ap bio sem 1
1/207
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
208 Terms
Passive Transport
The movement of particles from high to low concentration without the input of energy. includes diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion.
Active Transport
The movement of particles from low to high concentration requiring an input of energy. This energy can be from ATP molecules
Simple Diffusion
The random movement of small, nonpolar particles from a high to low concentration. through phospholipid tails.
Osmosis
The movement of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane. Moves from high concentration of water to low concentration of water (moves in the direction of more solutes)
Facilitated Diffusion
The movement of polar or charged particles across a membrane with the help of proteins. they cant get through on their own because they are polar and are hydrophillic
Endocytosis
The transport of large material into a cell using vesicles.
Exocytosis
The transport of large materials out of the cell using vesicles.
Concentration gradient
difference in the concentration of a substance from one location to another
ATP
energy molecule used for active transport, made by the mitochondria
selectively permeable
a property of cell membranes that allows some substances to pass through, while others cannot
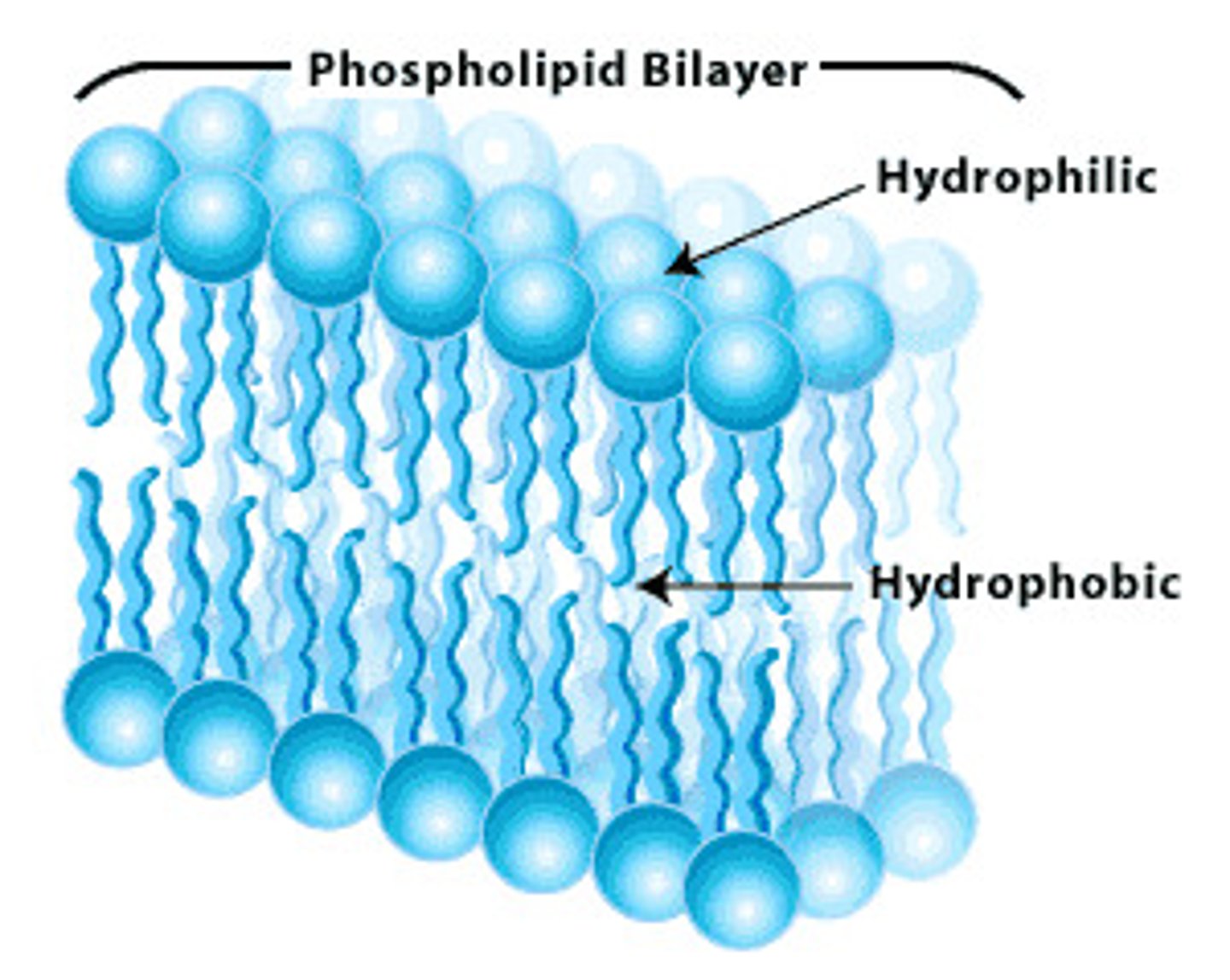
polar head
A phosphate that is the water loving portion of the phospholipid
hydrophobic tails
directed toward the center, avoiding water
Up/against a gradient is from a region of _____ to _____ concentration?
low to high
down/with the gradient from a region of _____ to ____ concentration?
high to low
cellular respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen to make ATP
Mitochondria
An organelle found in large numbers in most cells, cellular respiration takes place here
Glycolysis
the breakdown of glucose, step 1 of cellular respiration.
products of glycolysis
a little ATP, carrier molecules (H+ and e-), pyruvate
reactants of glycolysis
glucose
Products of Krebs Cycle
CO2, a little ATP, carrier molecule (H+,e-)
CO2
waste product of cellular respiration. made in Krebs
H20
Waste product of ETC; made when O2, Electrons and Protons combine
electron transport chain
Step 3 of CR. Most ATP is made here! A series of proteins make ATP.
ATP synthase
Large protein that uses energy from H+, e-, and O2 to bind ADP and a phosphate group together to produce ATP
carrier molecules
electron and proton carriers; shuttle electrons to the ETC
aerobic respiration
Respiration that requires oxygen
Reactants of ETC
e-, H+, O2
Products of ETC
Water and ATP (a BUNCH)
steps of cellular respiration
glycolysis, krebs cycle, electron transport chain
cellular respiration equation
glucose +O2---> CO2+ H2O +ATP
goal of cellular respiration
to convert the chemical energy in food (glucose) to chemical energy stored in ATP
goal of glycolysis and krebs
make carrier molecules to supply the ETC with e- and H+
the CO2 we breath comes from
pyruvate
polymer
A large molecule composed of repeating structural units or monomers.
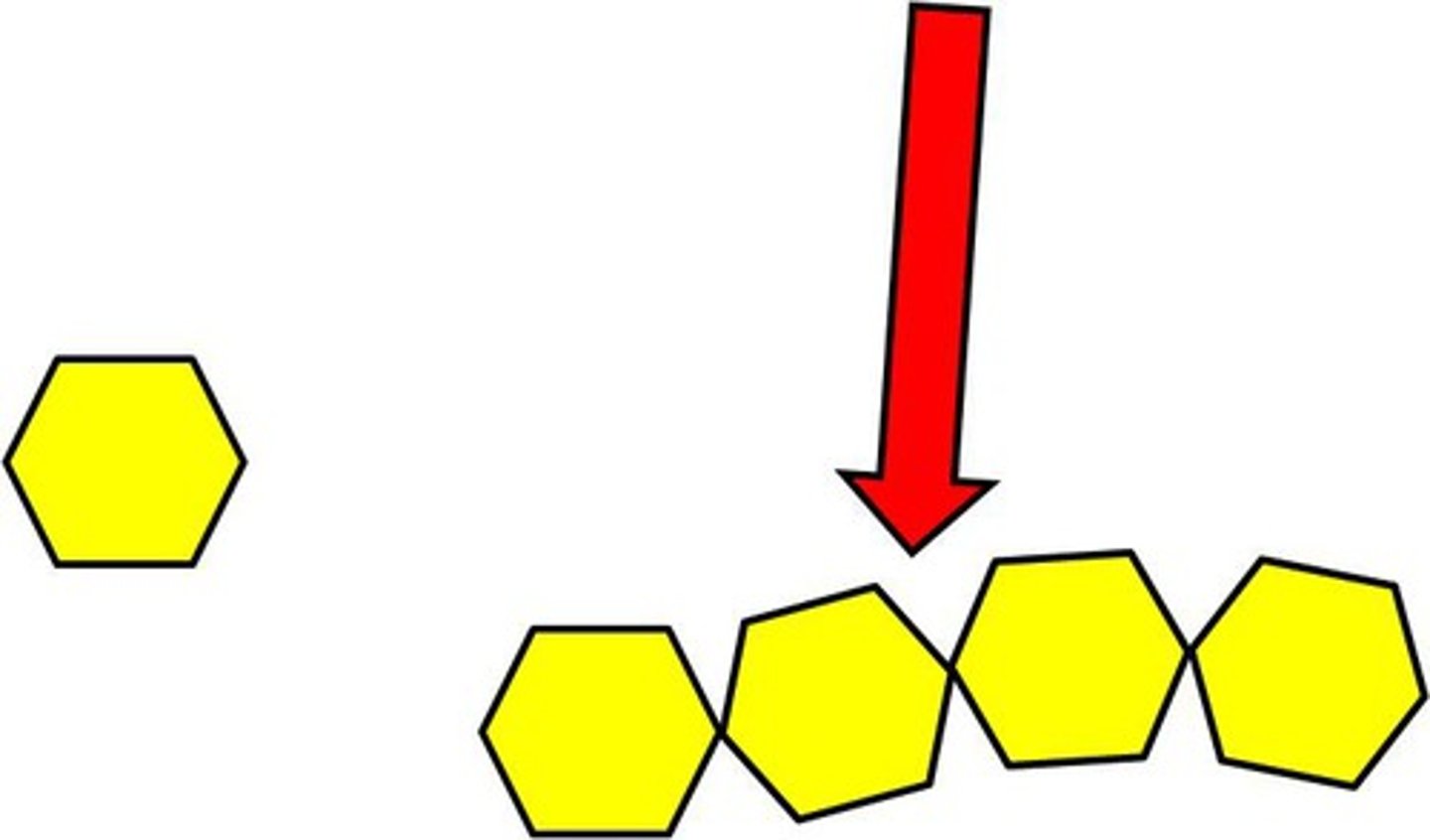
carbohydrate
Compound used for structure and short term energy (e.g., sugars, starches, and cellulose)
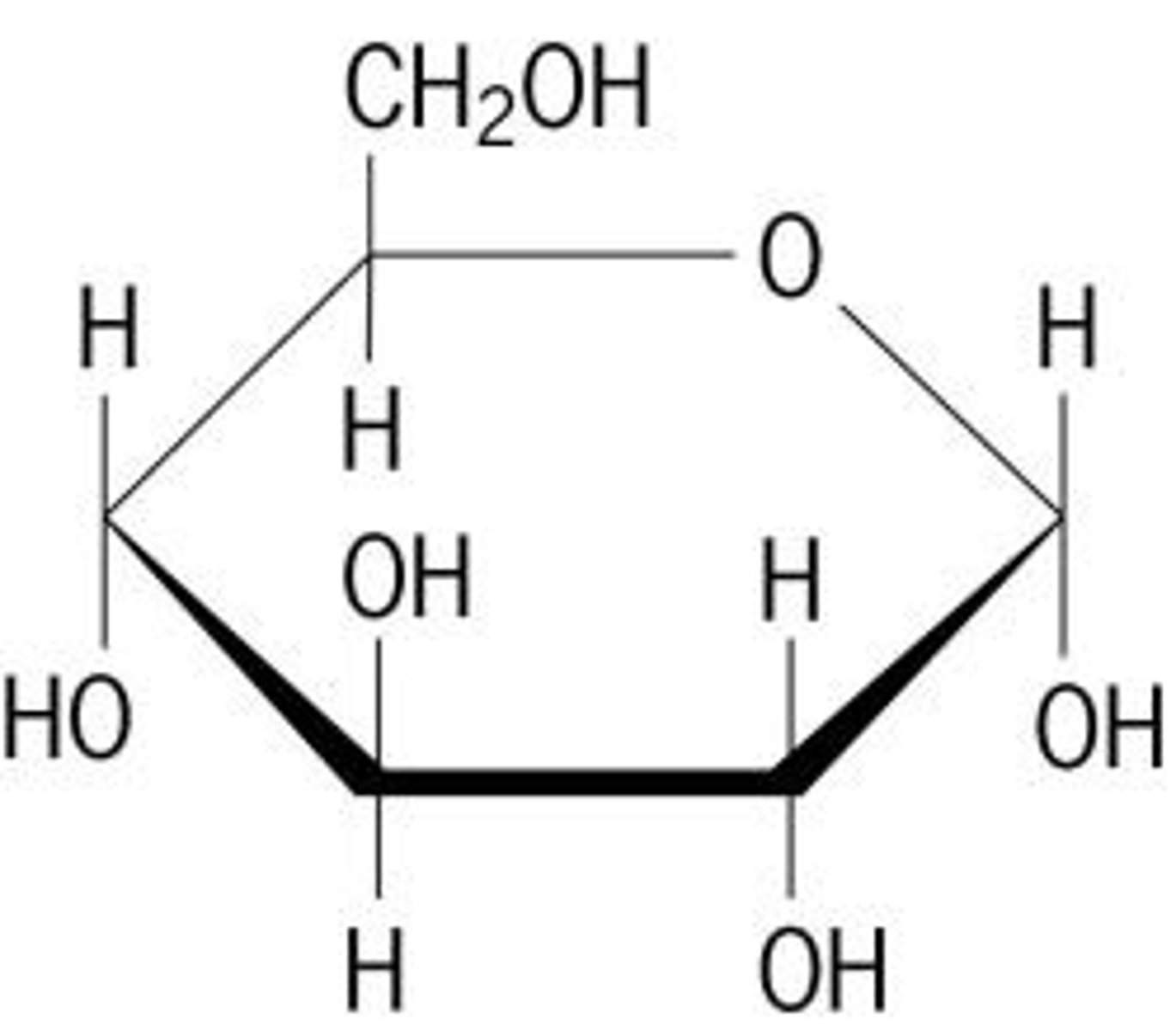
protein
Class of nutrients made up of amino acids. They are needed to build and repair body structures, and to regulate almost all processes in the body
lipid
Organic molecules made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and store food energy until needed (fats, oils, waxes)

nucleic acid
A biological macromolecule (DNA or RNA) composed of the elements C, H, N, O, and P that carries genetic information. stores the information needed to make proteins.
