Ch 22 questions
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
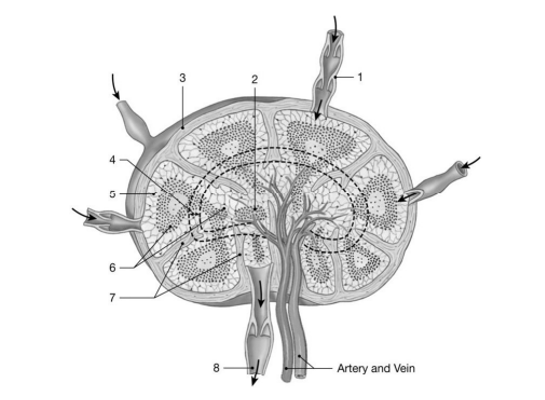
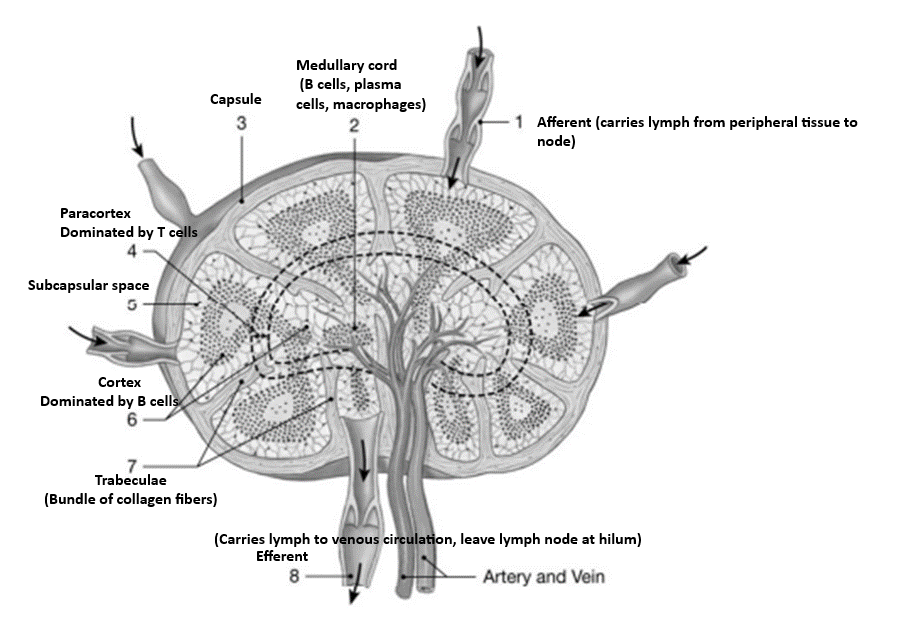
Lymph nodes do all of the following except
A) remove excess nutrients from the lymph.
B) accumulate cancer cells.
C) remove debris and pathogens from the lymph.
D) produce antibodies through B cells.
E) monitor the contents of lymph.
remove excess nutrients from the lymph.
Immunoglobulins, formed of five subunits, that are the first antibodies to be produced in response to infection, are
A) IgA. B) IgD. C) IgE. D) IgG. E) IgM.
IgM
Immunoglobulins that are primarily found in glandular secretions such as saliva and tears are
A) IgA. B) IgD. C) IgE. D) IgG. E) IgM.
IgA
Immunoglobulins that are most abundant and are responsible for resistance against many viruses, bacteria, and bacterial toxins are
A) IgA. B) IgD. C) IgE. D) IgG. E) IgM.
IgG
The only antibodies that normally cross the placenta are
A) IgA. B) IgD. C) IgE. D) IgG. E) IgM.
IgG
Mary is having an allergic reaction in which her mast cells and basophils are sensitized and active. Which immunoglobulin is responsible for this reaction?
A. IgA
B. IgD
C. IgG
D. IgE
E. IgM
IgE
During the primary response, which antibody peaks sooner? During the secondary response, which antibody level is higher?
A) IgM; IgG
B) IgG; IgM
C) IgD; IgE
D) IgE; IgA
E) IgA; IgG
IgM; IgG
The medullary cords of a lymph node contain ________ lymphocytes and plasma cells.
