Amino Acids & Protein Structure Essentials
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering amino acid identities, protein structure levels, bonding, and related biochemical concepts.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
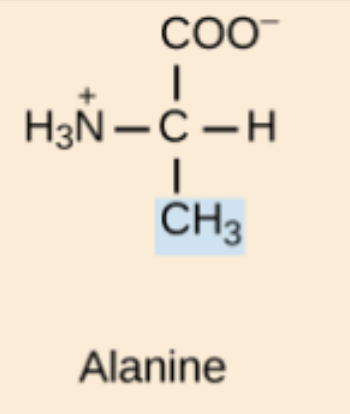
Alanine (Ala, A)
Non-polar, aliphatic amino acid.
Arginine (Arg, R)
Basic, positively charged amino acid.
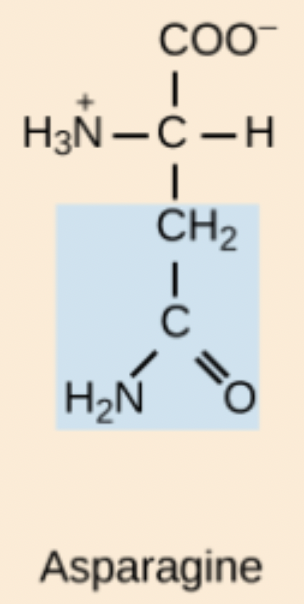
Asparagine (Asn, N)
Polar amino acid with an amide-containing side chain whose hydrogens do not ionize with pH changes.
Aspartic Acid (Asp, D)
Hydrophilic, acidic, negatively charged amino acid; deprotonated form is aspartate.
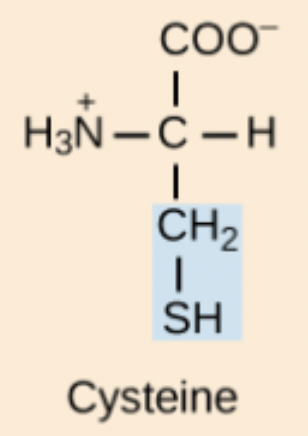
Cysteine (Cys, C)
Polar amino acid containing a thiol (sulfhydryl) that can form disulfide bonds; only amino acid with R configuration.
Glutamic Acid (Glu, E)
Acidic, negatively charged amino acid; deprotonated form is glutamate.
Glutamine (Gln, Q)
Polar amino acid with an amide side chain.
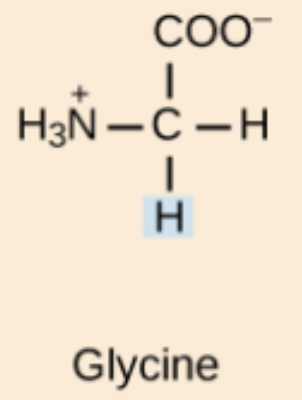
Glycine (Gly, G)
Non-polar, aliphatic amino acid; the only achiral proteinogenic amino acid.
Histidine (His, H)
Basic, positively charged amino acid containing an aromatic imidazole ring often found in enzyme active sites.
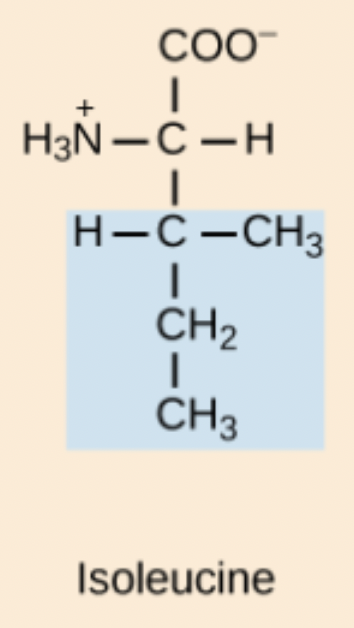
Isoleucine (Ile, I)
Non-polar, aliphatic amino acid.
Leucine (Leu, L)
Non-polar, aliphatic amino acid.
Lysine (Lys, K)
Basic, positively charged amino acid.
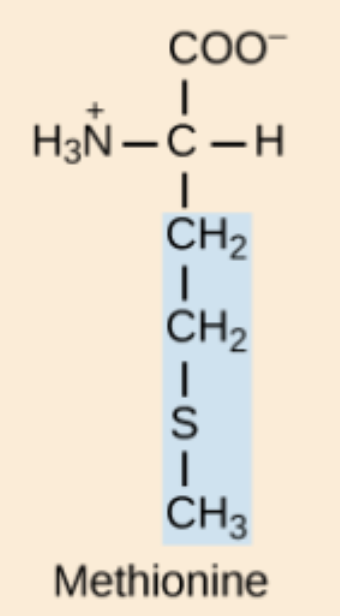
Methionine (Met, M)
Relatively non-polar amino acid containing sulfur; one of two sulfur-bearing amino acids.
