Derm micro 12/3/25
1/106
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This flashcard set covers key vocabulary and definitions from the lecture on dermatology, focusing on various skin infections, their causative agents, and relevant treatment options.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
yeast
malassezia furfur
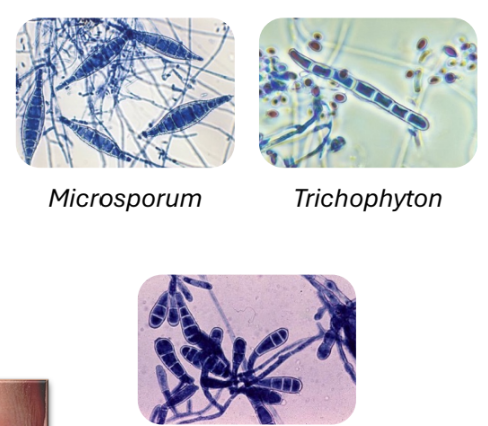
monomorphic molds
Dermatophytes:
• Microsporum
• Trichophyton
• Epidermophyton
dimorphic molds
Blastomyces dermatididis (skin lesions only)
dna, non enveloped viruses
• Parvovirus B19
• Human Papilloma Virus (warts)
dna enveloped viruses
• Herpes Simplex Virus
• HHV6 (roseola)
• HHV8 (Kaposi's)
• Varicella Zoster Virus
• Molluscum Contagiosum Virus
rna non enveloped virus
coxsackievirus (HFMD)
rna enveloped virus
• Measles (Rubeola)
• Rubella (rash only)
parvoviridae
non-enveloped, ssDNA, linear
Parvovirus B19
papillomaviridae
non-enveloped, dsDNA, circular
Human Papilloma Virus
herpesviridae
enveloped, dsDNA, linear
Herpes Simplex Virus
HHV6 (roseola)
HHV8
Varicella Zoster Virus
poxviridae
enveloped, dsDNA, linear, replicates in cytoplasm
Molluscum Contagiosum Virus
picornaviridae
non-enveloped, ssRNA, positive, non-segmented
Coxsackievirus
paramyxoviridae
enveloped, ssRNA, negative, non-segmented
Measles (Rubeola)
matonaviridae
enveloped, ssRNA, positive, non-segmented
Rubella
gram positive cocci
• Staphylococcus aureus – including MRSA
• Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A Streptococcus)
gram positive rods
• Cutibacterium acnes
• Bacillus anthracis
• Clostridium perfringens
gram negative rods
• Eikenella corrodens
• Pasteurella multocida
• Pseudomonas aeruginosa
• Vibrio vulnificus
spirochetes
borrelia burgdorferi
intracellular
rickettsia ricketsii
staph aureus
cocci in clusters, catalase positive, coagulase positive
strep pyogenes
cocci in chains, catalase negative, beta-hemolytic, bacitracin sensitive
clostridium perfringens
obligate anaerobe, spore-forming
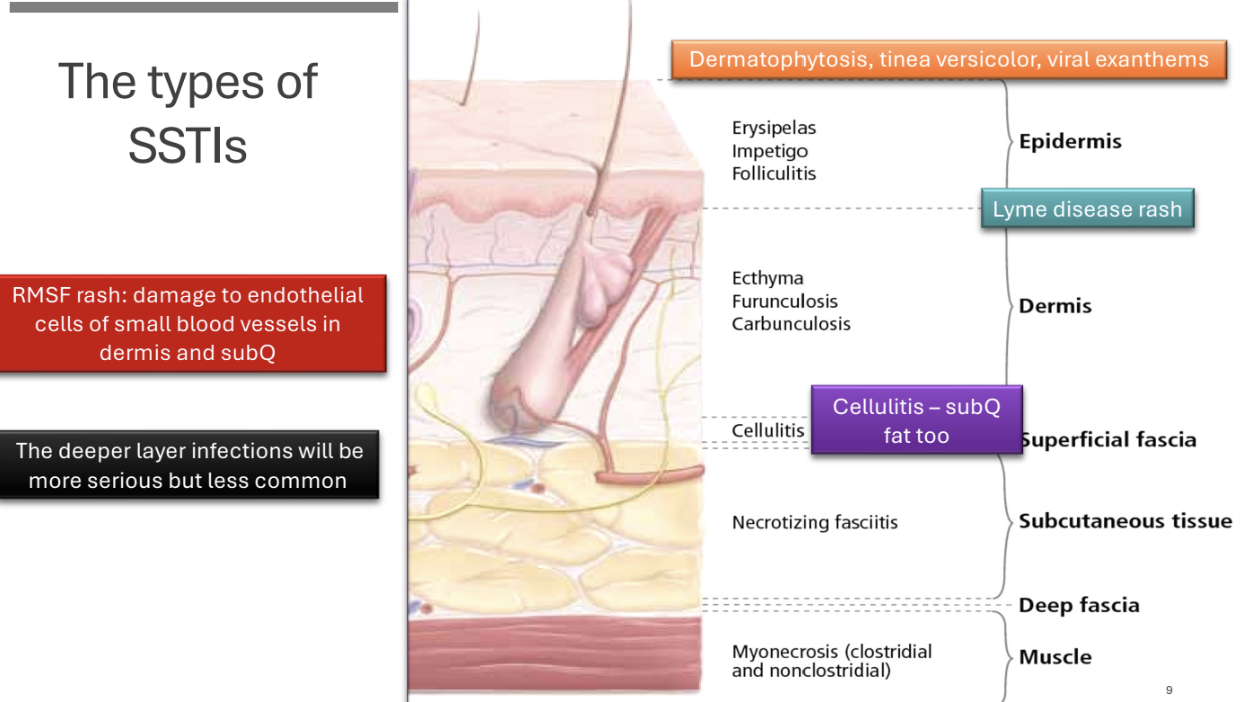
types of SSTIs image
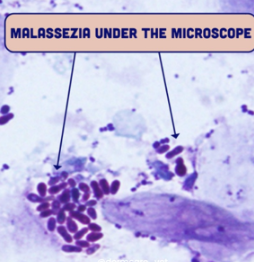
malassezia furfur
§ Normal flora (low levels)
§ Lipophilic: feeds on skin lipids
Production by sebocytes and keratinocytes
