ANSC 1401 - Growth, Development & Reproduction
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Dr. Jackson
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
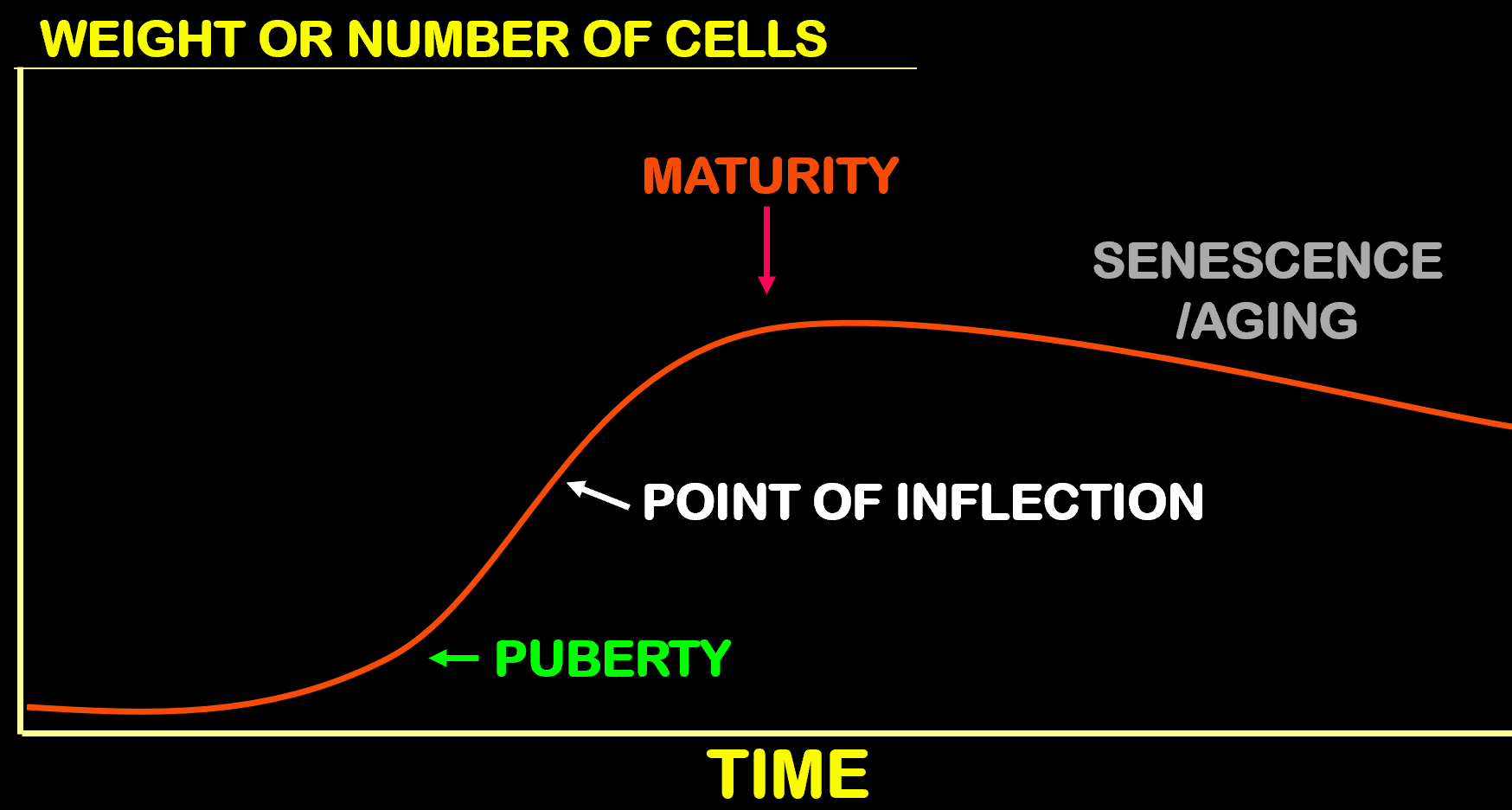
What is Growth? Why do we measure it that way?
