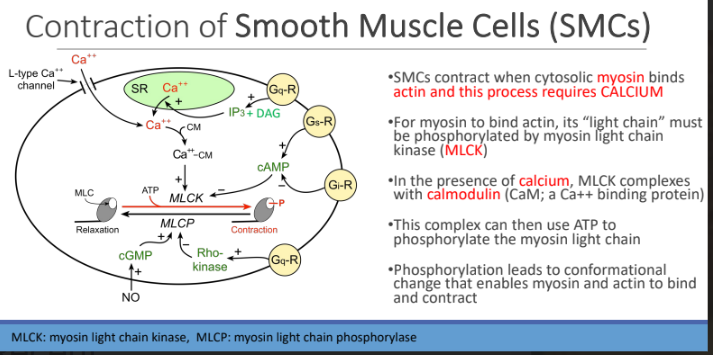
Contraction of Smooth Muscle Cells (SMCs): SMCs contract when cytosolic myosin binds?
actin and this process requires CALCIUM
For myosin to bind actin, its “light chain” must be?
phosphorylated by myosin light chain kinase (MLCK)
In the presence of calcium, MLCK complexes with?
calmodulin (CaM; a Ca++ binding protein)
MLCK complexes Calmodulin can then use ATP To?
phosphorylate the myosin light chain
Phosphorylation leads to
conformational change that enables myosin and actin to bind and contract
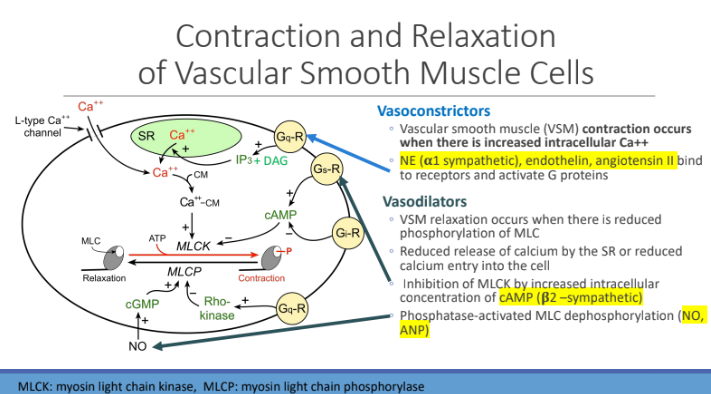
Contraction and Relaxation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells: Vasoconstrictors: Vascular smooth muscle (VSM) contraction occurs when there is INCREASED?
intracellular Ca2+
Vasoconstrictors: What bind to receptors and activate G protein
Norepinephrine (NE) (α1 sympathetic)
endothelin
Angiotensin II
Vasodilators: VSM relaxation occurs when there is reduced?
phosphorylation of MLC
Vasodilators: Reduced release of?
calcium by the SR or reduced calcium entry into the cell
Vasodilators: Inhibition of MLCK by increased intracellular concentration of?
cAMP (β2 –sympathetic)
Vasodilators: Phosphatase-activated?
MLC dephosphorylation (NO, ANP)
In cardiovascular disease, a decrease in endothelial nitric acid synthase (eNOS) is a contributing factor to endothelial dysfunction. A decrease in eNOS would cause a decrease in NO production and....
A. A decrease in myosin light chain phosphatase (MLCP) activation and vasoconstriction.
B. An increase in myosin light chain phosphatase (MLCP) activation and vasodilation.
C. A decrease in myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) activation and vasodilation.
D. An increase in myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) activation and vasoconstriction.
A decrease in myosin light chain phosphatase (MLCP) activation and vasoconstriction.
Blood Pressure = Cardiac output (CO) x Systemic Vascular Resistance (SVR) review
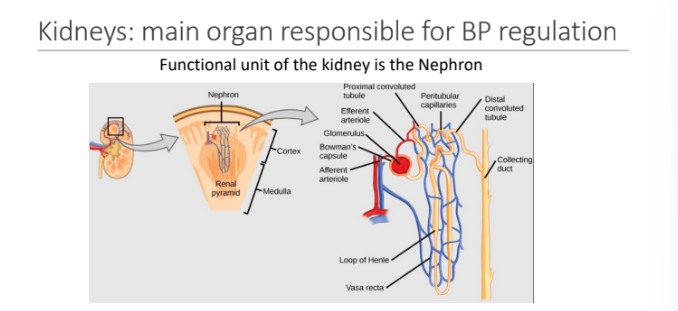
What is the main organ responsible for BP regulation?
