Energy Balance & Obesity
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
What is energy balance?
relationship between dietary intake + energy expenditure

Dietary intake gives...
Energy and calories
Examples of dietary "in" intake
Carbs, protein, fat, alcohol
Energy expenditure burns...
Energy and calories
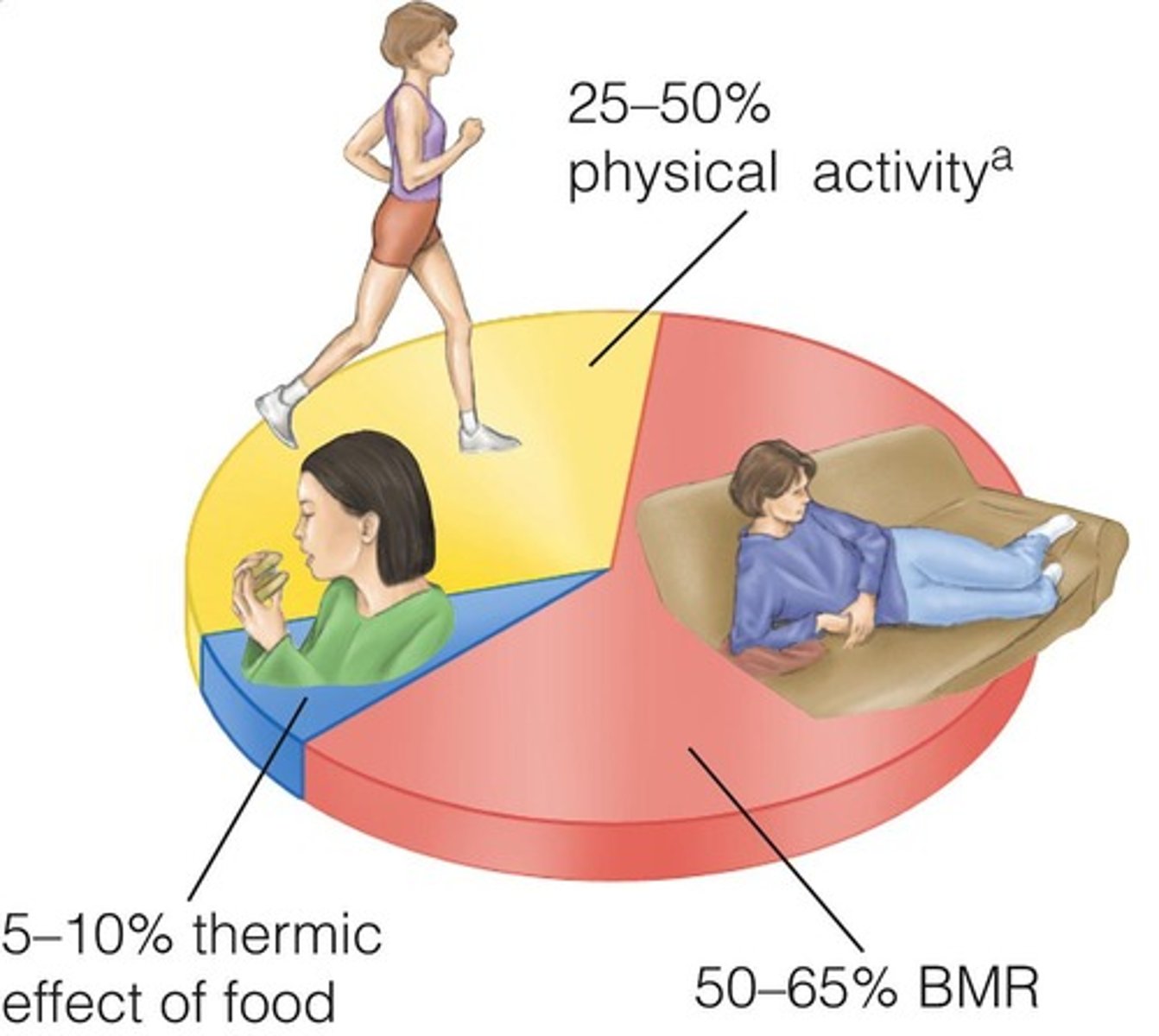
What are the components of energy expenditure? ("out")
Basal metabolism, thermic effect of food, and physical activity.
What does Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) represent?
minimal amount of calories used by body to maintain basic physiological functions.
(cost of staying alive)
Where does the majority of energy expenditure come from?
BMR (50-65%)
What does BMR maintain?
