Embalming 1504.2 - Exam 2
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
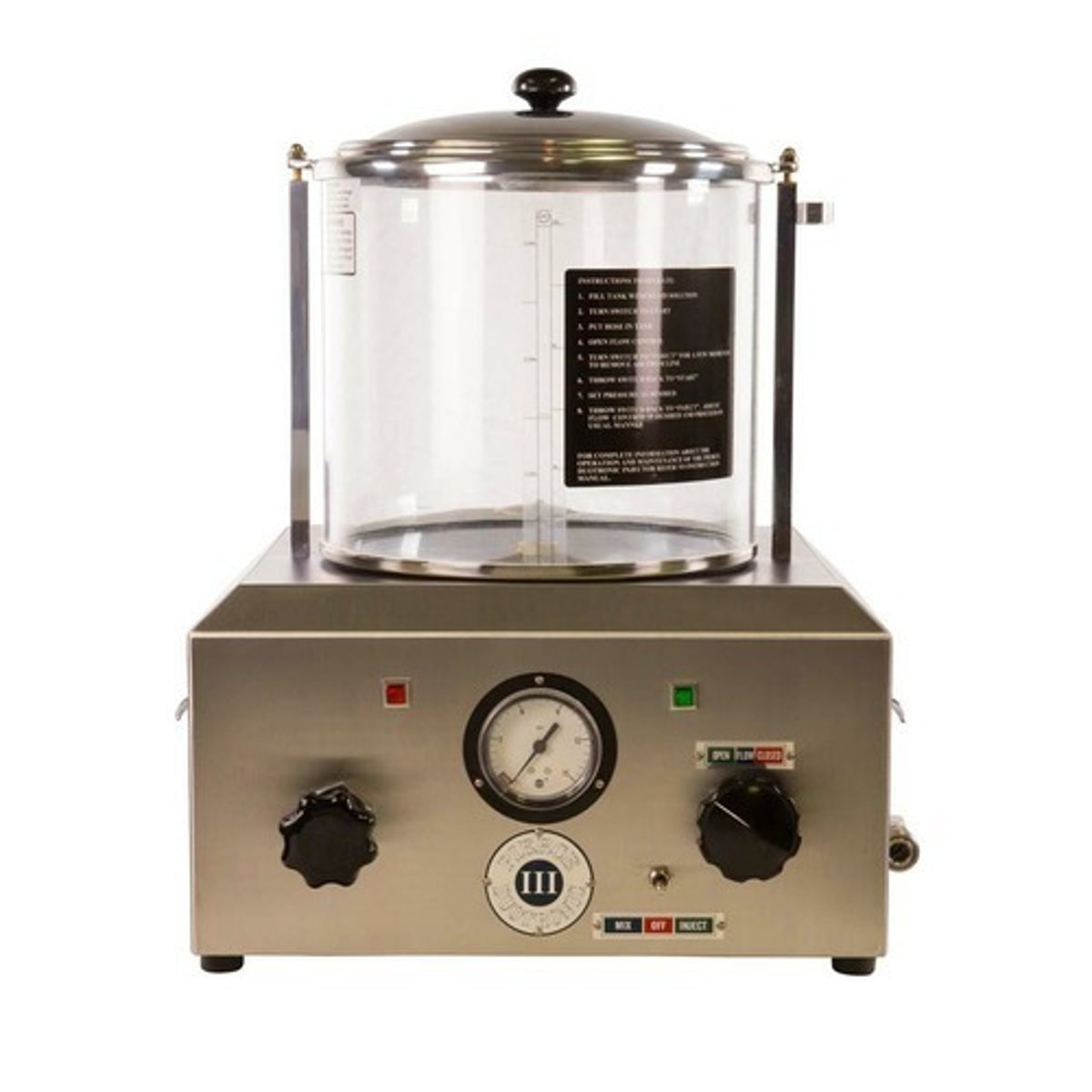
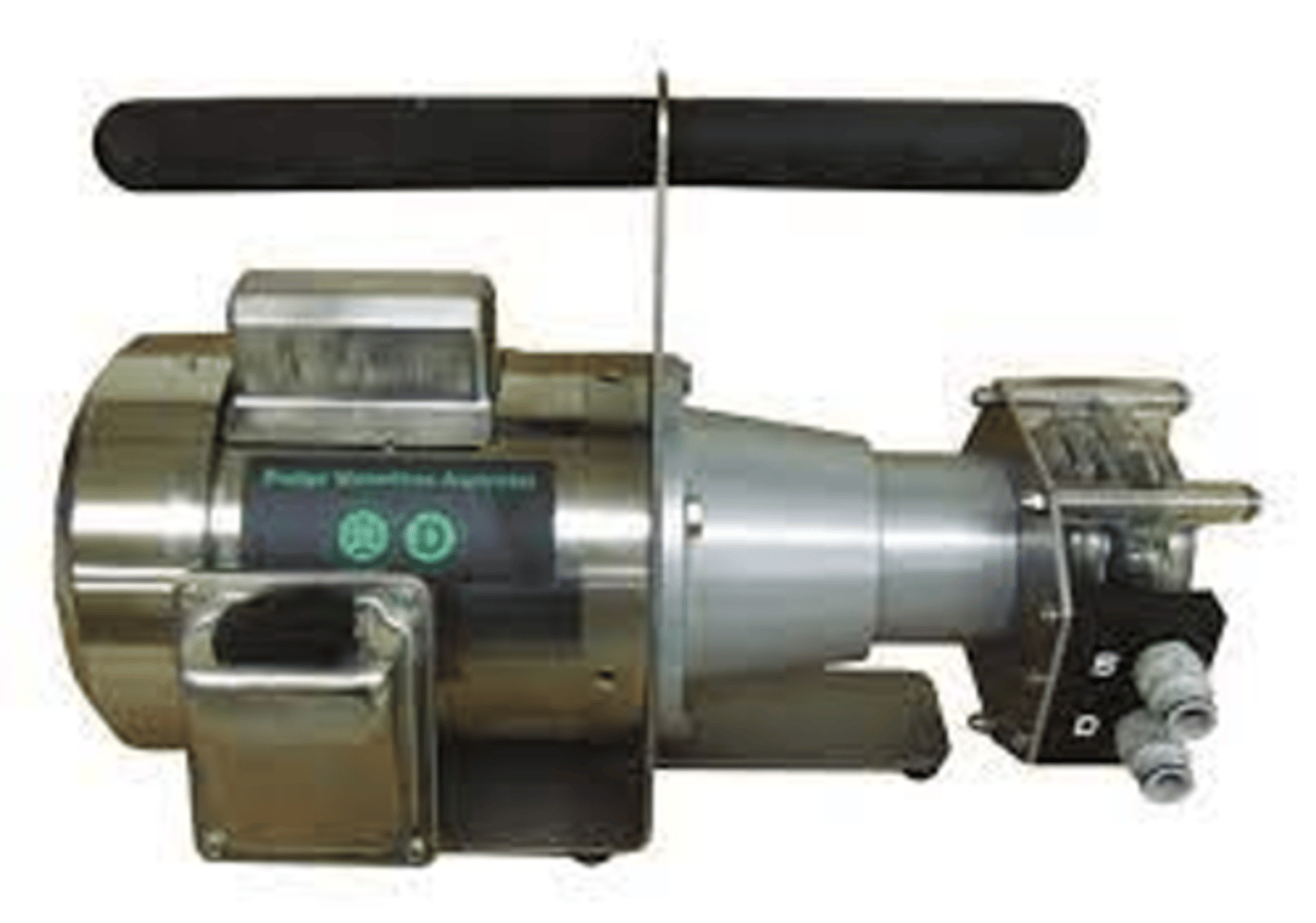
Pressure Machine (centrifugal force pump)

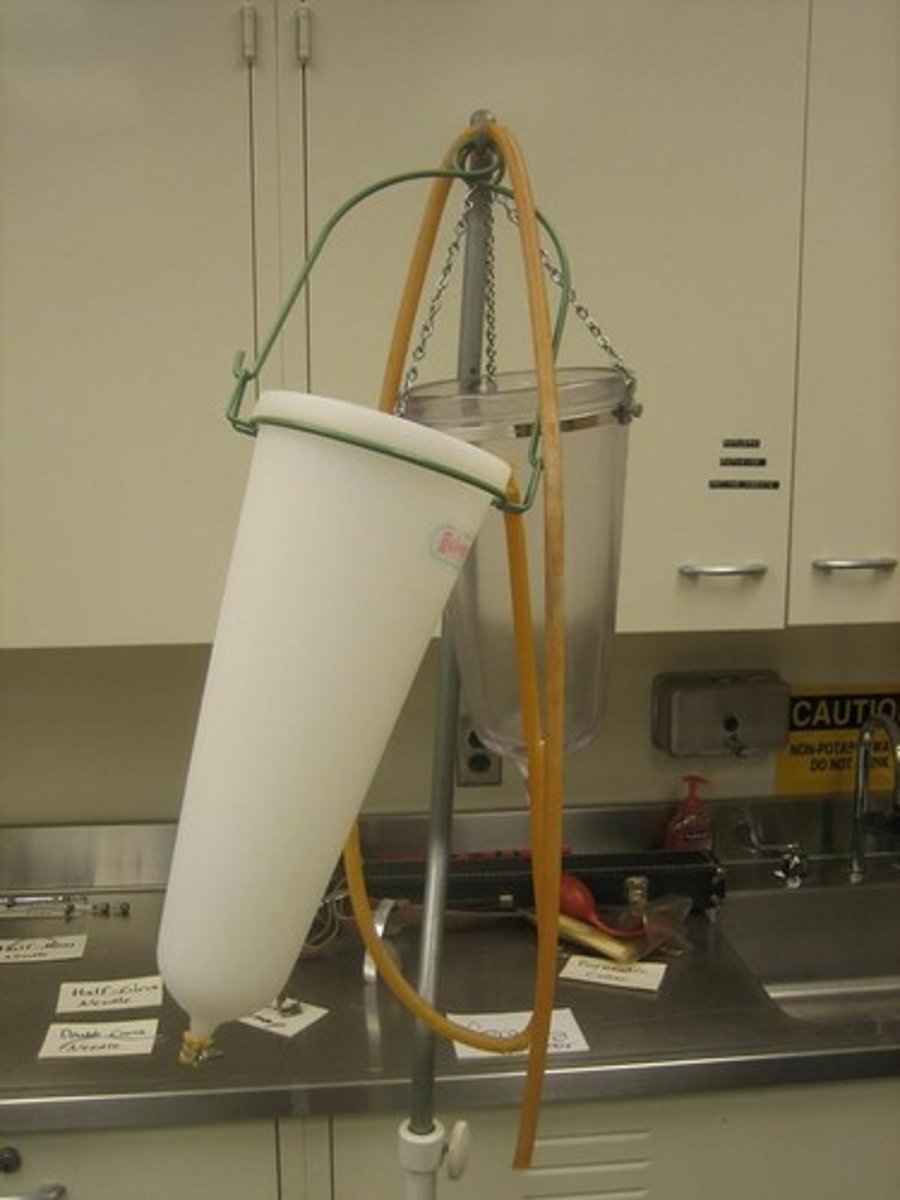
gravity injector (percolator)
fluid is poured into a large glass reservoir that has a delivery hose attached to the bottom of the bowl; percolator is elevated above the body to create the necessary pressure in the delivery hose to allow the embalming solution to flow into the arterial system

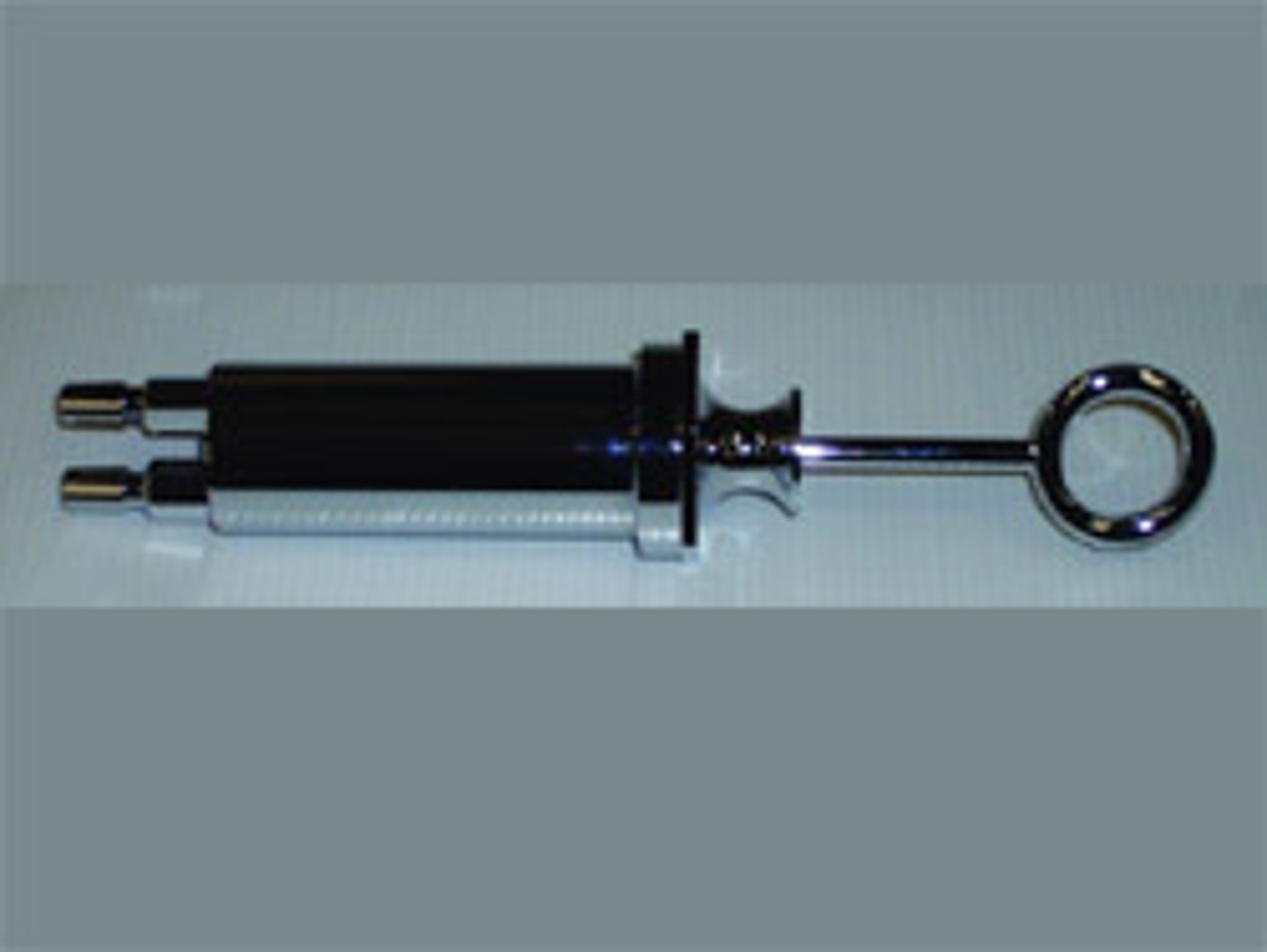
hand pump
handheld service is a pump with two slip-hubs to which hoses can be attached, one hub delivers air to create pressure; the other hub creates a vacuum

