CSCS Ch 1 - Structure and Function of Body Systems
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Skeletal muscles are under the control of the ____ ____ which activates the skeletal muscle cells or fibers through the motor neurons of the ____ ____ ____
Cerebral Cortex; Peripheral Nervous System
The _____ system of the human body consists of bones, joints, muscles, and tendons configured to allow the great variety of movements characteristic of human movement
Musculoskeletal
T/F: The muscles of the body can only pull, not push. It is the bony lever system that allows muscle pulling forces to occur resulting in the push or pull of forces against external objects
True! → The muscles of the body do not act directly to exert force on the ground or other objects
The ____ ____ consists of the skull (cranium), vertebral column (vertebra C1-coccyx), ribs, and sternum
Axial skeleton
The _____ _____ includes the shoulder (or pectoral) girdle ( L and R scapula and clavicle); bones of the arms, wrists, and hands (L and R humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges); the pelvic girdle (L and R coxal or innominate bones); and the bones of the legs ankles, and feet (L and R femur, patella, tibia, fibula, tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges)
Appendicular skeleton
Junctions of bones are called ____
Joints
____ joints allow virtually no movement
Fibrous (i.e. sutures of the skull)
_____ joints allow limited movement
Cartilaginous (i.e. intervertebral disks)
______ joints allow considerable movement
Synovial (i.e. elbow and knee) → Sport and exercise movements occur mostly at synocial joints whose most important features are low friction and large ROM
Articulating bone ends are covered with smooth ____ _____ and the entire joint is enclosed in a capsule filled with _____ _____
Hyaline cartilage; synovial fluid
_____ joint examples: elbow, knee
Uniaxial (1 DOF)
____ joint examples: ankle, wrist
Biaxial (2 DOF)
____ joint examples: shoulder, hip
Multiaxial (3 DOF)
Vertebral Column:
___ cervical
___ thoracic
___ lumbar
___ sacral
___ coccyx
7 C-Spine, 12 T-Spine, 5 L-Spine, 5 Sacral, 3-5 Coccyx
_____ is fibrous connective tissue that covers the body’s more than 430 skeletal muscles. Is continuous with the tendons at the ends of the muscle
Epimysium
The tendon is attached to ____ _____, a specialized connective tissue covering all bones; any contraction of the muscle pulls on the tendon, and in turn, the bone
Bone periosteum
Muscle fibers under the epimysium grouped in bundles are called _____
Fasciculi
The muscle fiber bundles (fasciculi) are surrounded by connective tissues called _____
Perimysium
Each muscle fiber is surrounded by connective tissue called _____
Endomysium
Endomysium is encircled by and continuous with the fiber’s membrane which is called the _____
Sarcolemma
The junction between a motor neuron (nerve cell) and the muscle fibers it innervates is called the motor end plate, or the _____ _____
Neuromuscular Junction
T/F: Each muscle cell can have multiple neuromuscular junctions
False! → Each muscle cell only has one neuromuscular junction, although a single motor neuron innervates many muscle fibers, sometimes hundreds or even thousands
A motor neuron and the muscle fibers it innervates are called a ___ ___
Motor Unit
The ____, which is the cytoplasm of a muscle fiber, contains contractile components consisting of protein filaments, other proteins, stored glycogen, and fat particles, enzymes, and specialized organelles such as mitochondria and the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Sarcoplasm
____ contain the apparatus that contracts the muscle cell, which consists primarily of two types of myofilament (myosin and actin)
Myofibrils
What are the two primary types of myofilaments?
