Endo/Repro Exam 1: Collaborative Study
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Thyroid gland
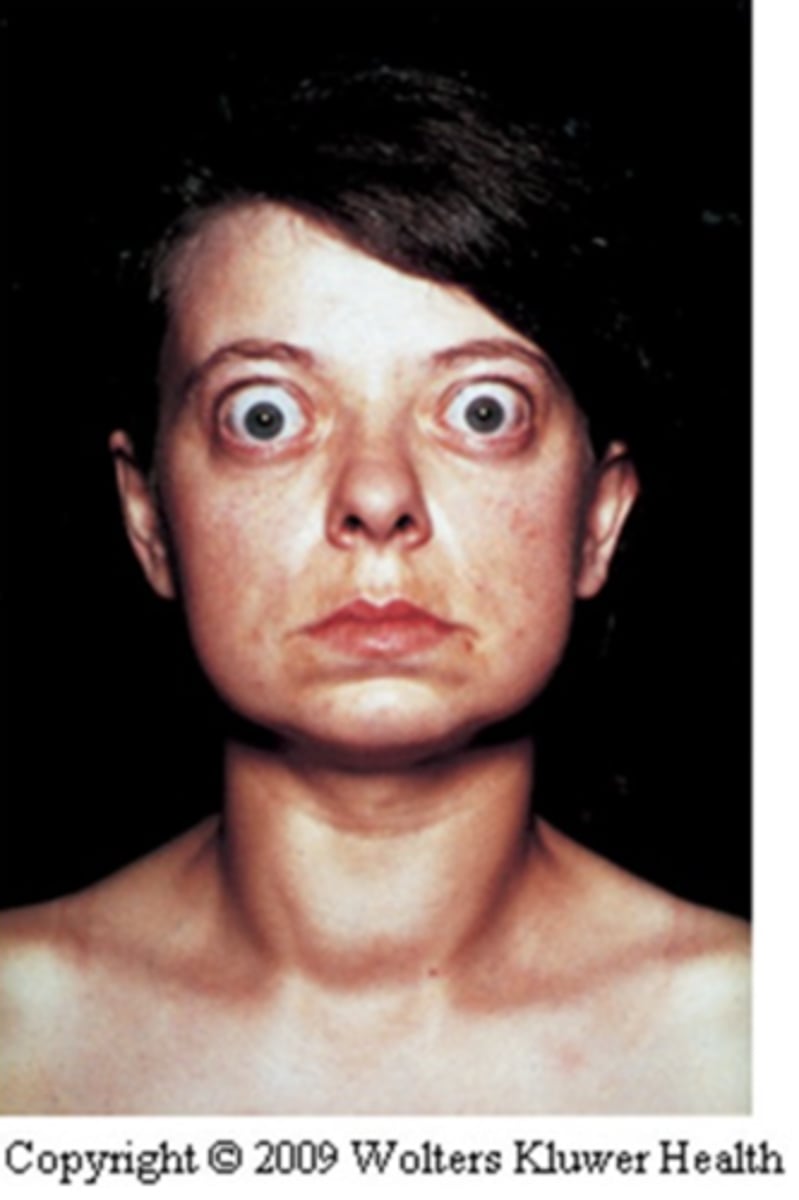
A 40-year-old female patient presents heat intolerance, easy nervousness, difficulty sleeping. Her eyes are bulging as the picture below.
Her physical examination shows weight loss, increased heart rate. Her neck examination shows a soft, diffuse, nonnodular midline mass that is mobile on swallowing.
The histologic appearance of this organ on the neck under normal health condition would show as the picture on the top. The histologic examination of this patient shows as the picture on the bottom.
What is this organ?
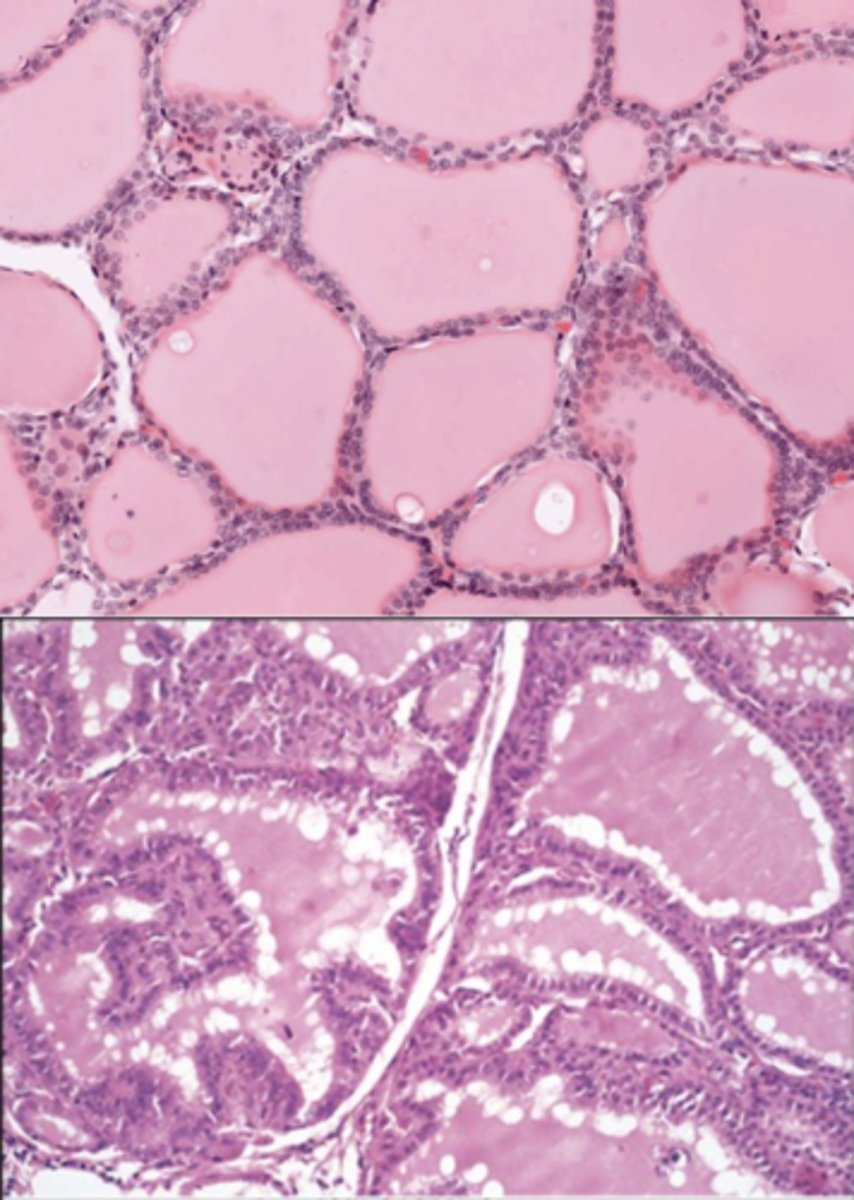
- Thyroglobulin - Store thyroid hormone
- Follicular cells - Release thyroid hormone
- Parafollicular cells - Store calcitonin
A 40-year-old female patient presents heat intolerance, easy nervousness, difficulty sleeping. Her eyes are bulging as the picture below.
Her physical examination shows weight loss, increased heart rate. Her neck examination shows a soft, diffuse, nonnodular midline mass that is mobile on swallowing.
The histologic appearance of this organ on the neck under normal health condition would show as the picture on the top. The histologic examination of this patient shows as the picture on the bottom.
List the cell types in the epithelium and describe their functions.
