Liver and pancreas study guide
1/49
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Bilirubin becomes soluble/excreted
Bilirubin is produced from the breakdown of hemoglobin in red blood cells. It is initially insoluble in water; therefore, it is transported to the liver, where it undergoes conjugation, becoming soluble. This conjugated bilirubin is then excreted into bile and eventually eliminated from the body through feces.
urobilinogen, stercobilin, urobilin are formed
Urobilinogen is formed in the intestines when bilirubin is converted by gut bacteria.
Some urobilinogen is reabsorbed into the bloodstream and transported to the kidneys, where it is converted into urobilin, which gives urine its yellow color.
The rest is converted into stercobilin, which gives feces its brown color, thus aiding in the excretion of waste.
What nm is the diazo rxn and bilirubin measured at?
Bilirubin is always measured at 450nm but
Azobilirubin is measured around 575nm
What goes into Dbil testing and Tbil testing
Total (TBil) = Direct (Conjugated) + Indirect (Unconjugated)
DBil is directly measured
Malloy-evelyn method
50% methanol to measure tBil
Jendrassik-Grof method
Caffiene-benzoate-acetate
what are the four interferences for bilirubin?
Light - breaks down bilirubin
Room temp- increased degredation
Hemolysis- decreases the reaction of
bilirubin with diazo, giving falsely low resultsLipemia- causes error in spectrophotometric
readings
Kernicterus
Deposition of unconjugated bilirubin in nuclei of brain and nerve cells causing cell destruction and encephalopathy
Pre-hepatic jaundice causes
Due to a hemolytic process or ineffective erythropoiesis or neonatal jaundice
Pre-hepatic jaundice testing

Hepatic jaundice
actual damage to the hepatocytes
Hepatic jaundice test results
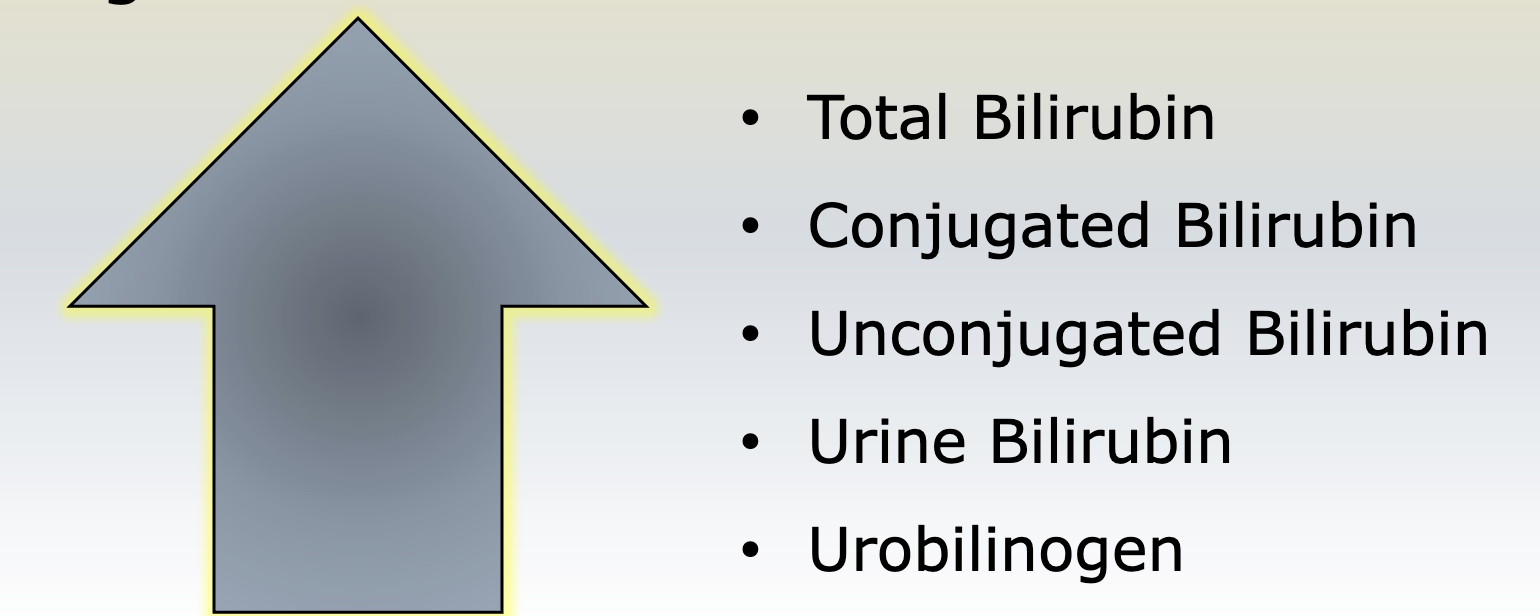
Post hepatic jaundice
blockage of bile flow, cant excrete bilirubin
Post-hepatic jaundice tests
Ammonia testing what does it mean and what does it identify?
