Applied Biochemistry - Nucleotide Metabolism
1/206
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Info from Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry by Emine E Abali; Susan D Cline; David S Franklin; Susan M Viselli
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
207 Terms
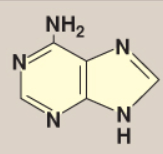
Name this base.
Adenine
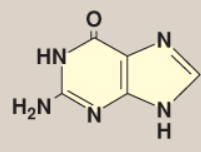
Name this base.
Guanine
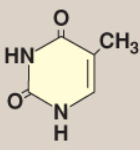
Name this base.
Thymine
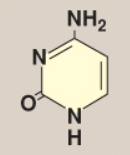
Name this base.
Cytosine
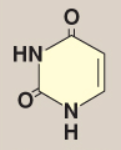
Name this base.
Uracil
What are the names of DNA/RNA purines?
Adenine and Guanine
What are the names of DNA/RNA pyrimidines?
Thymine, cytosine, and uracil
What makes a purine different from a pyrimidine?
Purines are double-ringed
How do thymine and uracil differ?
Thymine has a methyl group
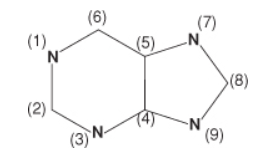
Azaserine, a drug with research applications, inhibits glutamine-dependent enzymes. Incorporation of which of the ring nitrogens in the generic purine structure shown would most likely be affected by azaserine?
9
A 42 year old male undergoing radiation therapy for prostate cancer develops severe pain in the metatarsal phalangeal joint of his right big toe. Monosodium urate crystals are detected by polarized light microscopy in fluid obtained from this joint by arthrocentesis. This patient’s pain is directly caused by the overproduction of the end product of which of the following metabolic pathways?
Purine degradation
Which one of the following enzymes of nucleotide metabolism is correctly paired with its pharmacologic inhibitor?
A. Dihydrofolate reductase—methotrexate
B. Inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase—hydroxyurea
C. Ribonucleotide reductase—5-fluoracil
D. Thymidylate synthase—allopurinol
E. Xanthine oxidase—probenecid
A
A 1-year-old female patient is lethargic, weak, and anemic. Her height and weight are low for her age. Her urine contains an elevated level of orotic acid. Activity of uridine monophosphate synthase is low. Administration of which nucleoside is most likely to alleviate her symptoms?
Uridine
What laboratory test would help in distinguishing an orotic aciduria caused by ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency from that caused by uridine monophosphate synthase deficiency?
Blood ammonia level would be expected to be elevated in ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency that affects the urea cycle, but not in uridine monophosphate synthase deficiency
What makes up a nucleoside?
Pentose sugar + base
What bond connects the parts of a nucleoside together?
An N-glycosidic bond
What is the name of the ribonucleoside of adenine?
Adenosine
What is the name of the ribonucleoside of guanine?
Guanosine
What is the name of the ribonucleoside of cytosine?
Cytidine
What is the name of the ribonucleoside of uracil?
Uridine
What is the name of the deoxyribonucleoside for adenine?
Deoxyadenosine
What is the name of the deoxyribonucleoside for guanine?
Deoxyguanosine
What is the name of the deoxyribonucleoside for cytosine?
Deoxycitidine
What is the name of the deoxyribonucleoside for thymine?
Thymidine
What makes up a nucleotide?
Sugar + base + phosphate group(s)
What bond connects a nucleoside to a phosphate group?
An ester linkage to the 5’-OH group of the pentose sugar
Are the second and third phosphate/nucleotide bonds positive or negative?
Negative
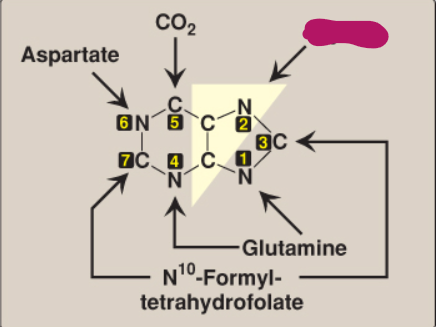
What compound contributes these atoms to a purine ring?