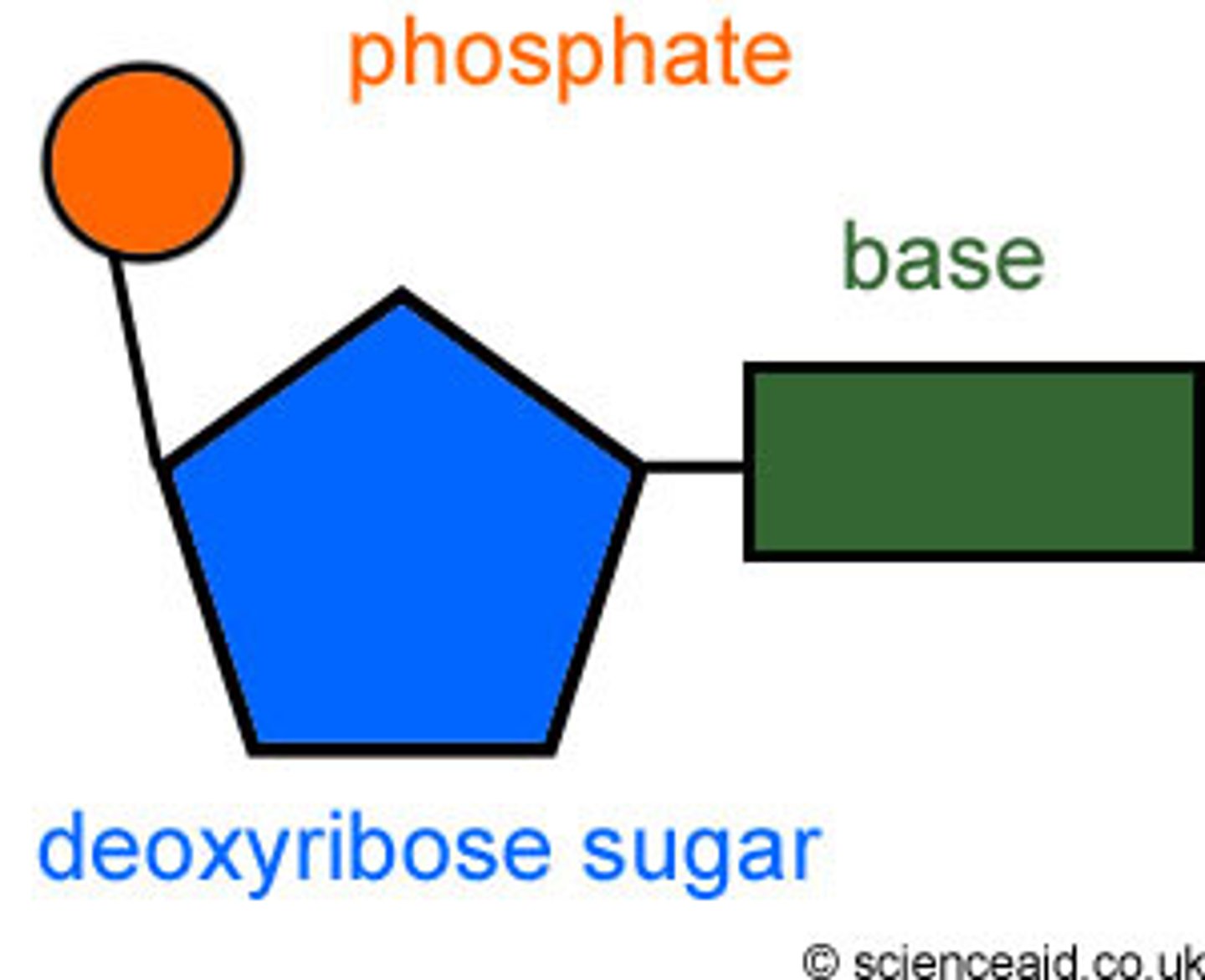
nucleotide
Monomer of nucleic acids made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. there are 4 types in DNA
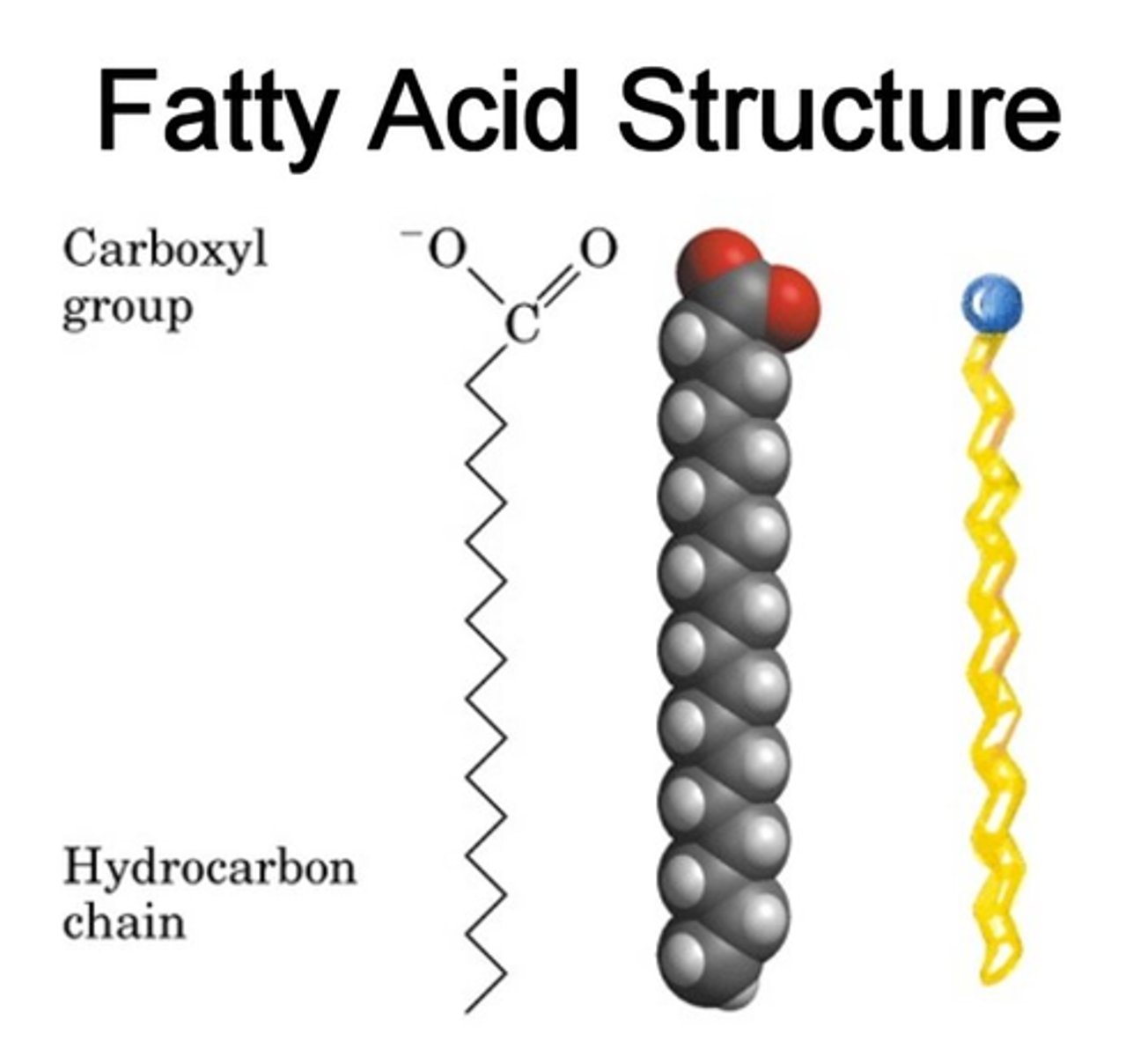
fatty acid
These are hydrophobic and make up the "tails" in the membrane
macromolecule
A very large molecule (as of a protein, nucleic acid, or carbohydrate) built up from smaller chemical structures
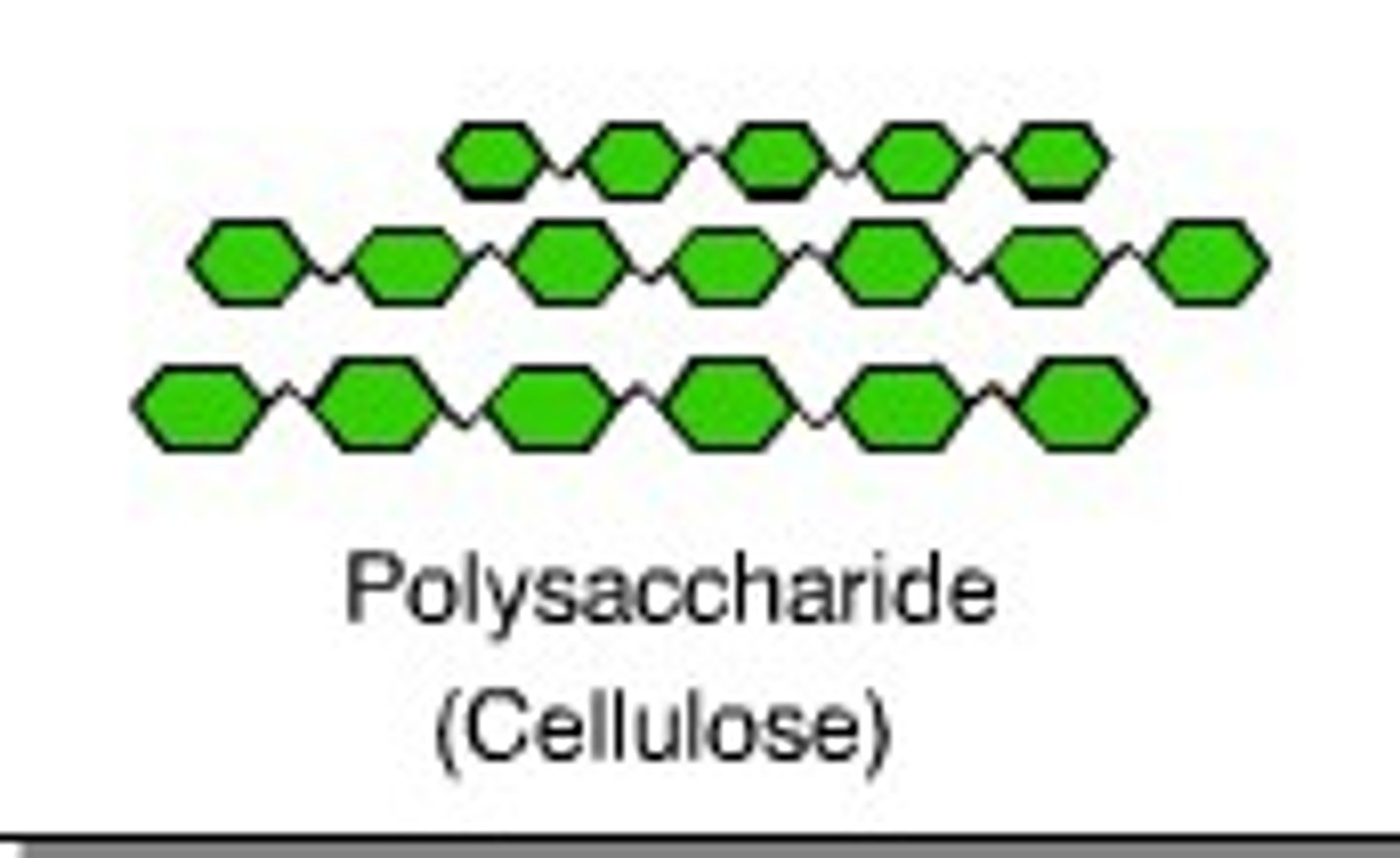
polysaccharide
a carbohydrate that is composed of many monosaccharide units joined together
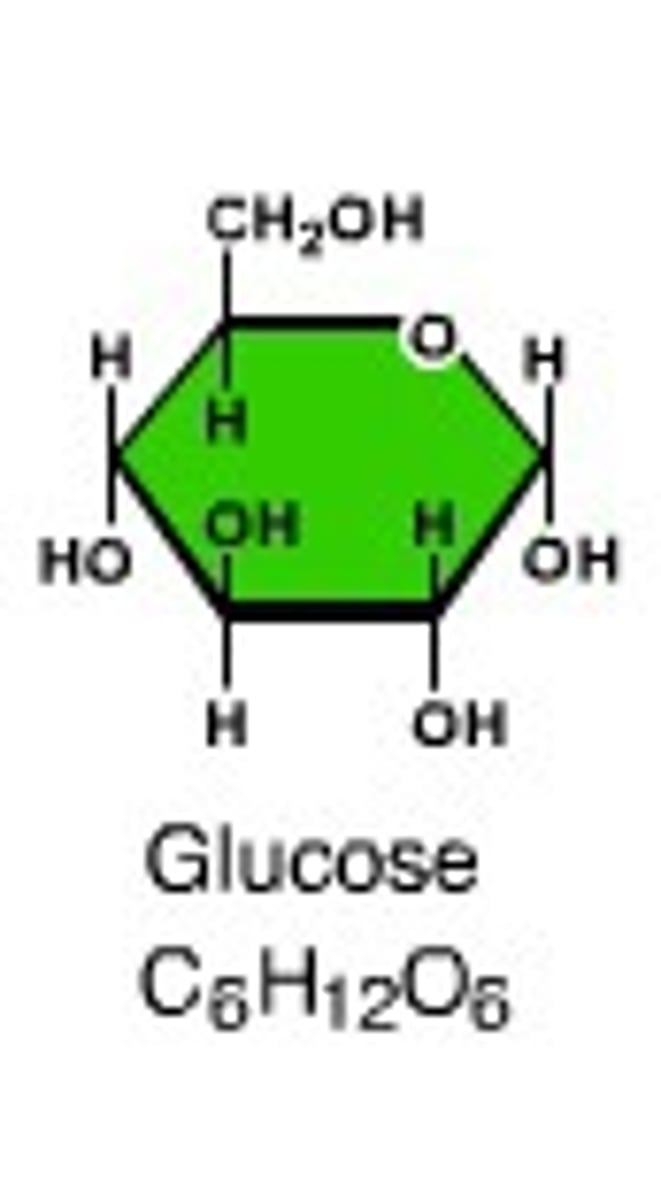
monosaccharide
A simple sugar that is the basic subunit of a carbohydrate
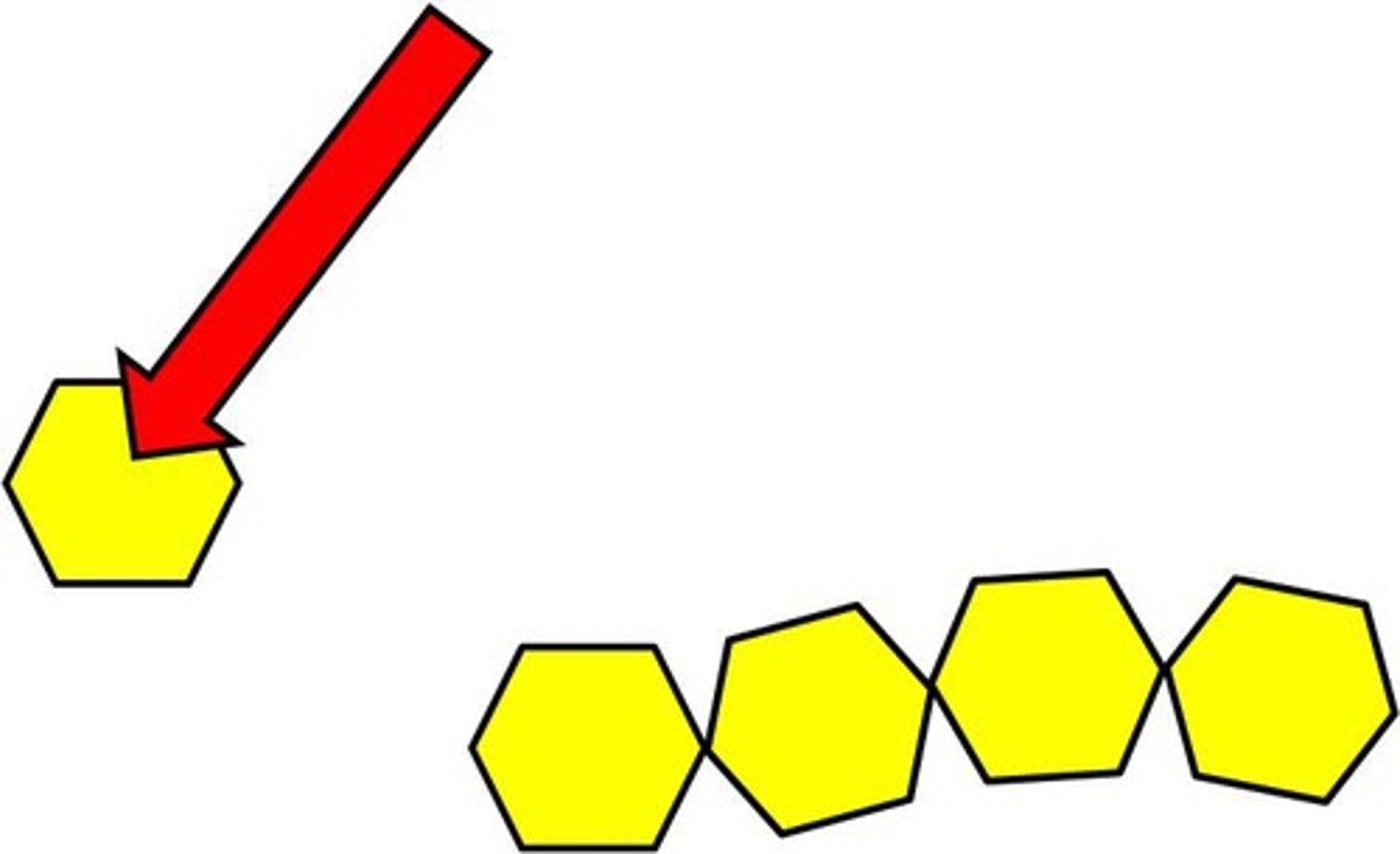
Monomer
A simple building block that can join together to form polymers
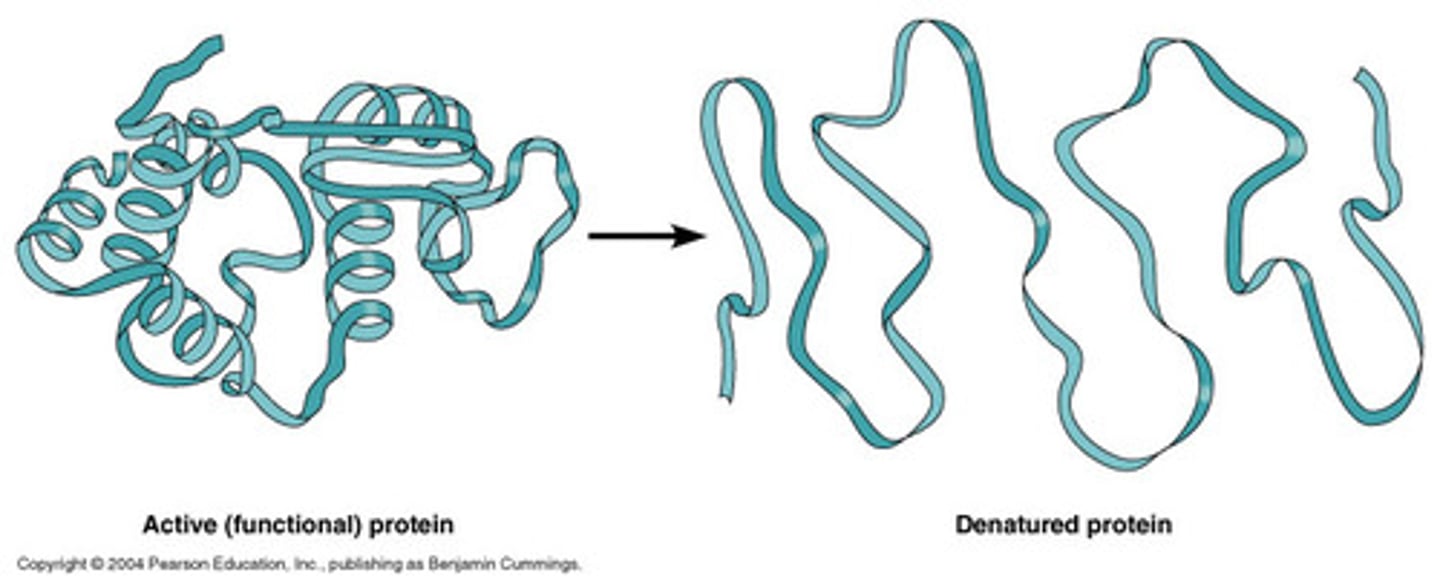
Denature
A change in the shape of a protein (such as an enzyme) that can be caused by changes in temperature, salt, or pH .
