PHAR 523 Exam 1 (Dosage)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 11:21 PM on 9/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
1
New cards
Solution
mixture of two or more components that form one homogenous mixture
2
New cards
Solvent (vehicle)
carries the drug into the patient
3
New cards
Solute(s)
molecules dissolved in the solvent (API and excipients)
4
New cards
Drug particle
solid with a particle size and surface area
5
New cards
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API)
part of the drug that is responsible for the health effects.
6
New cards
Dissolution
Process by which a solid solute enters a solution (or amount of drug substance that goes into a solution per unit time under standardized conditions)
7
New cards
Rate of dissolution
how much is dissolved over a fixed amount of time
8
New cards
Solubility
maximum concentration (saturated) of a solute that can dissolve in a solvent at a given temperature
9
New cards
Extent
how much dissolved
10
New cards
How do drugs move across membranes and bind to receptors?
get absorbed into a solution and then they become lipophilic
11
New cards
Saturation solubility
a solution containing maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a solvent
12
New cards
List the 4 factors that affect solubility
Pressure, temperature, solvent, other solute molecules in solution
13
New cards
solute-solute interaction
the removal/separation of a solute molecule from a solid state (will require energy)
14
New cards
solvent-solvent interactions
separation of the solvent molecules in order to form a cavity (required energy)
15
New cards
solute-solvent interactions
the insertion of the solute molecule into the cavity produced by the solvent (releases energy)
16
New cards
unsaturated solutions
bulk solution, most pharmaceutical systems are unsaturated
17
New cards
super saturated
solution that contains more solute that can dissolve at a given temperature (see precipitates)
18
New cards
Heat of solution
the net amount of heat energy that is absorbed or released when a solute dissolved in a solvent
19
New cards
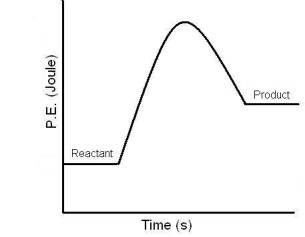
Endothermic
Absorbs heat (feels cold)
20
New cards
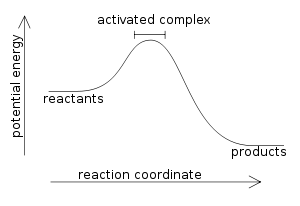
Exothermic
Releases heat (feels warm)
21
New cards
List the 3 types of dissolution
Endothermic dissolution, exothermic dissolution, temperature independent dissolution
22
New cards
Endothermic dissolution
less energy is released when water bonds to the solute than it takes to separate the solute (energy decreases)
23
New cards
Exothermic dissolution
More energy is released when water bonds to the solute than it takes to separate the solute (energy increases)
24
New cards
Temperature independent dissolution
heat is not released or absorbed (solubility isn’t affected by temperature changes)
25
New cards
List the factors that affect solubility
molecular size, chemical substitutions, solid state structure, and melting point/boiling point.
26
New cards
How does molecular size affect solubility?
bigger molecular weight (MW), less soluble
27
New cards
How does melting point/boiling point affect solubility?
If you have a higher melting/boiling point you will have lower solubility (inversely related)
28
New cards
How does chemical substitutions affect solubility?
Higher number of substitutions, the greater the solubility will be.
29
New cards
How does polarity affect solubility?
polar increases solubility, nonpolar decreases solubility
30
New cards
How does solid state structure affect solubility?
Crystalline has low solubility, amorphous as high solubility
31
New cards
crystalline structure
Regular pattern, high stability but low solubility, polymorphism
32
New cards
amorphous structure
disordered arrangement, low stability but high solubility, crystallize overtime
33
New cards
crystalline polymorphs
solids that have more than one crystalline form; stability increases but bioavailability decreases
34
New cards
solvate
drug and solvate molecules associated together in producing a crystal
35
New cards
hydrate
solvate with water as the solvent
36
New cards
The greater the degree of solvation, the
lower the solubility and dissolution rate as compared to the anhydrous form
37
New cards
What are the 3 dosage forms of solvents?