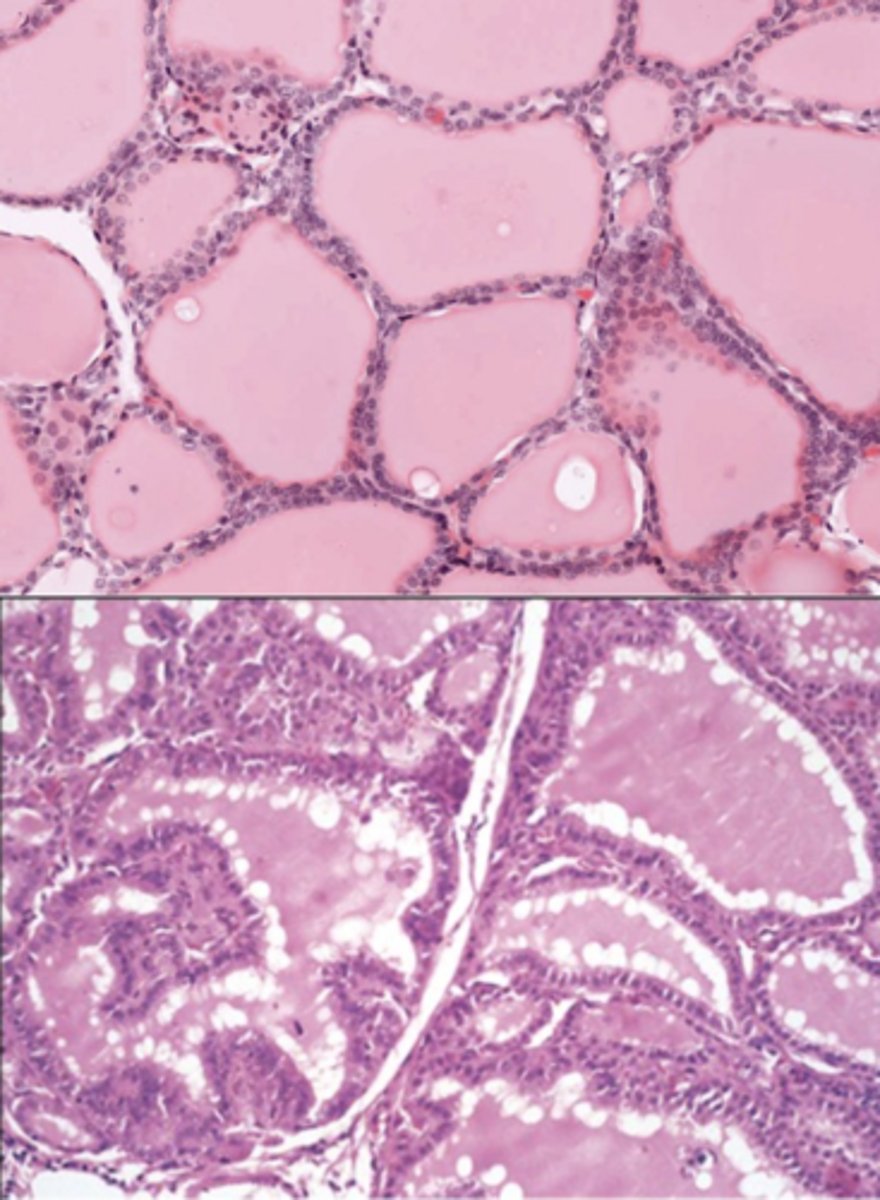
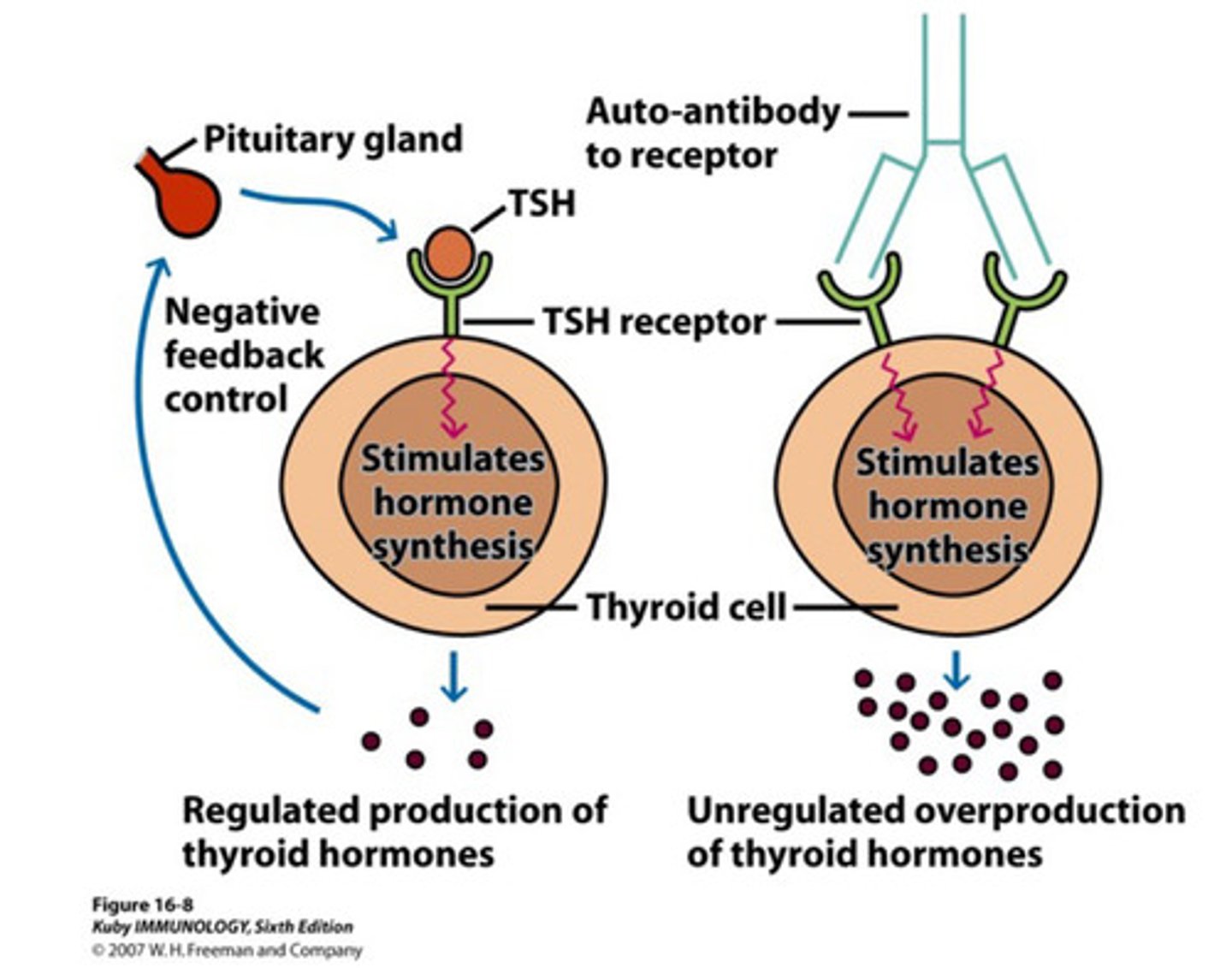
Grave's disease
The patient’s thyroid is diffusely hyperplastic. The follicles are lined by tall columnar epithelial cells that project into the lumina. These cells actively resorb the colloid in the centers of the follicles, resulting in the "scalloped" appearance of the edges of the colloid.
Lab test indicates positive Thyroid Stimulating Immunoglobulins (TSIs).
What is most likely the patient’s diagnosis?
b. Increased T4 and decreased TSH
A patient has Grave's disease. Their blood test shows...
a. Decreased T4 and increased TSH
b. Increased T4 and decreased TSH
c. Normal T4 and increased TSH
d. Normal T4 and decreased TSH
e. Normal T4 and normal TSH
Grave's disease
What disease is represented in this image on the right?
Adrenal gland
A 72-year-old man presented to the ER with hypertension, headache, palpitation, and
diaphoresis. He was diagnosed with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A and died on the
second day after admission due to sudden cardiac arrest. Endocrine organs from him were
being examined for pathology at autopsy.
An illustration of one organ obtained from autopsy is shown below. This organ has an outer cortex and an inner medulla, wrapped by a CT capsule.
What is this organ?