A) medullary
B) NK
C) cordal
D) B
E) cytotoxic
B
The cells responsible for humoral immunity are the ________ cells.
A) suppressor T
B) B
C) helper T
D) NK
E) cytotoxic
B
Each of the following is a physical barrier to infection except
A) body hair.
B) epithelium.
C) complement.
D) basement membranes.
E) secretions
complement
A crime scene investigator found that a biological fluid sample contains a large amount of IgA-type antibody. This fluid is probably
A) lymph. B) interstitial. C) tears. D) blood. E) serum.
tears
An infection and inflammation of the aggregated lymphatic nodules in the pharynx is called
A) lymphosis.
B) indigestion.
C) laryngitis.
D) tonsillitis.
E) lymph edema.
tonsillitis
Lymphocytes provide an adaptive or specific defense known as the
A) inflammation of tissues.
B) immune response.
C) lymphocytic response.
D) adaptive defense.
E) phagocytic respons
immune response
Newborns gain their immunity initially from
A) contact with viruses and bacteria.
B) early immunizations during routine neo-natal check-ups.
C) antibodies passed across the placenta from the mother.
D) breast milk.
E) contact with siblings.
antibodies passed across the placenta from the mother.
During a primary immune response, the
A) only the IgM titer is affected.
B) IgG titer is initially higher than the IgM titer.
C) IgM titer and the IgG titer rise in parallel.
D) IgM titer is initially higher than the IgG titer
IgM titer is initially higher than the IgG titer
Lymphocytes may be found in which of the following tissues or organs?
A) lymph nodes
B) spleen
C) tonsils
D) thymus
E) All of the answers are correct
All of the answers are correct
The attraction or repulsion of certain cells to chemicals in their environment is called
A) diapedesis.
B) infection.
C) cytotoxicity
D) polarity.
E) chemotaxis.
chemotaxis.
The body's innate defenses include all of the following except
A) complement.
B) the skin.
C) inflammation.
D) antibodies.
E) interferon
antibodies
________ cells enable the immune system to respond quickly and robustly if the same antigen is encountered a second time.
A) Primary B) Secondary C) Transponder D) Memory E) Responder
Memory
Autoantibodies are
A) the first step in immunological competence.
B) produced by activated T cells.
C) produced during an allergic reaction.
D) important in tissue rejection reactions.
E) directed against the body's own antigens
directed against the body's own antigens
Compared to blood capillaries, lymph capillaries exhibit all of the following except that they
A) are smaller in diameter.
B) have no basement membrane.
C) have only a tunica interna.
D) have walls of endothelial cells that overlap like shingles.
E) are frequently irregular in shape
are smaller in diameter.
The movement of phagocytes through the capillary wall is calle
A) diapedesis.
B) chemotaxis.
C) adherens.
D) diffusion.
E) transcytosis
diapedesis.
Lymphatic vessels are located in almost all portions of the body except the
A) throat.
B) groin.
C) CNS.
D) periphery.
E) renal arterie
CNS
Immunity that results from exposure to an antigen in the environment is called ________ immunity.
A) naturally acquired active
B) passively acquired
C) natural passive
D) innate
E) automatically acquired
naturally acquired active
________ exists when the immune system does not respond to a particular antigen.
A) Versatility B) Memory C) Adaptation D) Tolerance E) Immunity
Tolerance
In an experimental situation, a rabbit is exposed to a viral antigen to which it makes antibodies. These antibodies are then purified and injected into a human with the same viral disease. This is an example of
A) active immunization. B) alloimmunity. C) innate immunity. D) natural immunity. E)passive immunization
passive immunization
Stem cells that will form B cells or NK cells are found only in the
A) kidneys. B) liver. C) thymus. D) spleen. E) red bone marrow
red bone marrow
The ________ lymphatics leave the lymph node at the hilum.
A) descending B) ascending C) afferent D) lateral E) efferent
efferent
Examples of physical barriers against pathogens include
A) sebaceous glands.
B) mucus.
C) epithelia.
D) epidermal layers.
E) All of the answers are correct
All of the answers are correct
Lymphocytes
A) respond to antigens.
B) are actively phagocytic.
C) are primarily found in red bone marrow.
D) decrease in number during infection.
E) destroy red blood cells.
respond to antigens.
T is to ________ as B is to ________.
