EXAM 1 Radiobiology Review
1/94
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch 29, 30, 36
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
What is Covalent Bonding
characterized by the SHARING of electrons
“CO-Parenting”
What is Ionic Bonding
Occurs when two atoms are bound together by the attraction of their opposite charges
(Giving up electrons)
Deterministic Effect AKA
EARLY EFFECTS
What is Deterministic Effect?
biologic response whose severity varies with radiation dose
A DOSE THRESHOLD USUALLY EXISTS - Minimum amount needed to cause a response
Stochastic Effect AKA
LATE EFFECT
What is Stochastic Effect?
Radiation response increases with increasing radiation dose
There is NO threshold dose - ANY AMOUNT OF RADIATION CAN CAUSE A RESPONSE, THE MORE AMOUNT OF RADIATION THE GREATER THE RESPONSE
List deterministic effects
GI Syndrome
CNS Syndrome
tissue damage to skin
tissue damage to gonads
cytogenic damage
List stochastic effects
bone CA
Lung CA
Thyroid CA
BREAST CA
tissue damage to skin
Tissue damage to eye
% Of how much water is the body made of?
80%
What are some of the duties of water in the molecular composition?
needed to aid in digestion
helps fight infections
assists in removing toxins in body
lubricates and cushions joints
carries oxygen and nutrients to cells
regulates body temp
assists in metabolism working properly
protects spinal cord and other important tissues
% of how much protein is the molecular composition?
15%
How is protein structured?
are long-chain macromolecules that consist of a linear sequence of amino acids attached by peptide bonds
how many amino acids are used in protein?
22 amino acids are used in protein synthesis
protein synthesis metabolic production of proteins
amino acids = ?
Protein
What is Proteins role in the molecular composition?
provides structure and support to all cells, organs, tissues and systems
Gives energy
helps grow / repair cells
produces neurotransmitters to leep brain working properly
maintains proper pH balance of body fluids
aids immune system to function properly
How else can protein function?
Enzymes, hormones, and antibodies
Enzymes
molecules needed in small quantities to allow biochemical reactions
Hormones
molecules that are used for growth and development
Antibodies
primary defense mechanism against infections and disease
% of lipids in the molecular composition
2%
What are lipids?
are organic macromolecules made up of carbon, hydrogen, an oxygen
1 lipid molecule =
1 glycerol + 3 fatty acid
Where are lipids?
they are in all body tissue and are the structural portion of the cell membrane
Where are lipids located?
they are concentrated under the skin as a thermal insulator
What are lipids used for?
they serve as duel for energy storage for the body
What are carbs made of and its main function?
Made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen - their structure is different
What is the main function of carbs?
provide fuel for cell metabolism
What are other names for Carbs?
Saccharides
monosaccharides
disaccharide
What does DNA do?
Controls cell function
What does DNA contain?
all genetic info necessary for cell replication
T/F DNA is radiation-sensitive ?
True
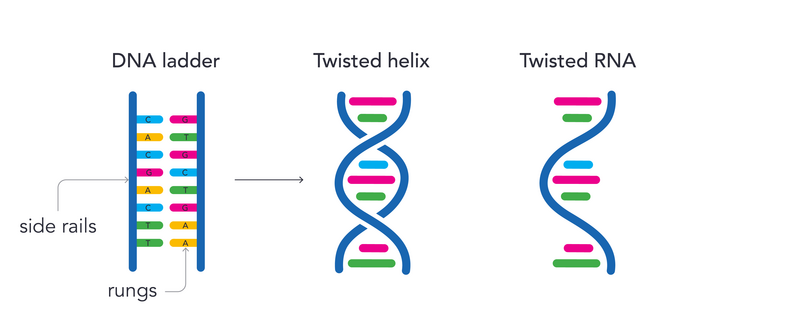
How is DNA structured?
Human DNA exists as a ladder
Side rails - sugar - phosphate molecules
Rungs - bases joined together by hydrogen bonds
Where is RNA located?
located mostly in cytoplam (but is also found in the nucleus)
What is RNA?
Molecules involved in the growth and development of a cell bu protein synthesis
main difference between organic and inorganic comopunds
organic compounds ALWAYS contain carbon, inorganic DOES NOT
Ex of Organic Compounds
DNA
TABLE SUGAR
BENZENE
METHANE
Ex of Inorganic
table salt or sodium chloride
carbon dioxide
diamond
Major Structure of human cell
nucleus
cytoplasm
Nucleus
A molecular strucure of DNA and some RNA, protein and water
Cystoplasm
Protoplasm that exists outside the cells nucleus
what happens to damaged cells by radiation?
cells may malfunction and die
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Channel or a series of channels that allows the nucleus to communicate with the cytoplasm
Mitochondria is known as?
Knon as the “engine of the cell”
Mitochondria is?
a large bean structure found within the cytoplasm of a cell that digest macromolecules for energy

Ribosomes
Small dot-like structure that is used for protein synthesis
Where are ribosomes scattered?
Scattered throughout both the cytoplasm and endoplasmic reticulum
Lysosomes
Small pea-like sacs that contain enzymes capable of digesting cellular fragment

Cell and its strucutre
All membranes consist of lipid-protein complexed that all small molecules and water to diffuse from one side to the other
What do experiments show regarding cells?
that the nucleus is much more sensitive than cytoplasm to the effects of radiation
Protein synthesis
metabolic production of proteins
necessary for survival
Cell proliferation
act of a single or a group of cells that reproduce and multiply
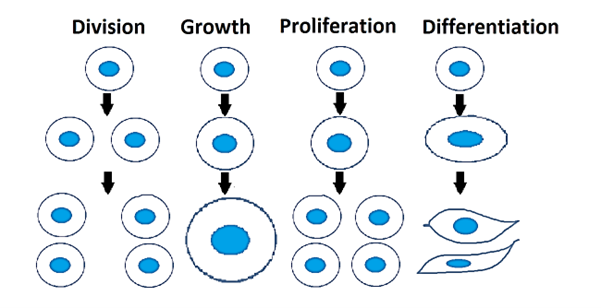
Genetic Cells include?