Glycine
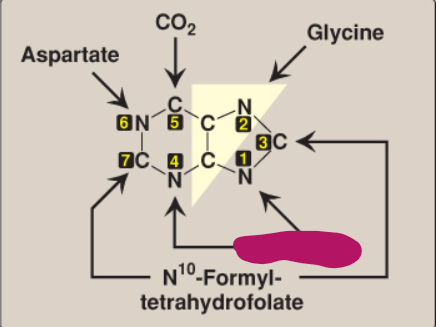
What compound contributes these atoms to a purine ring?
Glutamine
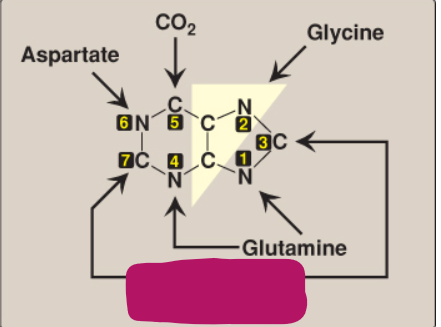
What compound contributes these atoms to a purine ring?
N10-Formyl-tetrahydrofolate
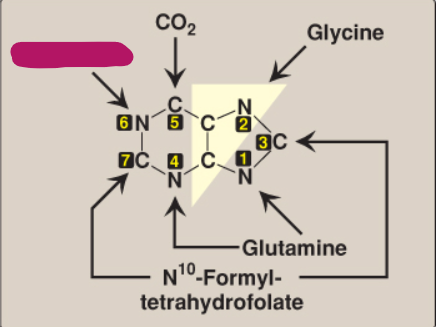
What compound contributes these atoms to a purine ring?
Aspartate
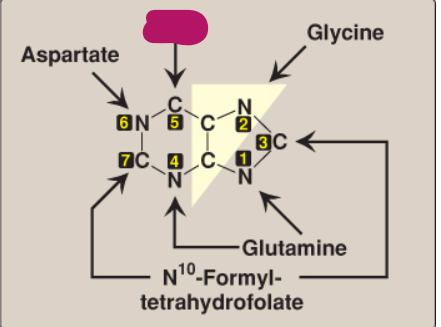
What compound contributes these atoms to a purine ring?
CO2
What is 5-Phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP)?
An activated pentose that participates in the synthesis and salvage of purines and pyrimidines
How is PRPP synthesized?
From ATP and ribose 5-phosphate catalyzed by PRPP synthetase
How is PRPP synthetase activated?
Inorganic phosphate
How is PRPP synthetase inhibited?
Purine nucleotides
What is the inhibition of PRPP synthetase called?
End product inhibition
What is the committed step of purine nucleotide biosynthesis?
5-phosphoribosylamine synthesis
How is 5-phosphoribosylamine synthesized?
By the amide group of glutamine replacing the pyrophosphate group attached to carbon 1 of PRPP
How is 5-phosphoribosylamine catalyzed?
By glutamine:phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase (GPTAT)
How is 5-phosphoribosylamine synthesis inhibited?
By AMP and GMP
How is the rate of 5-phosphoribosylamine synthesis regulated?
By the concentration of PRPP in the cell
After PRPP and 5-phosphoribosylamine are synthesized, what is made?
Inosine monophosphate
What is inosine monophosphate (IMP)?
The parent purine nucleotide for AMP and GMP
What is the base of IMP?
Hypoxanthine
Where is hypoxanthine found?
In tRNA
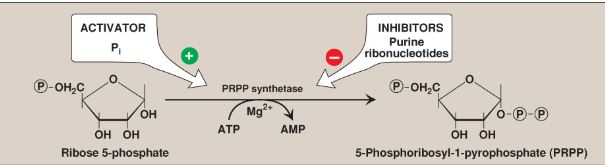
What does this demonstrate?
PRPP synthesis
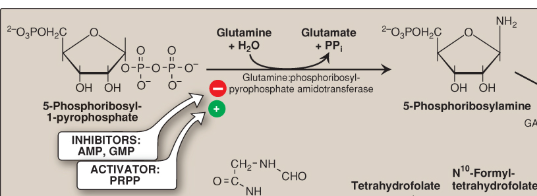
What does this demonstrate?
