Eduqas Biology A Level C1 - Photosynthesis
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Overall equation for photosynthesis
6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
What are the two stages of photosynthesis?
Light-dependent stage and light-independent stage
Photophosphorylation
An endergonic reaction bonding a phosphate ion to a molecule of ADP using energy from light (making ATP)
In what stage does photophosphorylation occur?
Light-dependent stage
What is the light-independent stage also known as?
Calvin Cycle
Structure features of a leaf that aids photosynthesis:
- Large surface area
- Thin
- Stomatal pores
- Air spaces in spongy mesophyll
- Spaces between palisade cells
How does a leaf having a large surface area aid photosynthesis?
It allows the leaf to capture as much light as possible
How does a leaf being thin aid photosynthesis?
Light can penetrate right through the leaf
How do stomatal pores in a leaf aid photosynthesis?
Allow CO₂ to diffuse into the leaf
How do the air spaces in the spongy mesophyll of a leaf aid photosynthesis?
They allow CO₂ to diffuse to the photosynthesising cells (palisade mesophyll)
How do spaces between palisade cells in a leaf aid photosynthesis?
They allow CO₂ to diffuse to the photosynthesising cells (palisade mesophyll)
Structural features of cells that aid photosynthesis:
- Cuticle and epidermis are transparent
- Cellulose cell walls are thin
- Palisade cells have a large vacuole
- Palisade cells are cylindrical and elongated and at right angles to the surface of the leaf
How does a cell having a transparent cuticle and epidermis aid photosynthesis?
Light penetrates through to the palisade mesophyll
How does thin cellulose cell walls of cells aid photosynthesis?
Light penetrates through to the palisade mesophyll
How does a palisade cell having a large vacuole aid photosynthesis?
As vacuole is large, chloroplats form a single dense layer at the periphery of each cell. This means they do not shade each other
How does palisade cells being cylindrical and elongated at right angles to the surface of the leaf aid photosynthesis?
More palisade cells can fit into the leaf
Structural features of Chloroplasts that aid photosynthesis:
- Large surface area
- Can move within palisade cells
- Can rotate within palisade cells
- Pigments are in a single layer at the surface of the thylakoid membrane
- 5 times as many chloroplasts in palisade cells
How does chloroplasts having a large surface area aid photosynthesis?
Allows for maximum absorption of light
How does chloroplasts being able to move in palisade cells aid photosynthesis?
If light intensity is low, they can move to the top of the cell for maximum absorption
If the light intensity is too high, they can move away from the top to prevent bleaching
How does chloroplasts being able to rotate within palisade cells aid photosynthesis?
Thylakoids have maximised absorption of light
How does pigments being in a single layer at the surface of the thylakoid aid photosynthesis?
Pigments will absorb more light
How does having more chloroplasts in a cell aid photosynthesis?
More chloroplasts means there is more light absorption and therefore more photosynthesis occurring
What is a pigment?
A molecule that absorbs specific wavelengths of light
What wavelength of light do the pigments absorb?
Around 420 to 700nm
What is an absorption spectrum?
A graph showing how much light is absorbed at different wavelengths
What is an action spectrum
A graph showing the rate of photosynthesis at different wavelengths
Action and absorption spectrum
When superimposed, a close correlation is seen. This suggests that the pigments responsible for absorbing light are the ones used in photosynthesis
What two things does a photosystem consist of?
An antenna complex and a reaction centre
What is a photosystem?
A protein complex in which photosynthetic pigments are arranged
What does a reaction centre contain?
Two molecules of the primary pigment, chlorophyll a
What is an antenna complex?
A collection of molecules in the thylakoid membrane of the grana that transfers energy from light to chlorophyll a, at the reaction centre
What happens when light falls on chlorophyll a?
Chlorophyll a absorbs the photons in the light, becoming excited. This excitation leads to the emission of electrons
What are the two types of photosystems?
Photosystem 1 and Photosystem 2
What is the primary pigment?
Chlorophyll a
What does the light-dependent stage produce?
ATP, Reduced NADP and Oxygen
What does the light-dependent stage use?
Light and water
What are the products of the light-independent stage?
Glucose, NADP, ADP + Pi
What does the light-independent stage use?
ATP, Reduced NADP, CO2
What photosystem comes first?