A net increase in the body’s protein
We measure protein because it is the most difficult to put on and take off of an animal
Fat, bone, and water are omitted because of how quickly it puts on weight and how quickly it is excreted
Average Daily Gain (ADG) Formula
(Final Weight - Initial Weight) / Number of Days
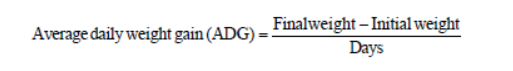
Growth Curve
Weight per Day of Age (WDA) & Formula
WDA contains an animal’s birth weight
It is NOT effective when measuring feed efficiency
Weight / Age in Days
Higher ADG/WDA
Both are desirable, but there is a limit
Sometimes need to back off to prevent metabolic issues such as acidosis
Needs to be a balance between amount feed fed and rate at which it is fed
The higher ADG/WDA is, the sooner an animal will go to the market, the less time it spends in a facility, and the expenses are lower.
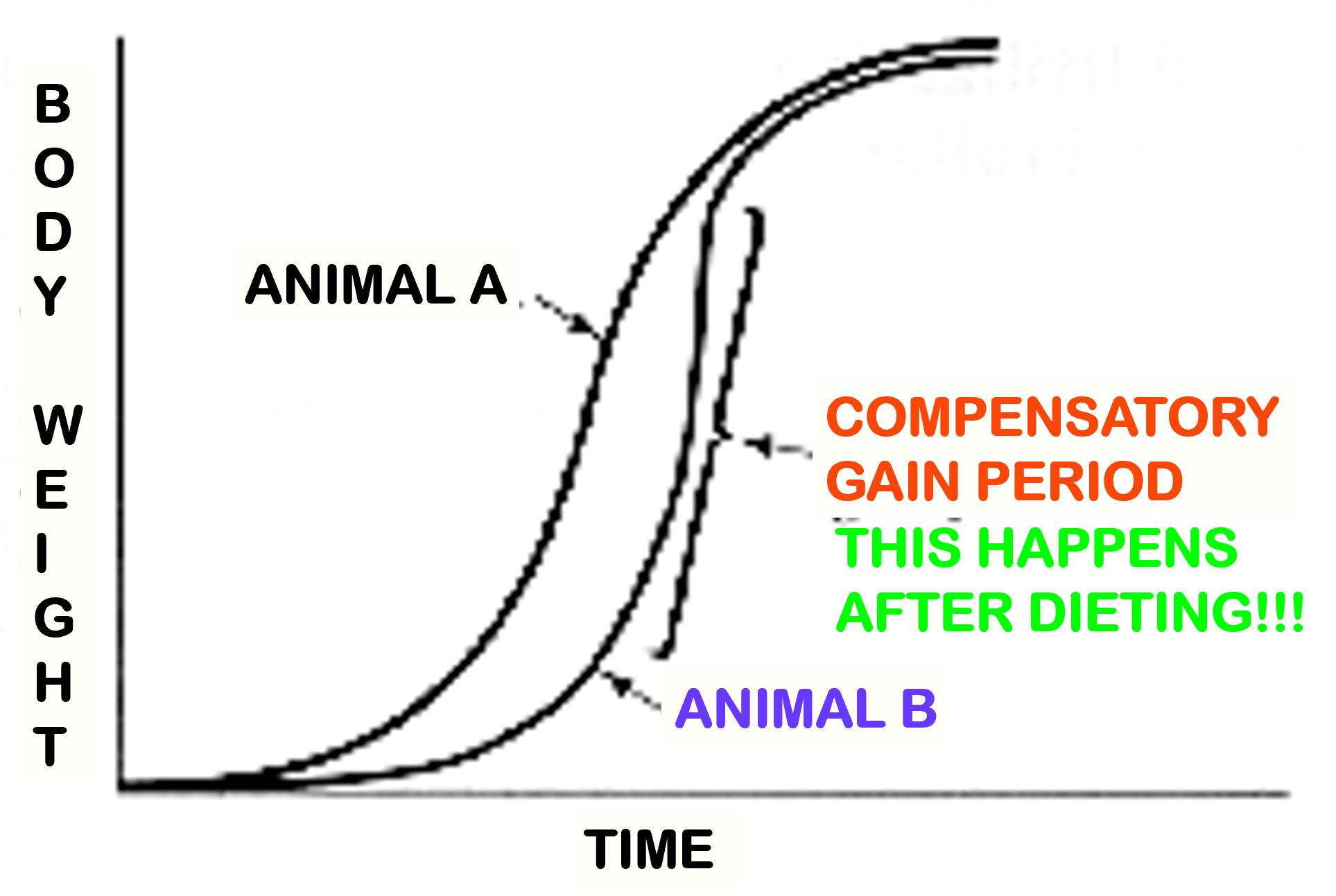
Compensatory Gain
A faster than normal rate of gain after a period of feed restriction
Who benefits from Compensatory Gain?
