UPDATED & FINAL Microbiology Polansky Cards, Clinical Laboratory Science Review (Micro), Clinical Microbiology Review - from Quick Review Cards for Medical Laboratory Science, 2nd Edition. Valerie Dietz Polansky, MEd, MLS (ASCP)
1/241
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
242 Terms
Cause Toxic Shock syndrome and food poisoning
S. aureus (cutaneous infections)
S. aureus is resistant to what antibiotic?
Penicillin
Common cause of hospital acquired UTI
Coagulase-negative staphylococci (CNS)
What is the hemolysis of S. aureus
Beta hemolytic
Novobiocin susceptible
S. epidermidis
Coagulase negative, Novobiocin Resistant Staphy
S. Saprophyticus
How does the catalase test work
Converts hydrogen peroxide to oxygen and water
Describe the pathogenicity of Group A Strep
Group A Strep (Strep Pyogenes)
1. Strep throat
2. Rheumatic fever
3. Glomerulonephritis
Oval GPC in chain and clusters
Streptococcus spp
Hemolysis of Group A Strep
Usually Beta heolytic ( wide zone)
What lysis RBCs, Platelets, and Neutrophiles in Group A Strep
Streptolysin O and Streptolysin S
To detect species that produce streptolysin O only, what must be done?
Stab into agar and place a coverslip over inoculum or incubate anaerobically
Group A is sensitive to what antibiotic?
Bacitracin
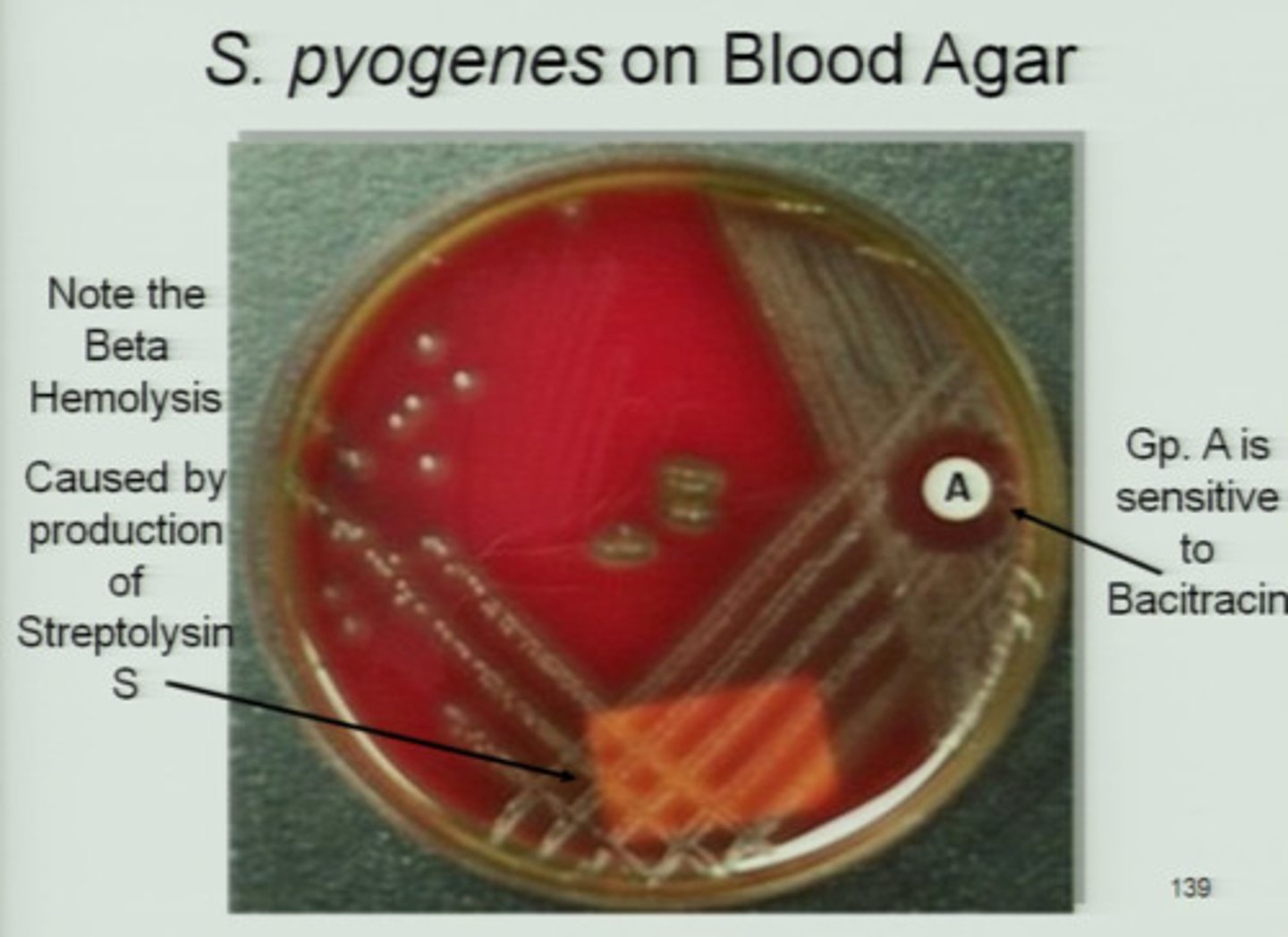
Group A is resistant and positive to?