5-phosphoribosylamine synthesis
Why do some anticancer drugs cause anemia and hair loss?
They inhibit human purine synthesis which causes the death of certain tissues
What energy source is used for AMP synthesis?
GTP
What energy source is used for GMP synthesis?
ATP and glutamine
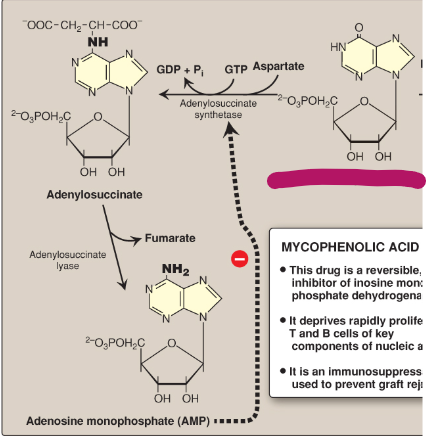
Name this section of AMP synthesis.
IMP
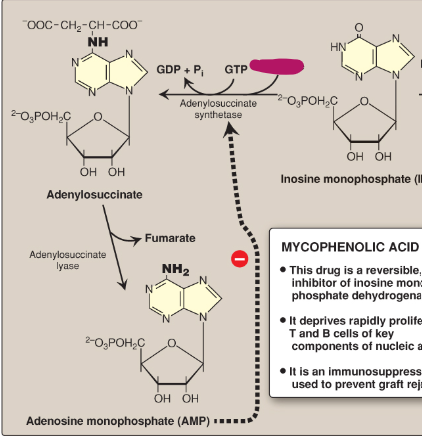
Name this section of AMP synthesis.
Aspartate
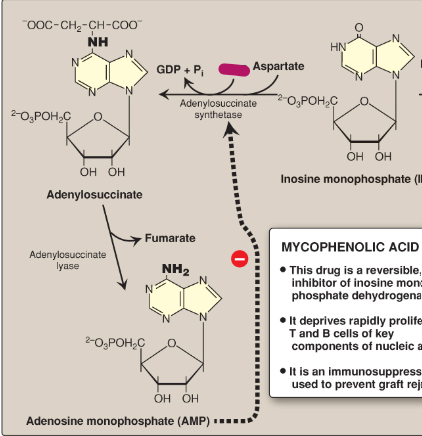
Name this section of AMP synthesis.
GTP
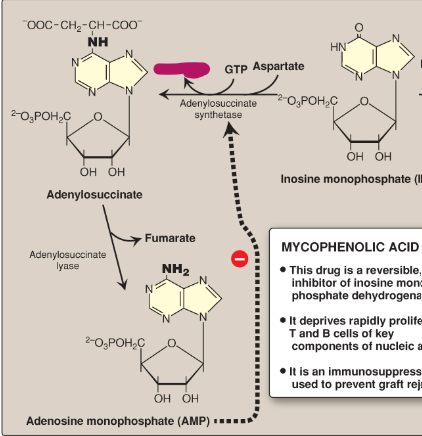
Name this section of AMP synthesis.
GDP + inorganic phosphate
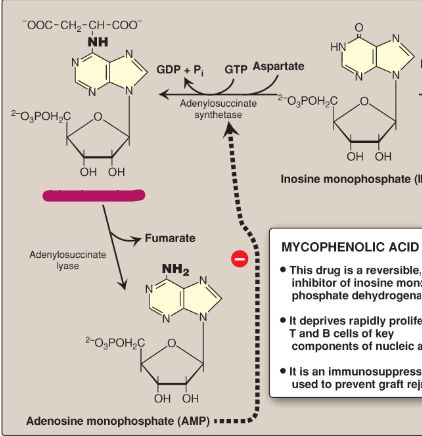
Name this section of AMP synthesis.
