Lab Ck 4: Respiratory and Digestion
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Respiratory System
system that supplies body with oxygen and rids it of carbon dioxide waste
External nose
externally visible portion of the nose
function=entrance of oxygen through nostrils
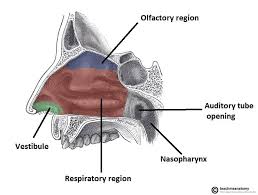
nasal cavity
internal portion of nose
lined with mucosa and made of pseudostratified columnar epithelium
bottom portion is formed by palates
function=warm, filter, and moisten air and to act as a resonating chamber
nasal septum
separates the nostrils
formed by vomer, ethmoid bone, and septal cartilage
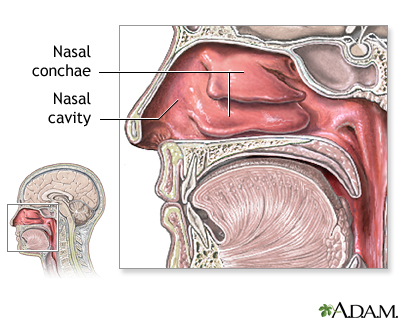
nasal conchae
inside the nasal cavity
comprised of superior, middle, and inferior
function= warm, moisten, and filter air and increase surface area to trap large particles
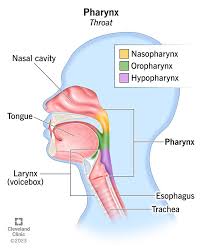
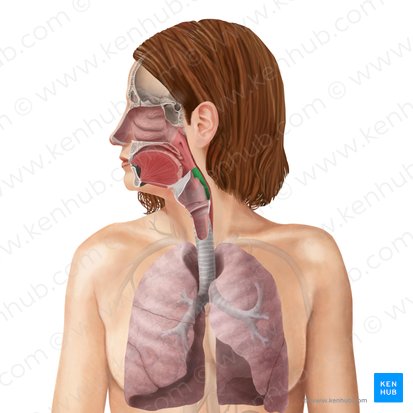
pharynx
passageway for both air and food
3 subdivisions
nasopharynx
superior portion of the pharynx
posterior to nasal cavity
provides a passageway for air from nasal cavity
has tonsils to protect from pathogens
laryngopharynx
extends from epiglottis to larynx
function=passageway for air and swallowed foods
includes tonsils to protect from pathogens
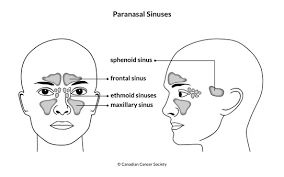
paranasal sinuses
surround the nasal cavity and are named for the bone in which they are located
function= resonance chambers for speech and warm/moisten air
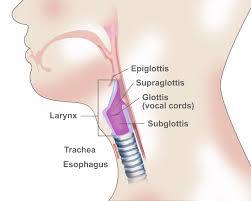
larynx
AKA voice box
connects laryngopharynx to trachea
function=air passageway, prevents food from entering lungs, voice production