Cow/Calf operators & Slaughterhouses DO NOT
Cannot withhold milk from calves, mothers typically sold
Slaughterhouses only sell meat, not the steer itself
Yearling Operators & Feedlots DO
Able to purchase cows at a smaller weight or have a skinnier build from being weaned and fed slow
Feedlot: If hard winter passes, yearling operations will have cattle eating less, so, when transferred they are able to have compensatory gain from the feedlot grain
Body Weight Graph
Secondary Sex Characteristics
Characteristics that make a male look like a male and a female look like a female
Efficiency and Why it is Important
The number of offspring born alive
The more born alive, the more one can sell, and the more income that is made
Factors Influencing Efficiency
Physiology of the reproductive tract
Genetics
Nutrition of the Sire & Dam
Not too fat or thin
More sperm produced on moderate nutrition
Females have a minimum fat requirement
If under, will not be able to conceive
Season/Daylength
Environmental Factors
Gestation Periods and Breeding/Birthing of Farm Animals
Swine: 3 month, 3 week, 3 day gestation; 2-3 litters per year
Sheep: 5 month gestation; breed in fall, lamb in spring
Cattle: 9 month gestation; year-round breeders
Horses: 11-12 month gestation; breed in spring, foal next spring
Heat vs Cold in affecting Efficiency
Heat
Anti-reproduction
Reduces efficiency in females
Causes sterility in males
Cold
Only extreme cold will cause issues
Testicle
Primary sex organ
3 Main Functions:
Produces sperm, sperm cells, and hormones
Endocrine: produces hormones (testosterone)
Seminiferous Tubules: Sperm cells are made
Germinal: Sperm is produced
Spermatogenesis
Epidiymis
Site where sperm cells are stored, mature, and become fertile
Vas Deferens
Tube that transports sperm from the Epididymis to the Urethra
Ampulla
Only found in rapid ejaculators: Bull, Ram & Billy
Acts as a temporary depot for sperm
Penis
Passageway for urine and semen
Two types:
Fibroelastic: has the sigmoid flexure — bull, boar & ram
Vascular: does not have a sigmoid flexure — stallion & dog
Sigmoid Flexure
S-shaped curve that retracts and extends the fibroelastic penis
Scrotum
Contains and protects the testicles as well as regulate the temperature
Contains the cremaster muscle: pulls testicles closer to the body cavity in cold weather and will drop them in hot weather
Monorchid vs Cryptorchid
Mono: One testicle fails to descend from the body into the scrotum
Crypto: Both testicles fail to descent
Castration
The removal of the testicles
Produces a barrow, steer, gelding, or whether
Effects of Castration
Slower growth
Fatten quicker
Higher meat quality
Less attitude/behavior problems
No secondary sex characteristics
GnRH (Gonadotropic Releasing Hormone)
Released from the hypothalamus
Stimulates the Pituitary Gland to release LH and FSH
LH (Luteinizing Hormone)
Released from the pituitary gland
Stimulates the secretion of testosterone in males
Stimulates the ovary to release a mature egg in females
FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone)
Released from the pituitary gland
Stimulates sperm development in males
Stimulates estrogen production in females
Prolactin
Starts and maintains milk production
Oxytocin
Stimulates milk letdown, contractions, and egg drop
Estrogen
Produced from an ovary follicle
Stimulates the development of secondary sex characteristics, duct growth in the mammary glands, and the “heat” period of a female
Prepares the uterus for pregnancy
Progesterone
Produced from a Corpus Luteum
Prepares the uterus for pregnancy
If female is pregnant, it will prevent ovulation for the time being
Maintains the pregnancy
Develops milk secreting tissue
Relaxin
Aids in birth/labor
Softens/relaxes the cervix for dilation
Ovary
Primary Sex Organ
Multi-functional
Produces estrogen and ovum (eggs)
Vulva
External genitalia
Vagina
Copulatory organ
Cervix
Separates the Vagina from the Uterus
Protective barrier!
