Psyc 375- Brain and Behaviour Exam 1
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
What are the 2 elements of the nervous system?
CNS (brain and spinal cord) & PNS(cranial and spinal nerves)
Embodied behaviour
movements we make and the movements we perceive in others are central to our behaviour
-we understand one another not only by listening to words but also by observing gestures and other body language
-the brain as an intelligent entity cannot be
divorced from the body's activities
Neurons
specialized nerve cells engaged in info processing
- carry signals from one location to another
- ~86 billion
Glia
Supports cells within the nervous system
1. Act as nerve glue
2. Supply nutrients to neurons
3. Act as insulation around axons
4. Remove pathogens and dead neurons
Behaviours
patterns in time
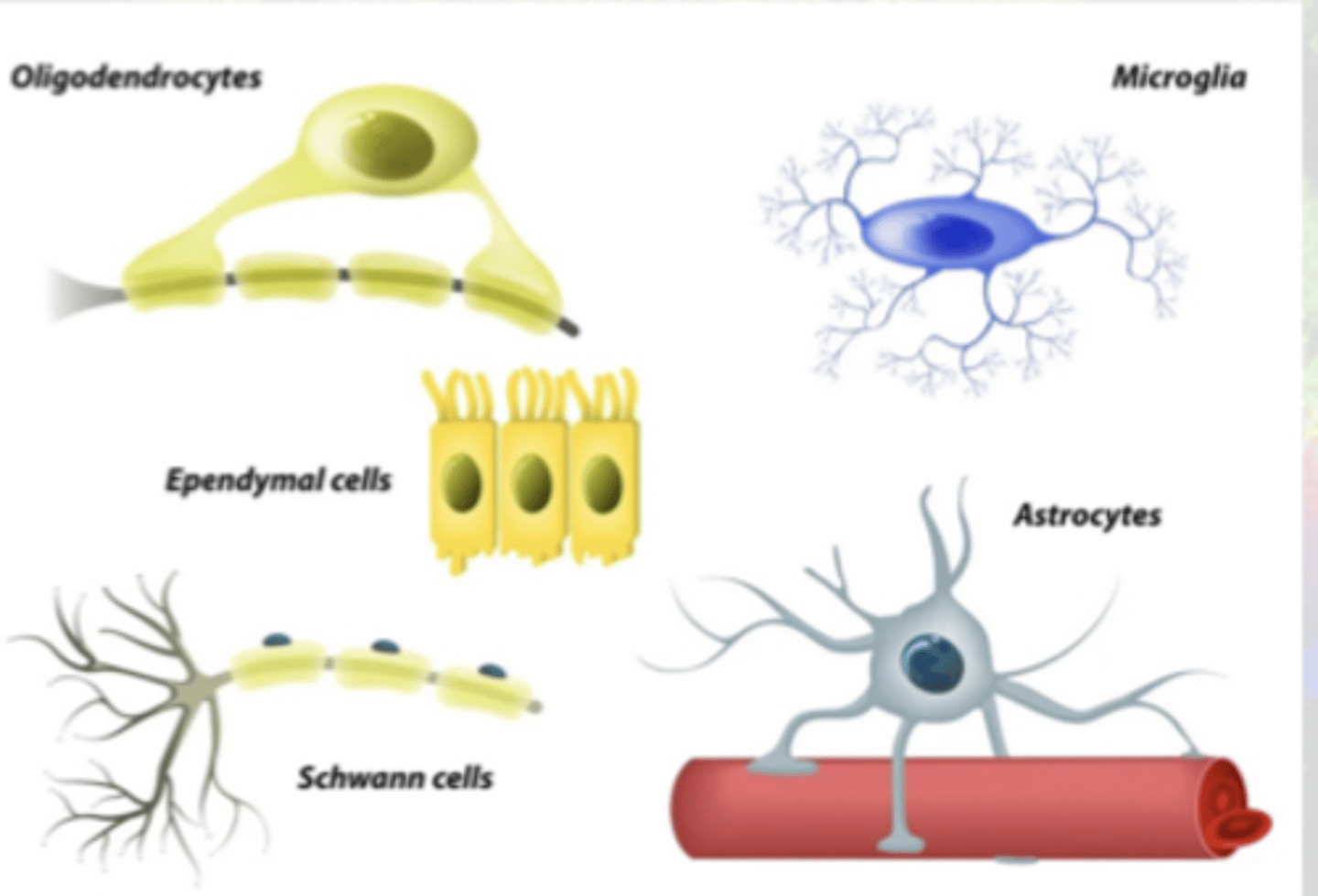
5 types of glial cell
Behaviour types
Innate (inherited ways of responding) & Learned (require experience & practice, depend on brain neuroplasticity)
3 historical perspectives
mentalism, dualism, materialism
Mentalism
Aristotle (intellect = psyche, brain just cools the blood)
Behaviour as a function of the non-material mind
Beginning of modern psychology
Dualism
Descartes (mind = pineal gland to direct flow of fluids)
Both non-material mind and material body contribute to behaviour
Mind-body problem = how does the mind and body interact
Materialism
Darwin & Wallace
Behaviour is a function of the NS w/o recourse to the mind
Evolution = explains unity & diversity of life
Evolution (2)
1. species today are descendants of ancestral species (descent w/ modification - movements = new stresses = adaptations)
2. Natural Selection is the mechanism for Evolution (heritable genetic variations + competition for resources = reproductive success)
Rules of Natural Selection
1. Individuals don't evolve, populations do
2. Heritable genes, not acquired traits
3. evolution is not goal directed (random variation)
Evolution of Nervous Systems
1. Neurons and muscles. Brain cells and muscles evolved together,
enabling animals to move. Neurons and muscles likely have their
origins in single-cell animals such as amoeba
2. Nerve net. The nervous system representative of evolutionarily
older phyla, such as jellyfishes and sea anemones, is extremely
Simple
3. Bilateral symmetry. In more complex animals such as flatworms,
the nervous system is more organized, and it features bilateral
Symmetry, The human nervous system is also bilaterally
symmetrical
4. Segmentation. The body of an animal such as an earthworm
consists of a series of similar muscular segments. Its nervous
system has similar repeating segments. The human spinal cord and
brain display such segmentation
5. Ganglia. In still more recently evolved invertebrate phyla,
including clams, snails, and octopuses, are clusters of neurons
called ganglia that resemble primitive brains and function
somewhat like them in that they are command centers
6. Spinal cord. In relatively highly evolved chordates—animals that
have both a brain and a spinal cord—a single nervous system
pathway connects the brain with sensory receptors and muscles.