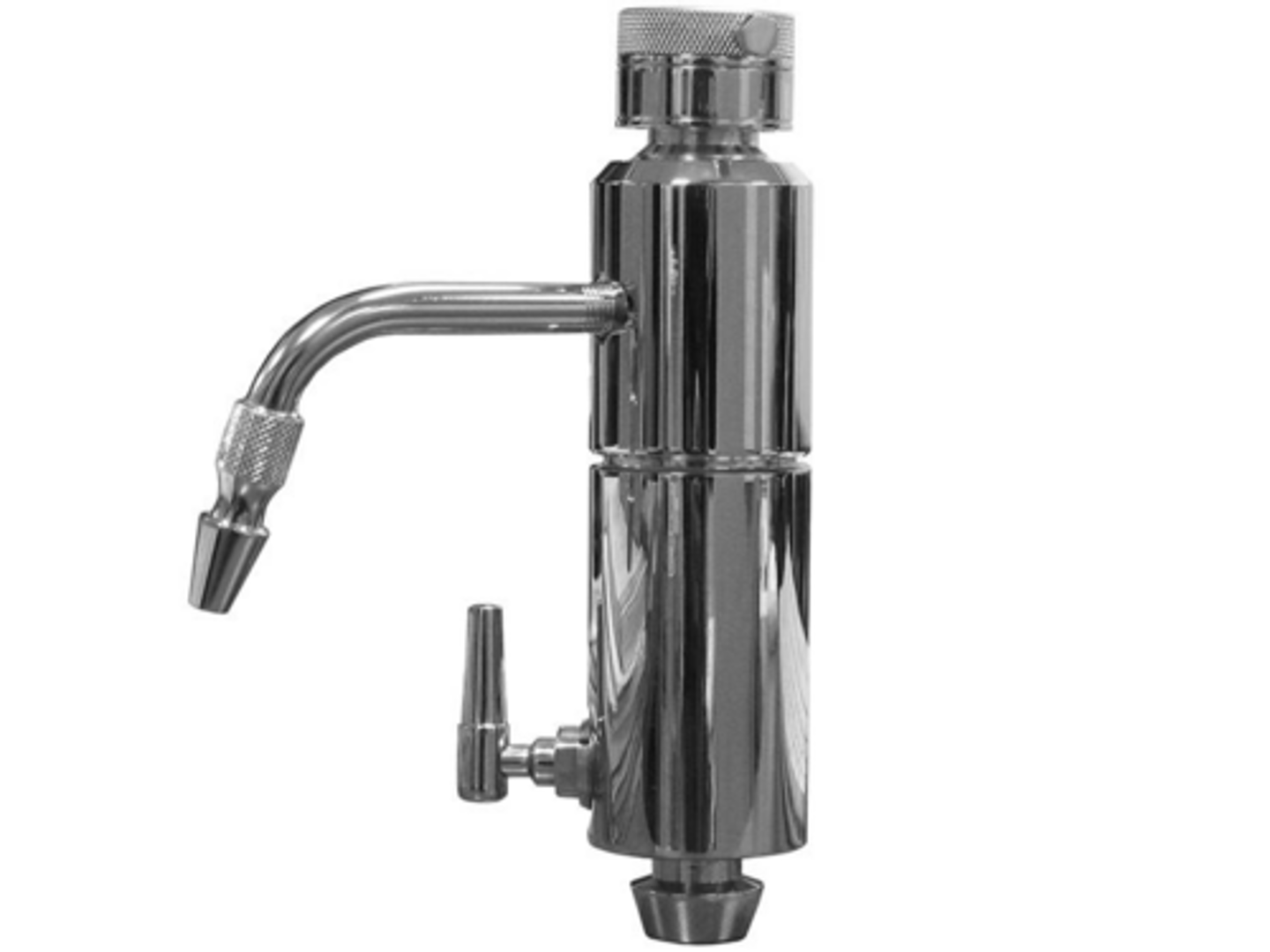
hydroaspirator
an aspirating device that creates a vacuum when water is running through it, is attached to a water faucet over a flush sink

electric aspirator
free standing aspirating device that required electricity instead of water to operate and create suction; are commonly selected when low water pressure is an issue

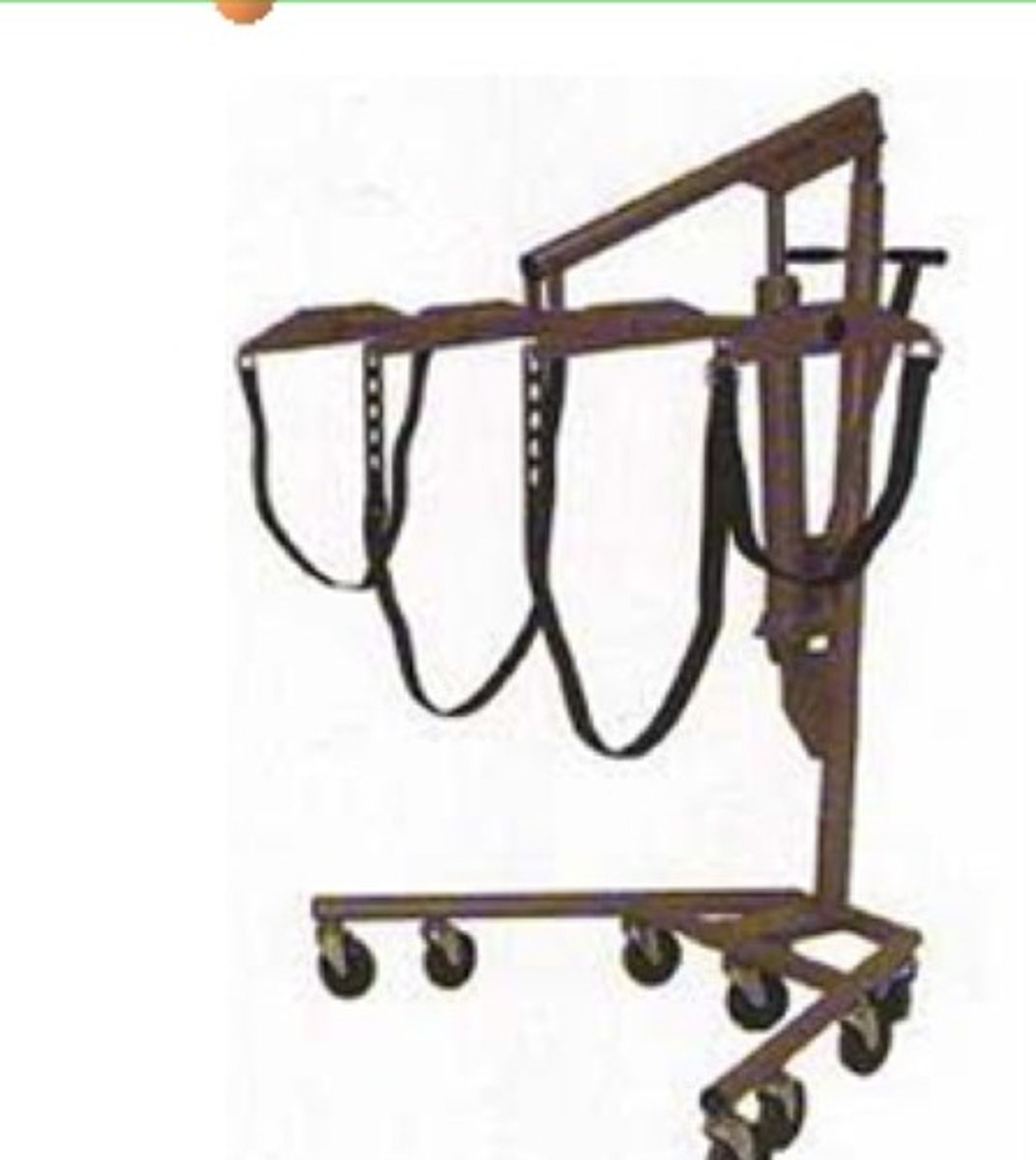
body lifts
essential for heavy lifting, used for both transferring and elevating a decedent

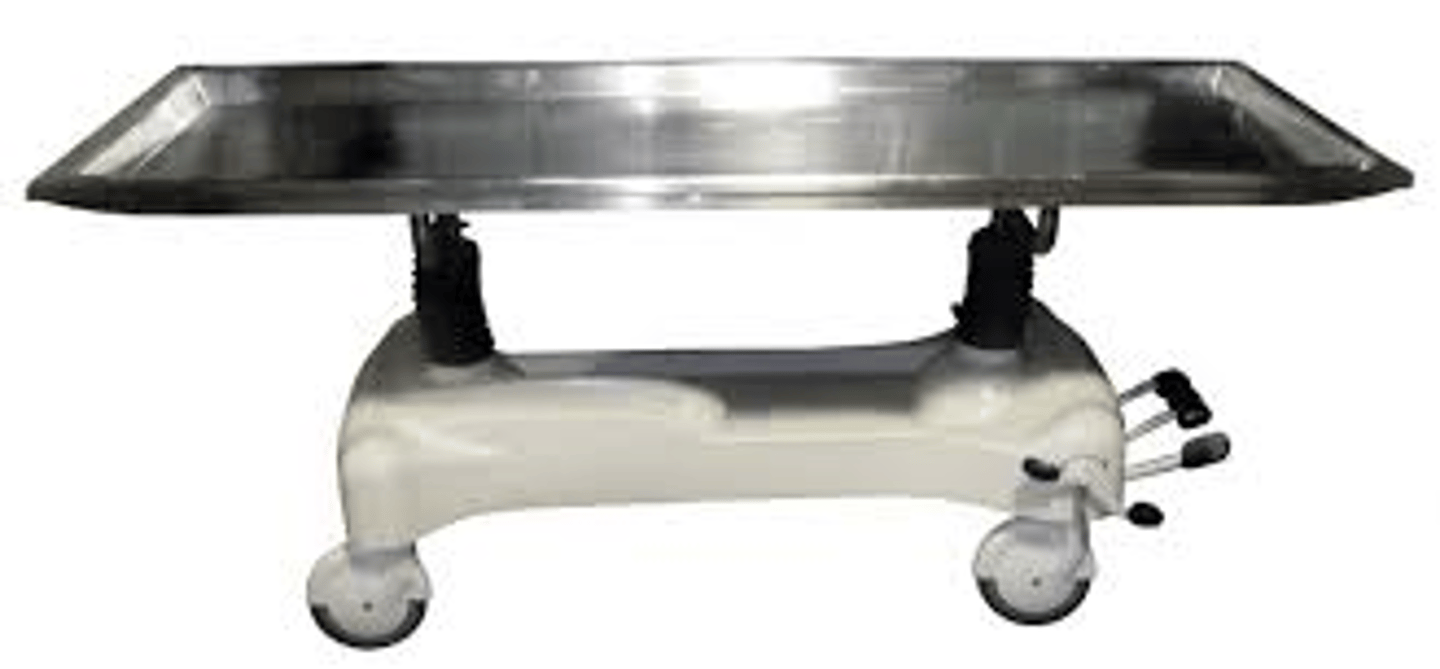
embalming table
porcelain or stainless steel; stationary or movable