function of lipids
make up cell membrane and long term energy storage
function of carbs
short term energy storage; structure
function of proteins
essential for the growth, development, and repair of all body tissues. THEY DO EVERYTHING!! enzymes
function of nucliec acids
store genetic information. holds the code for making protiens
pH
hydrogen ion concentration. Range from 0-14. Measures acidity . 0-6 acidic, 8-14 basic
surface tension
A measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid. in water it is really hard to break the surface! due to hydrogen bonding

High specific heat capacity
Water requires a lot of energy to change temperature. Helps maintain homeostasis and a constant temp of water. Due to excessive H-bonds between water molecules.
saturated fats
single bonds between carbons in a lipid molecule. packs closely together, solid at room temp
unsaturated fats
double bonds between carbon in a lipid molecule. DOES NOT pack closely together, liquid at room temp
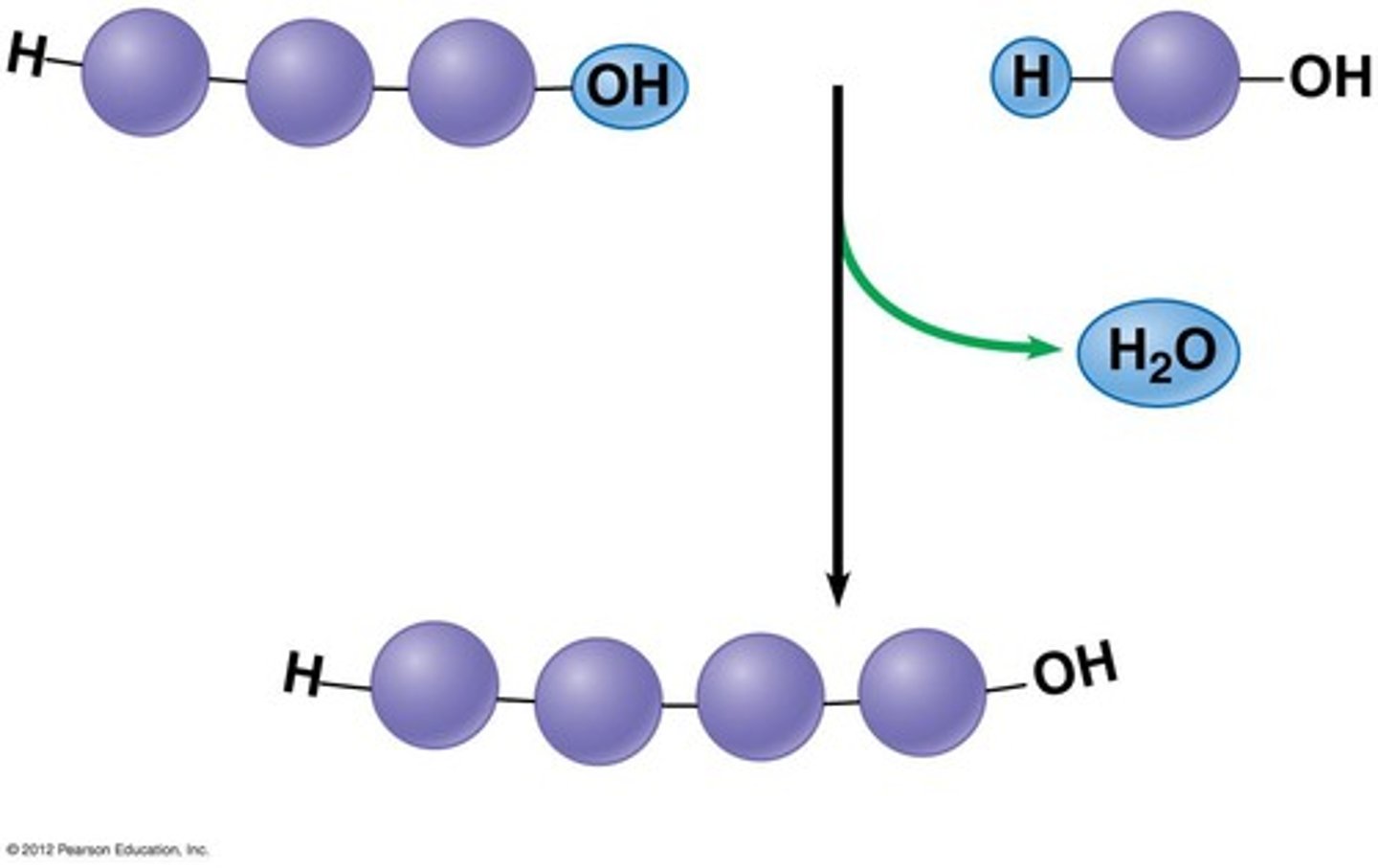
dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule.
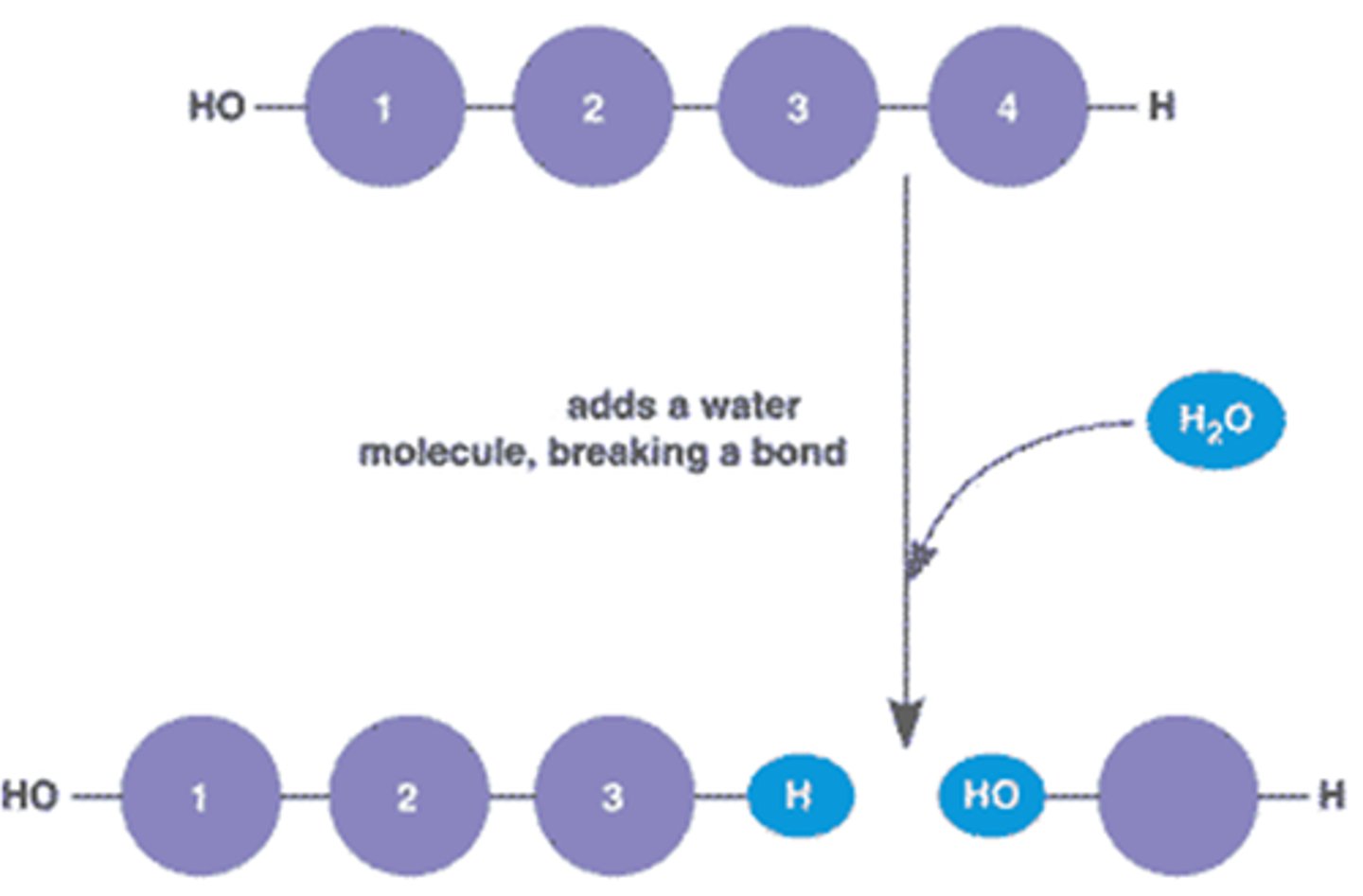
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
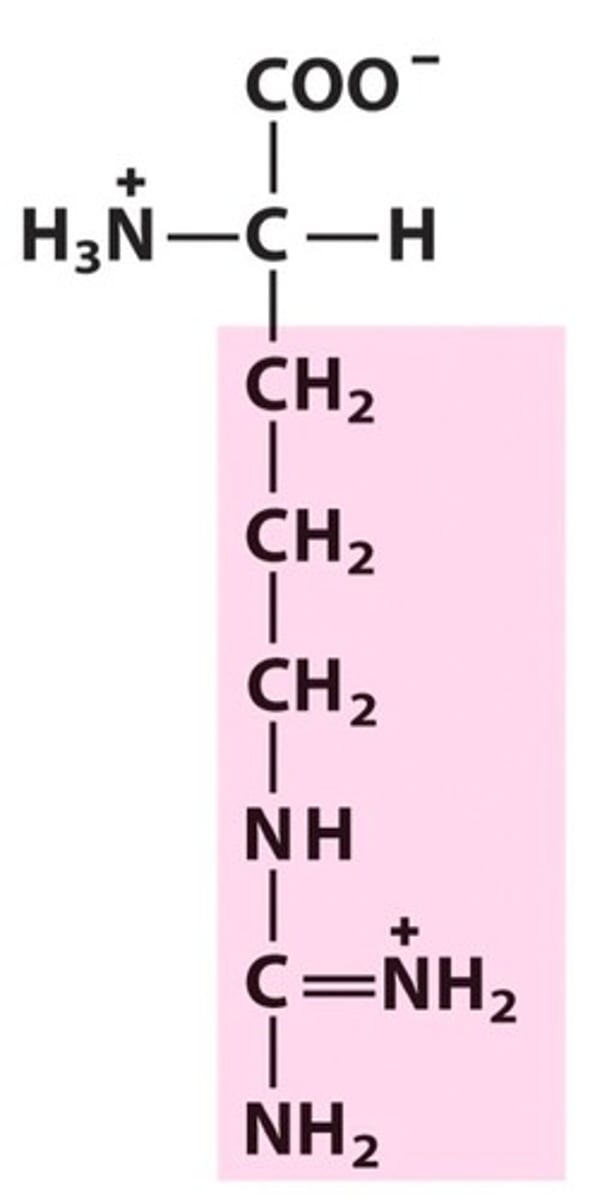
R group (side chain)
part of amino acid that determines the molecule's physical and chemical properties; determines folding
polar
Molecule with partial charges. Mixes with water.
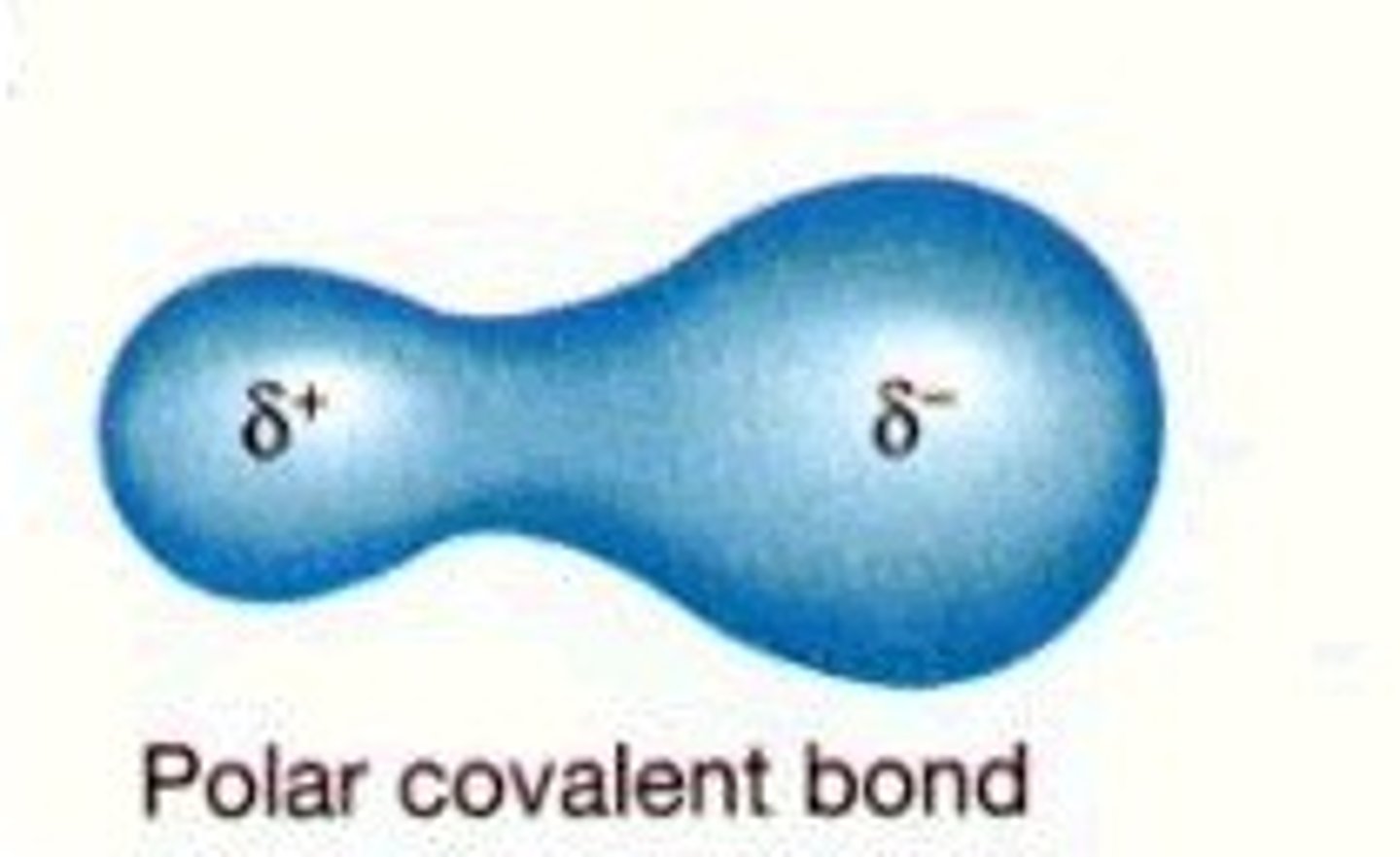
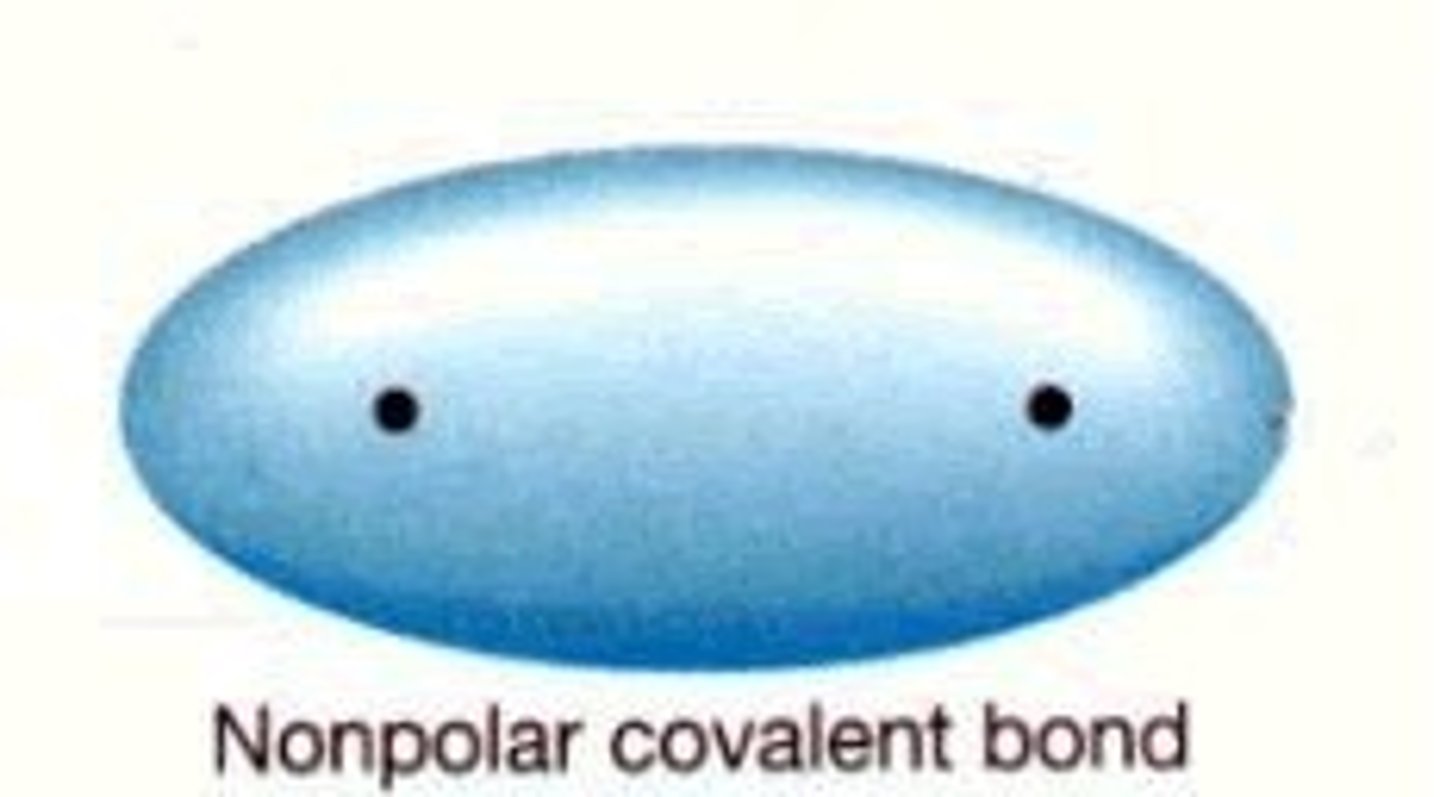
nonpolar
No partial charges. Do not mix with water.