§ Sebum: moisturize and protect skin and hair
Protective barrier
Prevents water loss
Shields against microbes (some), friction, UV radiation
§ Stratum corneum only
Scalp, face, chest, and back
pityriasis (tinea) versicolor
malassezia fungal infection.
§ Hypo- or hyper-pigmented
§ Finely scaly macules/patches
§ Trunk, neck, upper arms
§ More visible after sun exposure
folliculitis
malassezia fungal infection
§ Rarer, may be misdiagnosed as acne
§ Itchy follicular papules/pustules
Chest, back, shoulders, or face
§ Worse with heat, humidity, or steroid use
malassezia diagnosis
§ Wood lamp: Yellow/Silver “glow”
§ KOH prep of skin scraping
Round yeast forms and short “hyphal” forms (pseudohyphae)
“Spaghetti and meatballs”
malassezia treatment
Topical (also for maintenance):
§ Selenium sulfide lotion/shampoo
§ Zinc pyrithione shampoo (head and shoulders)
§ First line azoles: ketoconazole, clotrimazole, miconazole cream
§ Terbinafine (allylamine) cream
dermatophytes
Macroconidia on microscopy → diagnostic
§ Monomorphic molds
Soil, animals (including pets), humans
Contagious
§ Produce keratinases
Break down keratin, allow invasion into lower layers of epidermis
ONLY grow on keratinized structures
§ Scaling skin
§ Loss of hair (can be permanent)
§ Crumbling nails
§ Itching
epidermophyton
• Infects skin and nails but does not infect hair
• Causes common infections like jock itch and athlete’s foot
• Person-to-person; indirectly through contaminated surfaces/objects
microsporum
• Primarily infect skin and hair
• Zoonotic transmission (e.g., dogs)
• Ectothrix hair invasion (infection outside the hair shaft)
trichophyton
• Infect skin, hair, and nails
• More common in chronic, persistent infections
• Some are zoonotic (dogs, cats, cattle, horses)
only contagious fungal infections (human to human):
dermatophytes
dermatophyte infections
§ Tinea capitis: capit = head
Common in children
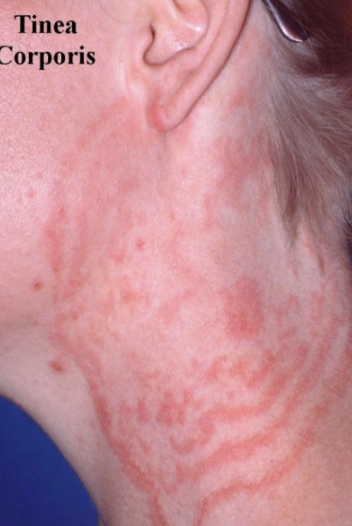
§ Tinea corporis: corpus = body
“ring worm”
§ Tinea cruris: cruris = groin (jock itch)
§ Tinea pedis: ped = foot (athlete’s foot)
§ Tinea unguium: unguis = nail
Onychomycosis: nail infection
§ Tinea barbae: beard
tinea corporis
body.