7. Brain. The chordate phylum, of which amphibians, reptiles, birds,
and mammals are class members, displays the greatest degree of
Encephalization, a true brain
Topographic maps
represent the different functional areas—
For instance, areas that control vision, hearing, touch, olfaction,
and movement
Connectome maps
represent the connections through which
each of these regions influences each other
Cladogram
displays groups of related organisms as branches on a tree
radiator hypothesis
the brain's radiator, the circulating blood, adapted into a more effective cooling system, brain size could increase.
-important because the brain's metabolic activity generates a great deal of heat and is at risk for overheating
-Homo skulls contain holes through which cranial blood vessels pass. Homo species had a much more widely dispersed blood flow from the brain
Measuring Intelligence
Spearman g factor: g for general intelligence factor
Flynn effect: the trend towards higher IQ
-the score change has not been accompanied by a similar increase in brain size. It is more likely that education and other life experiences explain the Flynn effect.
Gardner: proposed that humans have a number of intelligences — verbal, musical, mathematical, social, and so on
Weschler: adult intelligence scale
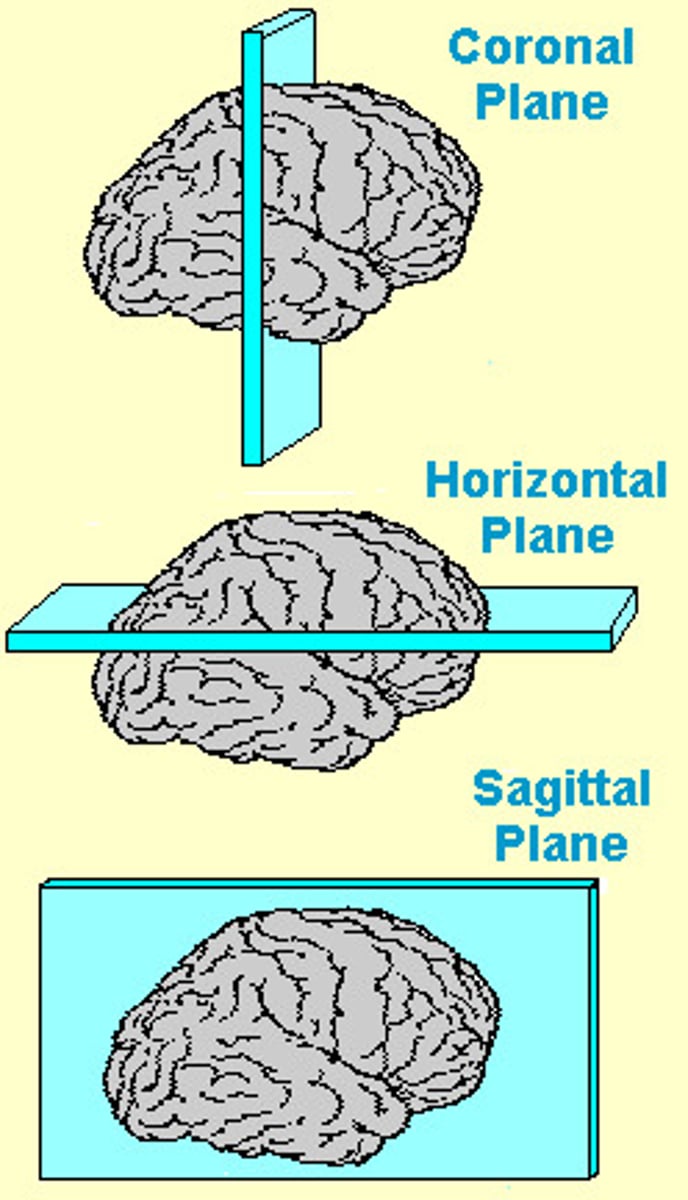
Plane of section
Views of brain
meninges 3 layers
Dura mater- "hard mother", tough fibrous outer layer
Arachnoid layer- "spiders web", thin sheet delicate connective tissue
Pia mater- "soft mother", moderately tough inner layer that clings to brains surface
Meningitis
inflammation of the meninges
-puts pressure on brain
-headache, stiff neck, stupor, coma, drowsiness, death
-treat with antibiotics