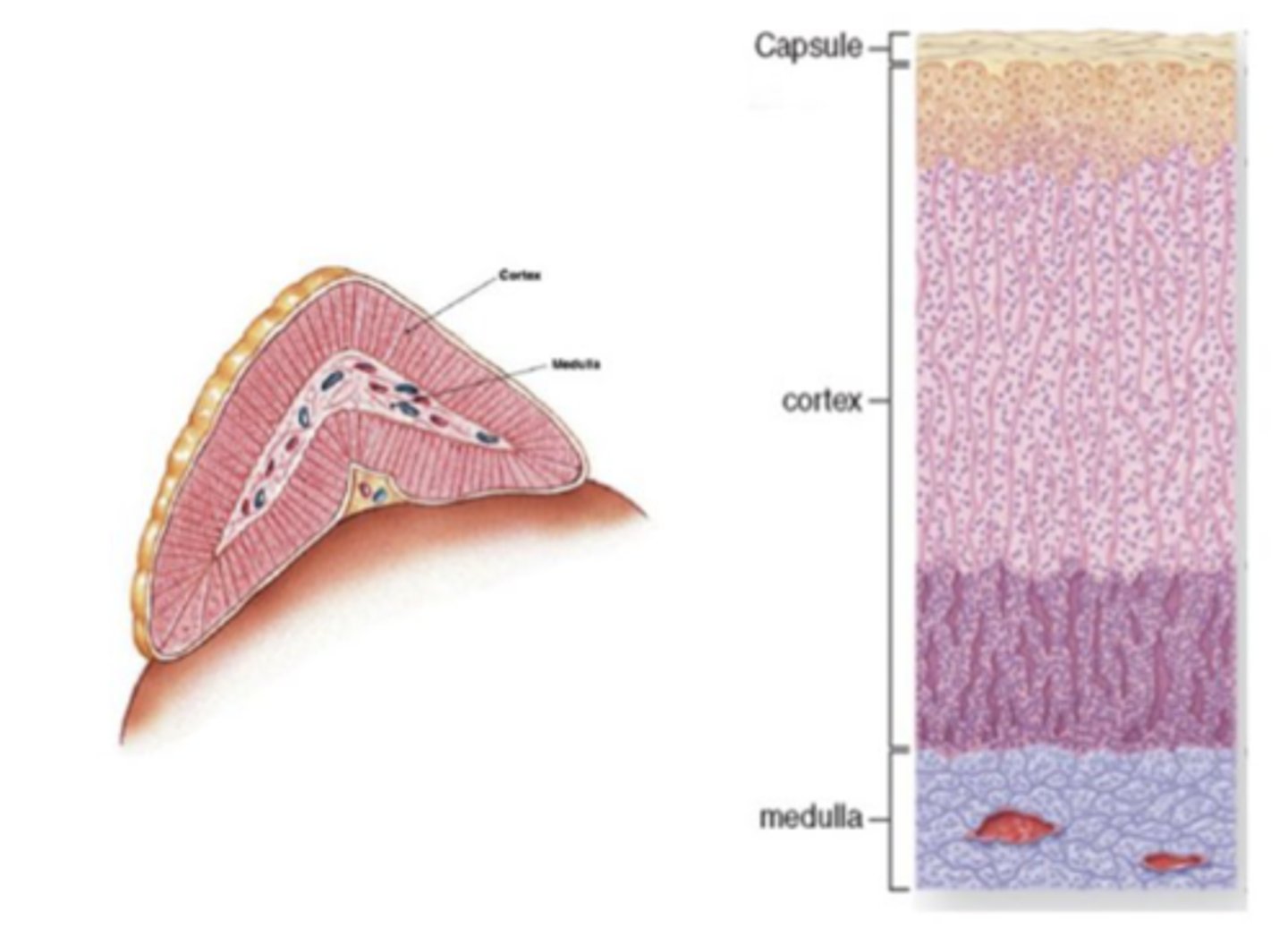
Pheochromocytoma
A 72-year-old man presented to the ER with hypertension, headache, palpitation, and
diaphoresis. He was diagnosed with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A and died on the
second day after admission due to sudden cardiac arrest. Endocrine organs from him were
being examined for pathology at autopsy.
The patient’s symptoms, hypertension, headache, palpitation, and diaphoresis, are caused by catecholamine-producing tumor of the chromaffin cells in medulla.
What is the name of the tumor?
Chromaffin cells act as modified post ganglionic neurosecretory cells and secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine
A 72-year-old man presented to the ER with hypertension, headache, palpitation, and
diaphoresis. He was diagnosed with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A and died on the
second day after admission due to sudden cardiac arrest. Endocrine organs from him were
being examined for pathology at autopsy.
The patient’s symptoms, hypertension, headache, palpitation, and diaphoresis, are caused by catecholamine-producing tumor of the chromaffin cells in medulla.
Please describe the neurosecretion function of chromaffin cells.
Zona glomerulosa
What layer of the cortex is at 1?
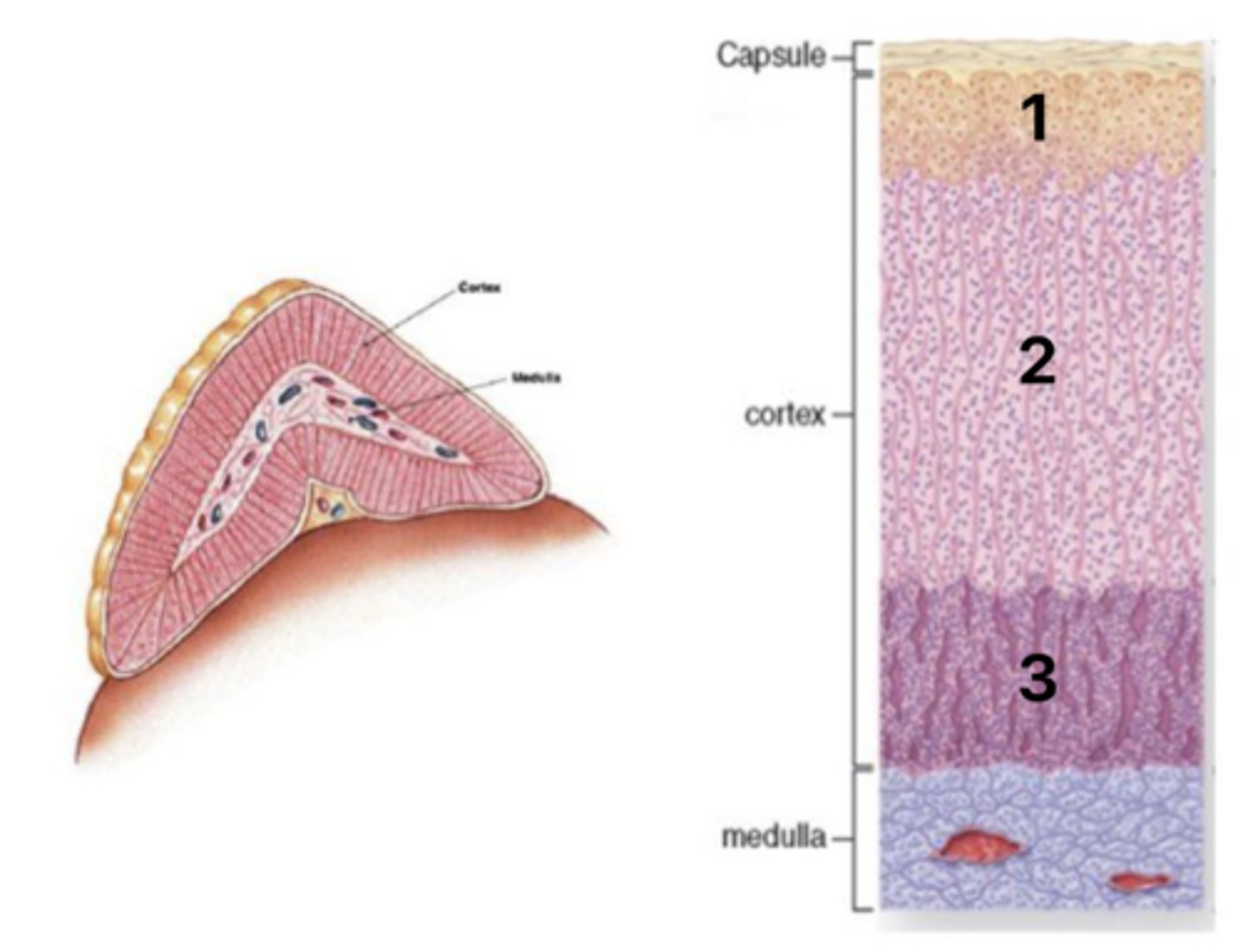
Zona fasiculata
What layer of the cortex is at 2?