Adenylosuccinate
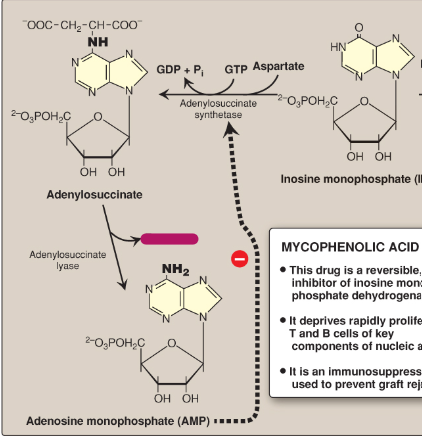
Name this section of AMP synthesis.
Fumarate
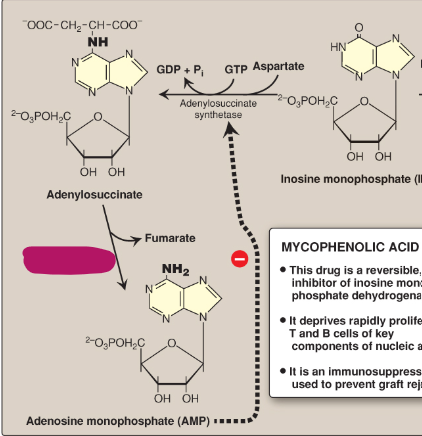
Name this section of AMP synthesis.
Adenylosuccinate lyase
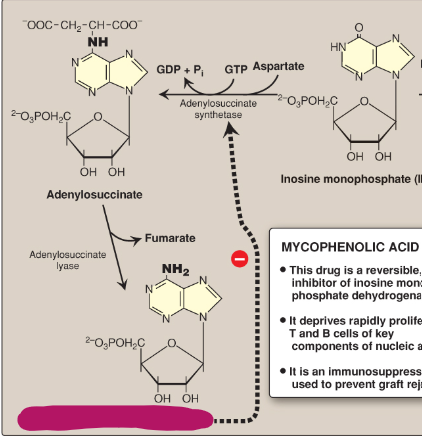
Name this section of AMP synthesis.
AMP
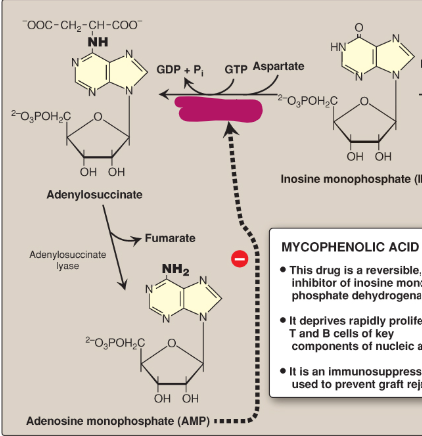
Name this section of AMP synthesis.
Adenylosuccinate synthetase
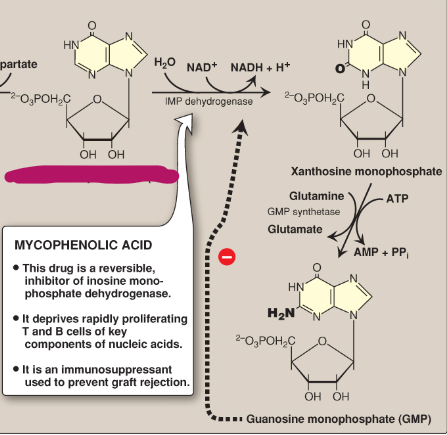
Name this section of GMP synthesis.
IMP
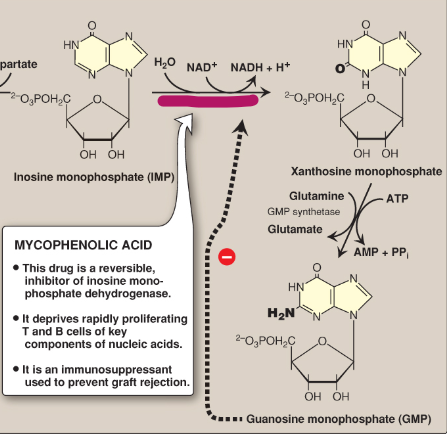
Name this section of GMP synthesis.