a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring
Species
Phenotype vs. Genotype
- Phenotype: expressed physical traits
- Genotype: Genetic make-up
discrete unit of heritable info & it's variations
Gene & allele
Mendelian Genetics
The pattern of inheriting characteristics that follows the laws formulated by Gregor Mendel
genetics = scientific study of heredity
heredity
passing on of genes from one generation to the next
(genes producing NS in different orgs. tend to be similar)
Stroke
the sudden appearance of neurological symptoms as a result of server interruption of blood flow
Stroke Symptoms
-weakness on contralateral side
-slowed behaviour
-vision problems
-loss of coordination/balance
Natural Selection + genetic inheritance + epigenetics =
foundations of materialistic approaches to neuroscience
Taxonomy
a system of naming and classifying species
Evolutionary descent of different species (simple -> complex)
Phylogeny
Encephalization Quotient
Quantitative measure of brain size obtained from ratio of actual brain size:expected brain size
Scientific method
attempt to obtain knowledge through the process of inquiry
Theory
A well-substantiated & widely accepted explanation for of natural phenomena
Natural Law
events in nature that happen the same way every time given specific conditions
Brain's primary function
Produce behaviours
Functions of the Nervous system
1. sensory input - conduct signals from sensory receptors to CNS
2. integration - analysis/interpretation of the sensory signals and forming responses
3. motor output - send commands to effector cells to carry out responses
Functions of CSF
1. Buoyancy
2. Protection
3. Chemical stability (removes waste products)
