RT PCR
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Goal of rtPCR
Detect presence of a target gene
Two dyes using intercalating method to detect PCR product
SYBR green
EtBr
On which ends are the fluorescent reporter and quencher on TaqMan
Fluorescent reporter is on 5’ end
Quencher on 3’ end
How does the DNAP remove the TaqMan probe
via 5’→3’ endonuclease activity
Draw the rtPCR graph
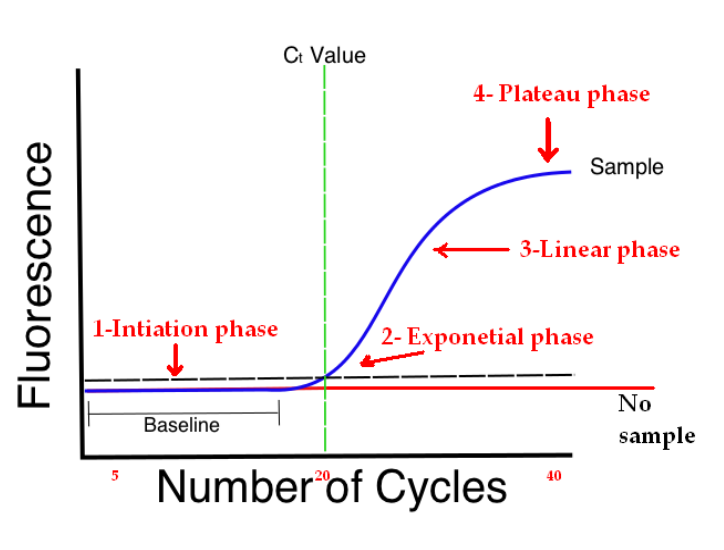
What should be done to properly calculate PCR Efficiency
Make serial 10-fold dilutions with known quantities of starting sample and plot them on a graph to get standard curve.
How to determine reaction specificity
Use a melt curve.
SYBR binds to dsDNA
Increase the temperature
As the temperature decreases, strands denature, resulting in lower fluorescence
2 purposes of absolute gene quantification
Check for chromosome or gene copy number
Measure viral loads
Goals of absolute and relative quantifications
Absolute focuses on gene or chromosome number, and viral loads
Relative focuses on tracking gene expression
Role of CYP1A
Detoxification of toxic compounds such as polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAH)
What properties of cells can flow cytometry measure
Size
Granularity
Fluorescence
3 pieces of flow cytometry
Fluidics, separate cells into droplets
Optical system
Electronic system
What principle does flow cytometry rely on to put cells individually into each droplet
Hydrodynamic focusing, involves injecting sample into sheath fluid which separate it into individual drops
FSC vs SSC
FSC measures cell size and surface area
SSC measure granularity/complexity/cytosolic structure
Uses of flow cytometry
Cell counting
Cell sorting
Analysis
Immunophenotyping
Functional assay