The Eye
1/181
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
182 Terms
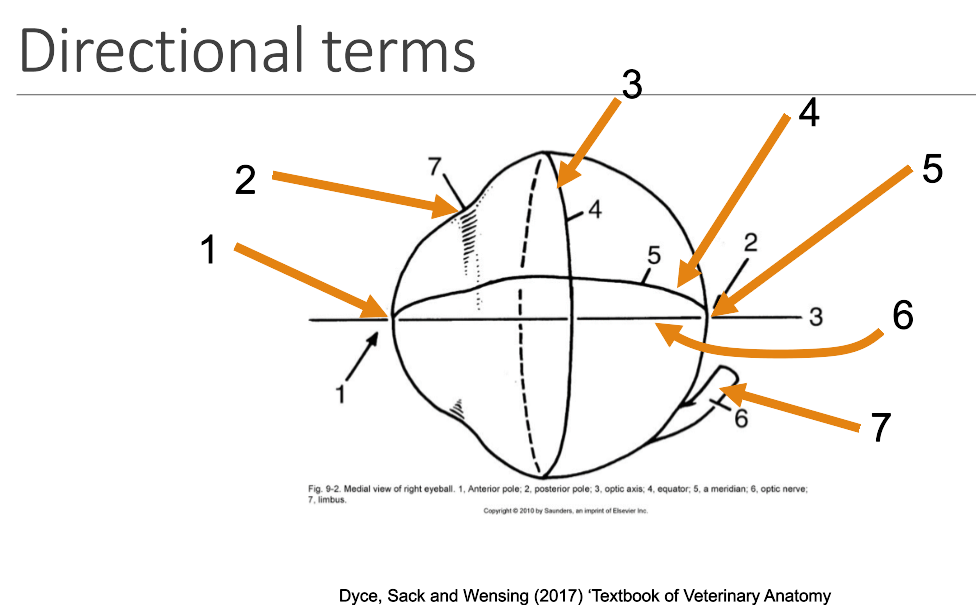
1
anterior pole
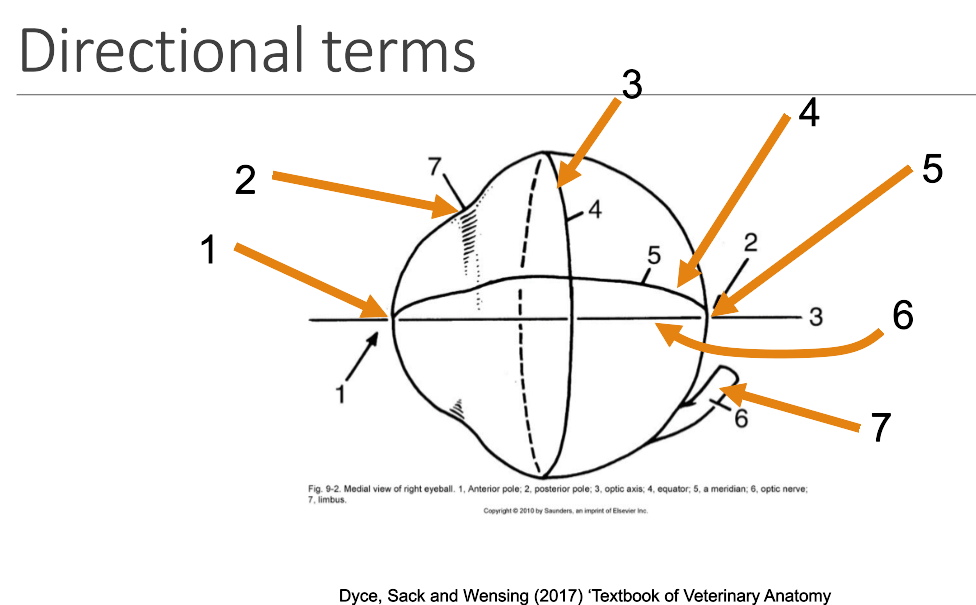
2
limbus
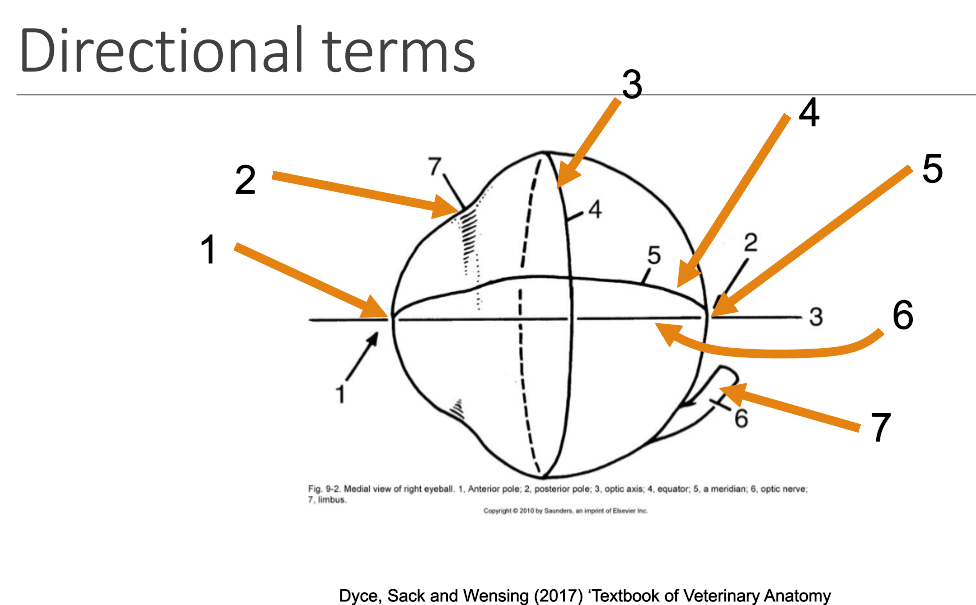
3
equator
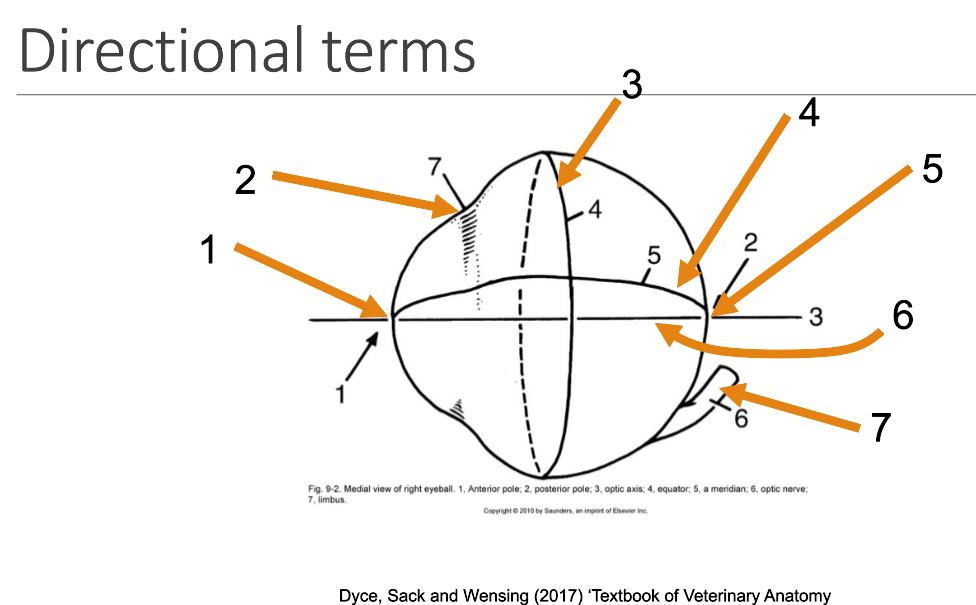
4
meridian
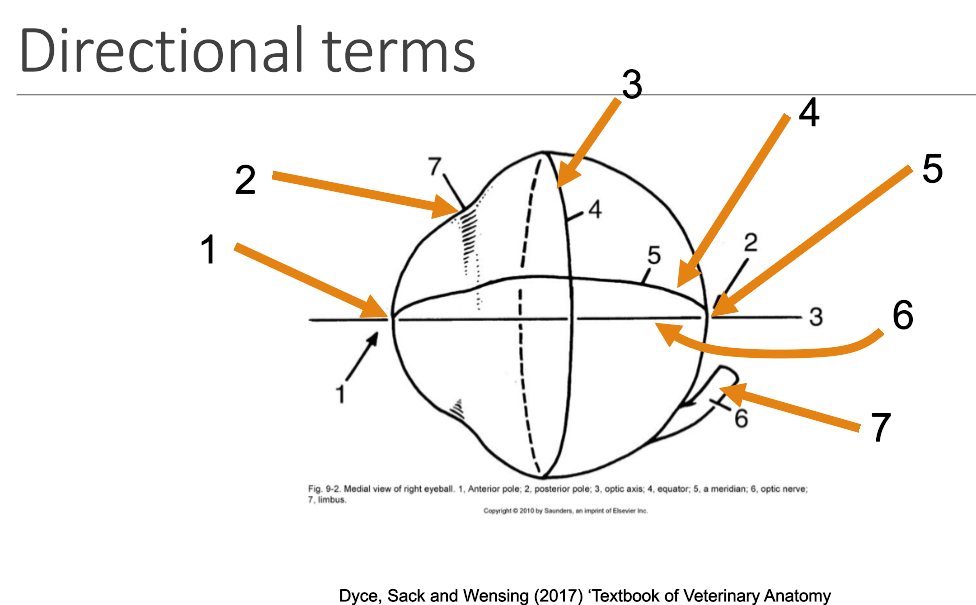
5
posterior pole
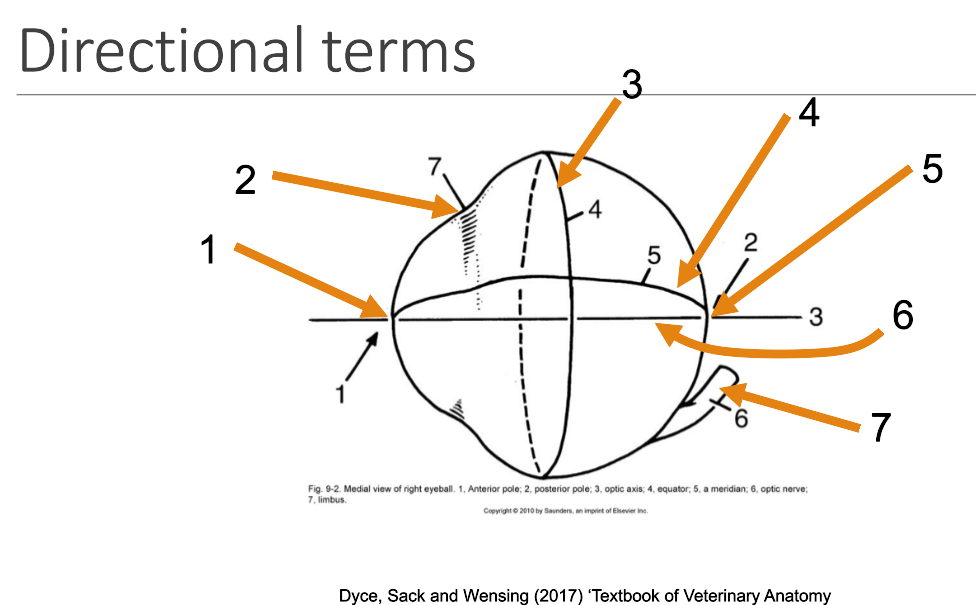
6
optic axis
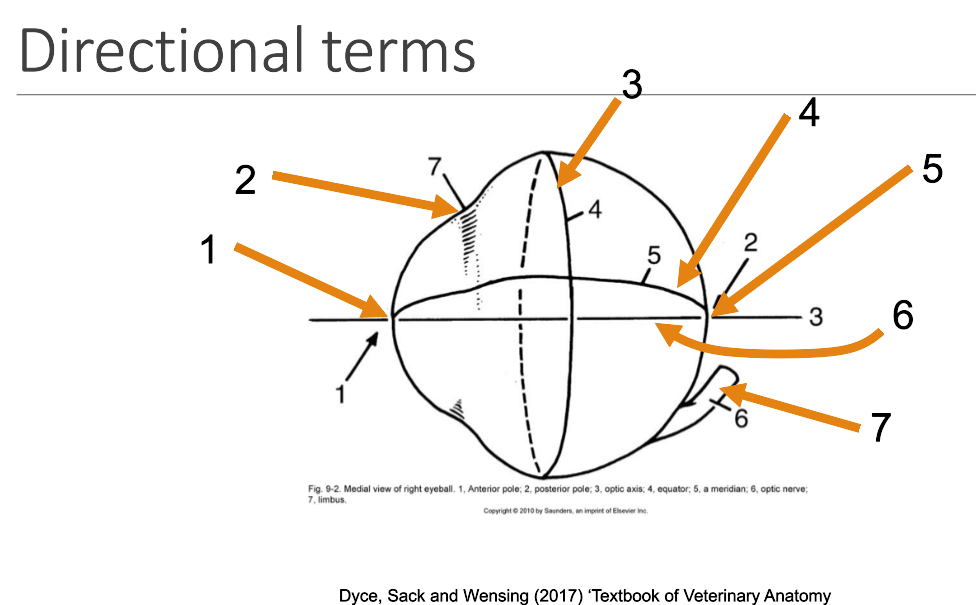
7
optic nerve
Why is the limbus clinically relevant
incision made here to access lens for cataracts surgery
What is the optic axis?