IMP dehydrogenase
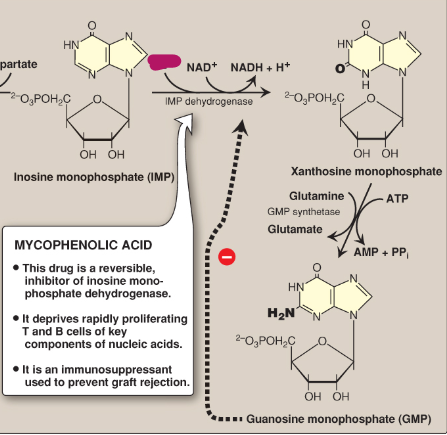
Name this section of GMP synthesis.
H2O
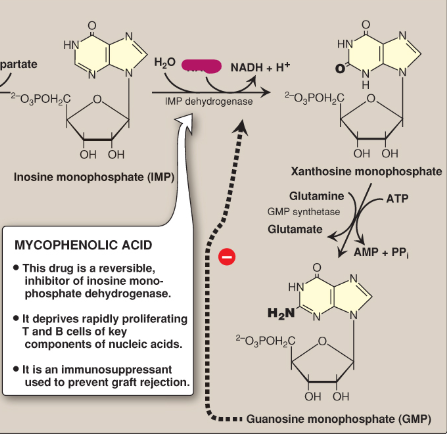
Name this section of GMP synthesis.
NAD+
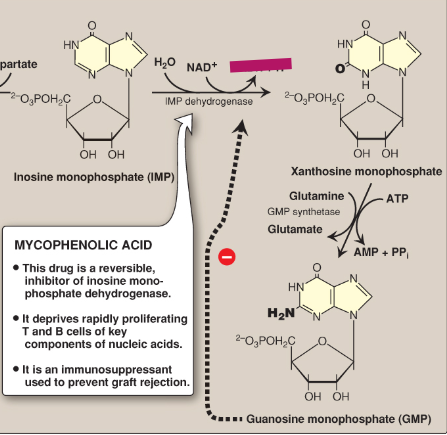
Name this section of GMP synthesis.
NADH + H+
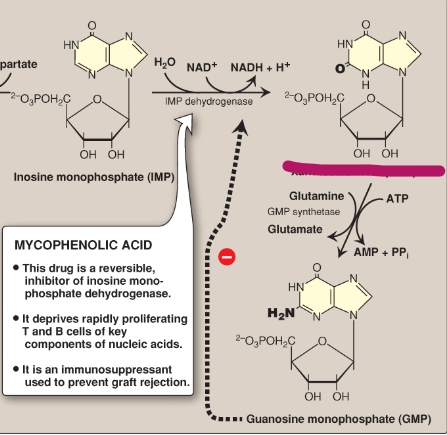
Name this section of GMP synthesis.
Xanthosine monophosphate
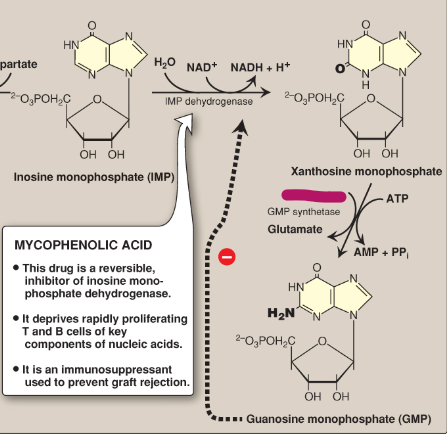
Name this section of GMP synthesis.
Glutamine
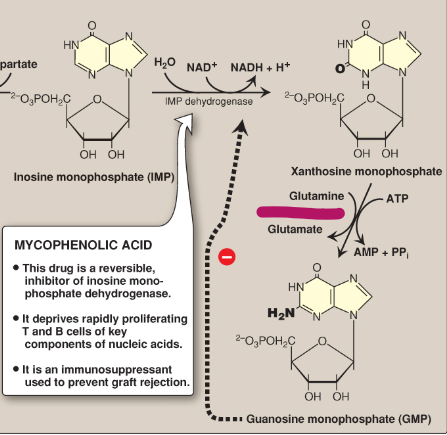
Name this section of GMP synthesis.
