Fluid Mechanics: Pressure, Pascal’s Principle, and Bernoulli’s Law
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What is pressure in the context of fluids?
Pressure is the ratio of force to the area over which the force is applied.
What determines whether soil will yield under weight?
Pressure, not force, determines whether the soil will yield.
What does Pascal's Principle state?
Any change in the pressure of a fluid is transmitted uniformly in all directions throughout the fluid.
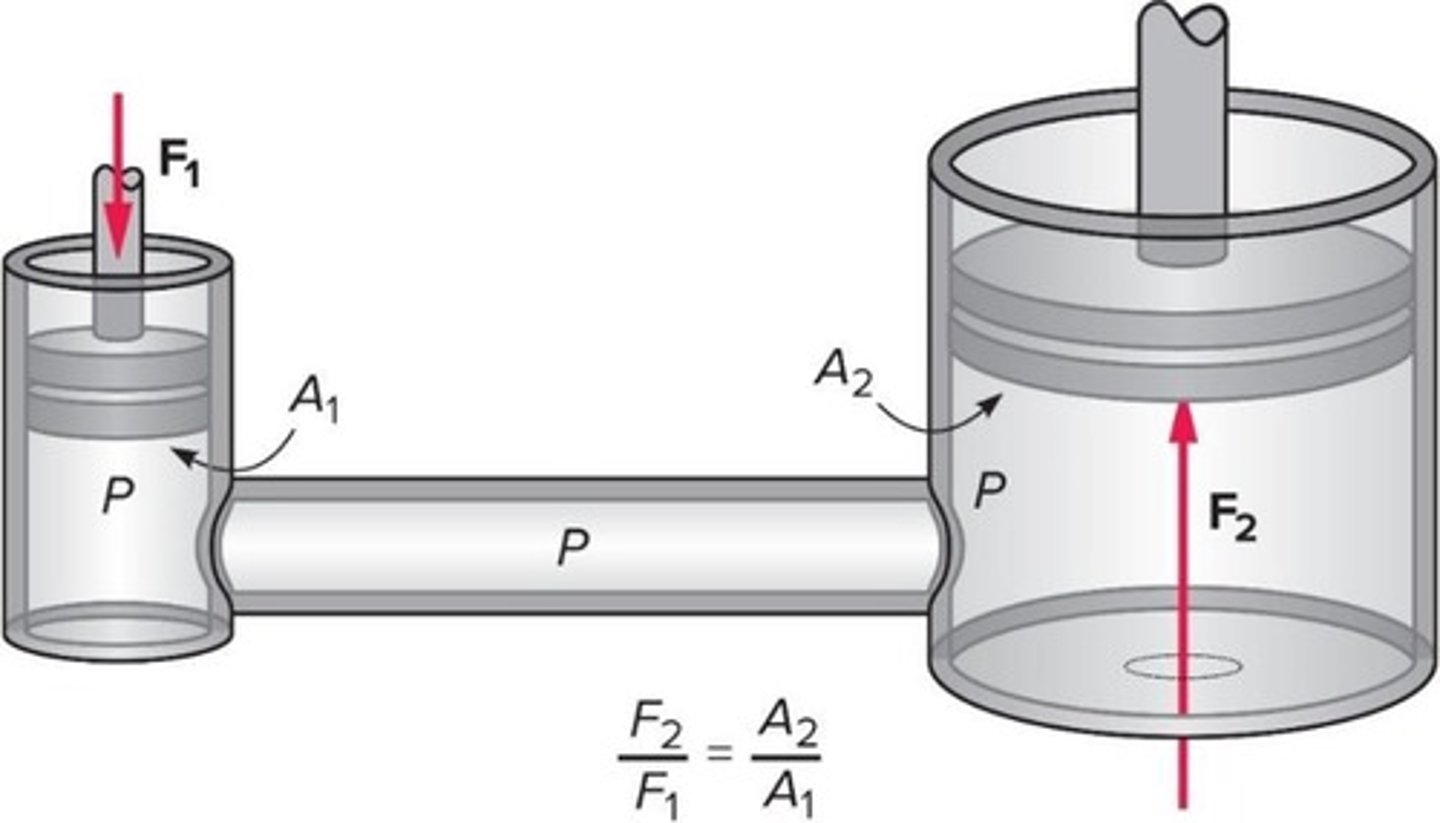
How does a hydraulic jack work?