light axis
What 2 parts does the eye consist of?
eyeball
adnexa
Where is the eyeball housed?
orbit of skull
What does the adnexa consist of?
orbit
para-orbital areas
eyelids
lacrimal apparatus
ocular muscles
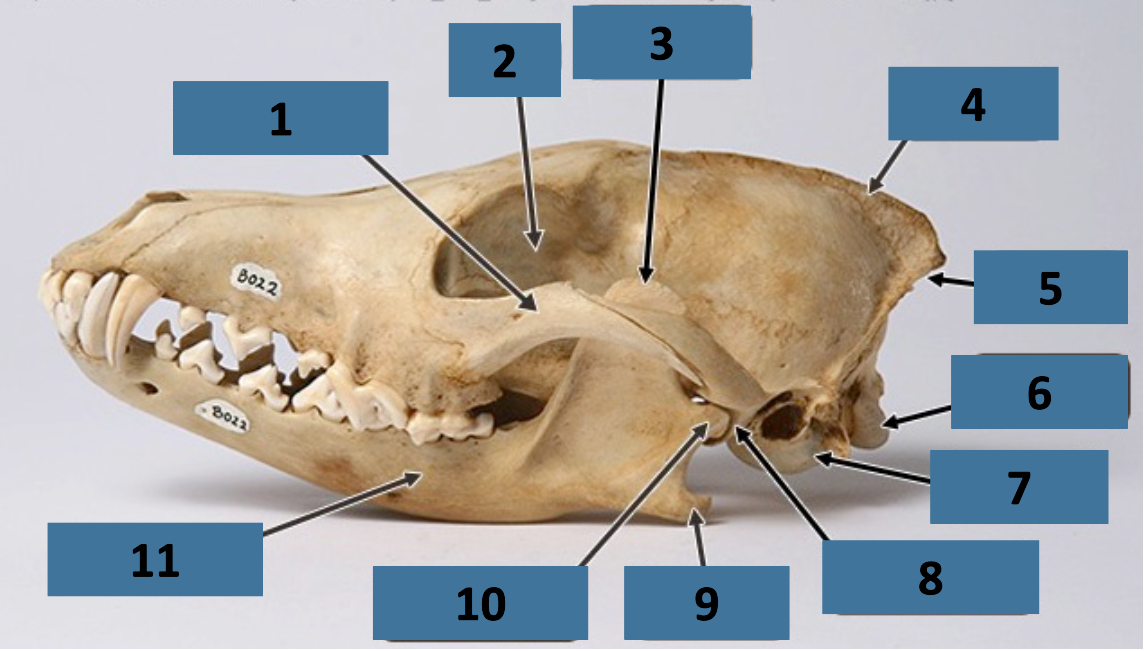
1
zygomatic arch
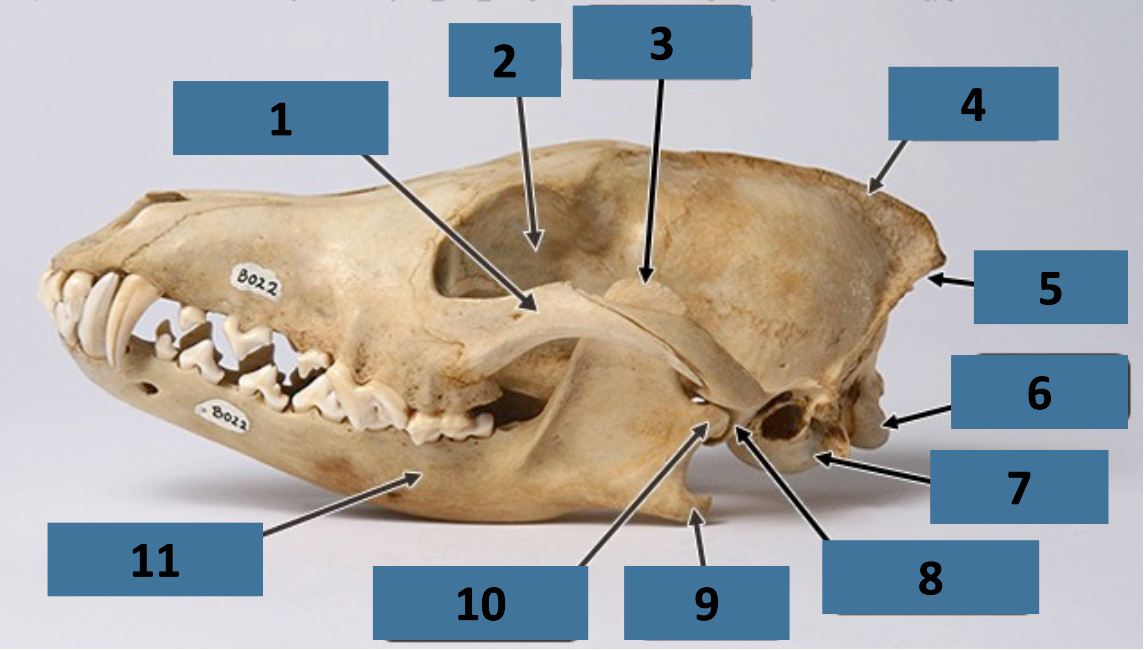
2
orbit
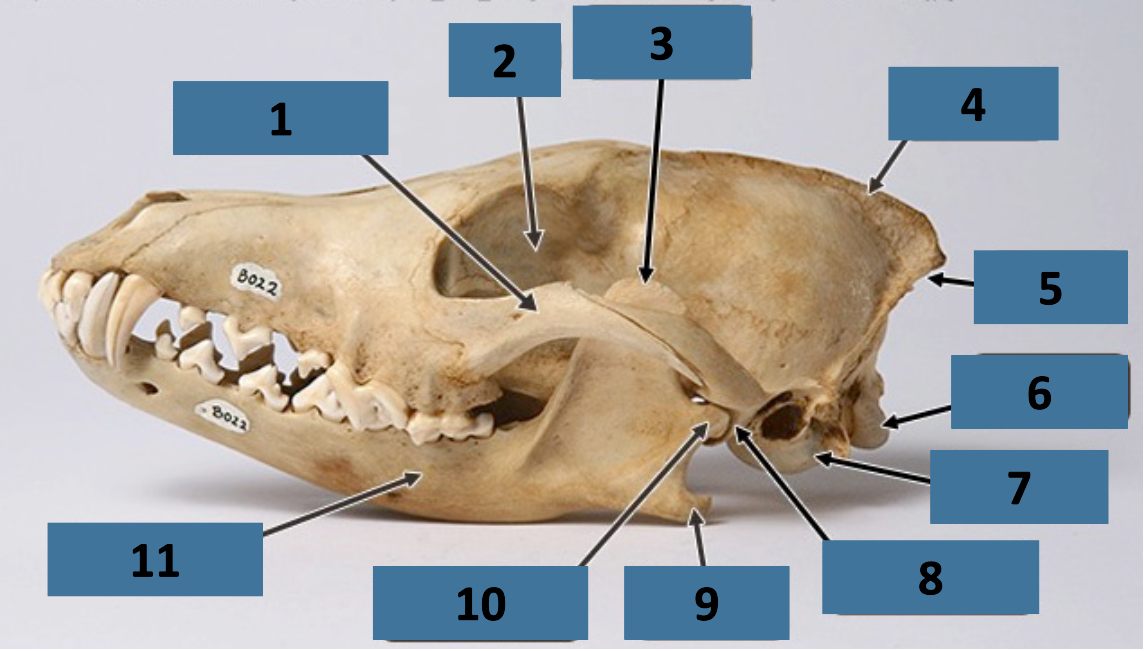
3
coronoid process
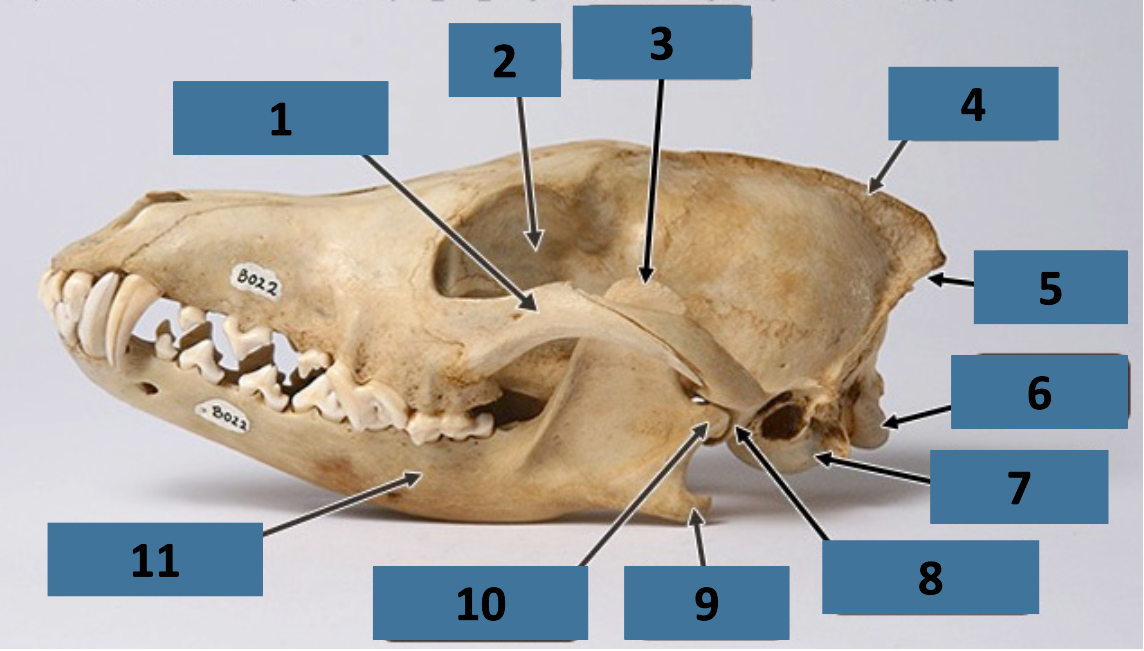
4
sagittal crest