PSII
What photosystems are involved with Cyclic Photophosphorylation?
Only PSI
What photosystems are used in Non-cyclic Photophosphorylation?
Both PSI and PSII
What is photolysis?
The splitting of water molecules by light
What does photolysis produce?
Hydrogen ions, electrons and oxygen
Describe Cyclic Photophosphorylation
- PSI absorbs photons from light
- Electrons in the chlorophyll a molecules are excited and emitted
- Emitted electrons are picked up by an electron acceptor
- Electrons are passed down a chain of electron carriers back to PSI
- As the electrons pass through the electron transport chain they generate energy
- This energy is used to make ATP (from ADP and Pi)
Why is cyclic phosphorylation cyclic?
Electrons that are emitted return to PSI after passing to the electron acceptor and through electron carriers
Describe Non-cyclic Photophosphorylation
- Electrons in PSII are excited by photons and are emitted, leaving the chlorophyll in PSII positively charged
- Photolysis occurs, releasing electrons (as well as hydrogen ions and oxygen) that neutralise the positive charge in PSII
- Meanwhile, the electrons emitted by PSII are picked up by an electron acceptor and passed down the electron transport chain to PSI
- Electron passage down the electron transport chain makes energy for production of ATP
- Electrons replace those lost by PSI
In Non-cyclic Photophosphorylation what do the electrons emitted by PSII do?
They travel down the electron transport chain to PSI to replace those lost by emission
In Non-cyclic Photophosphorylation what do the electrons emitted by PSI do?
They are picked up by an electron acceptor and then combined with hydrogen ions (protons) from water to reduce NADP
What happens to the oxygen produced in photolysis?
It diffuses out of the chloroplast and cell, then out through the stomata as a waste product
In what type of photophosphorylation is oxygen produced?
Non-cyclic
In what type of photophosphorylation is water split by photolysis?
Non-cyclic
In what type of photophosphorylation is NADP reduced?
Non-cyclic
In what type of photophosphorylation is ATP produced?
Both Cyclic and Non-cyclic
Which type of photophosphorylation occurs in all photosynthetic organisms?
Cyclic
Equation for photolysis
H₂O → 2H⁺ + 2e⁻ + ½O₂
The light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur in the...
photosystems
Excited electrons are picked up by .......... ........... and transferred down an electron transport chain
Electron acceptors
What are the four limiting factors in photosynthesis?
- CO₂ concentration
- Water
- Light Intensity
- Temperature
What is a limiting factor?
A factor that limits the rate of a physical process by being in short supply
How does CO2 concentration affect the rate of photosynthesis?
From 0% to 0.5%: an increase in carbon dioxide increases the rate of photosynthesis
From 0.5% to 1%: Carbon dioxide is no longer a limiting factor (increase in CO2 has no effect on rate)
After 1%: The stomata close, preventing CO2 uptake
How does light intensity affect the rate of photosynthesis?
As light intensity increases, the rate of photosynthesis increases. It is a limiting factor until 10,000 lux, where reactions occur at their maximum rate. The rate is constant and light intensity is no longer a limiting factor.
A very high light intensity will bleach chloroplast pigments, damaging them so they cannot absorb light efficiently
Light compensation point
The light intensity at which a plant has no net gas exchange as the volume of gases used and produced in respiration and photosynthesis are equal
How does temperature effect the rate of photosynthesis?
Until optimum temp: An increase in temperature increases the rate of photosynthesis. Kinetic energy of the molecules involved increases. Temperature is a limiting factor
After optimum temp: Too high of a temperature causes enzymes to denature and the rate decreases
How does water effect photosynthesis?