Uterus
Also known as the womb
Houses developing offspring
Uterine Horn
Fetus attachment site
Infundibulum
A funnel-shaped portion of the Fallopian Tube that picks up the egg/ovum after it has been ovulated
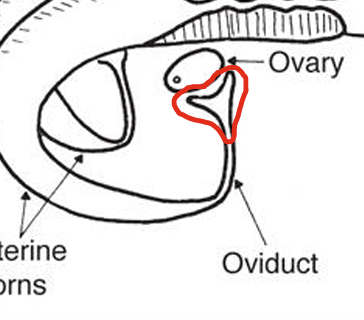
Oviduct
Also known as the Fallopian Tube
Transports the ovum and sperm
Fertilization site
Corpus Luteum
Not an organ
“Yellow body” that forms in the follicle of an ovary and released to prepare a uterus for pregnancy
If pregnancy occurs, it will release hormones to maintain said pregnancy
Types of Placenta
2 types depending on the species
Diffuse: Sows and Mares (solid)
Cotyledonary: Cows and Ewes (spotty)
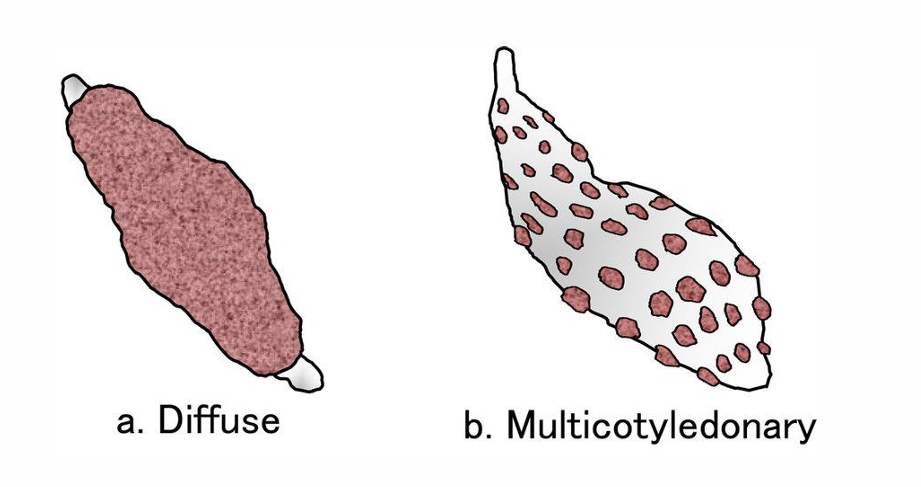
Functions of the Placenta
Transfers nutrients
Transfer of young’s waste
Protects from shock
Prevents microbe transmission
Secretes hormones
Artificial Insemination
The deposition of sperm collected from a male into a female when in estrus
AI Advantages
Greater use of superior males
Semen can be used after a males death
No attitudinal issues
No maintenance required in a sire
AI Disadvantages
Unproven sires can lead to poor genetics
Increased chance of inbreeding
Detection of a female in heat
AI Semen Collection Techniques
3 ways depending on species
Artificial vagina: Stallion
Mechanical Manipulation (Gloved Hand): Boar
Electrical Stimulation: Bull
What aspects of semen are important?
Concentration will dictate the number of sperm in an ejaculate
The higher the concentration, the more sperm that will exist within the ejaculate
NOT VOLUME!
Motility
No Abnormalities
Why do we dilute semen? What do we dilute it with?
It helps with the storage of semen as it is usually frozen for shipping
Diluted with:
Egg-yolk citrate
Milk
Fruit and Vegetable Juices
Glycerol and Antibiotics
Why do we store semen? How do we?
When shipping, semen must be properly stored so the sperm do not die.
Multiple methods of storage:
Straws: Most common/efficient
Others: Pellets, ampules and freeze drying
Semen Storage: Refrigeration vs Freezing
Semen can be frozen -320°F (or -196°C) or refrigerated depending on the species
Stallions: 1 day
Bulls: 3 days
Boars: 5-7 days (Does not freeze well)
Freezing (in liquid nitrogen)
Most semen can last up to 50+ years if the procedure is done properly
Semen Storage: Thawing
If semen is frozen to be stored, at some point it will need to be thawed. There are 2 thawing methods used.