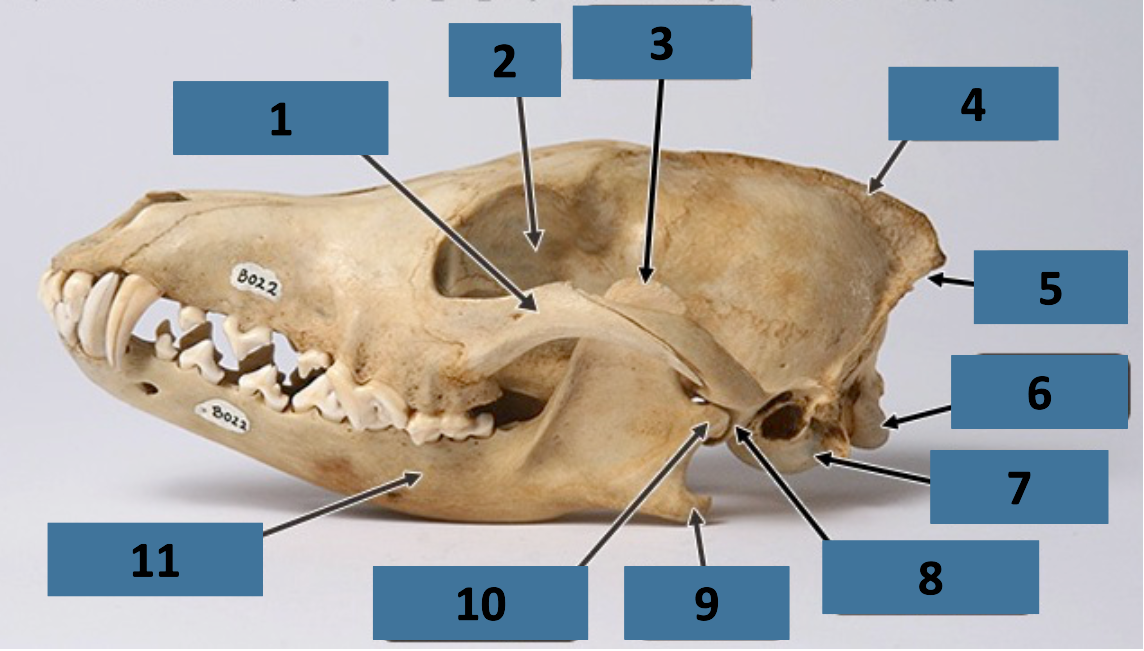
5
nuchal crest
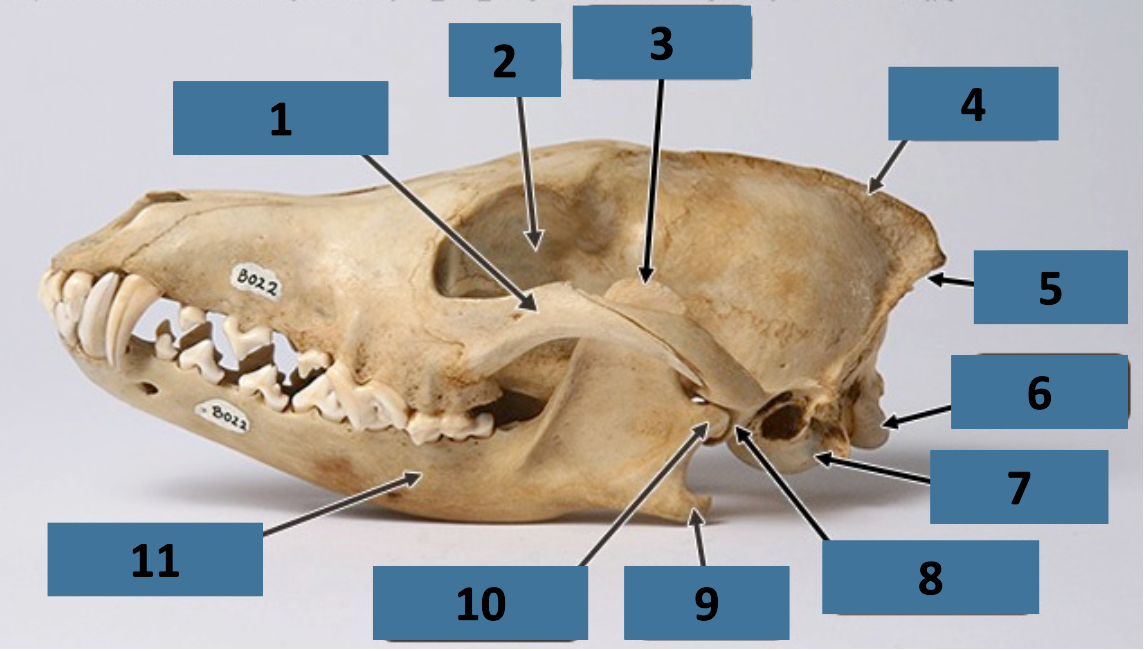
6
occipital condyle
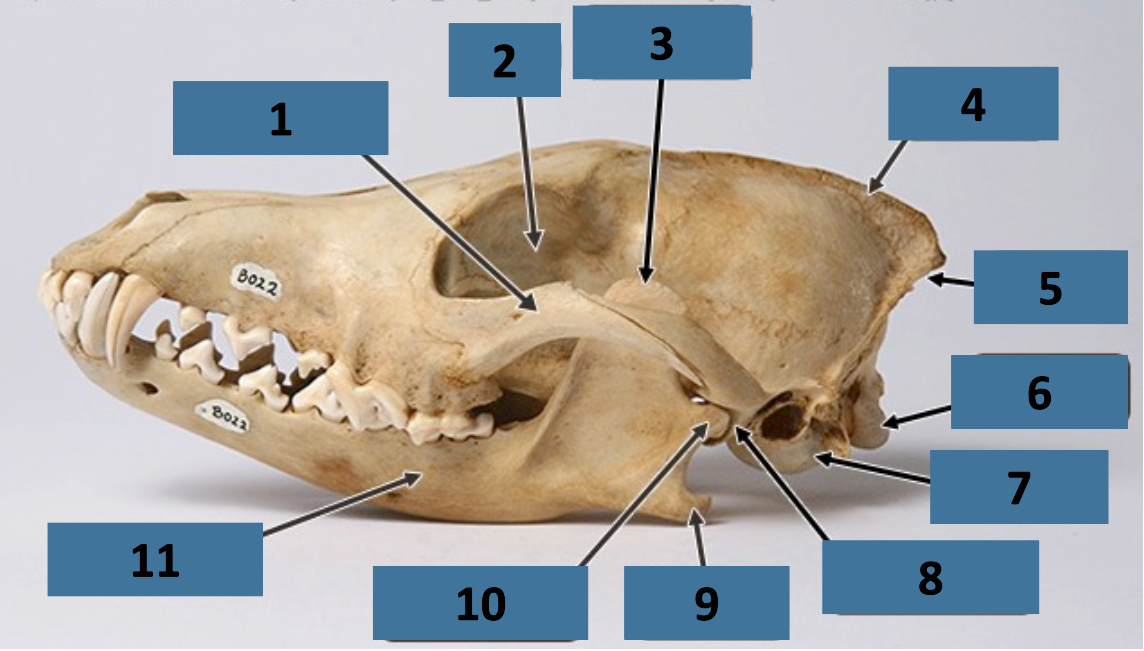
7
auditory bulla
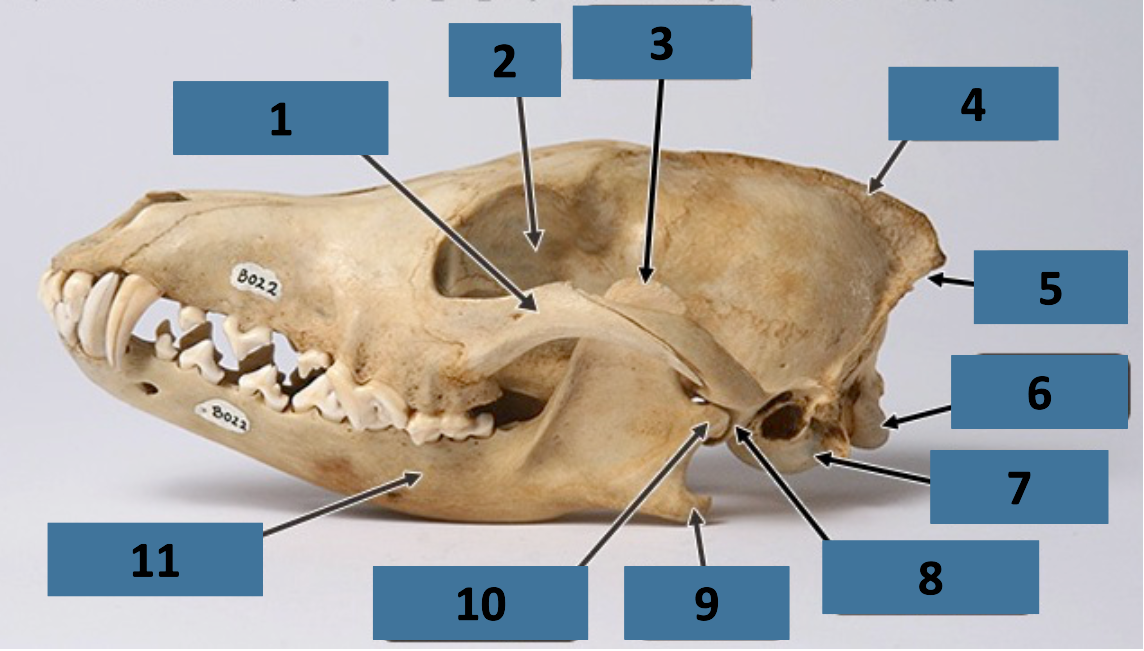
8
mandibular fossa
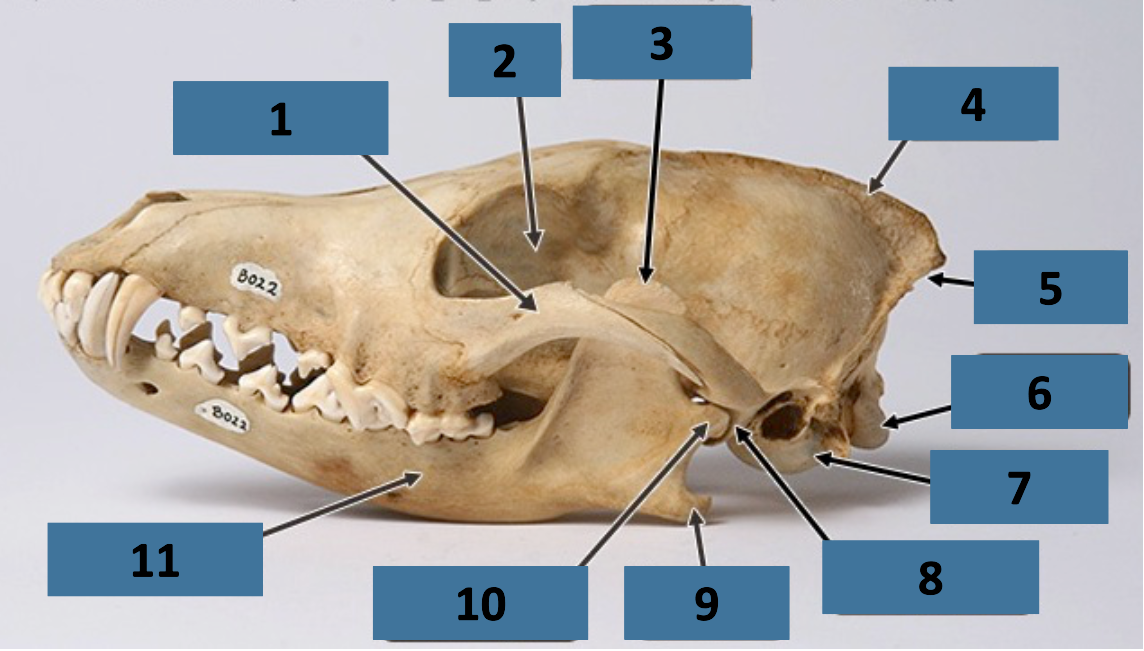
9
angular process
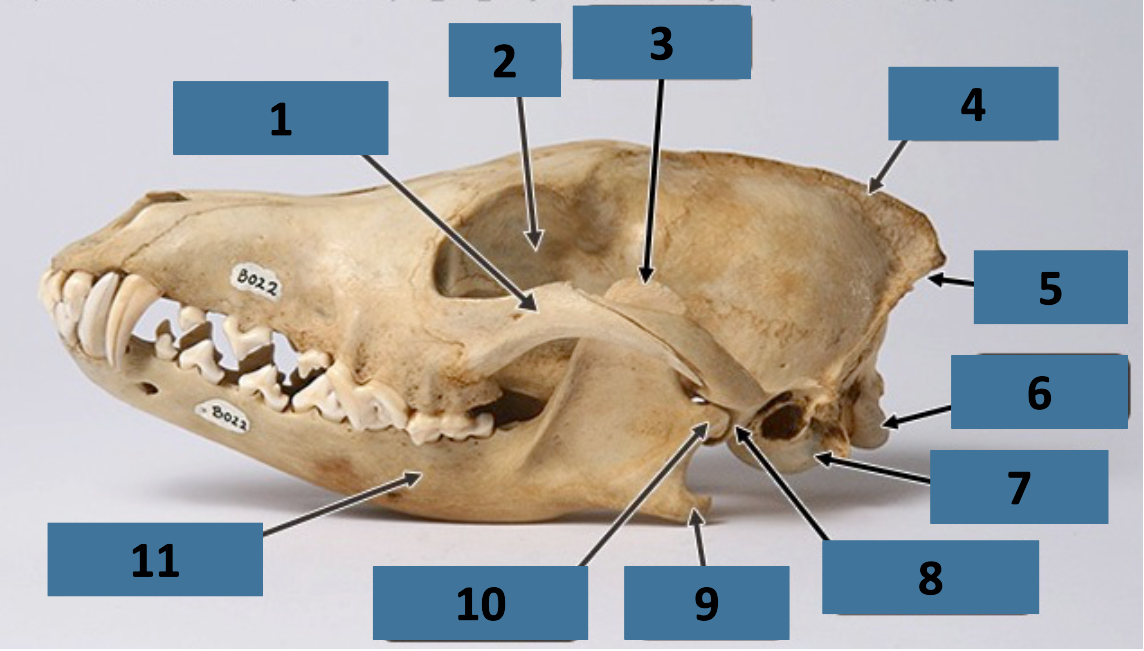
10
mandibular condyle
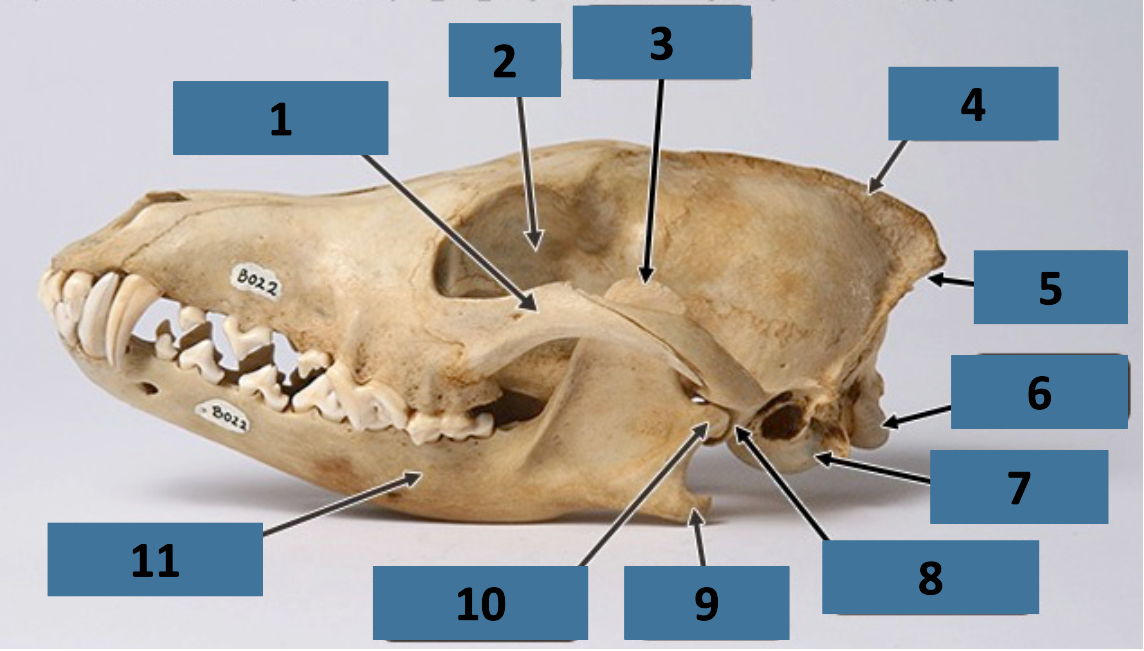
11
mandible