Resistant to SXT and Positive to PYR
Most common cause of neonatal septicemia and meningitis
Group B Strep ( S. agalactiae)
Group B Strep:
Resistant to?
Positive?
Resistant to Bacitraacin/SXT
Positive for: Sodium Hippurate/CAMP
S. bovis is part of what Lancefield Group
Group D Streptococci
Group D Strep nonenterococci is normal ----and --- flora
fecal
oral
Lancefield group D
Enterococcus
Enterococcus are
80%-----E. ---
15%----E.----
80% E. faecalis
15% E. faecium
Enterococcus
Hydrolyze Esculin----
Growth in 6.5% NaCl---
PYR----
Hydrolyze Esculin----Positive
Growth in 6.5% NaCl---Yes
PYR----Positive
What are the pathogenicity of S. pneumoniae
1. Labor pneumonia
2. Otitis Media
3. Meningitis
Gram Stain: Football Shaped
S. pneumoniae
What is the hemolysis of S. pneumoniae
alpha-hemolytic
S. pneumoniae Key Characteristics:
1. Bile Solubility
2. Optochin
1.Bile Solubility---Positive
2. Optochin:-----Sensitive
What causes subacute bacterial endocarditis
Viridan streptococci
Viridan streptococci Key Characteristics:
1. Bile Solubility--
2. Optochin---
Key Characteristics:
1. Bile Solubility-Neg
2. Optochin-Resistant
Lysostaphin is used to differentiate Staphy from what other genus
Micrococcus
Fermentation of glucose (OF tube ) helps differentiate Staphy from?
Micrococcus
What other Staphy species in addition to S. aureus produces a coagulase positive result
S. intermedius
Slime production is associated with what Staphy species
S. epidermidis
What enzymes contribute to the virulence of Staphy?
Hyaluronidase: damages basement membrane of tissues
Beta-lactamase: produces strains that are able to inactivate penicillin and ampicillin
Acetoin production helps distinguish what two staphy strains
1. S. aureus (+)
2. S. intermedius (-)
Rhodotorula growth on SBA
Pink-orange/red pigment
Causative agent of pediatric tinea capitis but not in adults
Microsporum audouinii