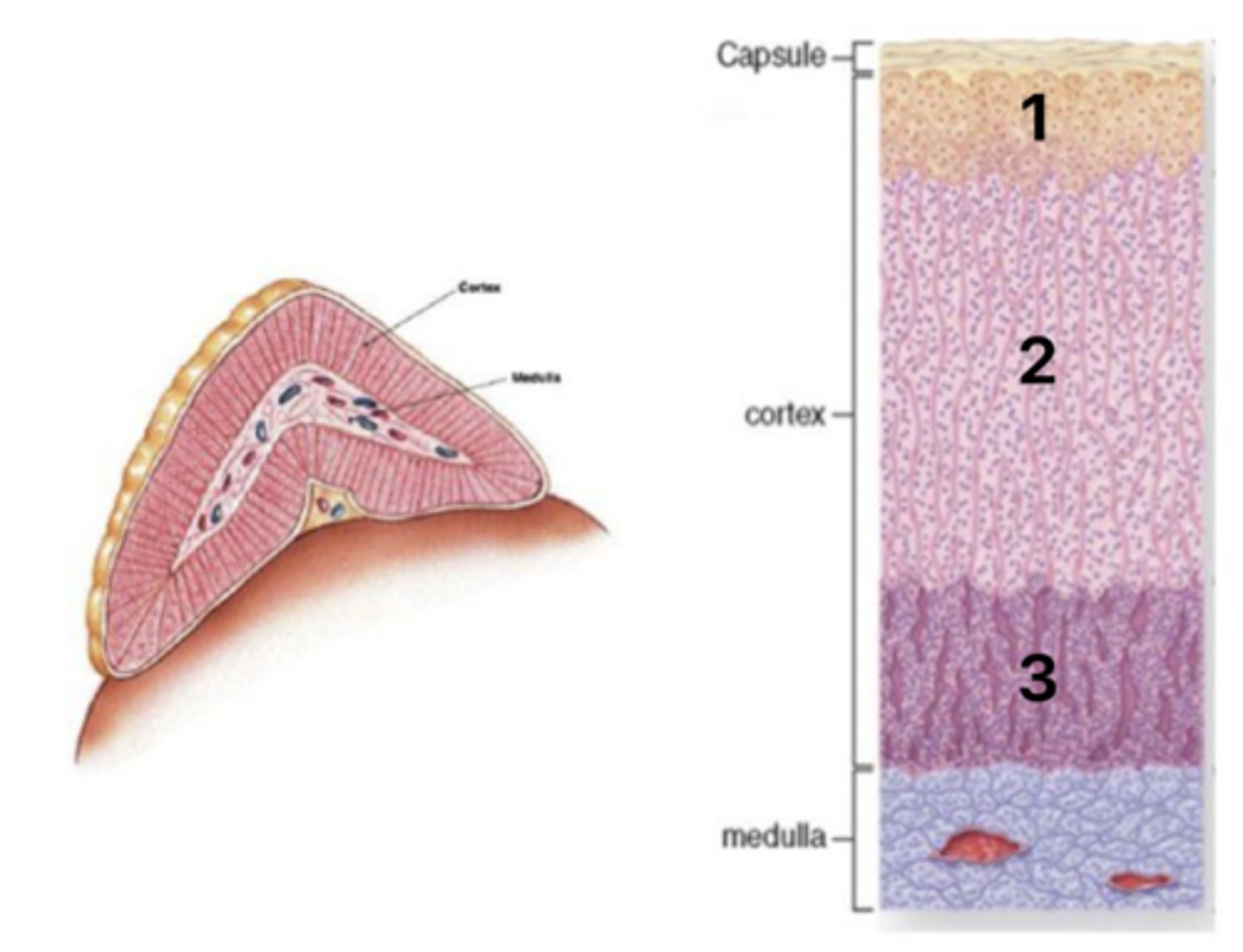
Zona reticularis
What layer of the cortex is at 3?
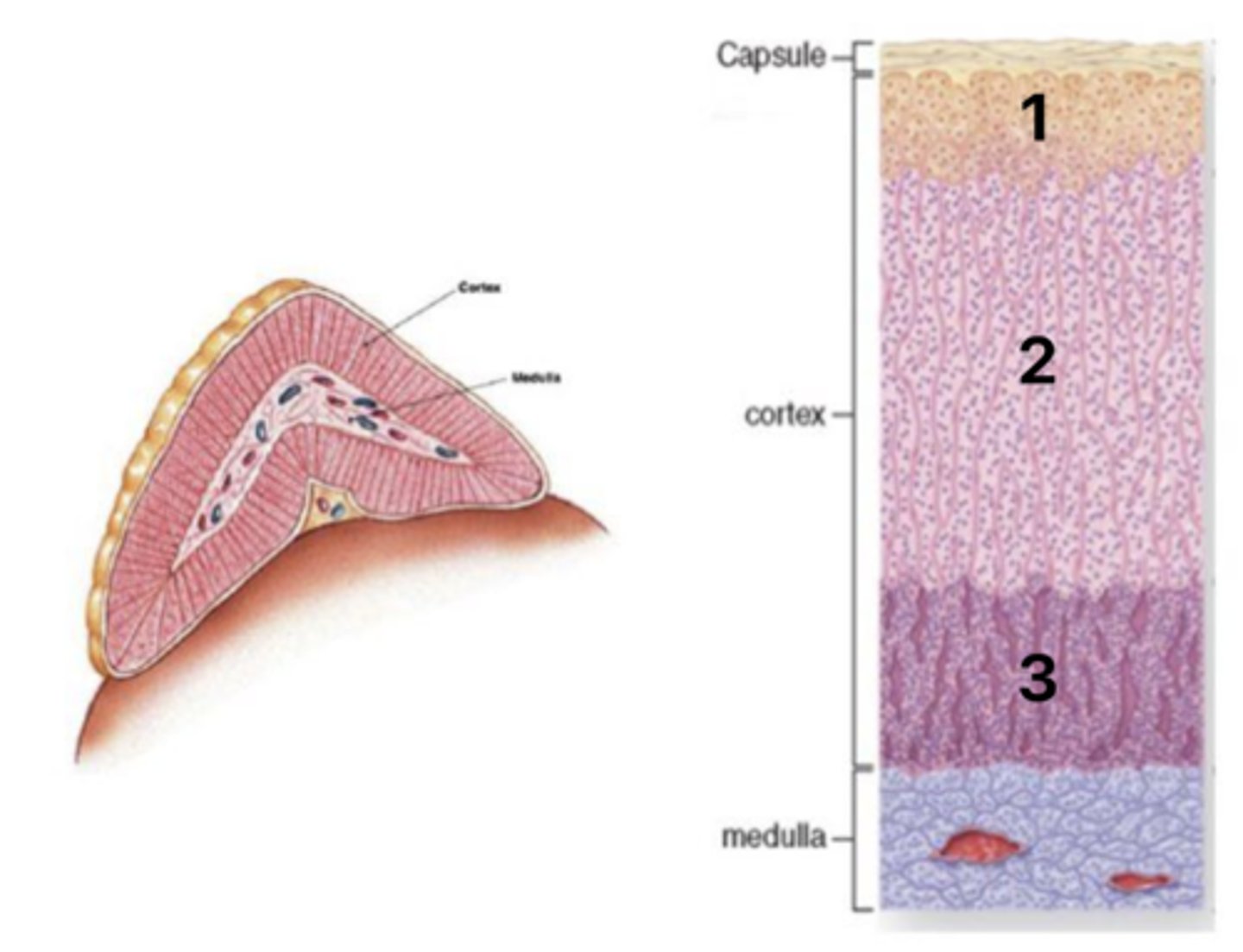
Mineralcorticoids (aldosterone)
What hormones are secreted in layer #1 of the cortex?
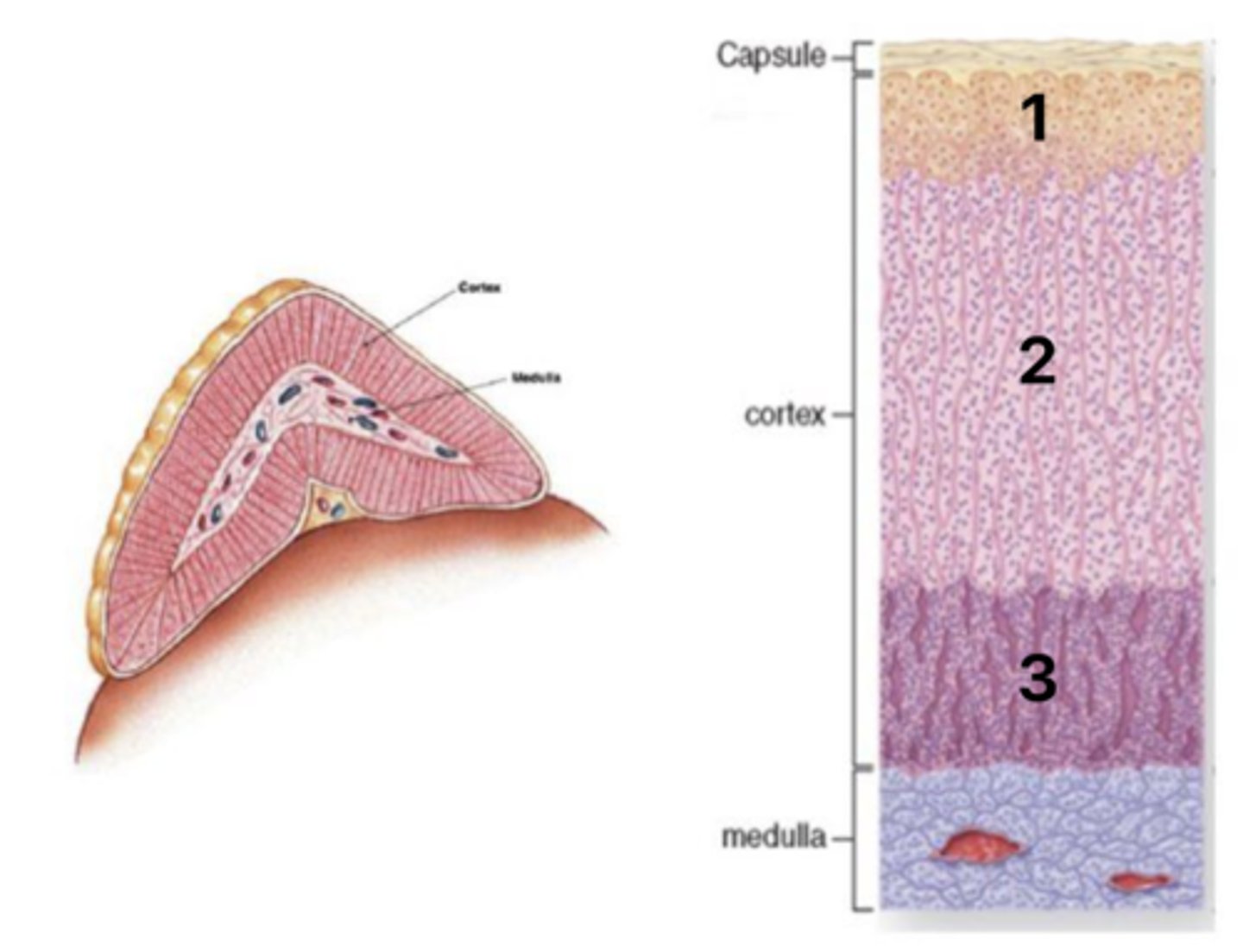
Glucocorticoids (coristol)
What hormones are secreted in layer #2 of the cortex?