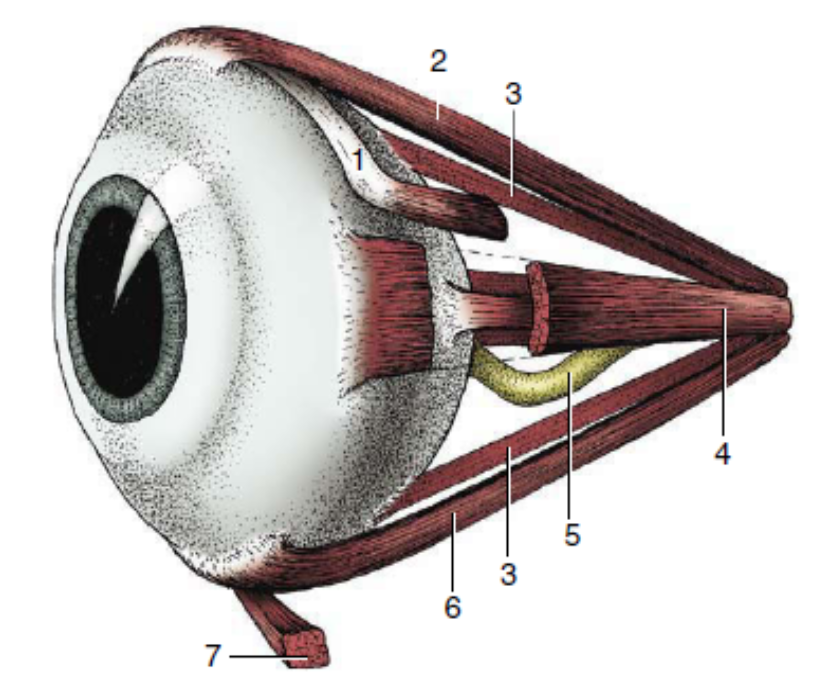
1
dorsal oblique muscle
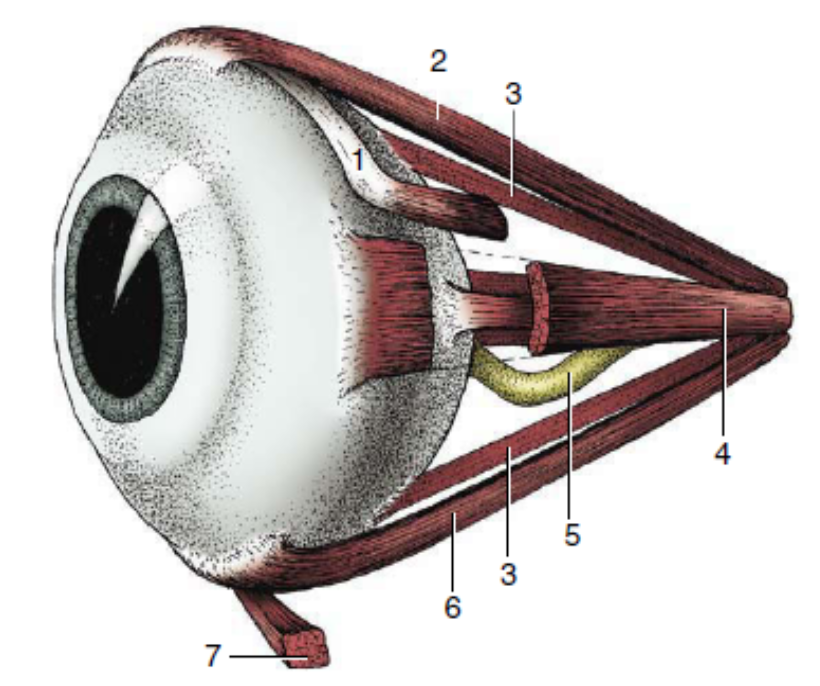
2
dorsal rectus muscle
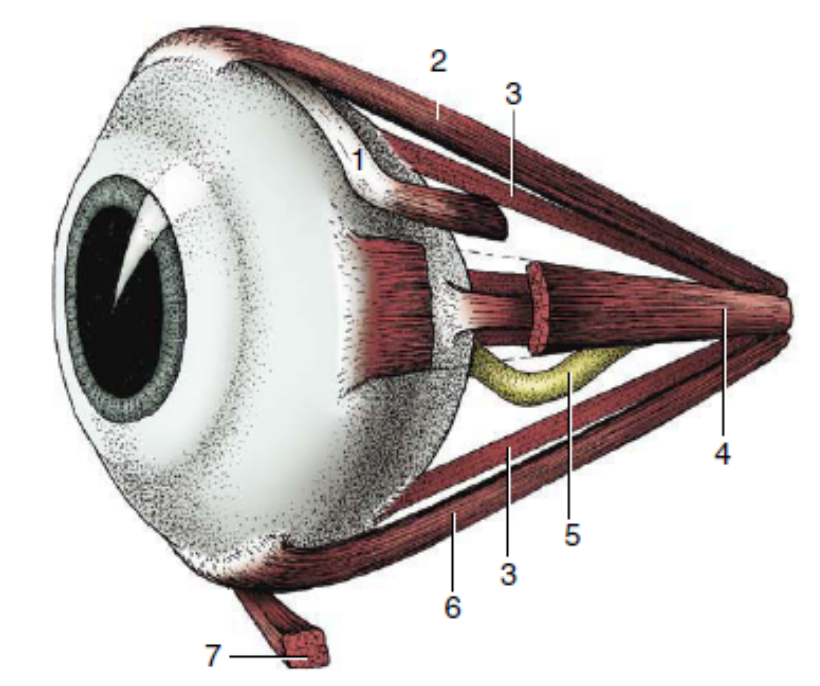
3
retractor bulbi
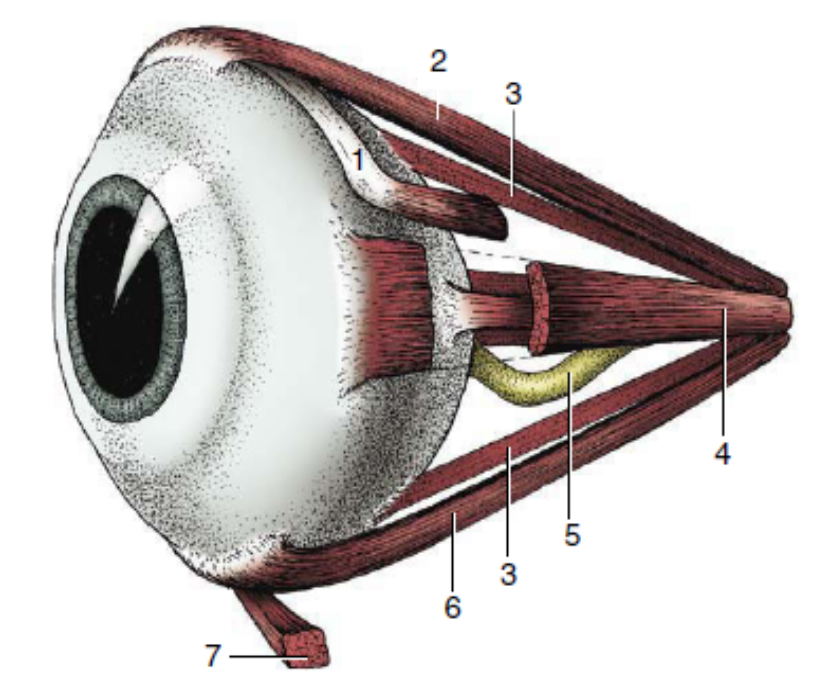
4
medial rectus muscle
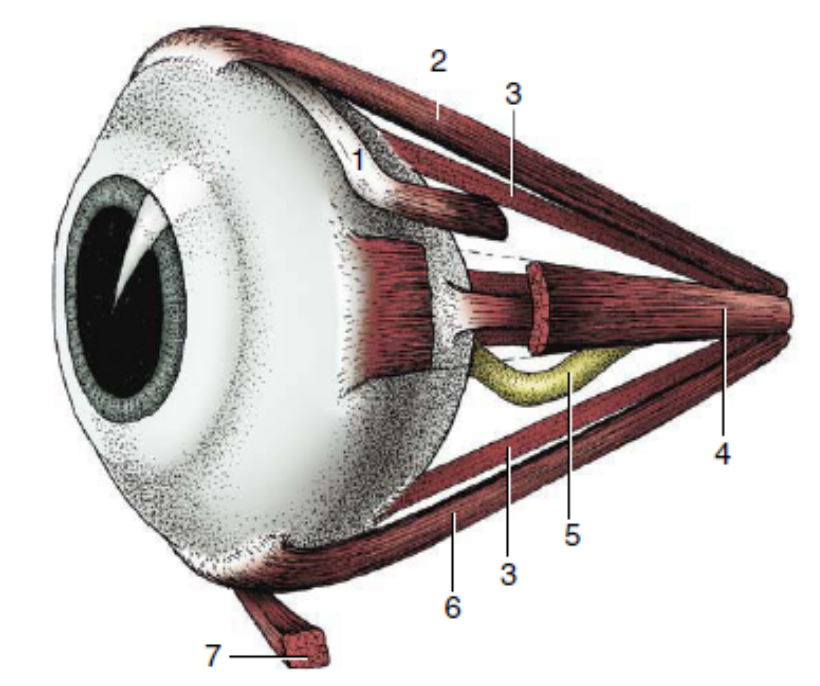
5
optic nerve
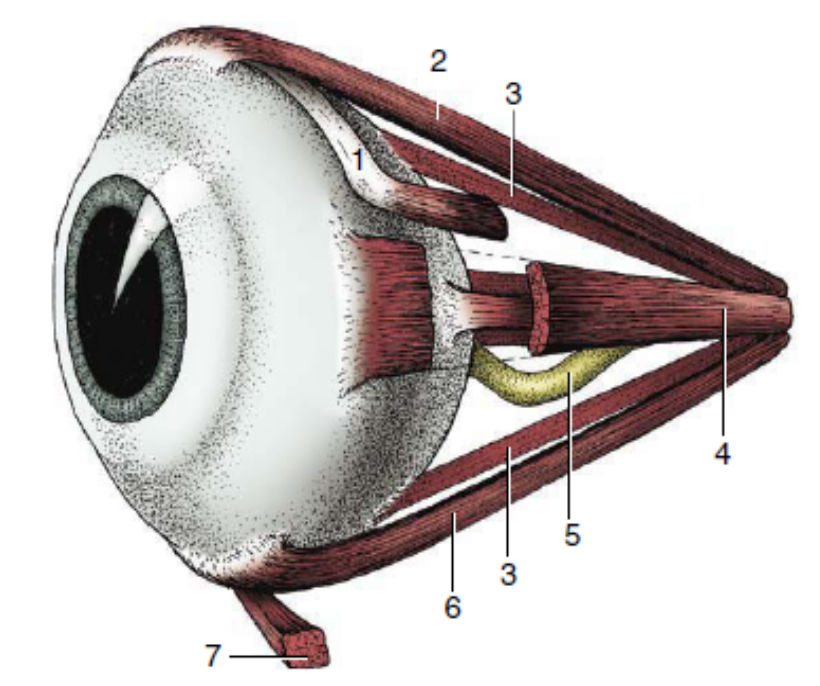
6
ventral rectus muscle
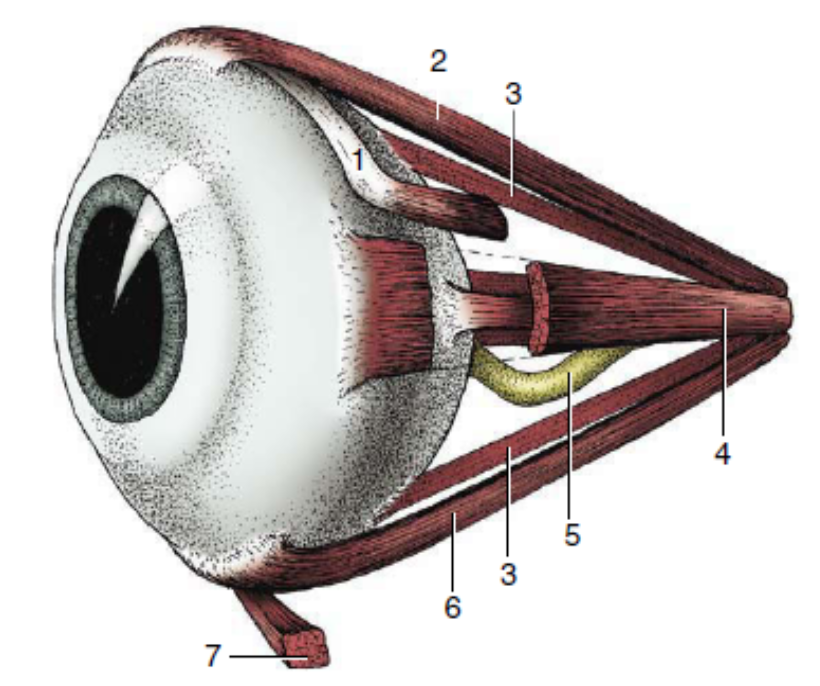
7
ventral oblique muscle