Water: fastest
Ice water: slowest
What is estrus synchronization? What methods do we use?
Prostaglandins and Progestins are used
Both mimic hormones like Progesterone
We can release hormones with several different methods:
CIDR (Controlled Intervaginal Drug Release): most common, releases progesterone
Megestrol Acetate (MGA): Delays estrus
Lutalyse: Can be injected or mixed in feed, controls timing of estrus, may not be as accurate
Regumate: Oral medication that suppresses estrus
How do we detect females in heat? What do we use?
Look at their actions
Some will show more signs than others
Marker Animals
Males who have undergone a vasectomy (gomers)
A chin-ball marker will be attached to their chin
When they mount a female, mark is left on her back
Kamar Patch
Teasers
vasectomized/gomer males
When should a female undergo AI?
Waiting a certain time after estrus begins will increase the chances of conception
Cow: 12-18 hours
Ewe: 15 hours
Sow: 30 hours
Mare: Days 3, 5, and 7
What species in AI used the most in?
Dairy Cattle
Also the easiest
Second is swine
Which notable factor increases the birthrate of an offspring?
A larger father
When completing AI in a sow, where should the sperm be placed? Where should sperm be placed for other animas?
Sow: Cervix
Any Other: Uterus
Embryo Transfer
Using superovulation to produce multiple eggs/ova, fertilizing them, flushing them from the donor female, then distributing the embryos to other females in estrus
Other females must be in the same stage of the estrous cycle
Like surrogacy
What species in Embryo Transfer used the most in?
Beef cattle
Utilized the most by purebred breeders
Advantages of Embryo Transfer
Able to extend the productivity of superior females
Able to continue the productive life of a fertile female who is unable to carry offspring
Able to breed out of season
Important genetic material can be stored for future use
Disadvantages of Embryo Transfer
Can be expensive for the farmer/rancher
Can cause infertility in a superior female
Response to superovulation is variable between females
Embryo Transfer Procedure
Align the donor and recipient females in their estrus periods
Superovulate the donor using PMSG or FSH
Inseminate the donor
Flush the embryos from the donor’s uterus
Ensure the embryos have no abnormalities
Transfer the embryos to the recipients
Embryo Transfer: Synchronization
To align the estrus periods of females, we use CIDR roughly 3 weeks before the flushing procedure
Embryo Storage
Like semen, embryos can be stored via freezing and preserved until needed.
Just because the donor produces a good embryo does not mean it will do well in a ____
Recipient
You need a good donor AND a good recipient!
Embryo Transfer: Flushing the Embryos
Sheep and goats are NOT flushed like cattle
Cattle are flushed using a catheter, a minimally invasive, non-surgical procedure
Sheep and goats MUST undergo surgery
Usually surgery for AI too
When are the embryos collected from cows during embryo transfer?
Days 6-7
What is hyperplasia? What is hypertrophy?
Hyperplasia: An increase in the number of cells
Prenatal growth
Hypertrophy: An increase in cell size
Postnatal growth
Relative heat period of animals
Cattle: 12 days
Swine: 24 days
Goats: 24 days
Horses: 96 days
What species goes into heat most frequently?
Ewes
Which species ovulates the most per estrus?
Sows
They have big litters!
In what order to the corpus albicans (CA), corpus luteum (CL) and the corpus hemorrhagicum (CH) occur?
CH, CL, CA
Which species should never be ejaculated using an electro-ejaculator?
Stallion
How is AI performed in goats?
Same as it is in Cows
What is adde to semen to prevent cell membranes from rupturing when sperm cells are frozen?
Glycerol
How often should we check if a cow is in heat?
Twice a day
Does thawing sperm in warm water increase the chances of conception?
Yes
What position are ewes in when they are flushed for embyro transfer?
Upside down
Tilted at an angle
What is the average conception rate for AI in ewes and goats?
Around 70%
Is Estrus or Estrous longer?
Estrous
From which type of energy do we lose fecal energy?
Gross energy
What shape is the line on the growth curve?
S-shaped