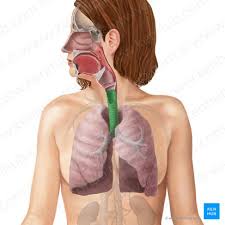
trachea
AKA windpipe
function= air passageway
solid c shaped cartilage allow food to pass while maintaining open passageway
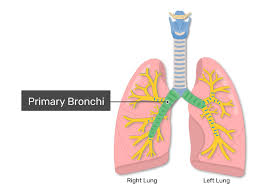
primary bronchi
where the trachea divides into 2, left and right bronchi
right one is wider, shorter, and more vertical
bronchioles
branch off of bronchi
passages less than 1 mm in diameter
branch off even more
bronchial tree
continual branching of respiratory passageways of the lungs
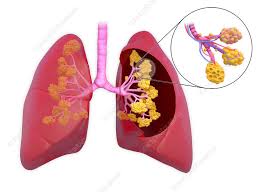
alveoli
small balloon like expansions
where gas exchange takes place
made up of squamous epithelium
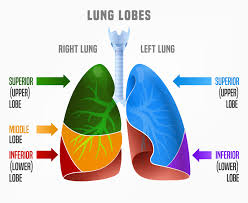
lungs (all lobes)
Right side: superior, middle, inferior
Left: superior, inferior
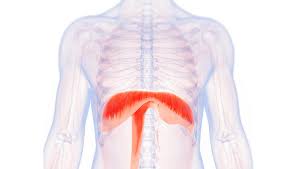
diaphragm
dome shaped muscle below the lungs that is essential to respiration
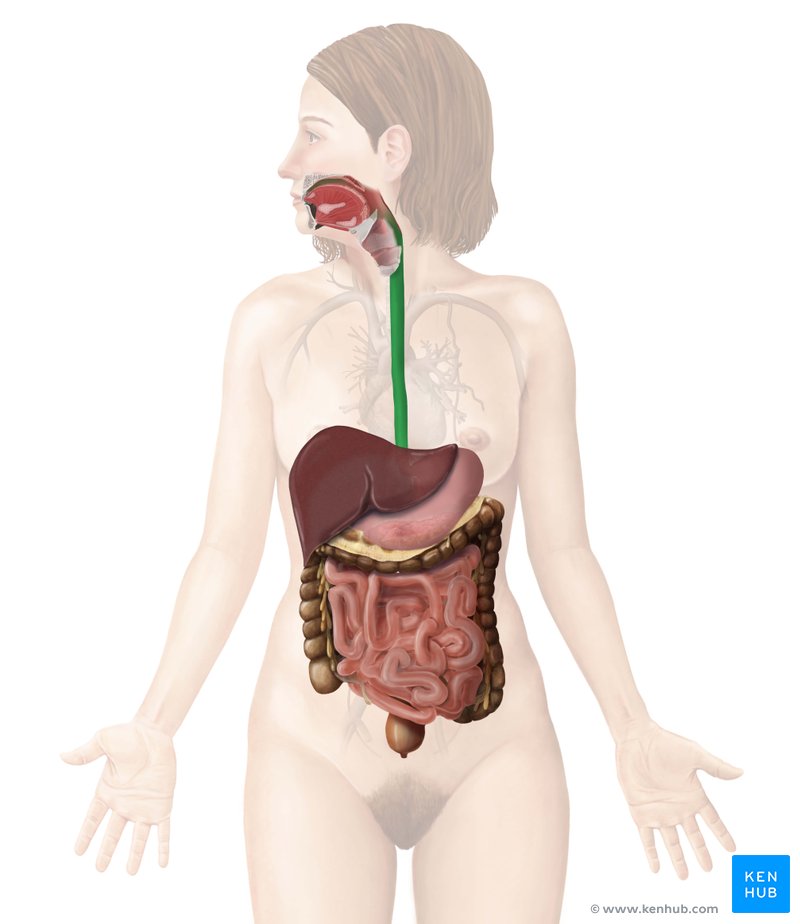
digestive system
provides the body with nutrients, water, and electrolytes needed for survival
ingests, digests, absorbs, and eliminates
alimentary canal
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine
gastrointestinal tract
AKA alimentary canal
accessory digestive organs
teeth, salivary glands, gallbladder, liver, and pancreas
oral cavity
AKA mouth
mucus lined cavity
teeth, tongue, salivary glands
mouth
AKA oral cavity
lips
protect anterior opening
cheeks
for the mouths lateral walls
palate
forms the “roof” or superior portion of the mouth
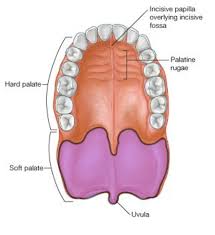
hard palate
anterior portion of palate
harder due to bones being under it
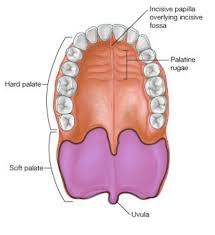
soft palate