4. Prevention of ischemia (reduced blood flow, and therefore, oxygen)- decrease in CSF deceases intracranial pressure, aiding blood perfusion
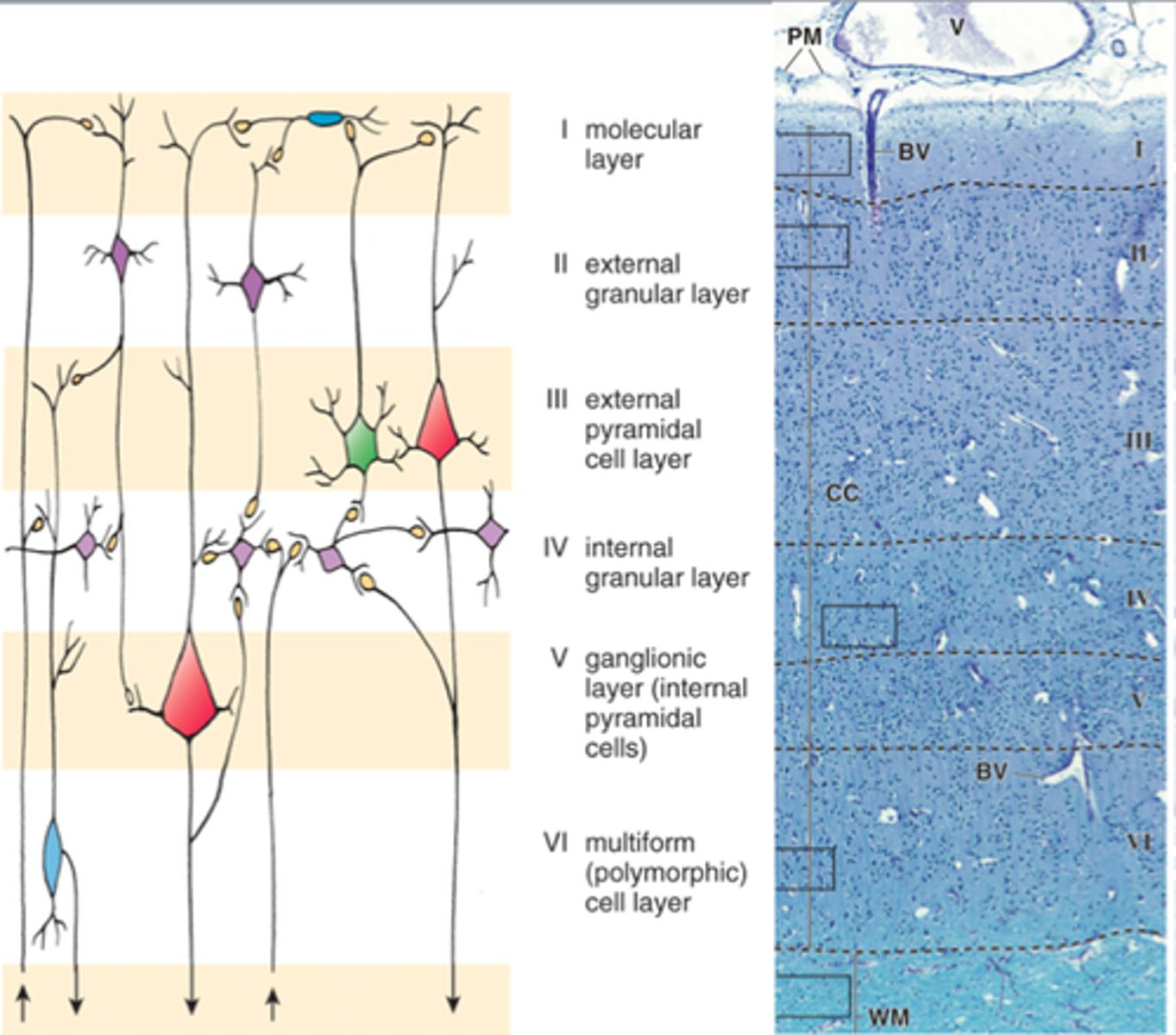
cerebral cortex
outermost layer of cerebrum
Coup
Site of impact for concussion
countercoup
An area of brain damage that occurs on the opposite side of the head from the original site of the blow, or coup
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE)
atrophy of the brain (result of neuronal death), enlargement f ventricles, and increases in the brain proteins associated with Alzheimer's disease
Cerebral arteries
Anterior cerebral artery
Middle cerebral artery
Posterior cerebral artery
4 lobes of the cerebral cortex
Temporal - audition, memory, learning
Occipital - Visual processing
Parietal - tactile, visual movement, attention
Frontal - execuitive functioning
Nuclei vs. ganglia
nuclei: in CNS, group of similar neurons forming a cluster
ganglia: like nuclei but in the PNS
Tracts vs. nerves
Tracts: large collections of axons coursing together in the CNS
Nerves: large collections of axons coursing together in the PNS
Brainstem
Evolutionarily oldest brain structure, receives afferent signals & sends efferent signals
Responsible for most unconscious, life sustaining behaviour
Hindbrain/midbrain/diencephalon
Hindbrain
Reticular Formation: nuclei & fiber pathways (sleep-wake/arousal)
Pons: bridge between cerebellum and rest of brain (vital body movements)
Medulla: vital functions (breathing/CV)
Cerebellum: motor learning/balance/posture/movement coordination)
Diencephalon
Thalamus: relay center - all sensory info organized/integrated/ projected
Hypothalamus: nuclei associated w/ temp/eating/drinking/sex, controls hormones
Pituitary Gland: contains/releases hormones
Midbrain