Phenylalanine (Phe, F)
Non-polar, aromatic amino acid.
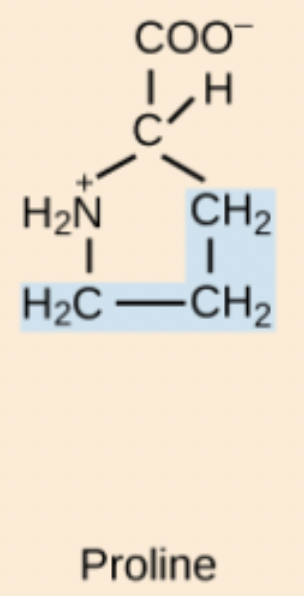
Proline (Pro, P)
Non-polar, cyclic amino acid whose rigidity induces kinks; commonly found at helix starts and β-turns.
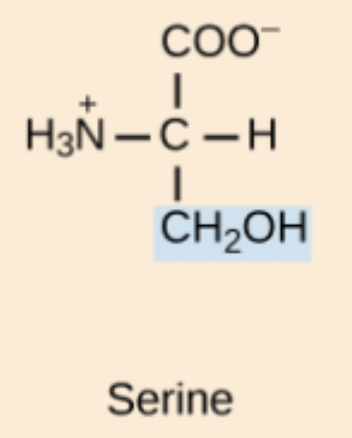
Serine (Ser, S)
Polar amino acid with a hydroxyl group.
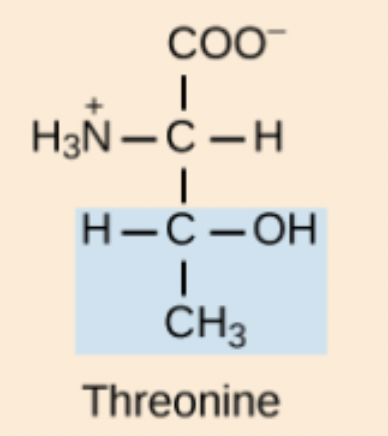
Threonine (Thr, T)
Polar amino acid with a hydroxyl group.
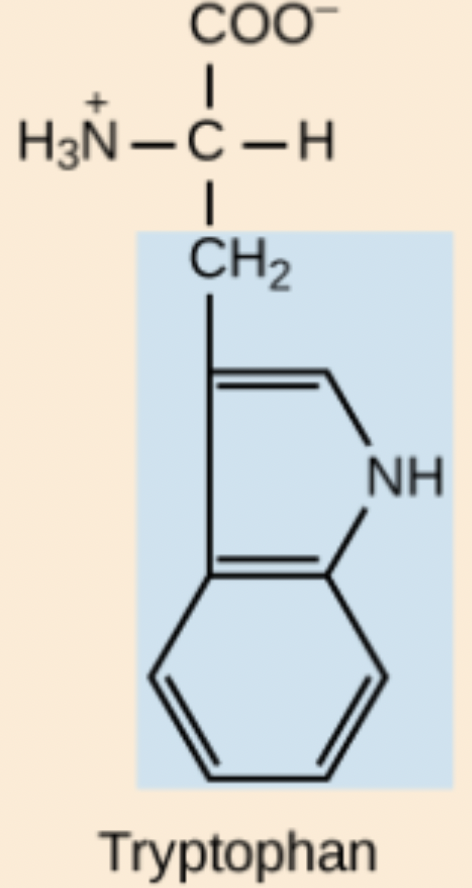
Tryptophan (Trp, W)
Non-polar, aromatic amino acid.
Tyrosine (Tyr, Y)
Slightly polar, aromatic amino acid due to its phenolic –OH.
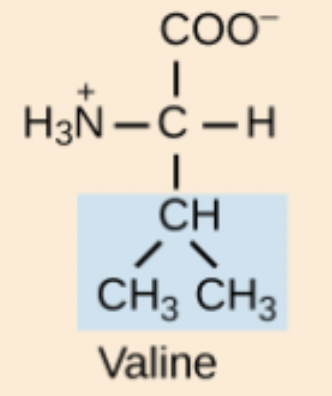
Valine (Val, V)
Non-polar, aliphatic amino acid.
Amphoteric
Able to act as both an acid and a base; property of amino acids.
Zwitterion
Molecule bearing both a positive and a negative charge simultaneously; typical form of amino acids at physiological pH.