Body temperature, pumps blood, breath, etc
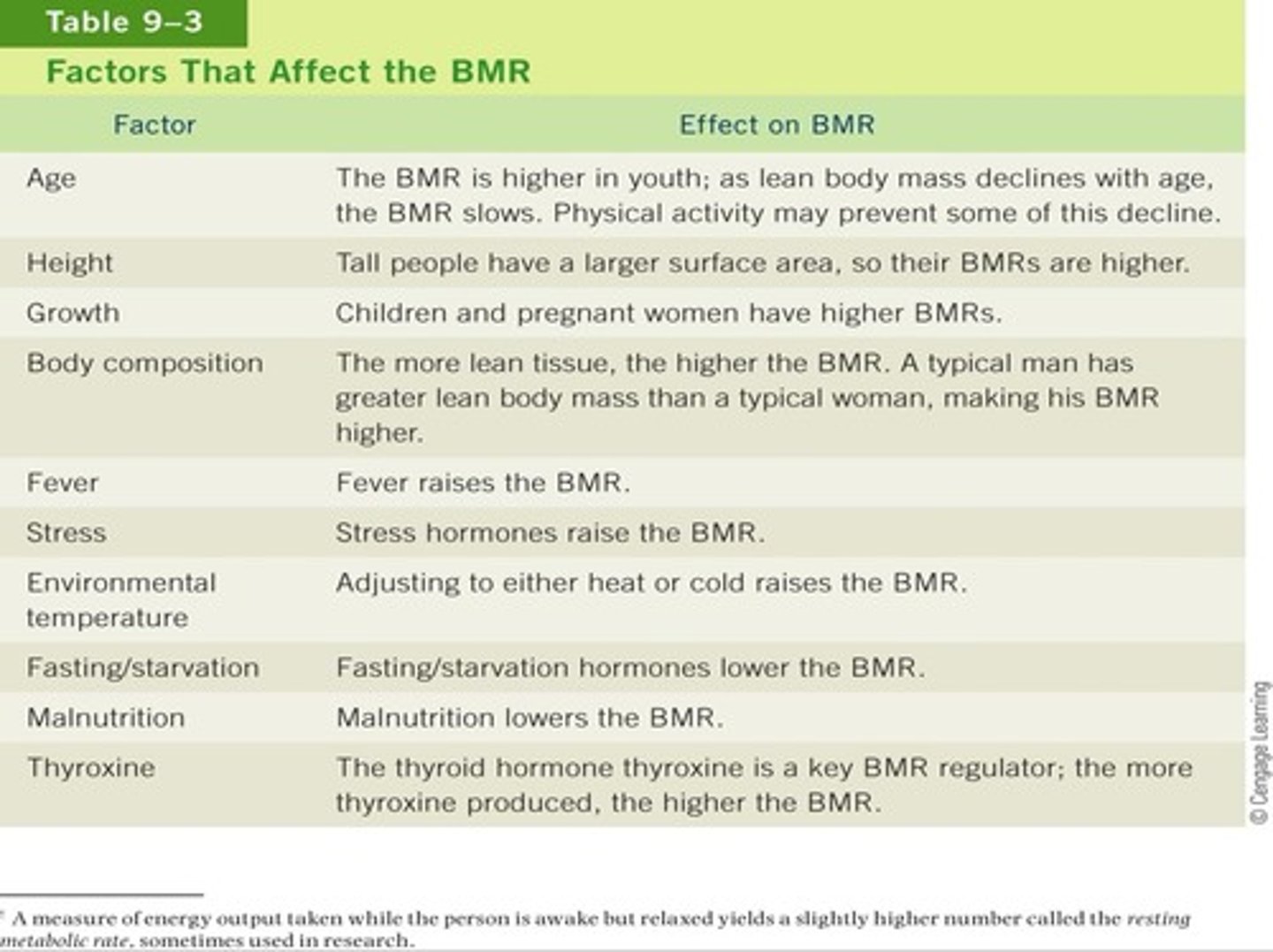
What factors influence BMR/ what affects BMR?
Age, sex, body composition, stress, fasting, malnutrition
What is the thermic effect of food?
energy cost of digesting + absorbing food
(E needed to chew)
What does malnutrition do to BMR?
LOWERS BMR
What does fasting/starvation do to BMR?
LOWERS BMR
What percentage of energy is lost due to the Thermic Effect of Food?
5-10%
What part of Energy expenditure CAN you control?
Physical ACTIVITY
What percentage of Energy expenditure comes from physical activity (average)?
25-50%
Why can energy expenditure vary?
Lifestyle, metabolism, time
Intake = Output ...
Weight maintenance
Intake < Output
Weight LOSS
Intake > Output
Weight GAIN
How is a healthy weight defined?
