Chapter 5 - Nutrition Basics
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
What do your nutritional habits help determine?
The risk of major chronic illness, including heart disease, cancer, stroke and diabetes.
Define nutrition
The science of food and how the body uses it in health and disease.
What does caloric needs depend on?
age
body size
sex
activity level
whether a person is breastfeeding or pregnant
Define vitamins
Organic (carbon-containing) micronutrients needed in small amounts for normal gowth, reproduction and maintenance of health.
How do vitamins act as coenzymes?
They facilitate action of enzymes to help initiate a variety of chemical body responses such as:
energy production
use of minerals
growth of health tissue
What do antioxidants do and what vitamins are they?
They help preserve health cells in the body. Key vitamin antioxidants include:
vitamin e
vitamin c
vitamin a precursor beta-carotene
How many vitamins do humans need?
13
4 fat soluable
9 water soluable
What are the fat soluable vitamins?
Vitamin A
Vitamin D
Vitamin E
Vitamin K
What are dietary sources of Vitamin A?
liver
milk
butter
cheese
fortified margarine
carrots
spinach
other orange and deep-green veggies and fruits
What are the major functions of Vitamin A?
mainteneace of vision
skin
linings of the nose, mouth, digestive and urinary tracts
immune function
What are dietary sources of Vitamin D?
fortified milk and margarine
fish oils
butter
egg yolks
sunlight on skin*
What are the major functions of Vitamin D?
development and maintenance of bones and teeth
promotion of calcium absorption
What are dietary sources of Vitamin E?
vegetable oils
whole grains
nuts and seeds
leafy veggies
asparagus
peaches
What are the major functions of Vitamin E?
protection and maintenenace of cellular membranes
What are dietary sources of Vitamin K?
green leafy veggies
smaller amounts widespread in other foods
What are the major functions of Vitamin K?
production of factors essential for blood clotting and bone metabolism
What are the six classes of essential nutrients?
protiens
fats
carbs
vitamins
minerals
water
Define essential nutrients
Substances the body must get from foods because it cannot manufacture them at all or fast enough to meet its needs; include proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, and water.
How many essential nutrients are there?
50
Define digestion
A process by which the foods you eat are broken down into compounds your gastrointestinal tract can absorb and your body can use
Define macronutrients
Essential nutrients required by the body in relatively large amounts.
Define mirconutrients
Essential nutrients required by the body in smaller amounts.
What is the function of protien?
forms important parts of muscles, bone blood, enzymes, some hormones and cell membranes
repairs tissue
regulates water and acid base balance
helps in growth
supplies energy
What are the major sources of protien?
meat
fish
poultry
eggs
milk products
legumes
nuts
What is the function of carbs?
main source of energy
supplies energy to cells in brain, nervous system and blood
supplies energy to muscles during exercise
What are the major sources of carbs?
grains → breads and cereals
fruits
veggies
milk
What is the function of fats?
supplies energy
isulates, supports and cushions organs
helps absorption of fat soluable vitamins
What are the major sources of fats?
animal foods
grains
nuts
seeds
fish
veggies
What is the function of vitamins?
promotes (initiats or speeds up) specific chemical reactions within cells
help unleash the energy store in carbs, proteins and fats
critical in the production of re blood cells and the maintenance of the nervous, skeletal and immune systems
some act as antioxidants
What are the major sources of vitamins?
fruits
veggies
grains
meat
milk
What is the function of minerals?
helps regulate bofy functions
aids in growth and maintenance of body tissues
acts as catalysts for release of energy
What are the major sources of minerals?
found in most food groups
What is the function of water?
makes up ~ 60% of body weight
provides medium for chemical reactios
transports chemicals
regulates temperature
removes waste products
What are the major sources of water?
fruits
veggies
liquids
Define kilocalories/calories
Measure of energy content in food; 1 kilocalorie represents the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 litre of water by 1 degree Celsius.
How many kilocalories does a person need a day to meet their energy needs?
2000
What three classes of essential nutrients supply energy?
fat → 9 calories / gram
protein → 4 calories / gram
carbs → 4 calories / gram
note that these are also macronutrients
Define protein
Essential nutrient; a compound made of amino acids that contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Define amino acids
The building blocks of proteins.
How many amino acids are essential?
9
How many amino acids can be produced by the body?
11
How many common amino acids are there?
20
What are complete proteins?
Proteins that supply all the essential amino acids in adequate amounts. Eg:
meat
fish
poultry
eggs
milk
cheese
soy
What are incomplete proteins?
