Minerals in Human Nutrition: Calcium, Iron, Zinc, and More
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What are macrominerals?
Minerals present in greater amounts in the body, with a recommended intake of ≥100 mg per day, including calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sulfur, sodium, chloride, and magnesium.
What are microminerals?
Also known as trace minerals, these are minerals with a recommended intake of <100 mg per day, including iron, copper, manganese, and iodine.
How are blood calcium levels regulated?
Blood calcium levels are regulated by vitamin D and parathyroid hormone (PTH), which trigger calcium absorption in the intestine and release from bones.
What is the primary function of calcium in the body?
Calcium is critical for building and maintaining bones, muscle contraction, and nerve transmission.
What dietary sources are rich in calcium?
Dairy products, canned sardines and salmon with bones, turnip greens, broccoli, and other green leafy vegetables.
What role does magnesium play in the body?
Magnesium is involved in over 300 biochemical reactions, including muscle and nerve function, blood glucose control, and blood pressure regulation.
What is the primary storage form of sulfur in the body?
The primary storage form of sulfur in the body is in amino acids, such as cysteine and methionine.
What minerals are involved in bone health?
Calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, and fluoride are essential for bone health.
What are the risk factors for osteoporosis?
Risk factors include age (especially >50 years), low calcium and vitamin D intake, sedentary lifestyle, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption.
What are the symptoms of pre-eclampsia?
Symptoms include headache, fatigue, protein in urine, and high blood pressure.
What is the role of iron in the body?
Iron is essential for the formation of hemoglobin, which carries oxygen in the blood.
What are dietary sources of heme and non-heme iron?
Heme iron is found in animal products like meat, while non-heme iron is found in plant-based foods like lentils and spinach.
What factors enhance iron absorption?
Vitamin C and consuming heme iron sources enhance non-heme iron absorption.
What are the unique symptoms of zinc deficiency?
Symptoms include impaired immune function, hair loss, diarrhea, and delayed wound healing.
What role does iodine play in the body?
Iodine is crucial for the production of thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism.
What are the effects of iodine deficiency?
Iodine deficiency can lead to goiter and cretinism, which affects physical and mental development.
What is the primary role of selenium in the body?
Selenium acts as an antioxidant and is important for thyroid hormone metabolism.