BMI
(body mass index)
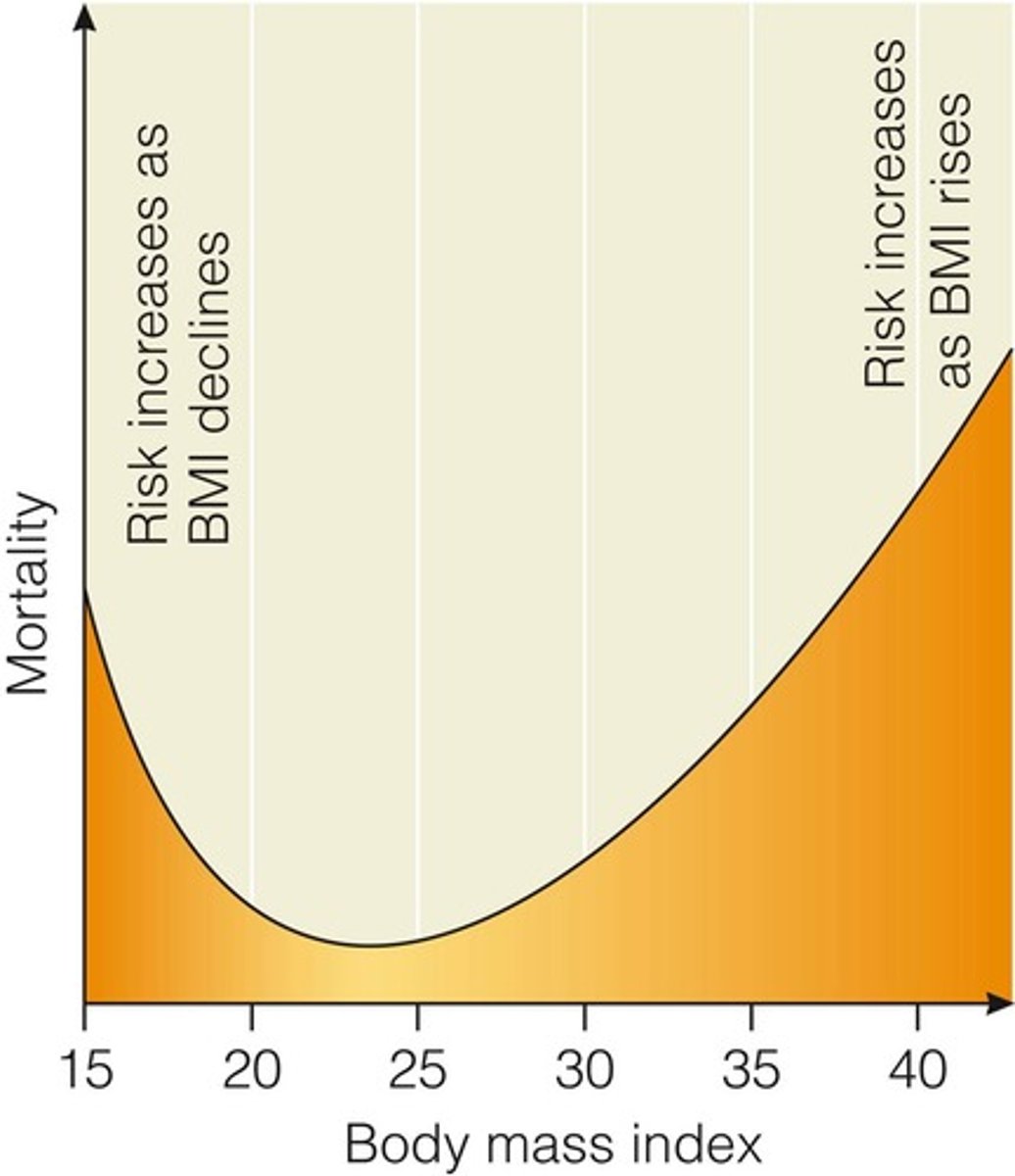
What is the significance of BMI?
It's associated with risk of death!
What is the formula for calculating Body Mass Index (BMI)?
BMI = weight (kg) / height (m)^2 or BMI = weight (lb) x 703 / height (in)^2.
