Reproductive Pharmacology
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Reasons for reproductive pharmacological interventions
Manipulate follicular waves
Induce ovulation
Control luteal phase
Oestrus synchronisation/stimulating ovarian activity/advancing onset of oestrus in seasonal species (influencing litter size)
Control/induce parturition
Misalliance
Suppressing reproduction
Explain the HPG (Hypothalamus Pituitary Gonads) axis
GnRH release from hypothalamus
FSH & LH release from pituitary
Release of testosterone, progesterone & oestrogen
GnRH (Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone) key features
•Peptide hormone
•Proteolytic degradation
•Short half life 70- 80 mins
Why should GnRH not be given continually?
Mimics the GnRH pulse generator
If given continually then GnRH receptors get downregulated so pituitary can't release LH & FSH
chemical castration
e.g. implants that continuously release GnRH
What do GnRH agonists do? What can it be used for?
Stimulate LH & FSH surge (due to acute release of gonadotropins from pituitary)
Induce ovulation
Improve synchronisation of oestrus/ovulation
Improve conception rates
What does GnRF stand for?
What does the vaccine do?
What can it be used for?
Gonadotrophin Releasing Factor
Induces antibodies against GnRH —> immunity (anti GnRF antibodies) develop around 1 weeks post 2nd vaccination
Chemical castration of pigs
can prevent boar taint if pigs are on farm for too long
What does LH do in females and males?
Females
- produces precursors for oestrogen production
- stimulates maturation and ovulation of follicles
- maintains function of CL
Males
increased testosterone by Leydig cells
What does FSH do in males and females?
Females
- growth & recruitment of immature follicles
- stimulates oestrogen synthesis
Males
promotes spermatogenesis
What produces gonadotrophins? What type of macromolecule are they?
Anterior pituitary (under hypothalmic control)
Glycoproteins —> more resistant to breakdown than peptides/proteins
metabolised by proteases
What can FSH induce in cows?
Superovulation
Why would PMSG (Pregnant Mare Serum Gonadotropin) be used instead of FSH? What is it used for?
Longer half life, cheaper
Oestrus induction & synchronisation
Why would HCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin) be used instead of LH? What is it used for?
Longer half life, cheaper
Inducing ovulation
'rig test' - stimulates production of testosterone
What are the functions of oestrogen in males and females?
Males
sexual behaviour
Female
- follicular growth
- optimise possibility of fertilisation
- increased receptivity
- trigger onset of parturition
- optimise chances of fertilisation
- increased growth of mammary gland
When would oestriol be used? What are its adverse effects?
treating urethral sphincter incompetence in spayed bitches
not to be used in whole bitches - impacts mammary glands and brain
adverse effects —> oestrogenic effects
What are the functions of testosterone in the male and female?
Male
- promotes spermatogenesis
- promotes sex gland secretions
- growth and sexual behaviour
Female
- substrate for oestrogen synthesis
- abnormal masculinisation
What is the only androgen used and what is it used for?
Nandralone (synthetic anabolic steroid)
- tissue repair (when excessive tissue breakdown has taken place)
- anaemia associated with renal disease
High doses of androgens inhibit the release of ___
Gonadotrophins
will suppress oestrus cycle
What can androgen receptor antagonists be used to treat? What are their adverse effects and why do they occur?
Used to treat prostatic hyperplasia & male hypersexual behaviour
Male hypersexual behaviour
Reduced ACTH
PUPD
Increased appetite
happens because receptor blockers have a similar structure to progesterone
What does delmadinone acetate do? What is it used to treat?
Inhibit FSH & LH -> decreases testosterone
long half life
treat hypersexual behaviour
'chemical castration'
What does progesterone do in females?
Endometrial secretion
Inhibits GnRH release
Inhibits reproductive behaviour
Maintains pregnancy
What do progesterone receptor agonists do? What can they be used for?
Inhibit GnRH release
Prolong luteal phase
Inhibits reproductive behaviour
Oestrus synchronisation
Suppress oestrus
Adverse effects of progestogens
Endometrial hyperplasia, endometritis, pyometria
Inhibition of ACTH
Behaviour changes
Glucocorticoid activity may induce diabetes mellitus
Why are progestogens not given via the oral administration route?
