SCI- Spinal Cord Injuries
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
SCI Life expectancy
Below Normal
lifetime of disability
Causes of death may be:
- pneumonia
- pulmonary emboli
- septicemia (infection in blood)
Tetraplegia
AKA quadriplegia
Involves cervical spine injuries
UE’s, LE’s and trunk are all impaired
Paraplegia
Involves injuries to thoracic spine
UE function is available
Varying degrees of LE and trunk involvement
Both loss of sesnory and motor information below level of lesion
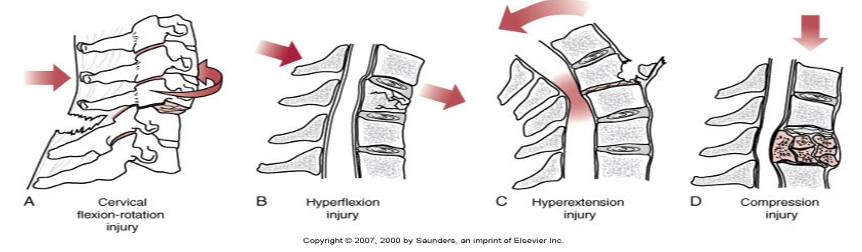
Mechanisms of Injury
Traumatic impact including compression, penetrating injuries, hyperextension, and hyperflexion
Vertebral subluxations, compression fractures, and fractures that encroach spinal cord.
May produce partial or complete transection of spinal cord
Mechanisms of Injury causes
• Flexion and rotation injuries from MVA rear-end accidents
• Hyperflexion injuries from head on collisions
• Hyperextension injuries from fall
• Compression injuries from osteoporosis, degenerative changes, diving injuries, falls from elevated surfaces
SCI medical intervention
pt immobilized
Meds administered o limit effects of injury
Surgery for spinal stabilization
Skeletal traction to help bony alignmet
Immobilization through various immobilizers (aspen cervical collar, jewit bracem TLSO, LSO, clamshell)
SCI in the clinic
Treatment:
is highly variable and depends on level of injury
May have abnormal tone or spasticity
How to name level of SCI
Identify bony segment involved (C for cervical, T for thoracic, L for lumbar)
Neurological level is most caudal segment of cord with intact sensory and 3/5 grade muscle strength
Example: C5 Spinal cord injury will have sensation and innervation to muscles with a C5 nerve root and MMT of at least 3/5.
If a muscle is innervated by more than one nerve root_________.
it may result in weakness and not full paralysis
Example: C5 spinal cord injury
• Subscapularis is innervated by C5, 6, & 7
• Will result in weakness due to 2/3 of the nerve roots being impacted by the injury
• Must have at least a 3/5 strength to be named at the C5 level
SCI: types of lesions
Complete
Incomplete
Brown Sequard syndrome
Anterior cord syndrome
Central cord syndrome
Dorsal column syndrome
Cauda equina injuries
Complete injuries