kidney
functional unit of the kidney is the Nephron
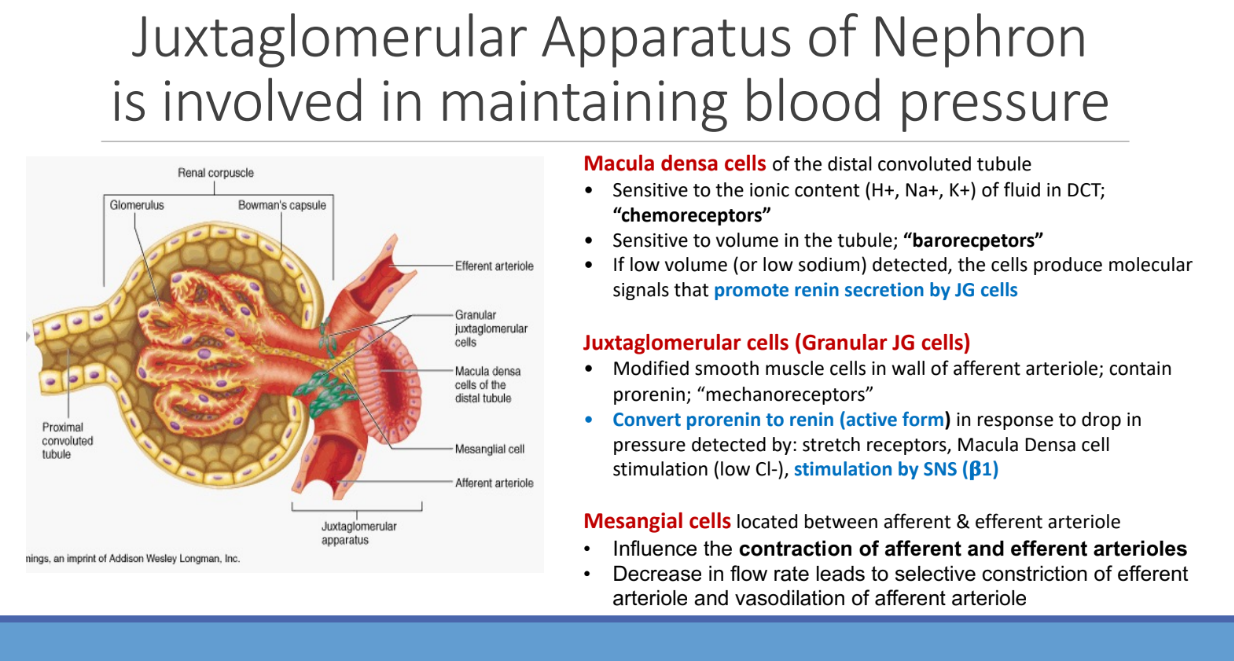
What of the Nephron is involved in maintaining blood pressure?
Juxtaglomerular Apparatus
Macula densa cells of the ______ tubule; It is sensitive to ____ content (H+ Na+ K+) of fluid in DCT called “___“
distal convoluted tubule; ionic; “chemoreceptors”
Macula densa cells is sensitive to?
volume in the tubule; “barorecpetors”
If low volume (or low sodium) detected, macula densa cells produce?
molecular signals that promote renin secretion by JG cells
What are Juxtaglomerular cells (Granular JG cells)? What do they contain?
Modified smooth muscle cells in wall of afferent arteriole; contain prorenin; “mechanoreceptors”
Juxtaglomerular cells (Granular JG cells) convert ___ to ___ in response to drop in pressure
prorenin; renin
Juxtaglomerular cells convert prorenin to renin (active form) in response to drop in pressure detected by what three things?
Stretch receptors,
Macula Densa cell stimulation (low Cl-),
Stimulation by SNS (β1)
Where are mesangial cells located?
