Kinesiology - after midterm
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
Metacarpals
from transverse arches that enhance grasp and hand manipulation
longitudinal arch allows for radial and ulnar aspects of palm to come together
Phalanges
proximal, middle, distal
thumb- proximal, distal
Metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint
Interphalangeal (IP) joint
hinge - flexion and extension
PIPs important for power grips and DIPs smaller and less movement
Cylindrical grasp
flexion around a tube shaped object
steering wheel
Spherical grasp
flexion around an object thats round
hold a ball
Hook grasp
simultaneous flexion of the PIPs and DIPS with extension of MCPs
carrying a briefcase or basket
Composite grasp
maximal flexion of all digits
ring and pinky finger generate more force than radial digits
Tip pinch
distal tips of thumb and index finger
threading a needle
three jaw chuck
tip of thumb against index and middle fingers
writing with pen/pencil
Lateral (key) pinch
pad of thumb pressed against radial side of index finger
turning key, presenting credit card
trigger finger
finger becomes lodged in a flexed position; can be caused by high repetition activities or high vibration
interventions: surgical release, activity modification, preventing prolonged flexion
Boutonniere Deformity
PIP flexion with DIP hyperextension - damage to the central slip
interventions: orthoses, splints
Swan neck deformity
PIP hyperextension and DIP flexion - laceration volar plate or damage to terminal tendon
interventions: orthoses, splint
Dupuytren’s contracture
abnormal thickening of palmar aponeurosis leading to contracture of ring and small finger
interventions: surgical release, injection, splinting, post op rehab, scar management
DeQuervain’s tenosynovitis
(texting thumb) CTD of the tendons of the first dorsal compartment
occurs from extended ulnar deviation and rapid thumb movement
osteoarthristis
common in fingers and thumbs
interventions: conservative movement, modalities splints, activity modification, adaptive equipment
tenodesis
fingers relaxed and wrist extended - causes fingers to flex - fist is created by passive tension
provides functional grasp for people with SCIs at C6
saddle joint
thumb - flexion/extension, palmar adduction/abduction, radial adduction/abduction
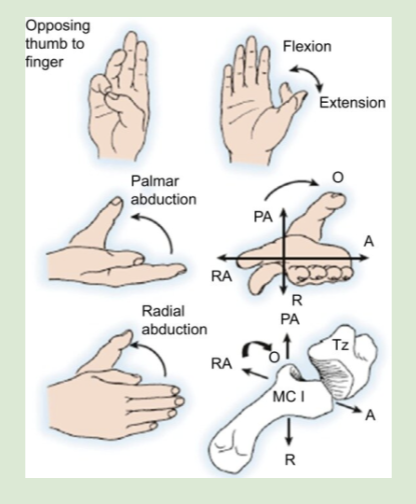
CMC arthritis
pain from repetitive use