GMP synthetase
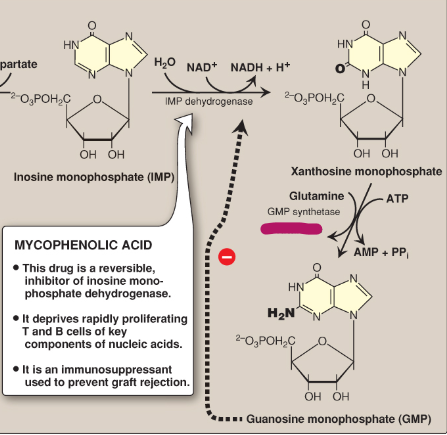
Name this section of GMP synthesis.
Glutamate
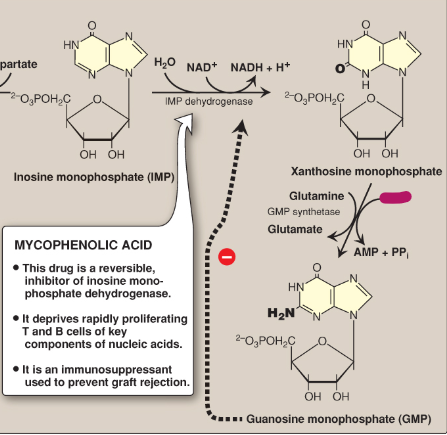
Name this section of GMP synthesis.
ATP
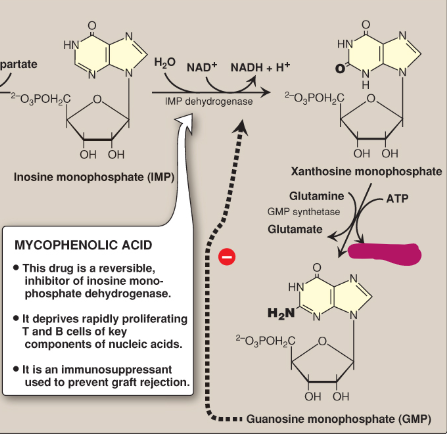
Name this section of GMP synthesis.
AMP + PPi
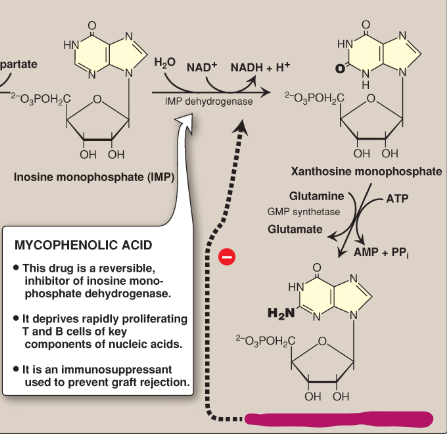
Name this section of GMP synthesis.
GMP
What is mycophenolic acid?
A reversible inhibitor of IMP dehydrogenase used as an immunosuppressant to prevent graft rejection
What converts AMP into ADP?
Adenylate kinase
What converts GMP into GDP?
Guanylate kinase
What converts GDP into GTP?
Nucleoside diphosphate kinase
What converts CDP into CTP?
Nucleoside diphosphate kinase
T/F: Conversion of monophosphates into diphosphates, and diphosphates into triphosphates, are reversible using the same kinases in the forwards direction as the backwards direction.
True
What purine nucleoside cannot be salvaged?
Guanosine
How is adenosine salvaged into AMP?
Phosphorylation by adenosine kinase
What catalyzes the salvage of hypoxanthine and guanine?
Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT)
What catalyzes the salvage of adenine?
Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT)
What compound donates their phosphate group in purine salvage?
PRPP
What is Lesch-Nyhan syndrome?
An X-linked recessive disorder associated with a high deficiency of HGPRT, which leads to excessive amounts of uric acid
Why is there a high amount of uric acid in patients with Lesch-Nyhan syndrome?
It is the end product of purine degradation. There are excess amounts as a result of purines not being able to be salvaged, and therefore GPAT not having inhibitors and creating more purines as a result.
