Skin and Ocular Infectious Diseases
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
epidermis
outer layer of the skin (keratinized)
dermis
middle layer of skin (connective tissue, glands, follicles)
subcutaneous tissue
deepest layer of skin (fat, vessels, nerves)
Exogenous
*route of infection
from outside (cuts, trauma, bites)
endogenous
*route of infection
from normal microbiota
staphylococcus aureus
Gram-positive cocci
catalase+, coaglualse +
diseases: folliculitis, impetigo, abscesses
staphylococcus epidermis
gram-positive cocci
catalase +, coagulase -
forms biofilms
causes chronic device-associated infections
streptococcus pyogenes
gram positive cocci in chains
catalase -, β-hemolytic
Diseases: impetigo, erysipelas, cellulitis, “flesh eating disease”
pseudomonas aeruginosa
gram-negative rod
oxidase +
found in water, soil, moist environments
typical infections: folliculitis, “simmers ear”, burn wounds
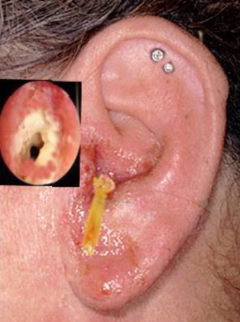
otitis externa “swimmers ear”
Anatomy: skin-lined canal → similar to other skin infections
Main pathogens:
• Pseudomonas aeruginosa (most common)
• Staphylococcus aureus
• Candida spp., Aspergillus spp. (fungal otitis)
Clinical: pain, itching, redness, swelling, discharge
Treatment: cleaning + topical antibiotics (ciprofloxacin) ± antifungals
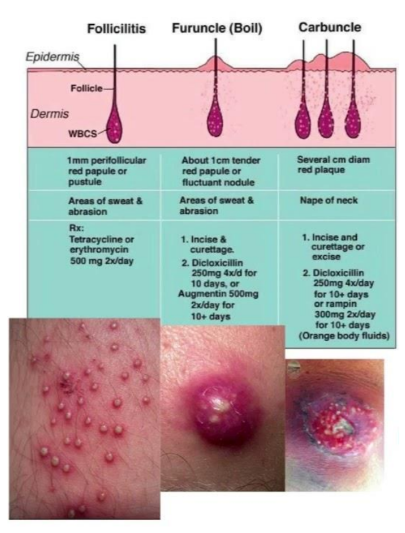
folliculitis
Inflammation/infection of the
hair follicle.
Main pathogen:
Staphylococcus aureus
Common sites: beard, scalp, chest,
thighs
Predisposing factors: shaving, friction,
occlusion, sweat
Treatment: hygiene + topical antibiotics
(mupirocin, clindamycin)
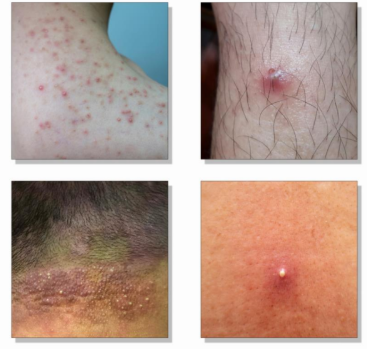
furuncle and carbuncle
Furuncle (boil): deep infection of hair follicle →
abscess
Carbuncle: cluster of interconnected furuncles
Main pathogen:
Staphylococcus aureus
Clinical: painful, red, fluctuant nodules with pus
Treatment: incision & drainage ± antibiotics (MRSA
coverage if needed)
Impetigo
Etiology:
Staphylococcus areas (most common)
streptococcus pyogenes
Clinical features:
honey-colored crust around the nose and mouth
blisters
Diagnosis:
swab from active lesion
treatment:
topical mupirocin
oral cephalexin, dicloxacillin, clindamycin
*common in children, spreads by contact/ scratching, and is very contagious
erysipelas
Infection of the dermic and lymphatic blood vessels
Etiology:
streptococcus pyogenes
Clinical features:
bright red, swollen, hot skin with raised borders
Diagnosis
swab from legion edge if open
cellulitis
Etiology:
Staphylococcus areas
streptococcus pyogenes
sometimes both
entry via. skin trauma, ulcers, surgical wounds
clinical features
redness, swelling, pain, heat, tenderness
poorly defined borders
diagnosis:
clinical evaluation
treatments
antibiotics
necrotizing fasciitis
infection of the fascia and deep subcutaneous tissue, often producing gas and necrosis
Pathogens:
streptococcus pyogenes
clostridium perfringens
clinical features:
severe pain
rapid swelling and skin discoloration (purple)
necrosis, blisters and crepitus (gas under skin)
diagnosis:
clinical suspicion with CT scan and tissue culture
treatment:
emergency surgery
IV broad-spectrum antibiotics
myositis
Infection of skeletal muscle tissue, often secondary to trauma or bacteria