Water is a limiting factor. It is not easy to see it's effect on photosynthesis alone as many systems are affected by water
Rule when using combined limiting factors
The rate of photosynthesis is controlled by the factor that is nearest to it's minimum value
Nitrogen usage in plants
Essential for synthesis of proteins, chlorophylls and nucleotides
Magnesium usage in plants
Required by all tissues. Forms part of chlorophyll molecule and also act as enzyme activators
Draw the Calvin Cycle
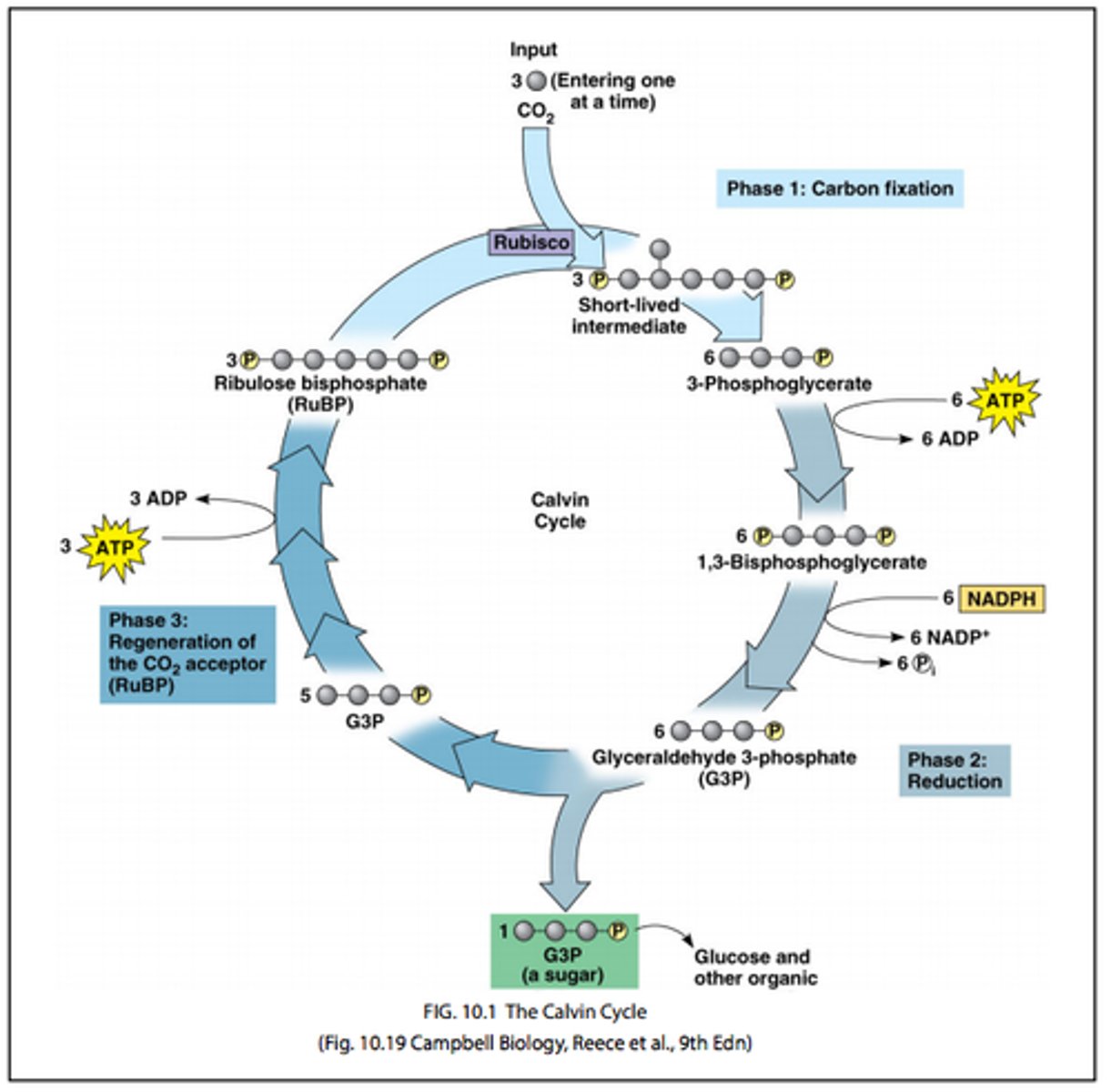
What is Rubisco?
An enzyme that catalyses the combination of carbon dioxide and ribulose bisphosphate
What is formed when CO2 and ribulose bisphosphate combine?
An unstable 6 carbon compound that then immediately splits into 2 3 carbon compounds, glycerate-3-phosphate
What does RuBP stand for?
Ribulose bisphosphate
What is the difference between RuBP and Rubisco?
RuBP is ribulose bisphosphate and is a 5 carbon organic compound in the Calvin cycle. Rubisco is an enzyme that catalyses the reaction of RuBP and CO2
What enzyme catalyses the reaction between RuBP and CO2?