What shape is the eyeball?
pretty much spherical
In what species does anteroposterior compression occur?
horses and cattle
What is the cornea?
transparent part of the anterior eye
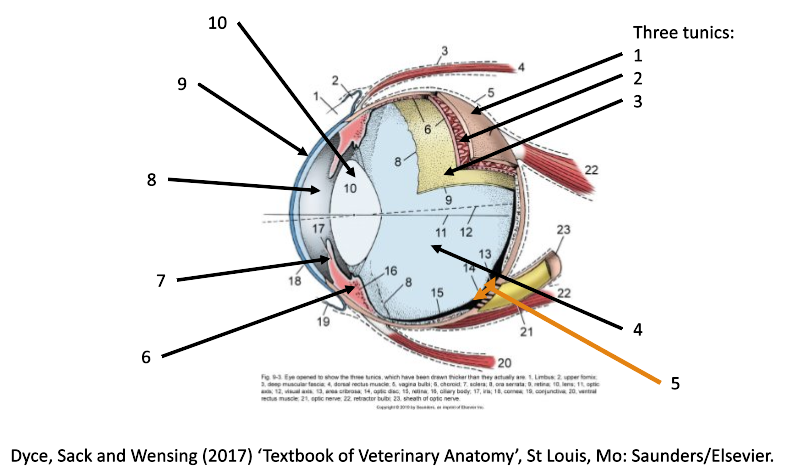
1
fibrous coat (sclera and cornea)
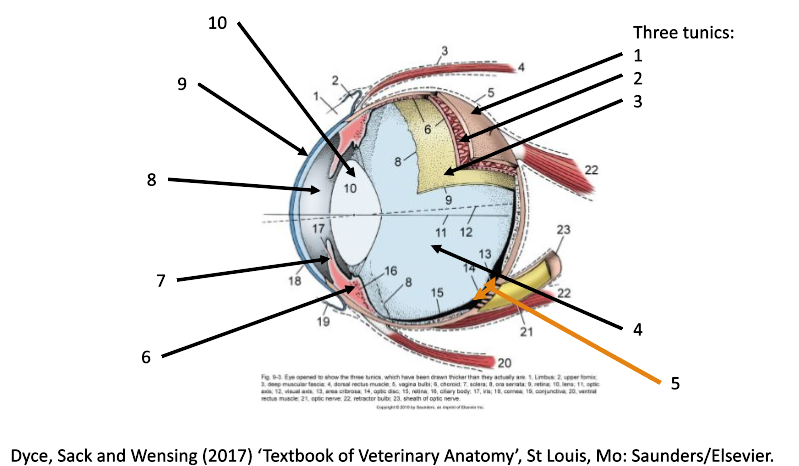
2
vascular coat (uvea)
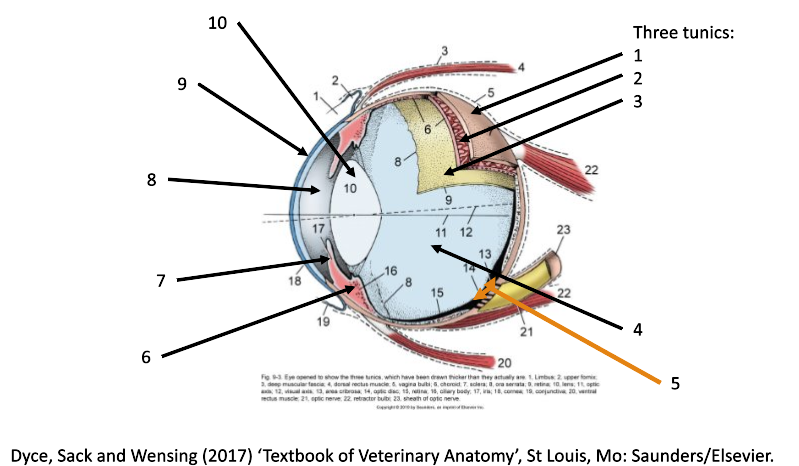
3
nervous coat (retina)
How many tunics in the eye are there?
