Management Exam 3
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
advantages of team work
wide information base
objective
creative
conditions for team success
supportive climate
time
complex problem
heterogeneous group
five stages of group development
forming
storming
norming
performing
adjourning
forming
stage of team development involving a period of orientation and getting acquainted
orientation, break the ice
leader: facilitate social change
storming
is the stage of team development in which individual personalities and roles emerge, along with resulting conflicts
conflict, disagreement
leader: encourage participation, surface differences
norming
refers to the stage of development in which conflicts are resolved and team harmony and unity emerge
establish order and conclusion
leader: help clarify group roles, norms, values
performing
members focus on problem solving and accomplishing the team’s assigned task
cooperation, problem solving
leader: facilitate task accomplishment
three team member profiles
contributors (act)
analyzers (reflect)
communications (relate)
contributor (action)
strengths:
dependable
systematic
efficient
pragmatic
organized
proficient
flaws:
perfectionist
inflexible
micro manager
communicator (people)
strengths:
people
diplomatic
outgoing
enthusiastic
supportive
flexible
perceptive
flaws:
vague
indecisive
aloof
analyzer (ideas)
strengths:
creative
independent
assertive
candid
principled
analytical
flaws:
arrogant
unrealistic
rigid
How to build the “perfect team”
The personalities are not that important
Good teams have 5 traits: psychological safety, dependability, good work structure and clear expectations, meaning (a sense of purpose in work), impact (clear contribution to greater good)
self awareness
being conscious of the internal aspects of one’s nature, such as personality traits, beliefs, emotions, attitudes, and perceptions, and appreciating how your patterns affect other people
motivation
arousal of enthusiasm and persistence to pursue a certain course of action
signs of low emotional intelligence
being argumentative, not listening, blaming others, emotional outbursts
EQ
The extent to which people:
self awareness (knowing one’s emotions)
self management (manage their emotions)
social awareness (recognizing emotions in others)
social skill (handling relationship)
empathy
good teams have members with high EQ
Group Problems
slow
personality conflicts
forming and norming stages
risky shift (group means higher tendency to take more than needed risk)
polarization (teams become more extreme)
groupthink
groupthink → group characteristics
cohesive, strong leaders, extended success
groupthink → symptoms
invulnerability
stereotyping
peer pressure
self - censorship
unanimity
groupthink → decision making errors
few alternatives
rejections of experts
selective bias of new data
no contingency plan
groupthink → outcome
lower performance
lower decision quality
5 conflict management styles
force, avoid, accommodate, compromise, collaborate
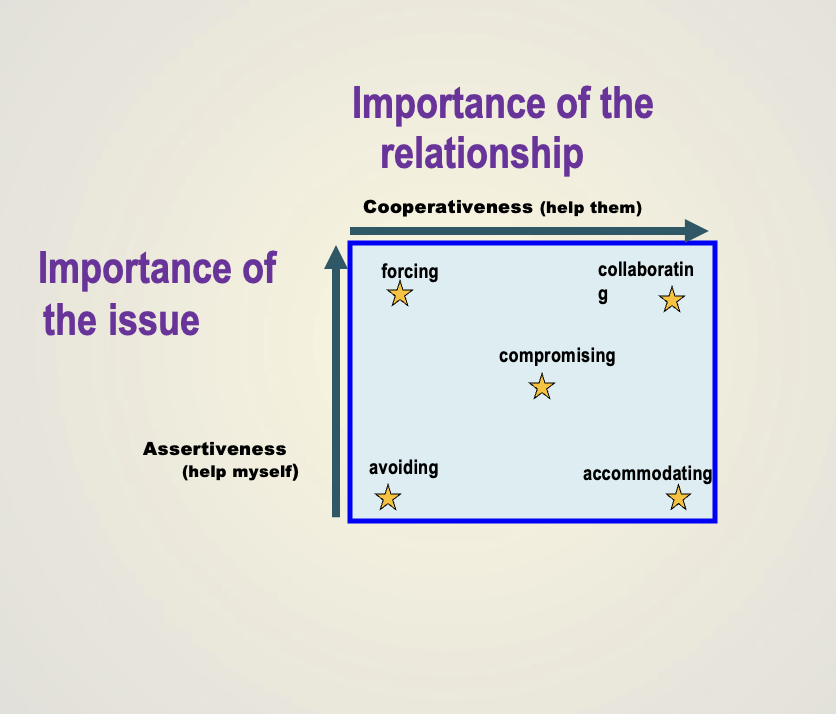
force/compete
goal: get your way
“i know what’s right”
“don’t question my opinion”
+ quick
- resentment
- no buy - in
avoid
goal: sidestep the issue
“I am neutral”
“let me think about it”
+ cool down
- escalation
- tension
compromise
goal: quick resolution
“Let’s both give a little”
+ quick
- mutual cost
- manipulation
accomodate
goal: satisfy the other side
“what can I do to please you”
+ indebtedness
- exploitation
- relationship
collaborate
goal: solve the problem
“this is my perspective, what is yours?”