A) thyroid-drawn; bowel-developed
B) thymus-dependent; bone marrow-derived
C) non-thymus-dependent; bottom-located
D) trabeculae-descended; bursa-origin
E) top-located; bottom-locate
thymus-dependent; bone marrow-derived
Innate defenses include
A) physical barriers.
B) inflammation.
C) phagocytic cells.
D) interferons.
E) All of the answers are correct
All of the answers are correct
The lymphatic system does all of the following except
A) transports gases to and away from lymph nodes.
B) transports lipids from the digestive tract.
C) eliminates variations in the composition of interstitial fluid.
D) helps maintain normal blood volume.
E) fights infection.
transports gases to and away from lymph nodes
The white pulp of the spleen is populated by
A) fibrous connective tissue. B) trabeculae. C) lymphocytes. D) veins. E) arteries
lymphocytes
Inflammation produces localized
A) swelling.
B) redness.
C) heat.
D) pain.
E) All of the answers are correct.
All of the answers are correct.
The various classes of immunoglobulins are differentiated on the basis of their
A) asymmetry.
B) antigen specificity.
C) light-chain variable segments.
D) heavy-chain constant segments.
E) reactivity.
heavy-chain constant segments.
Which of the following innate internal defenses work by interfering with viral replication?
complement proteins |
T lymphocytes |
interferons |
phagocytes |
interferons
Which of the following are primary lymphoid organs?
appendix and spleen |
lymph nodes and tonsils |
bone marrow and thymus |
spleen and thymus |
bone marrow and thymus
Which of the following areas in a secondary lymphoid organ allows intimate contact between blood and the lymphocytes?
germinal centers of the lymph nodes |
Hassall’s corpuscles of the thymus |
white pulp of the spleen |
red pulp of the spleen |
white pulp of the spleen
Where in the lymph node do the T cells first encounter antigens presented by dendritic cells?
medullary cords in the medulla |
germinal centers of the cortex |
deep in the cortex |
lymphoid follicles of the outer cortex |
deep in the cortex
What is the type of immunity one acquires through contracting a disease such as chicken pox from another infected person?
naturally acquired active immunity
The primary function of the lymphatic system is
defending the body against both external and internal threats. |
the production and distribution of plasma proteins. |
the production and maturation of leukocytes. |
circulation of nutrients and dissolved gases. |
the transport of hormones. |
defending the body against both external and internal threats.
The lymphatic system does all of the following except
helps maintain normal blood volume. |
transports lipids from the digestive tract. |
transports gases to and away from lymph nodes. |
fights infection. |
eliminates variations in the composition of interstitial fluid. |
transports gases to and away from lymph nodes.
All of the following are true of the thymus gland except that it
produces T cells. |
lies in the anterior mediastinum. |
reaches its greatest relative size during the second year of life. |
activates B cells. |
involutes after puberty. |
activates B cells.
Which class of cells is particularly abundant in the red pulp of the spleen?
Natural Killer cells |
neutrophils |
T lymphocytes |
macrophages |
B lymphocytes |
macrophages
If the thymus shrank and stopped making thymosins, we would expect to see an immediate decrease in the number of
red blood cells. |
T cells. |
NK cells. |
B lymphocytes. |
neutrophils. |
T cells.
Which of the following is not a secondary lymphoid tissue or organ?
tonsils |
spleen |
lymph nodes |
MALT |
thymus |
thymus
The lymphoid organ that acts like a filter as lymph passes through is
adenoids. |
lymph nodes. |
tonsils. |
appendix. |
thymus. |
lymph nodes.
The blood-thymus barrier is made up of
macrophages. |
mature T cells. |
immature T cells. |
plasma cells. |
epithelial reticular cells. |
epithelial reticular cells.
Lymphocytes that destroy foreign cells or virus-infected cells are ________ cells.
B |
helper T |
suppressor T |
cytotoxic T |
plasma |
cytotoxic T
Histamine increases blood flow and vascular permeability. This would account for all of the following changes that occur during inflammation except
chemotaxis of phagocytes. |
swelling of the inflamed tissue. |
redness of the inflamed tissue. |
heat of the inflamed tissue. |
movement of defense proteins and cells into the interstitial space. |
chemotaxis of phagocytes.