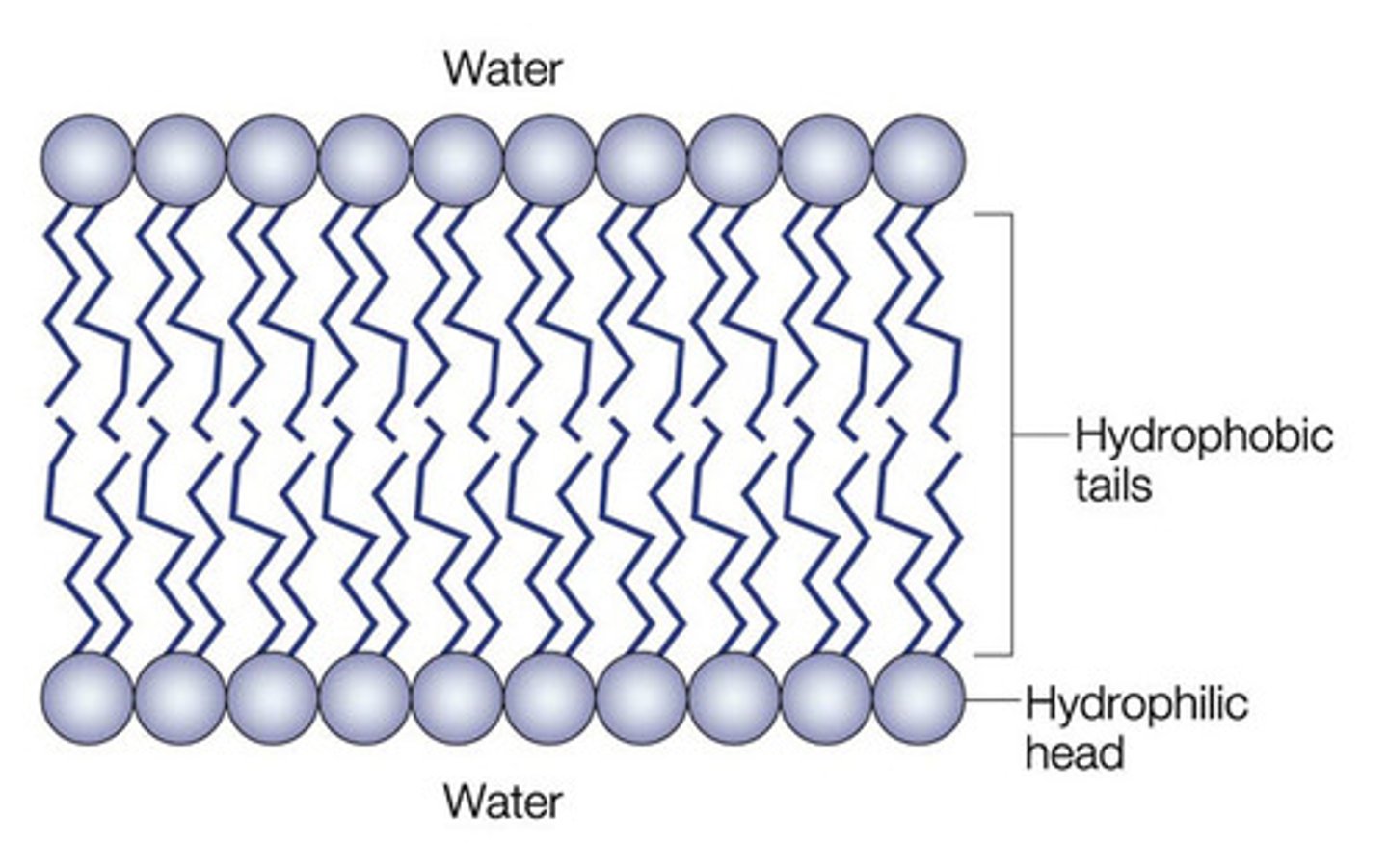
phospholipid bilayer
Plasma membrane layers composed of phospholipid molecules arranged with polar heads facing the outside and nonpolar tails facing the inside.
primary structure
The first level of protein structure; the specific sequence of amino acids making up a polypeptide chain.
secondary structure
The second level of protein structure; the regular local patterns of coils (alpha helix) or folds (beta sheets) of a polypeptide chain. occurs between interactions of the polypeptide backbone.
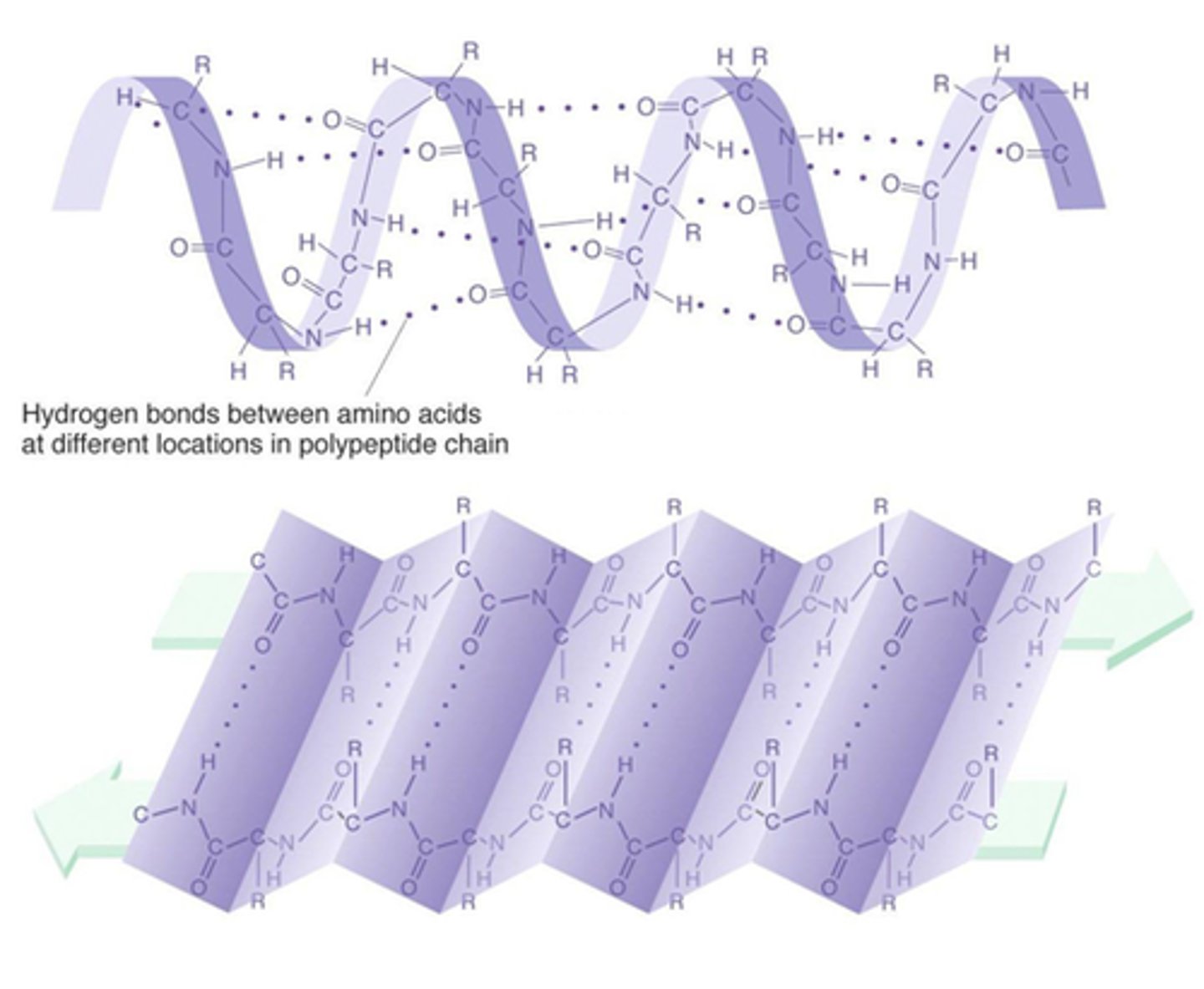
tertiary structure
is the result of folding due to interactions among R groups along the polypeptide chain. includes ionic interactions, disulfide bridges, hydrophobic/philic interactions.
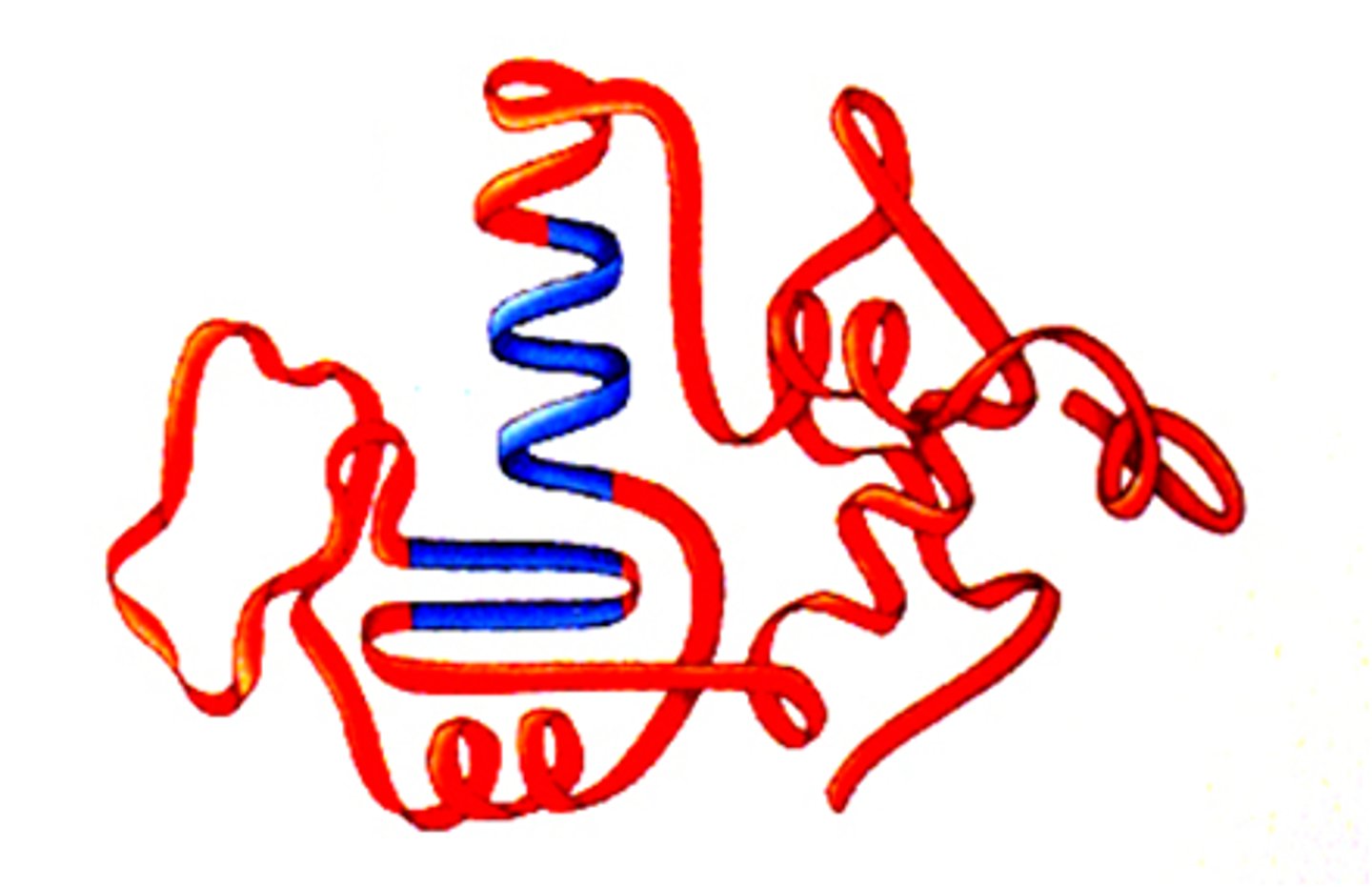
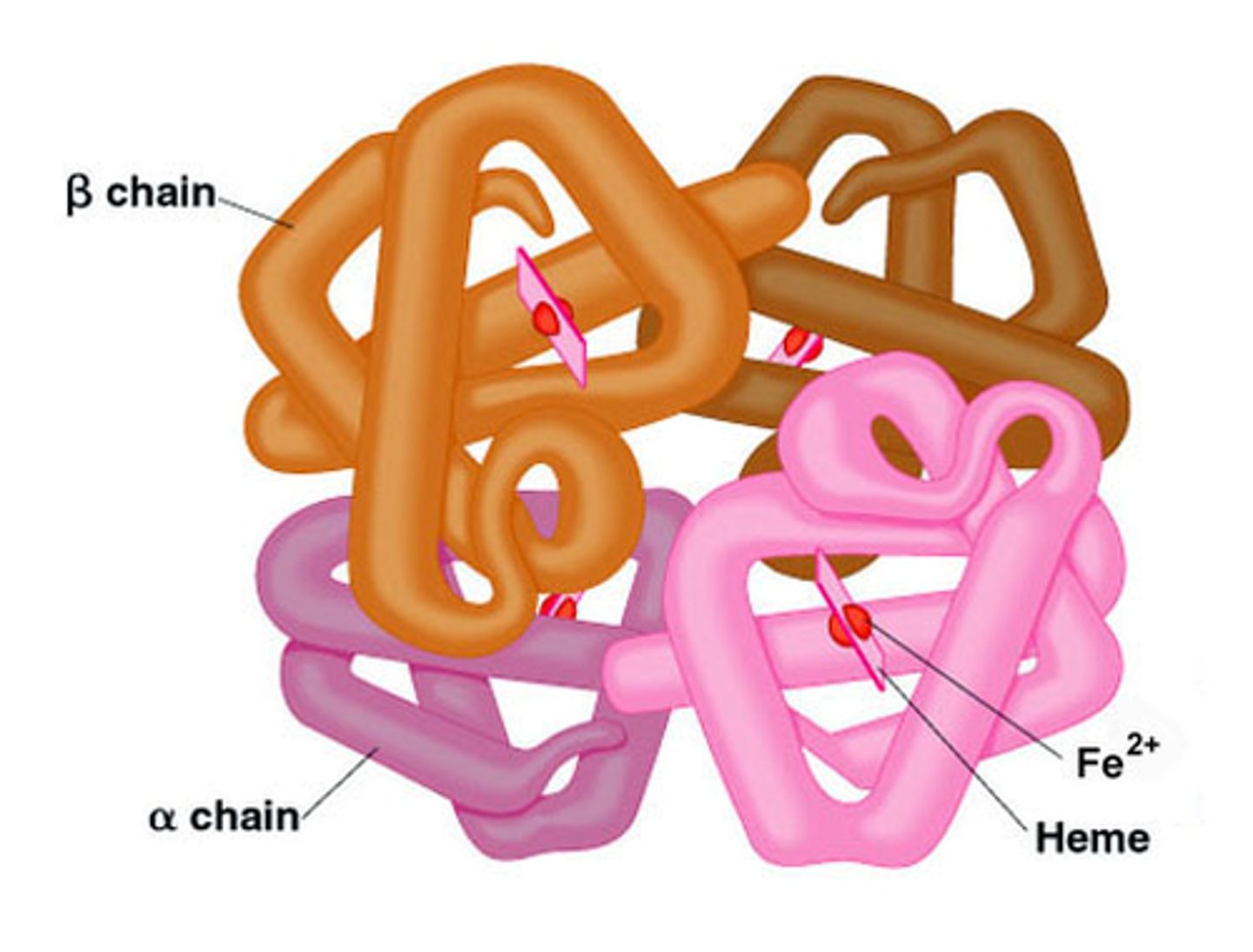
Quaternary Structure
the shape resulting from the association of two or more polypeptide subunits.