Myosin (thick) and actin (thin)
T/F: A myosin filament consists of a globular head, a hinge point, and a fibrous tail
True! → The globular heads protrude away from the myosin filament at regular intervals, and a pair of myosin filaments forms a crossbridge, which interacts with actin
Myosin and actin filaments are organized longitudinally in the smallest contractile unit of skeletal muscle, the _____
Sarcomere
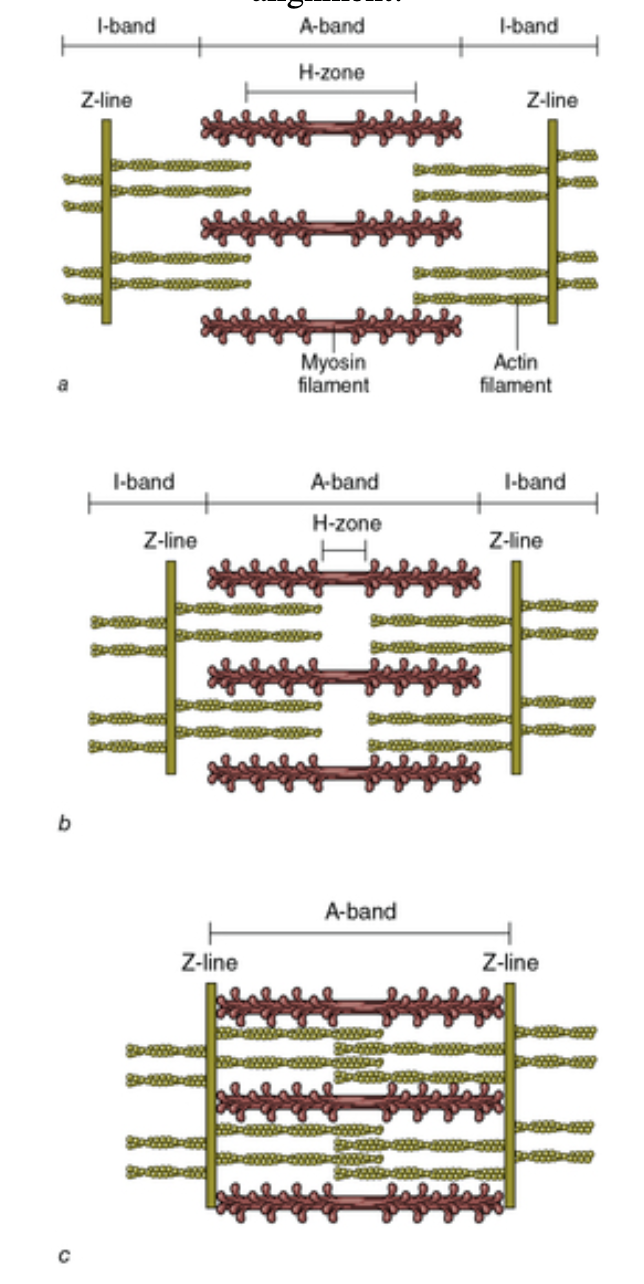
During a muscle contraction:
The __- ___ decreases as the actin slides over the myosin towards the center of the sarcomere
The __ - ___ also decreases as the Z-lines are pulled toward the center of the sarcomere
H-zone; I-band
Parallel to and surrounding each myofibril is an intricate system of tubules, called the ____ ____
Sarcoplasmic reticulum → terminates as vesicles are in the vicinity of Z-lines
T/F: Calcium ions are stored in the vesicles and regulation of this calcium controls muscular contractions
True!
How does a muscle contract at a cellular level?
T-tubules run between outlying myofibrils and are contiguous with the sarcolemma at the surface of the cell, discharge of an action potential (an electrical nerve impulse) arrives nearly simultaneously from the surface to all depths of the muscle fiber. Calcium is thus released throughout the muscle, producing a coordinated contraction
T/F: The discharge of an action potential from a motor nerve signals the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the myofibril, causing tension development in muscle
True!
____ - ____ theory: states that the actin filaments at each end of the sarcomere slide inward on myosin filaments, pulling the Z-lines toward the center of the sarcomere and thus shortening the muscle fiber.
Sliding-Filament Theory
Since only a very small displacement of the actin filament occurs with each flexion of the myosin crossbridge, very rapid, repeated flexions must occur in many crossbridges throughout the entire muscle for measurable ____ to occur
Movement
T/F: Force potential is highest when a muscle is fully contracted due to optimal crossbridge-actin alignment
False! →
In stretched muscle the I-bands and H-zone are elongated, and there is LOW force potential due to reduced crossbridge-actin alignment
When muscle contracts partially, the I-bands and H-zone are shortened. Force potential is HIGH due to optimal crossbridge-actin alignment
With contracted muscle, force potential is low because the overlap of actin reduces the potential for crossbridge-actin
In normal resting conditions, little calcium is present in the myofibril so very few of the myosin crossbridges are bound to actin. Where is most of the calcium stored?
In the sarcoplasmic reticulum
T/F: The myosin crossbridges can flex regardless of if they are attached to an actin filament
False! → Myosin must first attach to the actin filament
_____ is a protein that is situated at regular intervals along the actin filament and has a high affinity for calcium ions
Troponin
_____ is a protein that runs along the length of the actin filament in the groove of the double helix. This allows the myosin crossbridge to attach more rapidly to the actin filament and produce a force as the actin filaments are pulled toward the center of the sarcomere
Tropomyosin