Topic 8 - Corrosion
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Corrosion
loss of material (like erosion)
Electrochemical degradation
a process in metals that leads to corrosion
OIL RIG
Oxidation is Lose (an e-), Reduction is Gain (an e-)
Anode
site of oxidation where loss of electrons occurs
Cathode
site of reduction where gain of electrons occurs
Electrolyte
the electrically conductive medium in which the Anode and Cathode reside
Potential Difference
a voltage difference that must exist between the Anode and Cathode
Galvanic Corrosion
occurs when two dissimilar metals are immersed in a conductive solution and are electrically connected
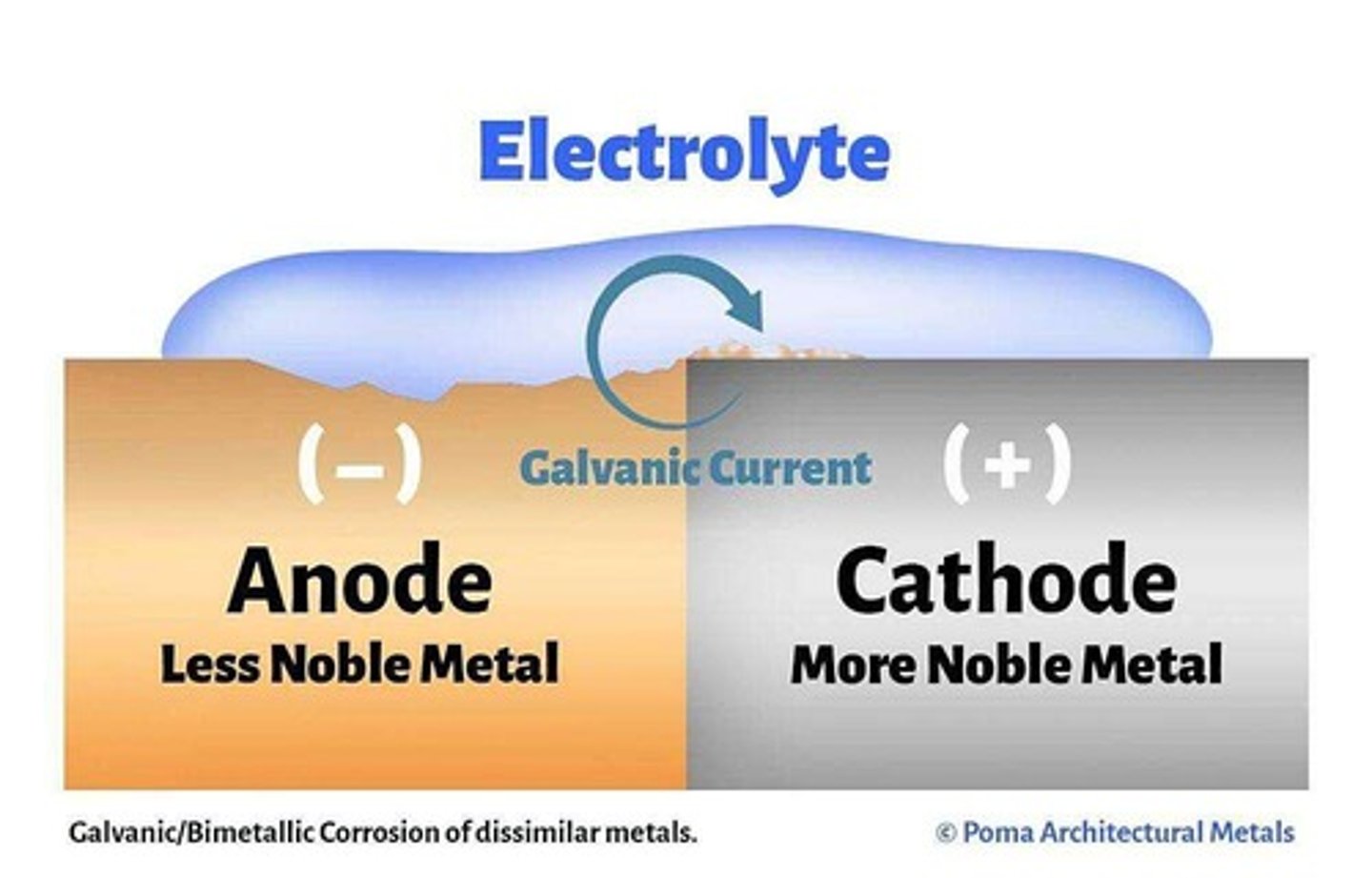
EMF
Electromotive Force, a metal's ranking in respect to reactivity
Uniform attack
evenly distributed corrosion
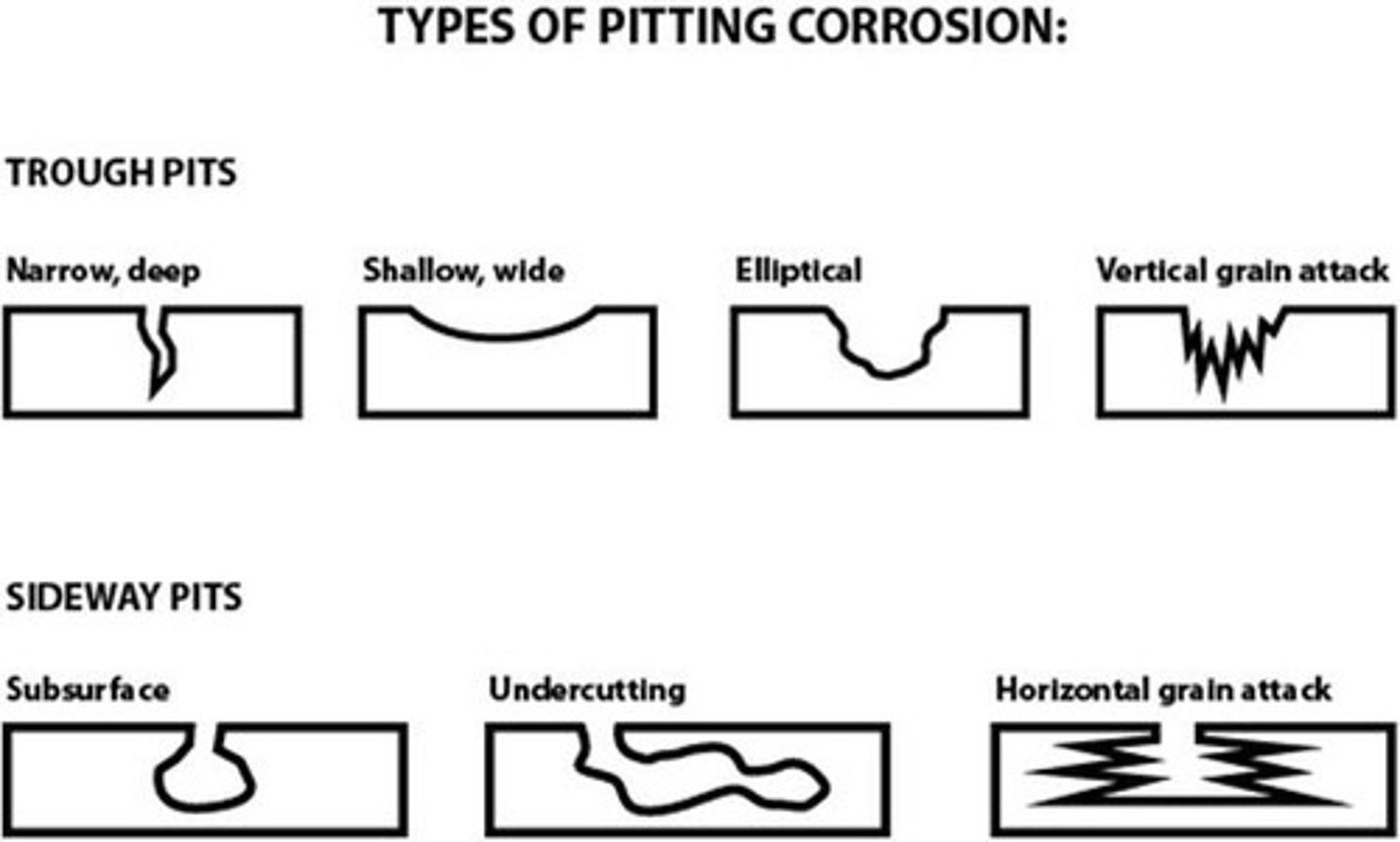
Pitting Corrosion
localized corrosion producing cavities/holes in a metal
Crevice Corrosion
attack of metal surface by a stagnant solution in crevices