Helps with diagnosing Reye Syndrome and evaluates urea metabolism
Contamination of ammonia test is
cigarette smoke, prolonged touniquet use, incorrect sample handling
Budd-Chiari
auto immune disease against many liver antigens,
causes hepatic vein occlusions, leading to fulminant disease
Which enzymes indicate hepatitis?
Elevated ALT and AST levels indicate hepatitis due to liver cell damage.
Which enzymes indicate cholestasis?
Elevated ALP and GGT levels suggest cholestasis from bile flow obstruction
Elevated ALP and GGT levels suggest cholestasis from bile flow obstruction
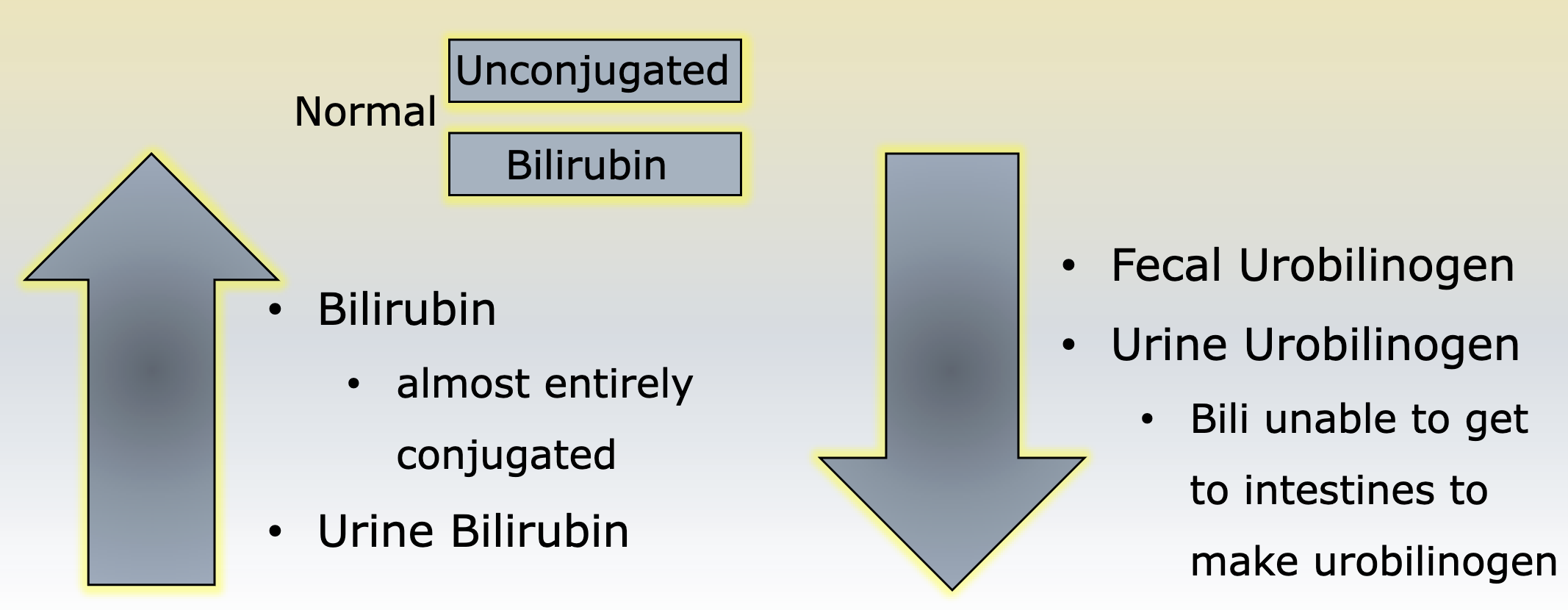
Wilsons disease
autosomal recessive inherited disorder involving not enough ceruloplasmin
what lab results are seen with wilsons disease
AAT deficiency is caused by
inborn error of protein metabolism resulting in emphysema and liver cirrohsis
What are the lab results for hemochromatosis?