§ “Traditional” “ ringworm”
§ Clearing, scaling and raised, red edges; dry
§ Expands out = Hyphae only seen on edges
§ Treatment: Topical 2-4 weeks
Terbinafine
Miconazole
Clotrimazole
dermatophytes diagnosis
§ Skin or nail scraping, hair plucking
KOH prep
Look for branched, septate hyphae
§ Wood lamp → especially for Tinea capitis
Look for fluorescence … not always positive
macroconidia clues
Microsporum = Spindle shaped
Epidermophyton = Beaver’s tail
Trichophyton = Cigar shaped
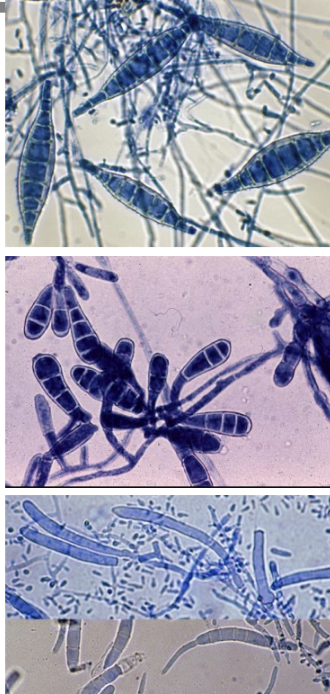
dermatophyte treatment
§ Cutaneous mycoses can be cured with topical therapy
Exception: Tinea capitis/barbae (drug must penetrate hair follicles) → Oral griseofulvin … microtubule inhibition, concentrates in keratinized structures
§ Topical
Imidazoles (clotrimazole, ketoconazole)
§ Oral
Terbinafine, azoles (fluconazole and itraconazole)
Usually for cases that aren’t responding/resistant
blastomycosis
§ Blastomyces dermatitidis
Mississippi River basin, Great Lakes, NE
Hunters, forestry workers, farmers, campers
§ Can disseminate to almost any tissue
Skin especially → chronic, painless, rough (verrucous)
§ Diagnosis
Broad-budding yeast in sputum, urine, tissues
Confirm by culture
§ Treatment
Itraconazole
Liposomal amphotericin B – life-threatening, CNS
HPV skin manifestation
• Verrucous warts (skin)
• Serotypes 1 and 2

HSV skin manifestation
• Grouped fluid-filled vesicles on an erythematous base
• Small, painful
• Can reactivate
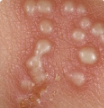
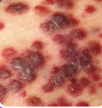
HHV8 skin manifestation
• Dark red/brown raised nodules or patches
• Kaposi sarcoma
• In HIV/AIDS patients, CD4 <200
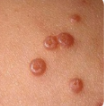
molluscum contagiosum skin manifestation
• Raised, round, skin-colored bumps with central umbilication
• Painless