Causes spontaneous abortions and meningitis in animals
Listeria Monocytogenes
What is the hemolysis of Listeria M
Beta Hemolytic
Translucent, gray
How does Listeria Monocytogenes look on CAMP
CAMP positive
-Shovel (not arrowhead)
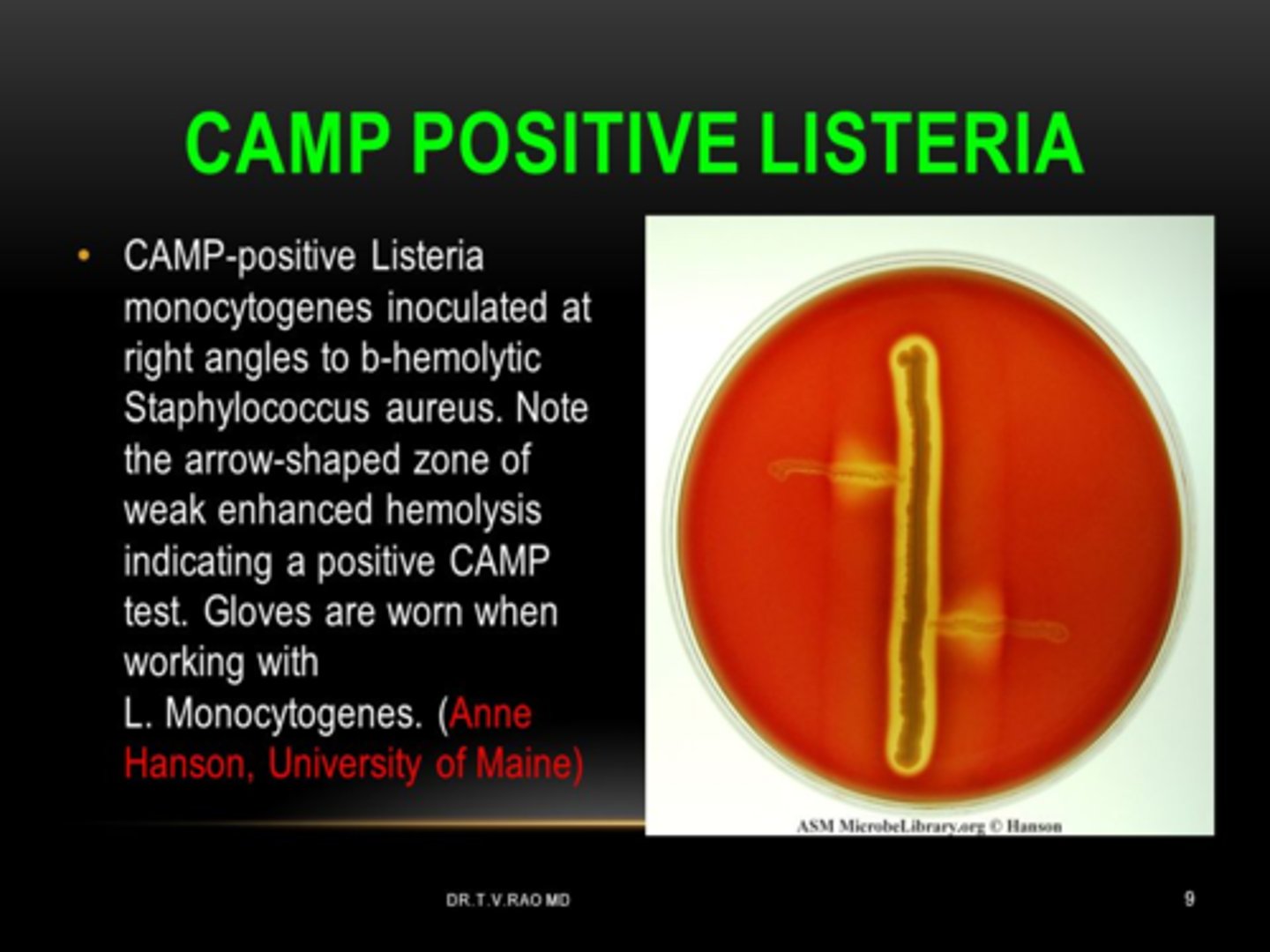
Key Characteristics of L. monocytogenes
1. Catalase---
2. Esculin----
3. CAMP---
4. Motility on wet mount---
Key Characteristics of L. monocytogenes
1. Catalase---POS
2. Esculin----POS
3. CAMP---POS: Shovel
4. Motility on wet mount---Tumbling Motility
L. Monocytogenes: Growth difference at RT vs 35C
Umbrella growth in motility agar at RT but not at 35C
Motility of L. Monocytogenes diff from what
Diptheroids
Catalase test diff L. Monocytogene from what
Group B Strep
Diphtheriae is characterized by -------- formed by----- and ------ at the back of the throat
Diphtheriae is characterized by pseudomembrane formed by dead cells and exudate at the back of the throat