What is an inherited cause of hyperuricemia?
HGPRT deficiency
What is urolithiasis?
The formation of uric acid stones in the kidneys
What is gouty arthritis?
The deposition of urate crystals in the joints
What are symptoms of Lesch-Nyhan syndrome?
Motor dysfunction, cognitive deficits, behavioral disturbances (self-mutilation)
What is ribonucleotide reductase?
A dimer composed of two nonidentical subunits that reduces purine and pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphates into their deoxy forms
How does ribonucleotide reductase reduce its disulfide bond after producing deoxyribonucleotides?
By thioredoxin
How does thioredoxin reduce its disulfide bond after reducing ribonucleotide reductase?
By NADPH + H+ catalyzed by thioredoxin reductase
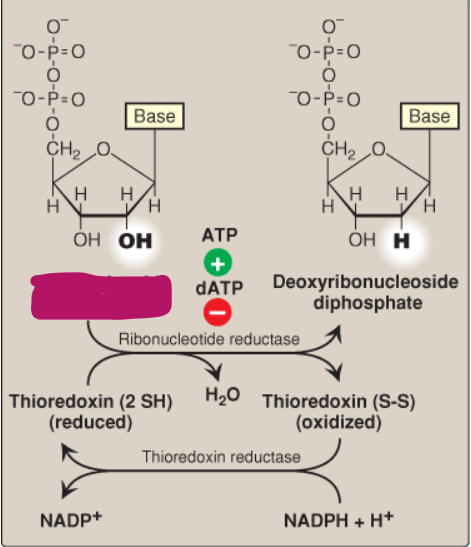
Label this deoxyribonucleotide conversion.
Ribonucleoside diphosphate
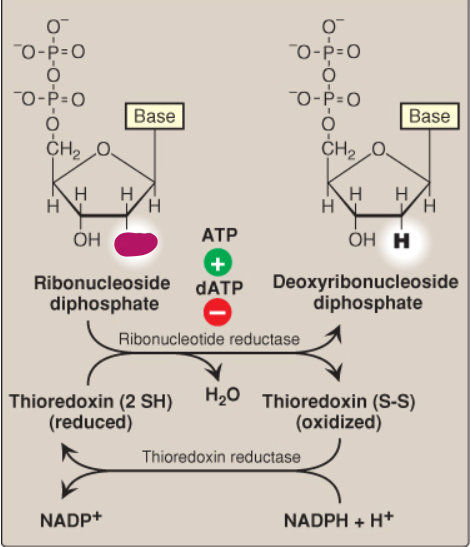
Label this deoxyribonucleotide conversion.
-OH
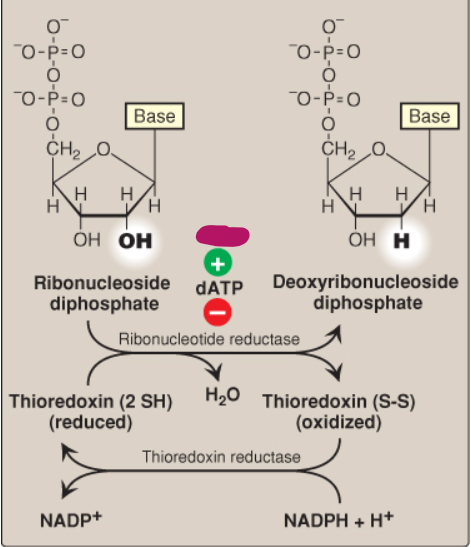
Label this deoxyribonucleotide conversion.
