GCSE Geography "The Living World" ; Tropical Rainforests
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
KEY CASE STUDY! (For this topic.)
Amazon Rainforest, Brazil, South America.
General TR: Density location
Found in close proximity to the Equator
Found in regions like South America, Southeast Asia and West Africa.
General TR: Climate
An equatorial climate;
High temperatures (around 27 degrees on average all year round.)
High rainfall ( around 2000mm of rainfall on average all year round.)
General TR: Water
Water = Distinct wet season (lasts about half a year.) with high rainfall.
Impacts on other parts of TR = Excess water can cause nutrient leaching to occur, causing soil to be infertile.
General TR: Soil
Soil = Latosols topsoil (red coloured, iron-rich soil) is formed due to rapid nutrient leaching.
Impacts on other parts of TR = Due to high nutrients concentration, plants have adapted by developing shallow roots systems.
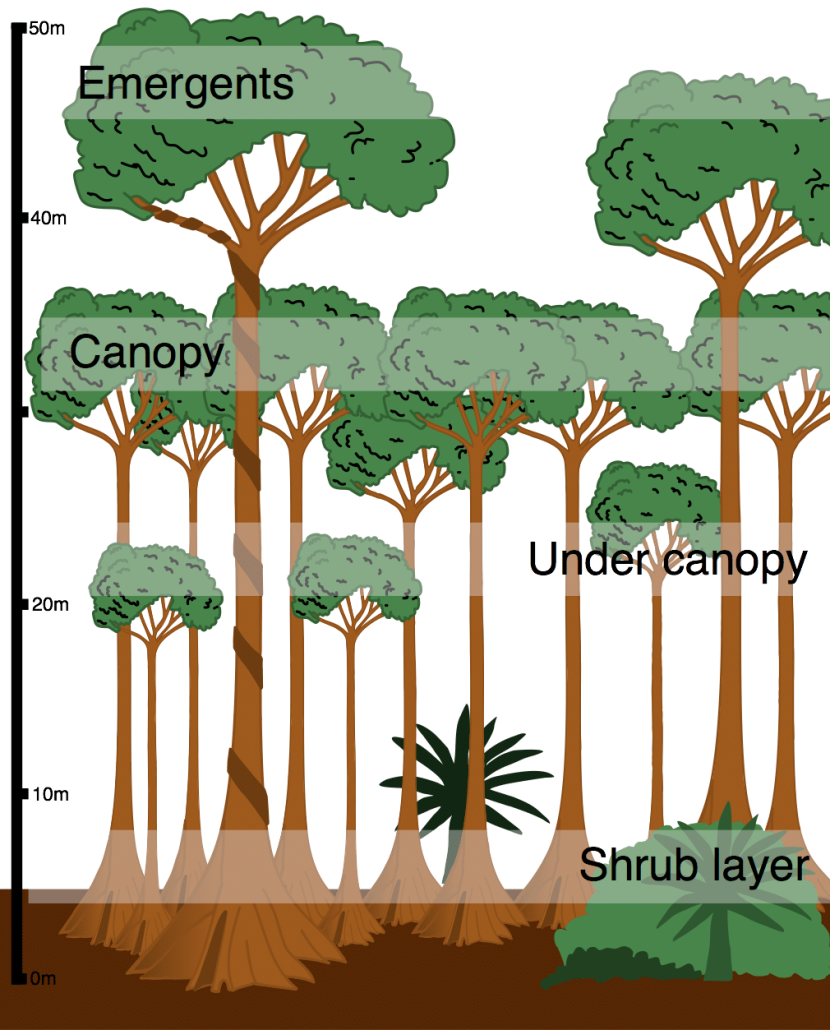
General TR: TR Layers
TR have high biodiversity levels due to the large range of habitats available in the layers of the TR. Some examples include;
Ground layer = Rodents ,e.g. Agouti (0m - 20m)
Undercanopy = Lizards, e.g. Panther Chameleon (20m - 30m)
Canopy = Climbing animals, e.g. Howler Monkeys (30m - 40m)
Emergent = Birds, e.g. Toco Toucan (40m ≤)
General TR: Plant adaptations
Some key plant adaptations are -
Epiphytes = Specially adapted plants capable of growing on other vegetation to grow themselves;
Lichens = Plants capable of growing tree barks and rocks.
Rainforest trees (e.g. the Kapok tree) = Have a number of adaptations in order to maximise growth;
Wide and waxy leaves = Maximises photosynthesis while ensuring surface run-off of rainfall.
