Chapter 3 - Light and Telescopes
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What are crests?
This is when waters waves interfere with each other and create constructive interferences. So, think of the highest points of the waves.
What are troughs?
This is when water waves interfere with each other to create destructive interferences. So, think of the lowest points of the waves.
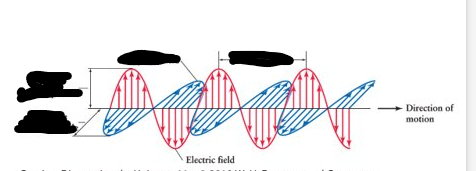
Label this image from left to right…
Electric Field Amplitude (the pink ones), Magnetic field amplitude (blue ones), magnetic field, wavelength.
Wave travels at a speed of ____ in empty space.
2 × 105 km/s
What did James Clerk Maxwell do?
In the 1860s, he combined and unified theories of electricity and magnetism and showed that both of these fields travel through space together in electromagnetic waves.
What did Einstein propose about light?
He believed that it travels as waves enclosed in packets called photons.
What did Ole Romer do to prove that light travels at a finite speed?
He used two eclipses of one of Jupiter’s moons to show that light does not travel infinitely fast by observing the moon at different dates. (therefore the Earth would be farther away at times)
Since we know that all types of electromagnetic radiation cannot reach Earth’s surface, what happens to it?
It gets absorbed or scattered by the gases in the air at different altitudes (like in the Mesosphere, thermosphere, stratosphere, troposphere). Some of it reaches the surface, while the rest is absorbed by atmospheric gases.
What is the primary mirror?
It is the large mirror used to gather and focus light in a reflecting telescope.
What is a focal point?
It is the surface of a mirror that is used to focus incoming light rays to a single point.
What is focal length?
It is the distance between the mirror and its focal point.
What does a Newtonian telescope use?
It uses a flat secondary mirror to redirect the focused image to the side of the telescope for viewing (think of a normal telescope).
What are the four most common telescopes?
Newtonian focus, Cassegrain focus, Nasmyth focus/coude focus, Prime focus.
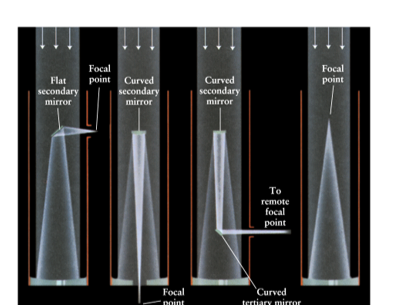
Name the type of focuses seen in the image from left to right.
Newtonian focus, Cassegrain focus, Nasmyth/coude focus, Prime focus.
True or false, a telescope with a primary mirror TWICE the diameter of another telescope’s primary mirror will be able to see twice as much detail as the smaller one.
Tru!