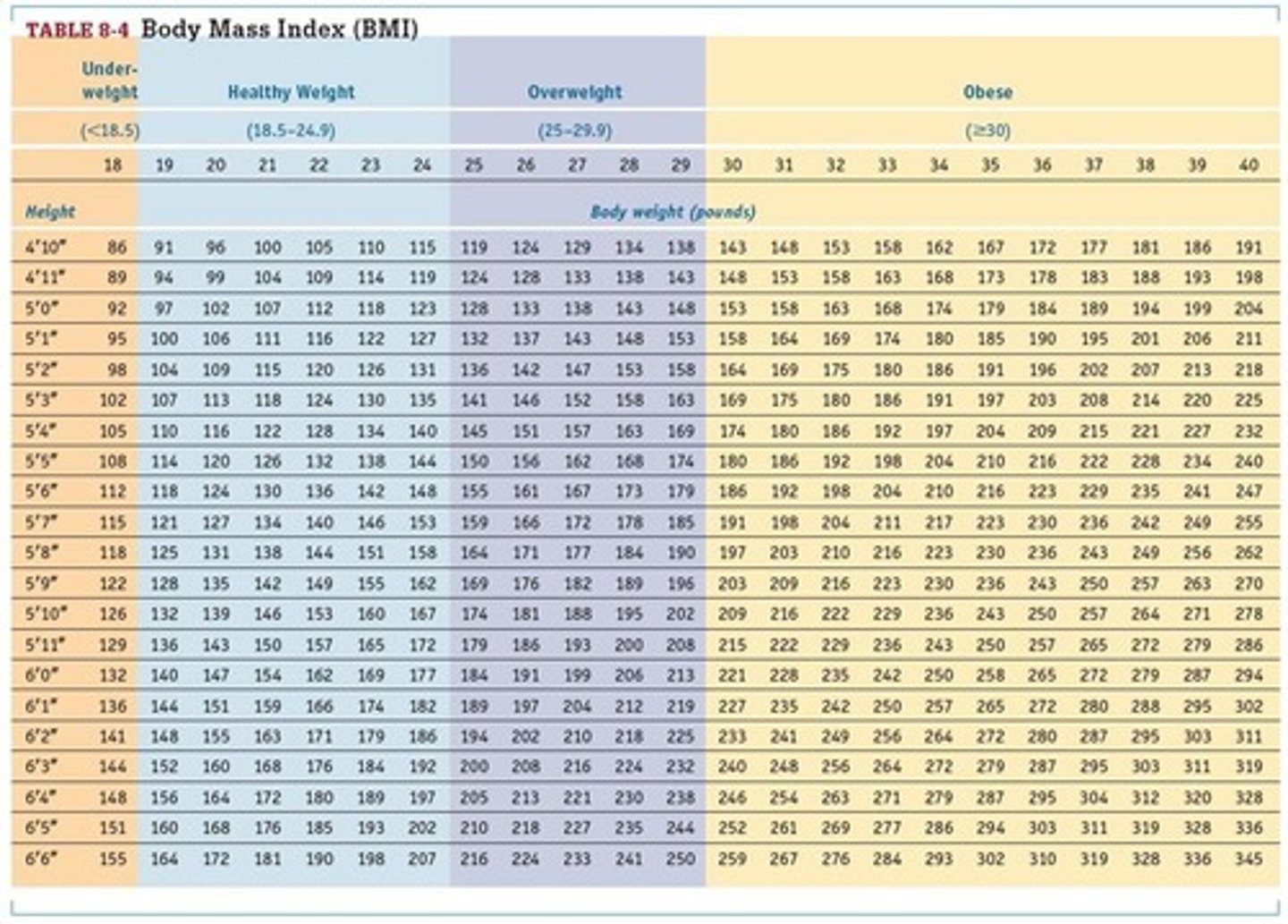
What BMI range is considered underweight?
BMI < 18.5
What BMI range is considered normal weight?
BMI 18.5 - 24.9
What BMI range indicates overweight?
BMI 25 - 29.9
What BMI value indicates obesity?
BMI of 30 or higher
What BMI is considered the lowest risk of death?
NORMAL weight (BMI= 18.5-24.9)
What are the highest risks of death?
EXTREMES
(<18.5/ underweight; 30+ higher/obese)
What are some risks associated with being underweight?
Decreased immune function, infertility, higher risk of heart disease + stroke.
What does an intake greater than output indicate?
Weight gain.
What does an intake less than output indicate?
Weight loss.
What does intake equal to output indicate?
Weight maintenance.
BMI of obesity=
30+
Obesity has (what) in the US since 2011
INCREASED (a lot!)
What are some obesity-related concerns?
Increased risk of chronic diseases, psychological issues, social stigma.
About (what fraction) of US adults are overweight or obese?
2/3
About (what fraction) of US children are overweight or obese?
1/3
What is the significance of BMI in health assessments?
helps classify weight categories + assess risk of death
What are some criticisms of BMI?
-Doesn't take into account muscle v fat
-Varies naturally by age
-Was originally based on European white men
-Are different cutoffs for different races/ethnicities
What are some alternatives to BMI?
-% Body fat
-Body fat distribution
-Visceral and subcutaneous fat
What is the average % body fat for men?
18-24%
What is the average % body fat for women?