Tectum: Posterior sensory structure (superior colliculus = visual, inferior colliculus = auditory)
Tegmentum: Anterior Motor structure (pain, innate species-specific)
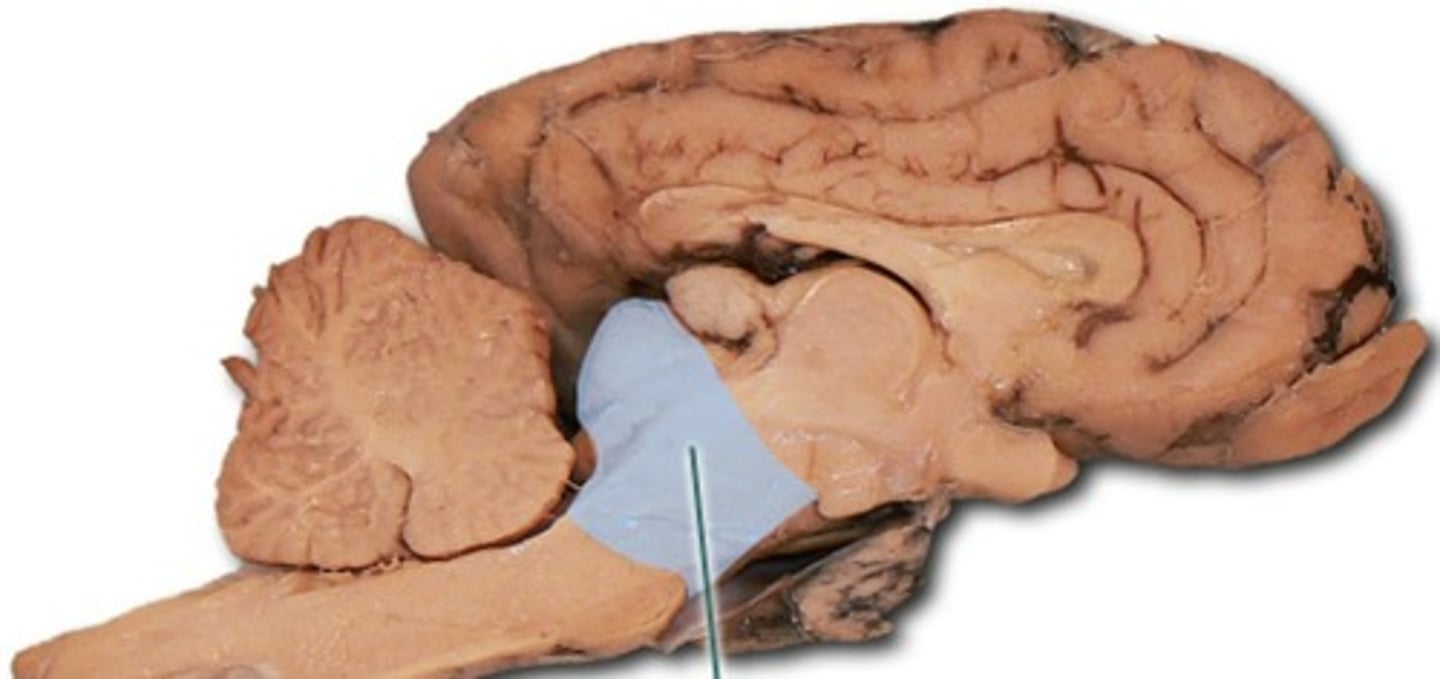
substantia nigra
An area of the midbrain that is involved in motor control and contains a large concentration of dopamine-producing neurons (damaged in parkinsons)
Forebrain
evolutionarily newest - coordinate advanced cognitive functions
cerebral cortex = cortex, olfactory system, basal ganglia
lateral geniculate
Receives info from the optic tract and relays it to visual regions in the cortex
suprachiasmatic nucleus
a cluster of neurons in the hypothalamus in the brain that governs the timing of circadian rhythms
Neocortex
Outermost layer - perception/planning/emotions/memory
Olfactory system
Send information from the olfactory bulb to the cortex pyriform
Limbic cortex
Emotional/motivational states, some learning/memory
Hippocampus: memory consolidation, spatial navigation
Amygdala: fear
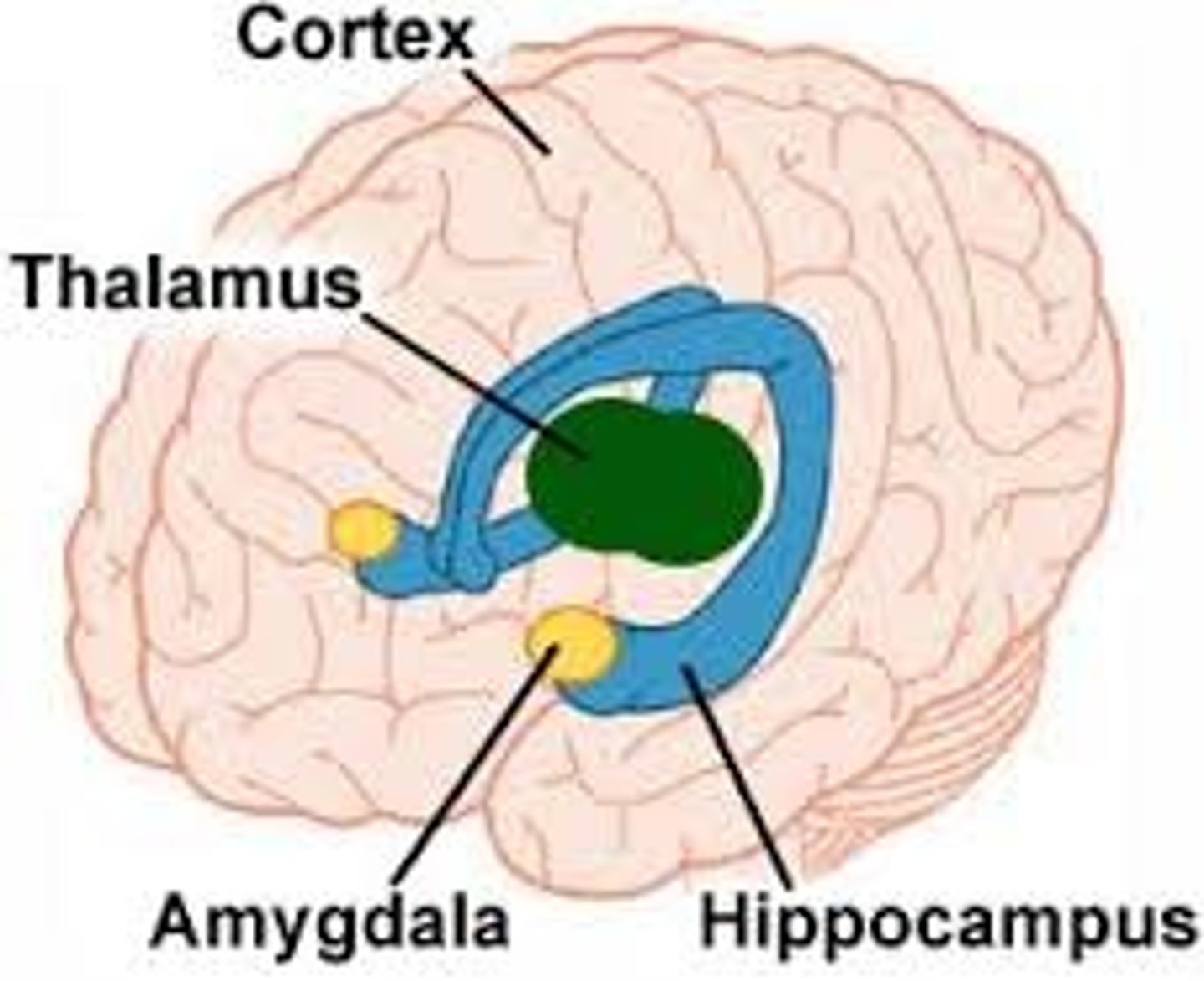
Basal Ganglia
coordination of voluntary movements
Caudate Nucleus, Putamen, Globus Pallidus (collectively known as the striatum)
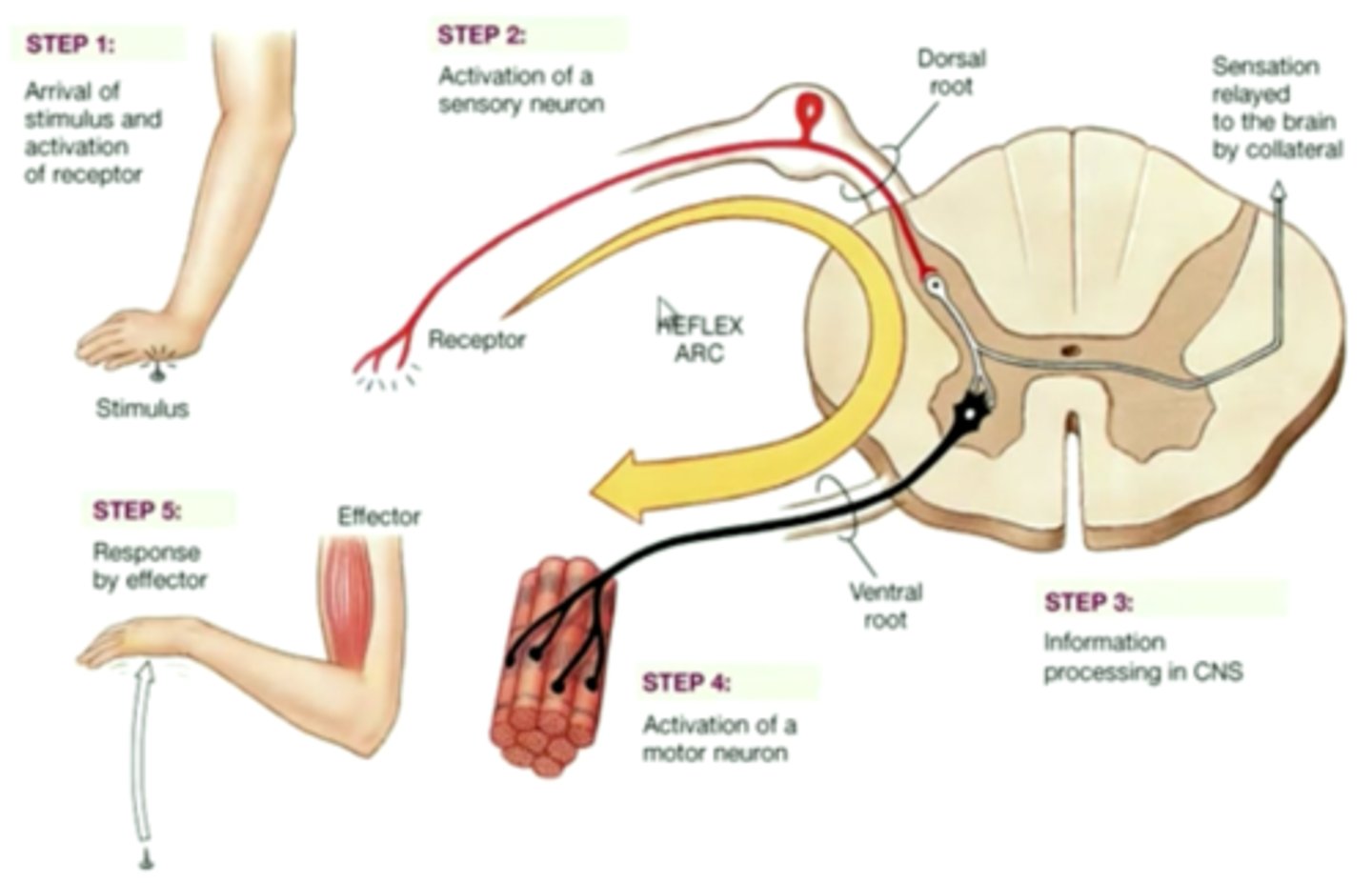
Somatic NS
Cranial Nerves - 12 pairs, sensory/motor of head, neck, & organs
Spinal Nerves - each associated with a dermatome (surface)
(cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal)
Law of Bell & Megendie
dorsal; Sensory info= afferent
Ventral; motor info = efferent
toxoplasmosis
a parasite that is most commonly transmitted from cats to humans by contact with contaminated feces
-On immune cells, specific calcium receptors act like 'mailbox' for the parasite to transmit its messages
Long term illness; -intermittent explosive disorder
-schizophrenia