Proteins that do not supply all the essential amino acids and come from plant sources. Eg:
legumes
beans
peas
lentils
nuts
What are fats also known as?
Lipds
Define fats
The most concentrated source of usable energy @ 9 calories / gram
What two fats are essential compnents of the diet?
linoleic acid
alpha-linolenic acid
What type of fat are linoleic acid and alpha-linolenic acid? (saturated, polyunsaturated or monounsaturated)
polyunsaturated
Is linoleic acid an omega 3 fatty acid or omega 6 fatty acid?
omega 6
Is alpha-linoleic acid an omega 3 fatty acid or omega 6 fatty acid?
omega 3
What are the functions of lineoleic and alpha-linolenic acid?
they are used to make compounds that are key regulators of many body functions, such as the maintenance of blood pressue and the progess of a healthy pregnancy.
What is the biochemical compostition of most food fats?
A triglyceride → a molecule of glycerlol with three fatty acids
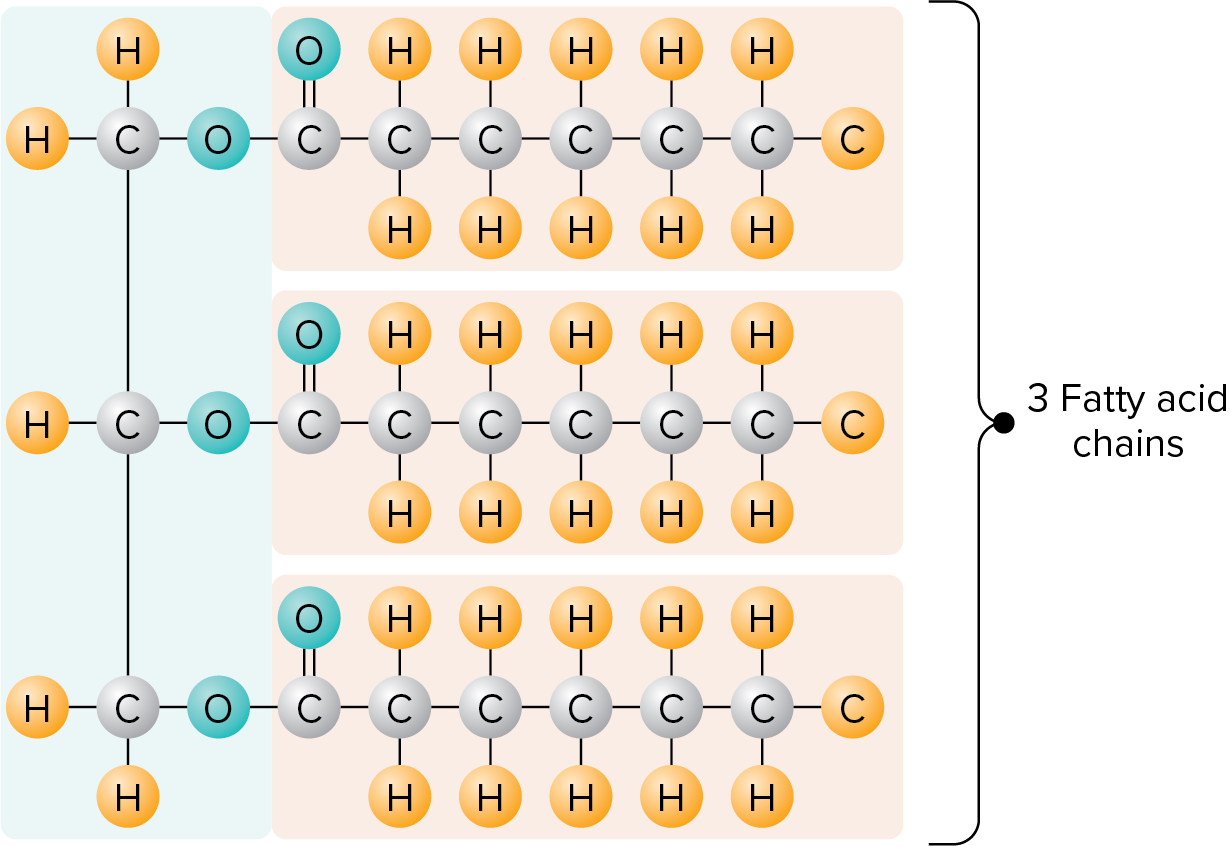
What are food fats usually composed of?
saturated fatty acids
unsaturated fatty acids
Food fats containing large amounts of saturated fatty acids are usually ______ at room temperature.
Solid
Food fats containing large amounts of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids are usually ______ at room temperature.