Intergranular Corrosion
corrosion along grain boundaries due to depletion
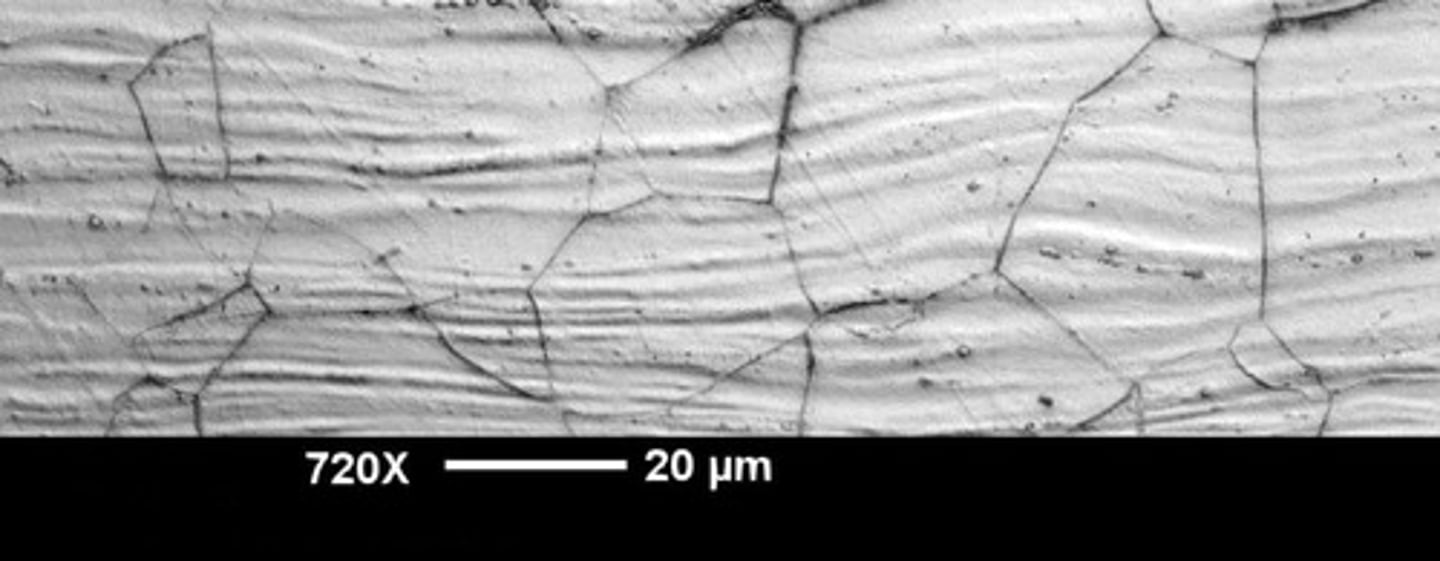
Stress Corrosion
corrosion at grain boundaries affected by tensile stress causing cracks
Hydrogen Embrittlement
absorption of diffusible hydrogen harmful to the toughness of steel
Corrosion Prevention
methods to prevent corrosion, including paint and epoxy
Passivation
formation of a protective oxide barrier under certain conditions
Sacrificial Anode