-suicide
-Brain inflammation, cognitive impairments, dementia and permanent rewiring of the brain
Sensory neurons (2 types)
Bipolar neuron: found in retina, conduct afferent info to the visual centres of the brain (SIGHT)
Somatosensory neuron: afferent info into the spinal cord (TOUCH)
motor neurons
-Complex dendrites, long axons that connect to muscles
-Located in the lower brainstem and spinal cord (exits via ventral route)
Autonomic NS
unconscious regulation of internal organs/glands
Sympathetic = fight/flight = primarily thoracic origin
Parasympathetic = calm = Primarily vagal origin
Camillo Golgi (1843-1926)
Golgi stain = silver nitrate solution stains 5-10% in entirity
Nerve Net Hypothesis = NS is an interconnected continuous network of fibres
Santiago Ramon y Cajal
Neuron Theory = NS made up of discrete cells
Anatomy of a Neuron
Dendrites - collect info (afferent)
cell body - protein synthesis/organelles
axon hillock
axon initial segment - signal integration (summation)
axon - singular process carries messages to other neurons
telodendria - end axon branches (terminal buttons) synapse on to next cells dendrites (efferent)
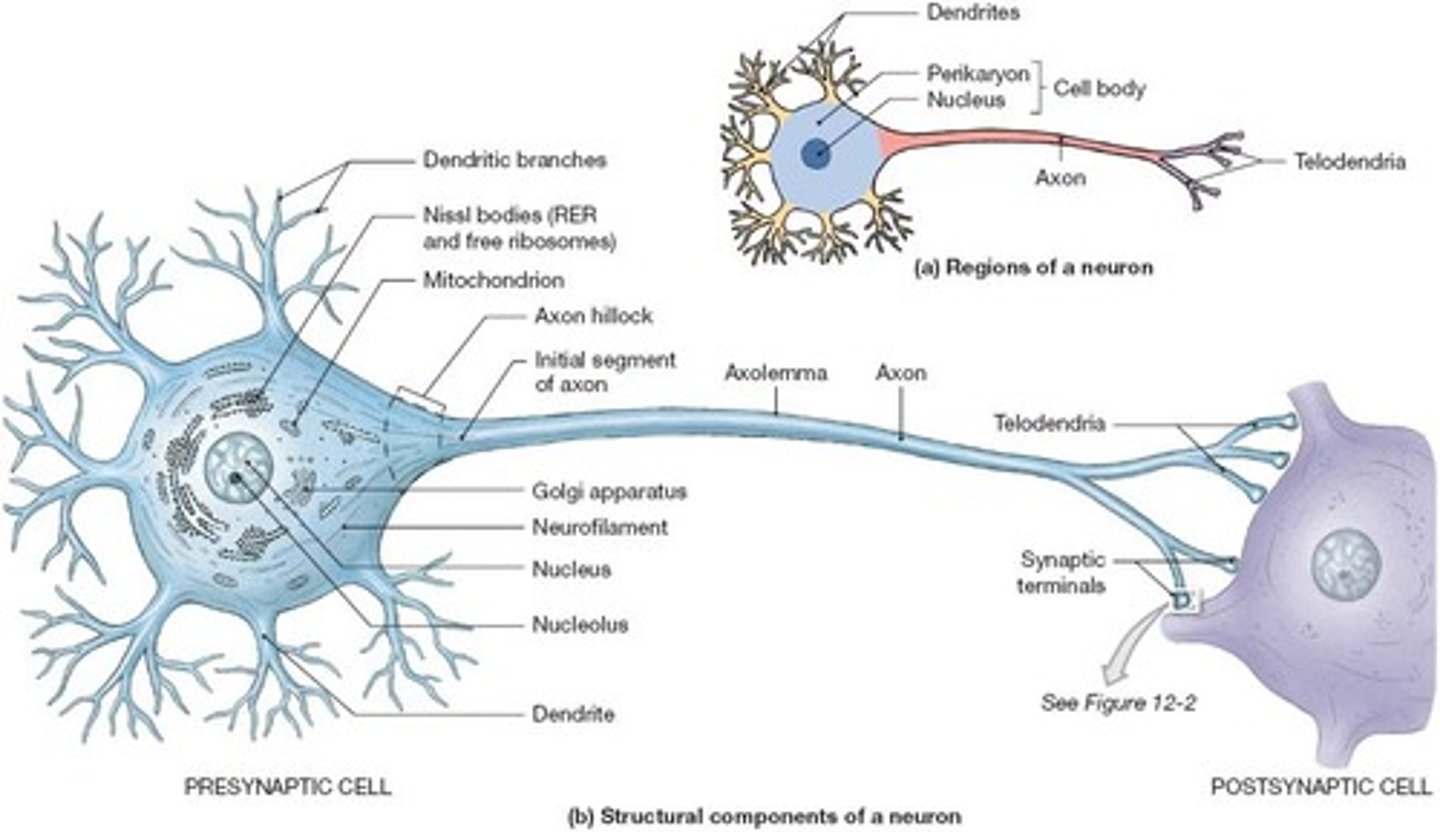
Neuron Doctrine (4 Tenets)
1. The basic functional unit of the nervous system us the neuron
2. Neurons are discrete cells
3. The neuron is composed of 3 par (dendrites, cell body, axon)
4. Information flows along the neuron in one direction
Neuron
Information processing units -> underlie plasticity
neural networks - functional groups connecting large areas of the brain/SC
Axon collaterals
branches of axon
Teleodendria
end branches of an axon
terminal buttons (end feet)
Knobs at the tip of an axon and points of near contact with the dendrites of other cells.