+ ownership
+ participation
+ problem solving
- time
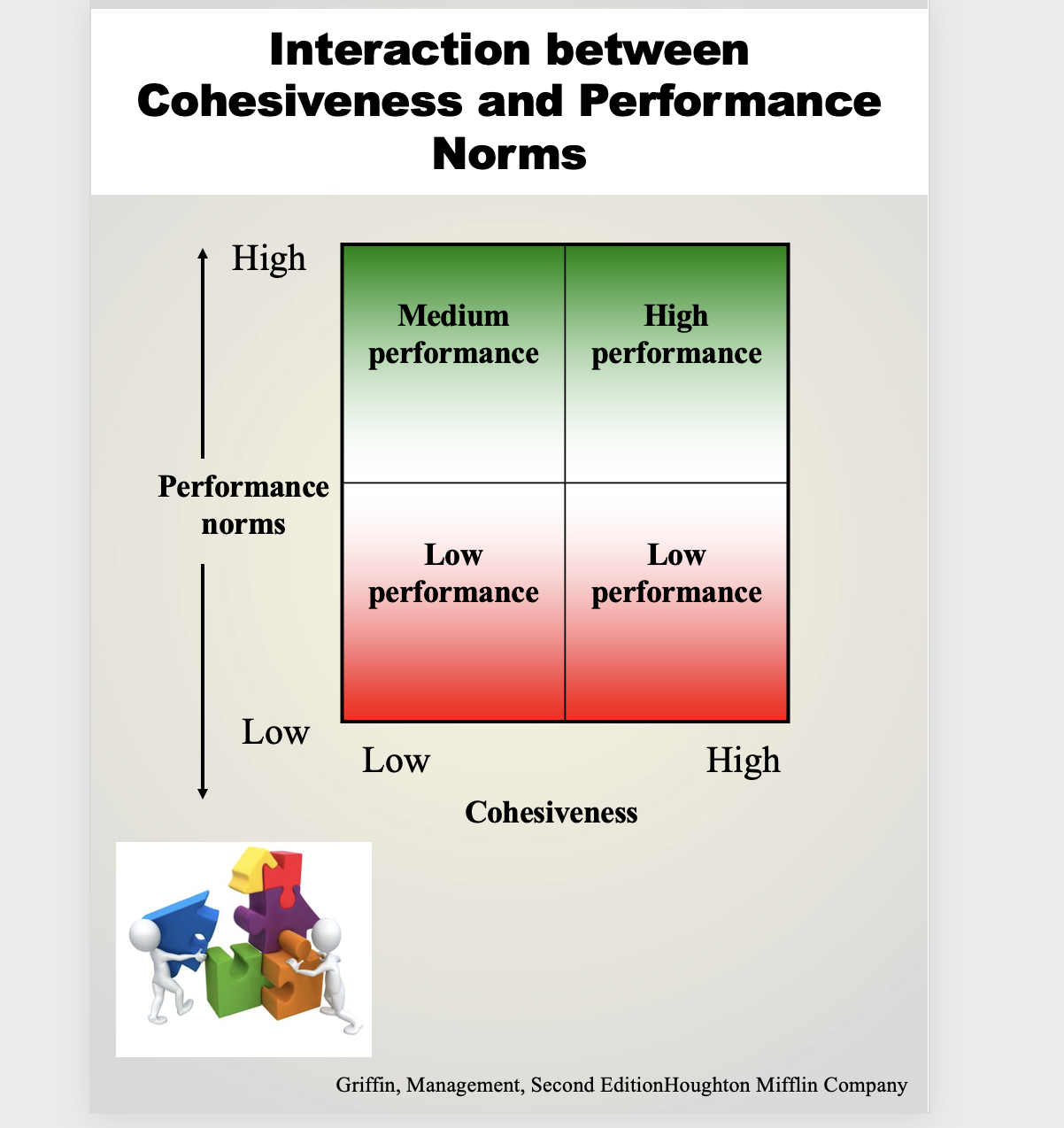
Interaction between Cohesiveness and Performance Norms
Resistance To Change
self - interest (they fear the change will be costly to them)
lack of understanding
lack of trust
uncertainty (about the consequences)
different assessment (of the benefits of change)
different priorities/ goals
Stages of Change (OD steps)
unfreezing (diagnosis) - members must be made aware of the problem and realize the benefits of change in order to be willing to change
changing (intervention) - introduce new procedures, habits, etc, be coaching and closely working with members
refreezing (reinforcement) - members must acquire new attitudes, procedures, habits, etc, and incorporate them into their routines
overcoming resistance to change
active participation (let people talk)
education and communication (inform/prepare people)
making only necessary changes
announcing changes in advance
allowing time to adapt
creating a change mindset
recruiting - select people who “fit”, select open - minded employees
training - change the people, teach skills, expose to new ideas
organization development - change the culture, build capacity to learn, create flexibility