posterior portion of the palate
no bone support
uvula
extension of the soft palate
function= swallowing, saliva production, preventing food from entering nasal cavity
tongue
muscle in the base of the mouth
function= speech, moving food while chewing,taste, swallowing
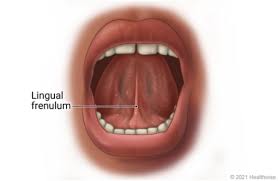
lingual frenulum
membrane that secures the tongue to the floor of the mouth
oral vestibule
space between the teeth and cheeks/lips
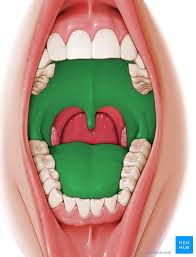
oral cavity
area that lies within the teeth and gums
tonsils
palatine tonsils: masses at the back of the mouth
lingual tonsils: back of the tounge
immune functions
esophagus
extends from laryngopharynx to the gastroesophageal sphincter
function= food passageway
wavelike motions
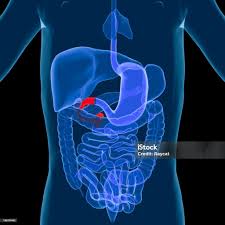
stomach
temporary storage unit for food and a place where mechanical and physical breakdown occurs
upper left quadrant
contains hydrochloric acid to breakdown food
viscous mucus secreted to protect stomach
lesser curvature
smaller curve of the stomach
greater curvature
larger curve of stomach
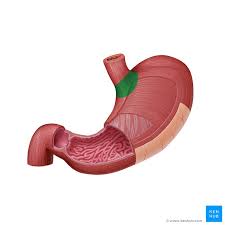
cardia
top area where food enters the stomach
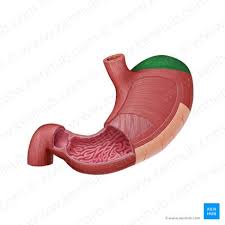
fundus
upper dome shaped region of the stomach
body
large middle part of the stomach
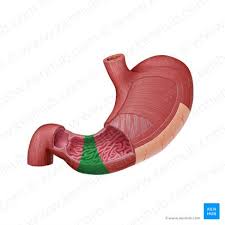
pyloric antrum
wider superior portion of the pyloric part
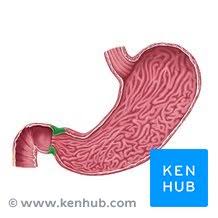
pyloric sphincter
valve that controls the stomach emptying inro the small intestine
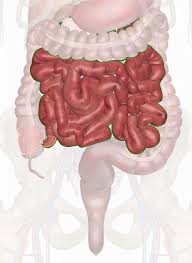
small intestine
long tube where almost all absorption takes place