Smooth bark = Allows for surface run-off of rainfall to take place.
Buttress roots = Specially adapted tree roots which spread over a wide area and penetrate deep in soil to maximise nutrient absorption.
General TR: Animals adaptations
Some key animal adaptation are -
Camouflage = Allows animals to avoid predators.
Flight = Allows for easier mobility through TR.
Adapted limbs = Allows for easier mobility through TR.
Nocturnal = Allows animals to conserve energy.
Amazon Rainforest; Biodiversity comparison
The entirety of the Amazon contains around 16,000 types of tree species.
In comparison, the entirety of North America has around 700 types of tree species.
General TR; Reasons for biodiversity
Some of the reasons for such a biodiversity are-
Lack of human interaction
Climactic conditions
General TR; Threats and issues with biodiversity
Some of the threats to the TR’s biodiversity are - PIA
Agriculture (“Slash-and-burn” methods)
Infrastructure (Deforestation demands)
Pollution (Global warming)
Some of the issues with these threats are - FE
Forced relocation of local inhabitants.
Extinction of animal and plant species.
Amazon Rainforest; Causes of deforestation
Some of the key causes of deforestation are - REMPS
Road building = The construction of the Trans-Amazonian Highway created an estimated 5 million hectares of deforested land.
Energy development = The construction of the Belo Monte Dam in the Xingu river caused 40,000 hectares of rainforest to be flooded.
Mineral extraction = The continuous expansion of the Carajas mine has cleared tens of hundreds of millions of trees.
Population growth = The growth of demand for tree-based products from a growing population (0.61% at 212.64 million as of 2024) has contributed to increased reliance of felling.
Substinence farming = Cattle ranching of the Amazon contributes to 80% of all its deforestation (1.5 million hectares per year in total.)
Amazon Rainforest; Rate of deforestation
The rates can be seen in the following;
1990s-2000s: High deforestation; (~20,000-30,000 km²/year), peaking at 27,000 km² in 2004.
2004-2012: 70% drop; Due to government interventions (e.g. the Action Plan), lowest at 5,000 km²/year by 2012.
2012-2018: Stabilization; Fluctuating around 6,000-8,000 km²/year.
2019-2021: Sharp increase; ~10,000 km² in 2019, peaking at 11,000 km² in 2020 due to relaxed regulations.
General TR: Impacts of deforestation
Some of the impacts are -
Economic impacts = More positive.
Improved infrastructure
Increased job opportunities
Cheaper utilities, e.g., cheap hydroelectricity
Environmental impacts = More negative.
Increased soil erosion due to higher exposure to torrential rain.
Increased CO2 emissions due to more trees being burnt.
Drier climate due to decreased rates of evotranspiration due to less trees. (Can also lead to increased number of forest fires.)
General TR: Importance of the TR to the World
Some of the key reasons are -
1) To People =
a) Medicine; 25% of all medicines come from the TR.
b) Resources; 37% of global coal reserves in Southeast Asia alone are in TR’s.
c) Indigenous tribes; Achuar Tribe, Peru = A group of tribespeople who rely on the TR for natural resources; made up of 10,000 people.
2) To the Environment =
a) Water; 20% of the world’s freshwater supply comes from the Amazon Basin.
b) Climate; 30% of the world’s oxygen supply comes from TR’s.
c) Biodiversity; TR’s contain around half of the world’s biodiversity.
General TR; Sustainable Management methods
Some key sustainable management methods include - CIDSE
1) Conservation =
Givaudan (a TN perfume corporation) which exchanges the conservation of parts of the Amazon in Venezuela for large volumes of tonka beans with Conservation International.
2) International Agreements =
The “International Tropical Timber Agreement” restricts the trade of unlicensed hardwood on the market to reduce illegal deforestation; involves 55 countries (29 producers, 25 consumers.)
3) Debt reduction =
“Debt-for-nature swapping” agreements, e.g. between U.S.A relieving Brazil of £13m of debt in exchange for the protection of large parts of the Amazon .
4) Selective logging =
The Malaysian Selective Logging Management System (40 year monitoring plan) = Has allowed for more sustainable and legalised logging of their TR to take place.
5) Ecotourism =
Santa Lucia Cloudforest Reserve, Ecuador = Has reduced the environmental effect of tourism, e.g. eco-lodge construction, while making it more beneficent to locals, e.g. the reserve employs over 6,000 people