What is the leading nutrient deficiency worldwide?
Iron deficiency is the leading nutrient deficiency globally.
What are potential causes of anemia?
Causes include iron deficiency, vitamin B12 deficiency, and chronic diseases.
What is the role of calcium in blood clotting?
Calcium is essential for converting prothrombin into thrombin, which is necessary for blood clot formation.
What dietary factors can hinder mineral absorption?
Phytates and oxalates found in certain plant foods can bind minerals and reduce their availability.
What is osteopenia?
Osteopenia is the weakening of bone density, which can lead to osteoporosis.
What is the recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for calcium for adults aged 19-50?
The RDA for adults aged 19-50 is 1,000 mg per day.
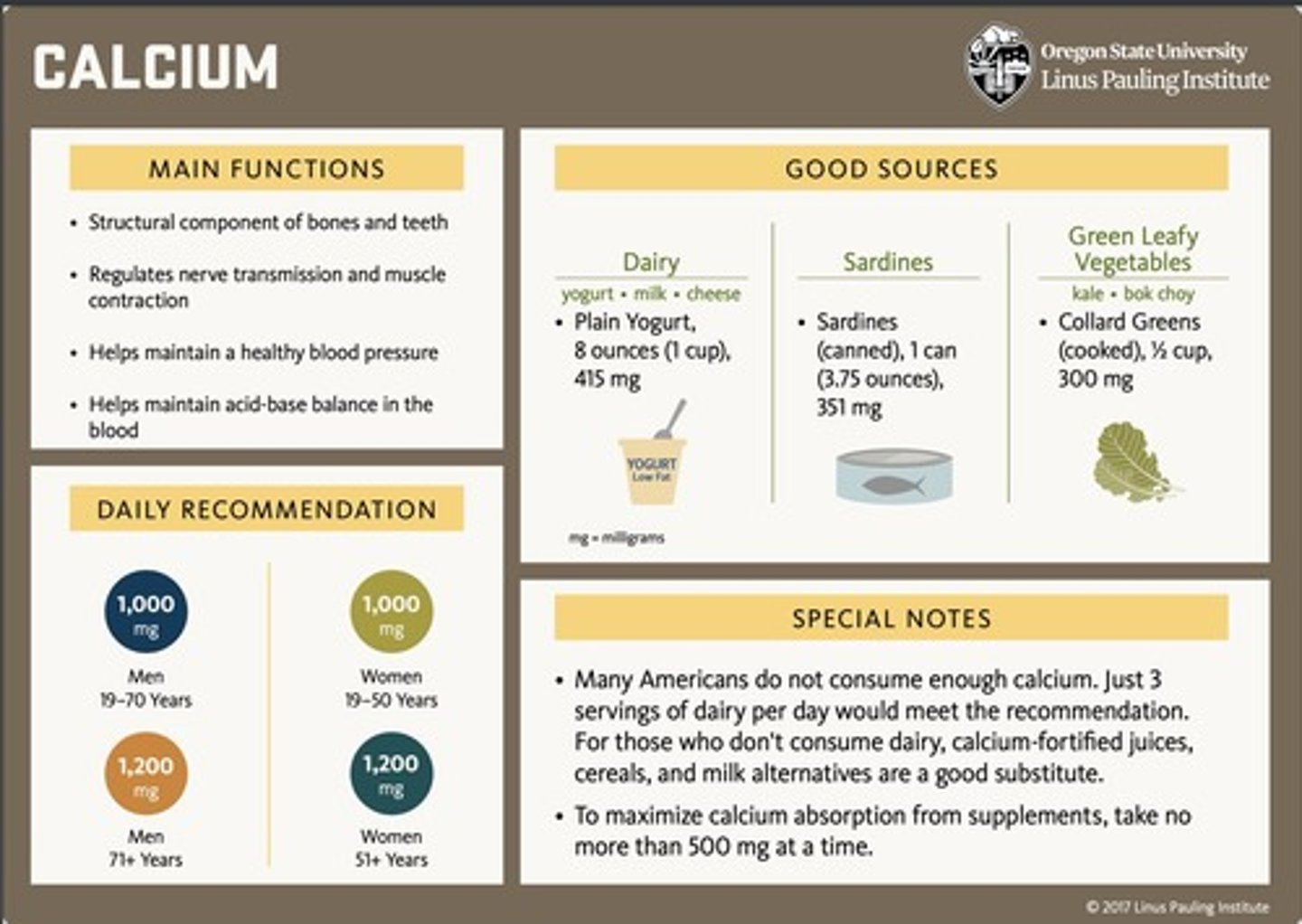
What is the RDA for calcium for females over 50 and males over 70?
The RDA is 1,200 mg per day for females over 50 and males over 70.
What is the significance of calcium in muscle cells?
Calcium is necessary for muscle contraction and the conduction of nerve impulses.
What percentage of phosphorus is found in bones?
85%
What is the primary role of phosphorus in the body?
Part of bones and teeth, facilitates enzyme function, and is a component of ATP, DNA, RNA, and phospholipids.
What is the recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for phosphorus in adults?
700 mg per day

Where is magnesium primarily stored in the body?
About 50% is located in bones, with the remainder in soft tissues and body fluids.
What are the primary functions of magnesium?
Component of hydroxyapatite in bone, ATP stabilization, muscle contraction, and cofactor for nearly 300 enzymes.
What is the RDA for magnesium for men and women?
400 mg per day for men and 320 mg per day for women.
What is the primary role of sulfur in the body?
Key element in amino acids, forms bridges in proteins, and is part of glutathione, an antioxidant.
What dietary sources are rich in sulfur?
Protein-containing foods, B-vitamins, and plant-based foods depending on soil sulfur content.
What is the primary role of iron in the body?
Assists in the delivery of oxygen to tissues and cells, found in hemoglobin.
What is iron-deficiency anemia?
A clinical condition where hemoglobin levels are too low due to inadequate iron intake or absorption.
What are the two forms of iron found in foods?
Heme iron (found in meats) and non-heme iron (found in plant-based foods).
What enhances non-heme iron absorption?
Vitamin C and the presence of meat, poultry, and fish in the diet.
What is the RDA for iron for men and women?
8 mg/day for men and women over 50, 18 mg/day for women ages 19 to 50, and 27 mg/day for pregnant women.