a method where a more reactive metal is used to protect another metal from corrosion
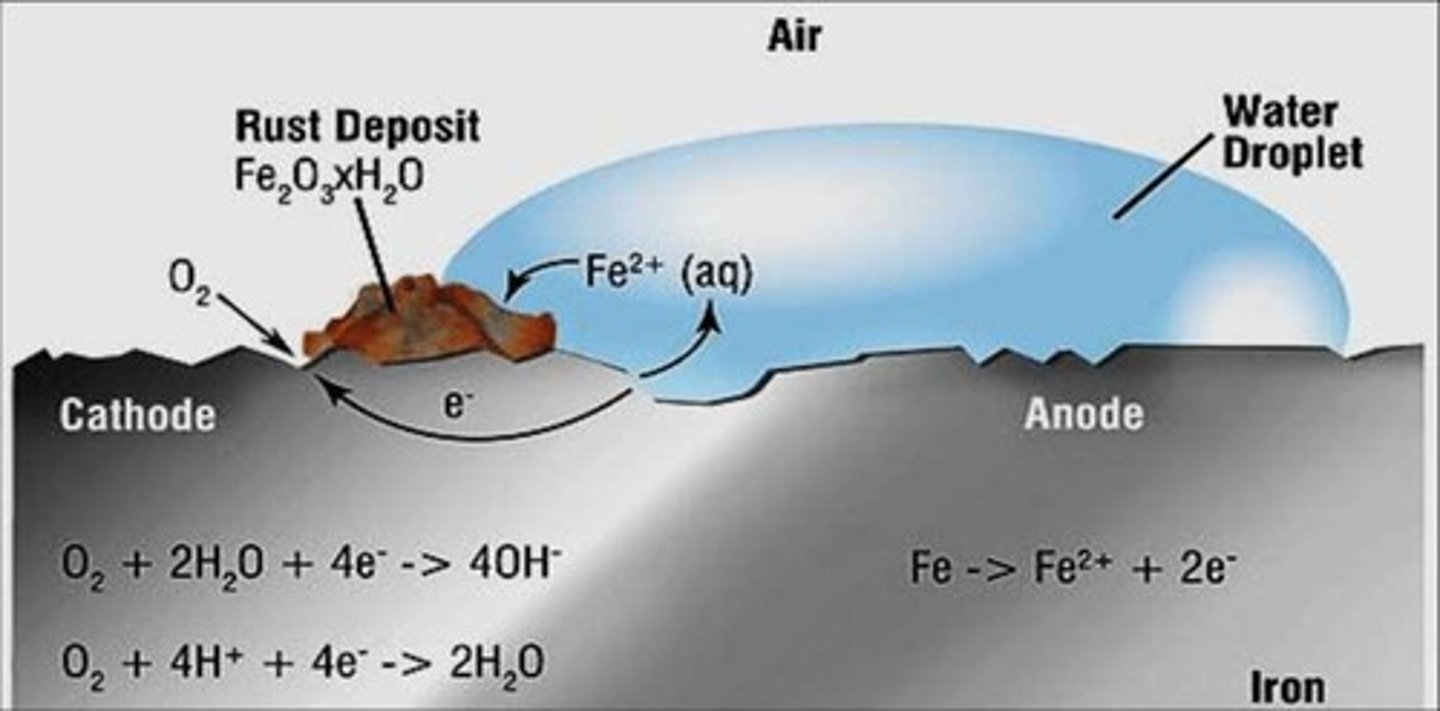
Rust
an example of oxidation involving iron in water containing dissolved oxygen
Zinc oxidation reaction
Zn → Zn2+ + 2e-
Iron oxidation reaction
Fe + ½O2 + H2O → Fe2+ + 2OH- → Fe(OH)2
Iron Hydroxide reaction
2Fe(OH)2 + ½O2 + H2O → 2Fe(OH)3
Iron oxide reaction
2Fe(OH)3 → Fe2O3 + 3H2O
Corrosive Environments
conditions that promote corrosion, such as moisture and sulfur