Oogonium of the female and the spermatogonium of the male
meiosis
when genetic cells proliferation (divide)
Somatic Cells
all other cells in the body
mitosis
when somatic cells proliferate (divide)
Somatic Effects
occur in the exposed individual
Somatic Short term effect
usually occur soon after an acute dose (10rads or greater within a few months of exposure)
ex: temp hair loss
Somatic Late term effect
occurs years after the exposure that caused it
ex: cancer and cataracts
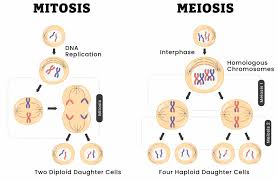
Mitosis
process of somatic cell division where a parent cell divides to form two daughter cells that are identical to the parent cell
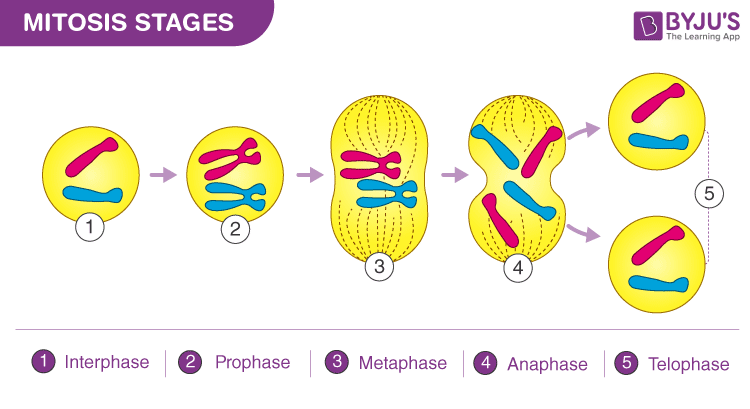
What are the subcategories of Mitosis
A. Prophase
B. Metaphase
C. Anaphase
D. Telophase
Pass My Anatomy Test
What is interphase?
is the period of growth of cells between division
What does each phase include?
Each cycle includes various states of cell growth, development, and division
Prophase -
nucleus and chromosomes enlarge and DNA take structural form
ENALRGE
Metaphase -
Chromosomes move and align themselves at the center of the cell
MOVE
Anaphase -
The sister chromatids of each chromosome divide and move toward opposite poles due to the shortening of the spindle fibers
DIVIDE
Telophase -
The Chromatids (now called chromosomes) are located on opposite poles. Nuclear membrane forms around the chromosomes which start to uncoil. The spindle fibers dissolve and disappear
Meiosis
Process if germ cell division that reduces that chromosomes in each daughter cell to half the number of chromosomes in the parent cell
What is the end result of Meiosis?
end result is 4 cells are created from the original 1 cell
Tissue
Collection of cells of similar structure and function
Organ
Collection of tissue of similar structure and function
Organ Systems in the body
nervous
digestive
endocrine
respiratory
reproductive
What is the LAW OF BERGONIE AND TRIBONDEAU
The radiosensitivity of tissue depends on the number of undifferentiated cells which the tissue contains, the degree of mitotic activity in the tissue and the length of time that cells of the tissue stay in active proliferation (duplication of cell)
What is LET
Linear Energy Transfer
LET is?
measure of rate at which energy is transferred from ionizing radiation to tissue
LET is expressed
in kiloelectron volts of energy trnasferred per micrometer (keV/um)
What is relative biologic effectivemness
ratio of the dose of standard radiation necessary to produce a given effect / dose of test radiation needed for the same effect
As LET radiation increases = ?
the ability to produce biologic damage also increase
Protraction
dose delivered continuously but lower dose rate
Fractionation
dose delivered at a high rate but divided into smaller doses (radiation therapy)
Oxygen Effect
tissue is more sensitive to radiation when irradiated in an oxygenated state
Oxygen Enhancement Ratio
Dose necessary under anoxic conditions to produce a given effect/dose necessary under aerobic conditions to produce the same effect
Diag x-ray are performed under what conditions?
of fully oxygenation
Radiation Dose - Response relationship
A graphic representation of the relationship between the amount of radiation absorbed by a cell (dose) and the amount of damage (response)
Linear dose response
response directly related to dose
higher the dose = higher the response
non-linear dose response
response varied with different doses
doubling the dose, does not double the response
Threshold
needs to meet a certain amount of dose in order to receive a response, other wise there is no response
non-threshold
any dose can produce a response
Deterministic Effect
Response usually follows high-dose exposure and an early response
threshold
Ex: radiation induced skin burn
Stocastic Effect
Low radiation exposure and appear as a late radiation response
Ex: CA, Leukemia, or genetic effects
Linear Dose Response
1 dose and increasing as dose increases
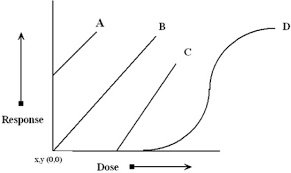
non Linear
varying dose
Leakage Radiation is emitted how?
from tube housing isotropically (emitted evenly from all directions)
Leakage Radiation should not exceed?
100 mR/hr at 1 meter
Scatter is produced primarily from ?
Compton interaction
What factors increase scatter?
high kVp
Large field Size
Thick body part