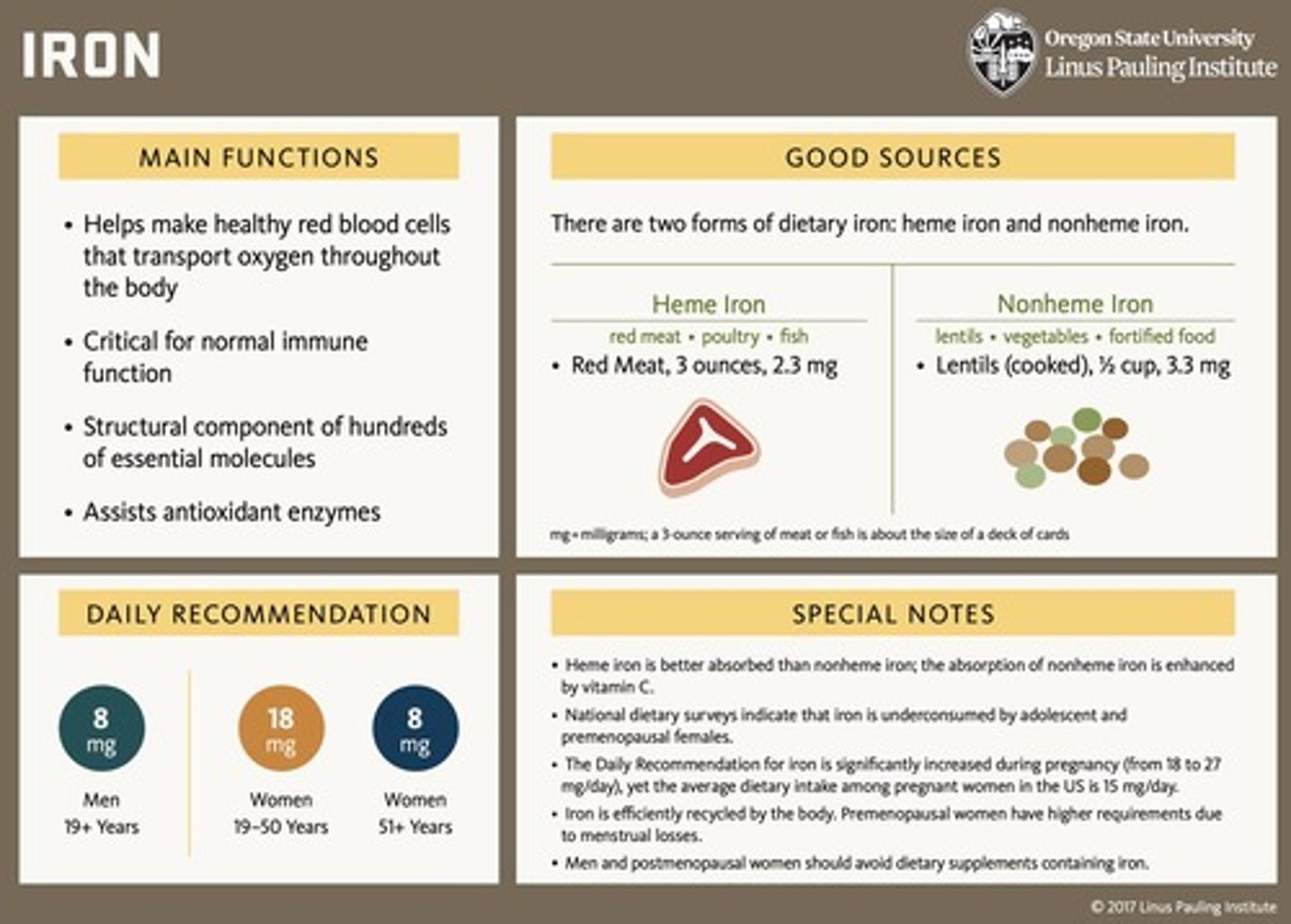
What are the symptoms of iron toxicity?
Abdominal pain, fatigue, depression, and potential liver damage.
What are the primary functions of zinc?
Development of sexual organs, antioxidant enzyme function, insulin release, and immune function.
What are the signs of zinc deficiency?
Dwarfism, poor sexual development, deformed bones, abnormal hair and nails, and poor wound healing.
What is the RDA for zinc for men and women?