axon Hillock
Cone shaped region of an axon where it joins the cell body. Juncture of soma and axon where the action potential begins
Classes of Neurons
1. Sensory - transduction, carry sensory info to CNS
2. Inter - association (CNS, complex dendrite arbour)
3. Motor - largest, stimulate muscle contraction
Interneurons (2 types)
Pyramidal cell- long axon, two set of dendrites
Purkinje cell- extremely branched dendrites, info from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
Glial Cells
Ependymal - CSF
Astrocyte - BBB, nutrition/support/repair
Microglial - defensive/immune
Oligodendrocyte - myelin in CNS
Schwann - myelin in PNS
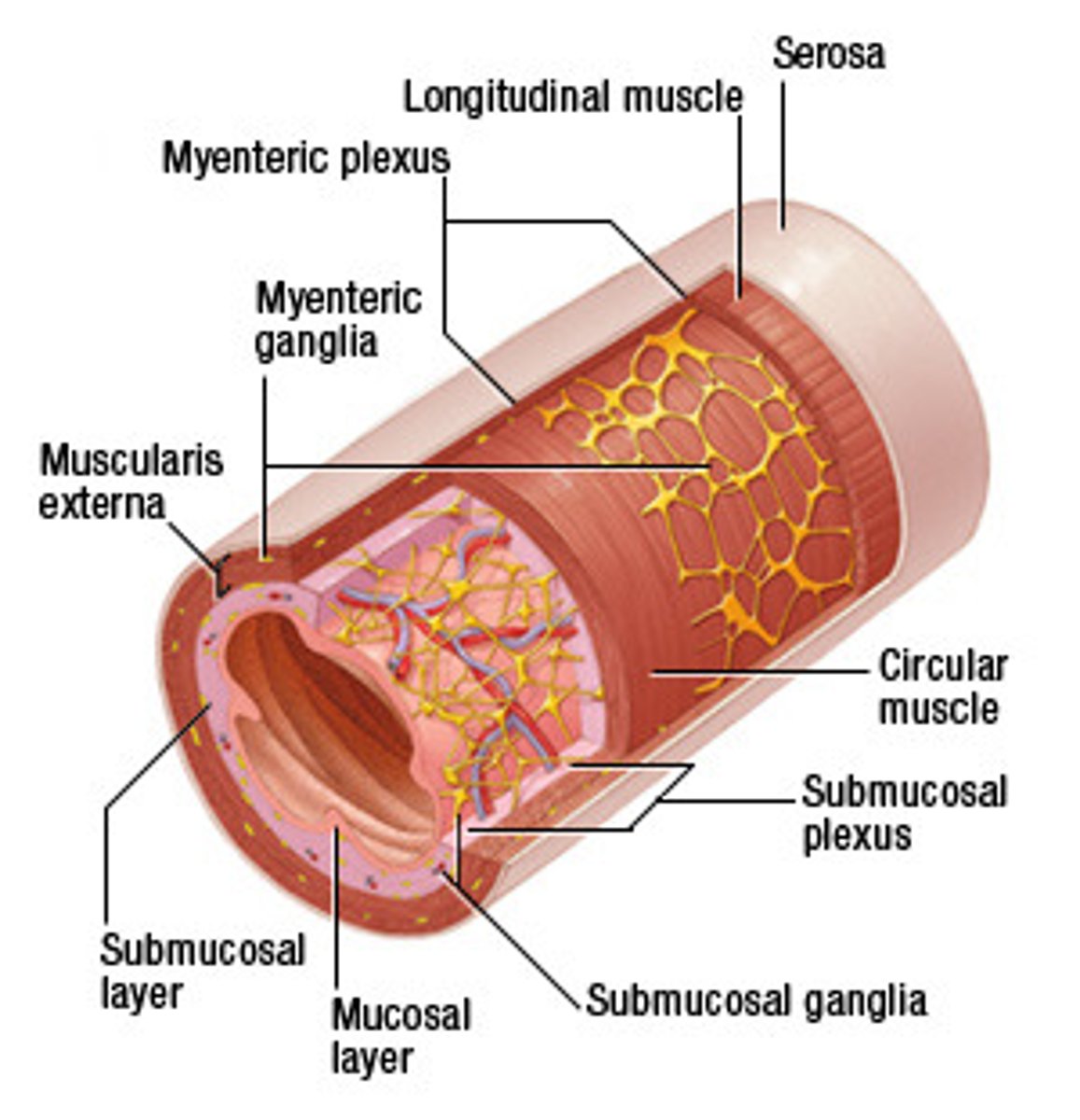
Enteric Nervous System (ENS)
neural tissue associated with the digestive system that is responsible for nervous control through autonomic connections
Biological Molecules
1. Carbohydrates
2. Lipids
3. Proteins
4. Nucleic Acids
Proteins
~50% dry mass
-polymers of amino acids (distinguished by R groups)
-biologically functional molecule consisting of 1+ peptides
-shape determines function
Nucleic Acid
-DNA/RNA
-chains (polymers) of nucleotides
-Phosphate groups + sugar + nitrogenous base
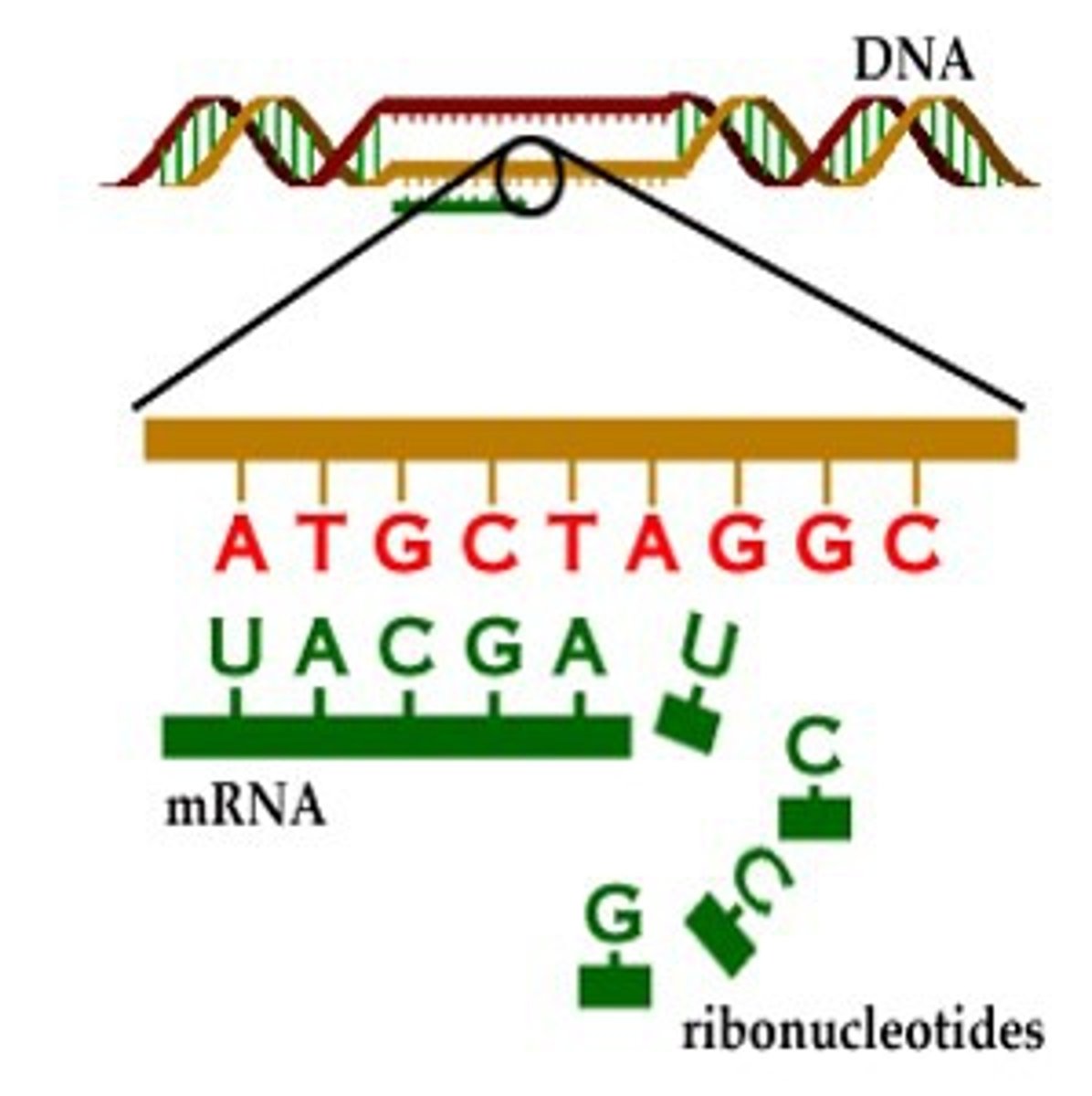
Transcription
synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template
Phospholipid bilayer
phospholipids = cell membrane
-hydrophobic tails = create selectively permeable membrane (only small, non-polar molecules can cross)
translation
Process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced (enters endoplasmic reticulum where ribosomes are )
Hydrocephalus
accumulation of fluid in the spaces of the brain, more dangerous in adults than babies
Blood-brain barrier
Protective barrier formed by astrocytes in combination with blood vessels
-Prevent toxins from entering brain
-Also prevents useful substances from getting through (antibiotics, etc)