3 subdivisions
duodenum
portion of small intestine that extends from pyloric sphincter to head of pancreas
jejunum
portion of small intestine that extends through most of the umbilical portion of the abdominal cavity
ileum
region of small intestine that is inferior and on the right of the abdominal cavity
pubic region
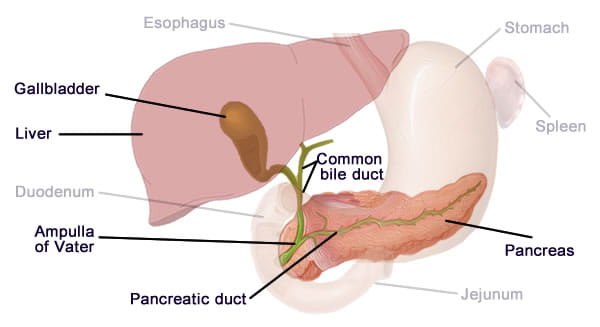
bile duct
tube that carries bile
area where bile enters the duodenum
microvilli
microscopic projections in the small intestine
increases the absorption
villi
fingerlike projections in the small intestine
on the mucosa tunic
increases absorption
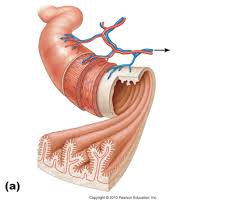
circular folds
deep folds in the mucosa and submucosa layers of the small intestine
spiral chyme to mix and slow it
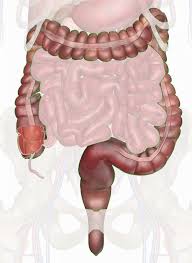
large intestine
extends from ileocecal valve to anus
3 subdivisions
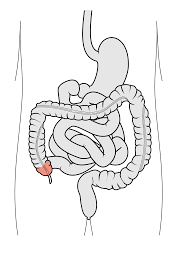
cecum
first part of the large intestine
absorbs fluids and lubricates waste
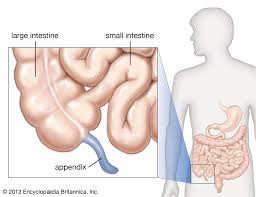
appendix
small finger like organ attached to the cecum of the large intestine
lower right abdomen
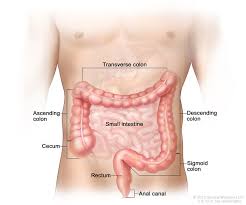
colon
longest part of the large intestine
absorbs water and some nutrients
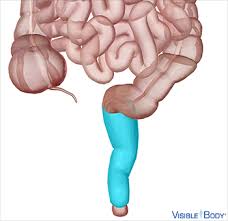
rectum
final portion of the large intestine
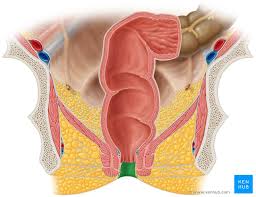
anal canal
tube at the end of the rectum
connects the rectum to the anus
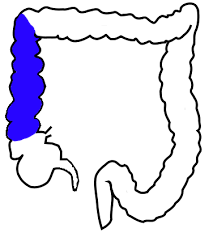
ascending colon
first part of the colon located on the right side
extends upward from cecum

transverse colon
part of colon that stretches across the abdomen, middle and longest part of the colon