slightly increased bilirubin, AST, and ALT
elevated serum iron, ferritin, and transferrin saturation
hyperglycemia due to pancreatic damage.
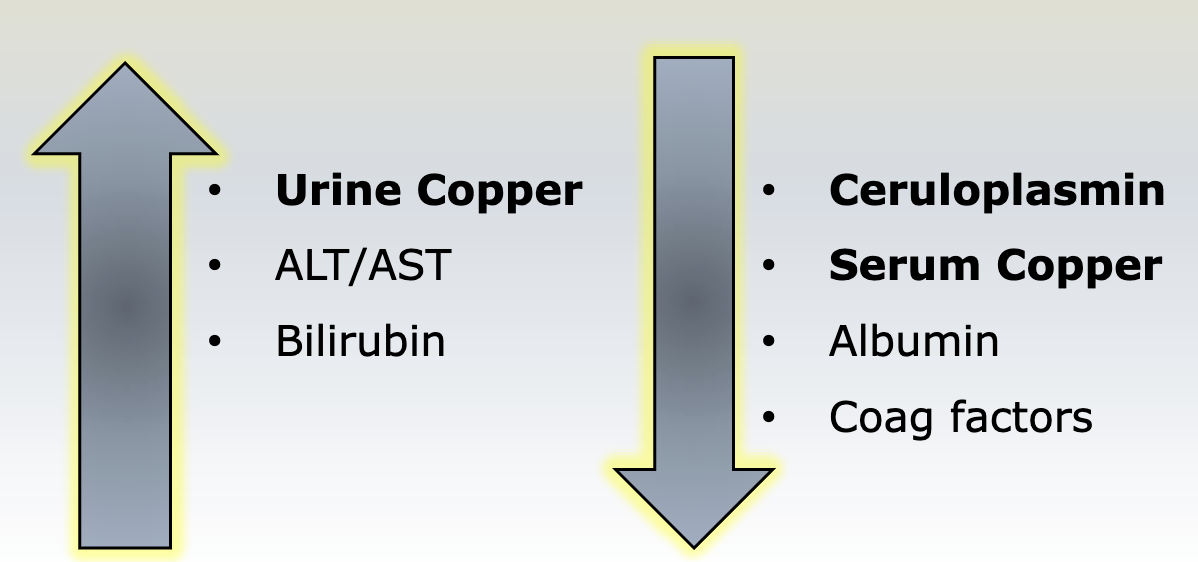
What labs would you see with alcoholic cirrhosis
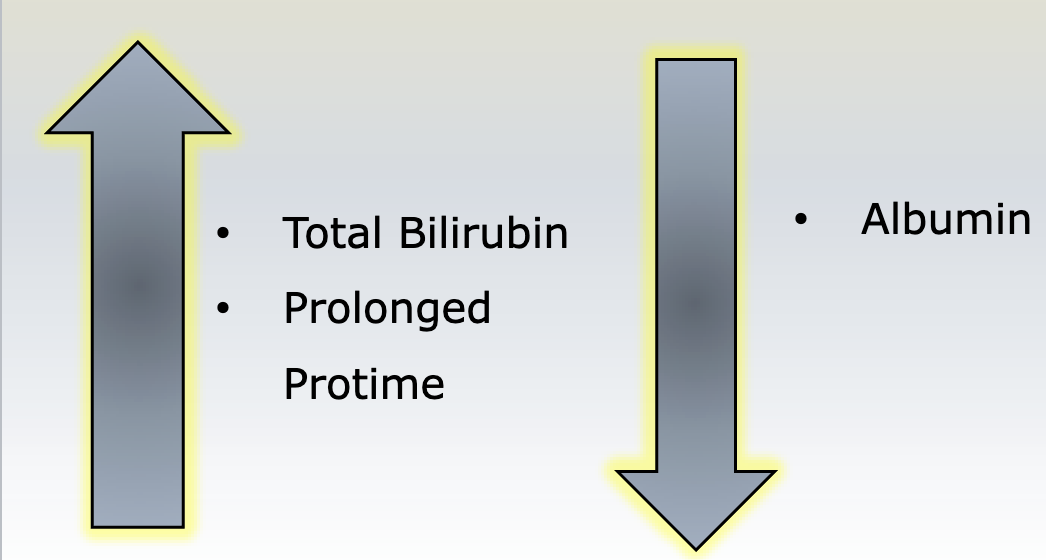
Primary biliary cirrhosis
chronic condition the causes progressive destruction of the intrahepatic bile ducts
What lab results are seen in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
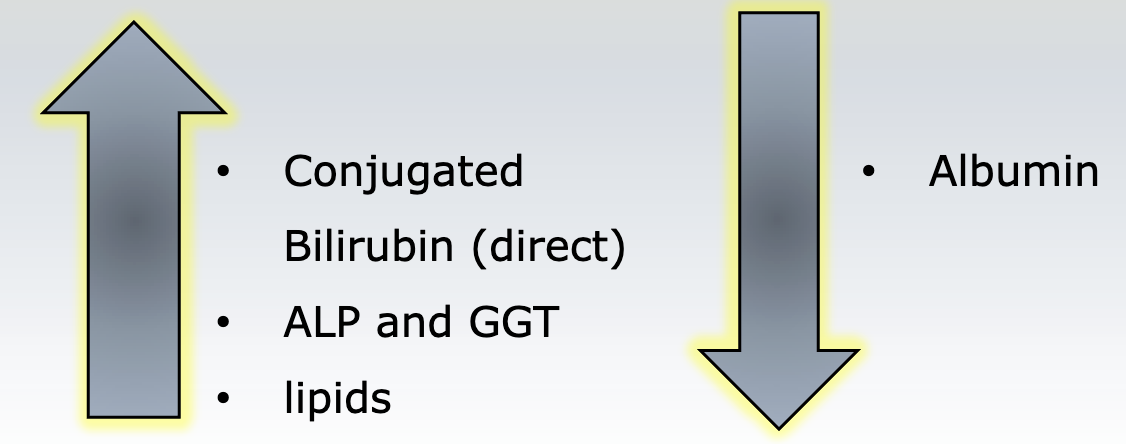
What symptoms must be present to diagnose Fulminant liver failure
neurological
Crigler-Najjar syndrome type I
No UDPGT
billi: 18-40mg/dl
Kernicterus
Crigler-Najjar syndrome type II
decreased UDPGT
Bili: 8-18mg/dl
kernicterus rare
Gilberts syndrome
decreased UDPGT and hepatic uptake
billi: normal 5mg/dl
increases during fasting, excercise, tylenol
Dubin-Johnson syndrome
Impaired biliary excretion, leading to conjugated bilirubin build up
Rotors syndrome
decreased hepatic uptake and storage, increased levels of unconjugated bilirubin
Obstruction enzymes
ALP, GGT
Hepatoellular enzymes
ALT, AST
Biliary injury- cholestatis leads to
increase of GGT and ALP
Hepatocellular damage (liver disease) leads to
primary increase in ALT and AST
chronic hepatocellular and cholestatic have decrease in
albumin
mild vs. severe is determined by
clotting factors
alpha cells produce
glucagon
Beta cells produce
insulin
delta cells produce
somatostatin
F cells produce
pancreatic polypeptide
What enzymes break down protein
protease
What enzyme breaks down lipids
Lipase
What enzyme breaks down complex carbs
amylase
Zollinger-ellison Syndrome
caused by gastrin-secreting tumors (gastrinomas) leading to excessive gastric acid production, resulting in recurrent peptic ulcers.
Leading causes of acute pancreatitis
alcohol abuse
biliary tract disease
What is the best indicator of pancreatitis
Lipase increasing within 4 hrs, peaks at 24, back to normal w/in 8-14 days
What is the second best indicator for diagnosing acute pancreatitis
Amylase
Chronic pancreatitis is caused by
chronic alcohol abuse
subnormal levels of enzymes