Leslie has a severe sore throat and the lymph nodes in her neck are swollen. This would indicate that
the lymph nodes have increased their secretion of thymosin. |
the lymph nodes are actively producing phagocytes. |
the focus of the infection is the lymph nodes. |
lymph is not flowing consistently through these lymph nodes. |
the lymph nodes contain an increased number of lymphocytes. |
the lymph nodes contain an increased number of lymphocytes.
A sample of John's blood shows a high level of pyrogens. This would indicate that John
has a sore throat. |
is running a fever. |
has swollen lymph nodes. |
is feeling achy. |
is producing T lymphocytes. |
is running a fever.
Free phagocytes found in the air sacs of the lungs are called
pleurocytes. |
histiocytes. |
alveolar macrophages. |
Kupffer cells. |
microglia. |
alveolar macrophages.
Which of the following is not a property of an IgG heavy chain?
binds one light chain |
binds complement in the constant region |
has one variable segment |
has one constant segment |
binds antigen at both ends |
binds antigen at both ends
Each IgG has ________ binding sites for attachment to antigenic determinants.
1 |
4 |
2 |
up to 8 |
as many as a 1000 |
2
In a routine examination, some blood is taken and analyzed. The results show a high IgM titer for the mumps virus but a low IgG anti-mumps titer. This would indicate the person
is relying on passive immunity. |
has just recovered from mumps. |
is immune to mumps. |
was recently infected with mumps. |
is allergic to mumps. |
was recently infected with mumps.
Stress suppresses the immune response through the action of __________.
interferons |
glucocorticoids |
colony-stimulating factors |
tumor necrosis factors |
glucocorticoids
Which of the following is NOT an effect of glucocorticoid secretion on the effectiveness of the immune response?
increased interferon activity |
reduced abundance and activity of phagocytes in peripheral tissues |
depressed inflammation response |
inhibition of interleukin secretion |
increased interferon activity
Kaposi's sarcoma is a type of cancer that is caused by the human herpesvirus-8. Which of the following would be the best treatment option for this type of cancer?
interferons |
interleukins |
colony-stimulating factors |
transforming growth factor beta |
interferons
An example of an immunodeficiency disease is __________.
type 1 diabetes |
AIDS |
thyroiditis |
rheumatoid arthritis |
AIDS
Which class of T lymphocyte is killed by the AIDS virus?
NK |
helper T |
cytotoxic T |
suppressor T |
helper T
An accumulation of lymph in a region where lymphatic drainage has been blocked is called
A) lymphopenia.
B) lymphadenopathy.
C) lymphoma.
D) lymphedema.
E) lymphosis.
lymphedema.
Place the following steps of NK cell killing in order.
1. Secretion of perforin
2. Realignment of Golgi apparatus
3. Lysis of abnormal cell
4. Recognition and adhesion
4, 2, 1, 3
The following are steps in the cell-mediated immune response. What is the correct sequence for these steps?
1. Several cycles of mitosis occur.
2. Antigen is engulfed and presented by a macrophage.
3. Cytotoxic T cells migrate to focus of infection.
4. T cells with specific receptors recognize the antigen.
5. T cells differentiate into cytotoxic T cells or T memory cells.
6. Cytotoxic T cells release perforin and/or lymphotoxin.
2,4,1,5,3,6
The following are steps in the cell-mediated immune response. What is the correct sequence for these steps?
1. Antigen is engulfed and presented by a macrophage.
2. T cell activation and cell division occur, producing cytotoxic T cells and memory T cells.
3. Cytotoxic T cells release perforin and/or lymphotoxin.
4. Inactive T cells with specific receptors recognize the antigen
1, 4, 2, 3
All of the following are characteristics of adaptive defenses except
A) versatility.
B) tolerance.
C) memory.
D) specificity.
E) present at birth.
present at birth.
What type of immunity develops after receiving a vaccine?
artificially acquired active immunity
Suppressor T cells act to
inhibit T and B cell activities
Class I MHC proteins
For T cells
Cass II MHC proteins
For B cells
When an antigen is bound to a Class I MHC molecule, it can stimulate a ________ cell.
A) B
B) plasma
C) helper T
D) cytotoxic T
E) NK
cytotoxic T
When an antigen is bound to a Class II MHC protein, it can activate a ________ cell.
