Chapter 3 - Arrangement of Electrons in Atom
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What did George Stoney do
George Stoney came up with the name electron
Neils Bohr
- Neils Bohr discovered the electron arrangement in atoms
- He did this by studying spectre
continuous spectrum
Contains many colours or wavelengths with no gaps
Emission line spectrum
Consists of coloured lines against a dark background emission line spectrum indicates the presence of energy levels in atoms
spectrometer
Instrument to examine the line specctrum of an element
Neils Bohr experiment
Bohr ran electricity through a vial of hydrogen noticed the hydrogen produced light then put this light through a prism
Result of Neils Bohr Experiment
Instead of a continuous spectrum Bohr saw a series of narrow lines he called this emission line spectrum
Evidence for energy levels
Elements produce a unique emission line spectra
Why do elements produce a different emission line spectra
Elements produce a unique spectrum due to the different number and arrangement of electrons
Bohrs Theory
1. Electrons orbit the nucleus along fixed paths called orbits or energy levels
2. Electrons in one orbit have a fixed amount of energy i.e quantised they have a fixed value
What happens if an atom is supplied with energy (Bhors Theory)
If an atom is supplied with energy in the form of heat electricity / heat electrons jump from low energy to high energy levels ( excited state)
What happens to excited state electrons
Excited state electrons are unstable and fall back down to a lower level after a short time
How is energy released (Bhors Theory)
Energy is released in the form of photon light and since electrons can only fall back to fixed energy levels only fixed amount of energy can be given off for that element
Energy level
The fixed energy value that an electron in atom may have
Ground level
Excited state
One which electrons occupy higher level than in the ground state
Frequency of light
The frequency of light emitted depends on the difference in energy between two energy levels
Frequency of light equation
E2 - E1 = hf
- E2 = Energy of higher energy level
- E1 = Lower energy level
- H - planks constant
What are energy levels represented by
The letter N
N = 1
N = 2
N=3
What are flame tests carried out with
Flame tests are carried out with salts of lithium, sodium , potassium, barium, strontum, copper and sodium
Method of flame test
1. Soak a wooden splint in some water
2. Drop a wooden splint in some salt
3. Hold the flint over a flame and observe the colour
Lithium
Crimson flame
Potassium
Lilac flame
Barium
Green flame
Strontum
Red flame
Copper
Blue green flame
Sodium
Yellow flame
Flame Tests Conclusion