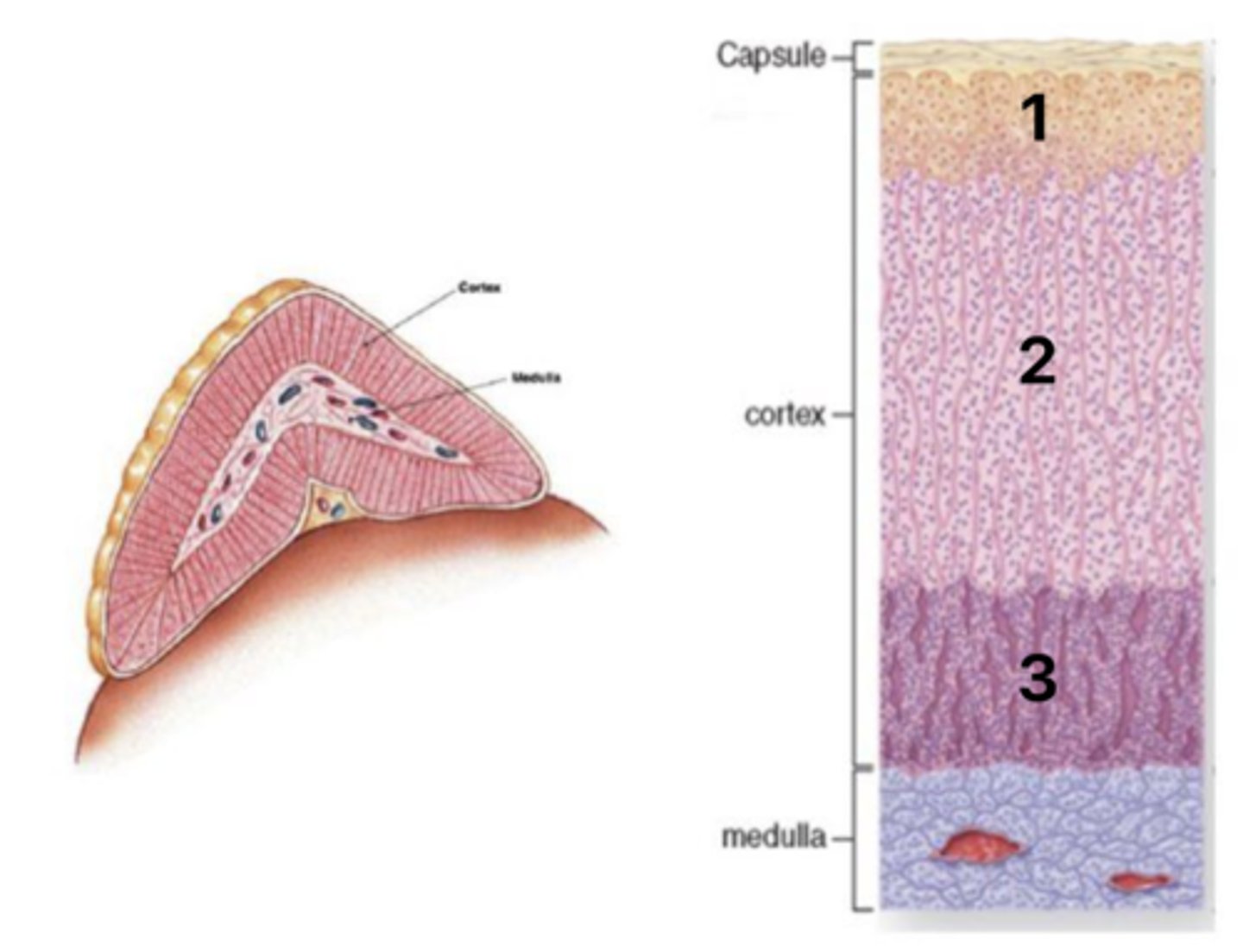
Androgens (DHEA, androstendione)
What hormones are secreted in layer #3 of the cortex?
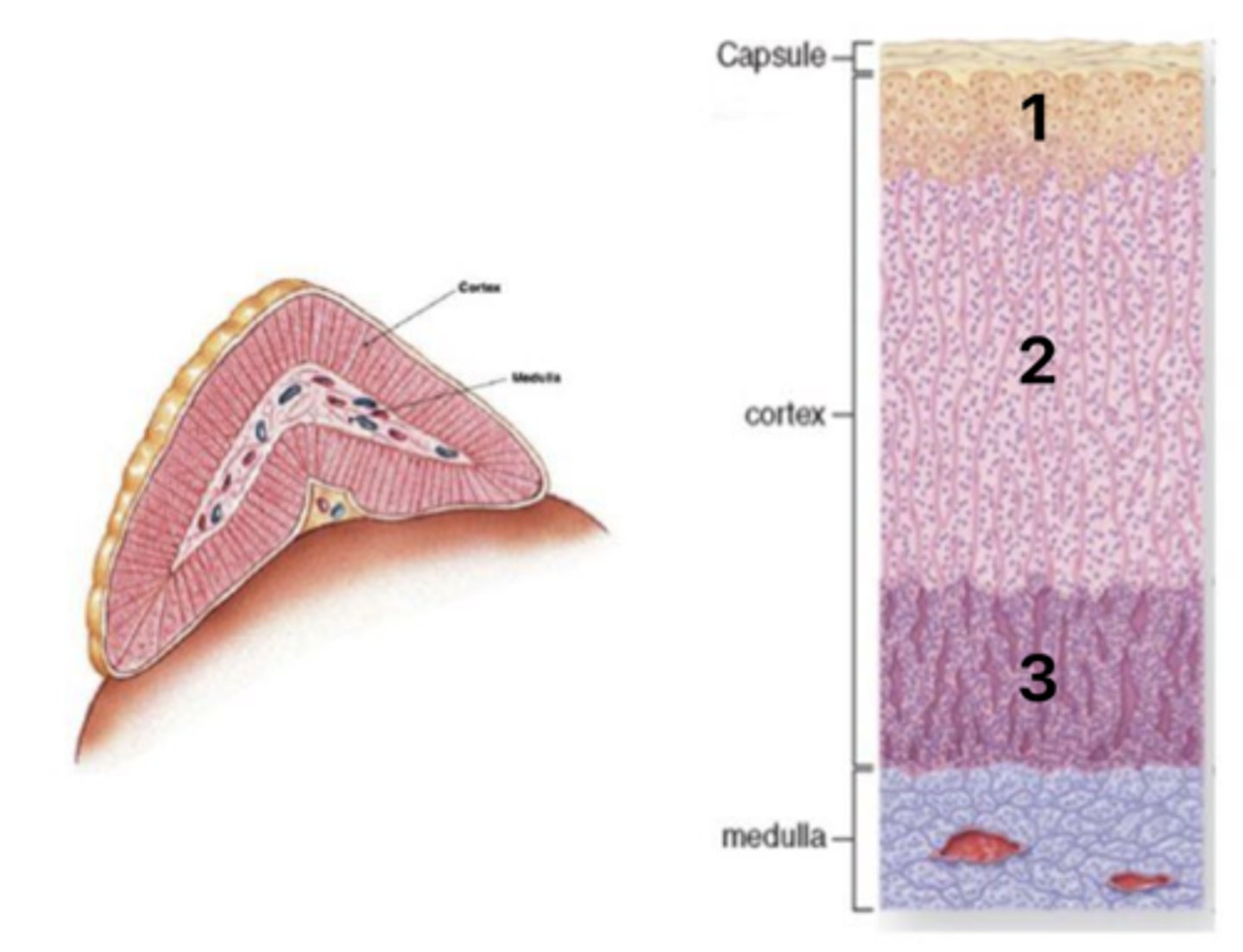
Regulation by ACTH and angiotensin II
What is the regulation of the adrenal cortex hormones?