3
What are the 3 tunics in the eye?
fibrous (sclera & cornea)
vascular (uvea)
nervous (retina)
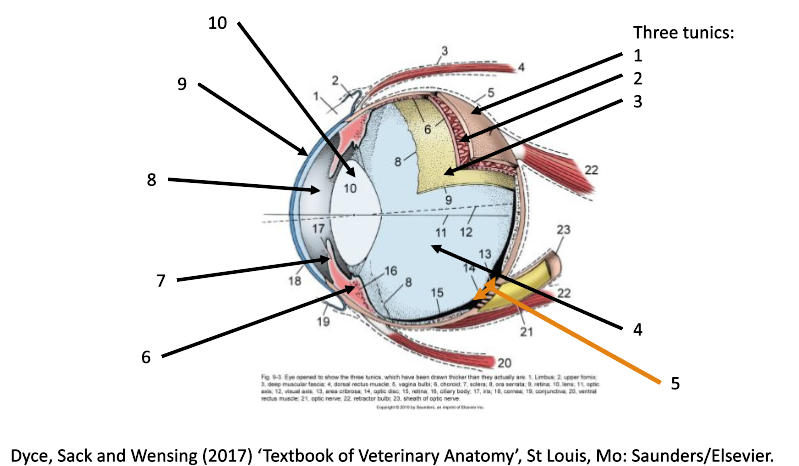
4
filled with vitreous humor (posterior chamber)
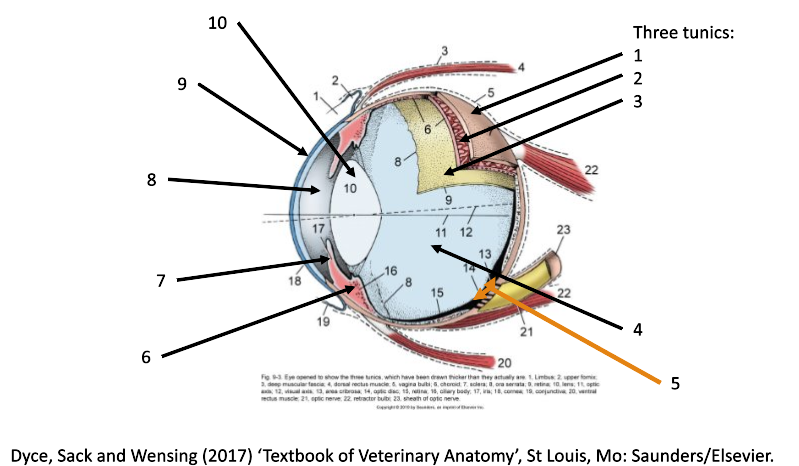
5
optic disc
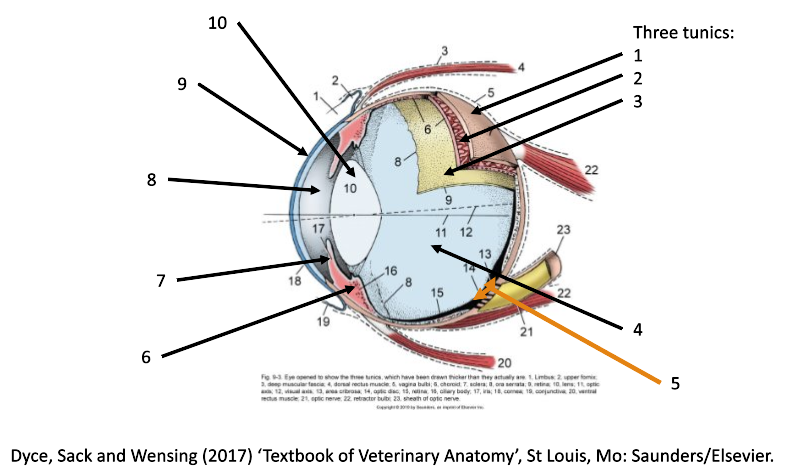
6
ciliary body
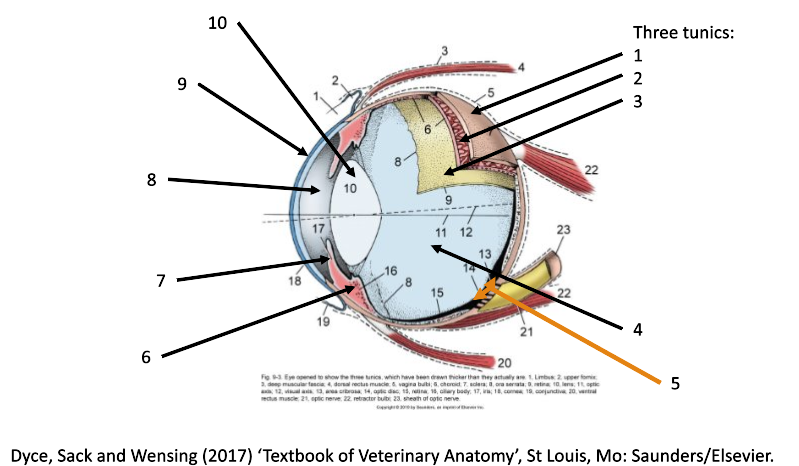
7
iris
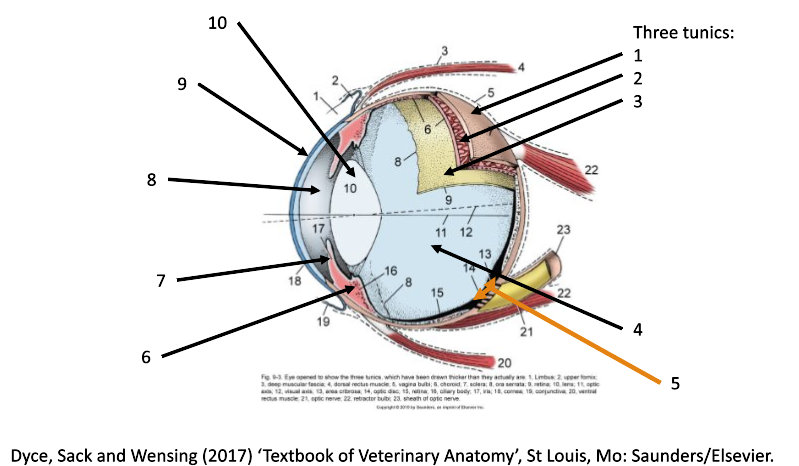
8
filled with aqueous humor (anterior chamber)
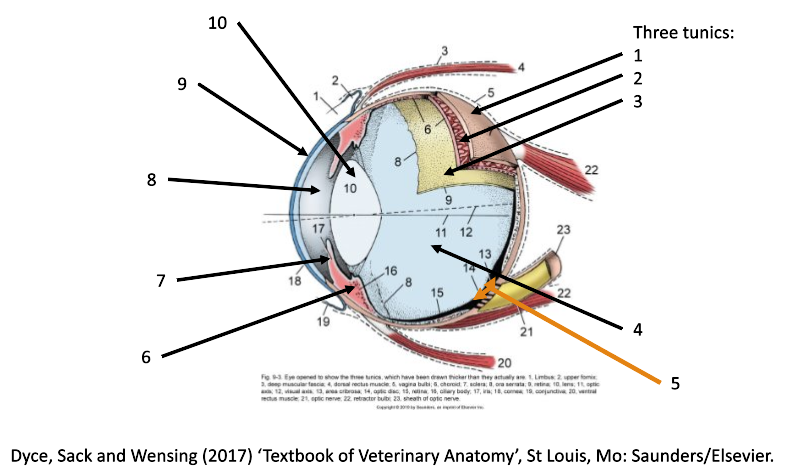
9
cornea
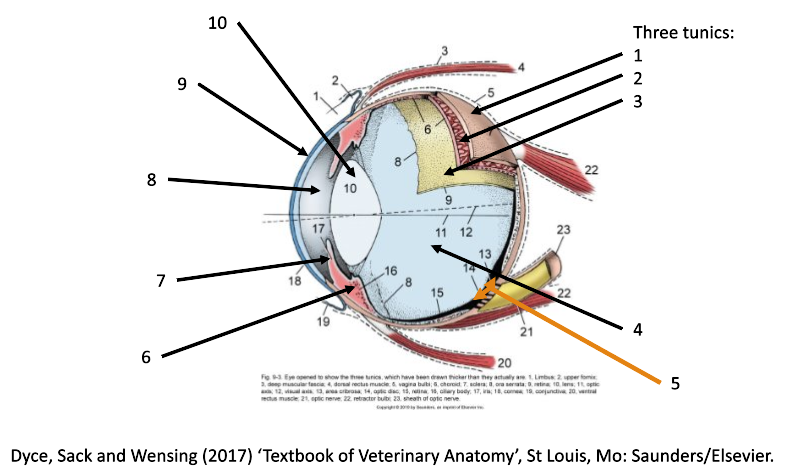
10
lens
What does the outermost layer/fibrous tunic consist of?
sclera
limbus
cornea
What does the middle layer/vascular tunic consist of?
choroid
ciliary body
iris
What does the innermost layer/nervous tunic consist of?
retina
What tissue is the fibrous tunic composed of?
dense collagenous tissue
What does the fibrous tunic provide?
form, shape and protection to the eye
What is the point where the sclera and cornea meet called?
limbus
What is the limbus?
where sclera and cornea meet
What colour is the sclera?
white
What fibres is the sclera composed of?
collagenous and elastic fibres
What is the sclera anteriorly covered in?
bulbar conjunctiva
How many extrinsic ocular muscles are there?
7
Where do the 7 extrinsic ocular muscles of the eye insert?
posteriorly to sclera
What happens posteriorly on the sclera?
extrinsic ocular muscles insert
penetrated by blood vessels and nerves
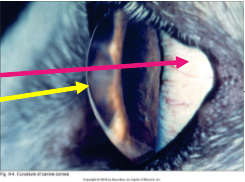
What is the pink arrow pointing to?
sclera
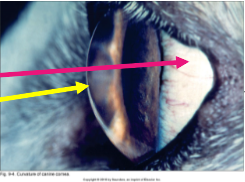
What is the yellow arrow pointing to?
cornea
Does the cornea contain blood vessels?
NO
Does the sclera contain blood vessels?