De Quervains Tenosynovitis
irritation of 1st dorsal compartment
APB and APL at extensor retinaculum
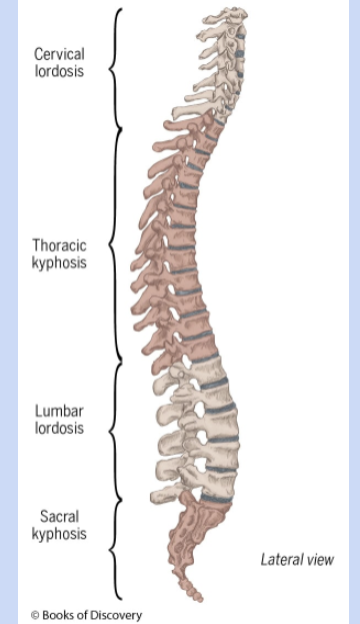
spinal column
cervical -7
thoracic - 12
lumbar -5
sacral -5
coccygeal -4
spinal column characteristics
spine acts as a spring - curves shrink and expand with exerted forces
provides stability for functional movement
anterior and posterior curves
anterior - kyphosis
posterior - lordosis
Atlanto-occipital joint
interface between skull and spinal column
C1-atlas - initial movements for flexion and extension
“yes” joint - nodding head yes
Atlantoxial joint
joint between C1 and C2
supplies much of the movement for rotation
“no” joint - shakes head no
Radiculopathy
nerve root compression resulting from narrowing of intervertebral forearm
can occur with fractures, OA, or thinning of intervertebral disks
leads to sensorimotor deficits in muscles or dermatomes in nerve roots
Rib fractures
mild fractures heal on own as intercostal muscles holds
severe fractures can impact lungs or other vital organs and requires surgery
Core stability
important motor component of occupational engagement - seating and stability
infant - crawling
adult - heavy objects
older adult - functional mobility
Hemiparesis
can occur from CVA or TBI
abnormal muscle tone, weakness, paralysis
can lead to vestibular, visual, or somatosensory issues

Spinal injuires
can occur from improper lifting, traumatic injury, age related changes
interventions: fusion, laminectomy
Spinal cord injury
high impact trauma - MVA, diving
injury blocks transmission of neurological signals from brain to body
Pelvis charactistics
stable base of support for head, arms, and trunk
requires balance to maintain symmetry of entire body
anatomical position = tilted anteriorly
Sacroiliac joint (SI)
designed to stabilize pelvis and has limited mobility
Acetabulum
socket for femoral head
illium, ischium, pubis
connect SI joint and pubic symphysis
Ischial tuberosity
primary point of pelvis contact with a seating surface
SITS bones - can feel when sit on hands
worry about them breaking down from repetitive sitting
pelvic floor
controlled by surrounding sphincter muscles that regulate urination and defecation
damage to these muscles can lead to incontinence and issues relating to sexual intimacy
Incontinence
stress incontinence - involuntary leaking of bowel/bladder due to increased abdominal pressure