Isoelectric Point (pI)
Average Pka1 and Pka2
The pH at which an amino acid carries no net charge.
Carboxylic acid 2.15
Amide 9.52
pI Calculation Rule
Average the two pKa values that correspond to the +1 and –1 charge states of the molecule.
Deprotonation Rule
When pH > pKa, the ionizable group is deprotonated; when pH < pKa, it is protonated.
Peptide Bond
Resonance-stabilized amide linkage joining amino acids; exhibits partial double-bond character.
Peptide Bond Formation
Condensation (dehydration) reaction that releases water.
Oligopeptide
Peptide consisting of ≤20 amino acid residues.
Polypeptide
Amino-acid chain longer than 20 residues.
Primary Structure
Linear sequence of amino acids held by peptide bonds.
Secondary Structure
Regular patterns (α-helices, β-sheets) stabilized by backbone hydrogen bonds.
Alpha Helix
Right-handed coil with 3.6 residues per turn and backbone H-bonds every fourth residue.
Beta Pleated Sheet
Sheetlike arrangement of peptide strands lying side by side, stabilized by H-bonds.
Proline’s Role in Secondary Structure
Its rigid ring introduces kinks, disrupting helices/sheets but stabilizing starts and turns.
Tertiary Structure
Three-dimensional folding driven by side-chain interactions: hydrophobic effect, H-bonds, salt bridges, disulfide bonds.
Quaternary Structure
Assembly of multiple tertiary subunits; enables stability, reduced genetic load, catalytic cooperation, and allostery.
Hydrophobic Effect
Non-polar residues bury inside proteins, increasing water entropy and driving spontaneous folding.
Solvation Layer
Ordered layer of solvent molecules surrounding a solute due to electrostatic interactions.
Fibrous Protein
Protein shaped as long strands or sheets.
Globular Protein
Protein with roughly spherical shape.
Conjugated Protein
Protein that contains a covalently bound prosthetic group essential for function.
Prosthetic Group
Covalently attached non-protein molecule (e.g., vitamin, metal ion) required for protein activity.
Glycoprotein
Protein with a carbohydrate prosthetic group.
Lipoprotein
Protein with a lipid prosthetic group.
Nucleoprotein
Protein with a nucleotide prosthetic group.
Subunit
Individual polypeptide chain within a quaternary protein complex.
Disulfide Bond
Covalent S–S linkage formed by oxidation of two cysteine residues.
Cystine
The disulfide-linked pair of cysteine residues.
Disulfide Bond Formation
Oxidation reaction joining two cysteines.
Peptide Drawing Direction
Written from N-terminus (left) to C-terminus (right).
N-Terminus
Free amino group at the beginning of a peptide chain.
C-Terminus
Free carboxyl group at the end of a peptide chain.
Sequencing
Laboratory determination of a protein’s primary structure, often via underlying DNA.
Amino Acid Titration Curve
Resembles two monoprotic curves (three if the side chain is ionizable).
High vs. Low pH Behavior
At high pH ionizable groups are deprotonated; at low pH they are protonated.
Disulfide Bond Disruption
β-Mercaptoethanol reduces S–S bonds, aiding protein denaturation.
Protein Structural Classes
Fibrous and globular proteins.