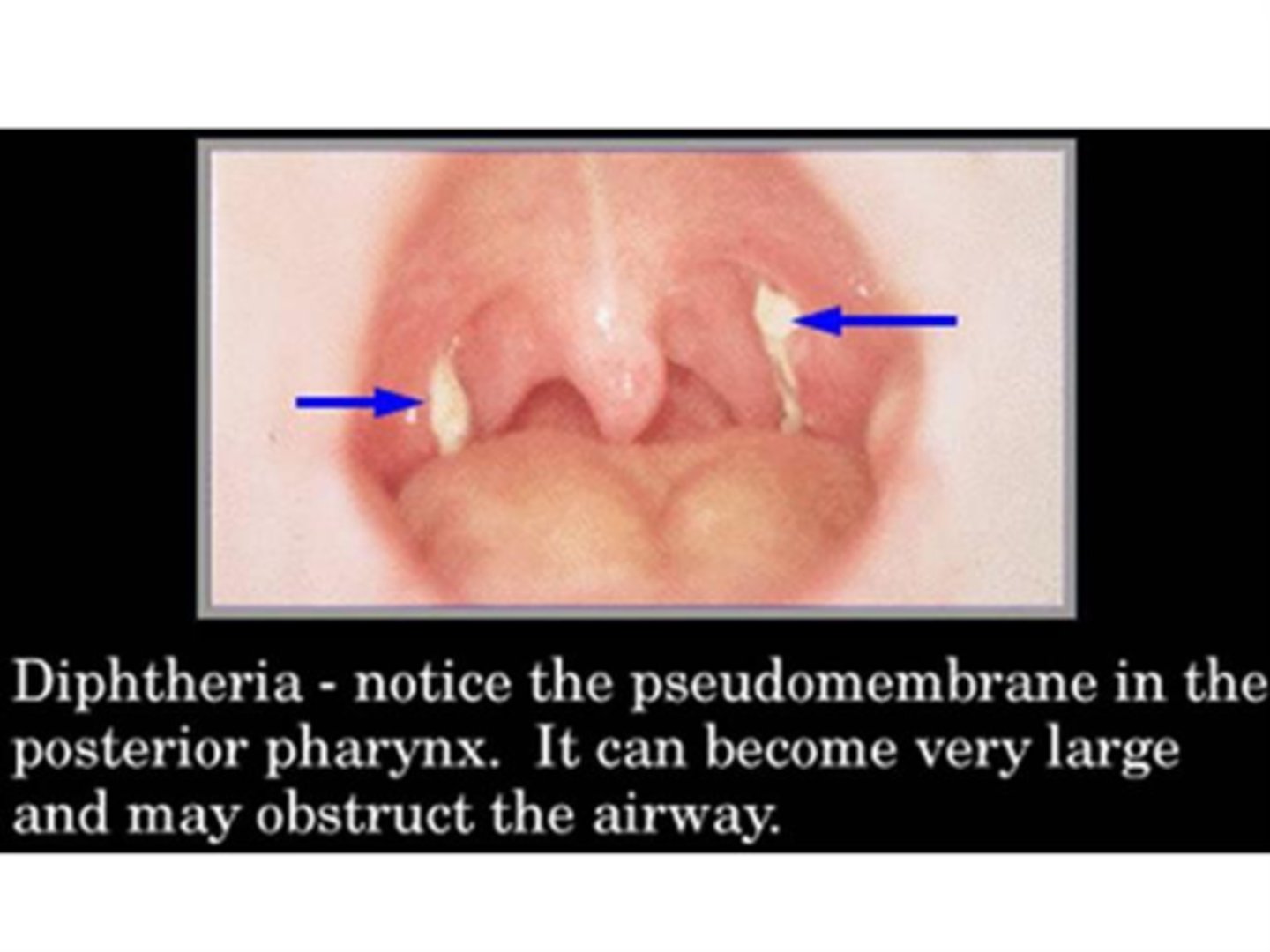
C. Diphtheria: Gray Black colonies with brown halos on what type of agar
Tindale agar
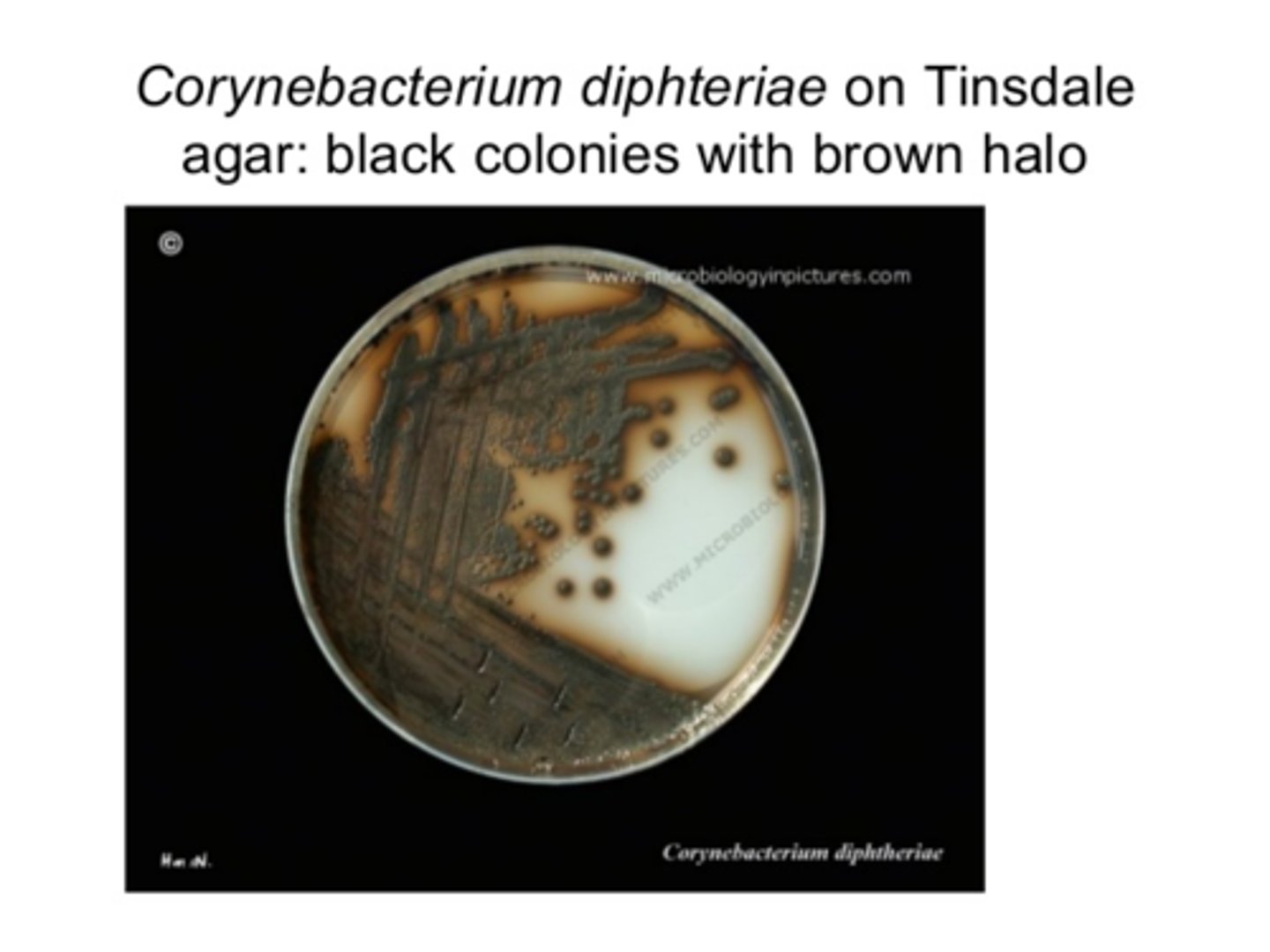
C. Diphtheria: Gray Black colonies what type of agar
Cystine tellurite
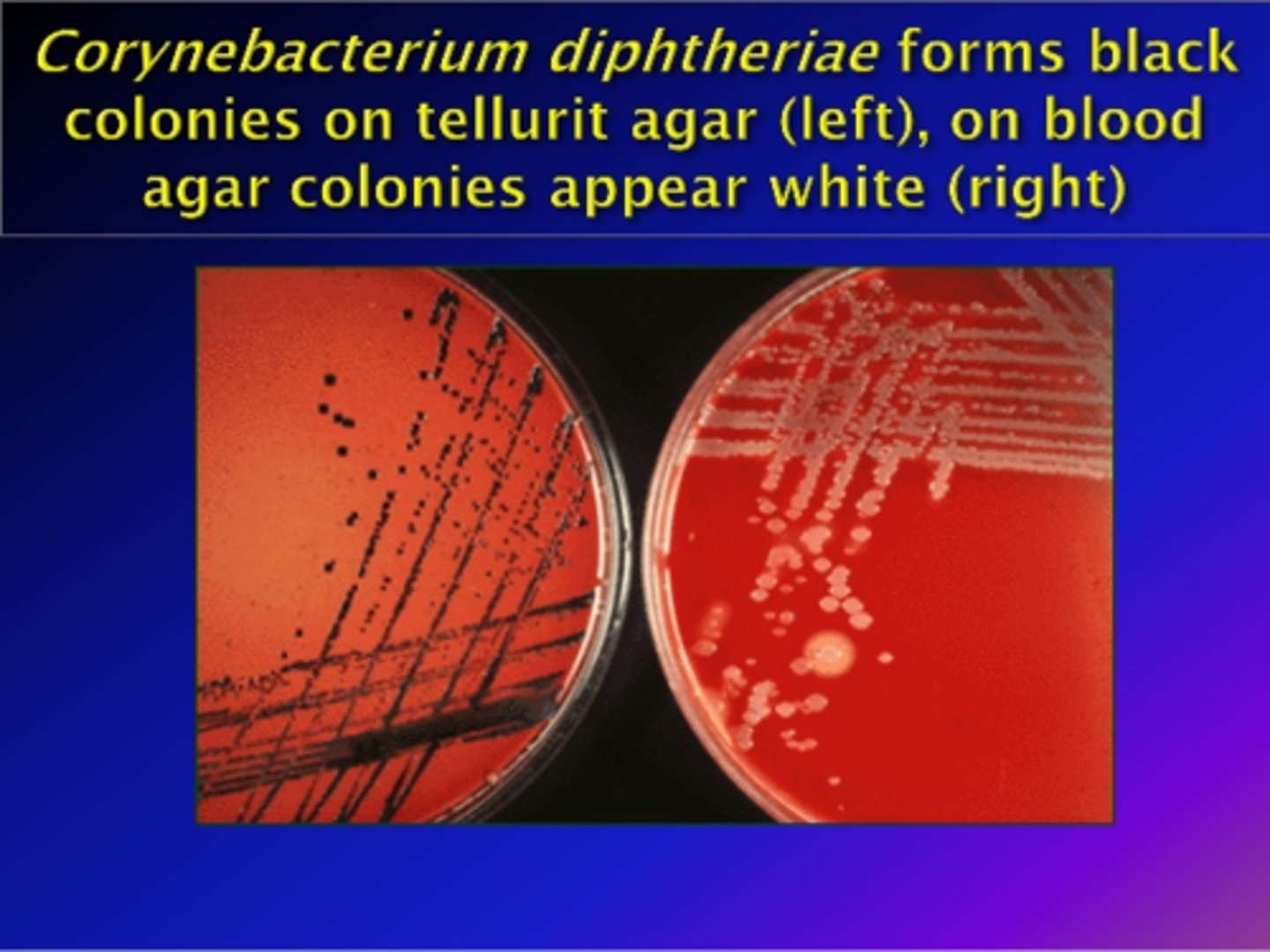
Loeffler medium stimulates growth and production of ------- granules in C. dihtheria
Metachromatic

Is C. diphtheria motile
No
Identifying characteristics on a gram stain of C. diphtheria
Chinese letters
The Elk test uses-----to detect ---- production for ------
anti-toxins, toxins, C. diphtheria
What is the pathogenecity of C. jeikeium
Hospital acquired
C. jeikeium is Rapid sucrose urea (RSU)?
Negative
What produces infections after prosthetic device implants?
C. jeikeium
Chopped meat broth is used for what organisms
Anaerobes
C. neoformans has a confirmatory growth on what type of agar
Niger seed (bird agar)
Cysticercosis is associated with what tapeworm?
Taenia solium.