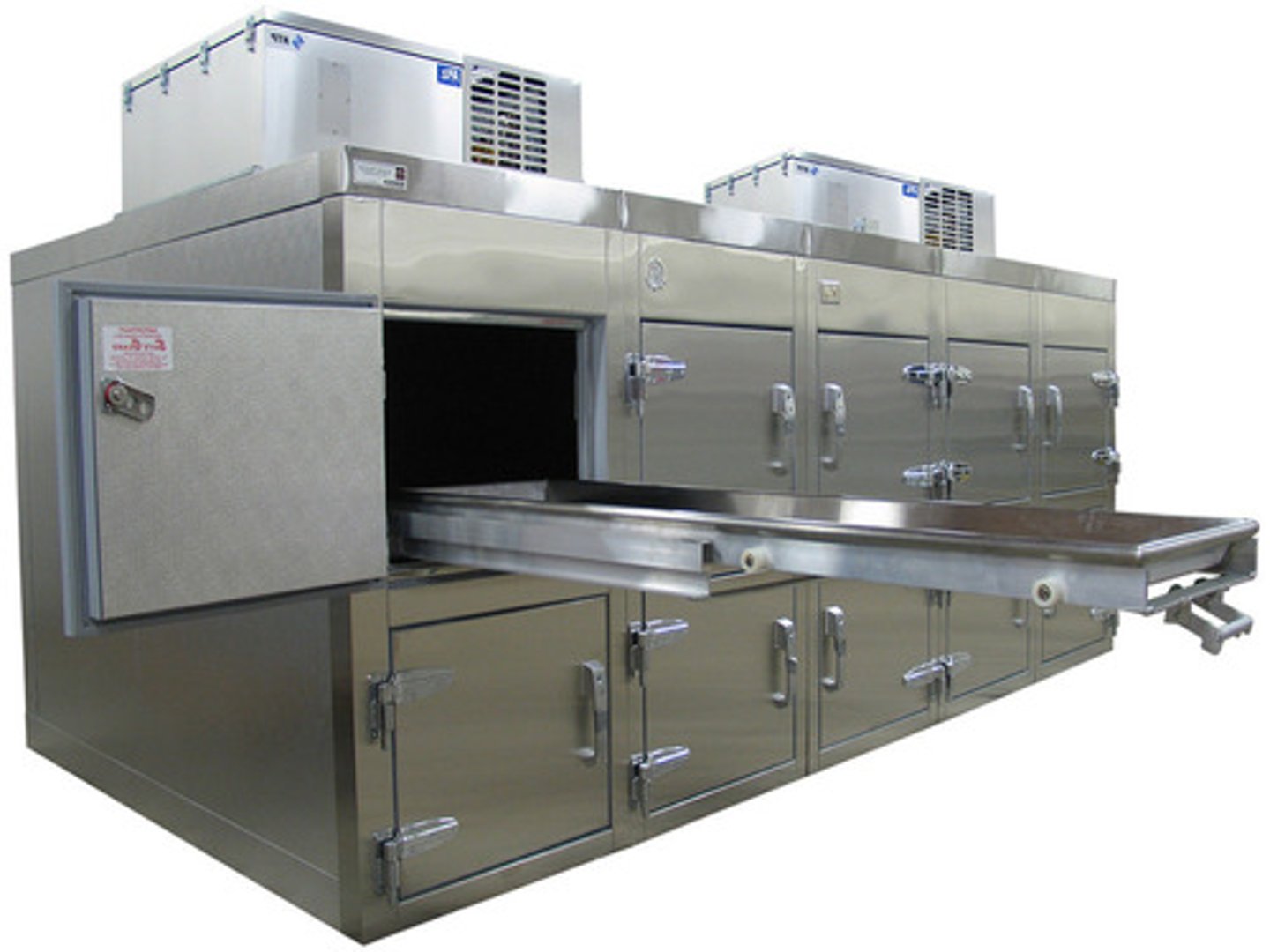
refrigeration unit
the purpose is to slow postmortem changes in the deceased body; human remains must be placed in a supine position; minimum temperature should be kept above freezing

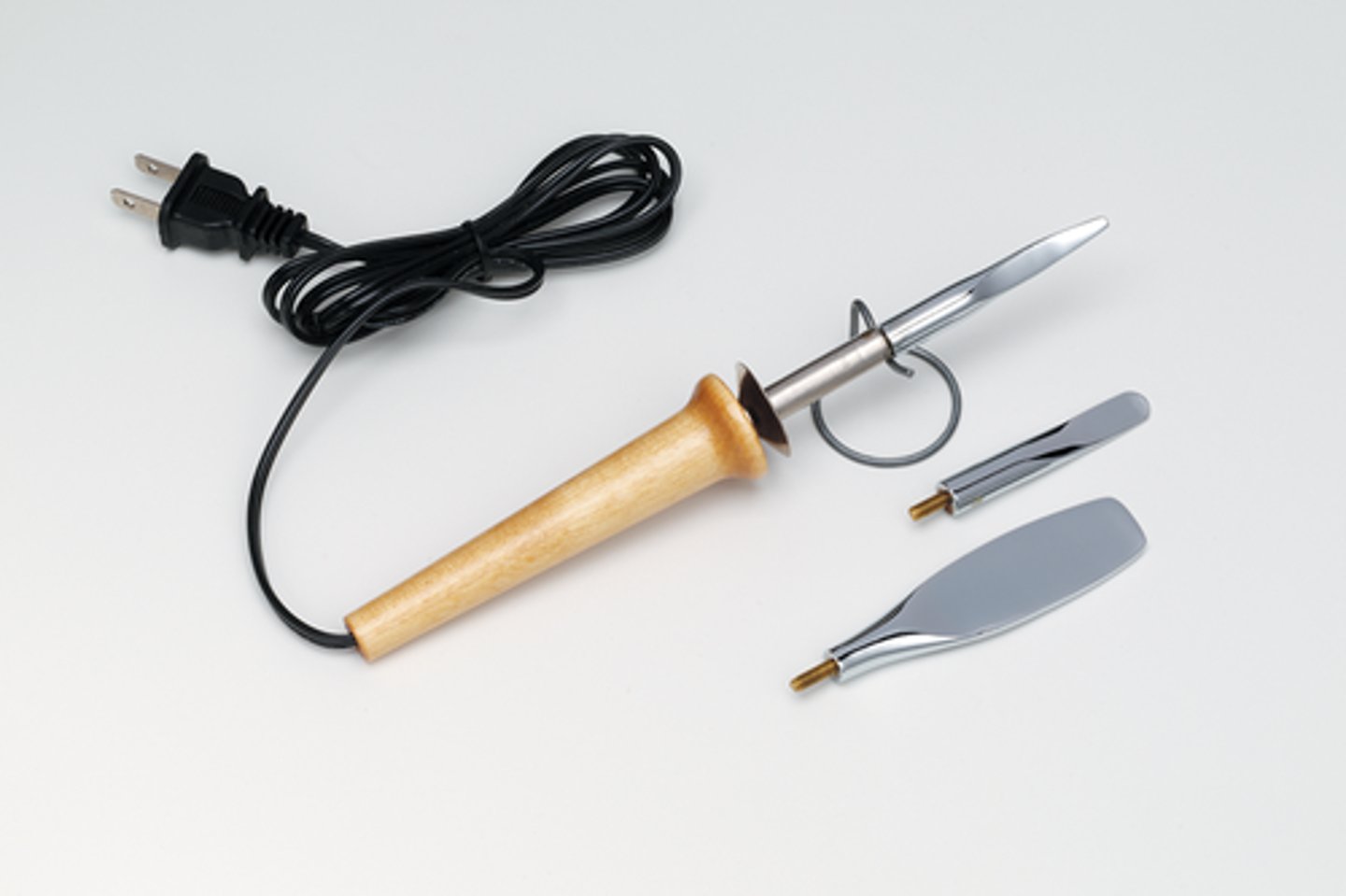
electric spatula

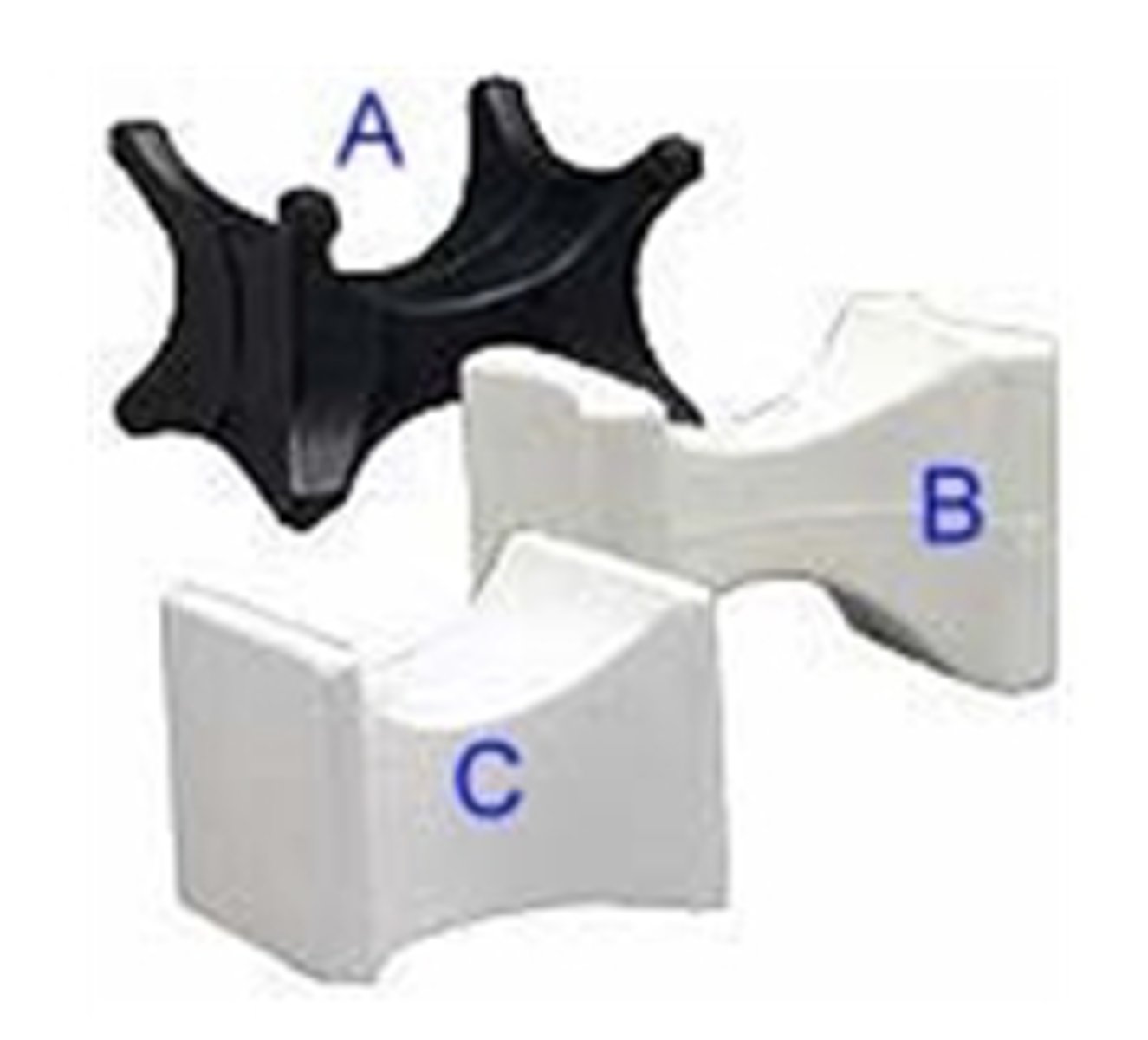
head block
used to elevate the head, neck, arms, and feet