-Henderson Paterson bodies on microscopy
VSV skin manifestation
• Lesions go through a progression; all can be seen at the same time during infection
• Macular to papular to vesicular lesions before crusting
• Shingles within single dermatome
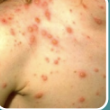
coxsackievirus skin manifestation
• Hand Foot Mouth Disease
• Painful, blister-like lesions
• Redness surrounding
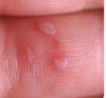
HSV diagnostics
Clinical
§ Characteristic grouped vesicles on an erythematous base that may ulcerate
§ Pain/tingling/burning prior to lesion appearance
§ History of similar symptoms
Laboratory
§ Gold standard = PCR on clinical specimen
§ Eye = Fluorescein staining for characteristic dendritic lesions in cornea
§ PANCE (historical test) = Tzanck smear
Scraping of lesion, Wright or Giemsa stain, multinucleated giant cells
HSV vs HFMD lesions
HSV
• Any age, recurrent (reactivation), common
• Prodrome of pain/burning/tingling
• Lesions surround each other at 1 spot
• Can have high fever
• Lesions very painful
• Can confirm with PCR or Tzanck smear (multinucleated giant cells)
HFMD
• Kids usually, palms, soles, around mouth; buttocks sometimes
• May have prodrome of sore throat, decreased appetite
• Low-grade or no fever
• Lesions “shallow” and “grey”; not as painful as HSV
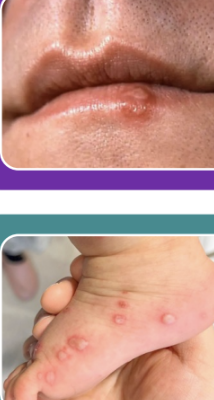
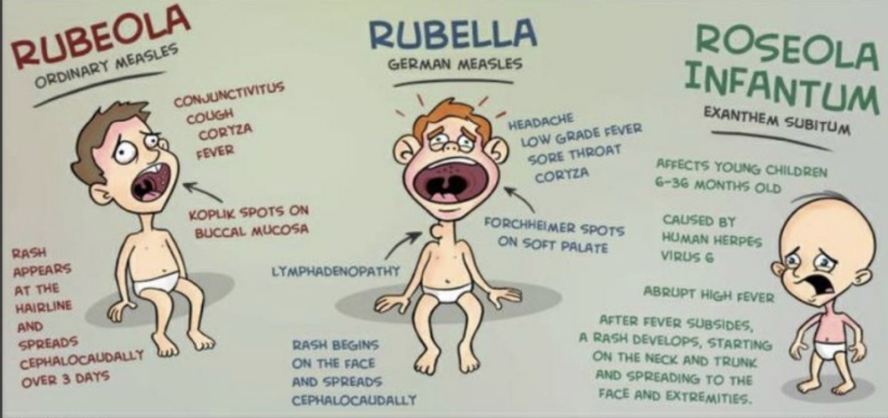
6 childhood exanthems chart
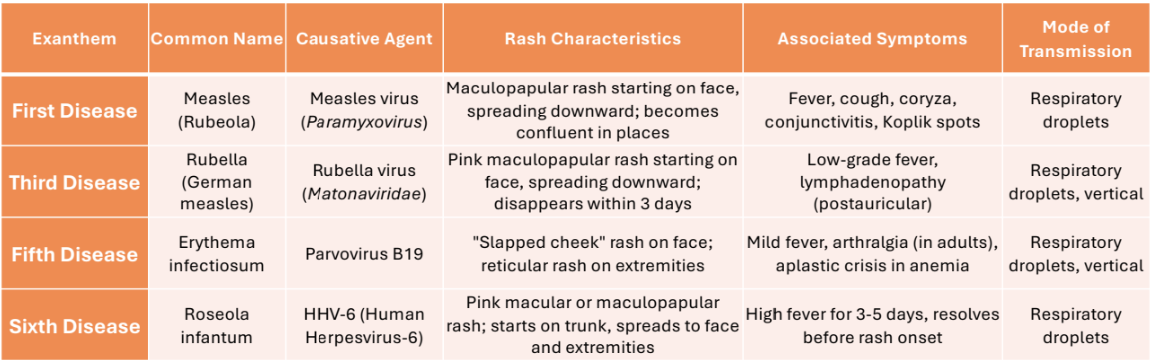
rubeola vs rubella vs roseola infantum graphic
congenital virus complications
Parvovirus B19
§ Aplastic crisis (infects RBCs)
§ Hydrops fetalis/fetal death
Rubella
§ Congenital: triad of cataracts, heart defects, deafness
Varicella
§ Congenital: Cicatricial (scar-like) skin lesions (dermatomal distribution), limb hypoplasia, microcephaly etc.