A force applied to a small piston creates a larger pressure that is transmitted to a larger piston, resulting in a larger force.
What is the atmospheric pressure at sea level?
The atmospheric pressure at sea level is 100 kPa, or 14.7 pounds per square inch.
What device did Torricelli invent and for what purpose?
Torricelli invented the barometer to measure atmospheric pressure.
What phenomenon did Otto von Guericke demonstrate?
He demonstrated the effects of air pressure using two bronze hemispheres that could not be pulled apart when air was evacuated.
What happens to air pressure as altitude increases?
Air pressure decreases as altitude increases.
What is Boyle's Law?
Boyle's Law states that the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure when temperature is held constant (PV = constant).
How does the density of a column of air change with altitude?
The density of a column of air decreases as altitude increases because air expands as pressure decreases.
If the pressure of a gas is increased from 1 atmosphere to 3 atmospheres, what happens to its volume?
The volume of the gas decreases according to Boyle's Law.
What is Archimedes' Principle?
The average density of an object compared to a fluid determines whether the object will sink or float in that liquid.
What is the relationship between force and area in the context of pressure?
Pressure is calculated as force divided by area (P = F/A).
What is the significance of the area of pistons in a hydraulic system?
The force exerted on a piston is proportional to the area of the piston, allowing for mechanical advantage.
What happens to a balloon as altitude increases?
A balloon expands as altitude increases due to the decrease in external atmospheric pressure.
What is the formula for calculating pressure?
Pressure (P) is calculated as force (F) divided by area (A): P = F/A.
What is the effect of atmospheric pressure on liquids?
Atmospheric pressure supports a column of liquid, such as mercury in a barometer.
What happens to the pressure in a fluid when it is compressed?
The pressure increases uniformly throughout the fluid.
What is the mechanical advantage in a hydraulic jack?
The mechanical advantage is the ratio of the output force to the input force, which can be calculated using the areas of the pistons.
What did Pascal's experiments with a barometer demonstrate?
They demonstrated the relationship between atmospheric pressure and the height of a liquid column.
What is the relationship between pressure and volume in a gas at constant temperature?
As pressure increases, the volume decreases, and vice versa, according to Boyle's Law.
How does the density of a fluid affect buoyancy?
An object will float if its density is less than that of the fluid, and sink if its density is greater.
What determines whether an object will sink or float in a fluid?
The average density of the object compared to the fluid.
What is the buoyant force?
The upward force that pushes objects back toward the surface in liquids.
State Archimedes' Principle.
The buoyant force acting on an object fully or partially submerged in a fluid is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object.
What causes the buoyant force in a fluid?
The increase in pressure that occurs with increasing depth in the fluid.
How does pressure vary with depth in a fluid?
Pressure is greater near the bottom of a fluid than at the surface due to the weight of the fluid above.
What happens to the buoyant force on a submerged block?
The pressure at the bottom of the block is greater than at the top, resulting in an upward buoyant force.
What determines the behavior of a floating object?
The balance between the object's weight and the buoyant force acting on it.
What occurs if the density of an object is greater than that of the fluid?
The object sinks because its weight is greater than the weight of the displaced fluid.
What occurs if the density of an object is less than that of the fluid?
The object floats until the weight of the displaced fluid equals the weight of the object.
What happens if the density of an object is equal to that of the fluid?
The object remains stationary in the fluid.
What is viscosity?
A measure of the frictional effects within a fluid.
How does viscosity affect fluid flow?
Higher viscosity results in larger frictional forces between layers of the fluid.
What is the relationship between flow rate and cross-sectional area in a pipe?
If the cross-sectional area decreases, the speed of the fluid must increase to maintain the same flow rate.
What is laminar flow?
Smooth flow of a fluid with parallel streamlines and no disturbances.