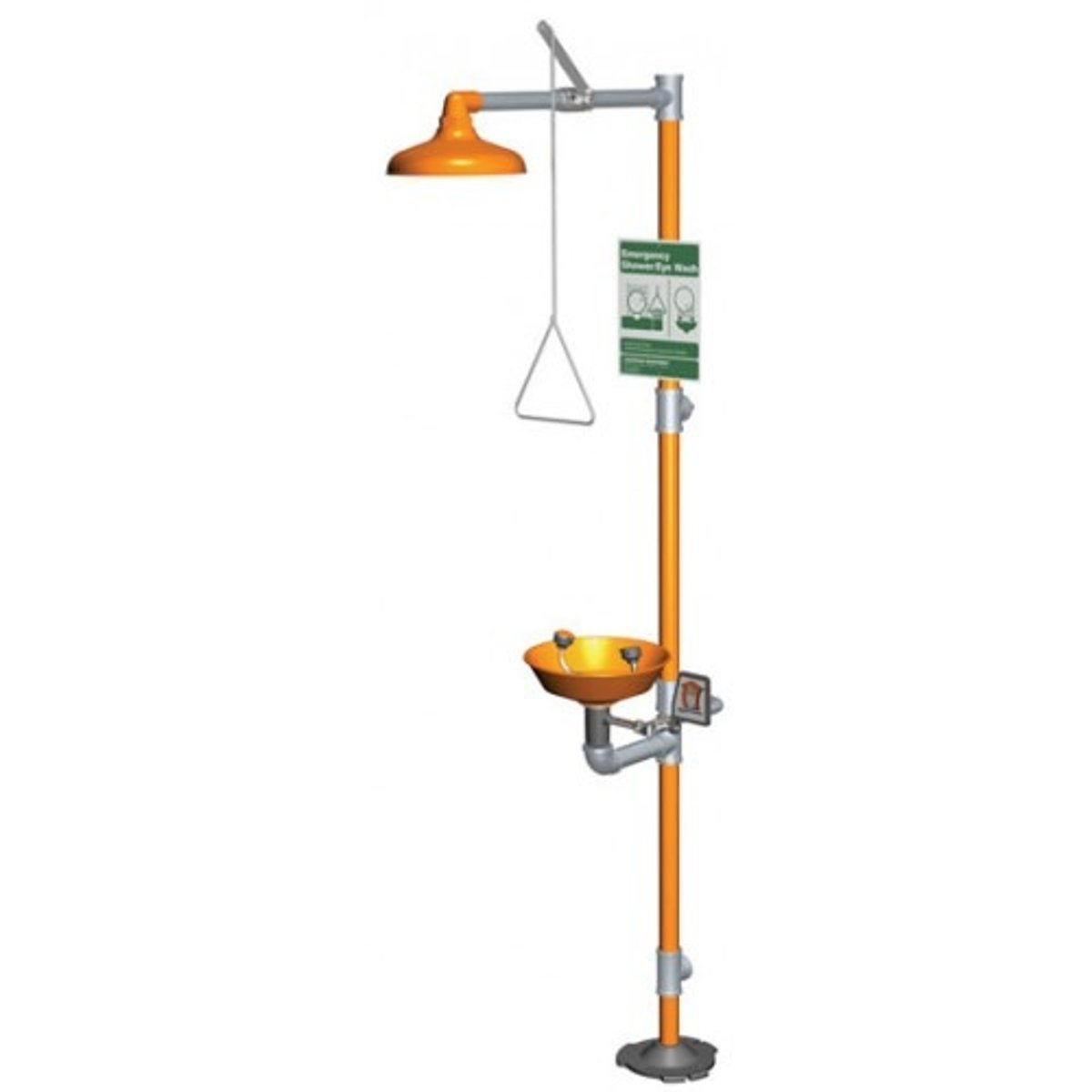
drench shower

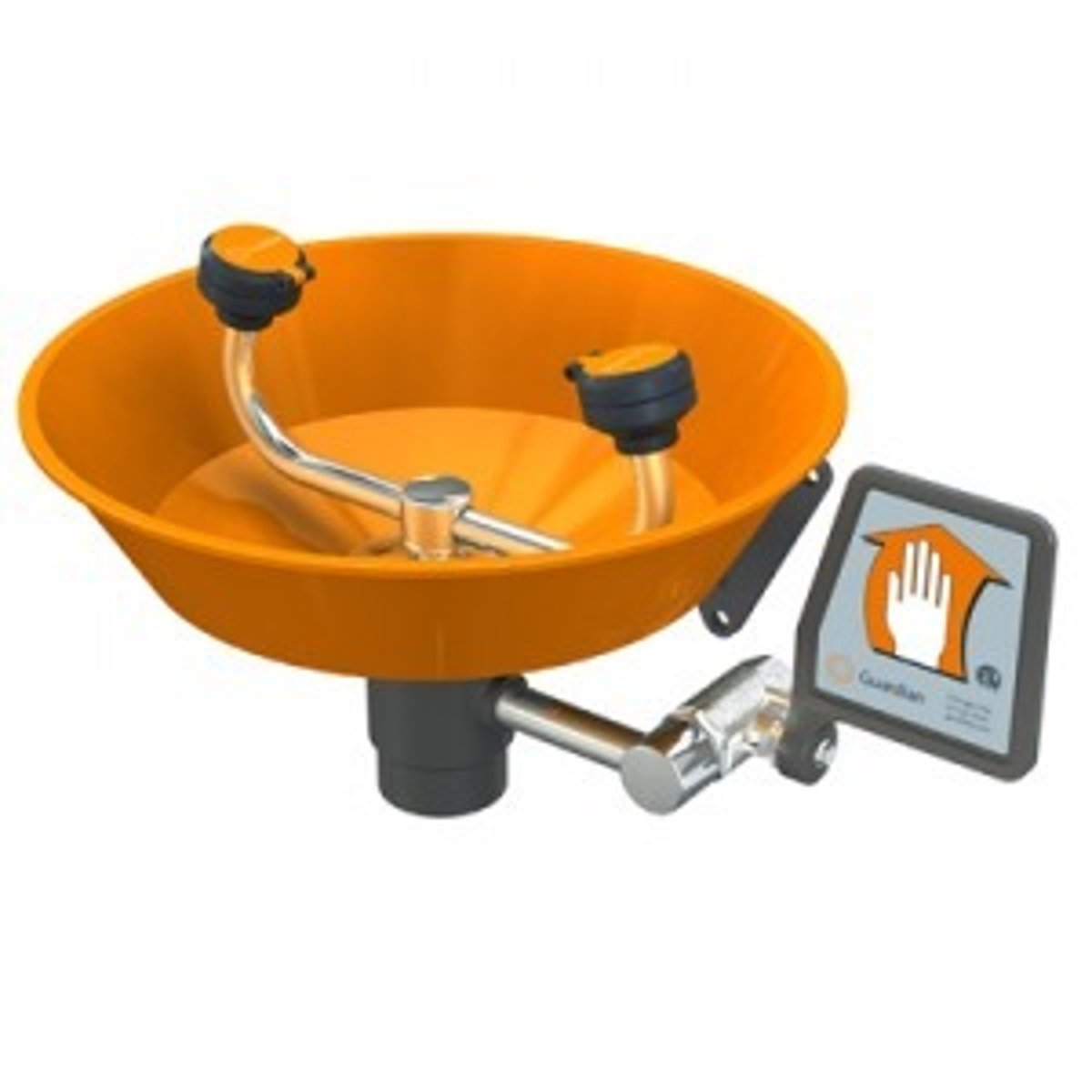
eyewash station

sharps container

biohazard waste

arterial tube/cannula
many lengths, types, and sizes; small diameters are used for infants, and distal arteries in adults, such as the radial and ulnar; large diameters are used for femoral and iliac arteries

aneurysm hook/needle
curve-tipped instruments chiefly used for the blunt dissection of tissues to locate and raise arteries and veins

scapel
sharp cutting instrument used for making incisions

scissors
used for cutting; can also be used to open arteries and veins
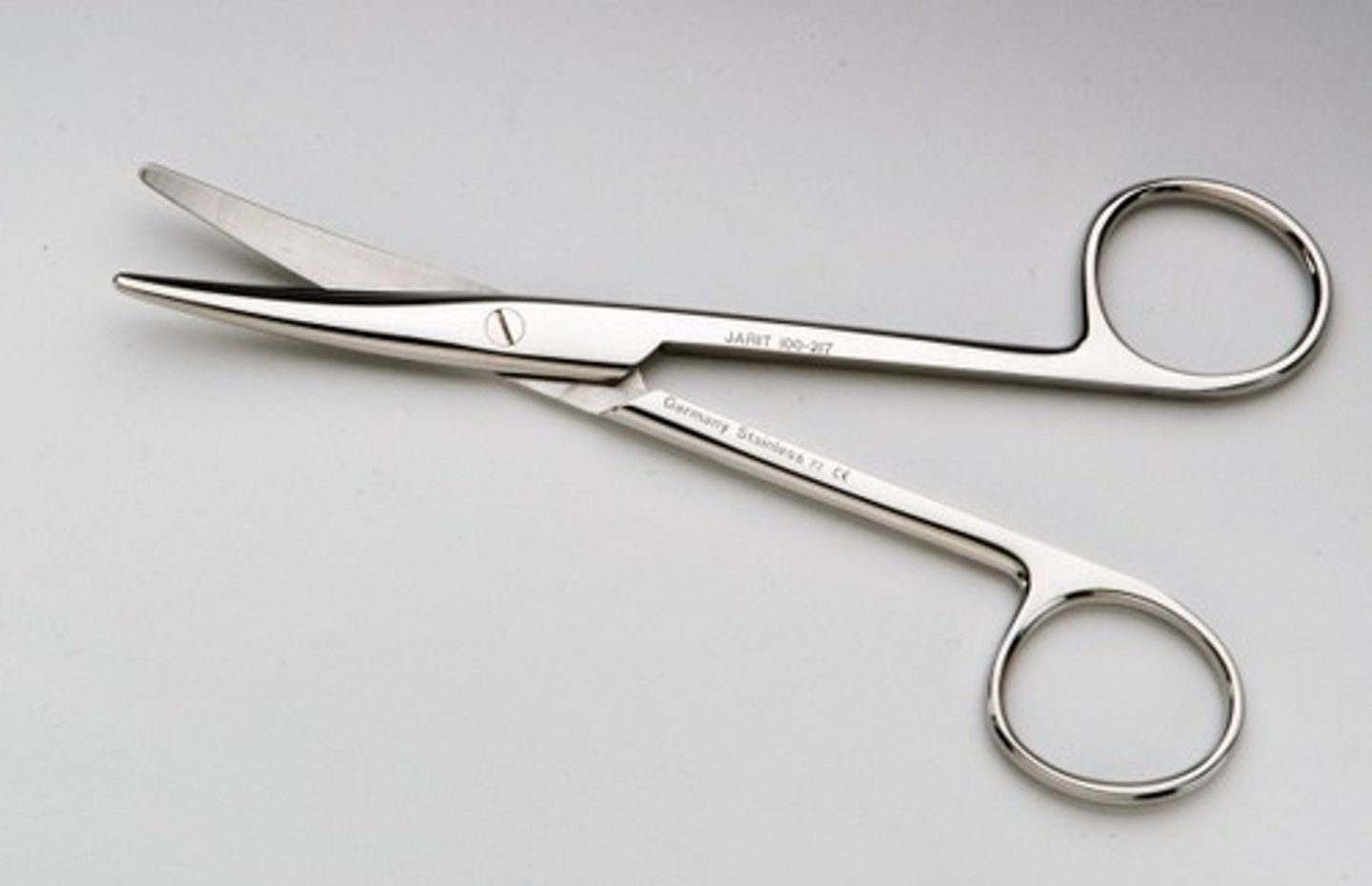
arterial fixation forceps (AKA arterial hemostats)
used to secure the arterial tube in the artery while the arterial tube is inside
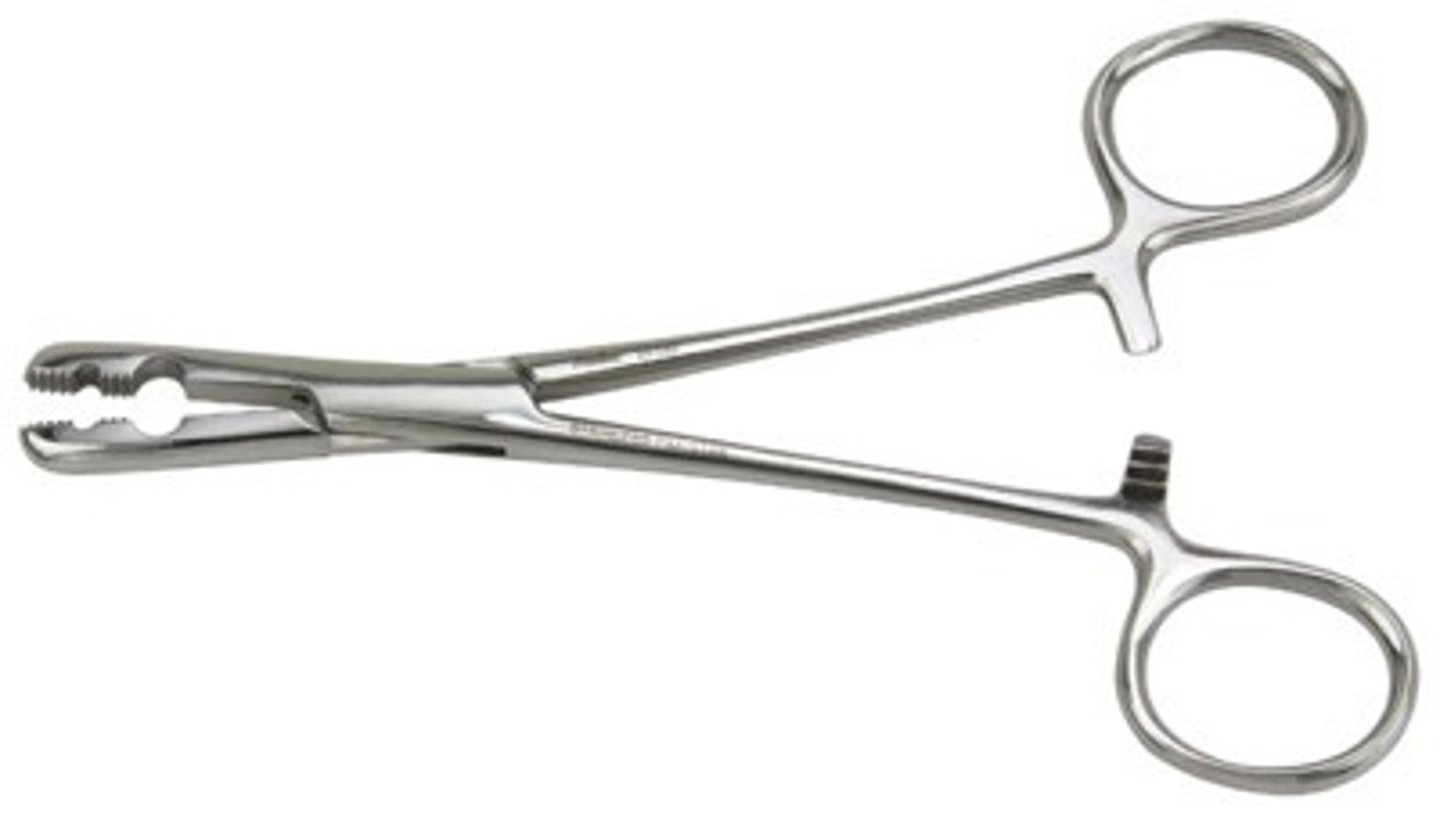
groove director
used to expand the vein and guide a drain tube or drainage device into place
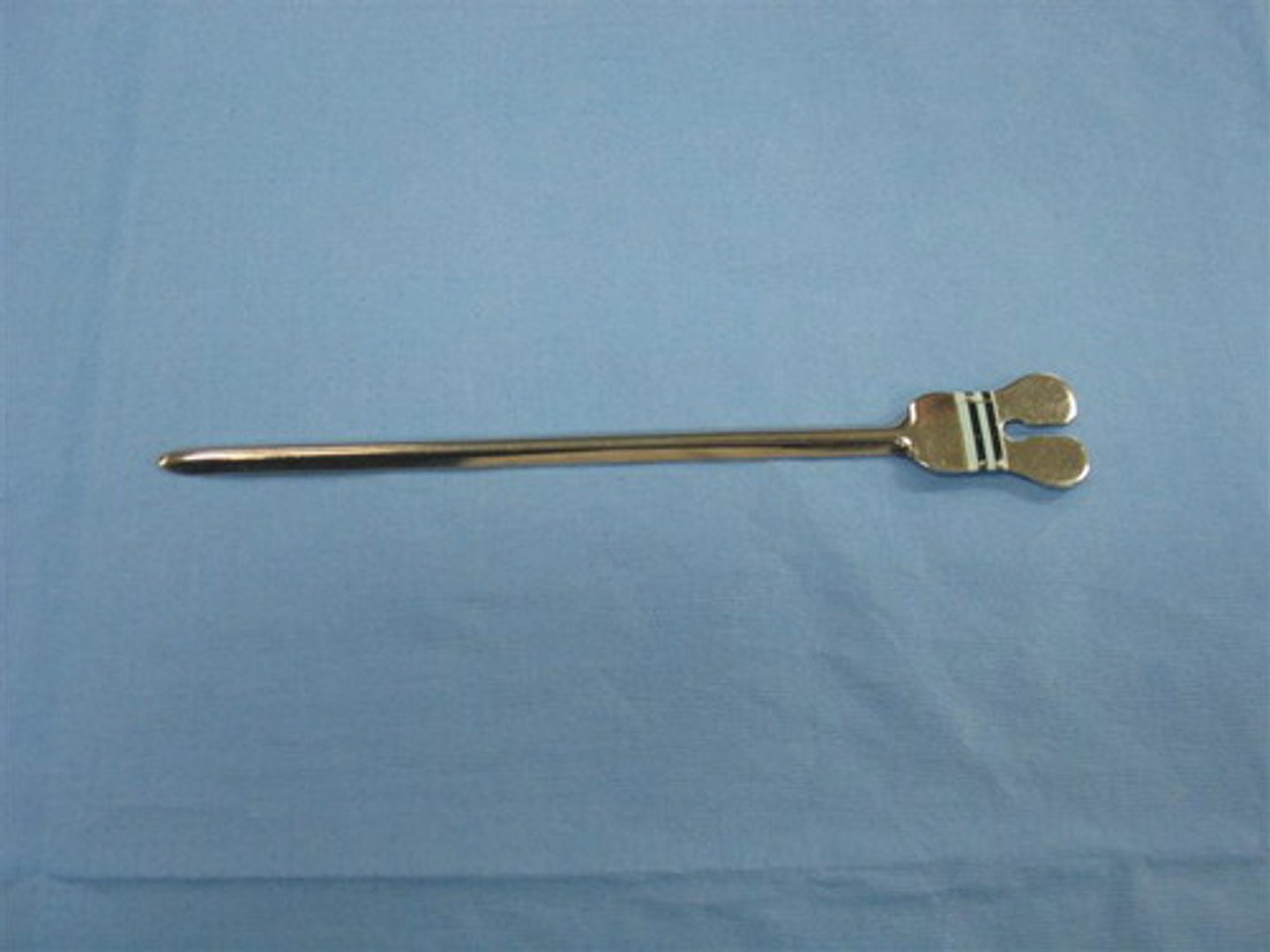
hemostats
can be used to clamp leaking vessel; the arterial version is used to hold the arterial tube securely in an artery

forceps (spring forceps)
instrument used for grasping and holding tissues, may be straight, curved, or angular