located between afferent & efferent arteriole
Mesangial cells influence what of the afferent and efferent arterioles
contraction
Mesangial cells: Decrease in flow rate leads to selective ____ of efferent arteriole and _____ of afferent arteriole
constriction; vasodilation
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS) regulates blood volume and arteriolar constriction
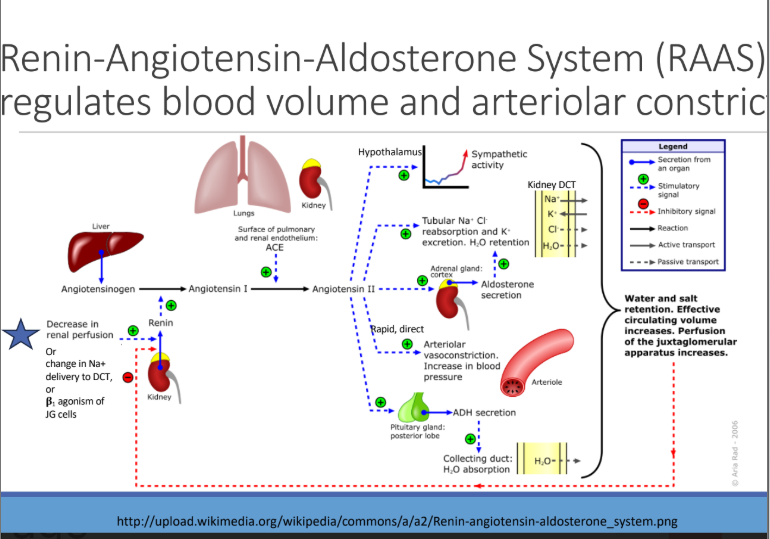
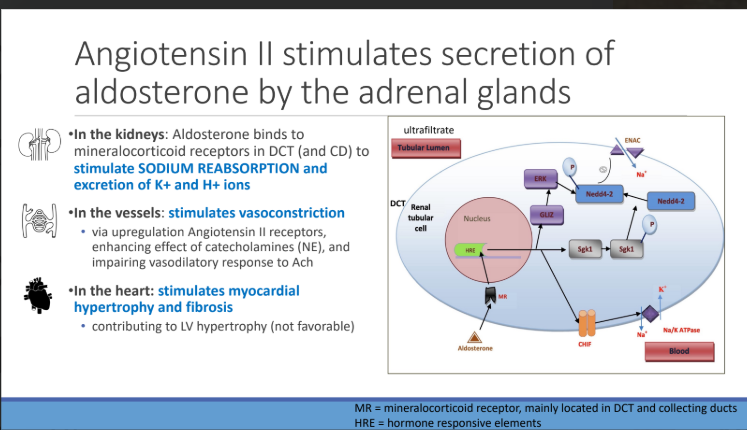
What stimulates secretion of aldosterone by the adrenal glands?
Angiotensin II
In the KIDNEYS: Aldosterone binds to mineralocorticoid receptors in DCT (and CD) to stimulate what reabsorption and what excretion?
SODIUM REABSORPTION and excretion of K+ and H+ ions
ANG II In the vessels: stimulates vasoconstriction via upregulation of? which enhances the effect of? and impairs vasodilatory response to?
Angiotensin II receptors,
Catecholamines (NE),
Ach
In the heart: stimulates?
myocardial hypertrophy and fibrosis contributing to LV hypertrophy (not favorable)
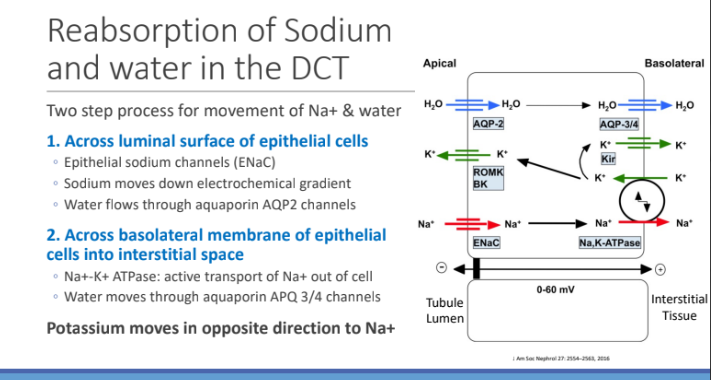
Reabsorption of Sodium and water in the DCT: It’s a two step process for movement of Na+ and water; What is the first step?
Across luminal surface of epithelial cells
Across luminal surface of epithelial cells: What type of sodium channels? Sodium moves down _____; water flows through _______ channels
Epithelial sodium channels (ENaC)
electrochemical gradient
aquaporin AQP2 channels
Reabsorption of Sodium and water in the DCT: It’s a two step process for movement of Na+ and water; What is the second step?
Across basolateral membrane of epithelial cells into interstitial space
Across basolateral membrane of epithelial cells into interstitial space: What does Na+- K+ ATPase do?
active transport of Na+ out of cell
Across basolateral membrane of epithelial cells into interstitial space: Water moves through?
aquaporin APQ 3/4 channels
Potassium moves in which direction?
opposite direction to Na+
What stimulate release of ADH from the posterior pituitary?
angiotensin II (and other stimuli)
Vasopressin (an anti-diuretic hormone) increases what in the kidney?
water resorption
Vasopressin increases water resorption in the kidney via increased transcription and insertion of?
aquaporin (water channels) in collecting duct cells
What is the main function (V2 receptors) of Vasopressin?
conserve water when receives signals that the blood volume is low
Vasopressin is a vasoconstrictor but ONLY when?
released in very high amounts (severe hypovolemic shock)
What is vasopressin released inhibited by?
ANP and cortisol
Reabsorption of Sodium and water in the CD: What does aldosterone increase the transcription of?
ENaC
Na+- K+ ATPase
Aldosterone increases what reabsorption and increase what secretion
Na+ and water reabsorption
K+ secretion