Measles
§ Sub-acute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE)
HSV treatments
§ Acyclovir, valacyclovir (less doses)
§ Can also be used to prevent reactivation
varicella treatment
IV acyclovir in immunocompromised
zoster treatments
Oral acyclovir, valacyclovir
human papilloma virus (HPV)
Microbe characteristics
• Papillomaviridae – non-enveloped, dsDNA (circular)
• DNA remains in nucleus
Integration occurs
E6 and E7 viral protein are made
Oncogenic
Reservoir/s and transmission
• Human-only pathogen
• Transmission is by direct contact: Fomites
Epidemiology
• Worldwide; MC STI in US – 18-59 yrs
• Different serotypes, different diseases
HPV replication strategy
§ Complex, tied to epithelial cell development
§ Attachment, endocytosis
Basal cell infection FIRST
§ Viral DNA is transported into nucleus
Can integrate into chromosome; mechanisms not known
Necessary for HPV-related cancer events
E6 and E7 proteins are oncoproteins –bind to and inhibits p53 and Rb, causing uncontrolled cell cycle
HPV oncogenic process
§ GENOME INTEGRATION
§ SYNTHESIS OF E6 and E7 proteins
§ Interact with p53 and pRb → cause their degradation (and inactivation)
§ P53 can’t work: no apoptosis
§ Rb can’t stop cell cycle proliferation
Regulate G1/S transition of cell cycle
condyloma acuminata (anogenital warts), laryngeal papillomas
§ HPV 6 and 11
§ “Cauliflower shaped” – can get large and interfere with defecation etc. in immunocompromised

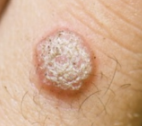
cutaneous warts (verrucae)
§ HPV 1 and 2
§ Rough, raised bumps on hands, fingers, and soles of feet
§ Most resolve, may need surgical removal (e.g., plantar warts)
§ Will reappear if not completely “excised”
Basal cells infected!
HPV wart treatments for immunocompetent
§ Topical salicylic acid, several weeks
Keratolytic; softens and removes infected keratinocytes
Requires patient compliance; can cause mild irritation
§ Cryotherapy (liquid nitrogen)
§ Electrosurgery / curettage
Physical removal of the wart
viruses w/ vaccines
Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR)
Live, attenuated
Varicella
Live, attenuated
Zoster
Shingrix: Recombinant, surface glycoprotein E
HPV
Recombinant, virus-like particles
Capsid proteins of HPV 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52, 58
leishmania major, braziliensis, mexicana
Microbe characteristics
• Flagellated protozoan
Reservoir/s and transmission
• Sandfly vector
Injects promastigotes during feeding
• No human-to-human contact, even cutaneous
Epidemiology
• Endemic: India, Bangladesh, Sudan, Ethiopia, and Brazil
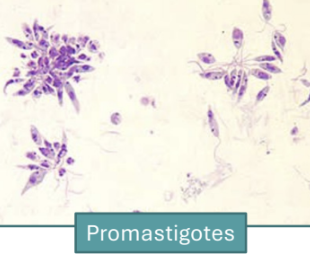
leishmaniasis
Sandfly bite during blood meal
• Injects promastigotes
Promastigotes (flagellated)
• Phagocytosed (preferentially) by macrophages
• Transform into amastigotes –DIAGNOSTIC inside macrophages
Sandfly bite
• Ingests infected macrophages
• Amastigotes
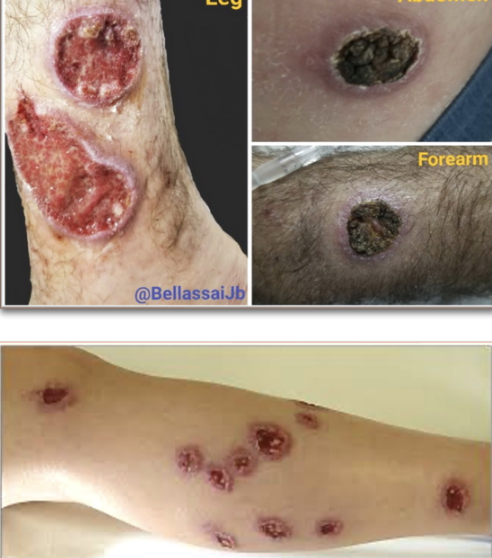
cutaneous leishmaniasis
§ Weeks/months after sandfly bite