Rapidly inactivated in liver following oral administration
What is the use of the progestogens:
- Altrenogest
- Proligestone
Synchronise oestrus in pigs & horses
Oestrus suppression in cats, dogs & ferrets
receptor antagonists can be used in abortions
Describe progesterone receptor blockers aglepristone
Only licenced in dogs & cats
Reduced progesterone support for pregnancy —> abortion & pyometra, induction of parturition
Binds to glucocorticoid receptors
How do prolactin inhibitors work? e.g. cabergoline
Increase dopamine which inhibits prolactin secretion
What are prolactin inhibitors used for and what are their adverse effects?
Cause galactostasis in false pregnancy
Induces luteolysis and can cause abortions
What are oxytocin receptor agonists used for? Adverse effects?
increase milk ejection
increase myometrial contractions
Can complicate uterine dystocia
What precautions should be taken when administering prostaglandin receptor agonists?
Wear Gloves —> PGF 2a is absorbed through the skin
Risk to pregnant women
Risk to asthmatics —> can cause bronchonstriction
More ___ is produced when it's darker so it can be used to ____ the oestrus cycle in sheep
Melatonin
Bring forward
melatonin implant used in sheep
(opposite effect in horses —> low melatonin allows cyclicity in horses)
What can B2 adrenergic agonists do? Why might they be used?
Relax smooth muscle in myometrium and airways dilate
- delay delivery in cattle
- aid obstetrical manoeuvres in dystocia e.g. malpresentation/malposture
- relax uterus for C section
- facilitate replacement of prolapsed uterus
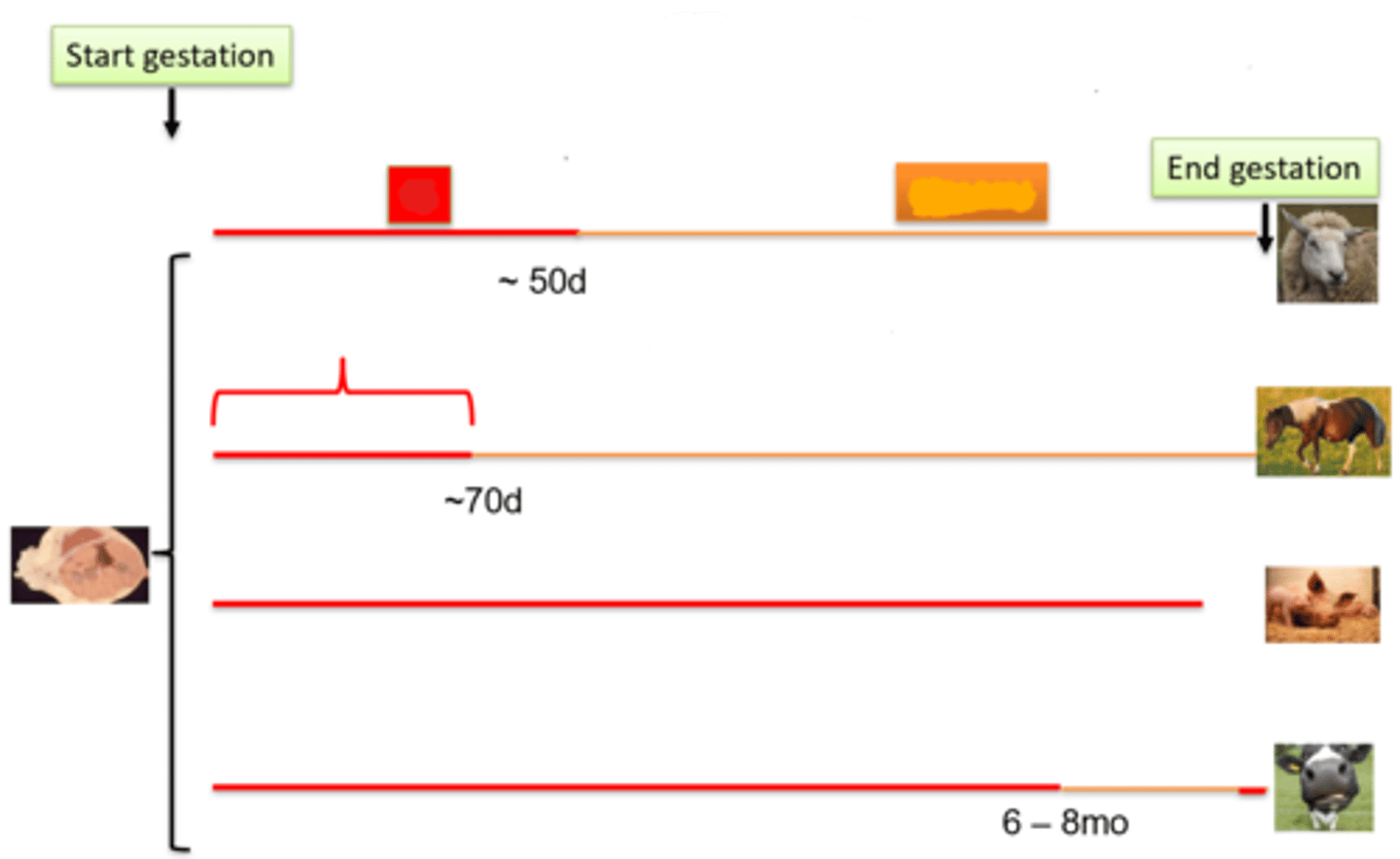
The red line represents when progesterone is produced by the ____
The orange line represents when progesterone is produced by the ___
CL
Placenta
When the CL produces progesterone, __ is given to terminate the pregnancy
When the placenta produces progesterone ___ is used to induce parturition
PGF 2a
Glucocorticoid agonist
What class of drug could be given to make sure a bitch does not get pregnant and if owners do not want to spay the bitch.
Progesterone receptor blockers —> prevents ovulation and terminates/prevents pregnancy
only licenced for small animals
What are the clinical signs of a false pregnancy in bitches?