OD Activities
team building
surveys feedback
large group interventions
training
communication
outreach
morale building
Change is the result of competition between two forces
driving forces: promote the change
restraining forces: resist the change
controlling the organization
goal: promote progress toward organizational goals
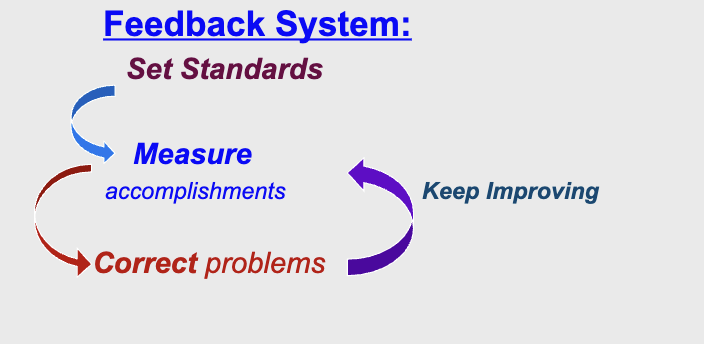
feedback system: set standards → measure accomplishments → correct problems → keep improving by going back to measure (cycle)
How important is control in your organization?
depends on firm size, competition, speed of change
control management goals
increase speed
reduce costs
improve quality
increase speed
measures: time to market
cycle time or lead time = time between start and end of a project
Reduce Costs
measures: efficiency (= input/output)
input = resources → work hours, money spent, time spent, space
measures productivity (=output/input)
output = results → customers served, sales, packages delivered, good produced
Improve Quality
effectiveness (goal - actual outcome)
Who operated control system
cybernetic (fully automated control process)
non cybernetic
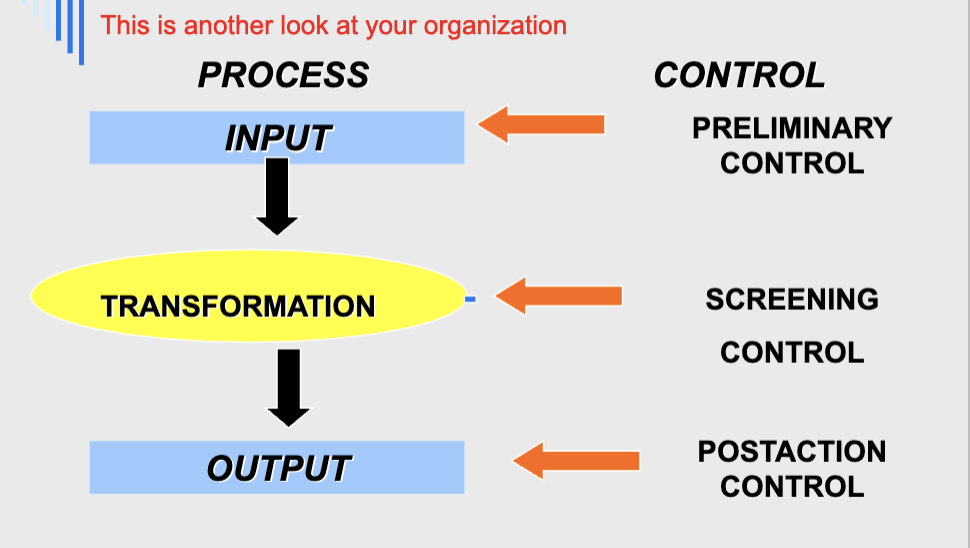
When do you control
preliminary
screening
poastaction
How do you control?