topicals, oral, or injections
38
New cards
Lipophilic compounds
compounds that dissolve in nonpolar solvents
39
New cards
semipolar solvent
falls between polar solvent and nonpolar solvent (capable of dissolving both polar and nonpolar)
40
New cards
cosolvents
solvents used in combination to increase a solute’s solubility
41
New cards
Pharmacokinetics
what the body does to the drug
42
New cards
Pharmacodynamics
what the drug does to the body
43
New cards
Fancy term for drug efficacy and toxicity
pharmacodynamics
44
New cards
bioavailability
subcategory of absorption and is the fraction (%) of an administered drug that reaches the systemic circulation
45
New cards
When is bioavailability 100%?
via IV injection
46
New cards
First pass effect
concentration of drug is greatly reduced before it reaches systemic circulation (occurs in liver mainly but also gut; bioavailability decreases)
47
New cards
Cmax
highest concentration of drug in the blood measured after a dose (typically happens a few hours after dose given)
48
New cards
Tmax
time of peak plasma concentration (Cmax) on the curve
49
New cards
Area under the curve (AUC)
overall amount of the drug in the bloodstream after a dose
50
New cards
Cmin
lowest concentration of the drug in the blood that is measured after a dose (happens right before receiving the usual dose)
51
New cards
t1/2
amount of time it takes to eliminate half of any drug from the body (important PK measure for showing how often a drug must be dosed)
52
New cards
Steady state
when a person is on a drug for a long enough time the concentration no longer builds up in the bloodstream (happens after about 5 half lives)
53
New cards
How do drugs move across a membrane
through a solution
54
New cards
liquid solution
homogenous solution compromised of a solute and solvent
55
New cards
Dissolve
to make or become liquid
56
New cards
Solubility (pt 2)
ability to dissolve in solution
57
New cards
Diffusion layer model
If dissolution is favored, considered soluble; if dissolution is not favored, considered insoluble
58
New cards
rate of dissolution
how fast a molecule moves into a solution
59
New cards
Noyes-Whitney equation
if any terms (excluding h) increase, dissolution increases (direct); if h increases, dissolution decreases (inverse)
60
New cards
How does surface area affect rate of dissolution?
increased surface area means increased rate of dissolution
61
New cards
Micronize
reduce particles to just a few microns in diameter
62
New cards
Saturation solubility (Cs)
concentration of stagnant later (higher Cs, faster dissolution rate)
63
New cards
concentration of bulk solution (Cb)
very close to zero
64
New cards
concentration gradient
Cs-Cb
65
New cards
basic salt form of a weak acid drug
salt form has better dissolution
66
New cards
acidic salt form of a weak base drug
dissolves faster in GI fluid; lower pH increases solubility
67
New cards
why are salts selected?
in order to improve bioavailability, manufacturability, and crystallinability
68
New cards
what happens when stagnant layer (h) gets thicker?
dissolution will decrease
69
New cards
what affects h (thickness)
agitation and viscosity of dissolution medium
70
New cards
Fick’s law
diffusion through the stagnant/diffusion layer determines how fast a molecule dissolves
71
New cards
Rate limiting step of drug dissolution is
diffusion across the stagnant layer (occurs slow)
72
New cards
advantages to increasing dissolution rate
to increase bioavailability (less dose has same effect, which could mean less side effects); alters pharmacokinetics
73
New cards
Ficks law of diffusion
rate of absorption= rate of diffusion
74
New cards
D
diffusion coefficient
75
New cards
S
surface area of membrane at absorption site
76
New cards
K
oil/water coefficient
77
New cards
h
membrane thickness
78
New cards
Ca
drug concentration at absorption site
79
New cards
Cp
drug concentration in plasma
80
New cards
P
permeability coefficient
81
New cards
absorption
passive diffusion across a lipophilic membrane
82
New cards
adsorption
adhesion of dissolved molecules to a solid surface
83
New cards
rate of absorption depends on
concentration gradient, lipophilic character of a drug (Ko/w), surface area of membrane, diffusion coefficient
84
New cards
concentration gradient
difference in the concentration of a substance from plasma to absorption site
85
New cards
Only drug in solution is capable of passing through membranes?
concentration gradient
86
New cards
what is desirable if drug is meant for local use?
low absorption
87
New cards
Class I
high solubility, high permeability
88
New cards
Class II
low solubility, high permeability
89
New cards
Class III
high solubility, low permeability
90
New cards
Class IV
low solubility, low permeability
91
New cards
Major factors governing rate of absorption
dissolution rate, solubility, intestinal solubility
92
New cards
lipophilicity
chemical attraction of a substance to lipid or fat molecules