A) B
B) plasma
C) helper T
D) cytotoxic T
E) NK
helper T
B cells are primarily activated by the activities of
A) antigens.
B) antibodies.
C) helper T cells.
D) macrophages.
E) plasma cells.
helper T cells.
CD8 markers are to ________ T cells as CD4 markers are to ________ T cells.
cytotoxic, helper
An abnormal cell would be identified by the immune system because it showed
Class I MHC proteins with an antigen bound.
Class II MHC proteins are present in the plasma membrane only when
an antigen-presenting cell has engulfed and is processing an antigen
A T cell can only become activated after being physically or chemically stimulated by the abnormal target cell in a process called
costimulation
Class II MHC proteins are found on which of the following cell types?
lymphocytes and antigen-presenting cells
Which class of MHC proteins presents exogenous antigens?
class II MHC proteins
Class I MHC proteins are recognized by which of the following cell types (that are destined to become T cells)?
CD8
Interferon alpha (α)
Stimulates NK cells
Interferon beta (β)
Secreted by fibroblasts
Slows inflammation
Interferon gamma (γ)
Secreted by T cells and NK cells
Stimulates macrophage activity
Cytokines
Chemical messengers released by tissue cells
Hapten (partial antigens)
attached to carrier molecule, enough to make immunity
Immediate hypersensitivity (type I)
Most commonly recognized type of allergy
Sensitization leads to production of large quantities of IgE
What types of cells are found in the white pulp of the spleen and in the red pulp of the spleen?
A) lymphocytes; epithelial reticular cells
B) lymphocytes; red blood cells
C) red blood cells; macrophages
D) red blood cells; lymphocytes
E) epithelial cells; endocrine cells
lymphocytes; red blood cells
When the immune response mistakenly targets normal body cells and tissues, a(n) ________ develops.
A) autoimmune disease
B) immunodeficiency disease
C) allergic response
D) cross-reaction
E) agglutination reaction
autoimmune disease
A sample of John's blood shows a high level of pyrogens. This would indicate that John
A) is feeling achy.
B) is producing T lymphocytes.
C) has a sore throat.
D) is running a fever.
E) has swollen lymph nodes.
is running a fever.
Which of the following is not a lymphocyte?
A) NK cells
B) plasma cells
C) memory T cells
D) macrophages
E) suppressor T cells
macrophages
Lymphatic vessels begin in peripheral tissues and ultimately drain into
A) veins.
B) peripheral capillary beds.
C) arteries.
D) the kidneys.
E) arterioles.
veins.
Lymphatic organs differ from lymphatic tissues in what way?
A) They contain T lymphocytes and lymphatic tissues do not.
B) They are found in the digestive tract and lymphatic tissues are found in the thorax.
C) They are surrounded by a fibrous capsule and lymphatic tissues are not.
D) They cannot produce antibodies, whereas lymphatic tissues can.
E) They occur throughout the body except in the head.
They are surrounded by a fibrous capsule and lymphatic tissues are not.
Most of the lymph returns to the venous circulation by way of the
A) right lymphatic duct.
B) thoracic duct.
C) cisterna chyli.
D) hepatic portal vein.
E) dural sinus
thoracic duct.
The effects of activating the complement system include all of the following except
A) destruction of target cell plasma membranes.
B) stimulation of inflammation.
C) inhibition of the immune response.
D) opsonization.
E) chemotaxis.
inhibition of the immune response.
Lymphatic tissue is found in the greatest quantity in
A) the adult spleen.
B) the adult thymus.
C) bone marrow.
D) the tonsils.
E) Peyer patches.
the adult spleen.
Fever is the maintenance of body temperature greater than
A) 105°F.
B) 99°F.
C) 98.6°F.
D) 102°F.
E) 99.5°F.
99°F.
Cytotoxic T cells can attack target cells with which of these chemical weapons?
A) secrete strong acid
B) secrete organic solvent
C) secrete free radicals
D) secrete a cytokine that triggers apoptosis
E) secrete mutant proteins
secrete a cytokine that triggers apoptosis
The cells that perform immunological surveillance are the ________ cells.
A) NK
B) plasma
C) B
D) helper T
E) suppressor T
NK