urge incontinence- inability to control bowel/bladder until an appropriate time for elimination
Pelvic organ prolapse
pelvic floor weakness leads to herniation of the uterus, recum, or vagina
lots of causes: heavy lifting, vaginal delivery, coughing
lots of symptoms: bulging/pressure in vag, pelvis pressure, UTI
intervention: surgical, pelvic floor exercise
Cystocoele
bladder falls into uterus
uterine prolapse
uterus drops into vagina
vaginal vault prolapse
top of vagina falls into vaginal canal
enterocoele
small bowel pushes against vagina
rectocele
rectal prolapse
Ankylosing spondylitis
inflammatory condition of the spine that can lead to fusion of skeletal structures
lots of immobility
intervention: compensatory strategies, medication, rehab
Sciatica
compression of sciatic nerve - caused by tightness in piriformis - compression of back of leg
intervention: stretching, activity modification
Pelvic alignment
tilted anteriorly in anatomical position
want to look at tilt, rotation, and obliquity (one hip higher than other)
important for positioning
Pelvic fractures
bladder, intestines, and kidneys can be affected due to close proximity
Intervention: severe cases surgery, period of non weight bearing
femur characteristics
longest bone - femoral head pairs with acetabulum to form hip joint
greater trochanter - axis for flexion and extension
medial and lateral epicondyle- attachment points for tendons and ligaments
Tibia characteristics
primary weight bearing bone of lower leg
medial malleolus- axis for ankle plantar flexion
Fibula characteristics
bears little weight, proximally articulates with tibia
lateral malleolus-
Patella characterstics
largest sesamoid bone in body
stabilizes knee during flexion - attached to quadriceps tendon which then turns into patellar ligament
Hip joint
ball and socket - flexion/extension, abduction/adduction, internal/external rotation
formed by head of femur and acetabulum- more surface area/more stability
supported by iliofemoral, ischiofemoral, and pubofemoral - internally supported by round ligament
Knee joint
Tibiofemoral - hinge - flexion/extension
ACL/PCL limit anterior/posterior gliding and rotation
LCL/MCL prevent genoveraum/valgus
IT band syndrome
repetitive strain of IT band
interventions: rest, activity modification, stretching, anti-inflammatory medication
Hip fractures
most involve proximal femur