Each metal provides a unique colour due to the unique electronic configuration of the elements and therefore different electronic transitions of energy levels
What is the second energy level called
Balmers theory (n=2)
What is frequency
Frequency is emitted as a photon of light
Light frequency (f)
Light frequency appears as a line of a particular colour of the emission line spectrum
What colour is emitted from electrons moving from energy level 3 to 2
Red
What did scientists find out
Scientists found out that the elements can absorb light
Experiment for absorption
White light is passed through a gaseous sample of an element and it was found that specific wavelengths were missing
What was observed in the continous spectrum
Dark lines were observed in the continuous spectrum that is called AAS these lines correspond exactly to the lines produced in the emission line spectra
AAS
Atoms of an element in the ground state absorb light of a particular wavelength unique to the element. This amount of light is directly proportional to the concentration of the element
Louis De Broglie
- Louis de Brogli discovered electrons wave nature
- He called this wave particle duality
- Electrons don't have a definite boundary because of wave particle duality which Heisenburg expanded upon
Hesienbergs UNcertainty
States that it is impossible to to measure the at the same time both the velocity and the position of an electron therefore it is impossible to specify the absolute boundary of an atom
Limitation of Bohrs theory
- Bohrs theory only worked for hydrigen and not multi electron atoms
- Bohr didnt take into account wave particle duality there is not a fixed distance between nucleus and electron
- Heisenbergs uncertainty principle is in conflict with Bohrs Theory
- Bohr didnt take sub levels into account
Atomic orbital
a region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron
Erwin Schrodinger
Worked out the probability of finding an electron in a sub level of an atom
S sublevel
1 orbital, 2 electrons, spherical
Sublevel
A subdivision of a main energy level and consists of one or more orbitals of the same energy
p sublevel
3 orbitals, 6 electrons, dumbbell shape, PX PY PZ
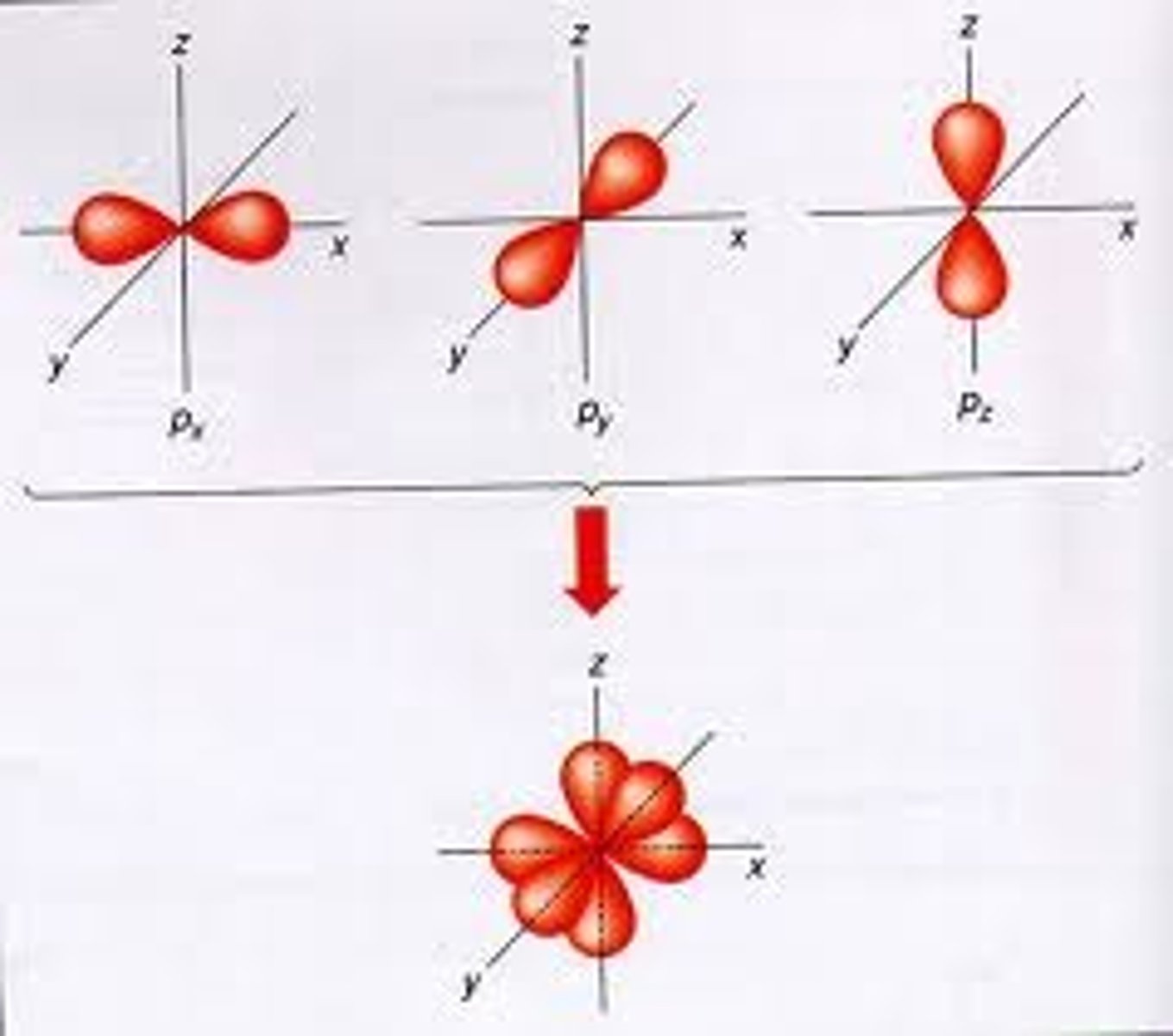
d sublevel
5 orbitals, 10 electrons
How does Bohrs theory expplain the emission line spectrum of a hydrogen and the evidence for energy values
- In ground state electrons occupy the lowest available energy level, electrons jump and move to a higher energy level if it absorbs energy then it becomes instable and falls back down
- Energy is emitted as a photon of light thus giving rise to a spectrum light emitted depends on the difference of energy between the 2 energy levels