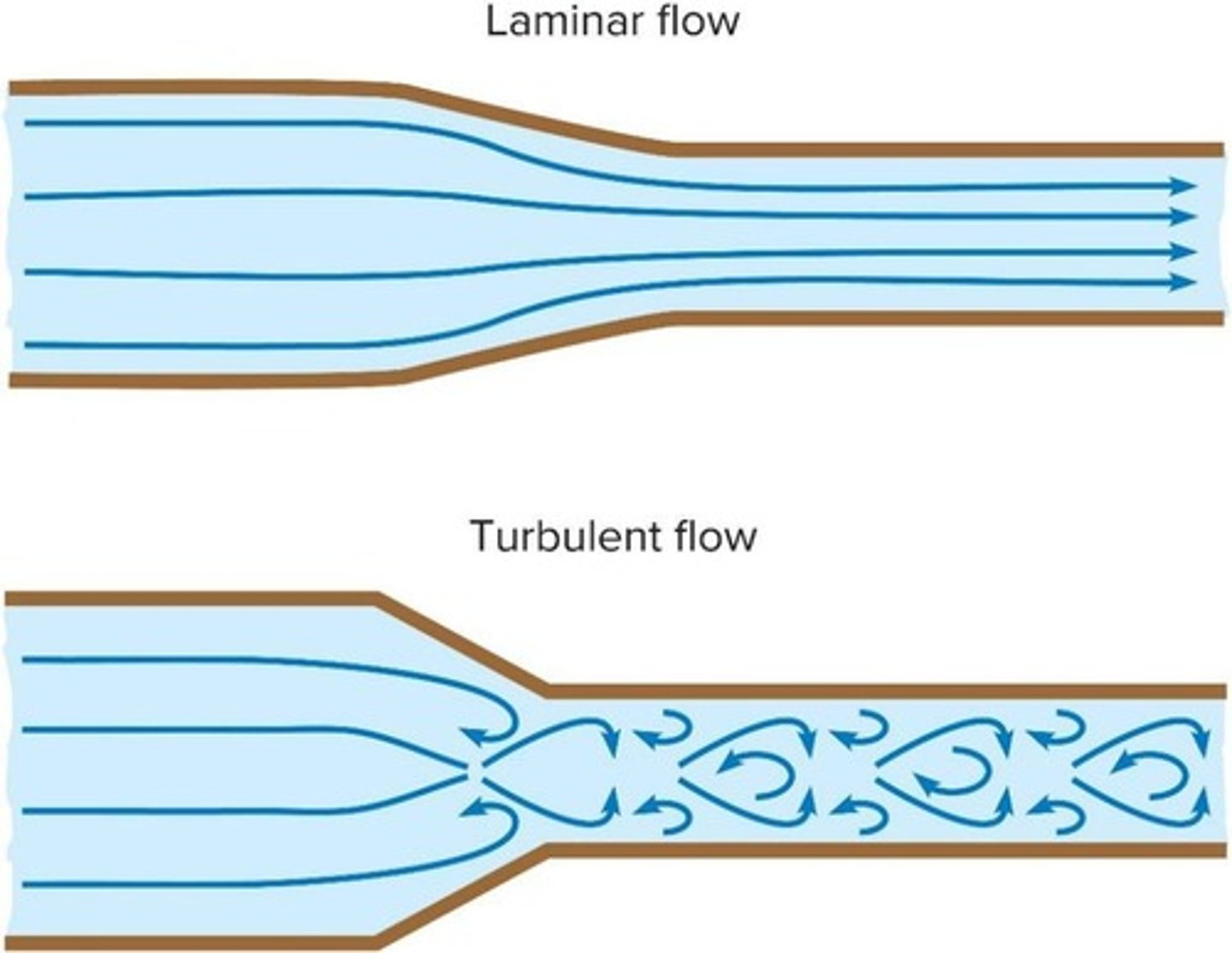
What is turbulent flow?
Flow characterized by eddies and whorls, where streamlines are not parallel.
What is Bernoulli's Principle?
The sum of pressure and kinetic energy per unit volume of a flowing fluid must remain constant.