hierarchical control
clan control/ decentralized control
Timing of Control
Hierarchical Control
hierarchy
rules
automation
computerization
standardized selection and training
budgets
non negotiable, rules put in place and there’s less freedom
clan/decentralized control
traditions
peer pressure
socialization
role models
teams
selection
training
personal interactions
modern control techniques
total quality management
JIT
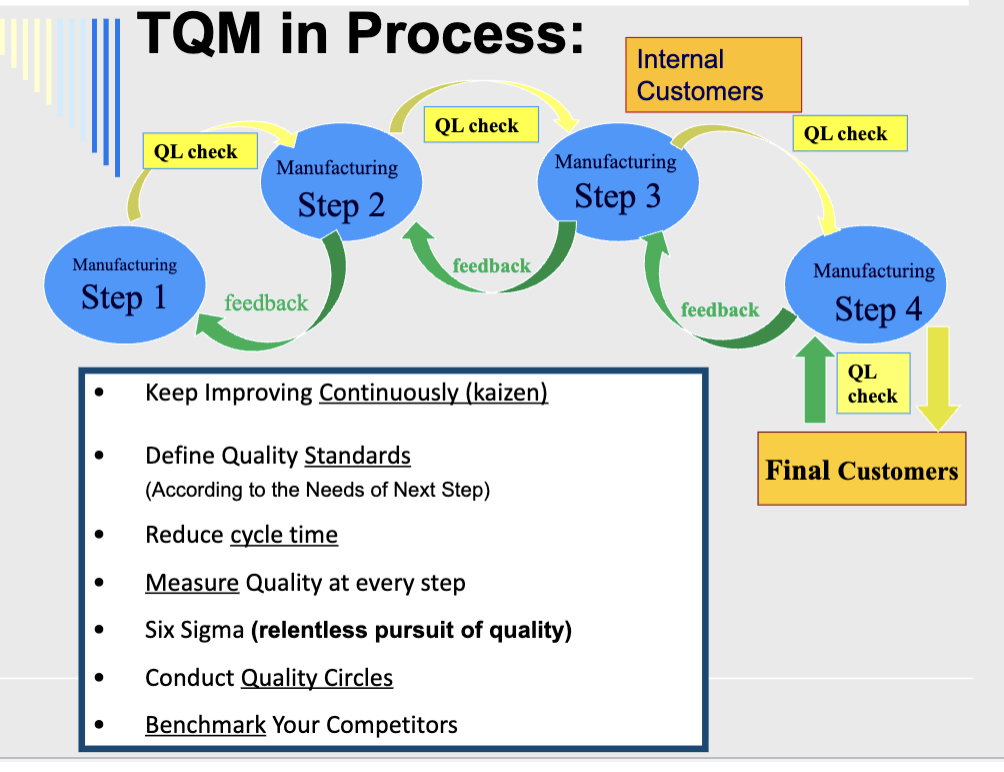
TQM in Process
keep improving continuously (kaizen)
define quality standards
reduce cycle time
measure quality at every step
six sigma (relentless pursuit of quality)
conduct quality circles
benchmark your competitors
an organization wide effort to infuse quality into every activity in a company through continuous improvement
Six Sigma
pursuit of perfect quality
tools to minimize defects and errors
use statistics: reduce variance in quality
quality control approach that emphasizes a relentless pursuit of higher quality and lower costs
inventory control
minimize inventory
serve customers
traditional inventory control
old: push approach
start → supplier → warehouse → store → customer
fixed interval: always in stock, cost of warehousing, risk of overstock
Inventory Control JIT (just in time)
new: pull approach
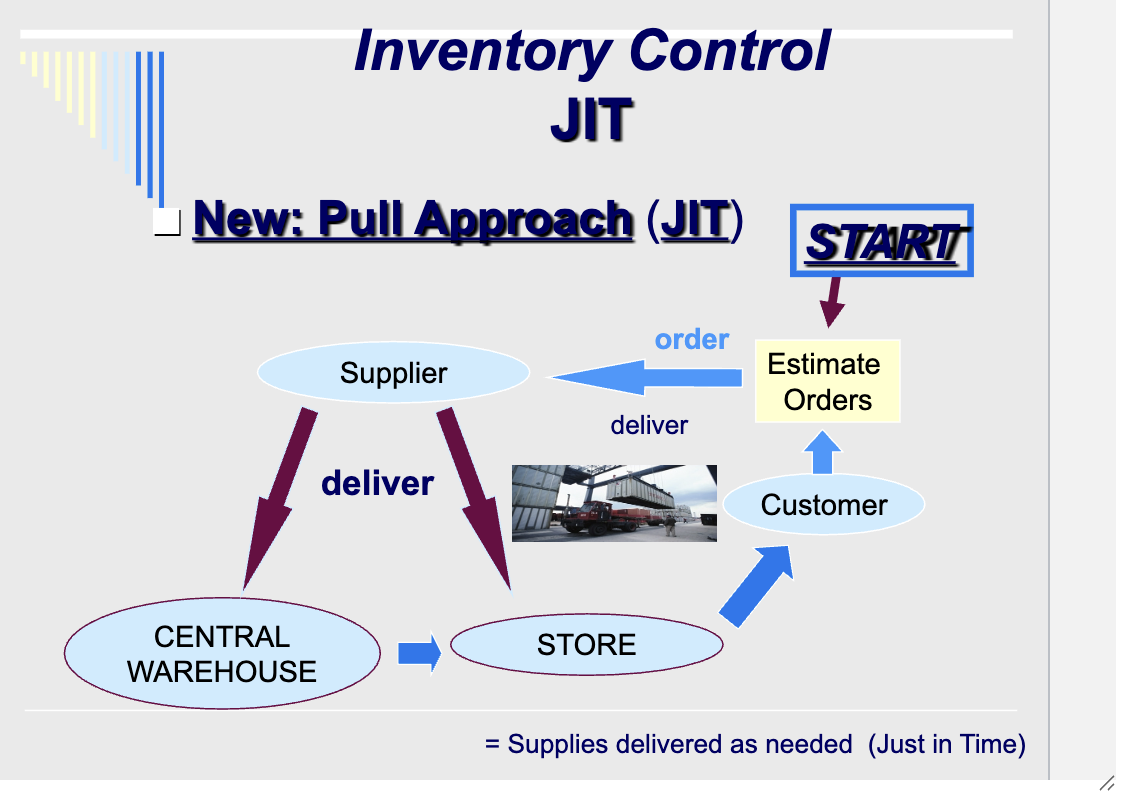
JIT (just in time inventory)
stockless production
kanban system
inventory turnover
how to measure inventory control
costs of goods sold
cost of average inventory
consequences of JIT
order small amounts as needed
many deliveries
expensive to set up
requires integrated computer system with suppliers
low inventory costs
= screening quality controls
Balanced Scorecard (4 areas to improve results)
financial perspective
measured by: revenue, expenses, net income, cash flow, asset value
customer perspective
customer satisfaction, customer retention, market share, brand strength
learning/growth perspective
employee satisfaction, employee turnover, employee skills, employee education
internal process perspective
inventory, orders, resource allocation, cycle time, quality control