Anorexia or weight gain
Beginning to lactate —> can lead to mastitis
Stealing toys (maternal behaviour)
all due to long luteal phase in the bitch
What class of drugs can be used to alleviate false pregnancy symptoms
Dopamine receptor agonists aka prolactin inhibitors —> inhibits lactation
How would you induce parturition in a term pregnant sheep?
Glucocorticoid agonist —> mimic cortisol
progesterone is placenta dependent
How would you induce parturition in a term pregnant sow?
PG F2a (prostaglandin F2a)
progesterone is CL dependent
How would you induce parturition in a pregnant heifer at:
8 month gestation
term pregnant
glucocorticoid agonist —> placenta dependent progesterone
PG F2a (prostaglandin F2a) —> CL dependent progesterone
What injection is often given to mares at stud 24hrs before they are served?
GnRH —> induces LH
OR
HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin)
A local pig farm wants to change from farrowing 20 sows every week to batch farrowing 60 sows every three weeks. Piglets are currently weaned at 4 weeks old. How could the farmer use pharmacological agents and/or changes in management to achieve this?
Weaning —> synchronises sows back into oestrus
and use of progesterone
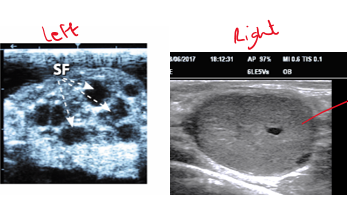
You are presented with a cow that has not been seen bulling i.e. not showing oestrus signs. On ultrasound, the left & right ovary appear as in the picture. How do you suggest this animal is managed.
In the right ovary, corpus luteum present —> cow has ovulated (normal) i.e. gone into oestrus and has been bulling —> farmer may have missed the signs
Give prostaglandin & tell farmer to look out for oestrus signs in next few days
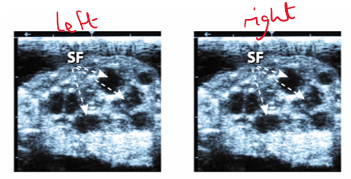
You are presented with a cow that has not been seen bulling. On ultrasound, the left and right ovary appear as in the image. How do you suggest this animal is managed?
Follicles shown but no CL
Could be in anoestrus/beginning of oestrus cycle/follicular phase?
Could revisit to decide?
Assume in follicular phase & just about to ovulate
Give progesterone for 10 days then prostaglandin after the 10 days —> synchronises the oestrus in order to spot the oestrus signs