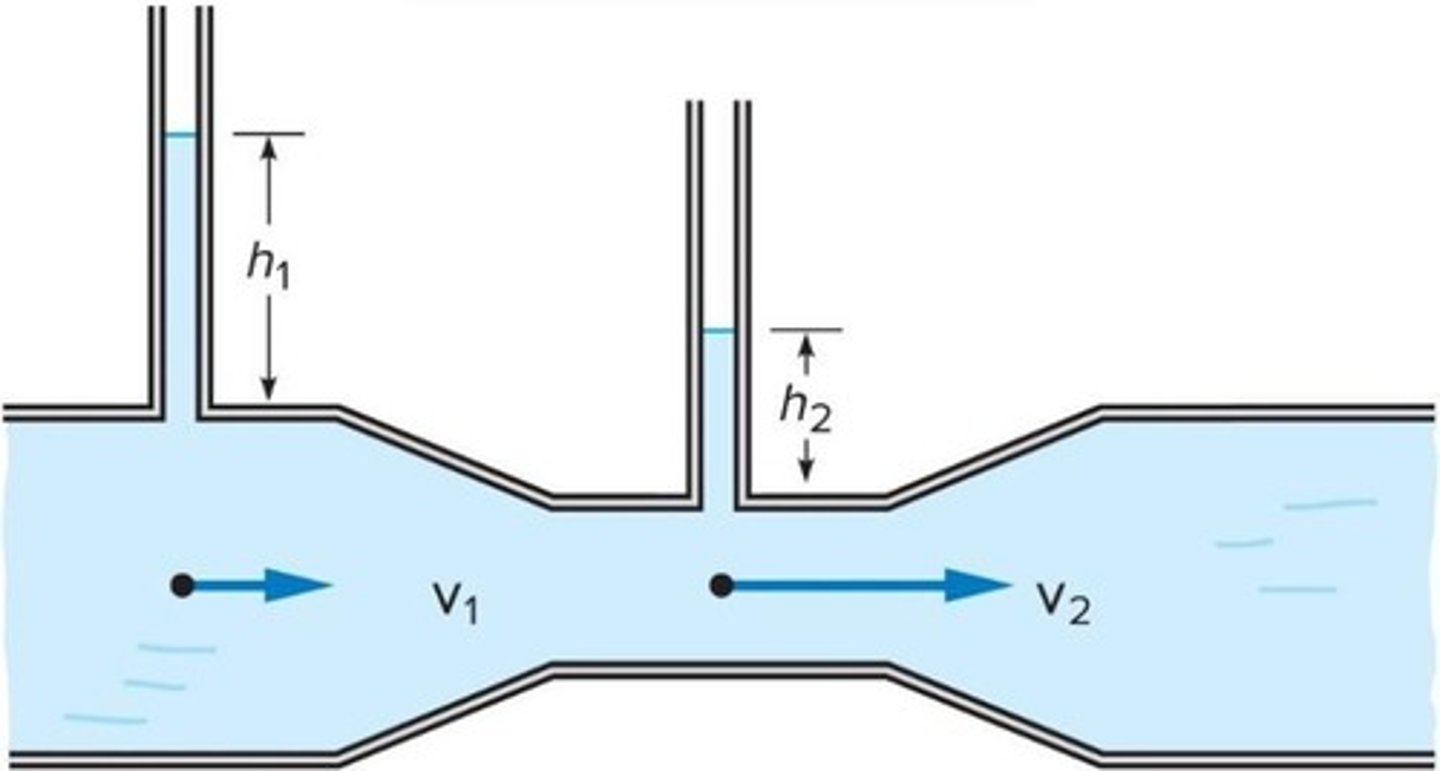
How does pressure vary in a pipe with varying diameter?
Pressure is greater in the wider section where fluid speed is lower.
How does an airplane wing generate lift?
The shape and tilt of the wing cause air to move faster over the top, creating lower pressure above the wing.
What causes a ball to be suspended in mid-air by a hair dryer?
The ball is held in an upward-moving column of air where the pressure is lowest in the center.