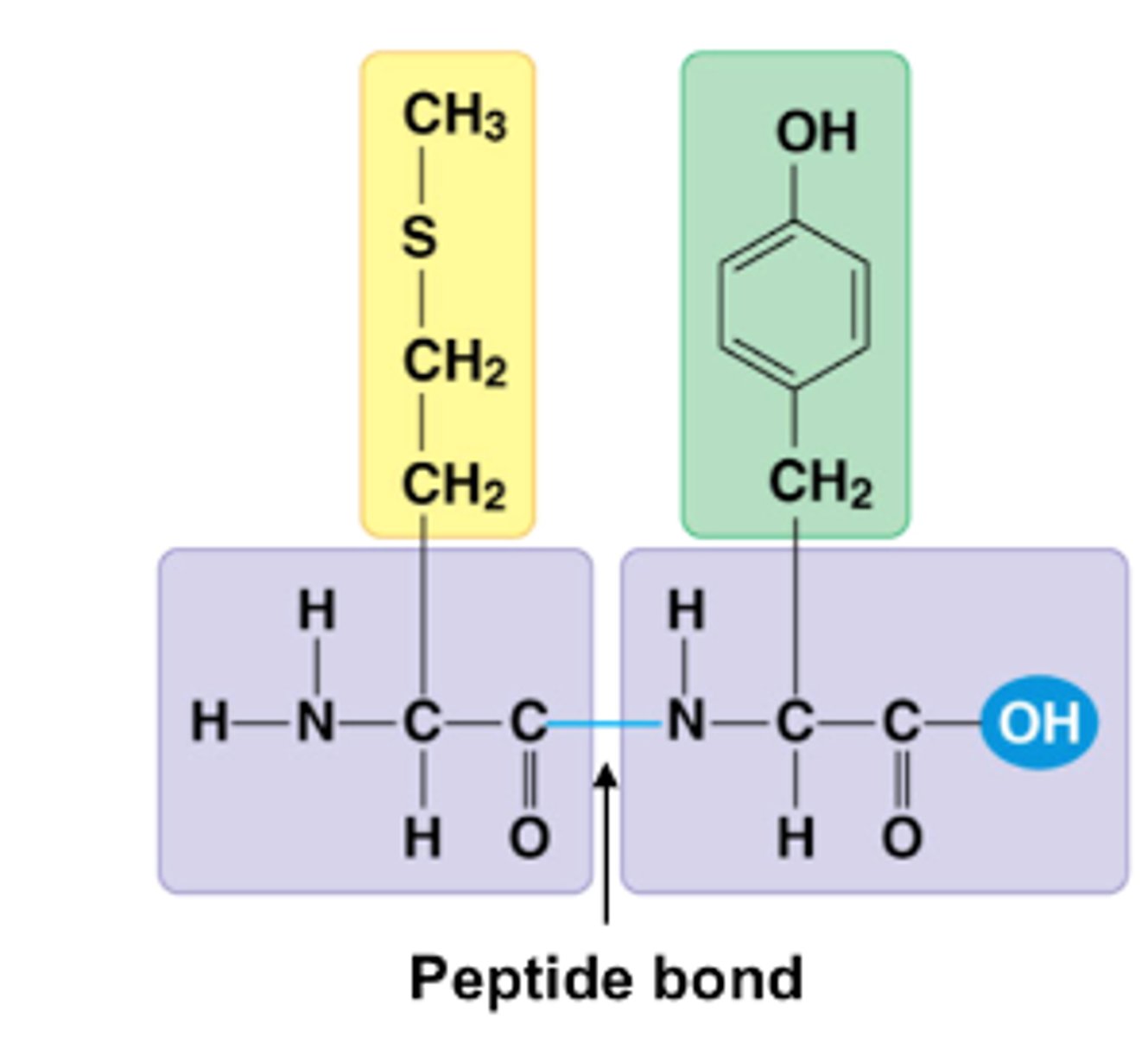
peptide bond
The chemical bond that forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid
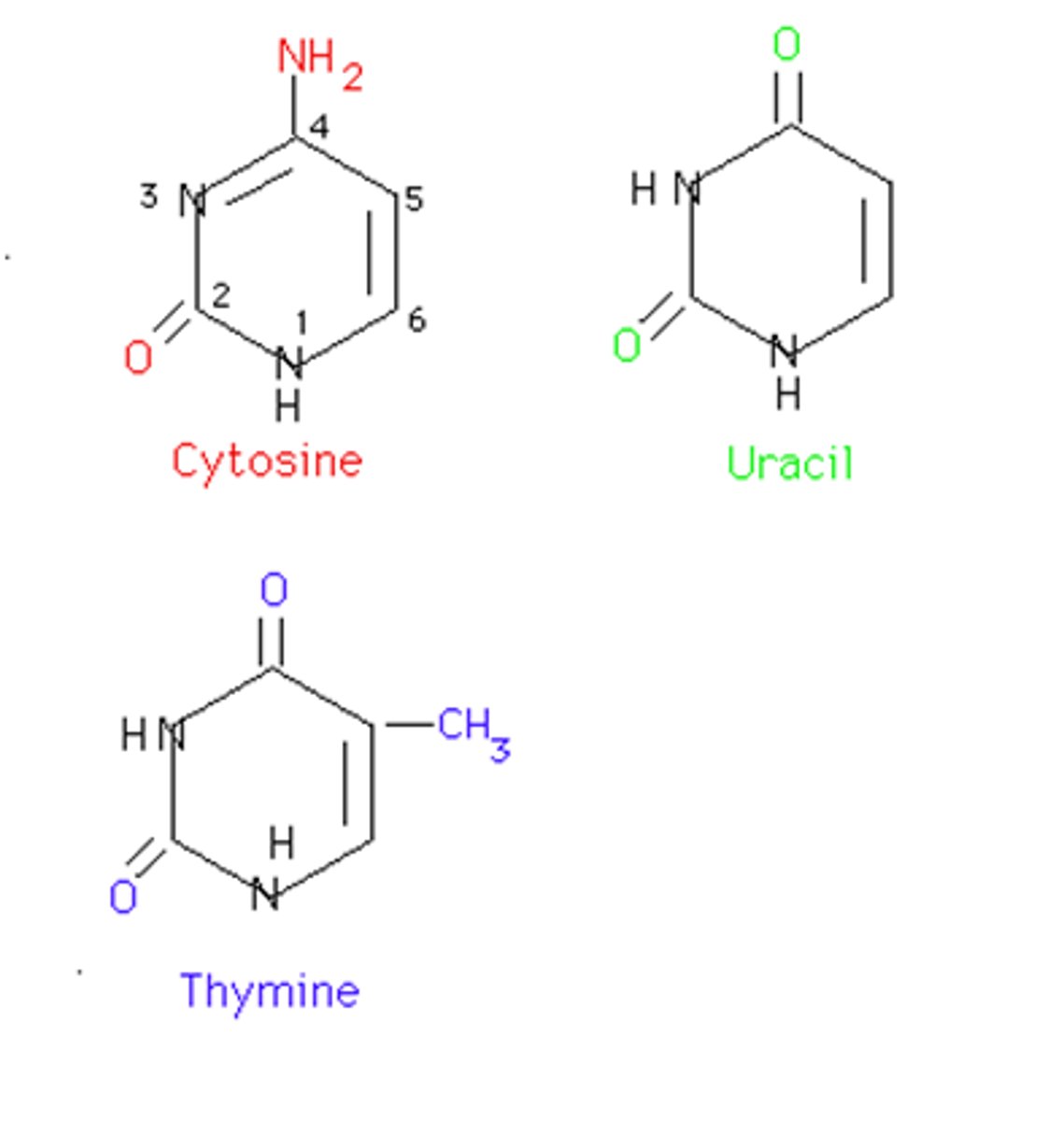
Pyrimidines
Bases with a single ring structure— cytosine, thymine, uracil
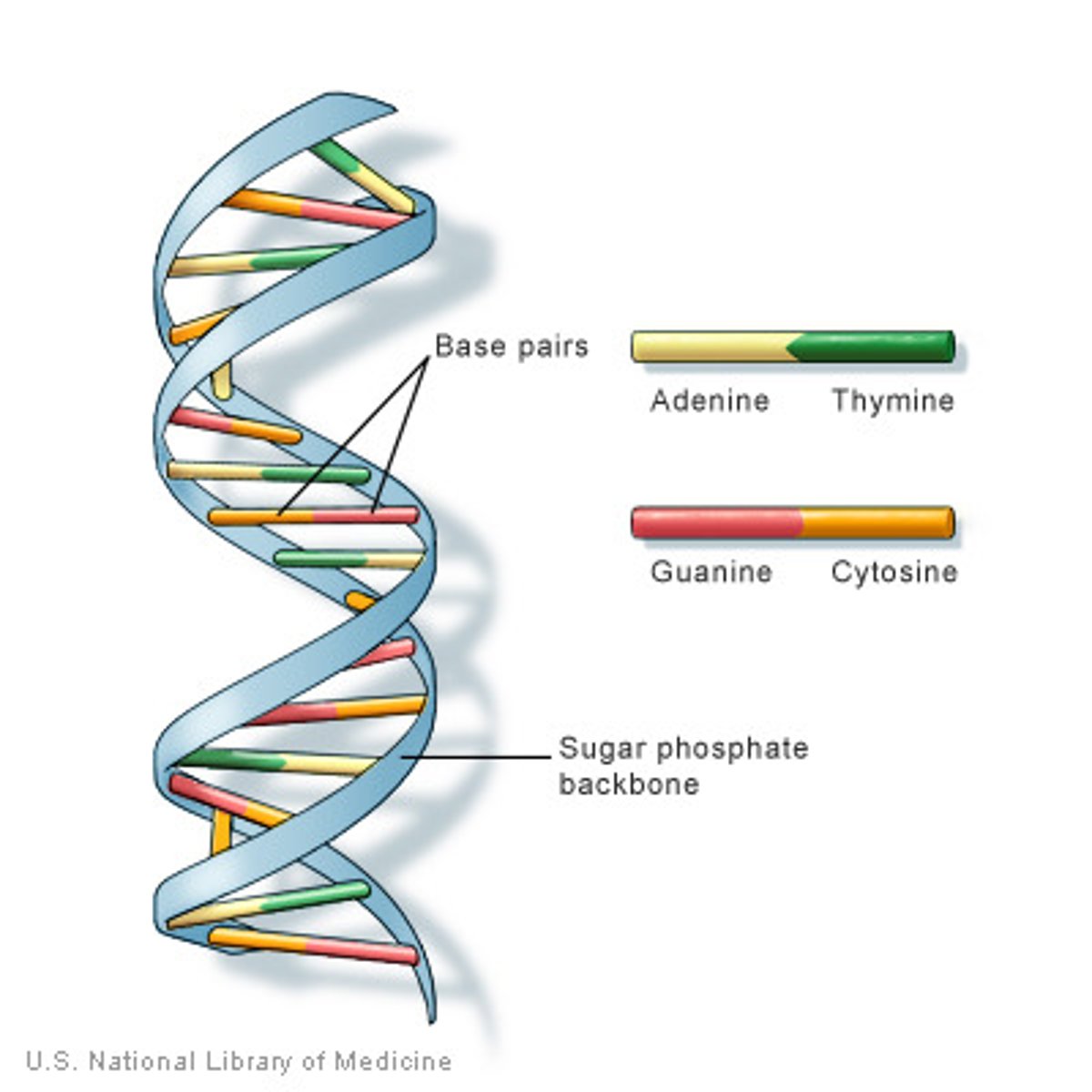
complementary base pairing rules
A always pairs with T
G always pairs with C
number of bonds between A & T
2 hydrogen bonds
number of bonds between G & C
3 hydrogen bonds
Starch
A storage polysaccharide in plants consisting entirely of glucose.
Cellulose
A substance (made of sugars) that is common in the cell walls of many organisms
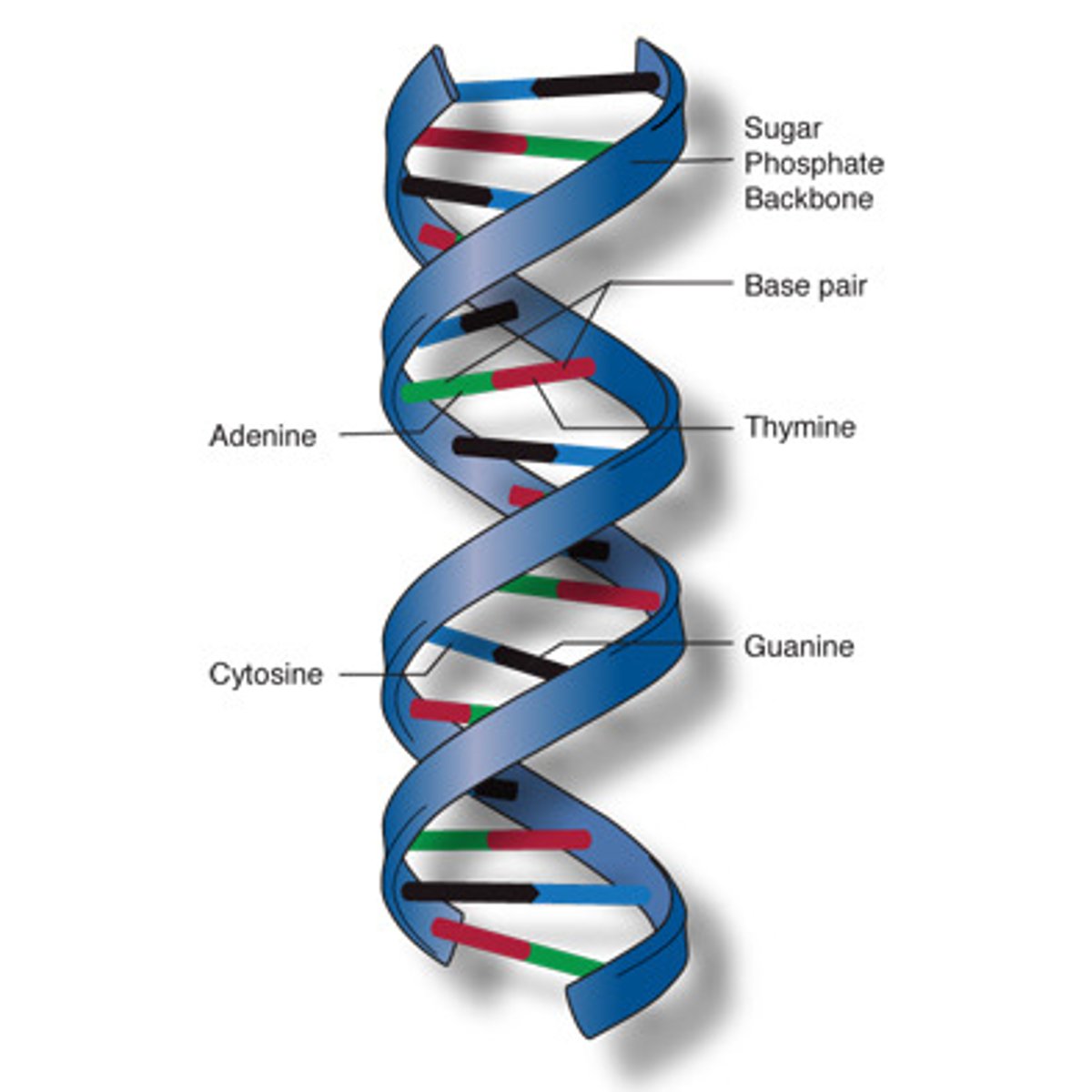
double helix
The form of DNA, referring to its two adjacent strands wound into a spiral shape.