25-31%
What is the unhealthy % body fat for men?
>25%
What is the unhealthy % body fat for women?
>32%
What are the 2 kinds of body fat distribution?
-Central (android) obesity
-Gynoid obesity
Central (Andrioid) obesity
men
relates to higher risk 4 obesity related disease
Describe what central obesity looks like
Around belly, upper torso, "beer belly"
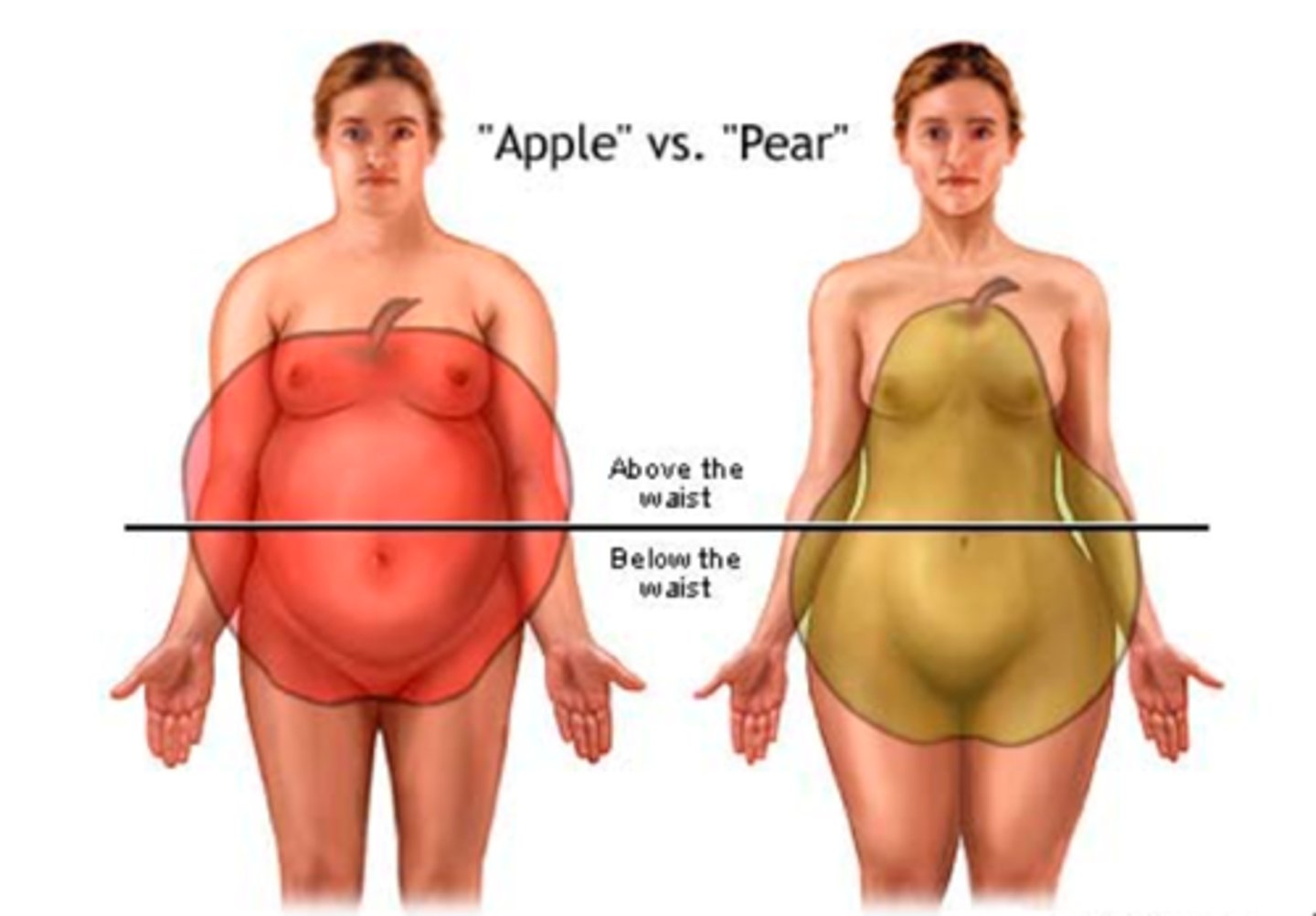
Gynoid obesity
women
less associated with obesity related diseases
Describe what gynoid obesity looks like
"Pear shaped", around lower torso, upper legs
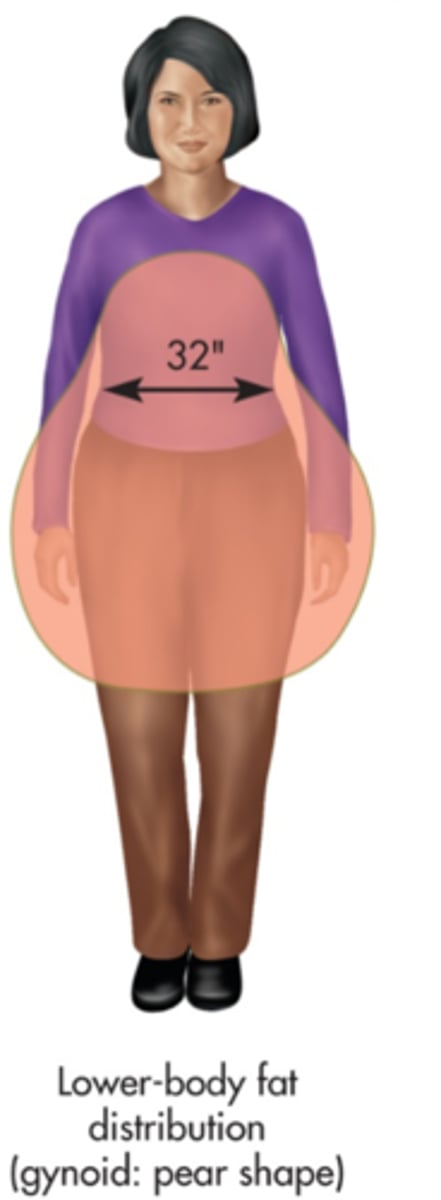

How can body fat distribution be estimated?
Waist circumference measurement
What is the role of physical activity in energy balance?
contributes to energy expenditure + aid in weight management
What is the impact of lifestyle on energy expenditure?
significantly affect BMR + thermic effect of food.
What is the relationship between obesity and chronic diseases?
Obesity increases the risk of conditions —> diabetes, heart disease, certain cancers.

How does age affect BMR?
decreases with age due to loss of muscle mass
What is the importance of understanding energy balance for weight management?
It helps individuals make informed dietary and activity choices to achieve or maintain a healthy weight.
What are the consequences of obesity?
Increased health risks, reduced quality of life, and higher healthcare costs.
What is the thermic effect of food influenced by?
It varies between individuals and can change over time.