§ Skin/mucosal papules that progress to nodule or ulcer
§ Raised, well-demarcated border “Volcano”
§ Painless OR painful
§ Can be destructive
§ Leaves a scar
cutaneous leishmaniasis diagnosis
• Gold standard: Direct visualization of amastigotes (Leishman-Donovan bodies) Giemsa-stained Bone marrow biopsy, skin lesion biopsy
Amastigotes inside macrophages
• Urine antigen test

scalded skin syndrome cause
• Staphylococcus aureus toxin breaks apart desmosomes
• Life-threatening, admit
Penicillinase-resistant, anti-staphylococcal –nafcillin, oxacillin etc; Vanc for MRSA
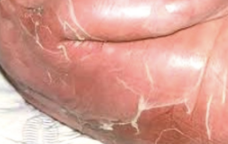
impetigo causes
• Streptococcus pyogenes (GAS)
• Staphylococcus aureus (bullous)
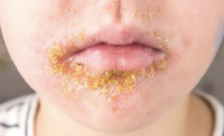
folliculitis causes
• Staphylococcus aureus
• Pseudomonas aeruginosa (hot-tub)

erysipelas cause
Streptococcus pyogenes (GAS)
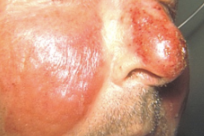
with staph aureus always consider:
MRSA
carbuncles/furuncles MC causes
• Staphylococcus aureus
• Furuncle = 1
• Carbuncle = multiple coalesce
skin abscesses MC cause
staph aureus
cellulitis MC cause
Streptococcus pyogenes (GAS), S. aureus
type 1 NF MC cause
• Polymicrobial
• Anaerobes (e.g. Bacteroides)
• Spontaneous
type 2 NF MC causes
• Streptococcus pyogenes (GAS)
• Staphylococcus aureus
myonecrosis MC cause
Clostridium perfringens
• Other Clostridial normal flora
acne vulgaris
white heads, black heads etc.
Cutibacterium acnes
Mild/moderate: topical benzoyl peroxide or topical clindamycin
cutaneous anthrax
Painless black eschar, surrounding edema (extensive)
Bacillus anthracis
Oral ciprofloxacin
scarlet fever
Fine, sandpaper-like rash, starts on trunk, spares palms and soles; ”strawberry tongue”
Group A Streptococcus
Penicillin OR amoxicillin
lyme disease
primary “Bullseye” rash – erythema migrans
Borrelia burgdorferi; tick bite
Doxycycline as soon as suspected
rocky mountain spotted fever
rash – wrists/ankles, moves inwards (centripetal)
Rickettsia rickettsii; tick bite
Doxycycline as soon as suspected
toxic shock syndrome
widespread, “sunburn-like” rash, skin peeling (palms and soles) after; bad vitals, vomiting, multi-organ involvement
Group A Streptococcus or Staphylococcus aureus expressing superantigen
Tx Directed (cultured): penicillin for GAS; clindamycin + nafcillin for MSSA; clindamycin + vanc for MRSA
uncomplicated vs complicated SSTIs
UC: Impetigo, erysipelas, simple cellulitis, simple abscess
§ Localized
§ Respond to I&D or short-course oral antibiotics
§ Streptococcus pyogenes, Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA/MRSA)
C: Deep abscesses, infected ulcers, diabetic foot infections, postoperative wound infections, necrotizing fasciitis
§ Extend deeper layers
§ May be immunocompromised
§ Often need surgical intervention, IV empiric and definitive antibiotics
§ Polymicrobial (Gram-positive, Gram-negative, anaerobes), MRSA, Enterobacteriales, Pseudomonas
MRSA risk factors
§ Prior MRSA infection