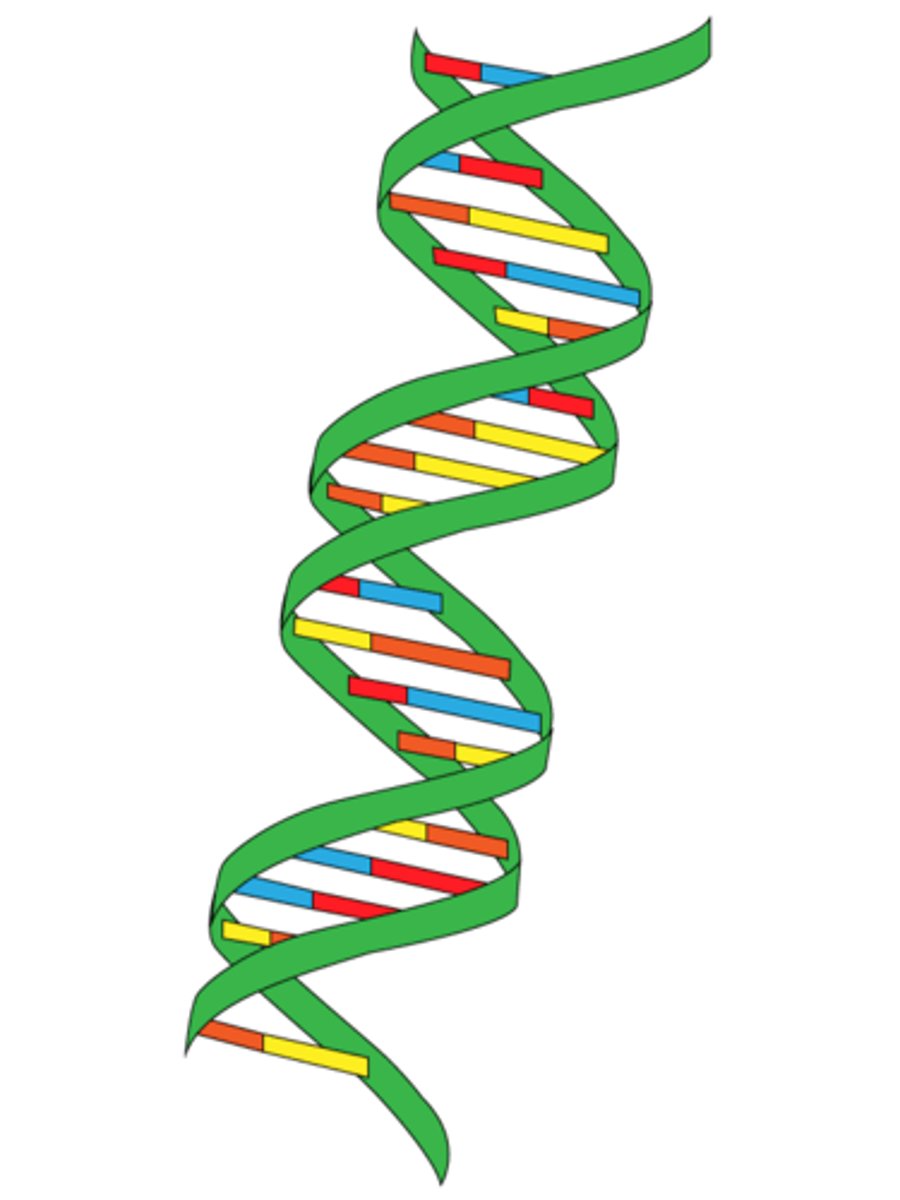
DNA backbone
Made of deoxyribose SUGAR and Phosphate. held together by covalent bonds
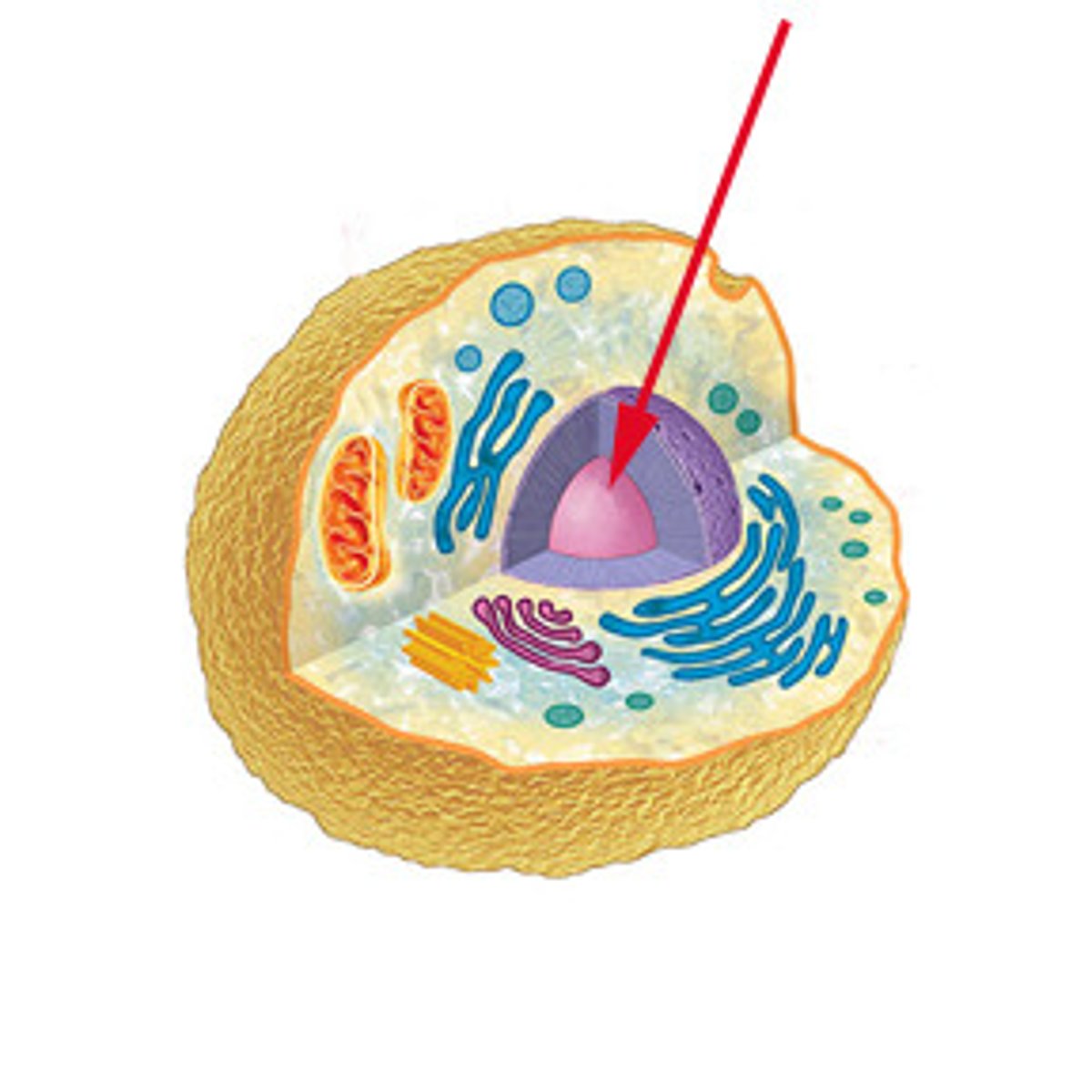
Nucleus
Dense organelle in eukaryotic cells, single rounded structure, has genetic material. Store the cells DNA and coordinates the cells activities. The brain of the cell.
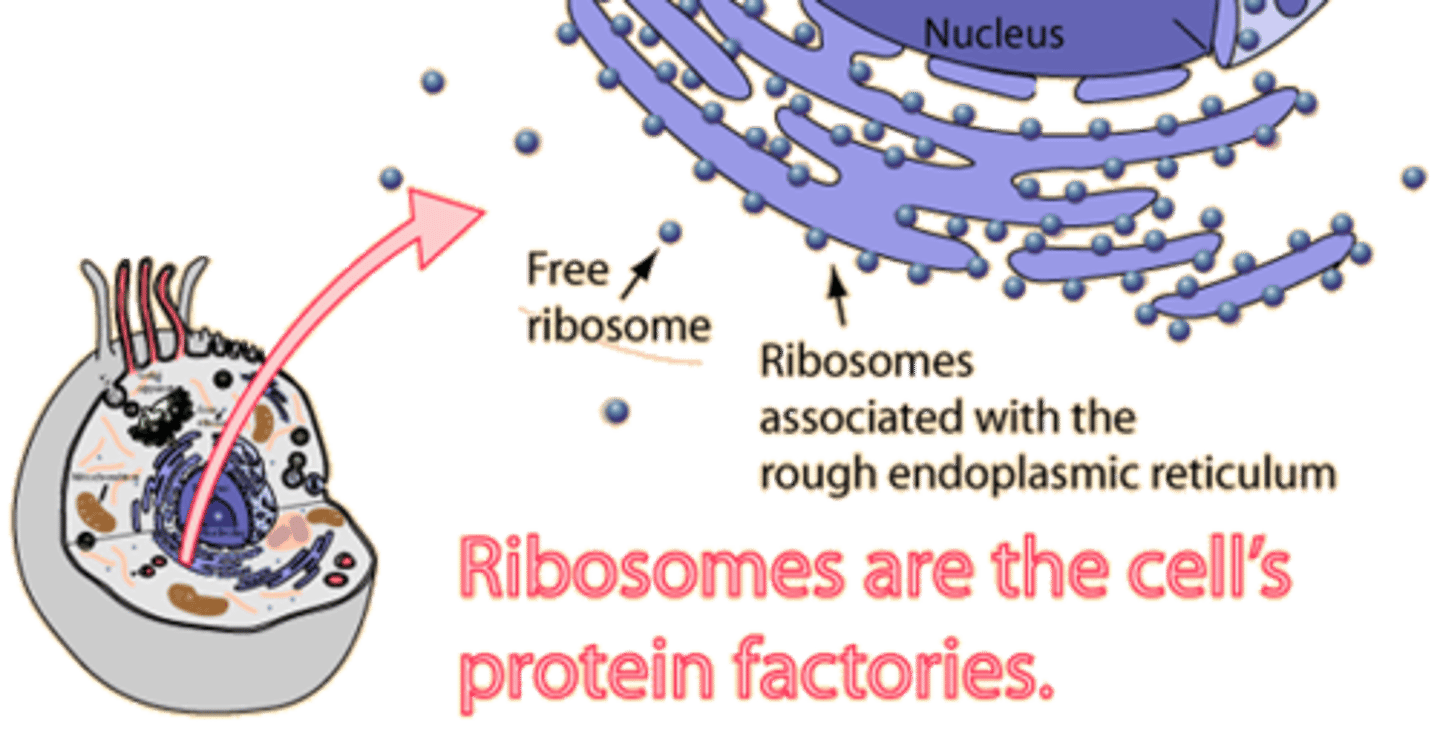
Ribosomes
Makes proteins, proteins do everything. can be on RER or free floating in the cytoplasm.
Golgi
involved in protein modification, distribution, and transport. this organelles looks like a stack of pancake-like membranes. Checks proteins and sends them to their appropriate location in or outside of the cell.
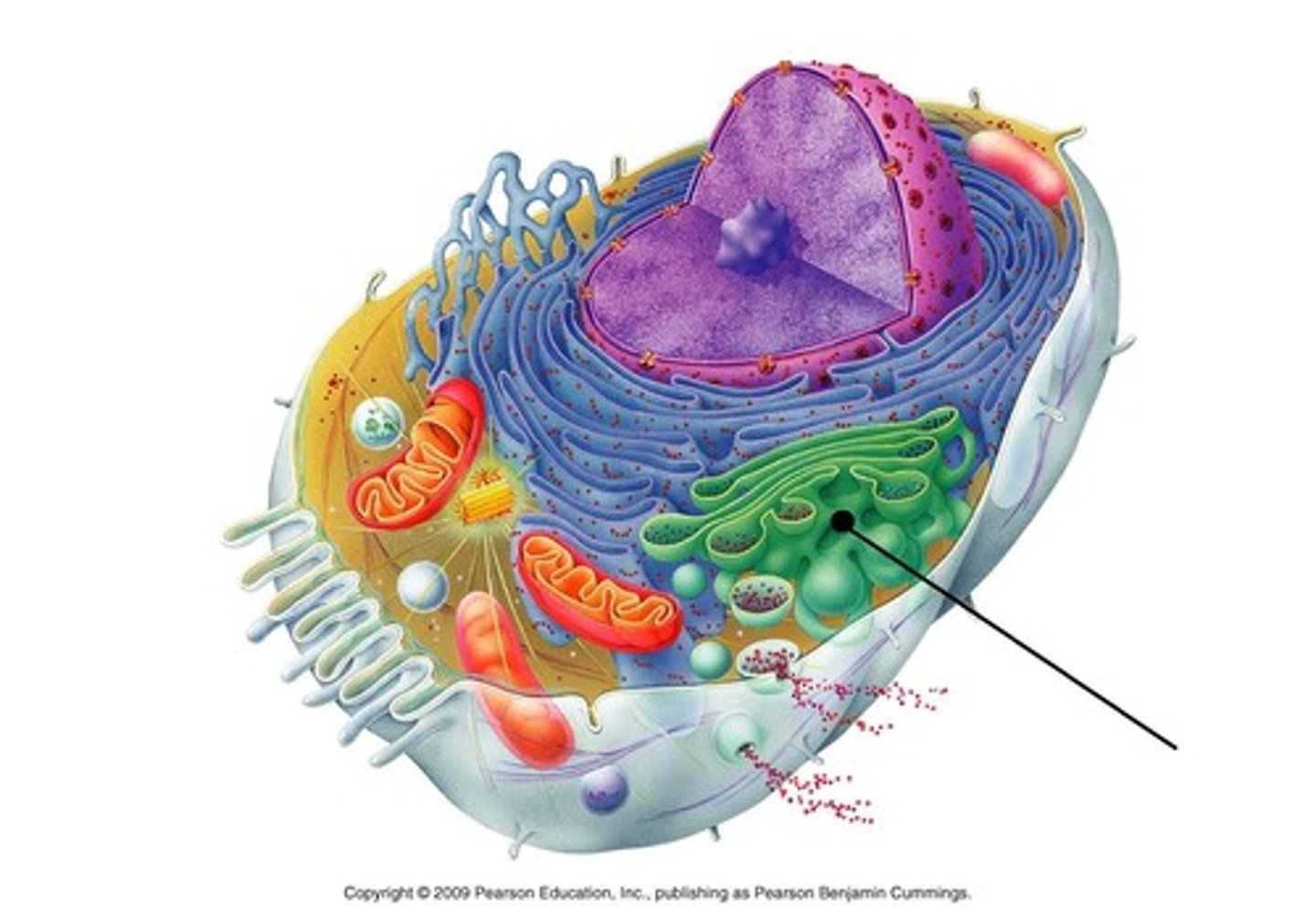
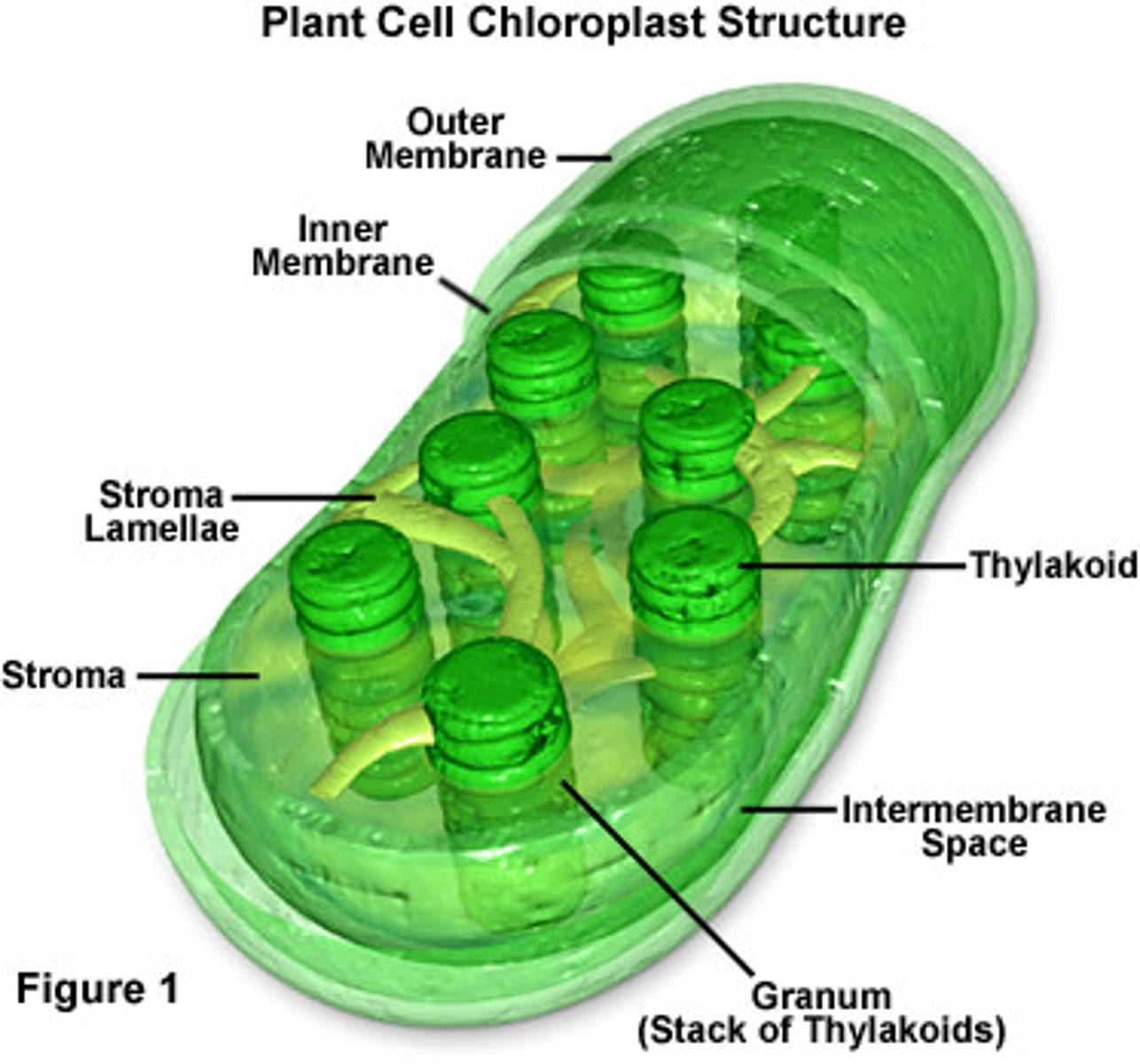
Chloroplast
in plants, photosynthesis takes place here. light energy is converted into sugar for the plant as food. plants then break down this food in the mitochondria
Lysosome
Recycles old organelles. Breaks down materials like wastes, food, or invaders.
