Excretion
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
What happens amino acids in excess to immediate requirements
They are respired to ensure that little is wasted as the molecules are a store of energy
Excess amino acids are carried to the liver in the blood plasma
Here they are absorbed by hepatocytes
What is the first stage of what happens to amino acids in the liver
Deamination
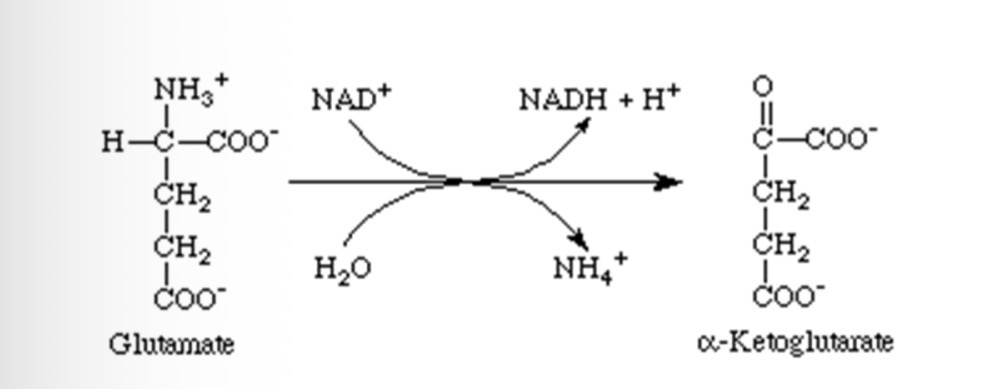
Describe deamination (3)
amino acid is oxidised by an enzyme catalyst
Amine group and a hydrogen atom are removed from the main structure of the amino acids
The amine group is reduced to ammonia by the addition of the hydrogen atom
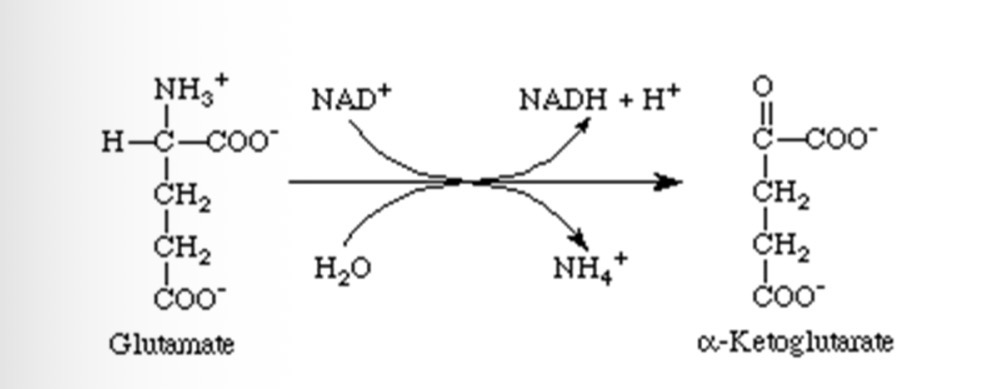
What happens to the non-nitrogenous portion of the deaminated amino acids
Can be respired, or converted to carbohydrate or lipid
What is the stage after deamination to get rid of ammonia
The urea cycle
Describe what happens to the ammonia during the urea cycle
enzymes in the liver cells catalyse the reaction of carbon dioxide with the ammonia
The less toxic nitrogenous compound, urea, is produced alongside water
CO2 + 2NH3 → CO(NH2)2 + H2O
What other nitrogenous excretory products can be produced other than urea
Uric acid or creatinine
How is urea excreted
urea and water are released from the liver cells to the bloodstream and transported to the kidneys through hepatic portal veins
The blood is filtered in the kidneys
Urea is a small and very soluble molecule, so it is easily passed out by the kidneys as a solution in the water (urine)