§ Recent antibiotic use (broad-spectrum); community or hospital
Esp. fluoroquinolones or B-lactams
§ Close quarters, contact sports, sharing personal items
§ Recent hospitalization or surgery / frequent healthcare contact
§ Residence in long-term care facility
§ Chronic wounds/ulcers
§ IVDU
impetigo
§ Highly infectious
§ Very common
§ Usually in children
§ Red sores on the face: nose and mouth / hands and feet
Over a week, sores burst and develop honey-colored crusts
Itchy
§ S. pyogenes MC cause
§ S. aureus strains that express exfoliative toxin → bullous impetigo (fluid-filled blisters)
Not systemic toxins like scalded skin syndrome
impetigo treatment
Mild: Topical mupirocin (protein synthesis inhibitor)
folliculitis
• Small, erythematous papules or pustules centered on hair follicles
May have a surrounding erythema
May spread deeper to cause furuncles/carbuncles
• Localized, often on beard area (face), scalp, arms, legs, trunk, or buttocks
• Mild pruritus or tenderness
Pain is uncommon
• S. aureus most common cause by far
Shaving, tight clothing, friction
Mild: topical mupirocin
• Hot tub folliculitis
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, exposure to contaminated water
Most cases resolve on their own
abscesses, carbuncles, furuncles
§ Furuncle: infection of hair follicle, surrounding skin and deep underlying subcutaneous tissue
Carbuncle: multiple furuncles have fused L
§ MC cause: MSSA and MRSA
§ Painful, erythema, mild edema
§ Pus can leak
§ Can have a fever
Management
§ Incision and drainage
Will be left open to heal
Drain pus, keep moist
§ Culture and sensitivity, especially if moderate/severe infection like MRSA
erysipelas
§ Malaise, fever, chills 48 hours before onset of rash
§ Infection of superficial dermis
Can extend to superficial cutaneous lymphatics
Peau d’orange (orange peel skin)
§ Area of erythema is well demarcated, raised
§ Fast development
§ Often affects the lower extremities
Face second most common
§ Burning, pain, itchy
§ Group A Strep
§ Outpatient: Penicillin or amoxicillin
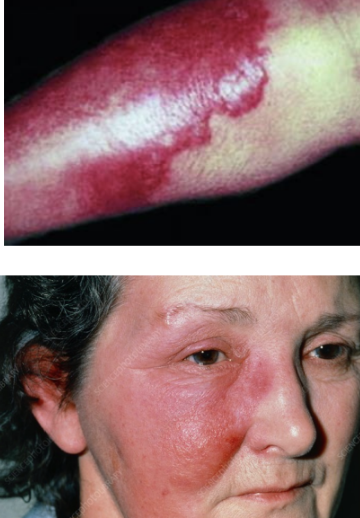
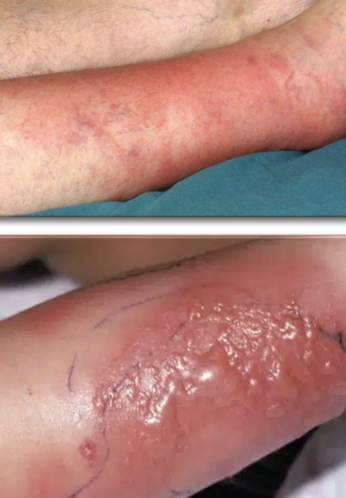
cellulitis
MSSA, MRSA, GAS
§ Bacterial invasion extending into reticular dermis and subcutaneous fat
Does not extend past subQ fat
Usually a good prognosis
§ Risk factors (local to site)
Skin trauma: Barrier disruption (abrasion, wound, ulcer, insect bite, IVDU)
Skin inflammation
Breaks in the skin between the toes
Preexisting skin infection: tinea pedis, impetigo, varicella
§ Risk factors (person)
Age
Edema (stretching of skin)
Obesity (stretching of skin)
Immunosuppression
§ Clinical fx
Warmth, erythema, pain, edema
Swelling can cause skin to break
Vitals usually OK
Borders ill-defined
Lower extremities most affected
Unilateral
Progresses slowly
Purulent or non-purulent, purulent suggests Staph
Abscesses can form: nodules are fluctuant
Vesicles, bullae (large fluid-filled cavities)
§ Complications
Bacteria can invade surrounding blood vessels