YES
What is the cornea composed of?
special kind of connective tissue arranged in a lamellar form
How do nutrients permeate through the cornea?
from vessels in the limbus
via lacrimal fluids and aqueous humor
What does the surface of the cornea have?
free nerve endings so very sensitive
What reflex is the nerve endings in the cornea involved in?
corneal reflex
What state is the cornea maintained in?
dehydrated state
What are the main functions of the cornea?
support of intraocular contents
refraction of light because of its curvature
transmission of light because of its transparency
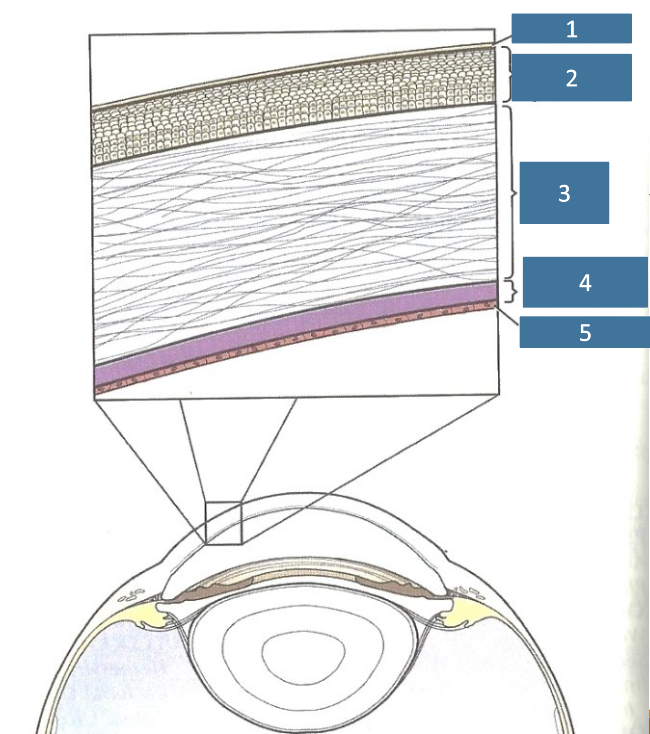
1
tear film
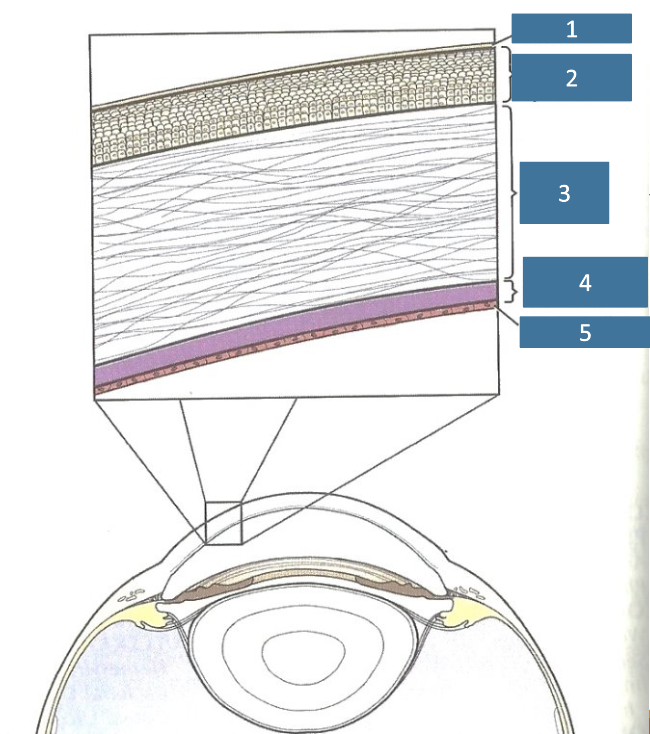
2
corneal epithelium
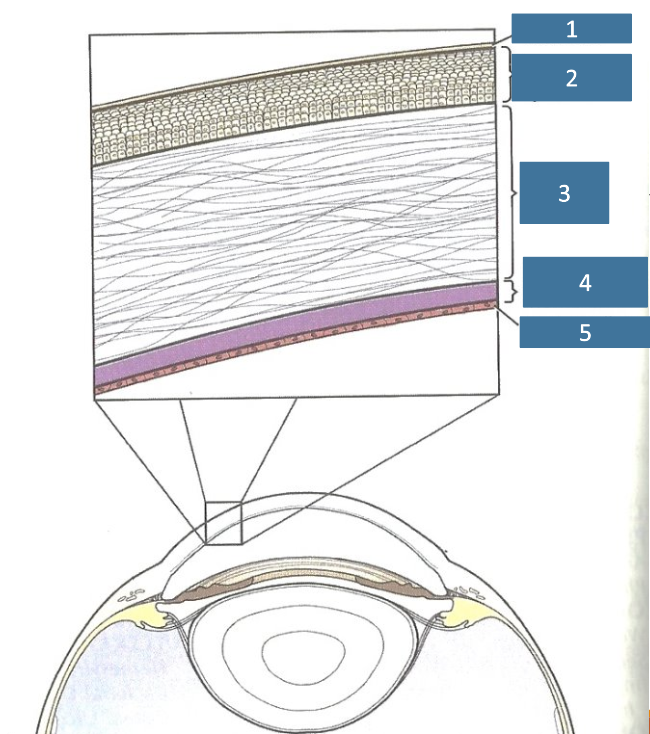
3
corneal stroma
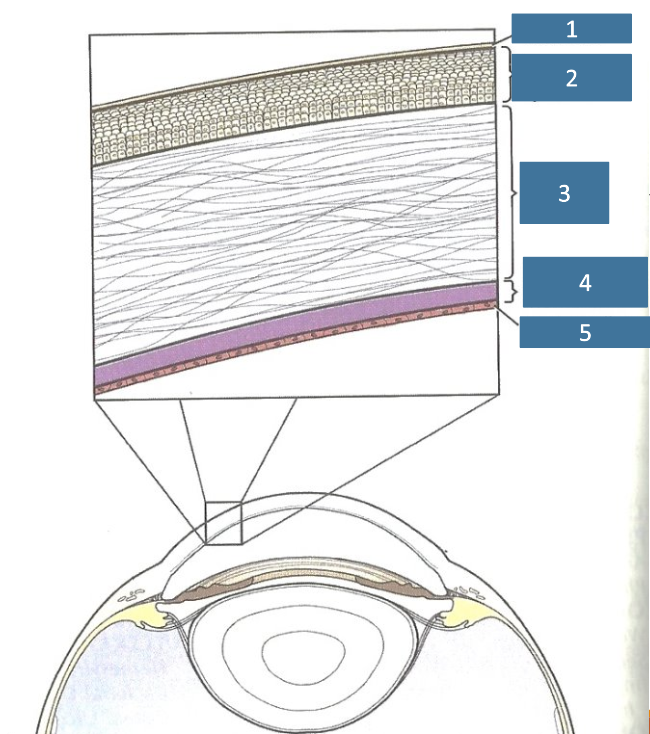
4
Descemet’s membrane
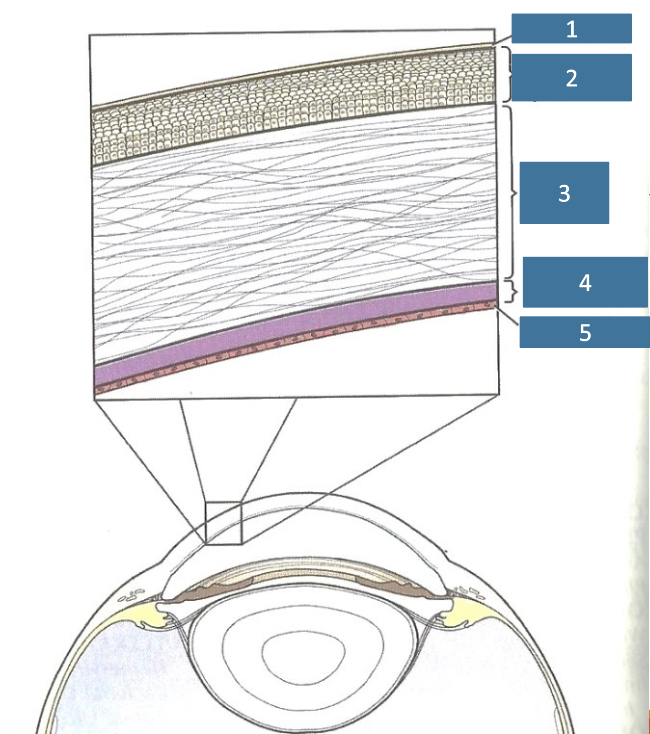
5
endothelium
What is the uvea?
middle vascular layer around the eyeball
What is the choroid?
lines sclera from optic nerve to near the limbus
What is the ciliary body?
thickened zone opposite limbus
What is the role of the iris?
projects into the anterior chamber of the eye
Is the choroid, ciliary body or iris most posterior?
choroid
Is the choroid, ciliary body or iris most anterior?
iris
What are the main roles of the uvea (middle layer)?
supply blood
elevates lens
regulates lens curvature
adjusts size of pupil
fundus
posterior part of internal eye visualised with an ophthalmoscope
What is the choroid firmly attached to?
sclera
What is the choroid?
dense network of blood vessels embedded into heavily pigmented connective tissue
Dorsally in the fundus, what does the choroid form?
light-coloured reflective area called the Tapedum lucidum
What structure in the eye are ‘cats eyes’ on roads based on?
tapetum lucidum
Why are canines adapted to have a tapetum lucidum?
nocturnal adaptation
Which species do not have a tapetum lucidum?
humans and pigs
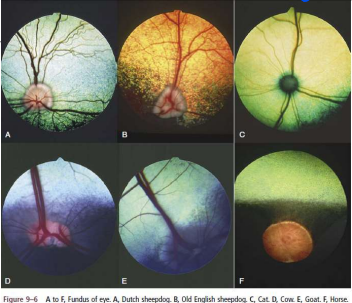
Which species has the least blood vessels?
horse
In what part of the eye are the blood vessels?
choroid
In what part of the eye is the optic disc?
retina
What is the ciliary body?
at level of limbus, vascular coat forms thick circular rounded mass, contains numerous muscle bundles
What is the main role of the ciliary body?