A amino acid structure
Ala
G amino acid structure
Gly
V amino acid structure
Val
L amino acid structure
Leu
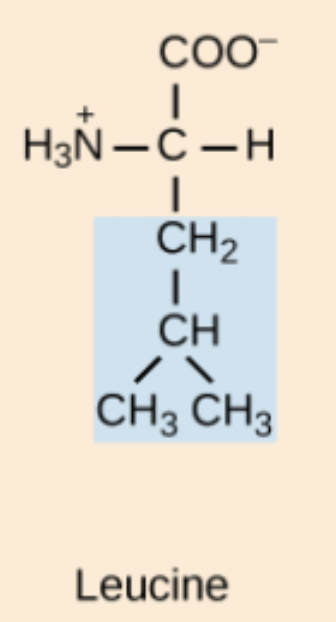
M amino acid structure
Met
I amino acid structure
Iso
S amino acid structure
Ser
T amino acid structure
Thr
C amino acid structure
Cys
P amino acid structure
Pro
N amino acid structure
Asn
Q amino acid structure
Gln
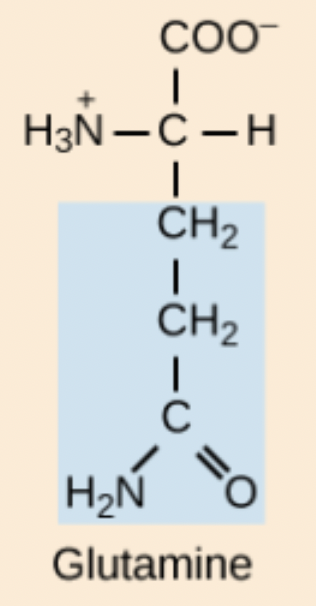
K amino acid structure
Lys
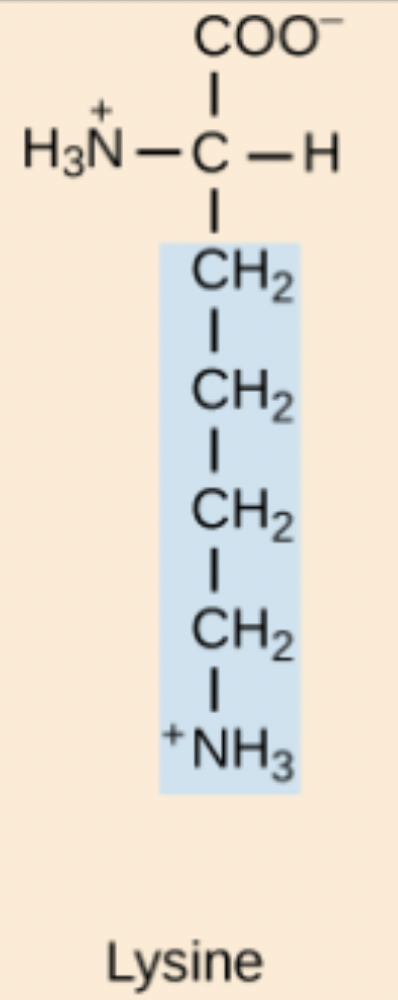