Pituitary gland
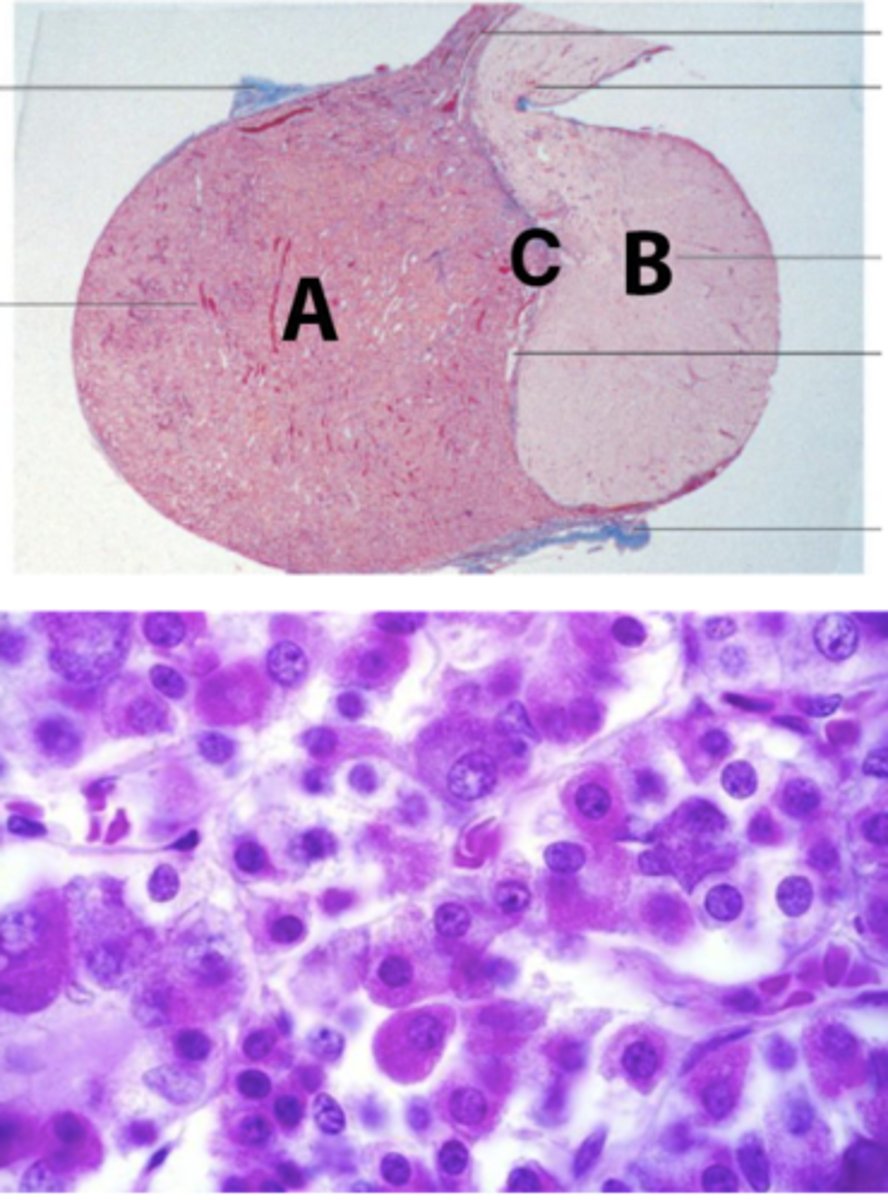
A 42-year-old female presents in the ER with shock, due to postpartum hemorrhage, following a normal delivery at home. Her blood pressure was undetectable, pulse rate was 130 per minute, and extremities were cold. Immediate care involved vascular expansion with colloids via a central venous catheter, followed by transfusion of packed red cells. The short-term evolution was marked by lactation failure, agitation, and convulsions. The medium-term evolution was marked by prolonged amenorrhea, fatigue, and apathy.
The patient is suffering from Sheehan's syndrome, which is characterized by partial or complete necrosis of this organ (shown in the picture) in women with severe blood loss and hypotension during delivery.
What is this organ?
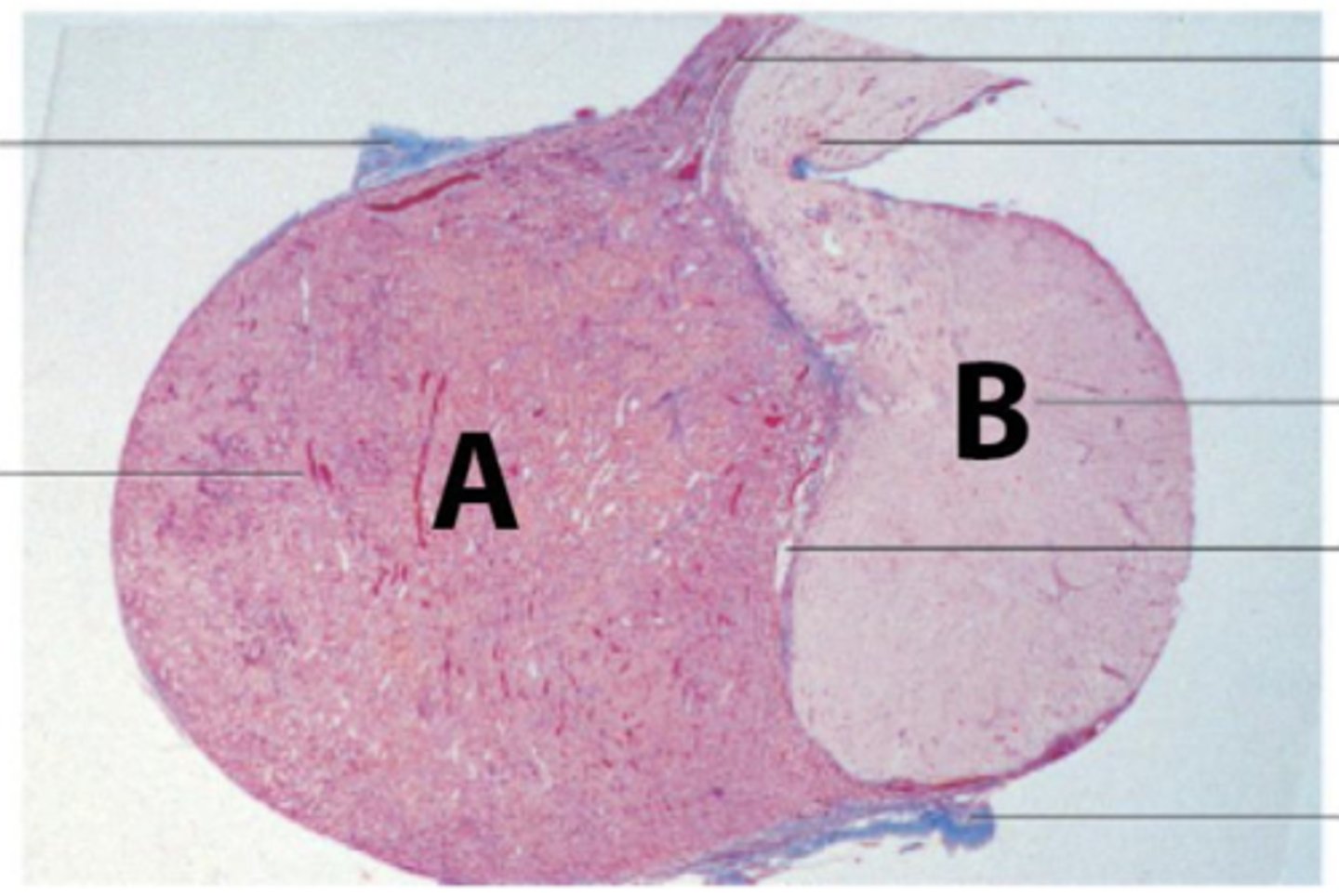
Anterior pituitary; Oropharynx ectoderm
The patient is suffering from Sheehan's syndrome, which is characterized by partial or complete necrosis of this organ (shown in the picture) in women with severe blood loss and hypotension during delivery.
What is at A? What is the embryological origin?