Cell Wall
a rigid protective covering outside the plasma membrane of the cells of plants and bacteria (prokaryotes). gives cells protection and structure.
Transport vesicles
small sacs of membrane that specialize in moving products into, out of, and within a cell.
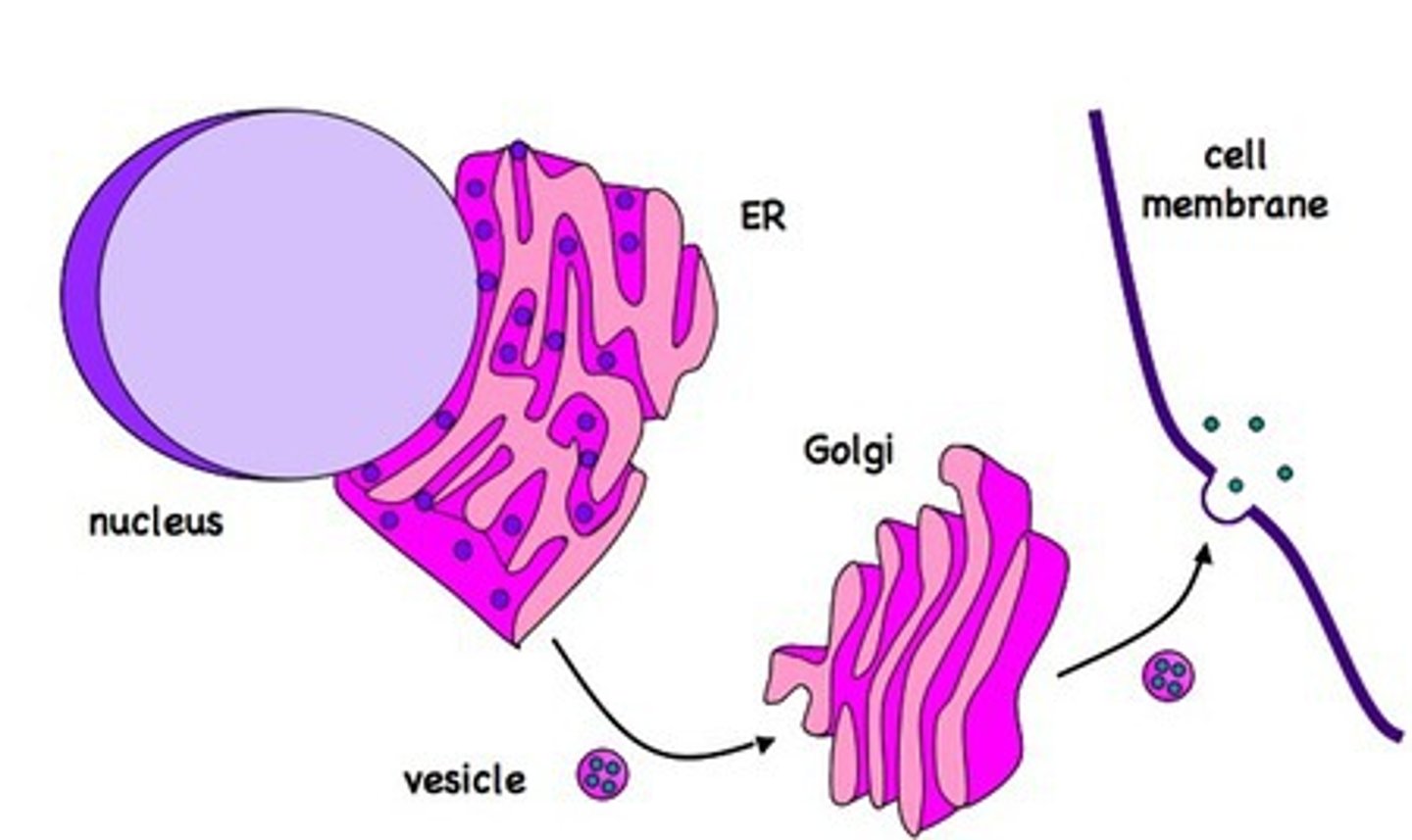
Rough ER
Has ribosomes attached. packages newly made proteins and send them to be further processed.
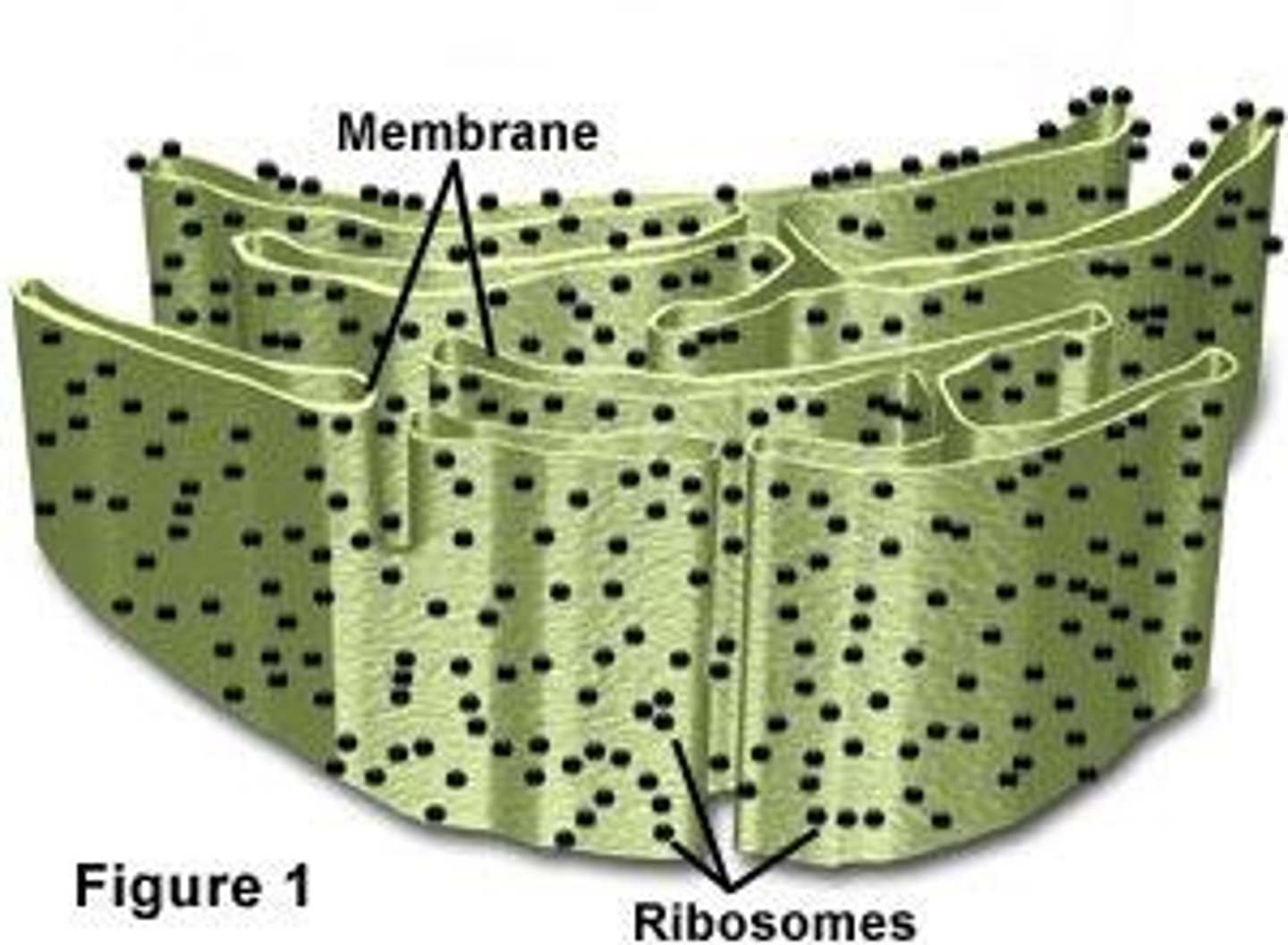
Smooth ER
Makes lipids
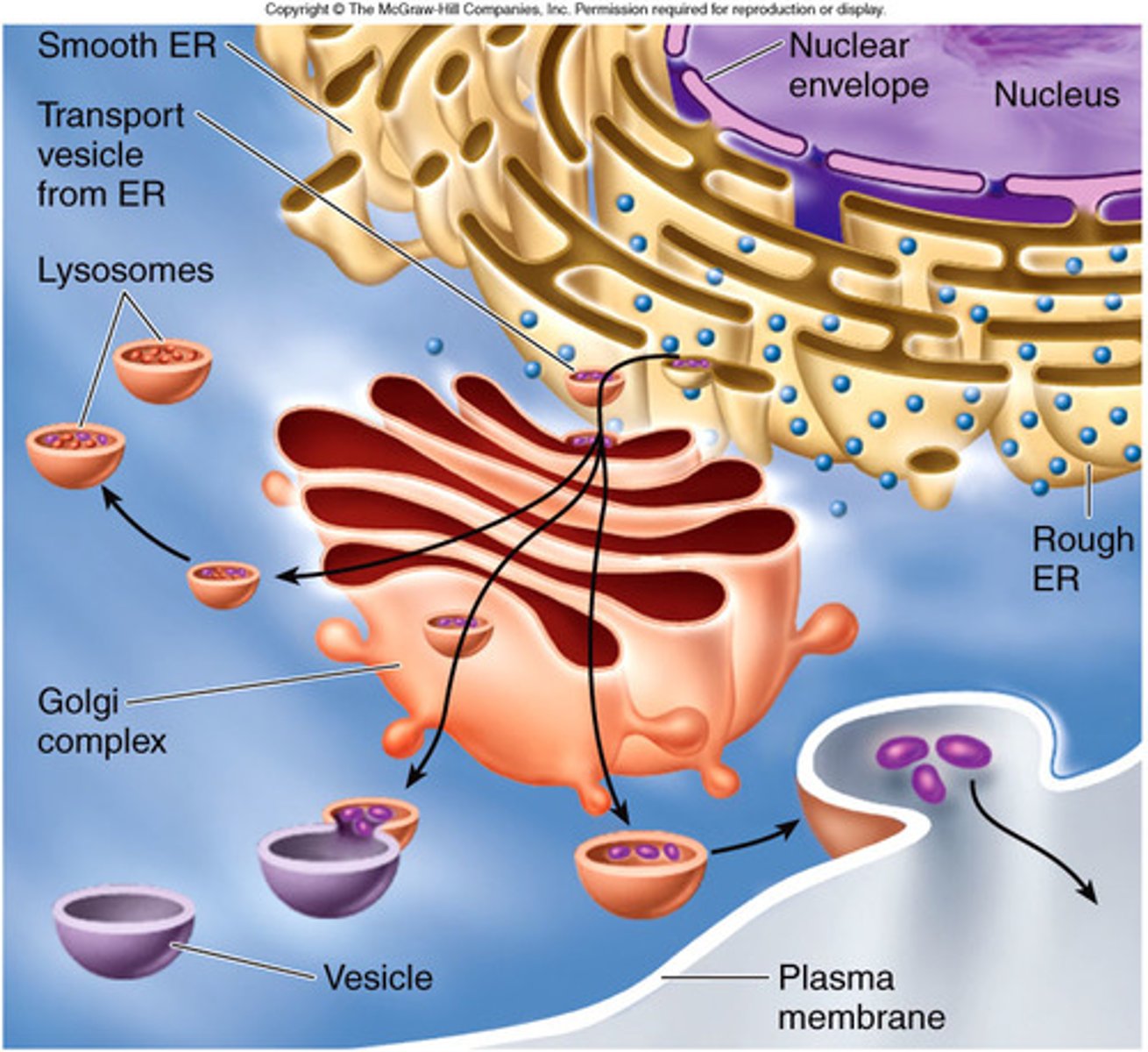
Organelles involved in protein synthesis
Nucleus (code for proteins), ribosomes (protein factory), Endoplasmic Reticulum (packs proteins), Golgi Apparatus (modifies and distributes proteins), Vesicles (transports proteins).
DNA
A macromolecule containing the genetic information
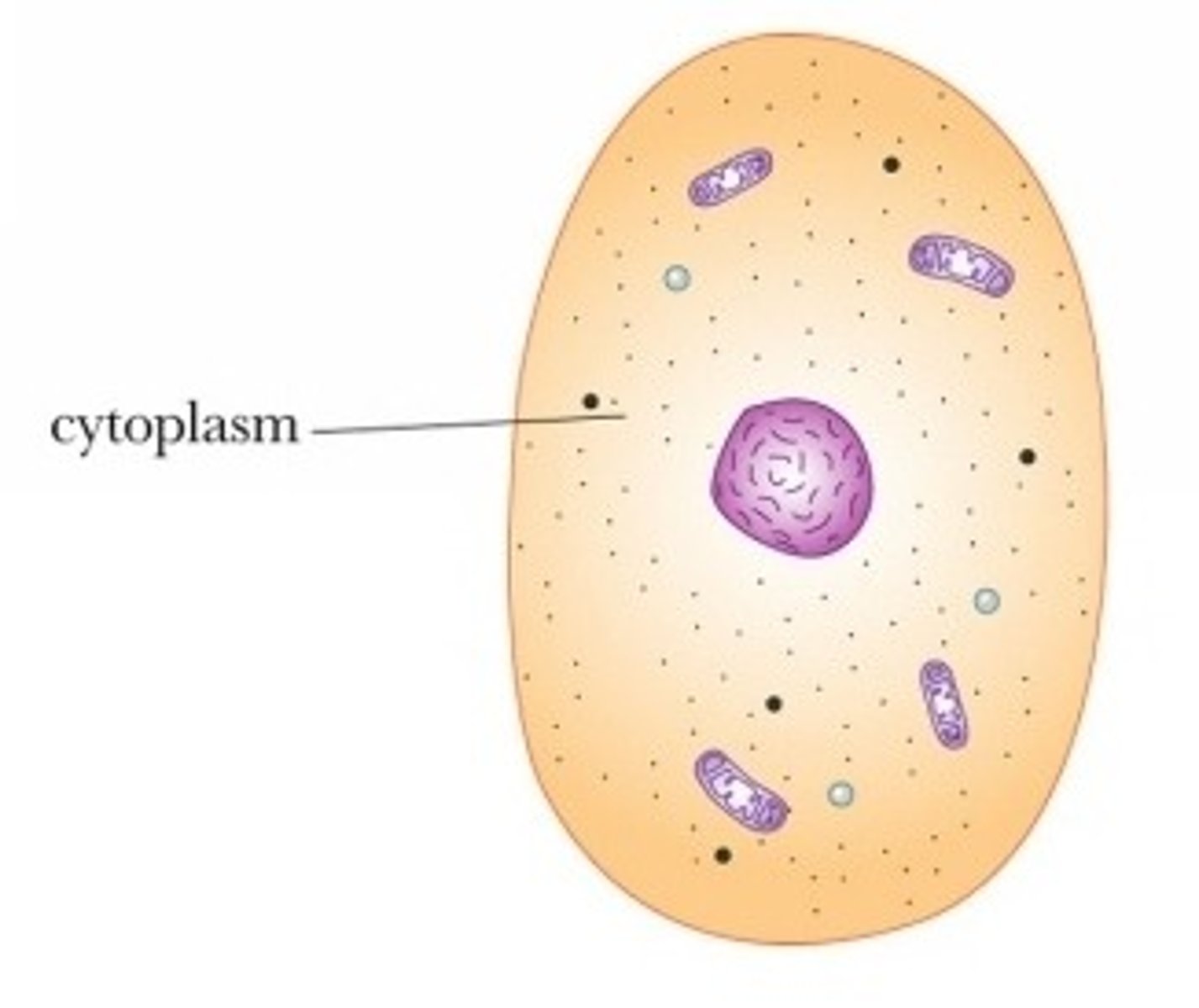
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
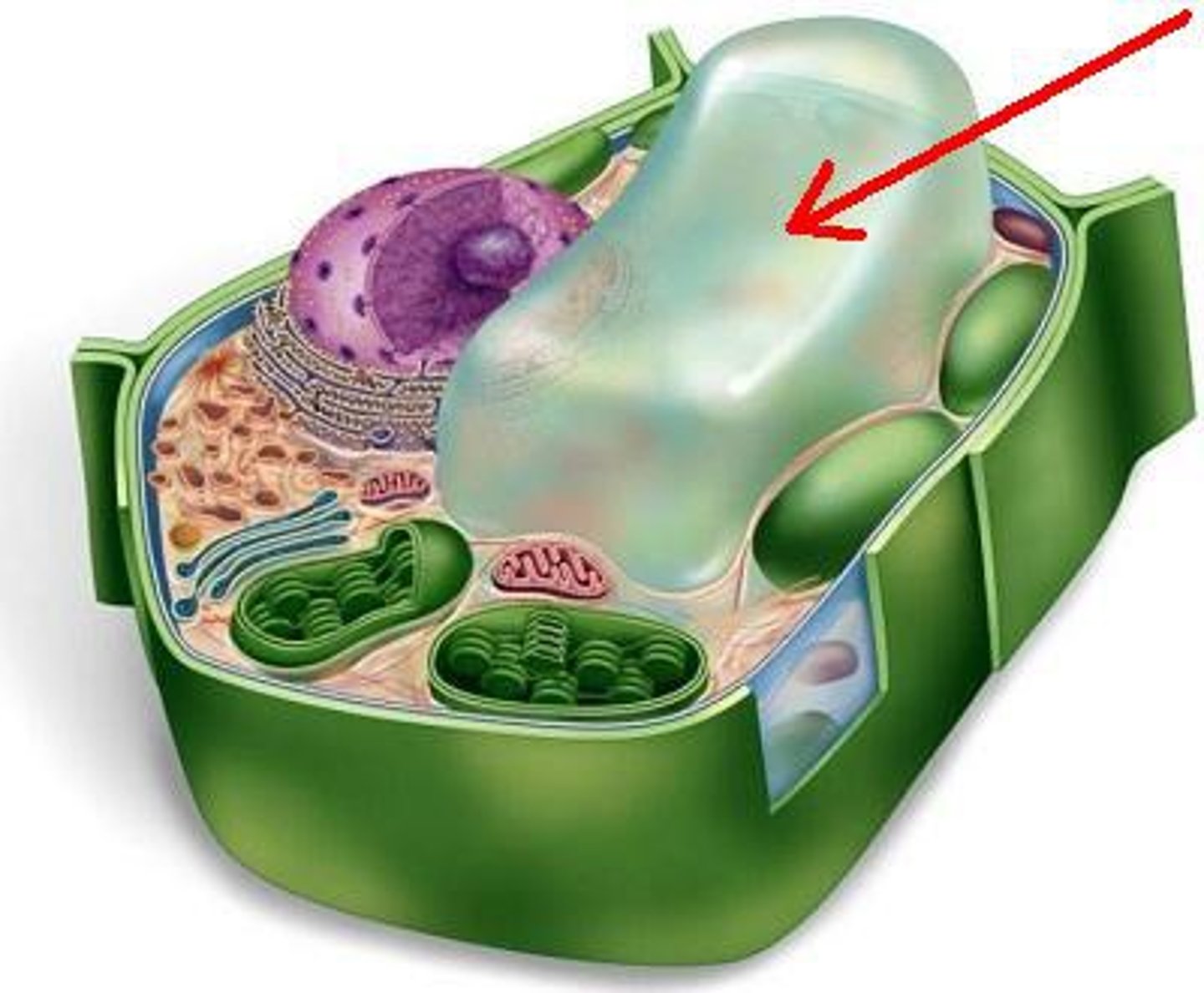
Vacuole
Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates. is very large in plants to store water.