11 mg per day for men and 8 mg per day for women.
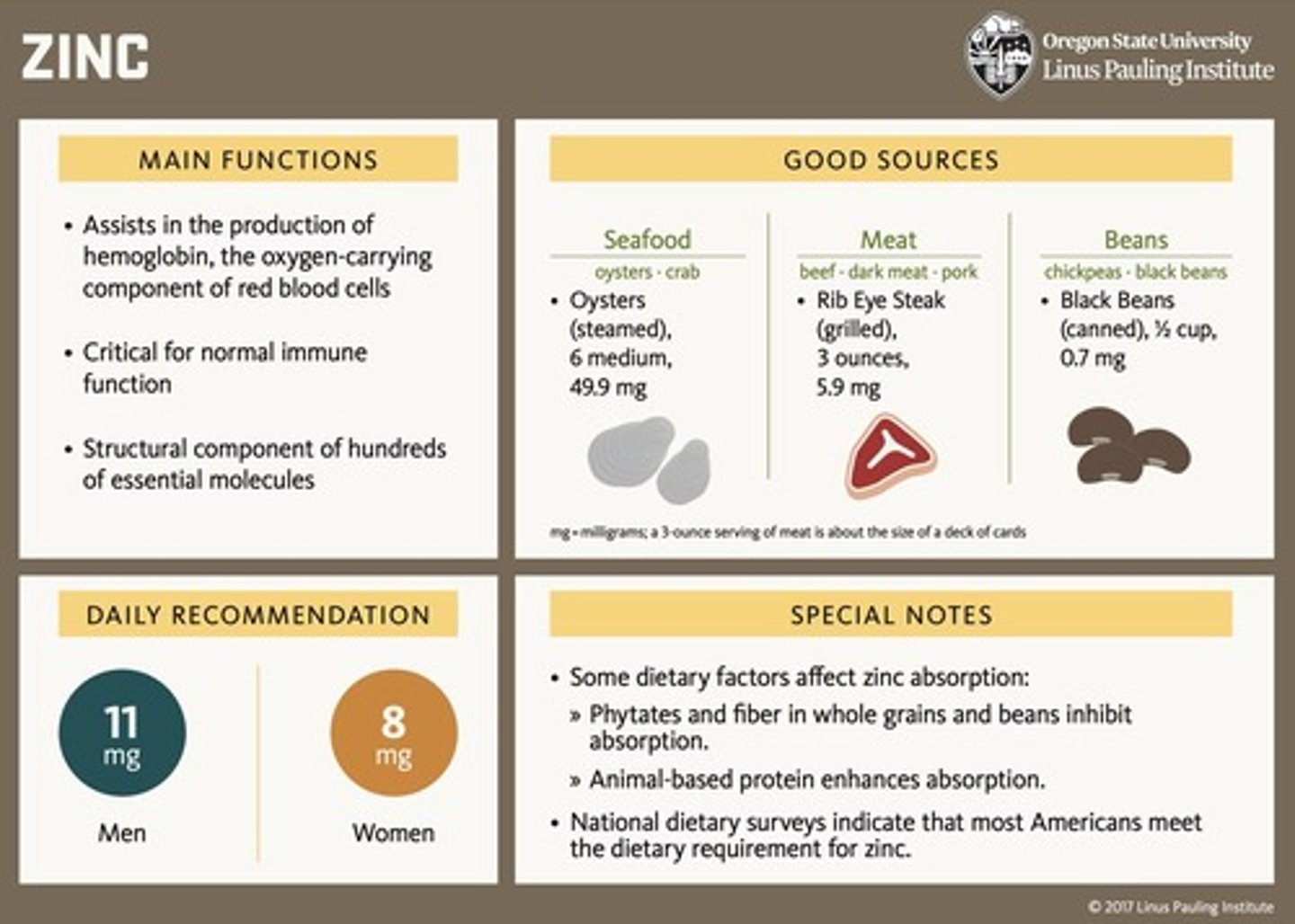
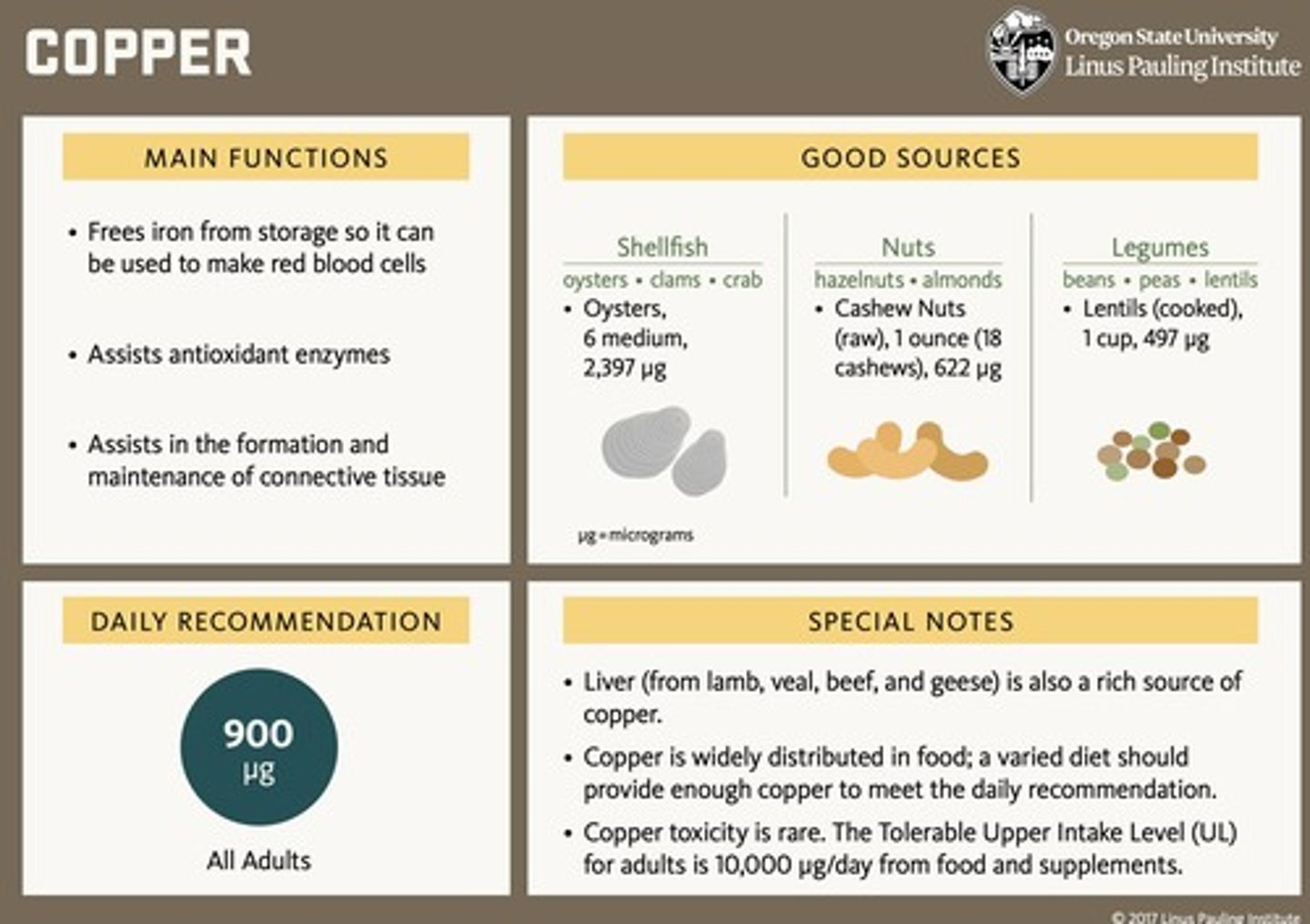
What is the primary function of copper in the body?
Iron use and incorporation into hemoglobin, antioxidant defense, and collagen strengthening.
What is the RDA for copper?
900 µg per day for adults.
What is selenium's most important role?
Supports the body's antioxidant defense system as part of the enzyme glutathione peroxidase.
What is the RDA for selenium?
55 µg per day for adults.
What is the primary function of iodine?
Facilitates the production of thyroid hormone, which controls the basal metabolic rate.
What is the RDA for iodine?
150 µg per day.

What condition can result from iodine deficiency during pregnancy?
Cretinism in offspring, characterized by stunted height and developmental delays.
What are good food sources of iodine?
Seafood, iodized salt, and plants grown in iodine-rich soil.