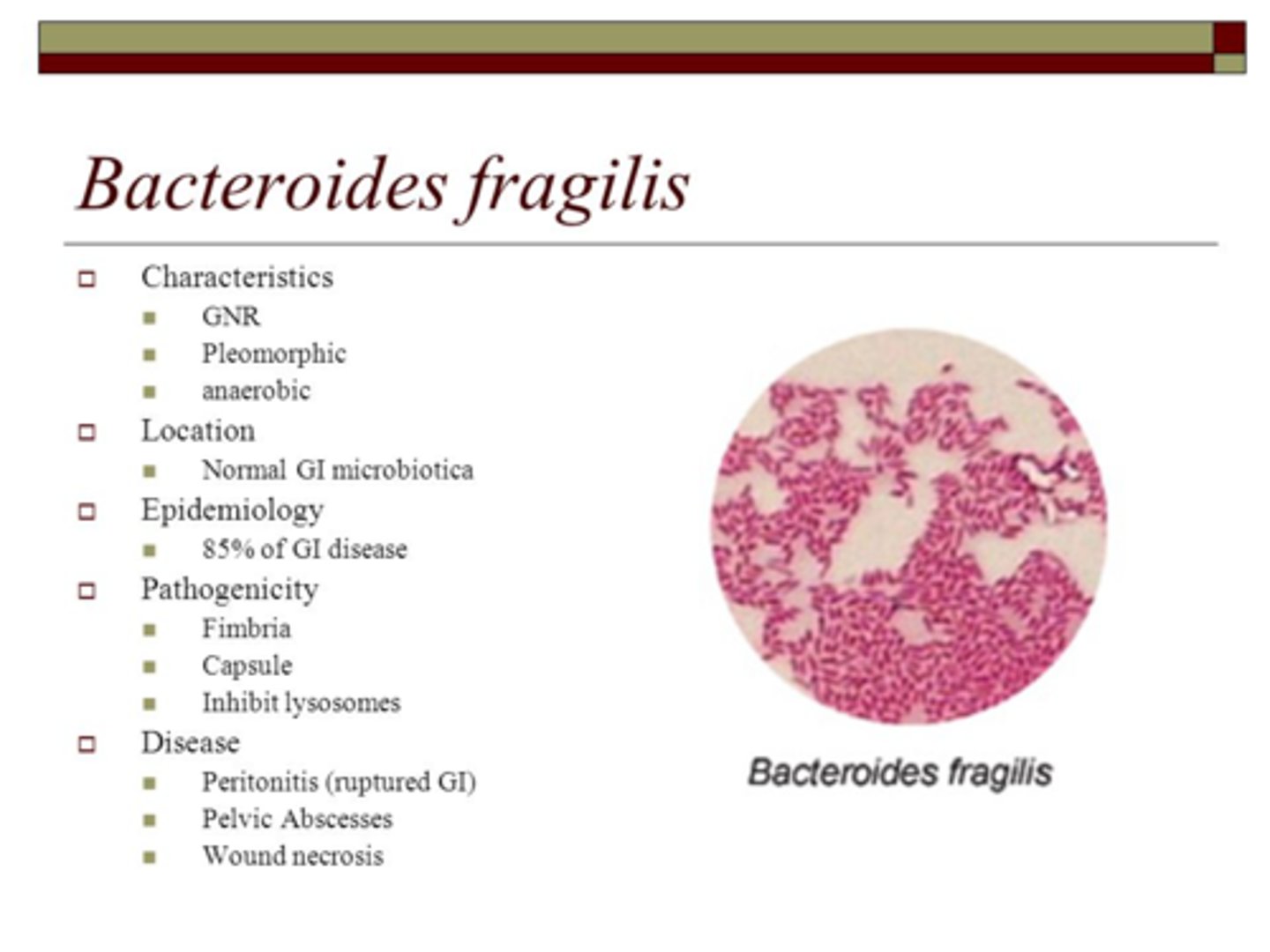
What is the predominant anaerobic bacteria of the human colon
Bacteroides fragilis
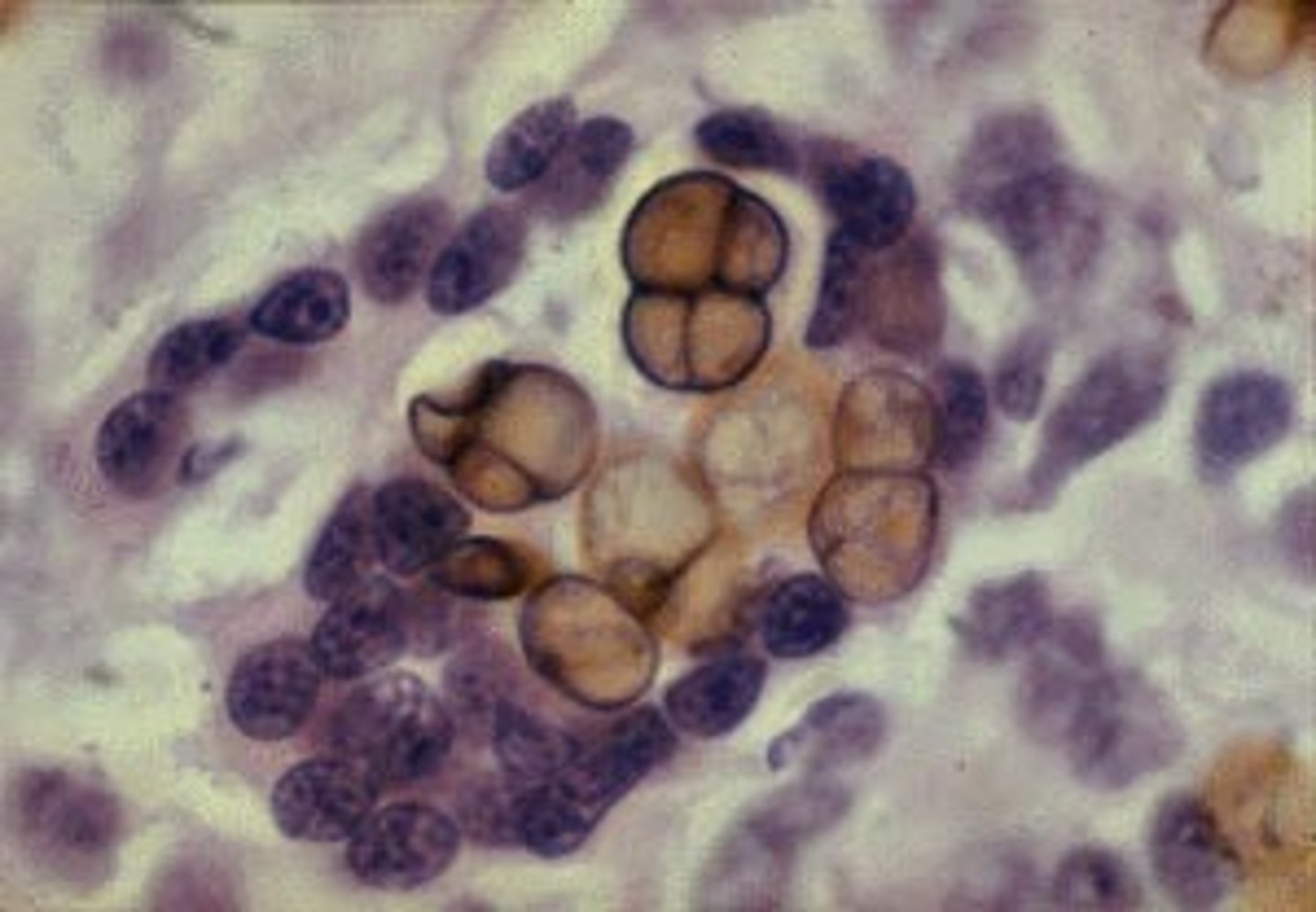
What fungal infection causes chromomycosis
Phialophora verrucosum
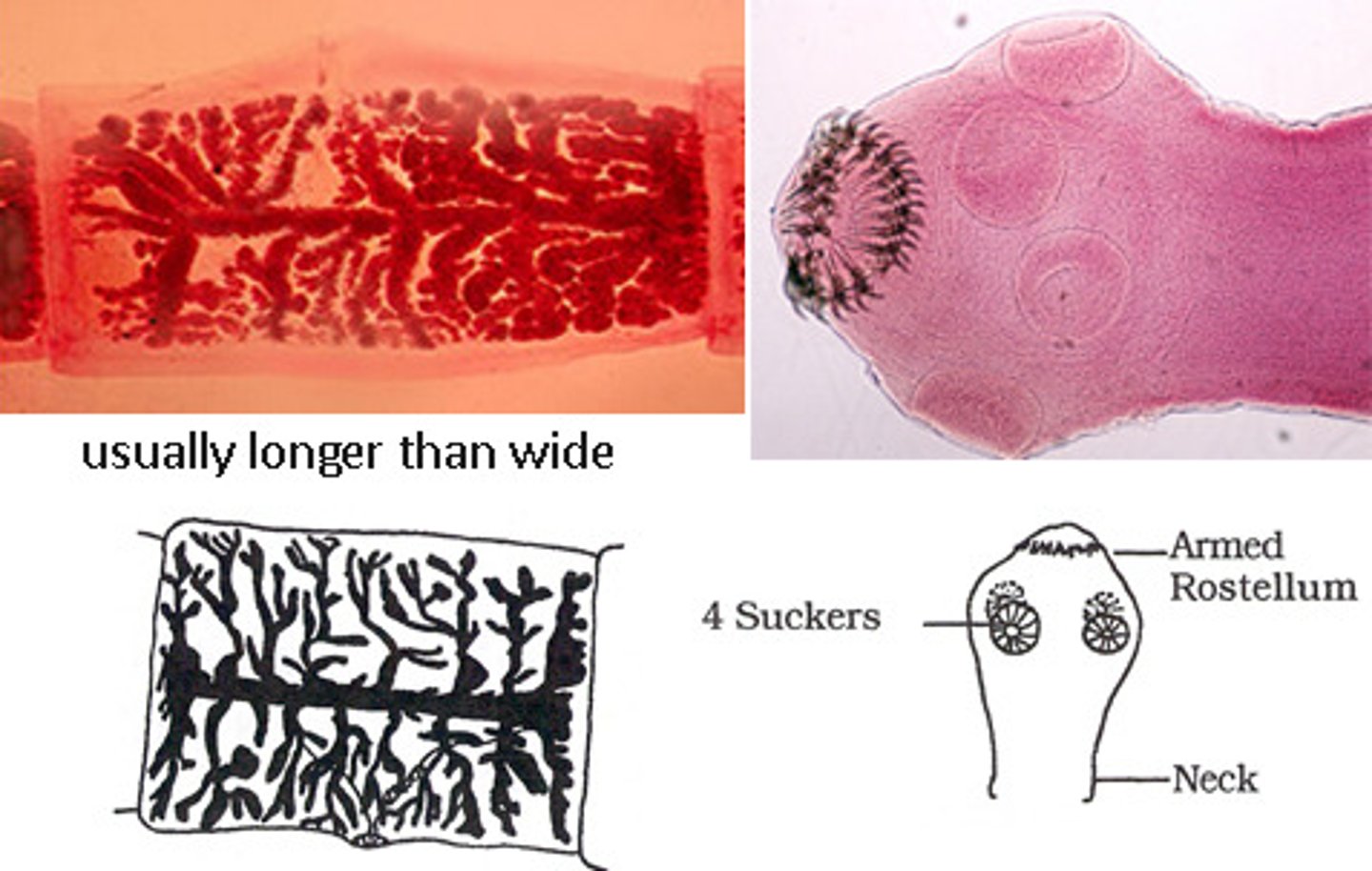
Term "hydatid sand" is used in reference to what tapeworm
Echinococcus species
What is the historical medium of choice for Francisella
Cysteine blood glucose agar is the historical medium of choice for ----
What type of hemolysis does S. aureus have
Beta hemolytic

Gram positive bacteria has which acid in the cell wall
Lipoteichoic acid and Teichoic acid in the cell wall that prevents decolorization in the gram stain
Gram positive bacteria is stained by what dye?