balancing financial goals (money - costs, profits) with critical success factors (strategy)
product innovation
change in the organization’s products or services
process innovation
change in production processes
how does the organization work
creativity
generation of novel ideas that may meet perceived needs or respond to opportunities for the organization
bottom up approach
encouraging the flow of ideas from lower levels and making sure they get heard and acted upon by top executives
horizontal linkage model
several departments, such as marketing, research, and manufacturing, work closely together to develop new products
open innovation
many companies extend the search for and commercialization of innovative ideas beyond the boundaries of the organization
innovation by acquisition
buying start-up companies to obtain innovative products and services, and usually the talent that created them
corporate intrapreneurship
attempts to develop an internal entrepreneurial spirit, philosophy, and structure to encourage employees to act like employees
idea champion
person who sees the need for and enthusiastically supports a productive change within the organization
idea incubator
organizational program that provides a safe harbor where employees can generate and develop ideas without interference from company bureaucracy or politics
new venture team
a unit separate from the mainstream organization that is responsible for initiating and developing innovations
skunkworks
separate, informal, highly autonomous, and often secretive group that focuses on breakthrough ideas
in-house venture
start up launched within the company rather than as a separate entity, seeks to nurture promising new businesses and stimulate entrepreneurship throughput the organization
people change
change the attitudes and behaviors of a few employees
culture change
major shift in the norms, values, and mind-set of the entire organization
Organization development (OD)
planned, systematic process of change that uses behavioral science techniques to create a positive corporate culture and improve the way people and departments relate to one another.