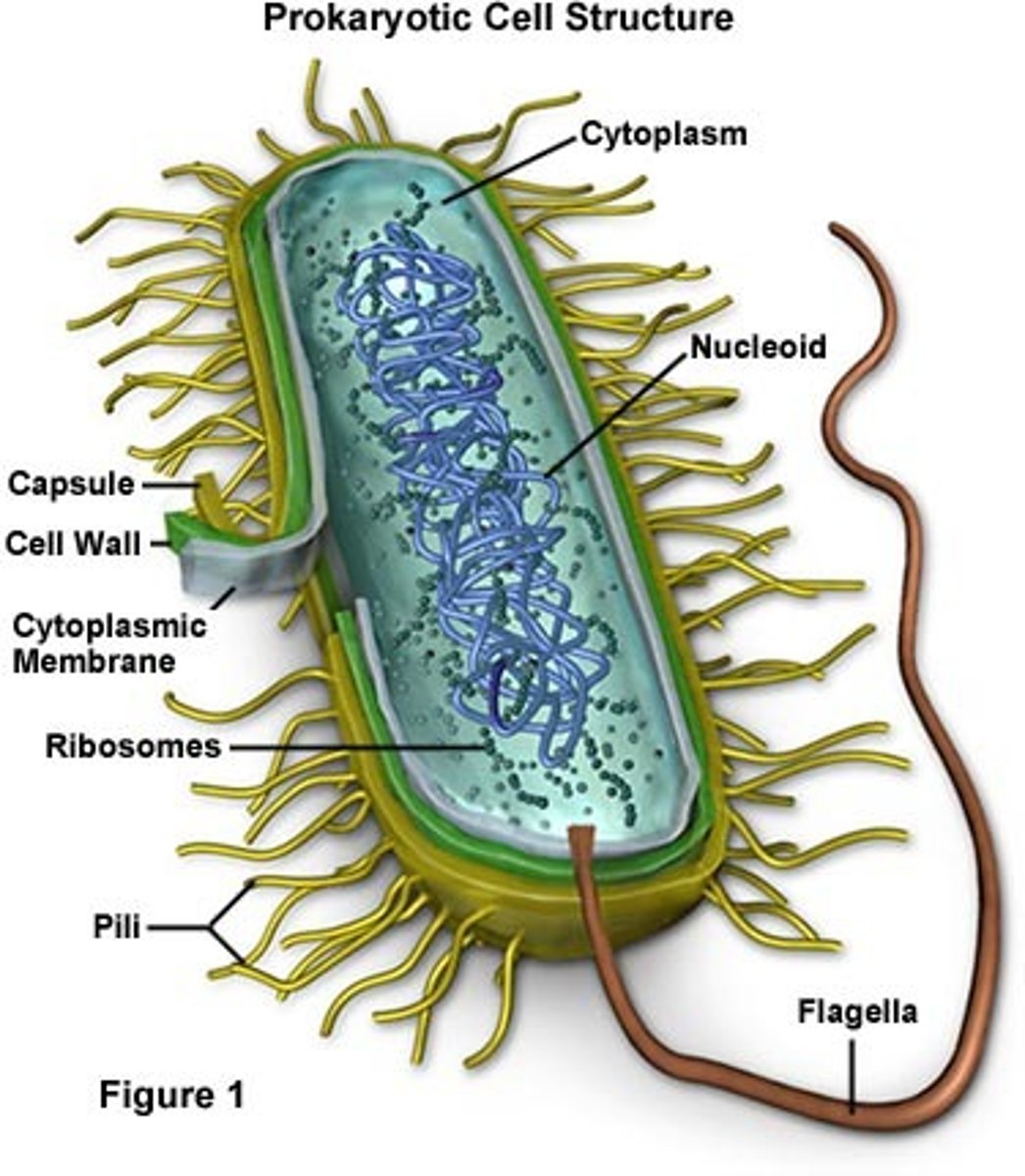
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
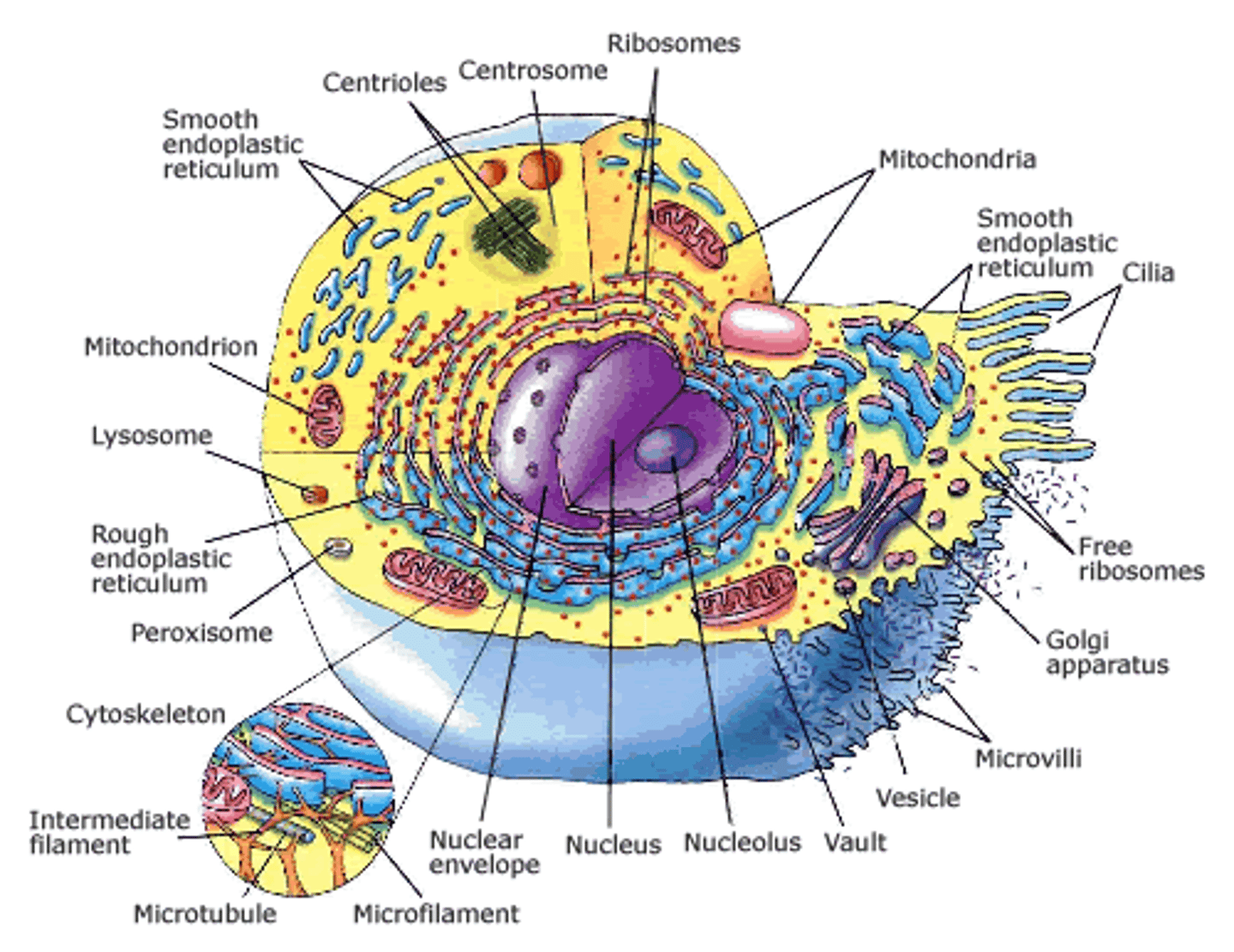
Eukaryote
A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles. very complex. plants, animals, and fungi
Organelle
A tiny membrane bound structure that carries out a specific function within the cell
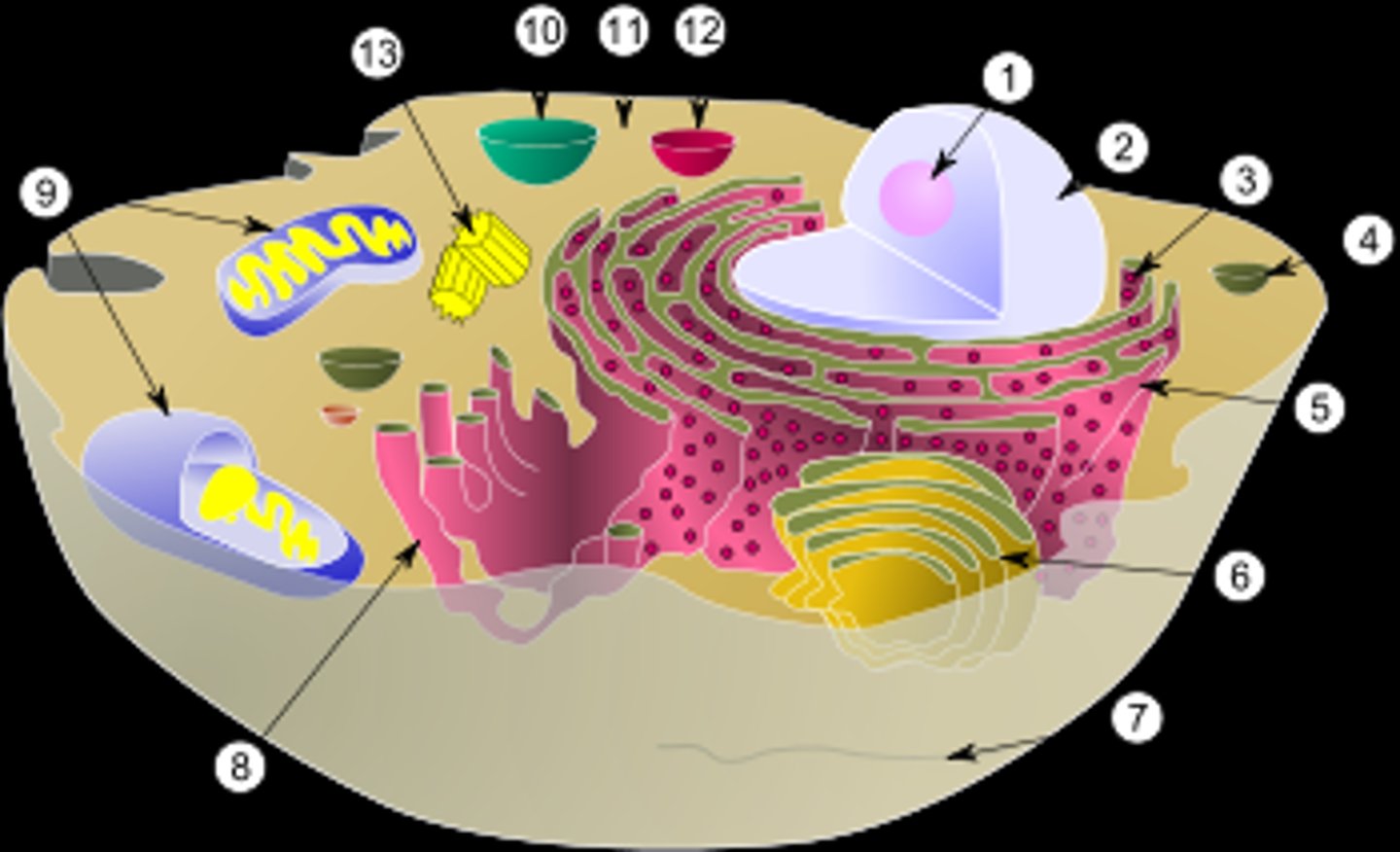
Cytoskeleton
network of protein filaments within some cells that helps the cell maintain its shape and helps move materials around the cell like a highway.
what structures do prokaryotes and eukaryotes share
cell membrane, cytosplam, ribosomes, DNA, (cell wall sometimes. plants/fungi are the only eukaryotes with a cell wall)
Properties of eukaryotic cells
Large in size, many pieces of linear DNA. can have specialized functions. more complex
have membrane bound organelles: Nucleus, Endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, Mitochondria, Chloroplast, smooth ER ect.
Properties of prokaryotic cells
- free floating DNA (no nucleus)
- no membrane bound organelles
- size: very small
- unicellular
-reproduce fast!
-evolve fast!
- bacteria
chromosome
piece of DNA
binary fission
copy DNA and divide a cell into 2 cells
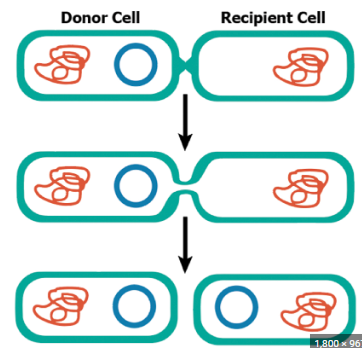
conjugation
transmission of plasmids from one prokaryotic cell to another via sex pilis
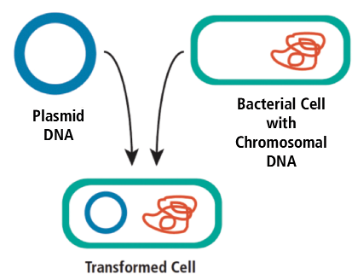
transformation
the uptake and use of DNA (plasmids) from surroundings and environment
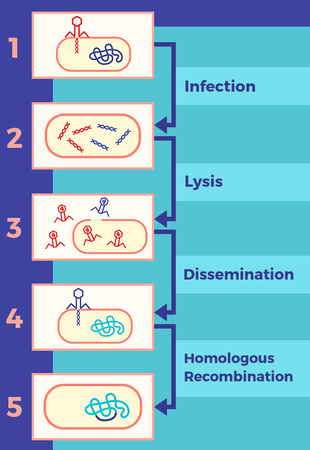
transduction
the process by which a virus transfers genetic material from one prokaryote to another, occurs when viruses infect prokaryotes and result of malfunction of viral infection
horizontal gene transfer
transmission of DNA within one generation
selectively permeable
only allow certain molecules in/out of cell due to molecule structure