What is the main focus of weight management strategies?
To achieve a sustainable balance between energy intake and expenditure.
What was the prevalence of obesity in all US states and territories in 2023?
No state or territory had a prevalence of obesity less than 20%.
Which states had a prevalence of obesity between 20% and <25%?
The District of Columbia and Colorado.
What percentage of adults are overweight or obese?
About 2/3.
What percentage of U.S. children are overweight or obese?
About 1/3.
What is a valid criticism of the Body Mass Index (BMI)?
BMI doesn't take into account muscle mass vs. body fat.
What are the average body fat percentage cutoffs for men?
18-24% is average; > 25% is unhealthy.
What are the average body fat percentage cutoffs for women?
25-31% is average; > 32% is unhealthy.
What type of obesity is more common in men?
Central (Android) obesity.
What type of obesity is more common in women?
Gynoid obesity.
What are the health consequences of obesity?
Higher risk for chronic diseases, infertility, and social stigma.
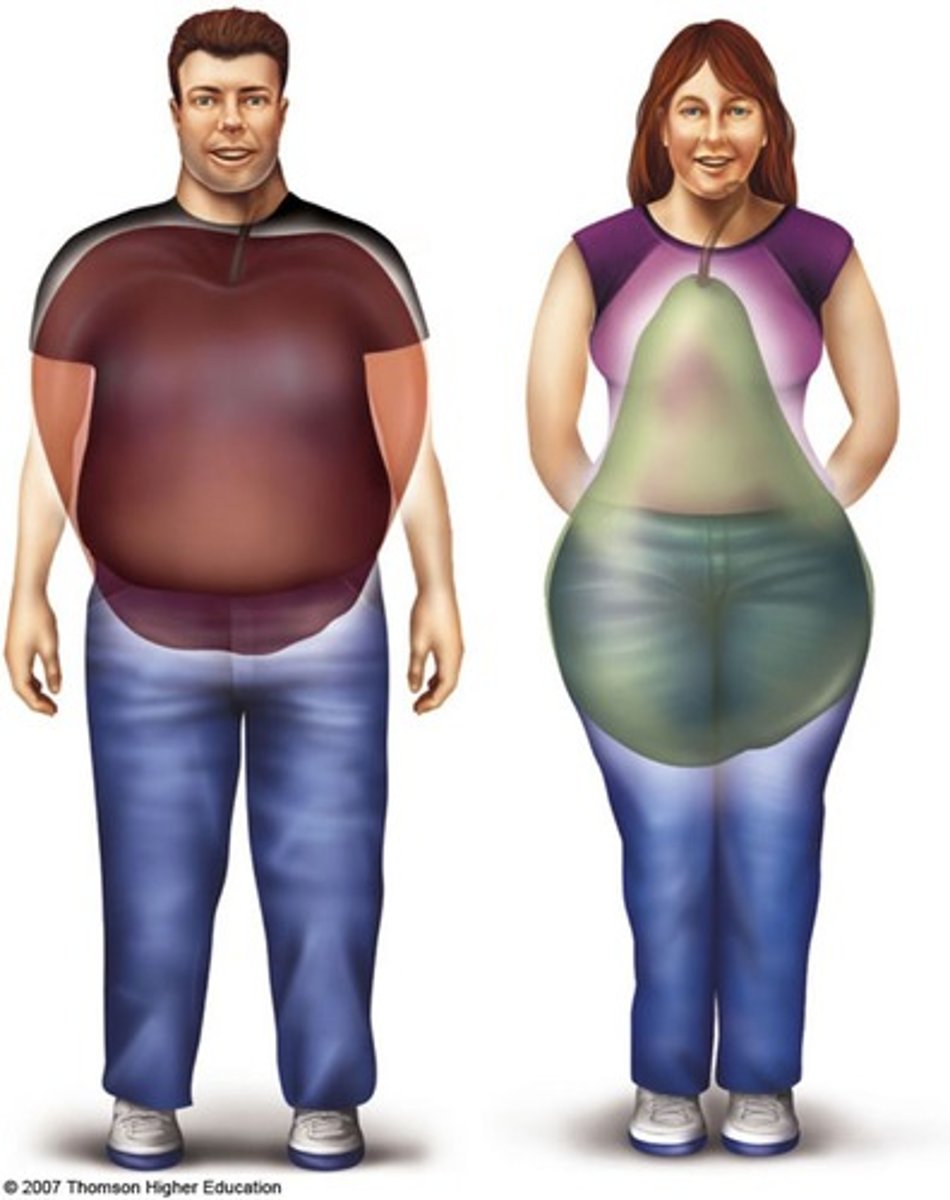

There are higher risks associated with (what type of fat)
Central/visceral fat!
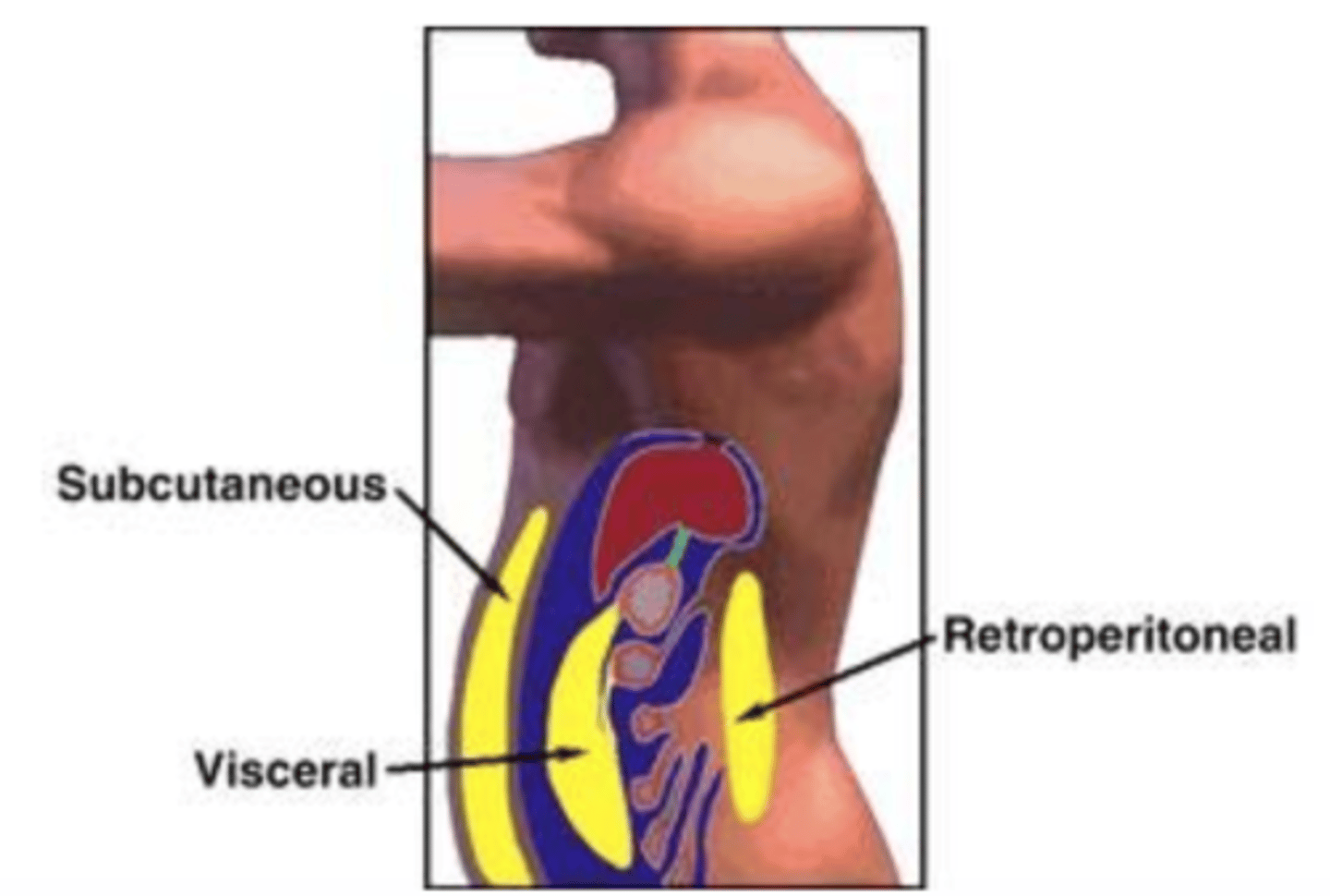
What type of fat increases risk of metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, and higher inflammation (adipokines)
VISCERAL FAT
Fat in between organs, and higher risk of obesity is what kind of fat?
VISCERAL (central) FAT
Fat located beneath the skin and a lower risk of obesity is what kind of fat?
SUBCUTANEOUS FAT
What are the obesity-related concerns?