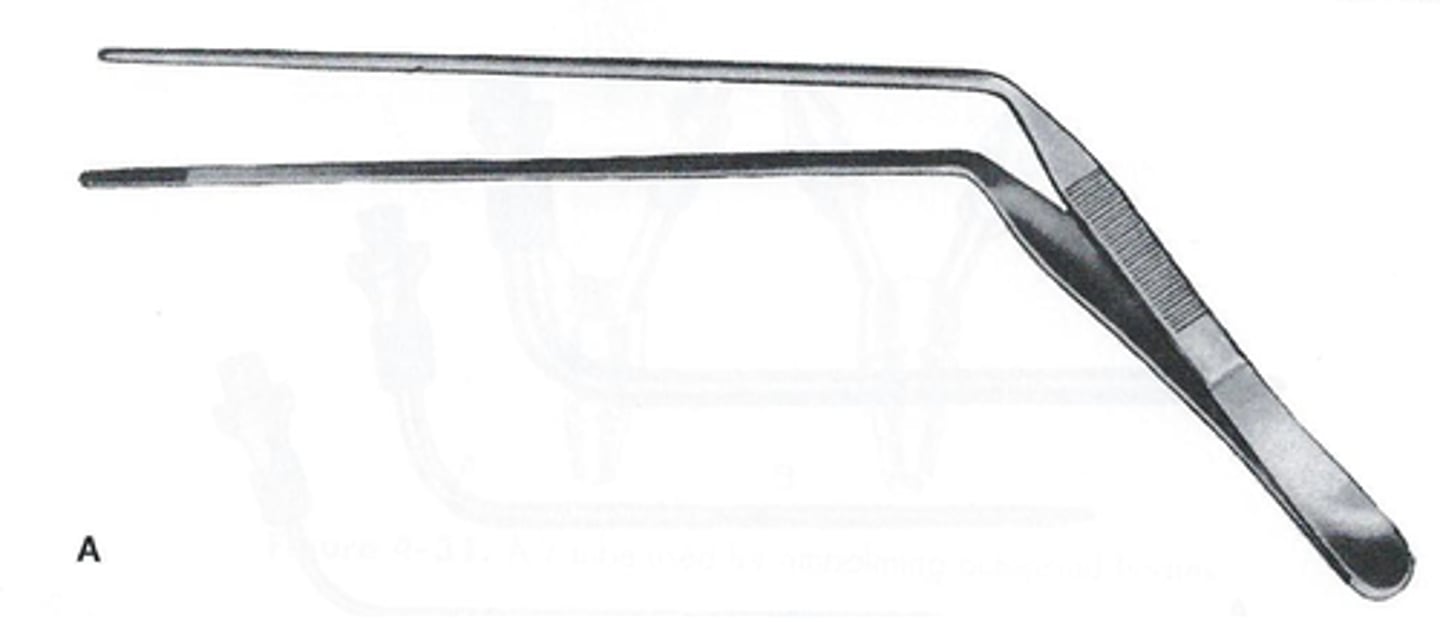
angular spring forceps
used as a drainage device are sometimes called drainage forceps; for use in the internal jugular vein, directed toward toward the heart

drain tube
a drainage device inserted into a vein toward the heart, can be used instead of angular forceps; has a plunger
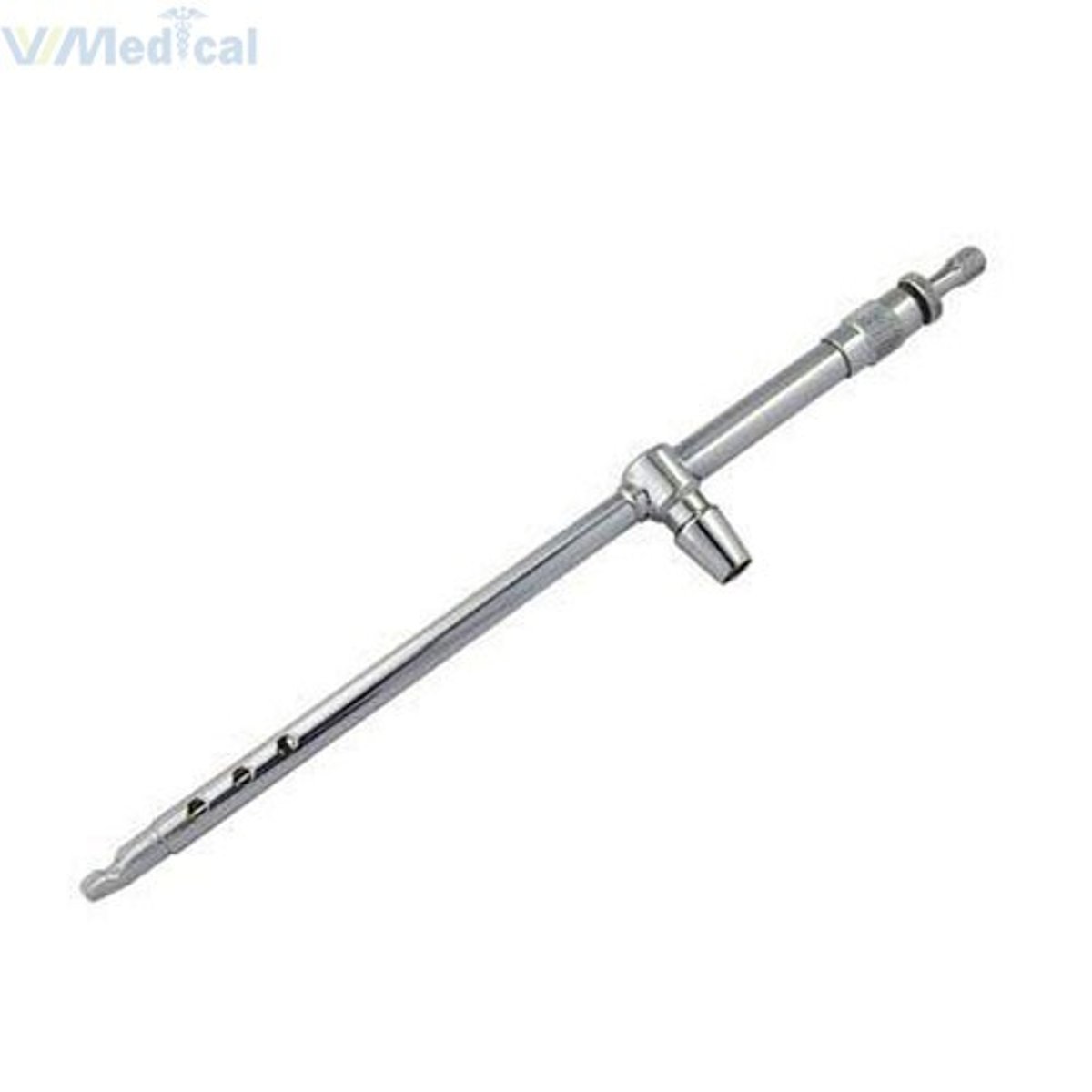

nasal tube aspirator
used to remove fluids from the nasal cavity and throat; placed through the nose and back of the throat

cavity injector
used to connect the cavity fluid bottle to a trocar; gravity is used to gain force
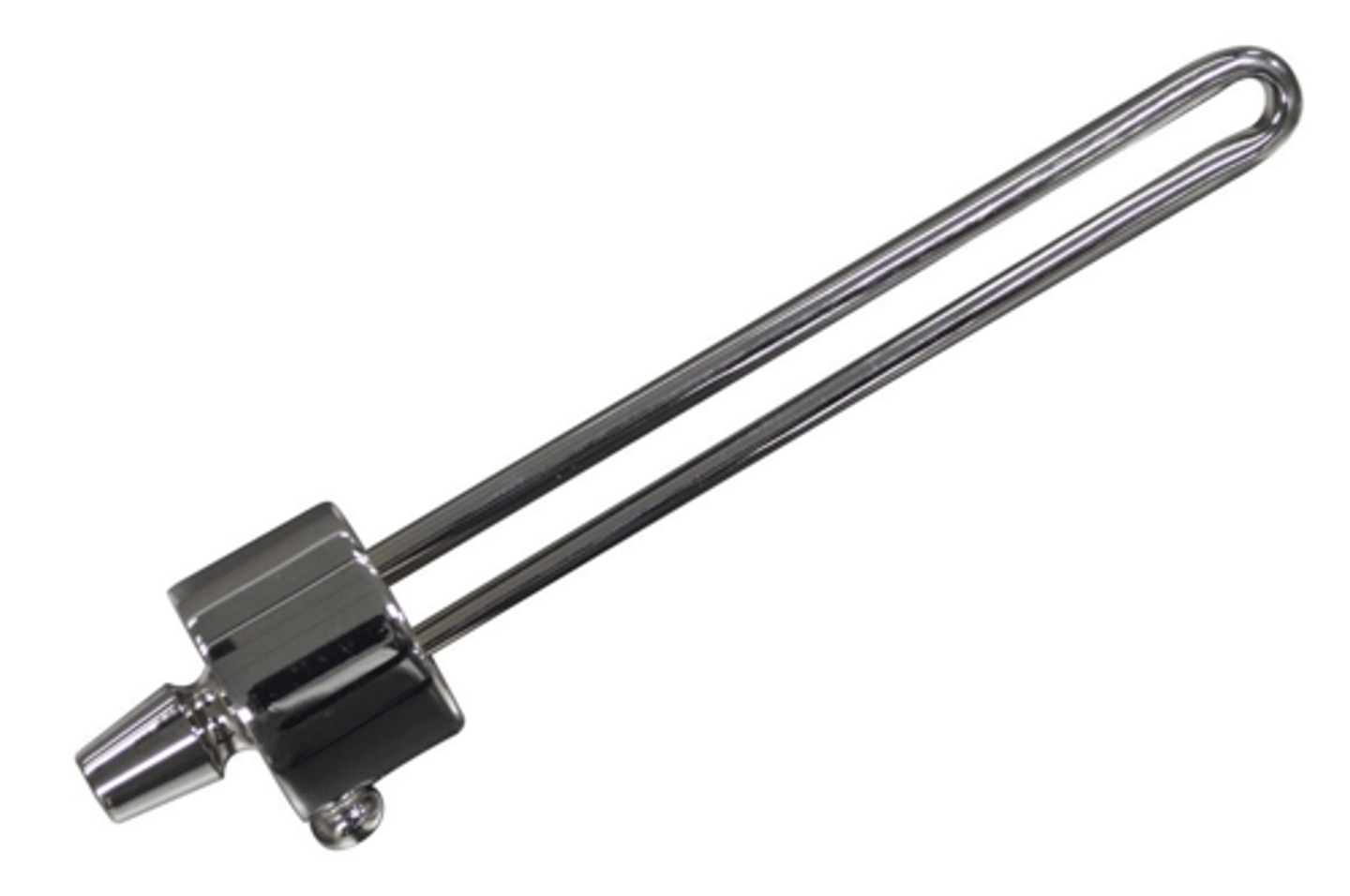
autopsy aspirator
used to aspirate blood and arterial solution that have been collected into the autopsied cavities; goes into open cavity to aspirate excess drainage