R amino acid structure
Arg
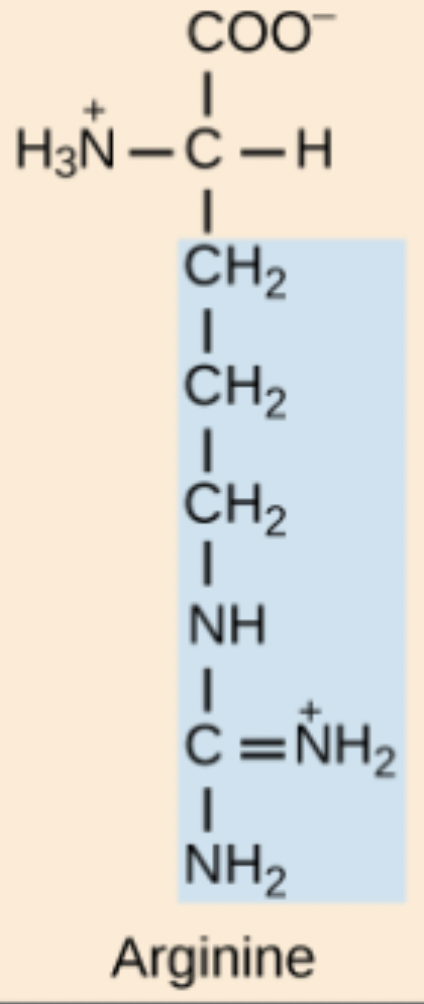
H amino acid structure
His
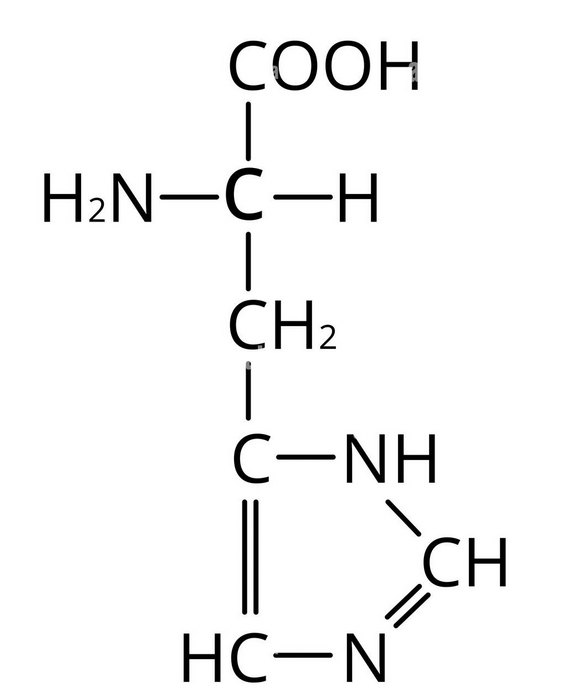
D amino acid structure
Asp or Aspartic acid
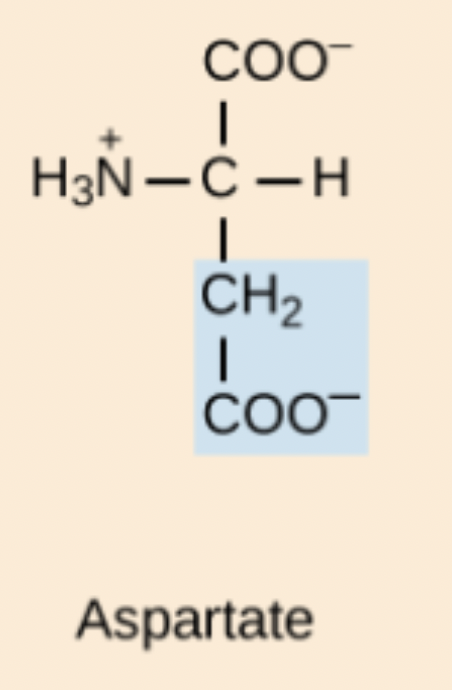
E amino acid structure
Glu or Glutamic acid
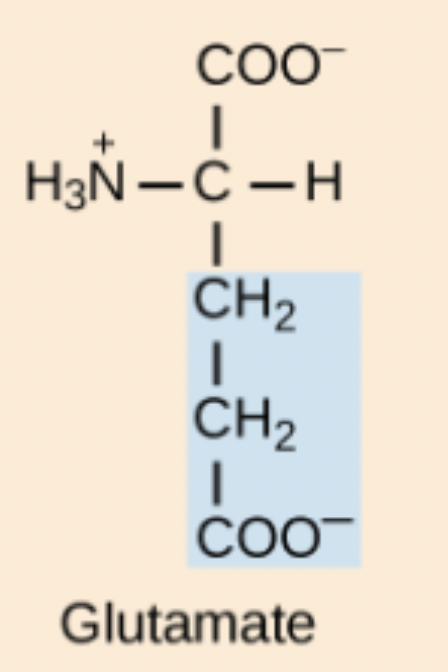
F amino acid structure
Phe
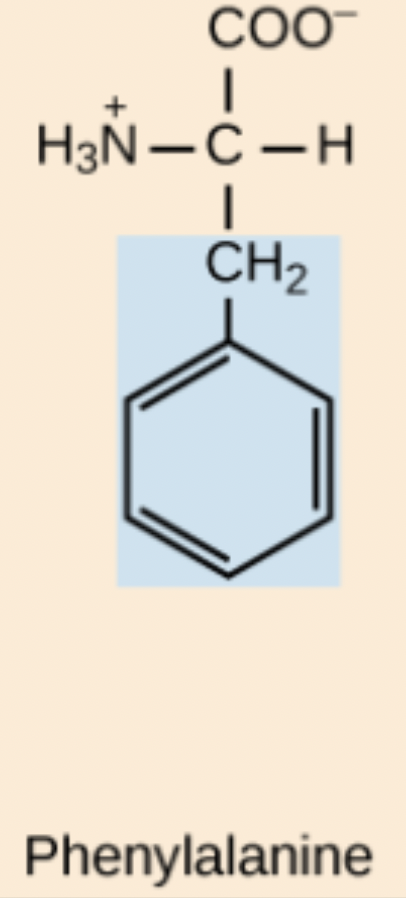
Y amino acid structure
Tyr
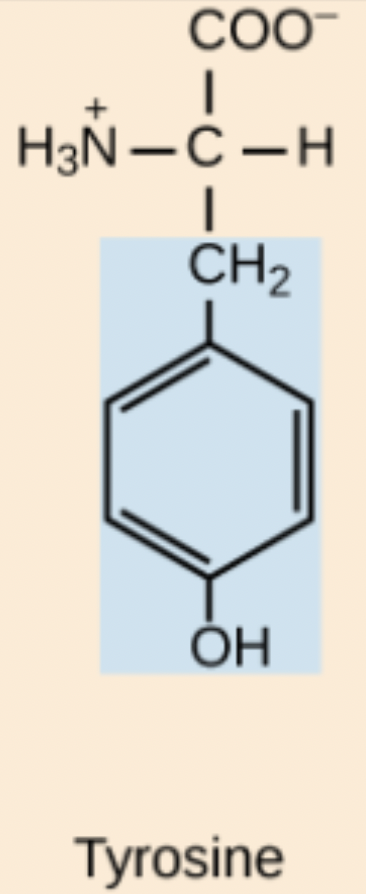
W amino acid structure
Trp