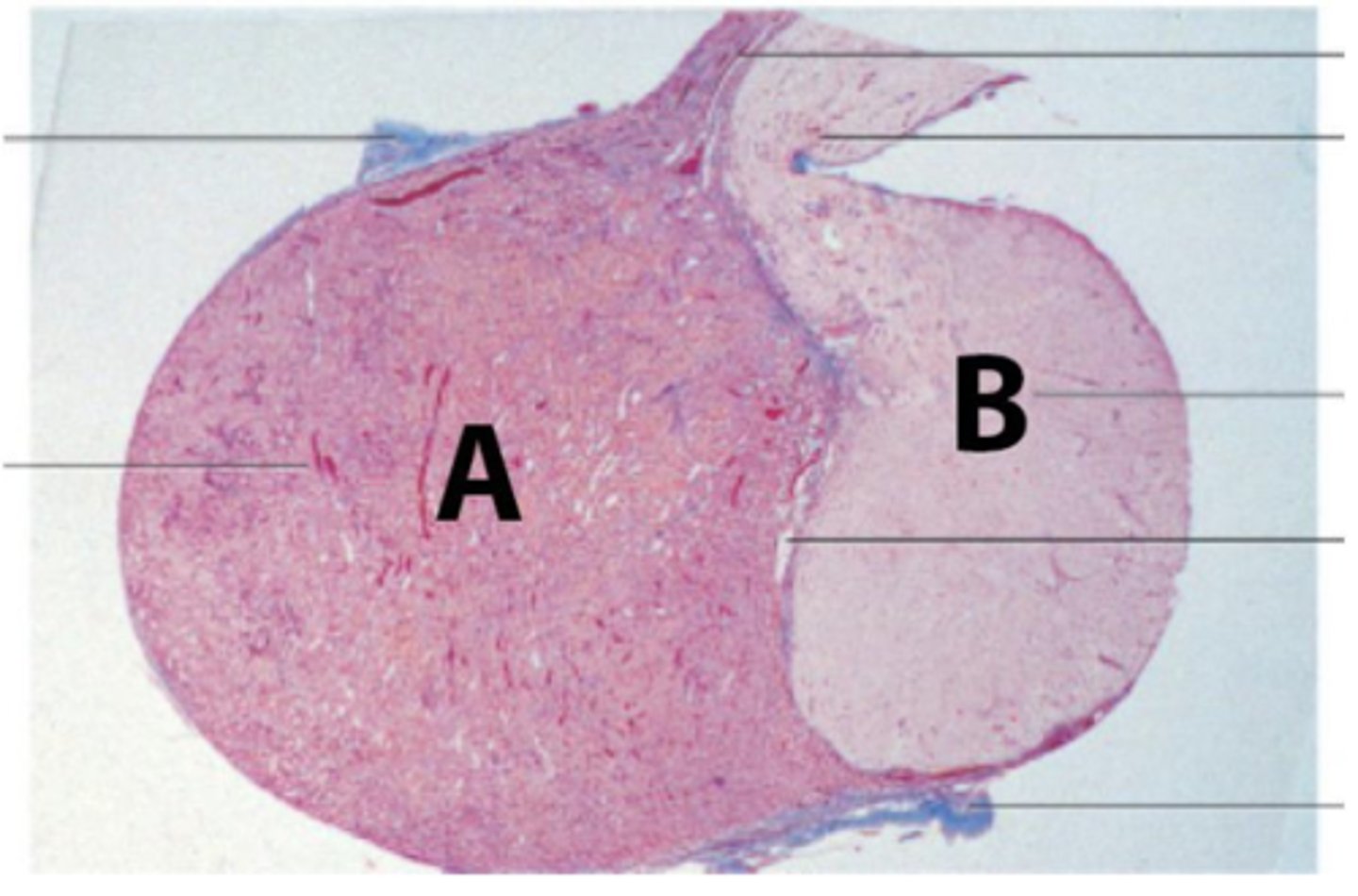
Posterior pituitary; Neuroectoderm
The patient is suffering from Sheehan's syndrome, which is characterized by partial or complete necrosis of this organ (shown in the picture) in women with severe blood loss and hypotension during delivery.
What is at B? What is the embryological origin?
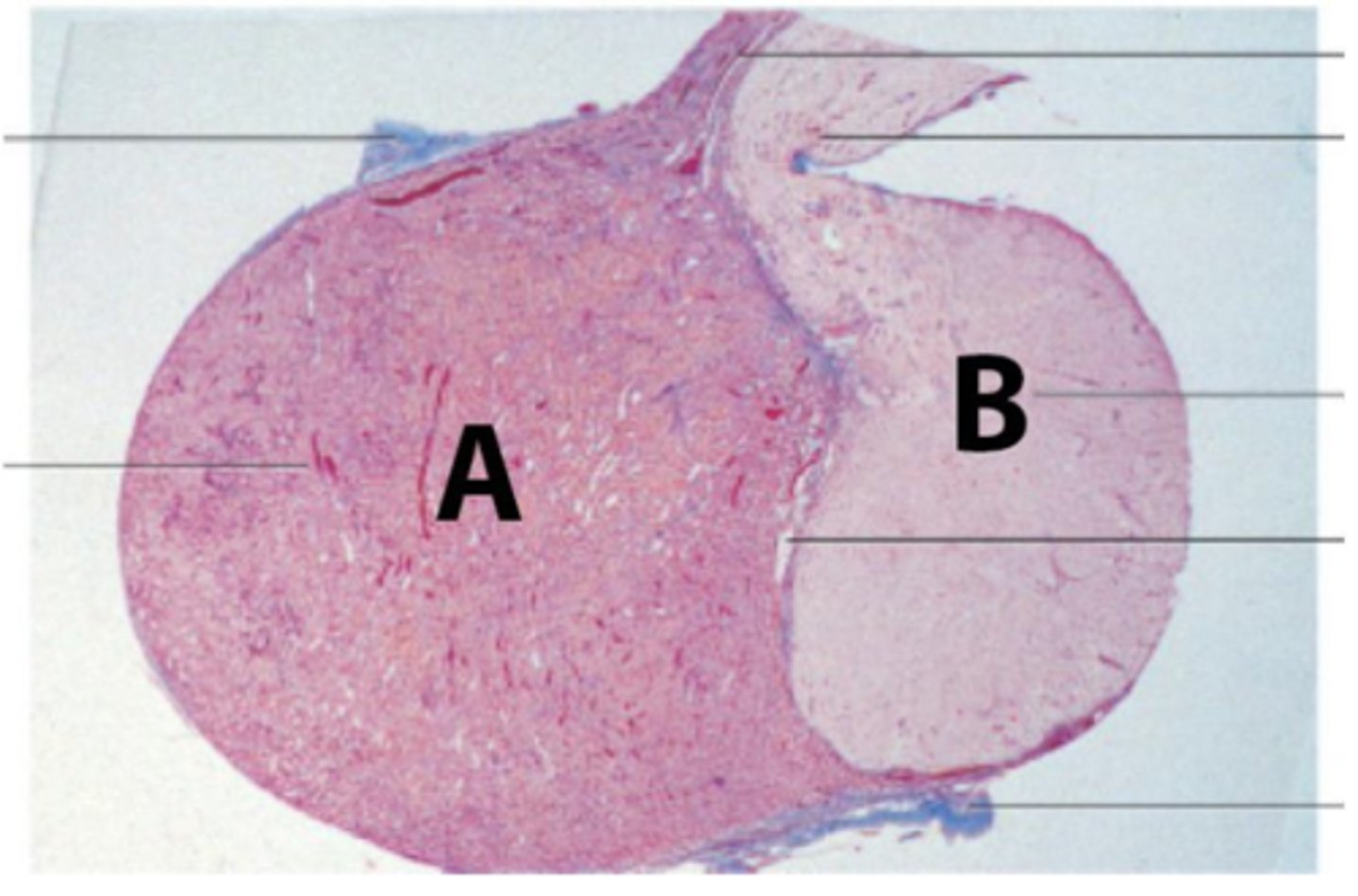
c. Low thyroxine (T4) and low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
The patient is suffering from Sheehan's syndrome, which is characterized by partial or complete necrosis of the pituitary gland in women with severe blood loss and hypotension during delivery.
Which of the following is an expected finding in the patient?
a. Elevated estrogen and elevated follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
b. Low estrogen and elevated FSH
c. Low thyroxine (T4) and low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
d. Low T4 with elevated TSH
e. Low cortisol with elevated adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
- LH
- FSH
- TSH
- Prolactin
- GH
- ACTH
List 6 hormones secreted by anterior pituitary gland (adenohypophysis), a high magnification session from part A is shown below in the second picture.