-Protects brain except for a few areas
Multiple Sclerosis
myelin sheath destruction. disruptions in nerve impulse conduction (both sensory and motor pathways)
Huntington's disease
A human genetic disease caused by a dominant allele; characterized by uncontrollable body movements and degeneration of the nervous system; defect in huntingtin gene that results in abnormal huntingtin protein that increases the number of CAG repeats on chromosome 4
-Results in brain cell death in basal ganglia and cortex
CRISPR
"Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats"
Cas9- enzymes that snips DNA
Brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)
Protein important for health of neurons
Val allele- most common
Met allele- produced slightly less effective form of BDNF protein
-Less retention among people with Met alleles
epigenetics
Examines the differences in gene expression related to environment and experience
Epigenetics: Histone modification
adding chemical modifications to proteins called histones
Methylenation either opens up and allows for transcription or blocking them
Epigenetics: DNA modification
Methyl groups bind to CG base pairs to block transcription
Epigenetics: mRNA modification
NcRNA binds to mRNA preventing translation
Gene/environment interaction
Methylation higher in hippocampus of people that have committed suicide
-Child abuse results in methylation of the GR gene
Conventional kinesin and cytoplasmic dynein
major microtubule-based motor proteins powering axonal transport of membrane-bounded organelles
circumventricular organs
structures that permit polypeptide hypothalamic hormones to leave the brain without disrupting the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and permit substances that do not cross the BBB to trigger changes in brain function
motor proteins involved in axonal transport
Kinesin and Dynein. Kinesin anterograde transport