Bacteremia, endocarditis, osteomyelitis, metastatic infection, sepsis, toxic shock syndrome
cellulitis diagnosis
Usually clinically – history, physical exam
Rule out others
Erysipelas – well-defined borders, more superficial
NF – poor vitals, fast-progressing, necrotic signs
Culturing is not required if uncomplicated/routine
Skin swabs = normal flora, not involved in infection
MRSA, treatment failure (rarer cause?), C&S may be required
Imaging is not helpful, except to visualize an abscess / differential DVT
cellulitis treatment
§ Mark margins to track spread
§ Early treatment essential
§ Therapy directed to Streptococcus pyogenes first
Cephalexin(covers MSSA too), or dicloxacillin / oxacillin
§ MSSA 2nd
§ If purulent, I&D may be needed
§ Cellulitis may appear to worsen the first 24-48 hours despite antibiotics → bacterial cell lysis
If MRSA suspected, but GAS most likely, mild: TMP-SMX and cephalexin, oral.
TMP-SMX not for GAS
eikenella corrodens tx
§ Oral Amoxicillin-clavulanate
§ * Consider polymicrobial infections with human bite wounds
pasteurella multocida tx
Oral Amoxicillin-clavulanate
pseudomonas aeruginosa tx
IV Piperacillin-tazobactam or Ceftazidime or Cefepime
vibrio vulnificus tx
§ IV … has ability to progress to sepsis FAST
§ Doxycycline AND a 3rd gen ceph (ceftriaxone, cefotaxime, ceftazidime)
if anaerobe probability, tx:
metronidazole, clindamycin
necrotizing fasciitis
§ Rare, but life-threatening infection of fascial planes and overlying subcutaneous fat
§ Muscle is usually spared (early stages) due to good blood supply and immune system
Clostridium doesn’t care
§ Risk factors similar to cellulitis plus:
Major penetrating trauma, recent surgery, malignancy
Diabetes: lower extremities, perineum (Fournier gangrene), head and neck region
necrotizing fasciitis mortality rates
§ Group A Streptococcus (monomicrobial): 25–30%
§ MSSA: 15-30%
§ MRSA: 20-40%, esp. if empiric therapy doesn’t cover
§ Polymicrobial (type I): 20–35%
§ Vibrio vulnificus: up to 50% or higher
Esp. in patients with liver disease
§ Aeromonas: 30–50%
§ Factors that increase:
Delayed diagnosis or inadequate surgical intervention (>24 hrs)
Chronic liver disease, diabetes, or immunosuppression
Septic shock at presentation
§ Despite optimal management, mortality remains high
necrotizing fasciitis symptom progression
§ Acute, RAPID progressing
Extensive destruction of affected tissue
Necrosis
§ Systemic toxicity
Tachycardia, fever, hypotension, tachypnea
§ Ill-defined erythema and borders
§ Edema that extends beyond erythema
§ Severe pain out of proportion to physical exam (early on)
§ Crepitus (popping/cracking, air under skin) … depends on cause
§ Bruising (ecchymoses) – ”dusky” color
§ Bullae – dark red/black
Type 1 necrotizing fasciitis
Polymicrobial – most common
• Aerobic and anaerobic
• At least one anaerobic species (e.g., Bacteroides) is isolated in combination with Enterobacteriaceae
• Streptococcus, Staphylococcus
• Post-surgery, diabetic foot infection, Fournier’s