Main Pathogens: staphylococcus aureus, clostridium
Forms:
Pyomyositis
gas gangrene
Symptoms: muscle pain, swelling, fever, tenderness, crepitus
Diagnosis: imaging
Treatment: IV antibiotics (vancomycin, piperacillin-tazobactam), surgical drainage
Surgical Wound Infection
Infection at surgical incision site, VERY common hospital-acquired infection
Main Pathogens
Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
staphylococcus epidermis
gram - bacteria
Prevention:
aseptic technique, skin disinfection, proper postoperative care
Pressure and Vascular Ulcer Infections
Chronic skin breakdown in immobile or vascular-compromised patients
Pathogens: polymicrobial—enterococcus, pseudomonas, and anaerobes
Management: debridement, pressure-relief, antibiotics
Prevention: repositioning, nutrition, daily wound assessment
Superficial Mycoses
Fungal skin infection affects outer epidermis
Cutaneous Mycoses
fungal skin infection that affects hair, nails, stratum, and corneum
Subcutaneous Mycoses
fungal skin infection that affects deeper tissue (traumatic inoculation)
Opportunistic Fungi
Fungal skin infection that affects immunocompromised people
Candida Infections
Part of normal microbiota in skin, gut, mouth, and vagina
Most common species: candida albicans
Main infections:
cutaneous candidiasis: rash in skin folds, under breasts
oral thrush: white plaque on tongue
Paronychia: nail fold inflammation
vaginal candidiasis: itching, discharge
Treatment: oral/ topical antifungals
Malassezia Infection
Lipophilic yeast
Diseases:
Pityriasis versicolor: hypo/hyper pigmented patches
Seborrheic Dermatitis: scalp, face
Catheter-related infections
Treatment: topical antifungals
Herpes Simplex Virus
DNA Virus - Herpesviridae family
HSV-1: oral infections, “cold sores”
HSV-2: genital infections
Varicella-Zoster Virus
Herpesviridae Family
Primary Infection: varicella (chickenpox)
Recativation: herpes zoster (shingles)
Treatment: vaccine, antibiotics, pain control
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
DNA Virus - papillomaviridae family
infects keratinocytes —> benign or malignant grows
HPV-16 and HPV-18: cervical cancer
Prevention: Vaccine
Common Lesions:
verruca vulgaris: common wart
plantar warts: soles of feet
anogenital warts: sexual transmission
Molluscum Contagiosum (Poxvirus)
DNA Virus - poxviridae family
Lesions: small, dome-shaped bumps
Common: immunosuppressed adults, children
Keratitis
Corneal Infection
inflammation/ infection of the cornea —> vision threatening
Main Causes:
infected contact lenses
HSV-1
Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus (HZO)
reactivation of Varicella-Zoster virus in the ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve.
Endophthalmitis - severe intraocular infection
Infection inside the eye (aqueous + vitreous humors).
Types:
• Exogenous: after surgery, trauma, or corneal perforation.
• Endogenous: from bloodstream (sepsis, endocarditis, etc.)
Symptoms: Sudden severe eye pain. Vision loss (rapid). Redness, eyelid swelling.
Hypopyon (pus in anterior chamber).
Treatment:
• Intravitreal antibiotics immediately.
• Vitrectomy in severe cases.
• Hospitalization and systemic antibiotics.