team building
OD intervention that enhances cohesiveness by helping groups of people learn to work together as a team.
survey feedback
OD change agents survey employees to gather their opinions regarding corporate values, leadership, participation, cohesiveness, and other aspects of the organization, then meet with small groups to share the results and brainstorm solutions to problems identified by the results
large group intervention
OD approach that brings together people from different parts of the organization (and often including outside stakeholders) to discuss problems or opportunities and plan for change
emotional contagion
refers to the people to absorb and express the emotions, moods, and attitudes of those around them
negativity bias
how the human mind reacts more quickly and strongly to perceived bad things than it does to good things.
social facilitation
the tendency for the presence of other people to influence an individuals motivation and performance
functional team
composed of a manager and subordinates in the formal chain of command
cross functional team
made up of employees at roughly the same hierarchal level but from different areas of expertise, include task force and special purpose teams
task force
group of employees from different departments who deal with a specific activity and exist as a team only until that task is completed.
special purpose team
team created outside the formal structure to undertake a project of special importance, such as developing a new product.
self managed team
consists of multiskilled employees who rotate jobs to produce an entire product or service; the team is often led by an elected team member
agile team
small, is focused on one piece of a larger project, and has complete responsibility along with all needed member expertise to produce a product or service
free rider
is a person who benefits from team membership but does not make a proportionate contribution to the team’s work
team cohesiveness
the extent to which team members are attracted to the team and motivated to remain a part of it
influenced by interaction, shared goals, personal attraction to the team, presence of competition, team success
team norms
informal operating guidelines that establish agreed-upon behaviors about how the team’s work will get done and what members can expect from each other
task conflict
conflict that results from disagreements about the goals to be achieved or the content of the tasks to be performed.
relationship conflict
results from interpersonal incompatibility that creates tension and personal animosity among people
faultlines
hypothetical dividing lines that are based on one or more demographic characteristics of team members, such as age, race, or ethnicity, or on nondemographic characteristics, such as personal values or attitudes
negotation
is a conflict management strategy whereby people engage in give-and-take discussions and consider various alternatives to reach a joint decision that is acceptable to both parties
integrative negotation
is a collaborative approach that is based on a win-win assumption, whereby the parties want to come up with a creative solution that benefits both sides of the conflict.
distributive negotiation
is a competitive and adversarial approach in which each party strives to get as much as it can, usually at the expense of the other party
feedback control model
establish strategic goals
establish standards of performance
measure actual performance
compare performance to standards
if inadequate: take corrective action and if adequate: do nothing or provide reinforcement
kaizen (continuous improvement)
is the implementation of a large number of small, incremental improvements in all areas of the organization on an ongoing basis
need for change
a disparity between actual and desired performance
algorithmic control
the use of software algorithms to set targets, measure performance, provide feedback, and decide rewards for employees
Total Quality Management (TQM)
organization wide approach to infuse quality into everyday activity in a company through continuous improvement
quality circle
a group of 6-12 volunteer employees who meet regularly to discuss and solve problems affecting the quality of their work
benchmarking
continuous process of measuring products, services, and practices against major competition or industry leaders