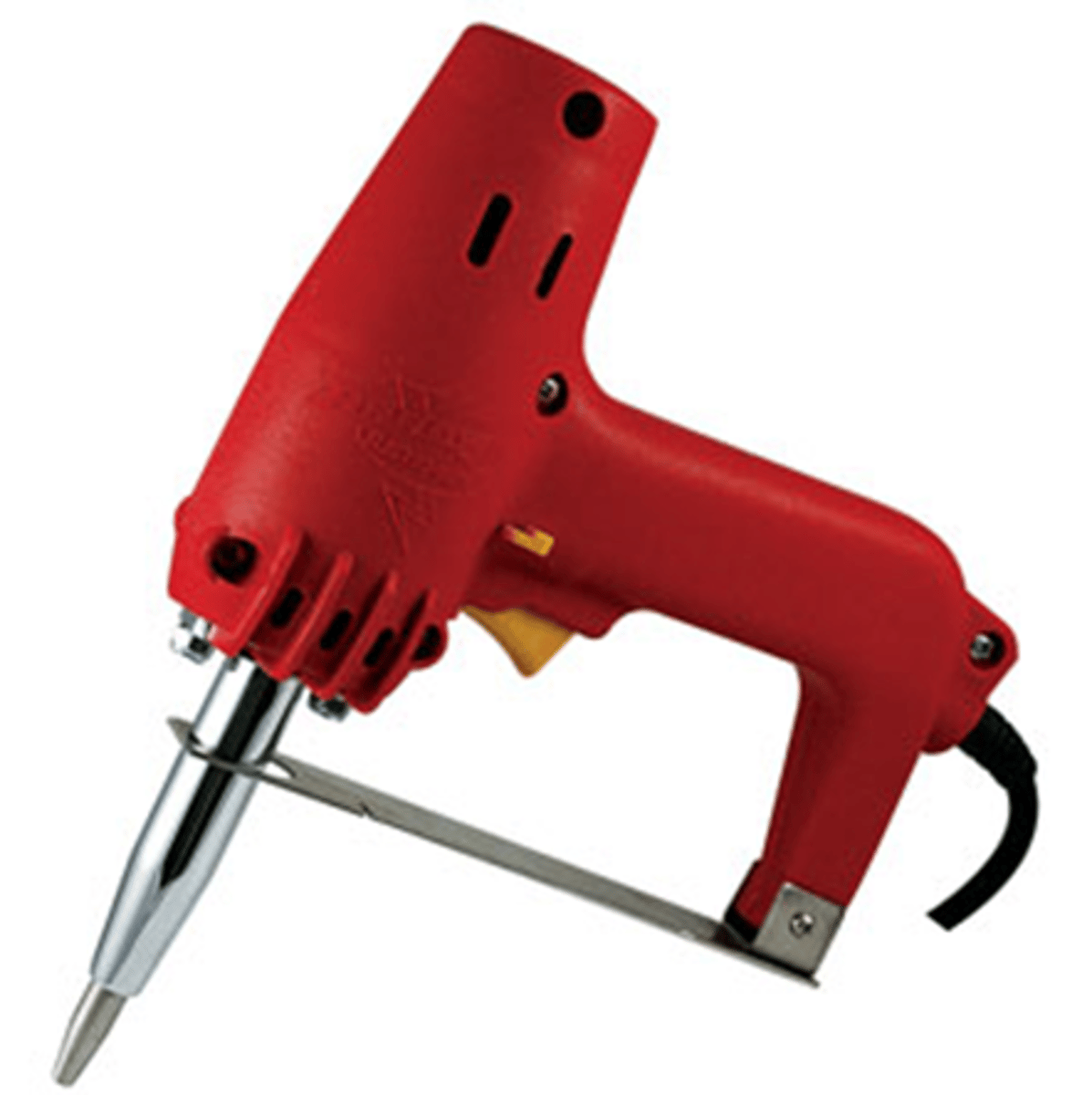
electric needle injector
electric device used to embed a barb attached to the end of a metal wire into the mandible and maxilla for closure of the jaw in a fixed position

injection brads/needles
wires that are twisted together to close the mouth
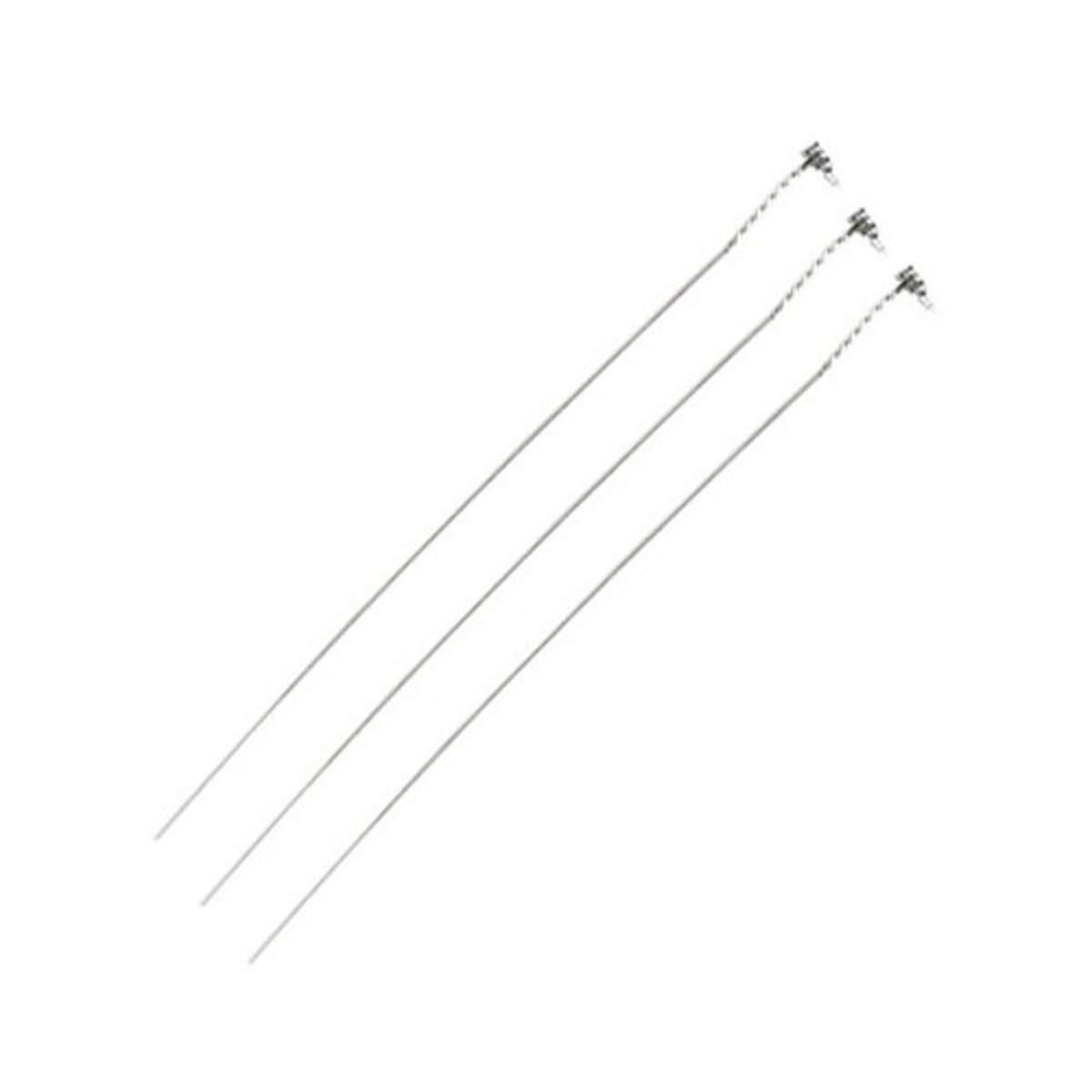

manual needle injector
manual device used to embed a barb attached to the end of a metal wire into the mandible and maxilla for closure of the jaw in a fixed position
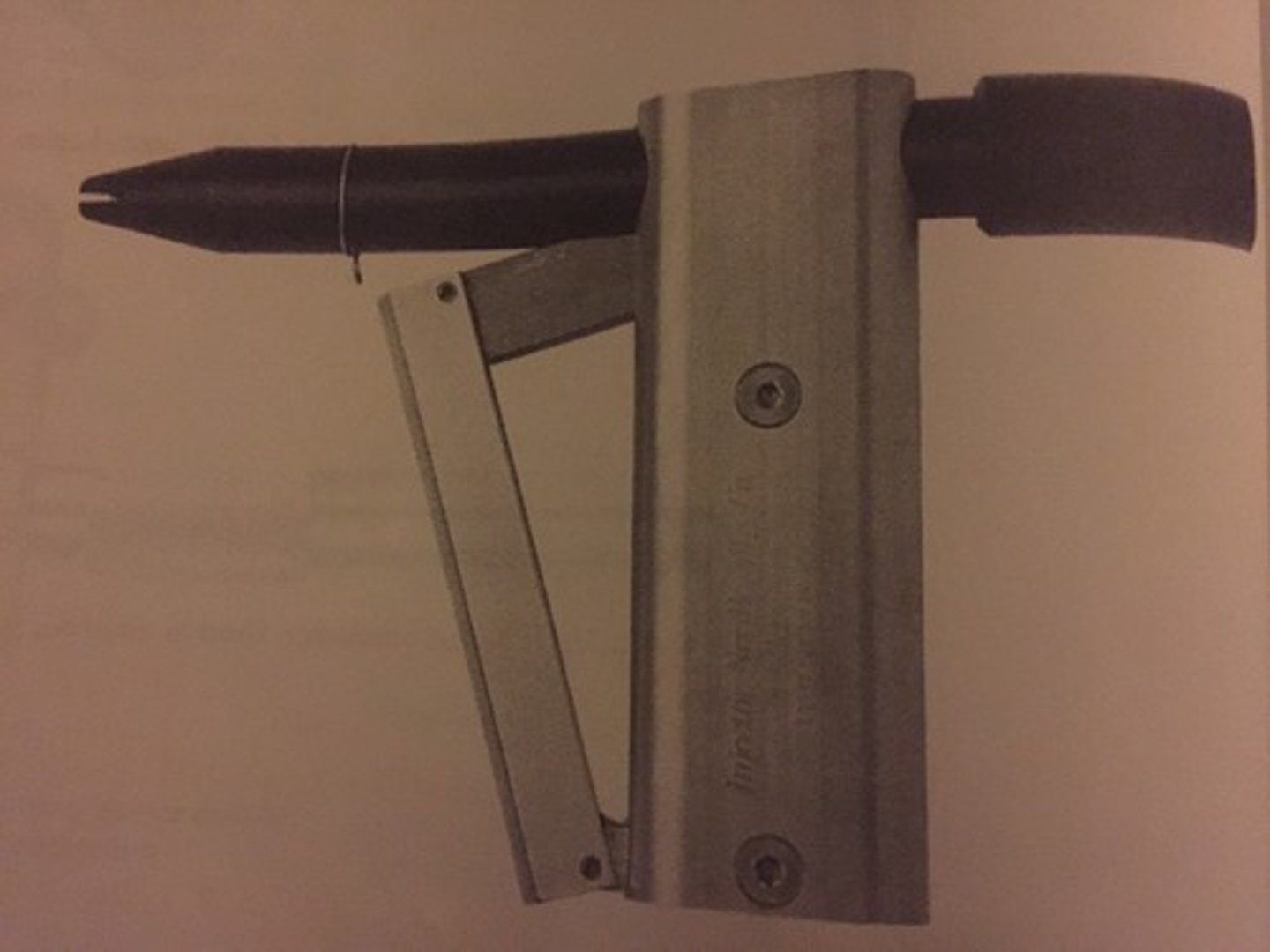
hypovalve trocar
designed for hypodermic injection only, the valve in thumb controlled to start and stop the flow of the solution
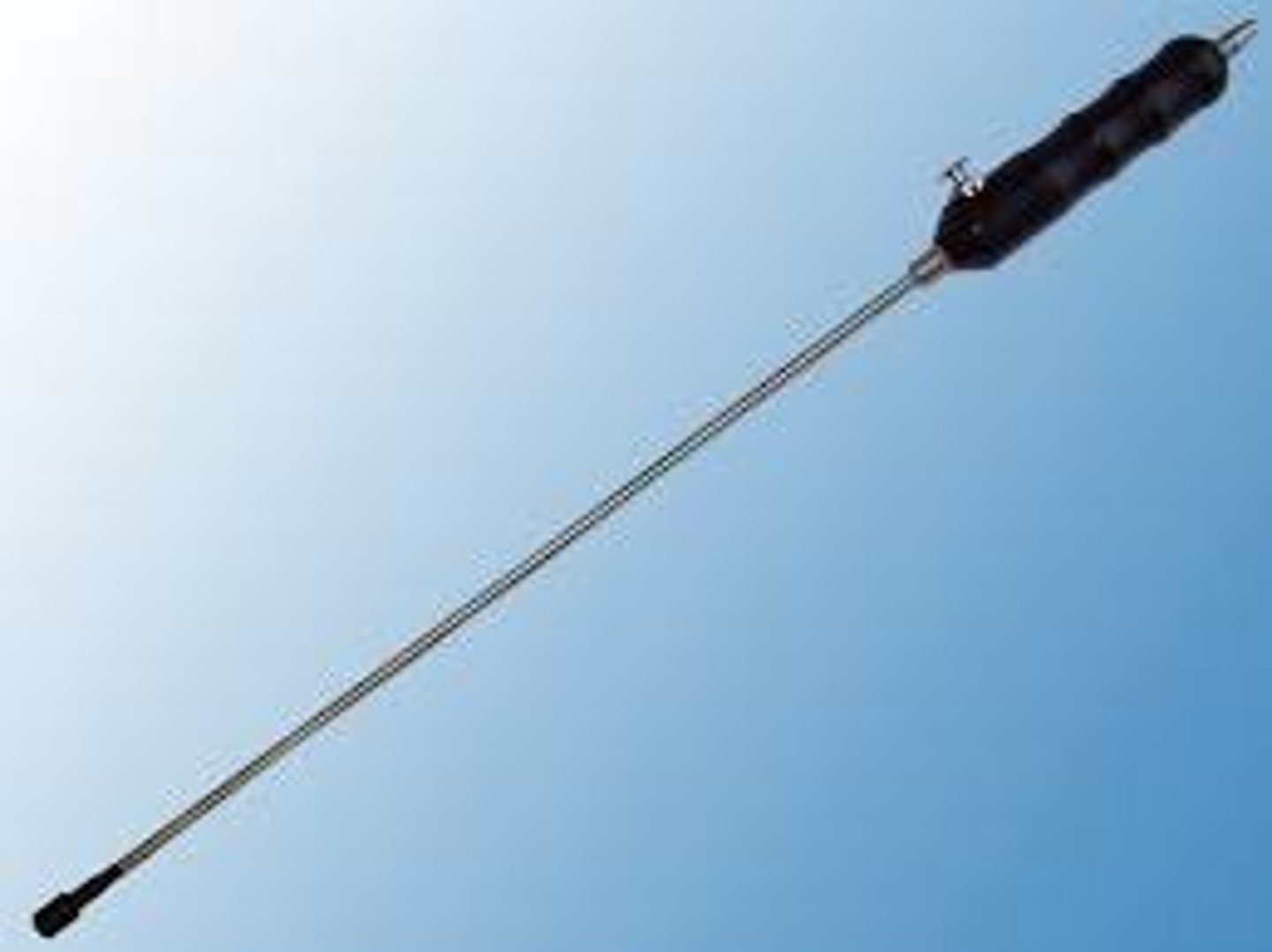