Rubisco
How is glycerate-3-phosphate (GP) converted into triose phosphate (TP)?
GP is reduced by reduced NADP (NADPH), with ATP as the energy source
What provides the energy for the conversion of glycerate-3-phosphate to triose phosphate?
ATP molecules
What are the products of the reduction of glycerate-3-phosphate?
- Triose phosphate
- NADP
- ADP and Pi
What molecule is reduced to make triose phosphate? And what molecules are required in this step?
Glycerate-3-phosphate is reduced
ATP and reduced NADP (NADPH) are required
Where does the ATP required in the Calvin cycle come from?
From ATP made in the light-dependent stage
How is glucose produced in the Calvin cycle?
In every cycle of the Calvin cycle 1 spare carbon is produced when triose phosphate is converted to RuBP
After 6 cycles, the 6 carbon molecule hexose is made.
Hexose can be converted to glucose.
How is triose phosphate converted to RuBP?
2 molecules of triose phosphate (3 carbons each) are combined, using the energy provided by ATP, to make a 5 carbon compound RuBP and spare carbons are eventually used to make other compounds such as glucose or amino acids
What provides the energy for the conversion of triose phosphate to RuBP?
ATP from the light-dependent stage of photosynthesis
How are carbohydrates made in the Calvin cycle?
Hexose made from triose phosphate can be converted into glucose molecules. These glucose molecules can be combined with other hexose sugars, or combined with eachother to made starch or cellulose
Why is it useful for plants to produce carbohydrates in the Calvin cycle?
Sucrose can be created for transport of glucose around the plant
Starch can be made for storage
Cellulose can be made, and is used in cell walls
How are fats made in the Calvin cycle?
Acetyl CoA can be synthesised from glycerate-3-phosphate and then converted into fatty acids
Triose phosphate can be converted into glycerol
Both fatty acids and glycerol combine to made triglycerides
Why is making lipids from the Calvin cycle useful in plants?
Lipids are used for buoyancy
Lipids are a store of metabolic energy (can be broken down during respiration)
Lipids are used in cell membranes
They have many other functions
How are proteins made in the Calvin cycle?
Glycerate-3-phosphate can be converted into amino acids
The amino group is derived from ammonium ions (NH⁺)
Why is it useful for plants to produce proteins in the Calvin cycle?
They are used in many ways, including to make enzymes and transport across memebranes
Draw the Z scheme