require internal fixation to repair and acute care OT
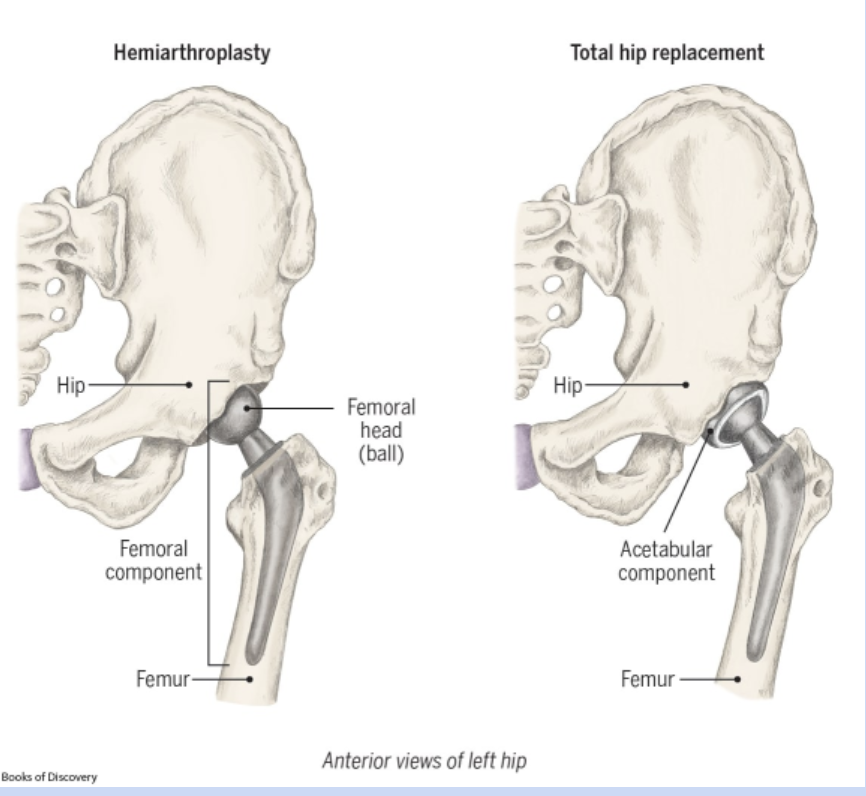
Hip arthroplasty (replacement)
replaces femoral head and acetabulum
hemiarthroplasty- replaces femoral head
no hip flexion past 90, no internal rotation, no crossing legs
collateral ligament injury
(ACL tear) - causes instability of knee
includes surgical repair and then post op therapy
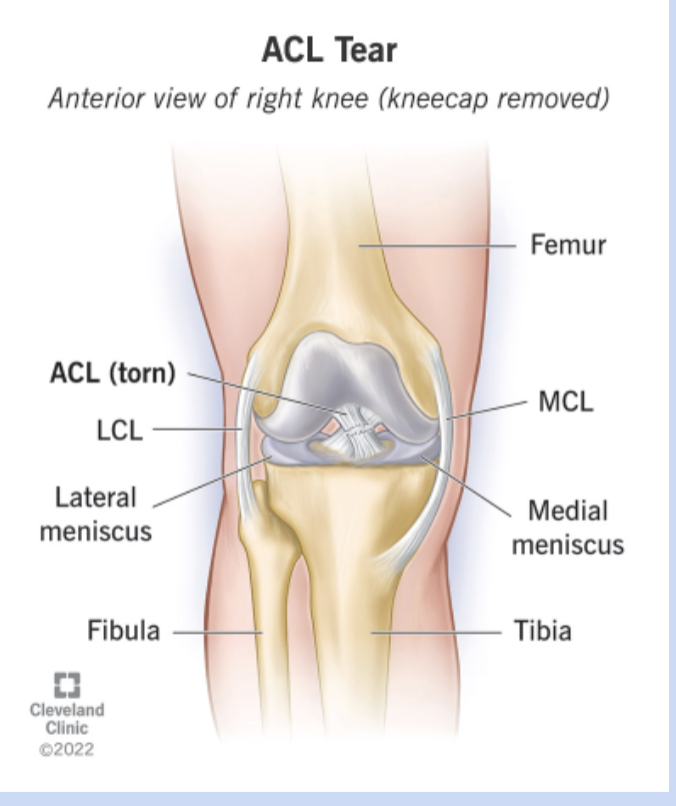
osteoarthritis
none or limited precautions - acute OT - outpatient PT
lower limb amputation
occurs from traumatic injury, PVD, diabetes
managing edema, joint contractures, shaping residual limb
lower limb amputation: Prosthetic
prosthetic phase- facilitating functional mobility, transfers, ADL participation
prosthetic training- can take up to a year, donning (put it on)/doffing (take off) prosthetic, bearing weight, increasing tolerance
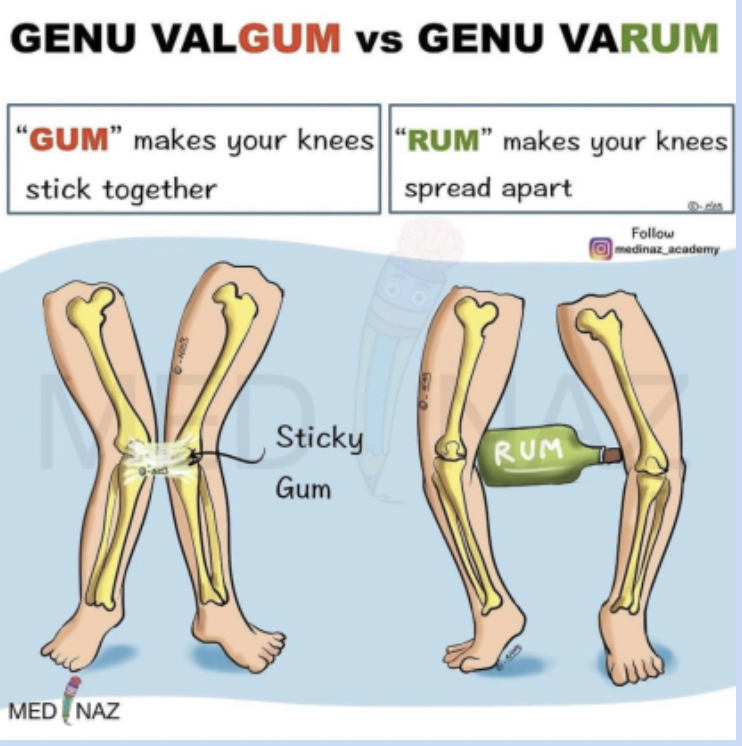
Genu varum and genu valgum
Tibia is not aligned with femur in straight line- can create imbalance of forces between femur and tibia
varum- bow leg
valgum- knock knee
Stability
the ability to maintain control of the position or movement of your body
depends on: vision, vestibular system, proprioception, tactile sensation
Base of Support (BoS)
parts of body or mobility devices that come into contact with ground - distance between those points
more points of contact + larger distance = better BoS
Center of Gravity (CoG)
focal point where gravity acts; where the weight of object is evenly distributed
COG lowers = stability increases
COG in anatomical: S2
bony landmarks that could wear away when bed bound
scapula, calcaneus, acromion etc
posture
relative position of body segments in response to demands of activity
depends on: sensory and motor input, voluntary and involuntary, lighting workspace and environment
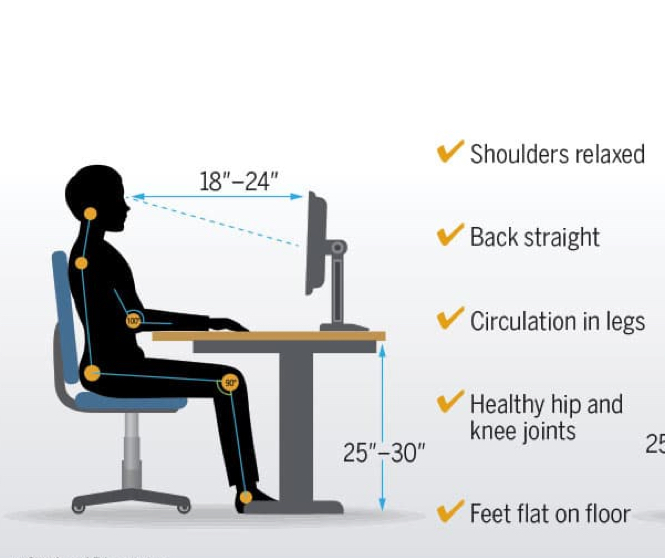
Ergonomics
fitting the workplace to the worker
lumbar spine supported, hips knees and elbows at 90, wrist neutral, monitor 18-24 inches away, head and neck neutral
functional mobility
moving from one position/place to another such as bed mobility, w/c mobility, and transfers
Bed mobility
use of logrolling, bridging, trapeze bar (SCI)
pain, generalized weakness, lack of mobility can lead to skin break down
Gait
step: heel strike to heel strike
step width: width between heals (BOS determined)
cadence: steps per minute
stance phase
heel strike