-Health coseq. (chronic diseases)
-Social conseq. (judged on appearance, stereotyped as lazy & no self control)
-Psychological conseq. (Feeling rejected, shame, depression, ineffective treatment can lead to sense of failure)
Name the major obesity-related disease risks
Diabetes, heart disease, stroke, hypertension, certain cancers, non alcoholic fatty liver disease, cirrhosis, liver cancer
What is epigenetics?
It refers to how environment and behaviors affect gene function.
What can epigenetics influence?
Tendency to gain weight or stay lean
What is the role of the gut microbiome in obesity?
Dysbiosis can cause obesity.
Maintenance of normal gut flora.
Dysbiosis
Microbial imbalance
Thermogenesis
Heat production
White adipose tissue
Energy storage
Brown adipose tissue (BAT)
Energy storage AND maintenance of body temperature
What type of fat is the heat generating tissue and may play a role in keeping people lean?
Brown adipose tissue (BAT)
What are some external cues to overeating?
Available foods, larger portions, and physical inactivity.
What type of food supply is a theory of obesity?
UNHEALTHY food
(addictive
What kinds of physical inactivity are theories of obesity?
-Screen time
-Sedentary jobs
What kinds of neighborhoods are theories of obesity?
-Built environment
-Need cars
-Food deserts
What are some lifestyle strategies for weight management?
Dietary strategies, physical activity, and behavior modification.
When lifestyle strategies aren't enough, what medical treatments of obesity exist?