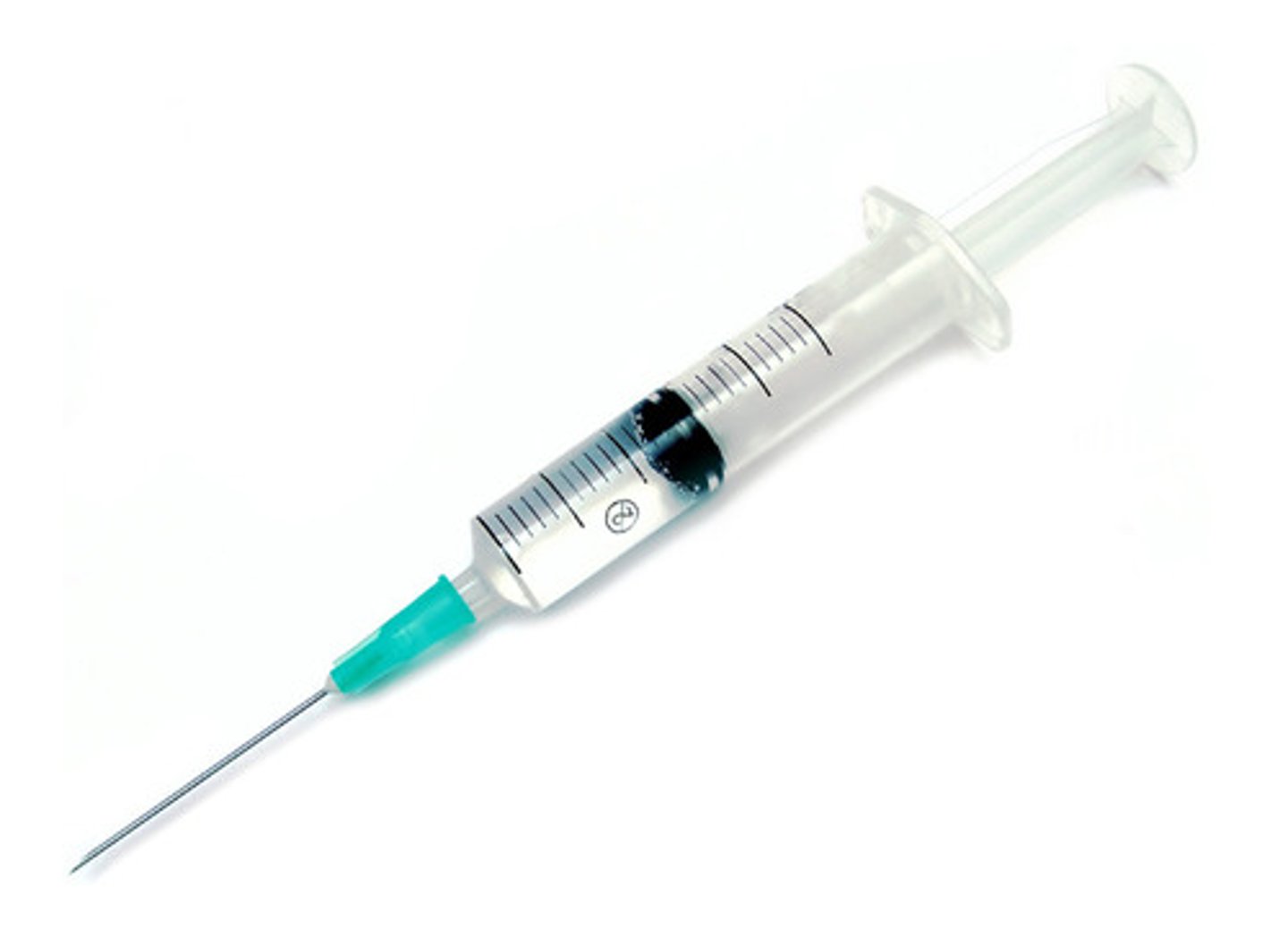
hypodermic syringe
used to inject embalming solution into areas that are more delicate; can be used to inject tissue builder
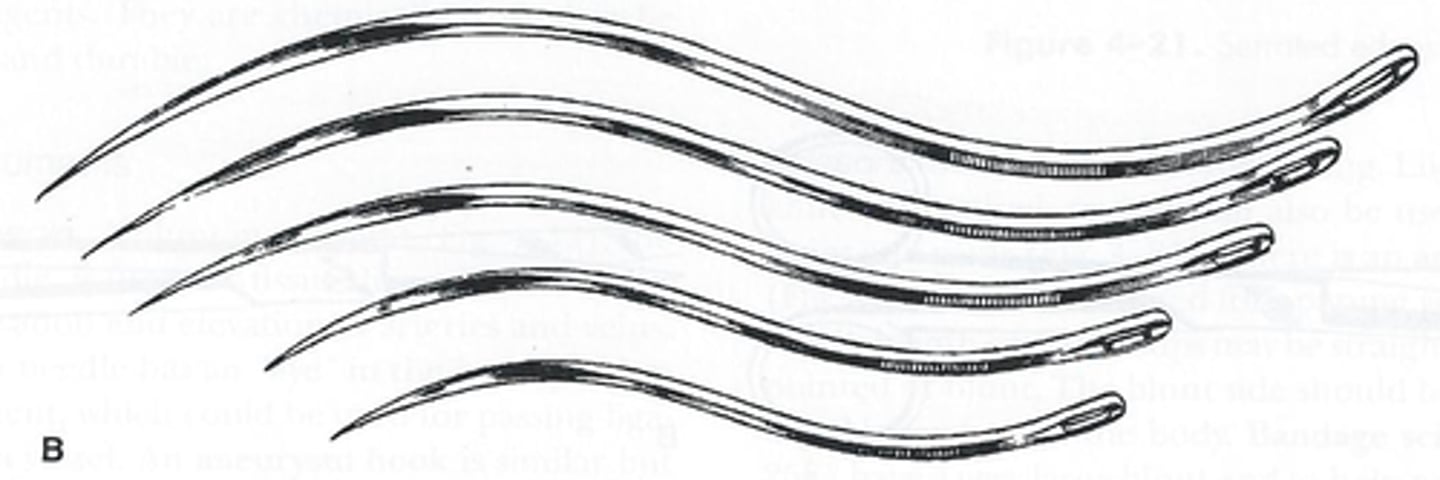
suture needles
used to close incisions (half-curved, double-curved, circle, and loopuypt)
eyecaps
plastic disks inserted beneath the eyelids to maintain closure and contour the closed eye; may be clear or opaque
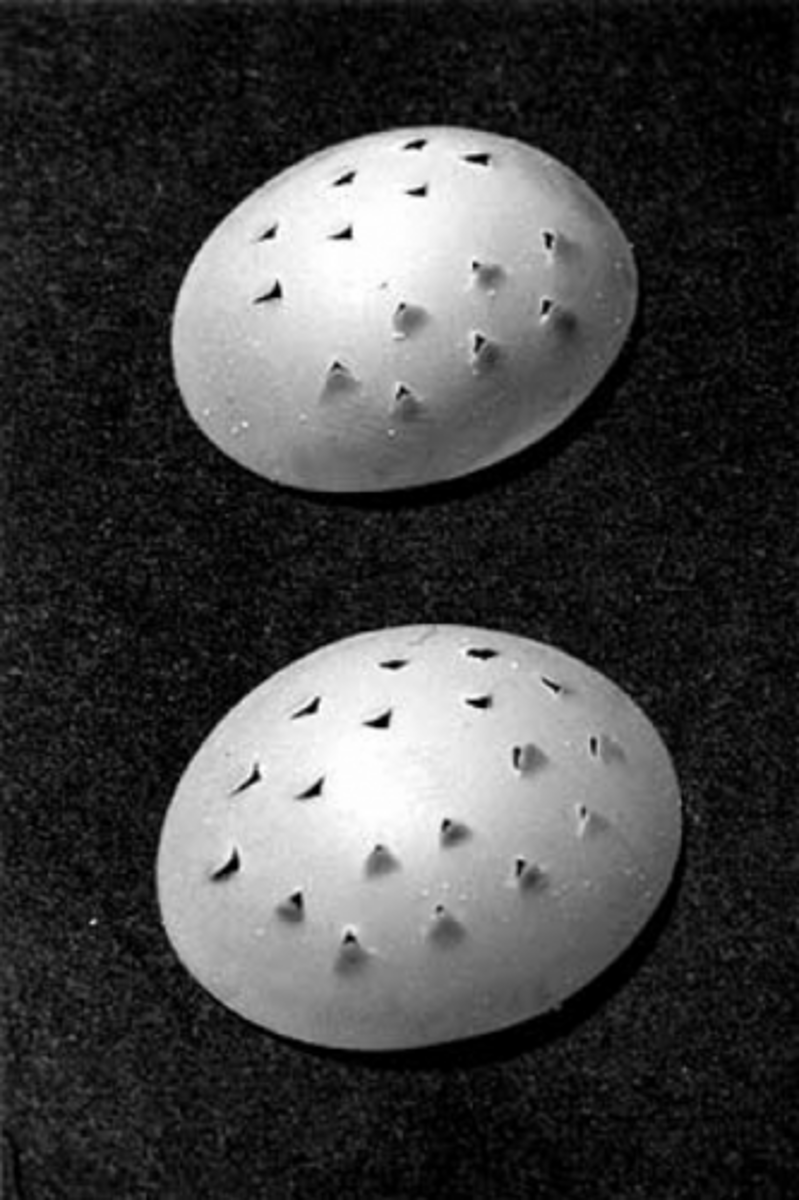

trocar buttons (and applicator)
used for closing the trocar insertion site
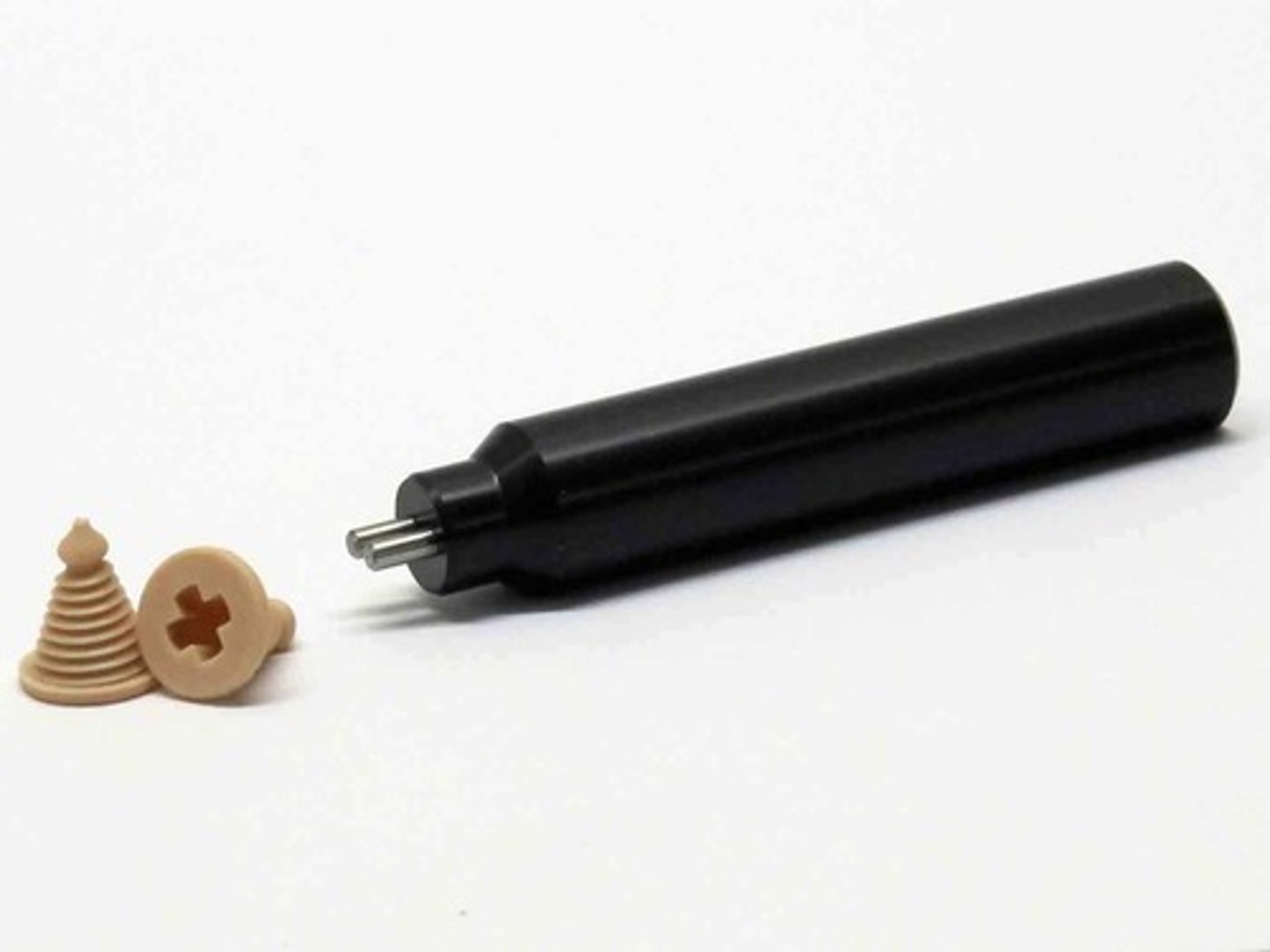