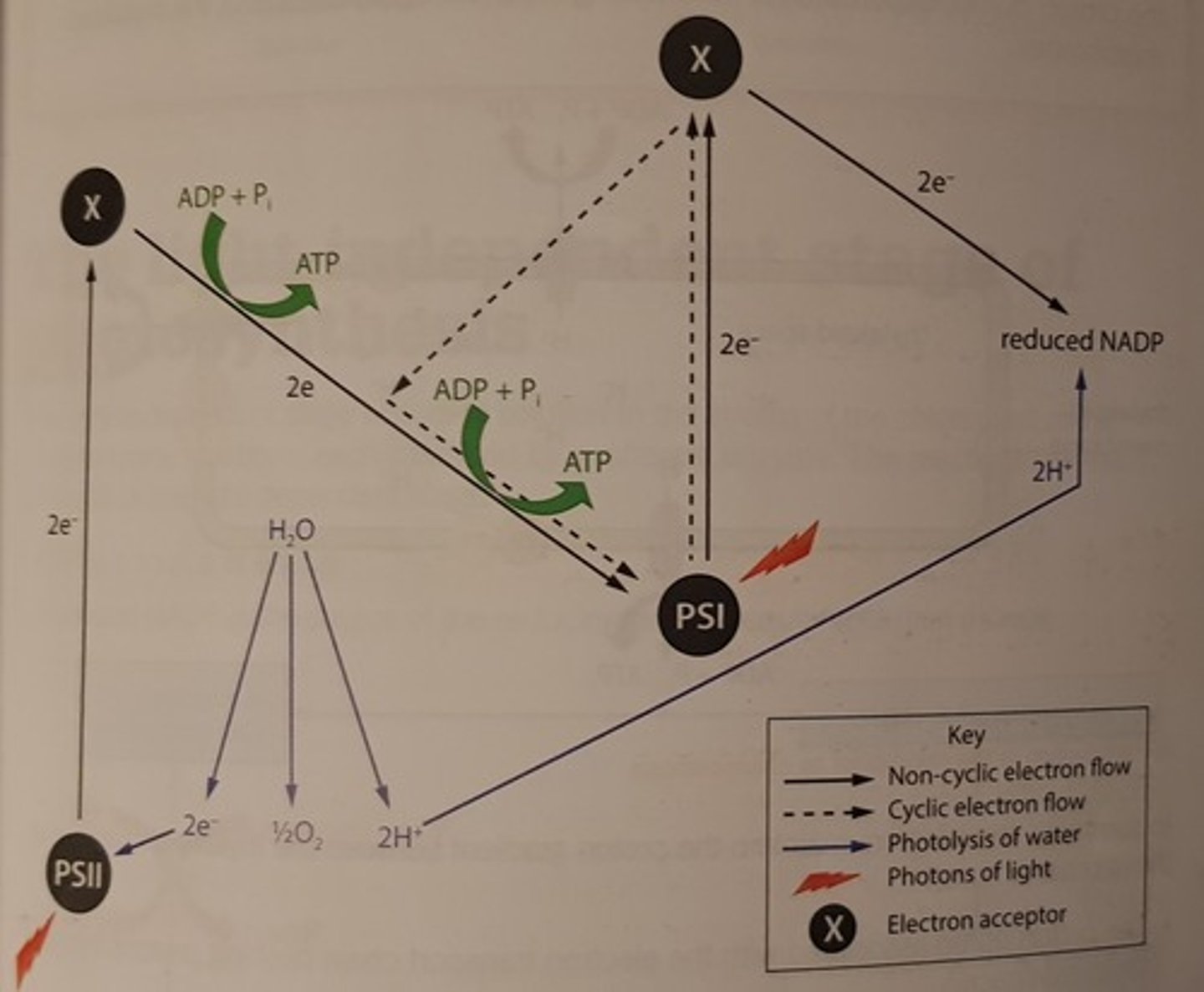
Describe the synthesis of ATP by chemiosmosis in photosynthesis:
- Electrons emitted by PSII travel down an electron transport chain
- The movement of electrons provides energy to pump protons across the thylakoid membrane into the thylakoid space
- An increase in protons creates an electrochemical gradient (as there are more inside than out)
- Chemiosmosis occurs, when H⁺ ions diffuse down their electrochemical gradient through ATP synthetase to the stroma
- This provides energy to make ATP from ADP and Pi
What is the location of the light-independent stage in a chloroplast?
In the stroma
What molecule is removed from the Calvin cycle?
Hexose
Where is magnesium found in plants?
In chlorophyll molecules
In addition to its role in the Calvin cycle, the enzyme Rubisco can also catalyse the combination of oxygen with Ribulose Bisphosphate. This causes cells to take up oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide when exposed to very bright light. This process is known as photorespiration
Suggest why photorespiration is a disadvantage to a plant
- Photorespiration uses up the available RuBP
- Therefore less carbon dioxide is fixed
- Due to this, photosynthesis is less efficient
- There are less products made, such as glucose
Apart from chlorophyll a, name three other pigments you would expect to be present in a photosystem
- Chlorophyll b
- Carotene
- Xanthophyll
State precisely where a photosystem would be found in a plant cell
Thylakoid (membrane) of a chloroplast
Diuron is a weed-killer which blocks the electron carrier binding site on photosystem II. This stops electron flow from PSII to the electron carrier. Diuron has no effect on PSI or other reactions in photosynthesis.
Explain the effects of Diuron on non-cyclic photophosphorylation and why cyclic photophosphorylation is not affected
- Diuron stops electrons from PSII being moved to PSI
- This prevents the reduction of NADP
- Cyclic only involves PSI, which is not effected
Describe the function of chlorophyll a
It absorbs light energy
State the wavelength which is most effectively absorbed by chlorophyll a
440nm
Why is it an advantage for a leaf to contain more than one pigment
Pigments each absorb a specific section of the visible light spectrum
Additional pigments increase the range of wavelengths absorbed from which energy is absorbed
Why do most leaves characteristically have a green colour?
All wavelengths except green are absorbed, and so green is reflected back into our eyes