Drugs, bariatric surgery
What are realistic dietary strategies for weight loss?
-Manage portion sizes
-Eat low E-density foods
-Avoid empty calories
-Follow an evidence-based food guide (MyPlate)
-Keep a food record
How can you manage portion sizes?
-Read labels
-Measure portion sizes
What does low energy-density foods mean?
Lots of volume and nutrients with fewer calories
What are some ways to feel full without adding calories?
Drink lots of water, chose high fiber foods, space meals and snacks every few hours to avoid getting overly hungry
Why must you eat a minimum amount of calories when losing weight?
To maintain BMR.
Super low kcal diet results in FAST weight loss= loss of muscle and lowers BMR
Why should you consider taking a multivitamin/mineral supplement when limiting food intake?
It's hard to get a nutritionally adequate diet on less than 1200 cals/day
What is a safe rate of weight loss per week?
½ to 2 pounds per week.
(No more than 2 pounds/week)
-About 10% body weight/6 months
How should you create a calorie deficit?
Combined dietary, behavioral, physical activity strategies
What are FDA approved anti-obesity medications designed to do?
Mimic the effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) in the body.
What are the forms of anti-obesity medications?
Semaglutide (wegovy)
Tirazepatide (zepboud)
Opportunities of GLP-1's
-Success of these medications supports that obesity is a disease
Challenges of GLP-1's
-Reduced food intake, more micronutrient deficiencies
-Weight loss includes both fat AND muscle