Liquid
What are the sources of saturated fatty acids in food?
animal products:
red meats
homogenized milk
cheese
hot dogs
lunchmeats
What are the sources of monounsaturated fatty acids in food?
plant products:
olive oil
canola oil
peanut oil
safflower oil
What are the sources of polyunsaturated fatty acids in food?
plant products:
soybean oil
corn oil
cottonseed oil
Can trans fats be naturally occuring?
Yes, in small amounts.
Define hydrogenation
A process by which hydrogens are added to unsaturated fats, increasing the degree of saturation and turning liquid oils into solid fats. Hydrogenation produces a mixture of saturated fatty acids and standard and trans forms of unsaturated fatty acids.
Why is hydrogenation used?
increases stability of oil so it can be reused for frying
improve texture of foods
increase shelf life
What are trans fats?
A type of unsaturated fatty acid produced during the process of hydrogenation; trans fats have an atypical shape that affects their chemical activity.
What are some dietary sources of trans fats?
deeo fried foods
baked and snack foods
stick margarine
Why are health experts concerned about Canadian’s consumption of trans fats?
they have triple negative effects on heart health
raises total cholesterol LDL (low-density lipoprotein)
lower HDL (high-density lipoprotein)
produce inflammation in blood vessels
Why are monosaturated fats better for you?
raises HDL
decreases risk of heart disease
Define omega 3 fatty acids
Polyunsaturated fatty acids commonly found in fish oils that are beneficial to cardiovascular health.
What is the function of omega 3s
reduce the blood clot tendency
inhibits inflammation and abnormal heart rythms
reduces blood pressure and risk of heart attack and stroke in some people
What do dietitians reccomend in regards to omega-3?
Canadians should increase the porptions of omega 3 in their diet by eating fish twice a week.
What fats should you consume less?
saturated
trans
What fats should you consume moderately?
monosaturated
polyunsaturated
omega 3 fatty acids
omega 6 fatty acids
What is the biochemical compostition of carbohydrates?
Various combinaions of sugar units called saccarides.
What are the two classifications of carbs?
simple
complex
What is the function of simple carbs?
Provides natural sweetness to foods.
What do simple carbs include?
sucrose
fructose
maltose
lactose
What are some food sources of simple carbs?
fruits
milk
honey
What do complex carbs include?
starches
fibre
most imortant dietary carbs
What are some food sources of complex carbs?
grains
legumes
tubers → potatoes and yams
What essential nutrients are unrefined complex carbs (whole grain) high in?
fiber
vitamins
minerals
other compounds
Why do complex carbs enter the bloodstream slowly?
They take longer to digest.
Define fibre
Non digestible carbs from plants.
What is the function of fibre?
It isn’t digested, but passes through the intesitnal tract and procided bulk for feces in the large intestine in facilitates waste elimination. In the large intestine some tyhpe of fibre are broken down by bacteria into acids and gases, which is why too much fibre leads to intestinal gas.
What are the benfits of fibre?
decrease risk of type 2 diabetes and heart disease
improve gastrointestinal health
What are the two types of fibre?
dietary (normal)
functional (isolated or synthesised in a lab)
Define minerals
Inorganic (non-carbon-containing) compounds needed in relatively small amounts for regulation, growth, and maintenance of body tissues and functions.
How many essential minerals are there?
17
Define major minerals (macrominerals)
Minerals that you need in larger amounts. >100mg per day
What are exampels of major minerals?
calcium
phosporus
magnesium
sulphur
sodium
potassium
chloride
Define trace minerals
Minerals that you need in smaller amounts.
What are examples of trace minerals?
zinc
iron
copper
selenium
iodine
flouride
Define osteroporosis
A condition in which the bones become dangerously thin and fragile over time.
How many Canadians are living with osteoporosis?
Approximately 2 million.
How long can you live without food?
Up to 50 days
How long can you live without water?
A few days
When the body uses oxygen or breaks down certian fats or proteins as a normal part of metabolism, it gives rise to:
free radicals
What type of enviornmental factos can increase free radical production?
excessive sunlight
certain drugs
stress
What does DRI stand for?
Dietary Reference Intakes
What does RNI stand for?
Recommended Nutrient Intakes
What are the Dietary Reference Intakes
Standards for nutrient intake designed to prevent nutritional deficiencies and reduce the risk of chronic disease.
Frequently reviewed as new nutrition related information becomes available
broader focus
When was the first official food rules published?
1942 (WWII)
What was the purpose of the orginal food rules?
It was a wartime nutrition program to improve the health of Canadians in the context of rationing and poverty.