regulates shape of lens
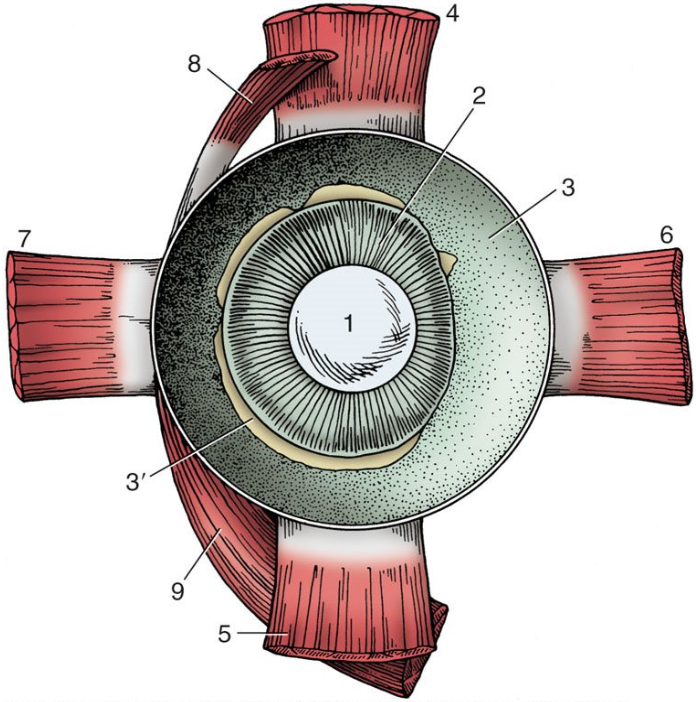
1
lens
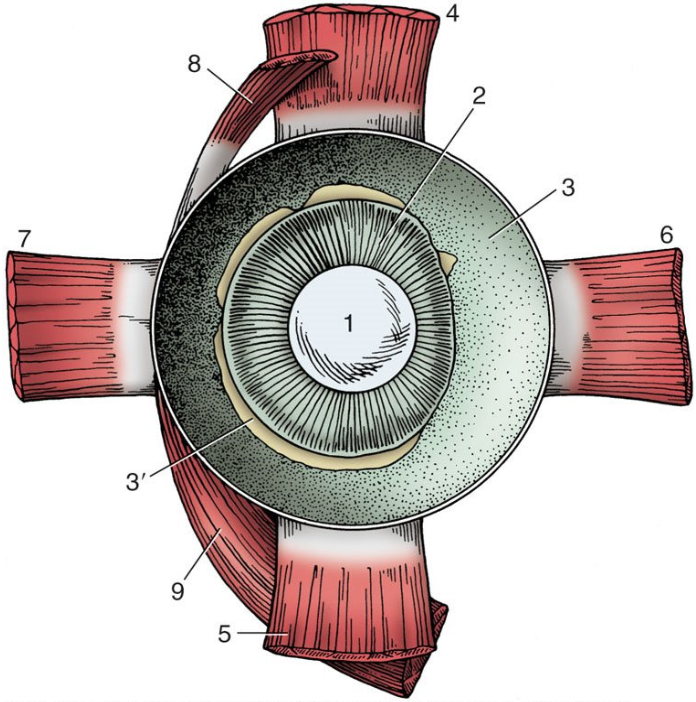
2
ciliary body
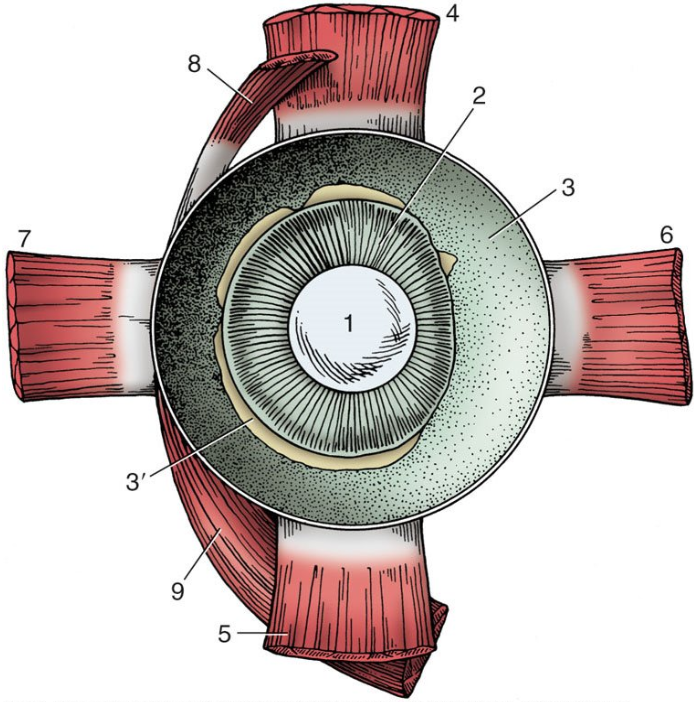
3
choroid covered by pigmented outer layer of retina
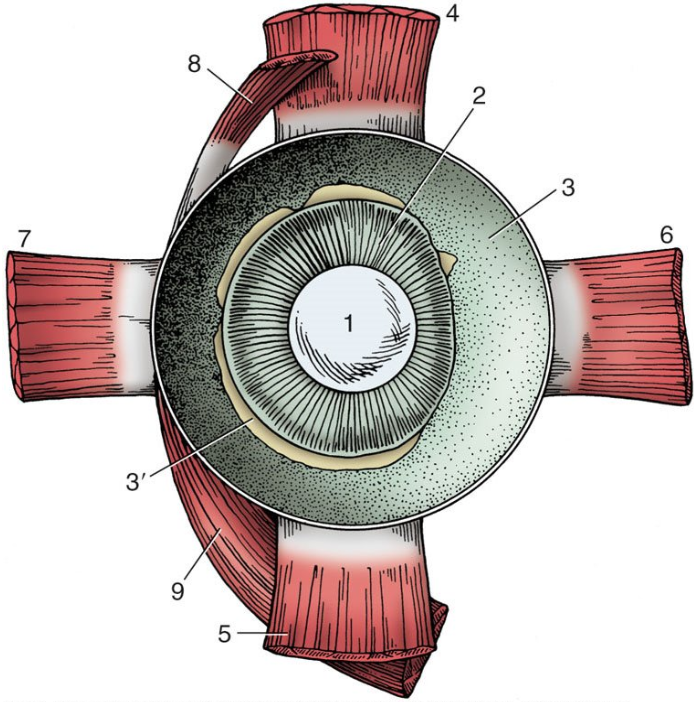
3’
remnants of inner nervous layer of retina (which has been removed)
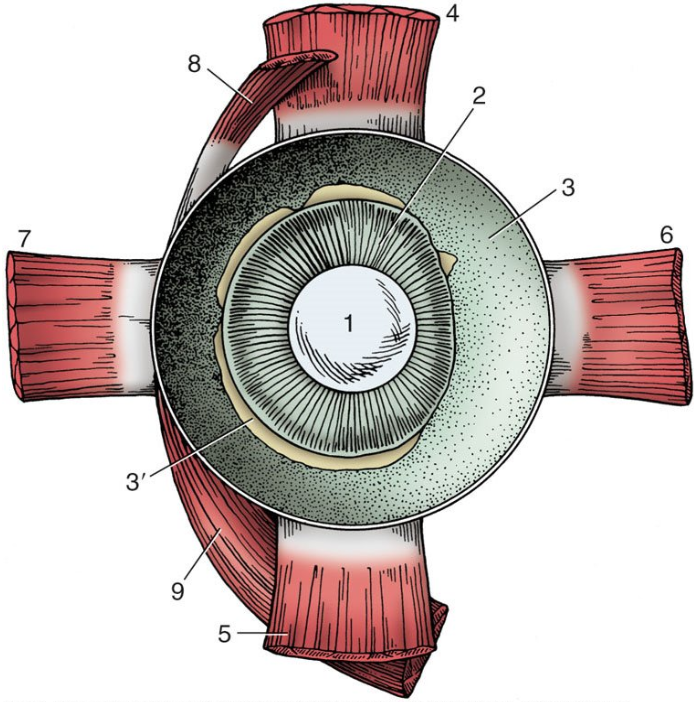
4
dorsal rectus muscle
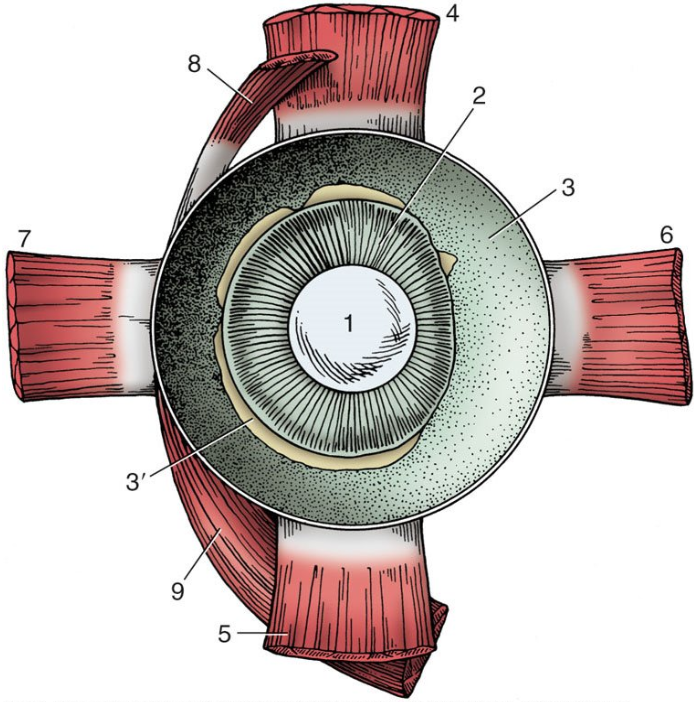
5
ventral rectus muscle
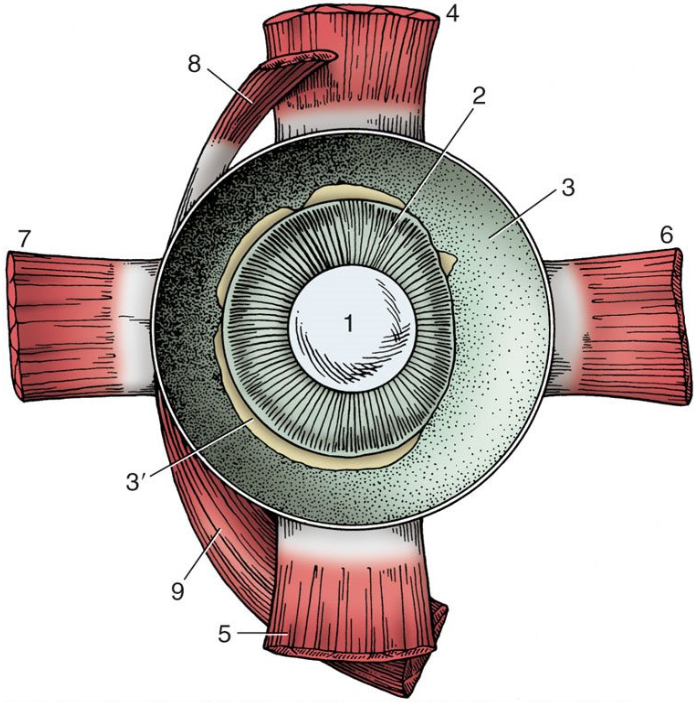
6
medial rectus muscle
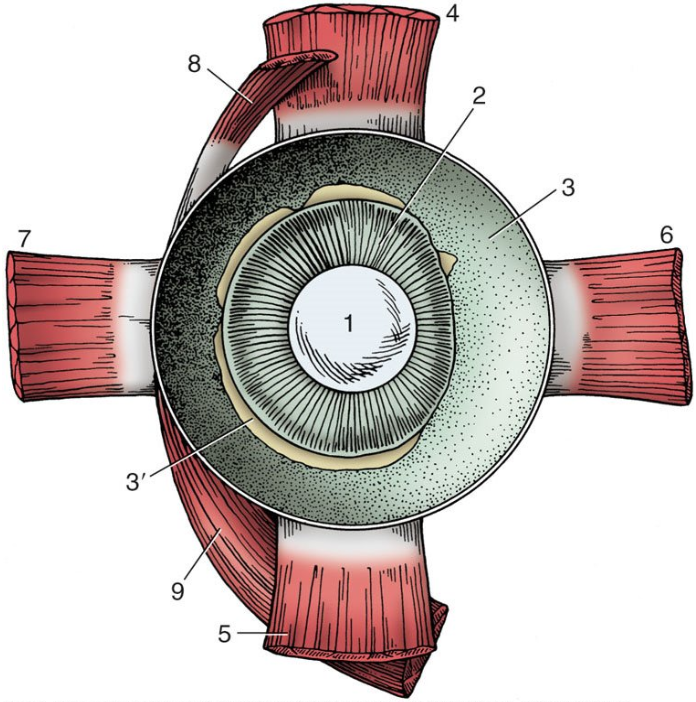
7
lateral rectus muscle