mouth formers
plastic devices used to maintain closure and contour of the mouth; may be clear or opaque
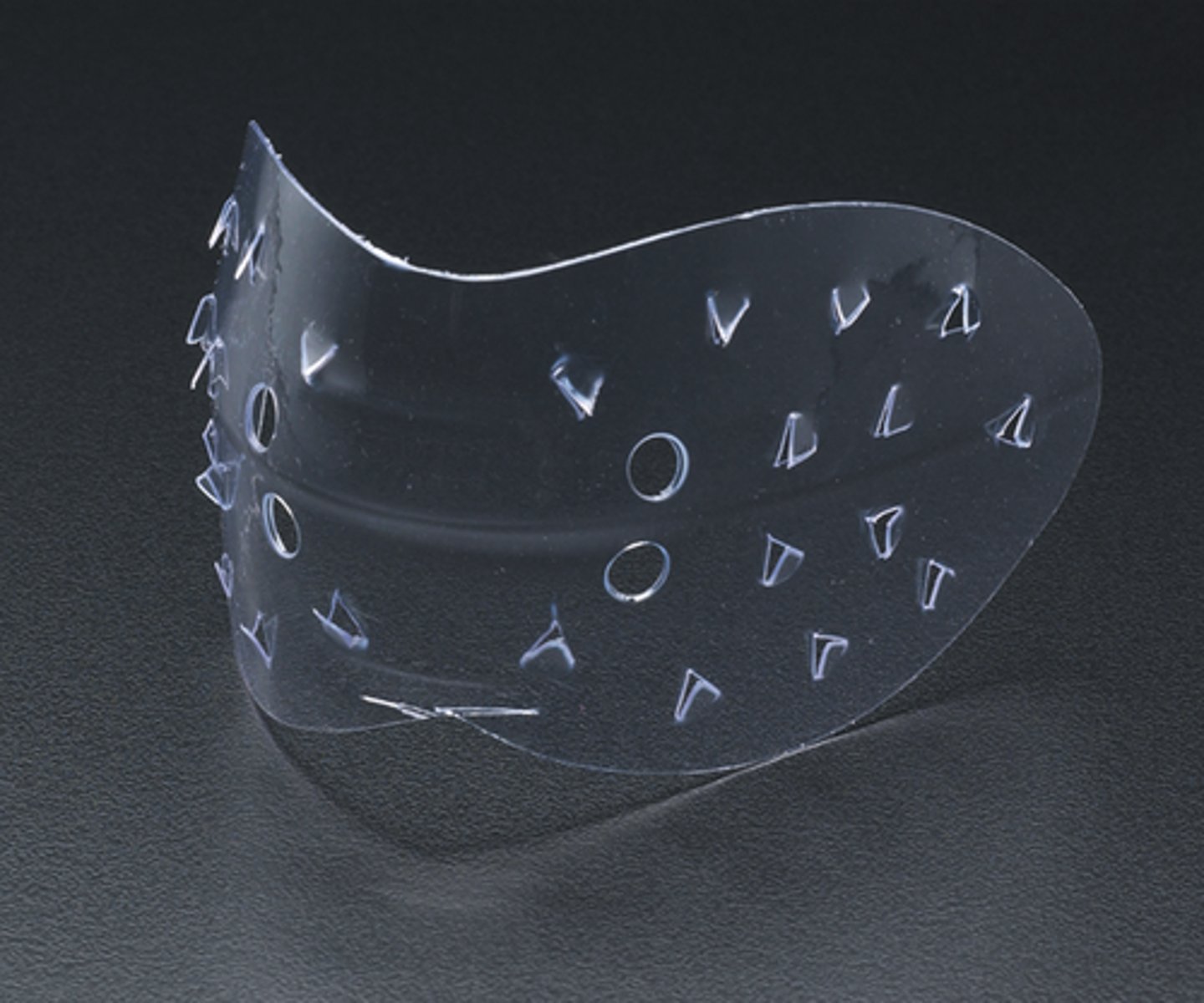

A/V closure (anal/vaginal)
used to stop leakage from the anus or vagina; has a channel that can be filled with absorbent powder
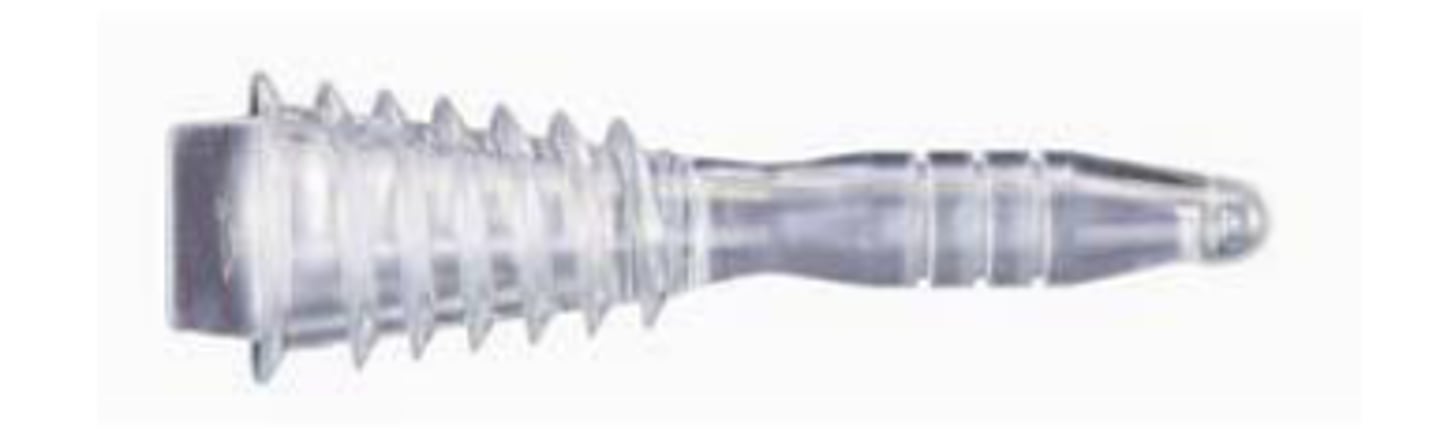

calvarium clamps
device used to fasten the calvarium to the cranium after a cranial autopsy

right-to-know laws
provide workers with direct access to information about the health risks of chemicals used in the workplace ; posting information for this information is mandatory
building permits
require detailed site plans and specifications to be submitted; plumbing, electrical, heating, and cooling systems and other construction requirements require these
Board of Health and a Board of Mortuary Science
Each state may have a _____________ of _____________ and a _____________ of _______________ Science that enact regulations governing the minimum standards for preparation rooms in that state
dressing room
room used for purposes other than arterial embalming, also called a holding or staging area
epoxy
___________ coatings on floors provide a seamless and nonslip surface that is easy to clean and disinfect
12-20
A number of states have adopted ___-___ air exchanges per hour for an average size embalming room
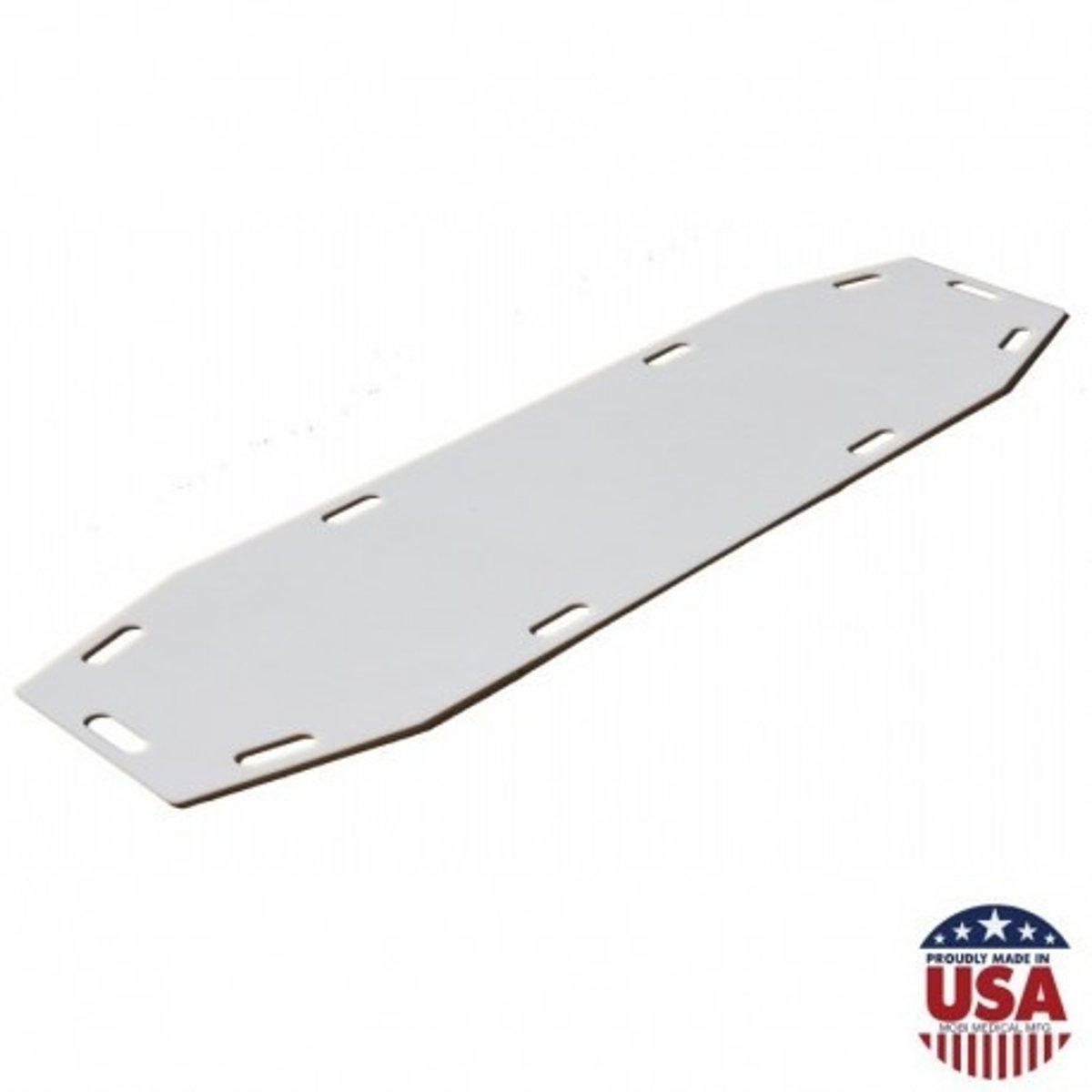
body transfer board
strong, nonabsorbent, and easily cleaned, placed beneath the body and used to move the remains from the mortuary cot to the embalming table

pressure
the force required to distribute the embalming solution throughout the body and is measured in pounds per square inch
potential pressure
the pressure reading on the gauge of the centrifugal machine, indicating the pressure in the delivery line of the machine with the rate-of-flow valve closed of the arterial tubing clamped shut
differential pressure
the difference between the potential pressure and the actual pressure reading; this is an indicator of rate of flow
actual pressure
the reading on the pressure gauge on the centrifugal pump when the rate-of-flow valve is open and the arterial solution is entering the body
stopcock
attaches to the delivery hose; stops and starts the flow of fluid from the arterial tube into the artery without turning the machine off
trocar
long hollow needle used for cavity aspiration and injection
separator (incision spreader)
holds an incision open
human remains (dead human body)
body of a deceased person, can include cremated remains
Thanatology
study of death
moribund
in a dying state; in the agonal period
death rattle
noise made by a moribund person caused by air passing through a residue of mucous in the trachea and posterior oral cavity
death struggle
semi-convulsive twitches that often occur before death
cadaveric spasm (instantaneous rigor)
immediate stiffening of the muscles of a dead human body
apparent death
the manifestations of life are feebly maintained
somatic death
death of the organism as a whole
cellular death
death of the individual cells of the body
antemortem
before death
postmortem
after death
clinical death
phase of somatic death lasting from 5-6 minutes during which life may be restored (e.g. CPR)
expert tests
tests performed by a medical professional (ex: stethescope, ophthalmoscope, EEg, EKG, evoked response, etc)
inexpert tests
tests performed by anyone that isn't a medical professional (ex: mirror fogging, ligature test, ammonia injection test, pulse, listening for respiration/heartbeat)
clinical death, brain death, biological death, and postmortem cellular death
the stages of somatic death:
clinical death
occurs when spontaneous respiration and heartbeat irreversibly cease
brain death
Occurs in a sequence of events that are a function of time without oxygen; the first part of the brain to die, usually in 5-6 minutes, is the cerebral cortex, next the midbrain dies, followed by the brain stem
biological death
the irreversible phase of somatic death and represents the cessation of simple bodily processes; the organs of the body no longer function
postmortem cellular death
the process during which individual cells die; may take a matter of hours depending on numerous variables
necrobiosis
the physiological or natural death of cells as they complete their life cycles
necrosis
the pathological death of body cells as a result of death processes (ex: gangrene)
agonal period
the period occurring just before death
agonal algor
cooling or decrease in body temperature just prior to death
agonal fever
an increase in body temperature just prior to death
agonal hypostasis
the settling of the blood in the dependent tissues of the body
agonal coagulation
occurs as the circulation of the blood slows and the formed elements of the blood begin to clot and congeal
agonal capillary expansion
the dilation of pores within the capillaries in an effort to send more oxygen to the tissues and the cells
agonal edema
an increase in the amount of moisture, or fluids, in the tissues and the body cavities
agonal dehydration
a decrease in the amount of moisture, or fluids, in the tissues and the body cavities
agonal translocation
redistribution of endemic microflora (bacteria) on a host-wide basis immediately before death
translocation
the movement of microorganisms from one area of the body to another
physical changes
affect the nature of the body (temperature, color, etc.) but not the fundamental structure of it
chemical changes
alter the molecular and chemical makeup of the body
antemortem subcutaneous emphysema
a distension of the body tissues by the presence of gas or air beneath the skin; antemortem condition brought about by a surgical procedure, trauma, or by the puncture or tear in the pleural sac or the lung tissue
gas gangrene
necrosis in a wound infected by an anaerobic gas-forming bacillus, the most common etiologic agent being Clostridium perfringens
chemotherapy, blood thinners, antibiotics, and vasodilators
agonal changes may be affected (lessened/increased) by certain therapeutic agents:
algor mortis
postmortem cooling of the body
intrinsic factors (endogenous)
factors WITHIN the body
extrinsic factors (exogenous)
factors involving the surrounding environment
hypostasis
blood and/or other fluids settling to the dependent portions of the body (can occur both antemortem and postmortem)
cadaveric lividity (livor mortis)
intravascular red-blue discoloration resulting from postmortem hypostasis of blood (can normally be removed through vascular embalming)
dehydration
loss of moisture from body tissue which may occur antemortem or postmortem
contact pallor
the areas where blood movement has been inhibited
imbibition
the ability of the cells to draw moisture from the surrounding area into themselves
sludge
the formed elements of the blood sticking together to form clumps
agglutination
intravascular; increase in viscosity of blood brought about by the clumping of particulate formed elements in the blood vessels
antemortem and postmortem
translocation of microorganisms can be both __________________ and ____________________
decomposition
separation of compounds into simpler substances by the action of microbial and/or autolytic enzymes