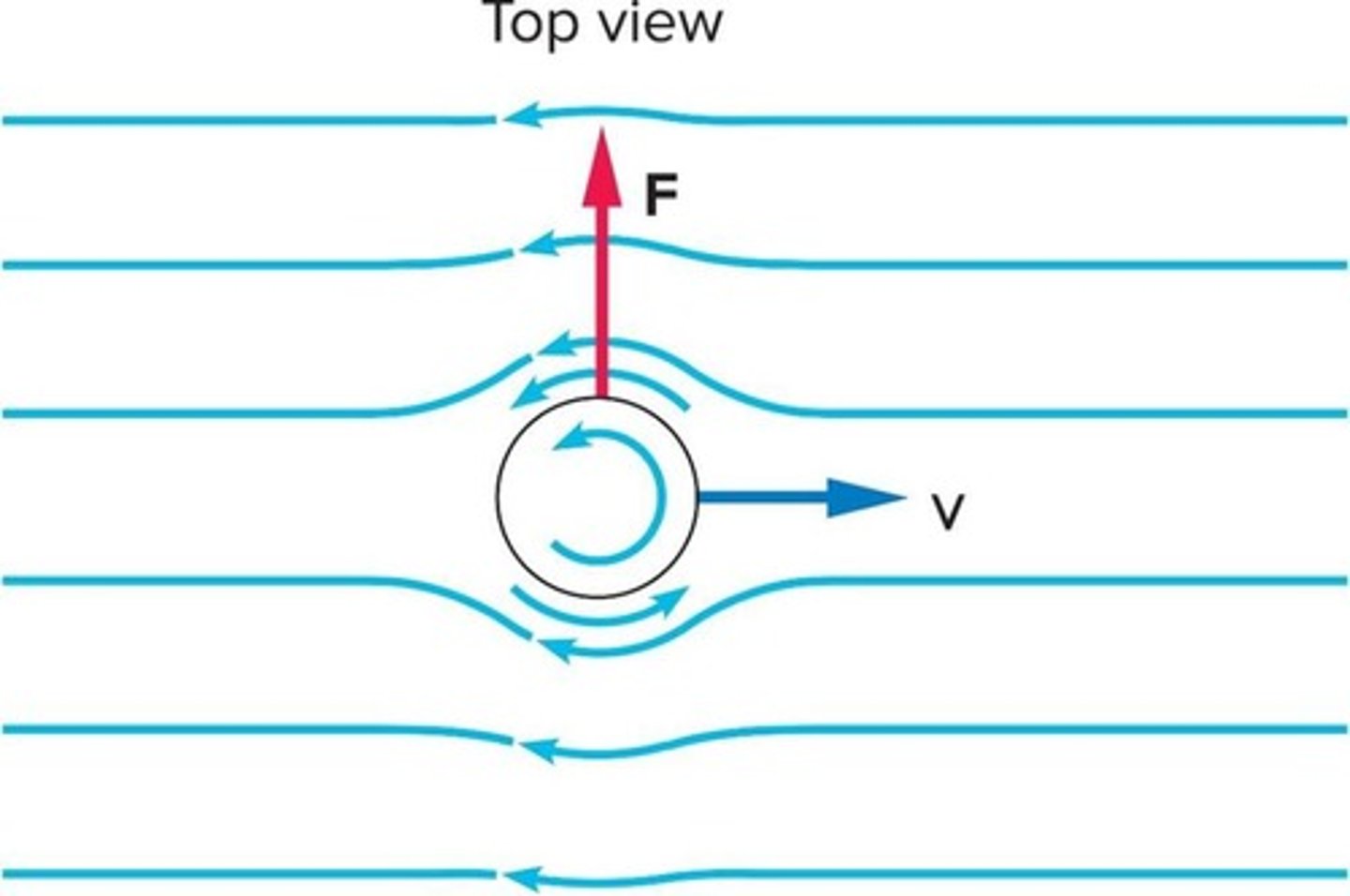
What causes a curveball to curve?
The spin of the ball creates a difference in air speed on either side, resulting in a pressure difference that causes the ball to curve.