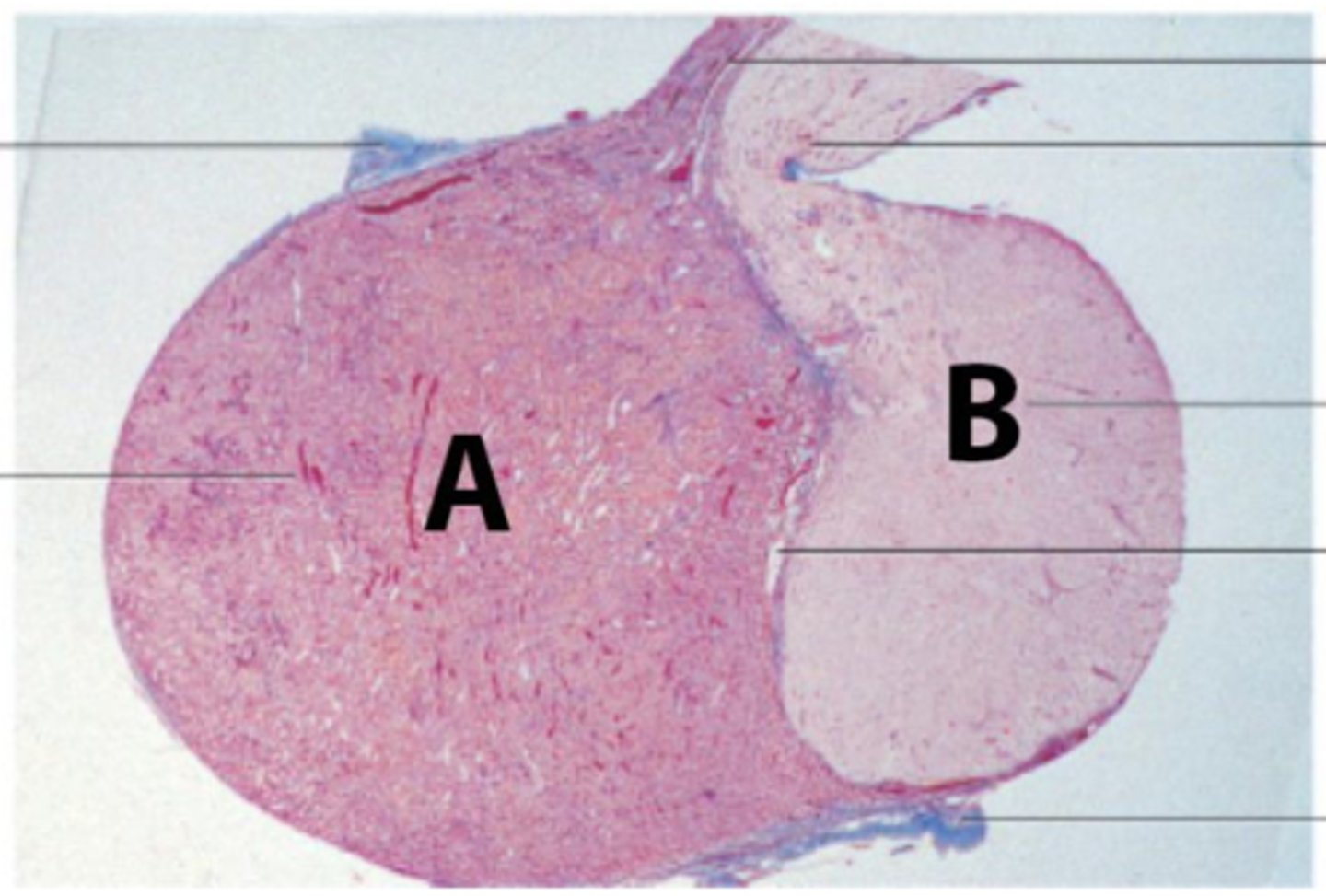
Prolactin - inhibited by dopamine
GH - inhibited by somatostatin
Which of the following hormones may be inhibited by upstream hormones from hypothalamus?
- LH
- FSH
- TSH
- Prolactin
- GH
- ACTH
- Oxytocin
- ADH/AVP
List 2 hormones released by posterior pituitary gland (neurohypophysis):
POMC
What is the prohormone synthesized by pars intermedia, shown as C in the picture?
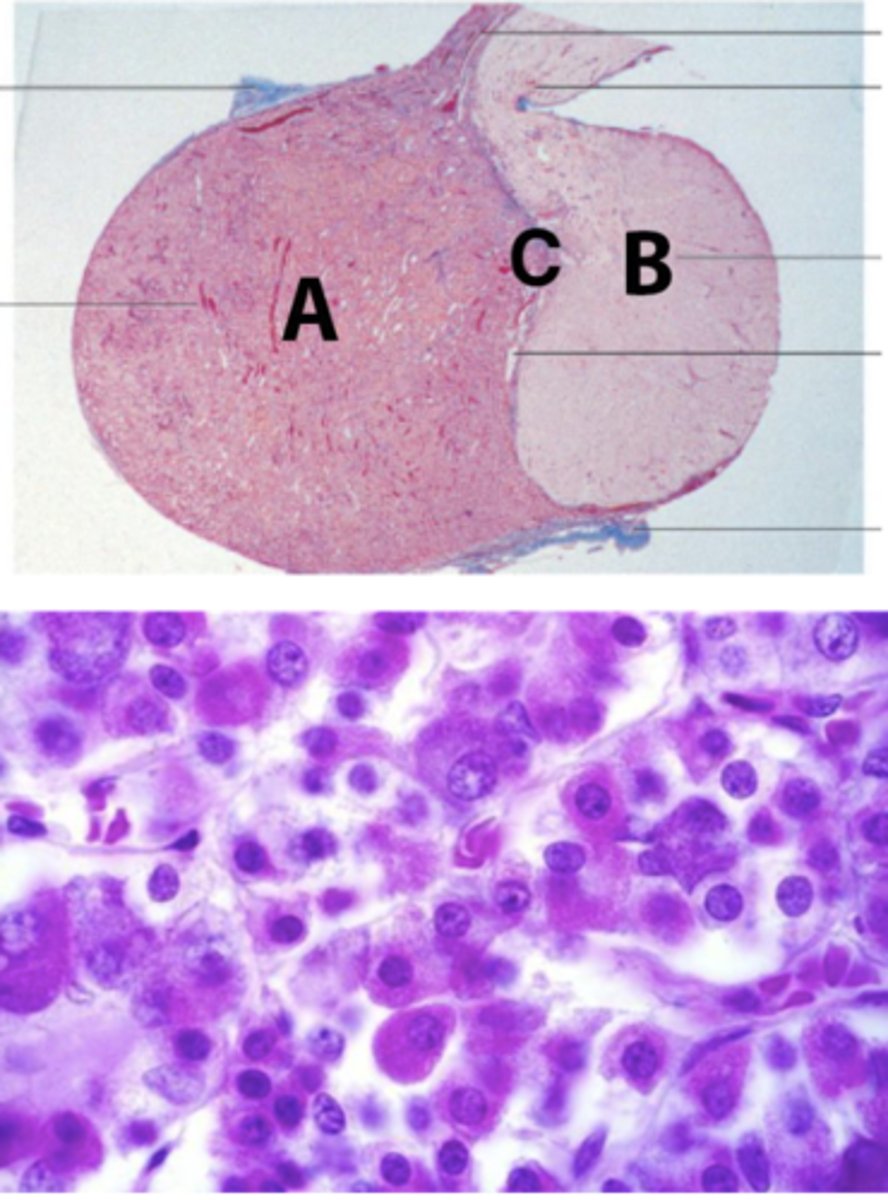
- MSH
- B endorphin
- ACTH
POMC is the prohormone synthesized by pars intermedia, shown as C in the picture. What are other hormones derived from this prohormone?
Prolactin
Clinical features of Sheehan's syndrome arise largely due to insufficiency of the adenohypophysis.
Which hormone deficiency causes lactation failure and amenorrhea?
ACTH
Clinical features of Sheehan's syndrome arise largely due to insufficiency of the adenohypophysis.
Which hormone deficiency leads to hypoglycemia (marked by agitation, and convulsions), fatigue and apathy?
C. Melatonin
Which of the following hormones are secreted by the pineal gland?
A. T3 and T4
B. Insulin
C. Melatonin
D. Calcitonin
E. Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
F. Cortisol
B. Insulin
Which of the following hormones are secreted by the beta cells in islets of langerhans of pancreas?
A. T3 and T4
B. Insulin
C. Melatonin
D. Calcitonin
E. Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
F. Cortisol
A. T3 and T4
D. Calcitonin
Which of the following hormones are secreted by the thyroid gland?
A. T3 and T4
B. Insulin
C. Melatonin
D. Calcitonin
E. Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
F. Cortisol
E. Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Which of the following hormones are secreted by the parathyroid gland?
A. T3 and T4
B. Insulin
C. Melatonin
D. Calcitonin
E. Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
F. Cortisol
F. Cortisol
Which of the following hormones are secreted by the andrenal gland?
A. T3 and T4
B. Insulin
C. Melatonin
D. Calcitonin
E. Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
F. Cortisol