ATP
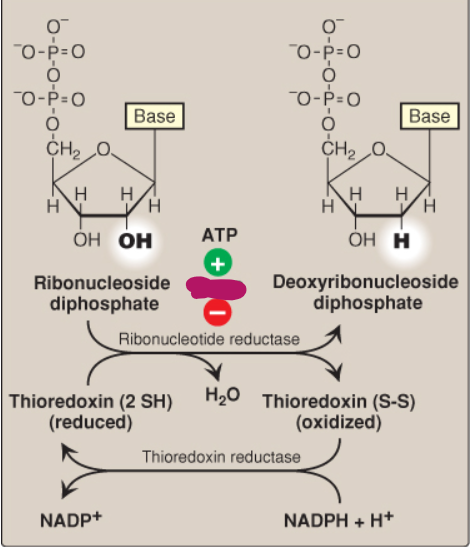
Label this deoxyribonucleotide conversion.
dATP
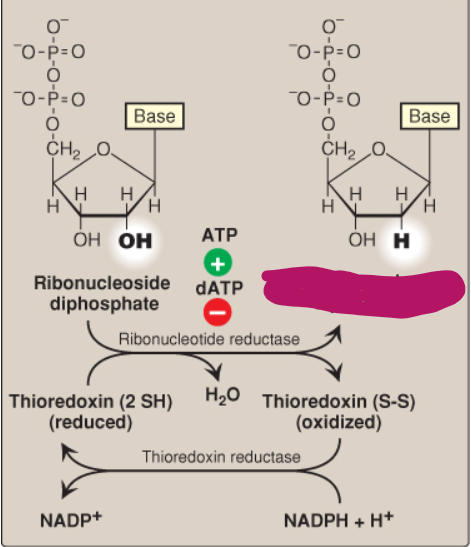
Label this deoxyribonucleotide conversion.
Deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate
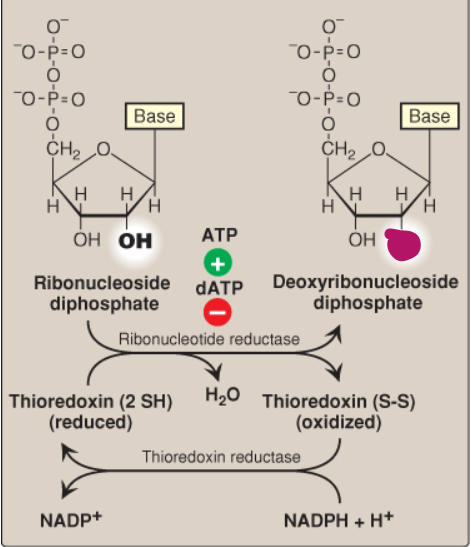
Label this deoxyribonucleotide conversion.
-H
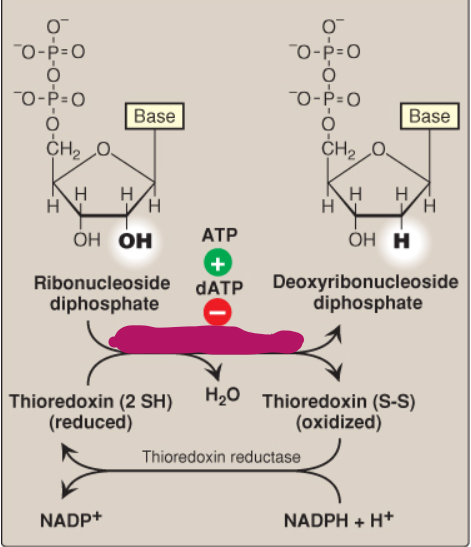
Label this deoxyribonucleotide conversion.
Ribonucleotide reductase
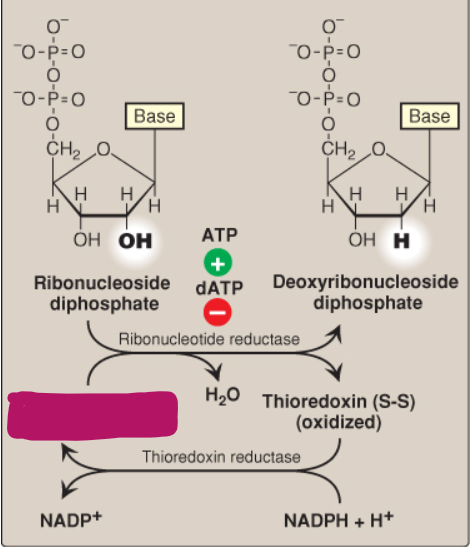
Label this deoxyribonucleotide conversion.
Thioredoxin (2SH) (reduced)