foot flat
midstance
heel off
toe off
swing face
acceleration
midswing
deceleration
trendelenburg
weakness in gluteus medius
causes lateral lean to affected side to compensate weakness
circumduction gait
muscle weakness in legs causes trunk and pelvis to compensate by laterally swinging leg to the side of the body to propel it forward
hemiplegia, OA of knee, general muscle weakness
foot drop
weakness or paralysis of ankle dorsiflexors impair heel strike
toes come into contact with ground before heel - dragging foot
stroke or tbi
hemiplegic gait
paralysis of one side of the body resulting from stoke, CVA, CP
hip is adducted and knee locked in extension
arm is flexed at the elbow and wrist is held against body - limits balance
Parkinsonian gait
affected by impaired perception and modulation of motor movements
shuffling feet with small forward movements and limited elevation of legs
weight is placed on heels with flexion of trunk
scissor gate
narrowing or crossing over of the legs during ambulation
associated with CP and other neurolgical diagnoses
ataxic gait
unique gait where strength and ROM are not compromised but coordination is
neurological impairment of the cerebellum
Tibia and Fibula
lateral and medial malleolus
Hindfoot
Talus- surface for ankle joint
Calcaneus- heel of foot
Midfoot
stabilized by plantar ligaments and plantar aponeurosis
stabilize and support weight
Proximal and Distal Tibiofibular joint
contribute to stability of ankle - interosseous membrane binds tibia and fibula together
Talocrural joint
hinge - dorsiflexion/plantar flexion
talus held between distal tibia and fibula
Subtalar joint
formed by calcaneus and inferior aspect of talus
provides inversion and eversion
MTP and IP
MTP allows flexion/extension and some abduction/adduction
IP flexion and extension
Typical ROM for inversion and eversion
Inversion - 35
Eversion - 15
Neurological Impairment of LE
joints and skin of foot are sending info to brain
assist in stabilizing uneven surfaces
consider how numbness/weakness may affect gait/mobility
Foot drop
inability to actively dorsiflex foot - foot may drag
innervation: AFO - holds foot in passive position to restore modified gate pattern
Plantar fascititis
inflammation of plantar aponeurosis - pain when bearing weight on foot
Intervention: rest, orthotics, modalities, stretching
Neck ROM
Flexion/extension - 45
Rotation- 45
Lateral flexion- 60