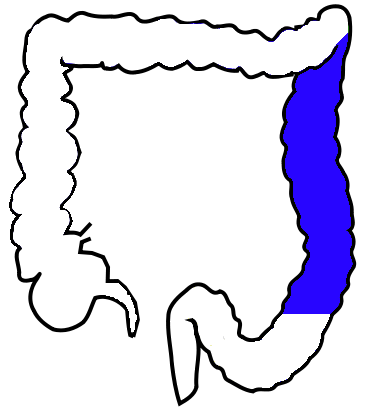
descending colon
part of the colon that begins to descend, located on the left side
descends into the sigmoid colon
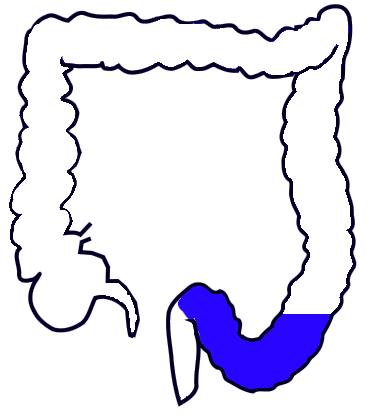
sigmoid colon
final part of the colon that joins with the rectum
pelvic region
anus
opening to the exterior of the body that excretes waste
teeth
accessory organ that mechanically begin digestion
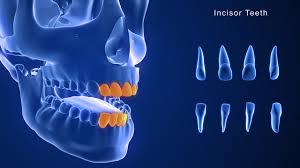
incisor
chisel shaped
best at shearing action used to bite
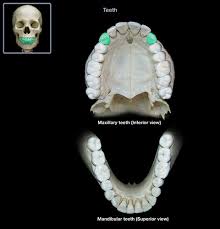
canines
cone shaped
tearing food
premolars
2 cusps used to gride
molars
broad crowns with rounded cusps used to grind
dental formula
designates the numbers, types, and positions of teeth in one side of the jaw
salivary glands
glands that secrete saliva
helps with digestion, swallowing, and oral health
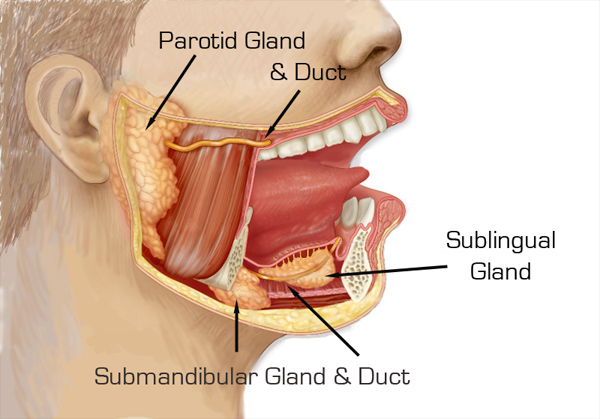
parotoid glands
large glands anterior to the ear, ducting over the second upper molar
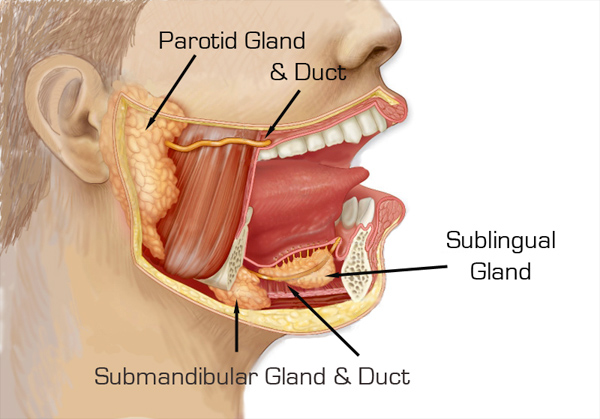
submandibular glands
medical aspect of the mandibular body in the floor of the mouth, ducting under the tounge to the base of lingual frenulum
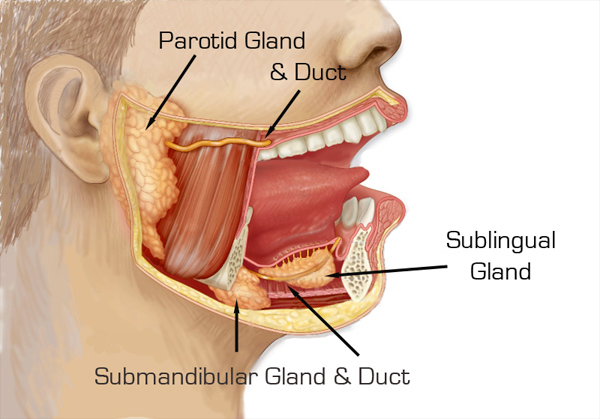
sublingual glands
anterior to the floor of the mouth, empty under the tongue
liver
produces bile to breakdown fats
common hepatic duct-bile duct
inferior to the diaphragm, more the the right than to the left
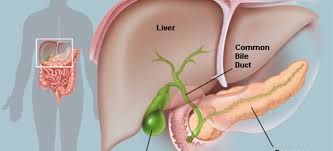
gallbladder
small green sac inferior to the liver
where bile backs into when digestion is not taking place
cystic duct
pancreas
produces enzymes to neutralize the acidic chyme