Crystal violet
Gram negative bacteria is stained by what dye?
Safranin
List the 4 types of media
1. Supportive
2. Enrichment
3. Selective
4. Differential
Type of media: Supports growth of most non-fastidious bacteria
Supportive Media,
EX Nutrient Agar, TSA
Type of media: Contains added growth factors, e.g., blood, vitamins, yeast extract
Enrichment Media,
EX: SBA< Chocolate, Brain-Heart Infusion, Buffered charcoal-yeast extract agar
Type of Media: Formulated to provide distinct colonial appearances based on certain biochemical rxn (e.g., lactose fermentation, hydrogen sulfide [H2S] production)
Differential
EX: EMB, MacConkey, HE, XLD
Sheep blood agar (SBA)
Media: Most Non-fastidious bacteria
Chocolate agar (CHOC)
Media: Haemophilus and Neisseria
Columbia colistin-nalidixic acid agar (CNA)
Media: GP
Phenylethyl alcohol agar (PEA)
Media: GPC and anaerobic GNR
Group A-selective strep agar with 5% sheep blood (SSA)
Media: Group A Strep from respiratory source
Eosin methylene blue (EMB)
Media: Enteric GNR
MacConkey (MAC) agar
Media: Enteric Gram Negative Rods
Sorbitol MacConkey (SMAC) agar
Media: E. Coli 0157h7
Hektoen enteric (HE) agar
Salmonella & Shigellain stool
Xylose lysine deoxycholate (XLD)
Salmonella & Shigellain stool
Salmonella-Shigella (SS) agar
Salmonella & Shigellain stool
Gram-negative broth (GN)
Salmonella & Shigellafrom stools & rectal swabs
Deoxycholate-citrate agar
Salmonella & Shigella
Campylobacterbroth
Campylobacter from stool
Campylobacterblood agar (Campy BAP)
Campylobacter from stool
Causes suppurative cutaneous infections,
toxic shock syndrome, food poisoning
S. aureus
Opportunistic pathogen.
Commoncause of hospital acquired UTI
Coagulase-negative staphylococci (CNS)
UTI in young sexually active females, urethritis & prostatitis in males
S. saprophyticus
Usually nonpathogenic.
Found in environment & on skin, mucous membranes,
oropharynx
Micrococcus
Enzyme catalase converts 3% hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to oxygen & water. Immediate bubbling.
Catalase Test
Staphylococci pos.
Streptococci & enterococci neg
Enzyme coagulase causes coagulation (tube test) or agglutination (slide test) in plasma.
Coagulase Test
S. aureus pos
Agglutination of latex beads coated with fibrinogen & abs to protein A (protein in cell wall of S. aureus).
Slide agglutination tests for S. aureus
S. aureus pos
Fermentation of mannitol results in color change from pink to yellow.
Mannitol salt agar (MSA)
-7.5% salt inhibits most organisms other than staph. All staph can grow on MSA. Rarely used for ID of
S. aureus today because other species ferment mannitol.
Organisms resistant to novobiocin grow to edge of disk.
Novobiocin susceptibility
-S. saprophyticus is resistant.
Other CNS susceptible
Causes 90% of strep infections.
Strep sore throat,
rheumatic fever,
glomerulonephritis,
scarlet fever (scarlatina),
erysipelas,
puerperal sepsis,
impetigo
Group A streptococci (GAS)
Sensitive to bacitracin.
Resistant to SXT. PYR pos
Most common is S. pyogenes.
Hemolysi due to O2-stable streptolysin S & O2-labile streptolysin O.
To detect species that produce streptolysin
O only, stab into agar, place coverslip over
inoculum, or incubate anaerobically
Normal flora of female genital tract.
Most common cause of neonatal septicemia & meningitis
Group B streptococci (GBS)
Resistant to SXT & bacitracin.
Sodium hippurate pos.
CAMP pos
S. agalactiae.
Vaginal & rectal swabs collected from pregnant women at 35-37 wk gestation.
Inoculated in selective
broth, e.g., LIM, GBS broth, StrepB Carrot Broth.
Normal in GI tract. Causes nosocomial
UTI, wound infections, bacteremia
Group D streptococci, nonenterococci
Hydrolyzes esculin
Most common is S. gallolyticus (formerly S. bovis).
Normal in mouth, GI tract, female genital tract. Causes nosocomial UTI, wound infections, bacteremia
Enterococcus
Hydrolyzes esculin.
Grows in 6.5% NaCl broth. PYR pos
Lancefield group D.
80% are E. faecalis,
15% E. faecium.
Normal in upper respiratory tract of some. Most
common cause of community acquired pneumonia.
Major cause of otitis media, meningitis in adults.
Infects sinuses, eyes
Streptococcus pneumoniae